Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis: A Molecular and Clinical Insight
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Process of Crystal Formation in Systemic Sclerosis
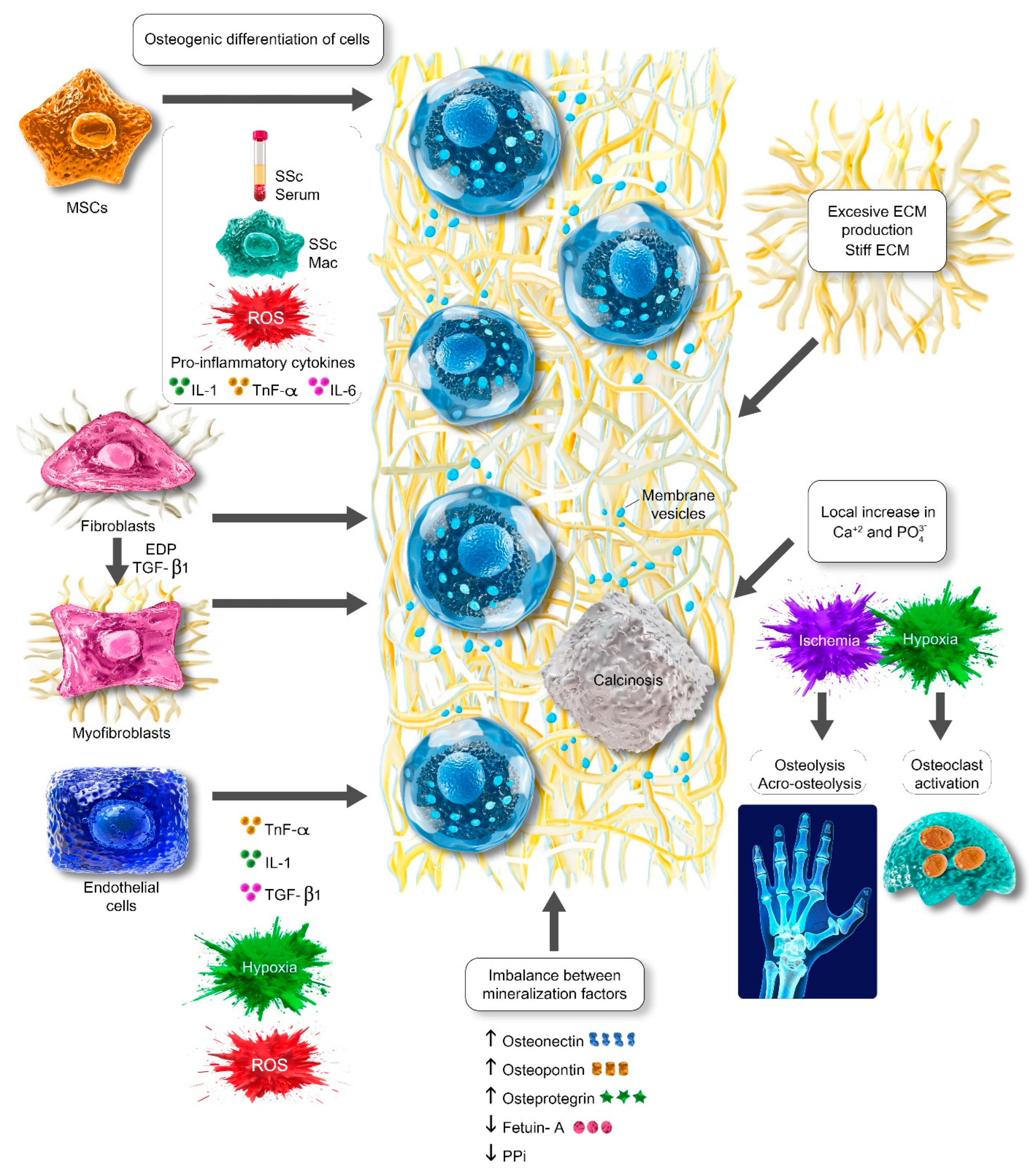
2.1. Osteogenic Differentiation of Cells
2.2. Local Increase in Calcium and Phosphate and Imbalance Between Mineralization Factors
2.3. Extracellular Matrix as a Template and Suitable Microenvironment for Calcinosis Development
2.4. Membrane Vesicles and DRP-1
3. Clinical Aspects of Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis
3.1. The Localization and Clinical Features of Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis
3.2. Complications of Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis
3.3. Treatment Modalities of Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varga, J.; Trojanowska, M.; Kuwana, M. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: Recent insights of molecular and cellular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2017, 2, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyndall, A.J.; Bannert, B.; Vonk, M.; Airò, P.; Cozzi, F.; Carreira, P.E.; Bancel, D.F.; Allanore, Y.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Distler, O. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: A study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Song, P.; Chung, L. Calcinosis in scleroderma. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Baron, M.; Rodriguez-Reyna, T.S.; Proudman, S.; Khanna, D.; Young, A.; Hinchcliff, M.; Steen, V.; Gordon, J.; Hsu, V.; et al. Calcinosis is associated with ischemic manifestations and increased disability in patients with systemic sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanzi, L.; Braschi, F.; Fiori, G.; Galluccio, F.; Miniati, I.; Guiducci, S.; Conforti, M.L.; Kaloudi, O.; Nacci, F.; Sacu, O.; et al. Digital ulcers in scleroderma: Staging, characteristics and sub-setting through observation of 1614 digital lesions. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieir, O.; Thombs, B.D.; Hudson, M.; Boivin, J.F.; Steele, R.; Bernatsky, S.; Hanley, J.; Baron, M. Prevalence, severity, and clinical correlates of pain in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2010, 62, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, A.L.; Gallas, A. Systemic sclerosis-related calcinosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2016, 1, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, E.; Addadi, L.; Andrés, M.; Sivera, F. Mechanisms of crystal formation in gout-a structural approach. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazzelli, V.; Dell’Orbo, C.; Borroni, G.; Bollati, A.; Montecucco, C.; Cerimele, D.; Rabbiosi, G. The role of the intercellular matrix in dermal calcinosis of the CRST syndrome. An electron-microscopic study. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 1992, 14, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, J.L.; Pernot, F.; Fedou, P.; Poubelle, P.; Bonnel, F.; Baldet, P.; Blotman, F.; Simon, L. Ultrastructural and crystallographic study of calcifications from a patient with CREST syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 1983, 10, 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Pokhrel, S. Hydroxyapatite: Preparation, properties and its biomedical applications. Adv. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, V.M.; Emge, T.; Schlesinger, N. X-ray diffraction analysis of spontaneously draining calcinosis in scleroderma patients. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 46, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y. Biochemical and molecular aspects of spectral diagnosis in calcinosis cutis. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2014, 16, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, T.; Sakae, T.; Nakada, H.; Kaneda, T.; Okada, H. Confusion between carbonate apatite and biological apatite (carbonated hydroxyapatite) in bone and teeth. Minerals 2022, 12, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, M.F.; Discher, D.E.; Péault, B.M.; Phinney, D.G.; Hare, J.M.; Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: Cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen. Med. 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jiang, N.; Li, M.; Zeng, X.; Tian, X. Mesenchymal stem cells and connective tissue diseases: From bench to bedside. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2023, 11, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.; Ryan, C.M.; Pathan, O.; Abraham, D.; Denton, C.P.; Butler, P.E. Characteristics of human adipose derived stem cells in scleroderma in comparison to sex and age matched normal controls: Implications for regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonteneau, G.; Bony, C.; Goulabchand, R.; Maria, A.T.J.; Le Quellec, A.; Rivière, S.; Jorgensen, C.; Guilpain, P.; Noël, D. Serum-Mediated Oxidative Stress from Systemic Sclerosis Patients Affects Mesenchymal Stem Cell Function. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumbe, B.G.T.; Ahmad, S.N.; Thomas, G.; Borukhson, L.; Abdi, B.A.; Lopez, H.; Garvin, C.; Jaynes, J.; Yates, C.; Martin, G.; et al. P155 Modelling calcinosis in systemic sclerosis through disease microenvironment-stem cell interactions: Effect of novel therapeutic peptide RP832c. Rheumatology 2021, 60, keab247-151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyo, S.; Yamaoka, K.; Sonomoto, K.; Oshita, K.; Okada, Y.; Saito, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Kanazawa, T.; Minami, Y.; Tanaka, Y. IL-6-accelerated calcification by induction of ROR2 in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells is STAT3 dependent. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Burdick, M.D.; Strieter, R.M. Human circulating fibrocytes have the capacity to differentiate osteoblasts and chondrocytes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, K.; Sicker, M.; Schmelzer, E.; Rupf, T.; Salvetter, J.; Schulz-Siegmund, M.; Bader, A. Multilineage differentiation potential of human dermal skin-derived fibroblasts. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, I.; Romano, E.; Fioretto, B.S.; Manetti, M. The contribution of mesenchymal transitions to the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 7, S157–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionescu, A.; Simionescu, D.T.; Vyavahare, N.R. Osteogenic responses in fibroblasts activated by elastin degradation products and transforming growth factor-beta1: Role of myofibroblasts in vascular calcification. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, K.A.; Herrick, A.L.; Watson, R.E.B. Systemic sclerosis skin is a primed microenvironment for soft tissue calcification-a hypothesis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2517–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Kuwana, M. Endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 7, S139–S146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Benedetto, P.; Ruscitti, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Vomero, M.; Navarini, L.; Dolo, V.; Cipriani, P.; Giacomelli, R. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 205, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manetti, M.; Romano, E.; Rosa, I.; Guiducci, S.; Bellando-Randone, S.; De Paulis, A.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to endothelial dysfunction and dermal fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, D.; Shore, E.M.; Lounev, V.Y.; Kaplan, F.S.; Kalluri, R.; Olsen, B.R. Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Duffhues, G.; García de Vinuesa, A.; Ten Dijke, P. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cardiovascular diseases: Developmental signaling pathways gone awry. Dev. Dyn. 2018, 247, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuan, D.T.B.; Zayed, H.; Eid, A.H.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Mangoni, A.A.; Pintus, G. A Potential Link Between Oxidative Stress and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Systemic Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Niu, W.; Dong, H.Y.; Liu, M.L.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.C. Hypoxia induces endothelial-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary vascular remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourji, K.; Meyer, A.; Chatelus, E.; Pincemail, J.; Pigatto, E.; Defraigne, J.O.; Singh, F.; Charlier, C.; Geny, B.; Gottenberg, J.E.; et al. High reactive oxygen species in fibrotic and nonfibrotic skin of patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 87, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielli, A.; Svegliati, S.; Moroncini, G.; Amico, D. New insights into the role of oxidative stress in scleroderma fibrosis. Open Rheumatol. J. 2012, 6, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.T.; Shao, Y.D.; Liu, Y.Z.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, Z.B.; Qu, S.L.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C. Oxidative stress in vascular calcification. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 519, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, H.P.; Zhao, J.J. Oxidative stress markers in blood in systemic sclerosis: A meta-analysis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.A.; Jeziorska, M.; Freemont, A.J.; Herrick, A.L. The differential expression of VEGF, VEGFR-2, and GLUT-1 proteins in disease subtypes of systemic sclerosis. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, S.; Raju, R.; Sandhya, V.K.; Advani, J.; Khan, A.A.; Harsha, H.C.; Prasad, T.S.; Sudhakaran, P.R.; Pandey, A.; Adishesha, P.K. A multicellular signal transduction network of AGE/RAGE signaling. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 7, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, A.; Komura, K.; Iwata, Y.; Ogawa, F.; Hara, T.; Muroi, E.; Takenaka, M.; Shimizu, K.; Hasegawa, M.; Fujimoto, M.; et al. Clinical significance of serum HMGB-1 and sRAGE levels in systemic sclerosis: Association with disease severity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.A.; Herrick, A.L.; Cordingley, L.; Freemont, A.J.; Jeziorska, M. Expression of advanced glycation end products and their receptor in skin from patients with systemic sclerosis with and without calcinosis. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, M.; Pope, J.; Robinson, D.; Jones, N.; Khalidi, N.; Docherty, P.; Kaminska, E.; Masetto, A.; Sutton, E.; Mathieu, J.P.; et al. Calcinosis is associated with digital ischaemia in systemic sclerosis-a longitudinal study. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 2148–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, A.; Stevens, K.; Chung, M.P.; Rodriguez-Reyna, T.S.; Proudman, S.; Baron, M.; Castelino, F.V.; Hsu, V.; Green, L.; Galdo, F.D.; et al. Change in calcinosis over 1 year using the scleroderma clinical trials consortium radiologic scoring system for calcinosis of the hands in patients with systemic sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 53, 151980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botou, A.; Bangeas, A.; Alexiou, I.; Sakkas, L.I. Acro-osteolysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avouac, J.; Guerini, H.; Wipff, J.; Assous, N.; Chevrot, A.; Kahan, A.; Allanore, Y. Radiological hand involvement in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avouac, J.; Mogavero, G.; Guerini, H.; Drapé, J.L.; Mathieu, A.; Kahan, A.; Allanore, Y. Predictive factors of hand radiographic lesions in systemic sclerosis: A prospective study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siao-Pin, S.; Damian, L.O.; Muntean, L.M.; Rednic, S. Acroosteolysis in systemic sclerosis: An insight into hypoxia-related pathogenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 3459–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usategui-Martín, R.; Rigual, R.; Ruiz-Mambrilla, M.; Fernández-Gómez, J.M.; Dueñas, A.; Pérez-Castrillón, J.L. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Hypoxia-Induced Alterations in Bone Remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Fava, A.; Carrino, J.; Del Grande, F.; Rosen, A.; Boin, F. Association of Acroosteolysis with Enhanced Osteoclastogenesis and Higher Blood Levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.G.; Rodrigues, M.; Águeda, A.; Rodrigues, J.; Marona, J.; Violante, A.; Oliveira, M. Osteolysis in Systemic Sclerosis: A Scoping Review. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 50, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.; Plaas, A.; Varga, J. Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis: Updates in Pathophysiology, Evaluation, and Treatment. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheiro, T.; Malvar Fernández, B.; Ottria, A.; Giovannone, B.; Marut, W.; Reedquist, K.A.; Garcia, S.; Radstake, T.R. Extracellular SPARC cooperates with TGF-β signalling to induce pro-fibrotic activation of systemic sclerosis patient dermal fibroblasts. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2258–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Termine, J.D.; Kleinman, H.K.; Whitson, S.W.; Conn, K.M.; McGarvey, M.L.; Martin, G.R. Osteonectin, a bone-specific protein linking mineral to collagen. Cell 1981, 26, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macko, R.F.; Gelber, A.C.; Young, B.A.; Lowitt, M.H.; White, B.; Wigley, F.M.; Goldblum, S.E. Increased circulating concentrations of the counteradhesive proteins SPARC and thrombospondin-1 in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Relationship to platelet and endothelial cell activation. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 2565–2570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davies, C.A.; Jeziorska, M.; Freemont, A.J.; Herrick, A.L. Expression of osteonectin and matrix Gla protein in scleroderma patients with and without calcinosis. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Y. Osteopontin in Bone Metabolism and Bone Diseases. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e919159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzali, M.; Kipari, T.; Ophascharoensuk, V.; Wesson, J.A.; Johnson, R.; Hughes, J. Osteopontin--a molecule for all seasons. QJM 2002, 95, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, J.M.; Krämer, R.; Meier, M.; Werfel, T.; Wichmann, K.; Hoeper, M.M.; Riemekasten, G.; Becker, M.O.; Haller, H.; Witte, T. Osteopontin in the development of systemic sclerosis--relation to disease activity and organ manifestation. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1989–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, S.; Roumeliotis, A.; Dounousi, E.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Liakopoulos, V. Biomarkers of vascular calcification in serum. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2020, 98, 91–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellino, G.; Corallini, F.; Bortoluzzi, A.; La Corte, R.; Lo Monaco, A.; Secchiero, P.; Zauli, G.; Trotta, F. The tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-osteoprotegerin system in limited systemic sclerosis: A new disease marker? Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, R.M.; Gamal, W.M.; Ghandour, A.M.; Abozaid, H.S.M.; Mohamed, M.E.; Emad, Y.; Abdel Galeel, A. Study of the osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor-kB ligand system association with inflammation and atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis. Immunol. Investig. 2018, 47, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovio, A.; Data, V.; Carignola, R.; Calzolari, G.; Vitetta, R.; Ventura, M.; Saba, L.; Severino, A.; Angeli, A. Circulating osteoprotegerin and soluble RANK ligand in systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 2206–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloli, L.; Ughi, N.; Massarotti, M.; Marasini, B.; Biondi, M.L.; Brambilla, G. Role of fetuin-A in systemic sclerosis-associated calcinosis. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 2638–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, V.; Varga, J.; Schlesinger, N. Calcinosis in scleroderma made crystal clear. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azpiazu, D.; Gonzalo, S.; González-Parra, E.; Egido, J.; Villa-Bellosta, R. Role of pyrophosphate in vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Nefrología 2018, 38, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, V.M.; Kozák, E.; Li, Q.; Bocskai, M.; Schlesinger, N.; Rosenthal, A.; McClure, S.T.; Kovács, L.; Bálint, L.; Szamosi, S.; et al. Inorganic pyrophosphate is reduced in patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.A.; Watson, M.L. Crystalcollagen relationships in bone as observed in the electron microscope. III. Crystal and collagen morphology as a function of age. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1955, 60, 596–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausch, A.J.; Quan, B.D.; Miklas, J.W.; Sone, E.D. Extracellular matrix control of collagen mineralization in vitro. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4906–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leask, A.; Naik, A.; Stratton, R.J. Back to the future: Targeting the extracellular matrix to treat systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, A.J.; Sen, S.; Sweeney, H.L.; Discher, D.E. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 2006, 126, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, A.S.; George, P.A.; Cooper-White, J.J. Directing osteogenic and myogenic differentiation of MSCs: Interplay of stiffness and adhesive ligand presentation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, C1037–C1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, Z.; Gostjeva, E.; Thilly, W.; Yaseen, B.; Lopez, H.; Mirza, M.; Hassuji, Z.; Vigneswaran, S.; Ahmed Abdi, B.; Hart, A.; et al. Pathogenic Activation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Is Induced by the Disease Microenvironment in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzumi, A.; Yoshizaki, A.; Matsuda, K.M.; Kotani, H.; Norimatsu, Y.; Fukayama, M.; Ebata, S.; Fukasawa, T.; Yoshizaki-Ogawa, A.; Asano, Y.; et al. Interleukin-31 promotes fibrosis and T helper 2 polarization in systemic sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaseen, B.; Lopez, H.; Taki, Z.; Zafar, S.; Rosario, H.; Abdi, B.A.; Vigneswaran, S.; Xing, F.; Arumalla, N.; Black, S.; et al. Interleukin-31 promotes pathogenic mechanisms underlying skin and lung fibrosis in scleroderma. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2625–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkovskiy, A.; Lund, M.; Siamansour, T.S.; Reine, T.M.; Kolset, S.O.; Sand, K.L.; Ignatieva, E.; Gordeev, M.L.; Stensløkken, K.O.; Valen, G.; et al. Mechanical stress alters the expression of calcification-related genes in vascular interstitial and endothelial cells. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 28, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Domínguez, M.P.; García-Collinot, G.; Saavedra, M.A.; Medina, G.; Carranza-Muleiro, R.A.; Vera-Lastra, O.L.; Jara, L.J. Clinical, biochemical, and radiological characterization of the calcinosis in a cohort of Mexican patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, F.; Fiori, G.; Braschi, F.; Amanzi, L.; Bruni, C.; Blagojevic, J.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Cometi, L.; de Souza Mueller, C.; Guiducci, S.; et al. Calcinosis in systemic sclerosis: Subsets, distribution and complications. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1610–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Chung, L. Subcutaneous calcinosis: Is it different between systemic sclerosis and dermatomyositis? J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2022, 7, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommanavar, S.; Hosmani, J.; Togoo, R.A.; Baeshen, H.A.; Raj, A.T.; Patil, S.; Bhandi, S.; Birkhed, D. Role of matrix vesicles and crystal ghosts in bio-mineralization. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2020, 38, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazzeroni, L.; Faggioli, G.; Pasquinelli, G. Mechanisms of Arterial Calcification: The Role of Matrix Vesicles. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2018, 55, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvvuri, B.; Lood, C. Mitochondrial Calcification. Immunometabolism 2021, 3, e210008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonrungsiman, S.; Gentleman, E.; Carzaniga, R.; Evans, N.D.; McComb, D.W.; Porter, A.E.; Stevens, M.M. The role of intracellular calcium phosphate in osteoblast-mediated bone apatite formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14170–14175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boraldi, F.; Lofaro, F.D.; Quaglino, D. Apoptosis in the Extraosseous Calcification Process. Cells 2021, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yapa, N.M.B.; Lisnyak, V.; Reljic, B.; Ryan, M.T. Mitochondrial dynamics in health and disease. FEBS Lett. 2021, 595, 1184–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, C.; Wei, Q.; Cho, S.G.; Dong, Z. Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics in acute kidney injury in cell culture and rodent models. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, S. Dynamin-related protein-1 as potential therapeutic target in various diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.A.; Maldonado, N.; Hutcheson, J.D.; Goettsch, C.; Goto, S.; Yamada, I.; Faits, T.; Sesaki, H.; Aikawa, M.; Aikawa, E. Dynamin-Related Protein 1 Inhibition Attenuates Cardiovascular Calcification in the Presence of Oxidative Stress. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.R.; Zhou, Y.J.; Sha, Y.; Wu, X.P.; Yang, J.Q.; Liu, F. Melatonin attenuates vascular calcification by inhibiting mitochondria fission via an AMPK/Drp1 signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6043–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Geng, B.; Cai, J. Mdivi-1, a mitochondrial fission inhibitor, reduces angiotensin-II- induced hypertension by mediating VSMC phenotypic switch. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, X.; Zhao, X.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced proliferation and glycolysis in airway smooth muscle cells via activation of Drp1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9255–9263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, L. Inhibitors of Mitochondrial Dynamics Mediated by Dynamin-Related Protein 1 in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 913904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davuluri, S.; Lood, C.; Chung, L. Calcinosis in systemic sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2022, 34, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikazu, D.; Mori, Y.; Saijo, H.; Fujihara, H.; Ko, E.C.; Hikiji, H.; Yonehara, Y.; Takato, T. A case of tumoural calcinosis in the temporomandibular joint associated with systemic sclerosis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 37, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadimi, H.; Nikdel, M.; Eshraghi, B. Bilateral calcinosis cutis of orbital walls in CREST syndrome. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2019, 4, NP1–NP4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, A.L.; Robbin, M.R.; Furey, C.G.; Easley, S.E.; Abdul-Karim, F.W.; Bohlman, H.H. Tumoral calcinosis in the cervical spine in a patient with CREST syndrome. A case report. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2006, 88, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motegi, S.I.; Sekiguchi, A.; Yonemoto, Y.; Mieda, T.; Chikuda, H.; Ishikawa, O. Demographic and clinical characteristics of spinal calcinosis in systemic sclerosis: Possible association with peripheral angiopathy. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanoglu-Guler, A.; Campochiaro, C.; De Luca, G.; Hughes, M.; Tufan, A.; Green, L.; Del Galdo, F.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Dagna, L. Calcinosis in systemic sclerosis: An update on pathogenesis, related complications, and management: A heavy burden still waiting to be lifted off patients’ hands. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2024, 66, 152431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanatta, E.; Desportes, M.; Do, H.H.; Avouac, J.; Doria, A.; Feydy, A.; Allanore, Y. Pseudotumoral calcinosis in systemic sclerosis: Data from systematic literature review and case series from two referral centres. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulman, N.; Slobodin, G.; Rozenbaum, M.; Rosner, I. Calcinosis in rheumatic diseases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 34, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morardet, L.; Avouac, J.; Sammour, M.; Baron, M.; Kahan, A.; Feydy, A.; Allanore, Y. Late Nailfold Videocapillaroscopy Pattern Associated With Hand Calcinosis and Acro-Osteolysis in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Baron, M.; Herrick, A.L.; Proudman, S.; Stevens, W.; Rodriguez-Reyna, T.S.; Vacca, A.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Hinchcliff, M.; Hsu, V.; et al. Calcinosis is associated with digital ulcers and osteoporosis in patients with systemic sclerosis: A Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 46, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norimatsu, Y.; Fukasawa, T.; Kabeya, Y.; Toyama, S.; Matsuda, K.M.; Kuzumi, A.; Yoshizaki-Ogawa, A.; Ichimura, H.; Yonezawa, S.; Nakano, H.; et al. The number of nail fold capillaries and nail fold bleedings reflects the clinical manifestations of systemic sclerosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, S.; Hsu, V. Are there risk factors for scleroderma-related calcinosis? Mod. Rheumatol. 2018, 28, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, V.D.; Ziegler, G.L.; Rodnan, G.P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. Clinical and laboratory associations of anticentromere antibody in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1984, 27, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, C.; Perin, J.; Zeger, S.; Wigley, F.M.; Hummers, L.K.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Rosen, A.; Shah, A.A. Cumulative disease damage and anti-PM/Scl antibodies are associated with a heavy burden of calcinosis in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 3636–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samões, B.; Guimarães da Fonseca, D.; Beirão, T.; Costa, F.; Vieira, R.; Terroso, G.; Ferreira, R.M.; Nicolau, R.; Saraiva, A.; Salvador, M.J.; et al. Assessment of calcinosis in Portuguese patients with systemic sclerosis—A multicenter study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, J.L.; Steen, V.D. The use of the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) to determine physical disability in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res. 1991, 4, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, M.; Sato, S.; Kikuchi, K.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Fujisaku, A.; Misaki, Y.; Hatamochi, A.; Kondo, H.; Takehara, K. Evaluation of functional disability using the health assessment questionnaire in Japanese patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, S.; Choudhury, M.R.; Haque, M.M.; Yeasmin, S.; Hossain, F.; Zaman, M.M. Functional disability and health-related quality of life among systemic sclerosis patients in Bangladesh. BMC Rheumatol. 2022, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çevik, R.; Em, S.; Nas, K.; Toprak, M.; Cengiz, G.; Çalış, M.; Sezer, İ.; Ünal Enginar, A.; Bora Karslı, P.; Sağ, S.; et al. Association of pain and clinical factors on disability and quality of life in systemic sclerosis: A cross-sectional study from Turkish League Against Rheumatism Network. Arch. Rheumatol. 2023, 38, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Ogura, T.; Ogawa, K.; Hirata, A.; Hayashi, N.; Izumi, Y.; Saito, E. Paraspinal and intraspinal calcinosis: Frequent complications in patients with systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1655–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, Z.; Fogelson, J.L.; Krauss, W.E. Bone but not Bone: Systemic Calcinosis Presenting as Lumbar Facet Pseudohypertrophy with Neurogenic Claudication. World Neurosurg. 2023, 180, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMehmadi, B.A.; To, F.Z.; Anderson, M.A.; Johnson, S.R. Epidemiology and Treatment of Peripheral Neuropathy in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluccio, F.; Allanore, Y.; Czirjak, L.; Furst, D.E.; Khanna, D.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Points to consider for skin ulcers in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2017, 56, v67–v71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuggioli, D.; Manfredi, A.; Lumetti, F.; Colaci, M.; Ferri, C. Scleroderma skin ulcers definition, classification and treatment strategies our experience and review of the literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Freemont, T.J.; Denton, J.; Herrick, A.L. Infected calcinosis of the knee in limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 2043–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangri, N.; Young, B.M. Soft-tissue infection and underlying calcinosis of CREST syndrome. CMAJ 2006, 175, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, C.P.; De Lorenzis, E.; Roblin, E.; Goldman, N.; Alcacer-Pitarch, B.; Blamont, E.; Buch, M.H.; Carulli, M.; Cotton, C.; Del Galdo, F.; et al. The 2024 British Society for Rheumatology guideline for management of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2024, 11, keae394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Chung, W.T. Dystrophic calcinosis in a patient with overlap syndrome (scleroderma and rheumatoid arthritis) treated by leflunomide: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuggioli, D.; Lumetti, F.; Colaci, M.; Fallahi, P.; Antonelli, A.; Ferri, C. Rituximab in the treatment of patients with systemic sclerosis. Our experience and review of the literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosounidou, S.; MacDonald, H.; Situnayake, D. Successful treatment of calcinosis with infliximab in a patient with systemic sclerosis/myositis overlap syndrome. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 960–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez Troncoso, J.; Nuño González, A.; Martínez Robles, E.; Sorriguieta Torre, R.; Robles Marhuenda, Á. Tofacitinib Is an Effective Treatment for Refractory Scleromyositis Associated with Anti-PM/Scl. Cureus 2023, 15, e34125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuggioli, D.; Lumetti, F.; Spinella, A.; Cocchiara, E.; Sighinolfi, G.; Citriniti, G.; Colaci, M.; Salvarani, C.; Ferri, C. Use of Neem oil and Hypericum perforatum for treatment of calcinosis-related skin ulcers in systemic sclerosis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060519882176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Barrio-Díaz, P.; Moll-Manzur, C.; Álvarez-Veliz, S.; Vera-Kellet, C. Topical sodium metabisulfite for the treatment of calcinosis cutis: A promising new therapy. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner-Nielsen, J.; Olesen, A.B. Treatment of Skin Calcifications with Intra-lesional Injection of Sodium Thiosulphate: A Case Series. Acta Derm. -Venereol. 2016, 96, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traineau, H.; Aggarwal, R.; Monfort, J.B.; Senet, P.; Oddis, C.V.; Chizzolini, C.; Barbaud, A.; Francès, C.; Arnaud, L.; Chasset, F. Treatment of calcinosis cutis in systemic sclerosis and dermatomyositis: A review of the literature. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, T.; Burt, M. A case report and review of calcinosis cutis. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 2024, rjae068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klifto, K.M.; Cho, B.H.; Lifchez, S.D. Surgical Debulking for Symptomatic Management of Calcinosis Cutis of the Hand and Upper Extremity in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2021, 46, 928.e1–928.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factor | Biological Effect | Clinical Significance in Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis |
|---|---|---|
| Osteonectin (SPARC) | Promotes mineralization and induces fibrotic processes via TGF-B [51,52] | Increased expression in fibroblasts and endothelial cells of patients with calcinosis |
| Osteopontin | Regulates mineralization and immune activation [55,56]. No significant link to calcinosis in SSc [57] | Increased serum levels in SSc but no association with calcinosis specifically |
| Osteoprotegerin | Reduces osteoclast activation through the blockage of receptor activation of nuclear factor-B ligand (RANKL) to RANK [58] | Significant in SSc patients with calcinosis, not elevated in all SSc patients |
| Fetuin-A | Inhibits calcification by stabilizing mineral salts [50,62] | Lower serum levels associated with calcinosis and lcSSc patients |
| Extracellular Pyrophosphate (PPi) | Regulates calcification through hydroxyapatite inhibition [63,64] | Imbalance contributes to ectopic calcification, with lower levels seen in SSc |
| Extracellular matrix (ECM) | Serves as a template for hydroxyapatite, fibrosis increases ECM stiffness, which facilitates calcinosis [66,67] | Excess ECM production promotes calcinosis, especially in high-pressure areas |
| IL-31 | Profibrotic cytokine. Enhances osteogenic differentiation under stiff ECM conditions [71] | Elevated in SSc, associated with increased osteogenic differentiation and fibrosis |
| Membrane Vesicles | Observed in ectopic calcification [78] Matrix vesicles from dying cells initiate mineralization | No direct evidence connecting vesicles to calcinosis in SSc |
| Mitochondria and DRP-1 | Regulates mitochondrial fission, linked to vascular calcification, promotes apoptosis and oxidative stress [80,81] | Implicated in the development of calcinosis in SSc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avanoglu Guler, A.; De Luca, G.; Dagna, L.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Campochiaro, C. Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis: A Molecular and Clinical Insight. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011257
Avanoglu Guler A, De Luca G, Dagna L, Matucci-Cerinic M, Campochiaro C. Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis: A Molecular and Clinical Insight. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(20):11257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011257
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvanoglu Guler, Aslihan, Giacomo De Luca, Lorenzo Dagna, Marco Matucci-Cerinic, and Corrado Campochiaro. 2024. "Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis: A Molecular and Clinical Insight" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 20: 11257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011257
APA StyleAvanoglu Guler, A., De Luca, G., Dagna, L., Matucci-Cerinic, M., & Campochiaro, C. (2024). Unraveling the Pathogenesis of Calcinosis in Systemic Sclerosis: A Molecular and Clinical Insight. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(20), 11257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011257







