Identification of Potato StPIN Gene Family and Regulation of Root Development by StPIN4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Analysis of Potato StPIN Family Genes
2.2. Chromosomal Localization and Gene Structure Analysis of Potato PIN Gene Family Members
2.3. Potato StPINs Protein Family Motif and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements of Potato PIN Gene Family Members
2.5. Expression of StPIN Gamily Genes During Potato Root Development
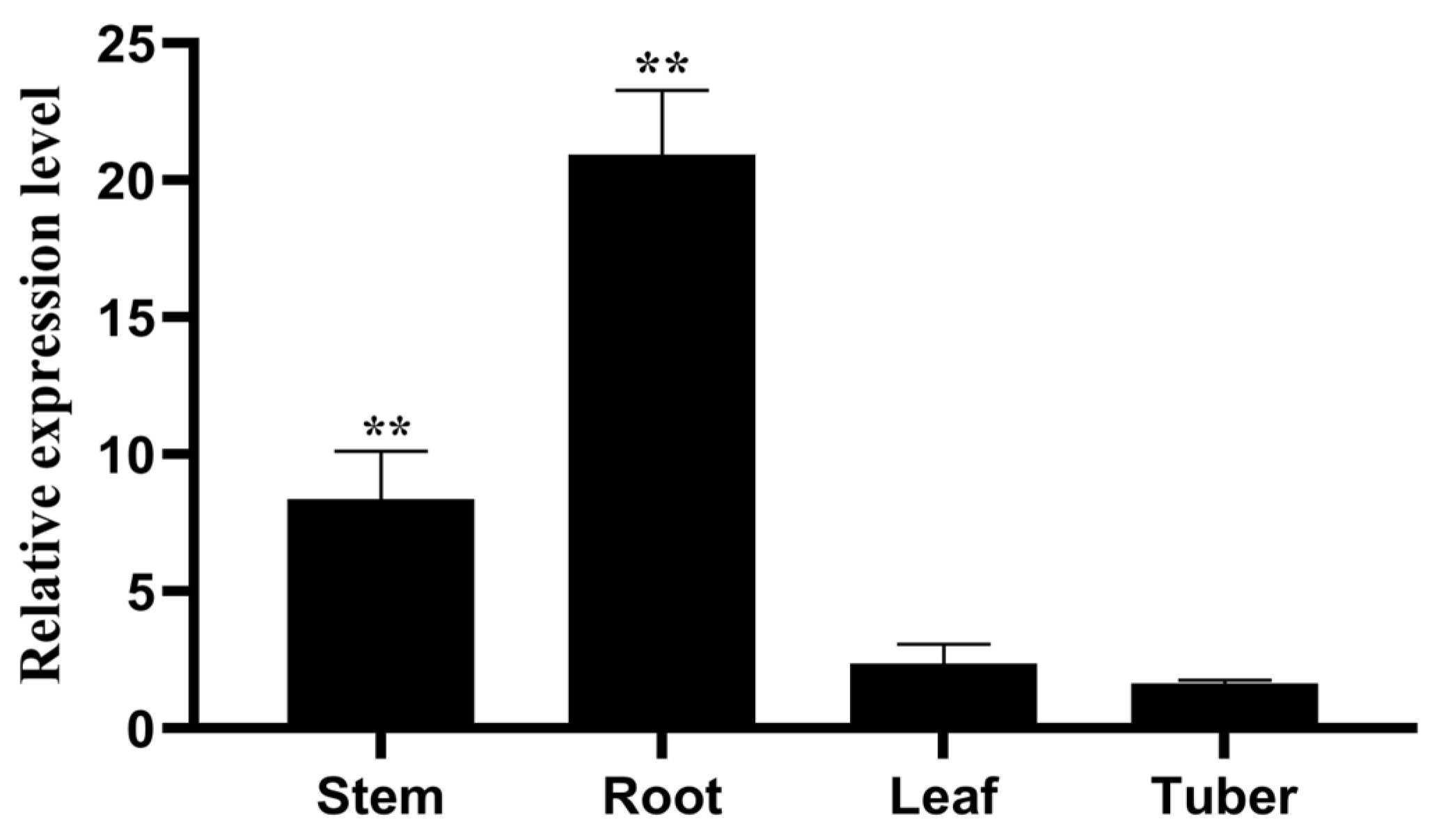
2.6. Tissue Differential Expression Analysis of StPIN4 Gene
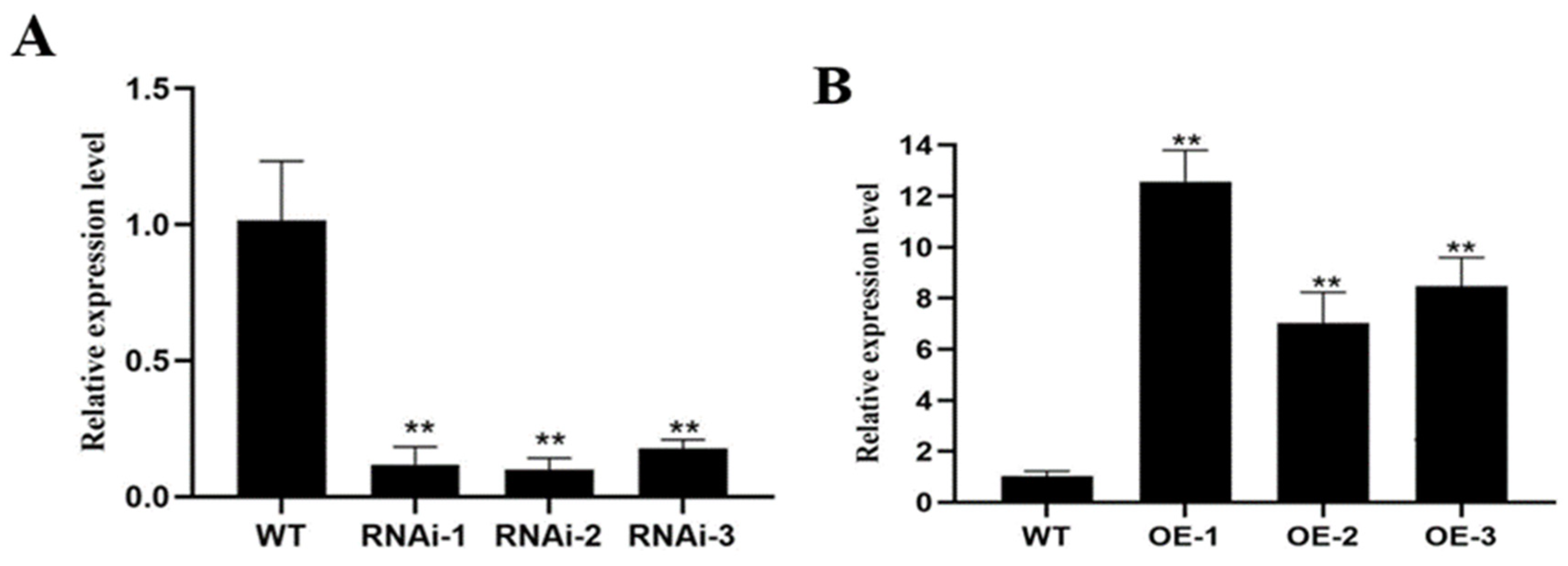
2.7. Acquisition and Assay of Transgenic Plants
2.8. qRT-PCR Analysis and RNA Validation
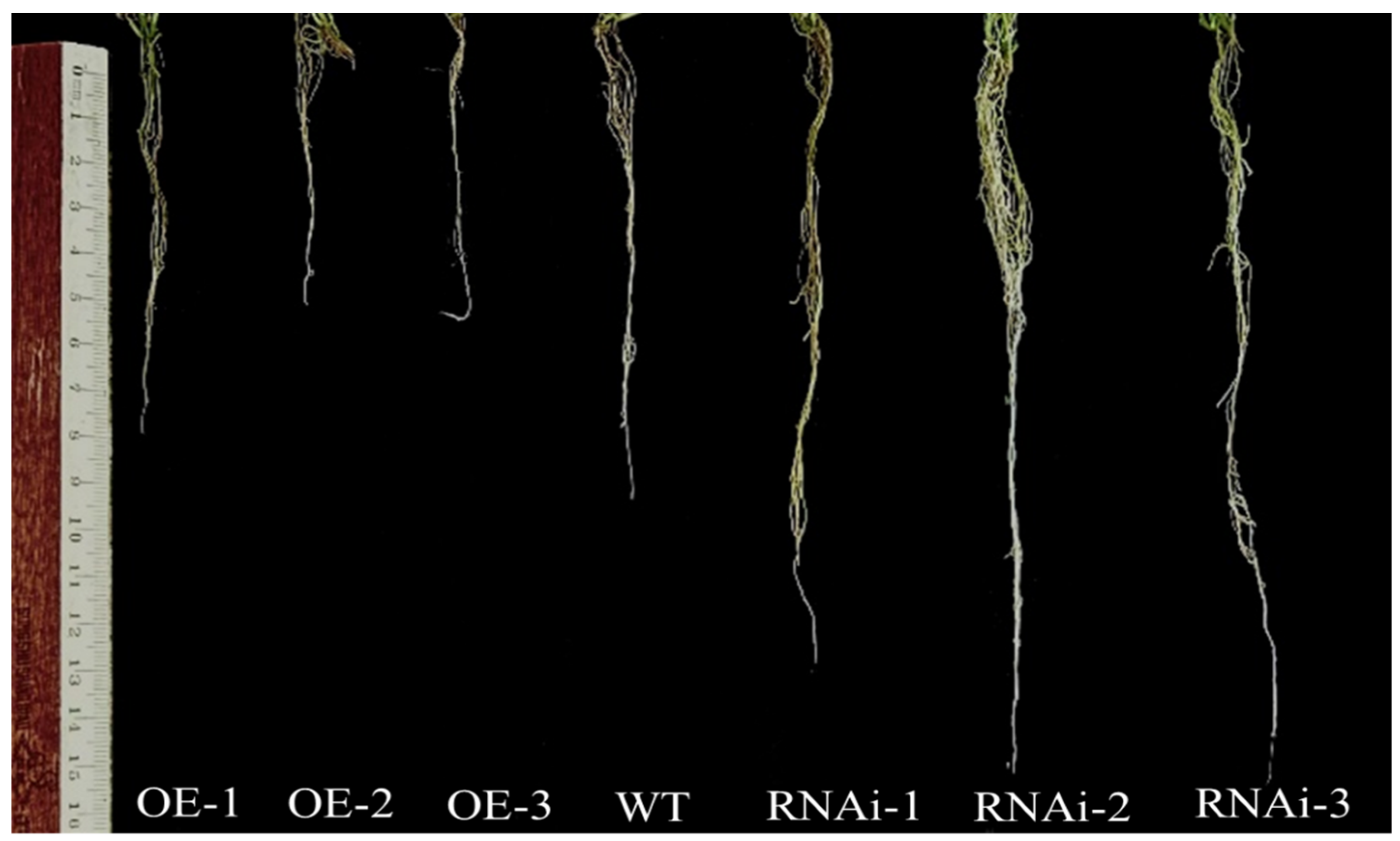
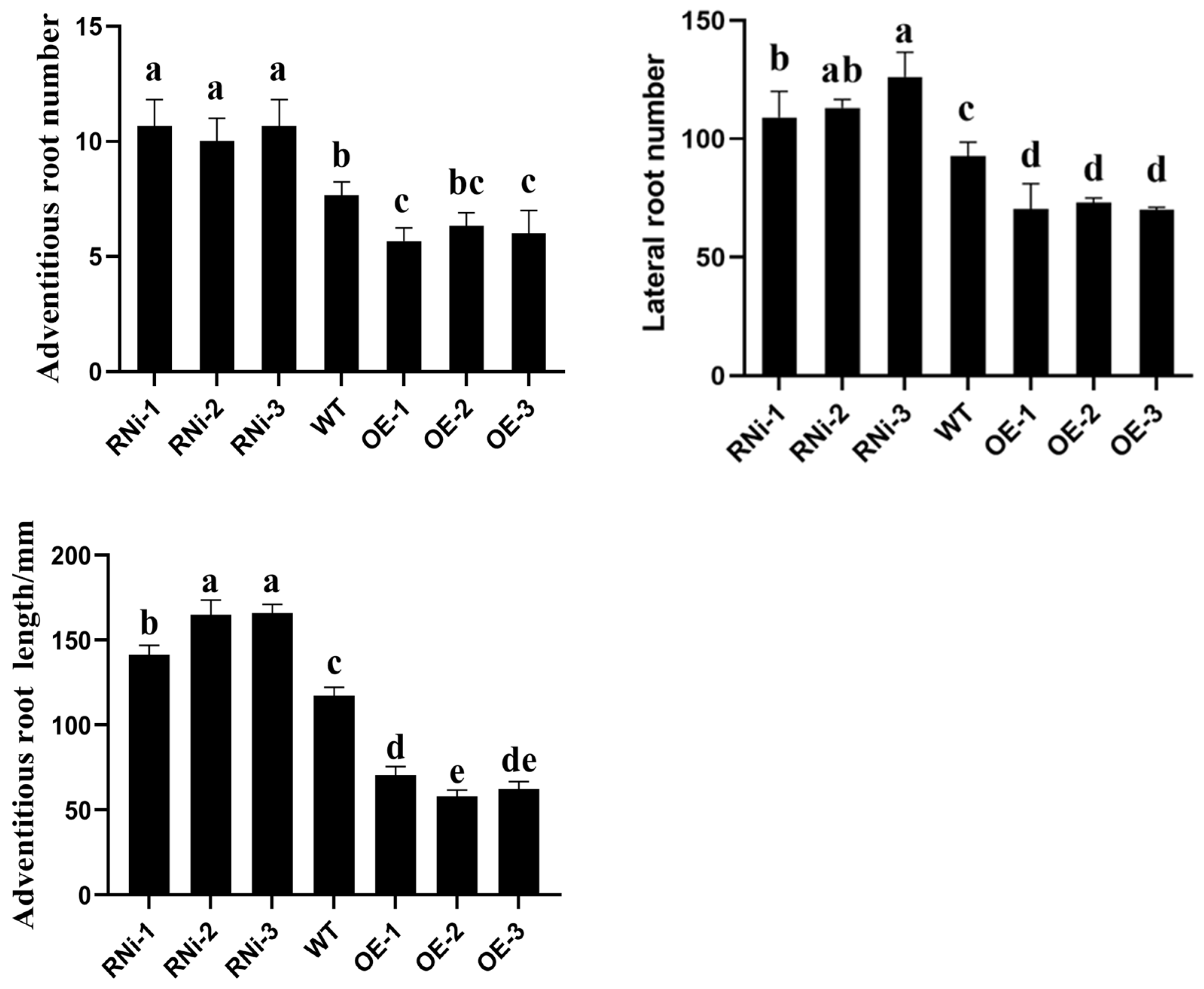
2.9. Phenotypic Assay of Transgenic Potato
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Identification and Annotation of Potato PIN Gene Family Members
4.3. Bioinformatics Analysis of StPINs
4.4. Gene Expression Analysis of StPINs
4.5. Construction of Expression Vectors for Potato Transgenic Plants
4.6. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
4.7. Analysis of StPIN4 Regulates Potato Root Development
4.8. Data Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Enders, T.A.; Strader, L.C. Auxin activity: Past, present, and future. Am. J. Bot. 2015, 102, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.A. Transmembrane auxin carrier systems-dynamic regulators of polar auxin transport. Plant Growth Regul. 2000, 32, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titapiwatanakun, B.; Murphy, A.S. Post-transcriptional regulation of auxin transport proteins: Cellular trafficking, protein phosphorylation, protein maturation, ubiquitination, and membrane composition. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péret, B.; Swarup, K.; Ferguson, A.; Seth, M.; Yang, Y.; Dhondt, S.; James, N.; Casimiro, I.; Perry, P.; Syed, A.; et al. AUX/LAX genes encode a family of auxin influx transporters that perform distinct functions during Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2874–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubeš, M.; Yang, H.; Richter, G.L.; Cheng, Y.; Młodzińska, E.; Wang, X.; Blakeslee, J.J.; Carraro, N.; Petrášek, J.; Zažímalová, E.; et al. The Arabidopsis concentration-dependent influx/efflux transporter ABCB4 regulates cellular auxin levels in the root epidermis. Plant J. 2012, 69, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Ueda, J.; Komaki, M.K.; Bell, C.J.; Shimura, Y. Requirement of the auxin polar transport system in early stages of Arabidopsis floral bud formation. Plant Cell 1991, 3, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazímalová, E.; Krecek, P.; Skůpa, P.; Hoyerová, K.; Petrásek, J. Polar transport of the plant hormone auxin—The role of PIN-FORMED (PIN) proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cai, M.; Chen, M.; Ke, W.; Pan, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Peng, C. Genome-wide characterization of PIN auxin efflux carrier gene family in Mikania micrantha. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecek, P.; Skupa, P.; Libus, J.; Naramoto, S.; Tejos, R.; Friml, J.; Zazímalová, E. The PIN-FORMED (PIN) protein family of auxin transporters. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiewka, M.; Bilanovičová, V.; Seifu, Y.W.; Nodzyński, T. The Nuts and Bolts of PIN Auxin Efflux Carriers. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Park, M.; Kesawat, M.S.; Cho, H.T. Functional analysis of the hydrophilic loop in intracellular trafficking of Arabidopsis PIN-FORMED proteins. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1570–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.R.; Hu, H.; Wang, G.H.; Li, J.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, P. Expression of PIN genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Tissue specificity and regulation by hormones. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Qin, G.; Si, P.; Luo, Z.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, P.; Xia, Q.; Lin, F.; et al. Analysis of Nicotiana tabacum PIN genes identifies NtPIN4 as a key regulator of axillary bud growth. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 160, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forestan, C.; Varotto, S. The role of PIN auxin efflux carriers in polar auxin transport and accumulation and their effect on shaping maize development. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhao, P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, H.; Yu, J.; Xiao, G. The PIN gene family in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum): Genome-wide identification and gene expression analyses during root development and abiotic stress responses. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, W.; Huang, Z.A.; Cho, M.; Yu, Q.; Wu, C.; Yu, C. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CaLAX and CaPIN gene families in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) under various abiotic stresses and hormone treatments. Genome 2018, 61, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Chen, J.; Lu, M. A survey of Populus PIN-FORMED family genes reveals their diversified expression patterns. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chai, C.; Valliyodan, B.; Maupin, C.; Annen, B.; Nguyen, H.T. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the PIN auxin transporter gene family in soybean (Glycine max). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattison, R.J.; Catalá, C. Evaluating auxin distribution in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) through an analysis of the PIN and AUX/LAX gene families. Plant J. 2012, 70, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Tie, S.; Sun, T.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Qi, J.; Yan, S.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Shen, C. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of ZmPIN, ZmPILS, ZmLAX and ZmABCB auxin transporter gene families in maize (Zea mays L.) under various abiotic stresses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallari, N.; Artner, C.; Benkova, E. Auxin-Regulated Lateral Root Organogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2021, 13, a039941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, C.; Pacurar, D.I.; Perrone, I. Adventitious roots and lateral roots: Similarities and differences. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 639–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonin, M.; Bergougnoux, V.; Nguyen, T.D.; Gantet, P.; Champion, A. What makes adventitious roots? Plants 2019, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, E.; Xie, Z.; Gustafson, A.M.; Carrington, J.C. microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 2005, 121, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Singh, D.; Saksena, H.B.; Sharma, M.; Tiwari, A.; Awasthi, P.; Botta, H.K.; Shukla, B.N.; Laxmi, A. Understanding the intricate web of phytohormone signalling in modulating root system architecture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Dong, Z.; Zhen, X.; Song, S.; Jiao, J.; Wang, M.; Song, C. Auxin and its interaction with ethylene control adventitious root formation and development in apple rootstock. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 574881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravec, J.; Kubes, M.; Bielach, A.; Gaykova, V.; Petrásek, J.; Skůpa, P.; Chand, S.; Benková, E.; Zazímalová, E.; Friml, J. Interaction of PIN and PGP transport mechanisms in auxin distribution-dependent development. Development 2008, 135, 3345–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.M.; Cho, H.S.; Jeon, J.H. PIN-mediated polar auxin transport facilitates root-obstacle avoidance. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Chen, S. Health benefits of the potato affected by domestic cooking: A review. Food Chem. 2016, 202, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojon, A.; Nacry, P.; Davidian, J.C. Root uptake regulation: A central process for NPS homeostasis in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhang, M.; De Smet, I.; Ding, Z. Designer crops: Optimal root system architecture for nutrient acquisition. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, H.; Nai, G.; Lu, S.; Ma, W.; Chen, B.; Mao, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of PIN gene family under phytohormone and abiotic stresses in Vitis Vinifera L. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plant 2022, 28, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Chen, Q.; Qu, Y.; Liu, P.; Jiao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Deng, X.; Zheng, K. Identification and functional analysis of PIN family genes in Gossypium barbadense. PeerJ. 2022, 10, e14236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omelyanchuk, N.A.; Kovrizhnykh, V.V.; Oshchepkova, E.A.; Pasternak, T.; Palme, K.; Mironova, V.V. A detailed expression map of the PIN1 auxin transporter in Arabidopsis thaliana root. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; An, H.S.; Wang, Y. Low expression of PIN gene family members is involved in triggering the dwarfing effect in M9 interstem but not in M9 rootstock apple trees. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanneste, S.; Friml, J. Auxin: A trigger for change in plant development. Cell 2009, 136, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, S.; Beis, D.; Wolkenfelt, H.; Murfett, J.; Guilfoyle, T.; Malamy, J.; Benfey, P.; Leyser, O.; Bechtold, N.; Weisbeek, P.; et al. An auxin-dependent distal organizer of pattern and polarity in the Arabidopsis root. Cell 1999, 99, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blilou, I.; Xu, J.; Wildwater, M.; Willemsen, V.; Paponov, I.; Friml, J.; Heidstra, R.; Aida, M.; Palme, K.; Scheres, B. The PIN auxin efflux facilitator network controls growth and patterning in Arabidopsis roots. Nature 2005, 433, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieten, A.; Vanneste, S.; Wisniewska, J.; Benková, E.; Benjamins, R.; Beeckman, T.; Luschnig, C.; Friml, J. Functional redundancy of PIN proteins is accompanied by auxin-dependent cross-regulation of PIN expression. Development 2005, 132, 4521–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewska, J.; Xu, J.; Seifertová, D.; Brewer, P.B.; Ruzicka, K.; Blilou, I.; Rouquié, D.; Benková, E.; Scheres, B.; Friml, J. Polar PIN localization directs auxin flow in plants. Science 2006, 312, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feraru, E.; Friml, J. PIN polar targeting. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, I.C.R.; Hammes, U.Z.; Schwechheimer, C. Activation and Polarity Control of PIN-FORMED Auxin Transporters by Phosphorylation. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz Rosquete, M.; Waidmann, S.; Kleine-Vehn, J. PIN7 Auxin Carrier Has a Preferential Role in Terminating Radial Root Expansion in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.T.; Xiang, Z.X.; Li, W.; Gao, X.; Lu, Y.T. Osmotic stress represses root growth by modulating the transcriptional regulation of PIN-FORMED3. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleine-Vehn, J.; Ding, Z.; Jones, A.R.; Tasaka, M.; Morita, M.T.; Friml, J. Gravity-induced PIN transcytosis for polarization of auxin fluxes in gravity-sensing root cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22344–22349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.J.; Xie, C.H.; Liu, J. Optimization of agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation system of potato in vitro potato and introduction of antisense class I patatin gene. Acta Agron. Sin. 2003, 29, 801–805. [Google Scholar]
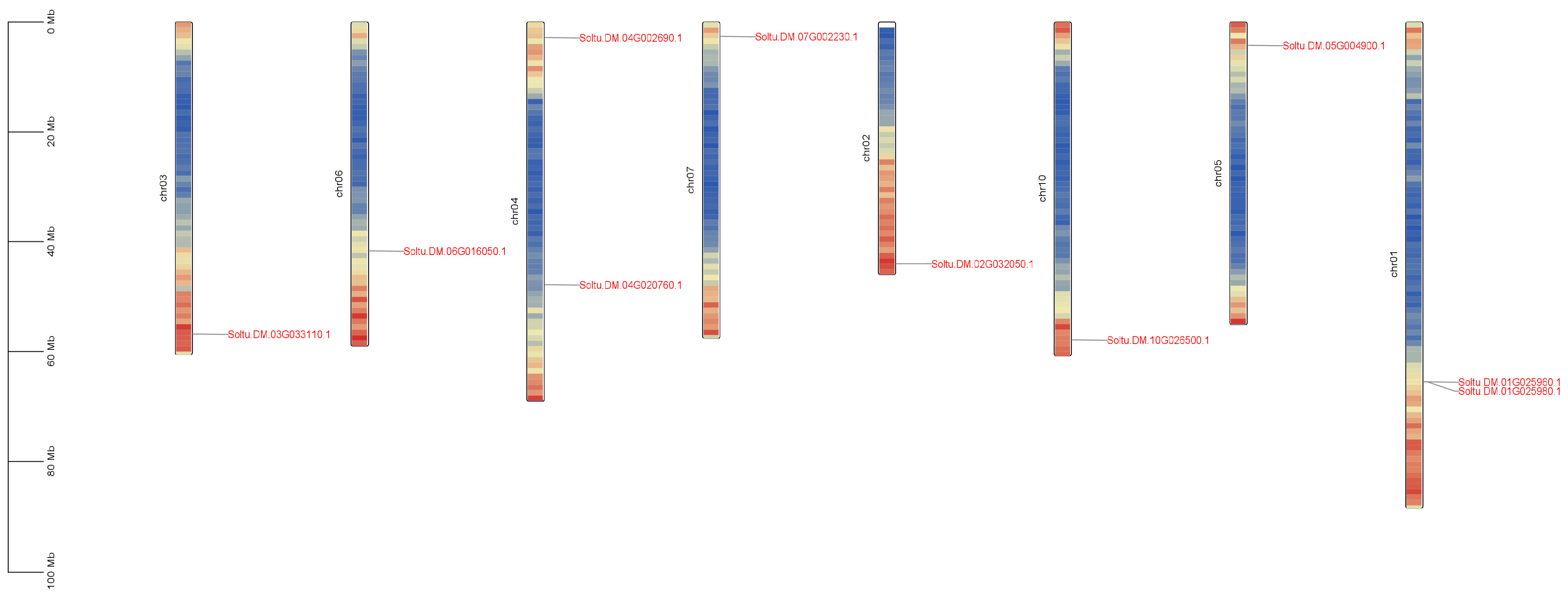
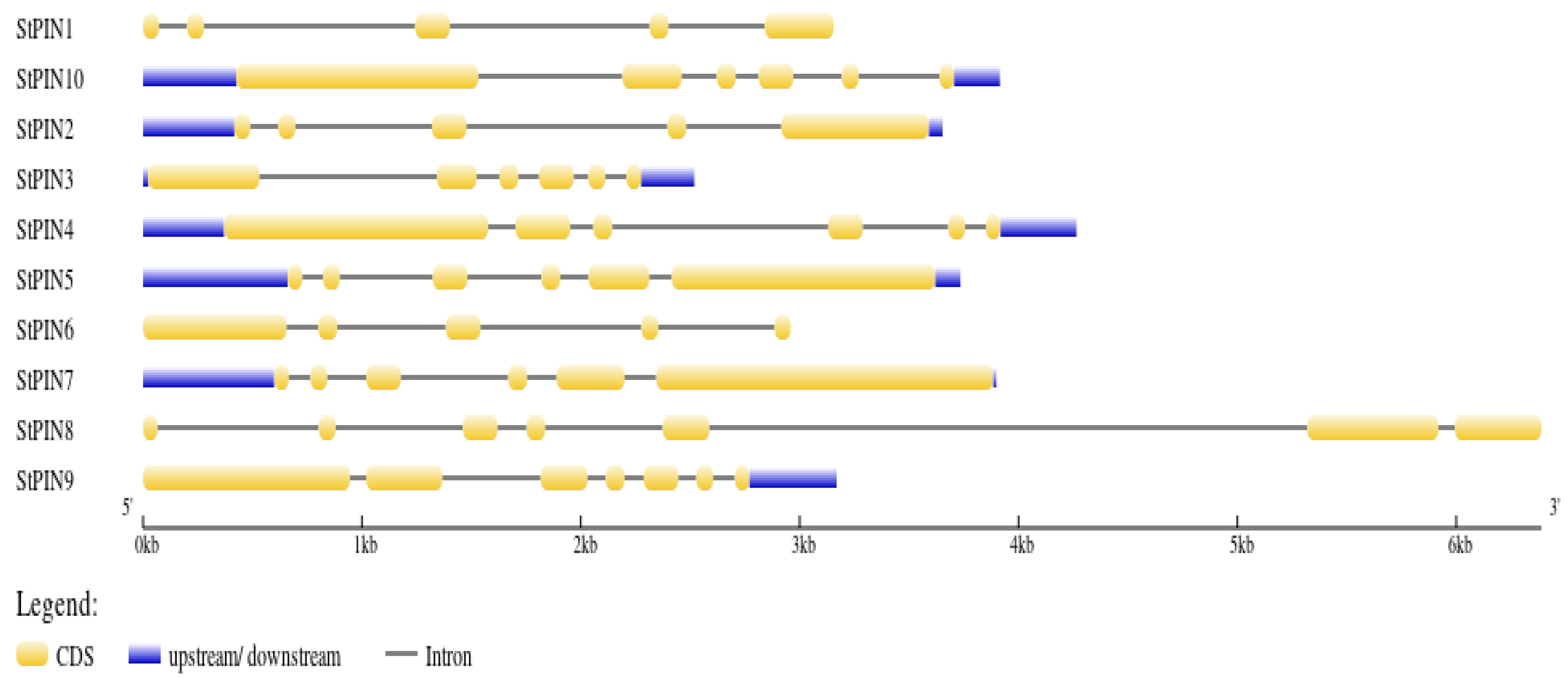

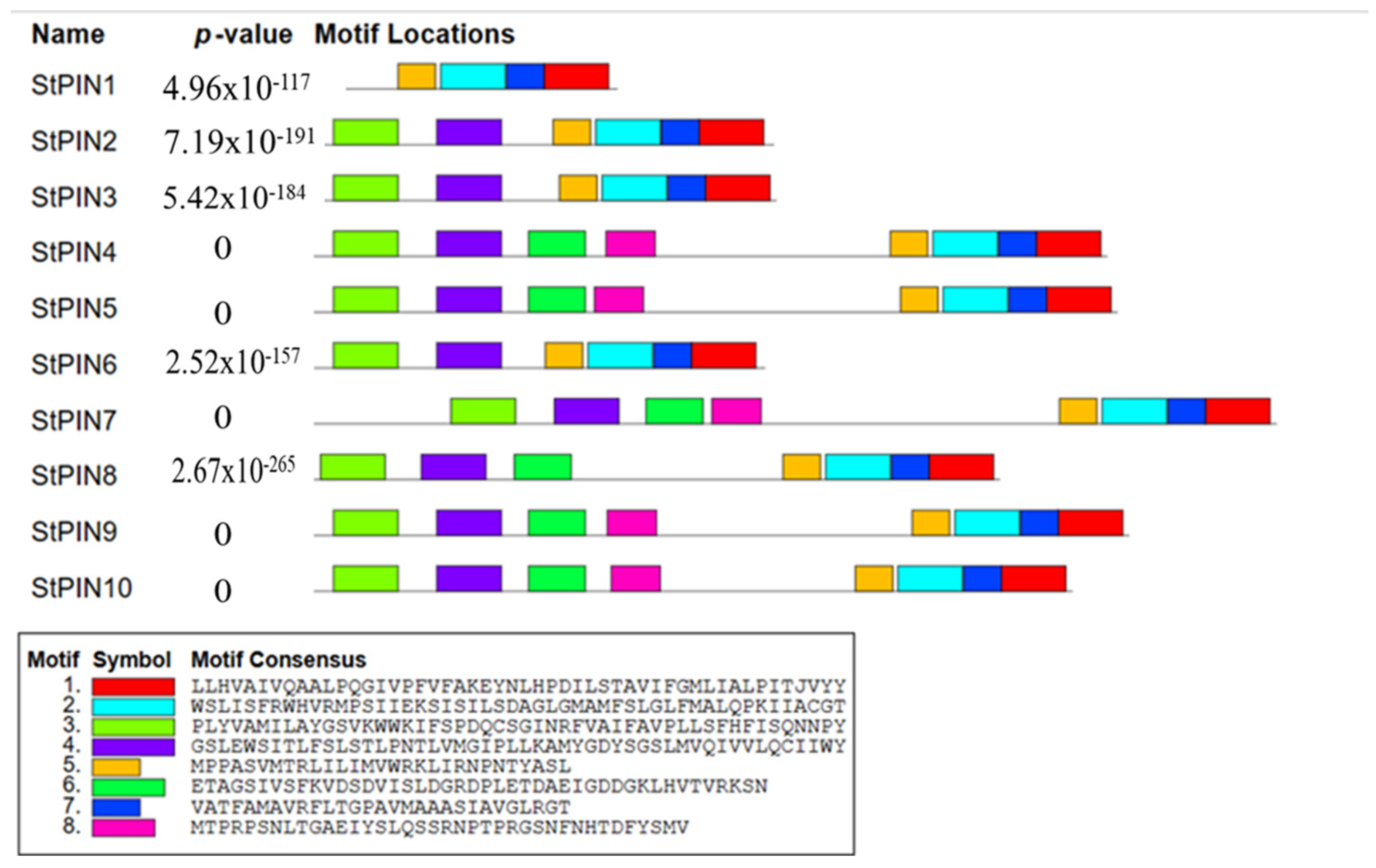

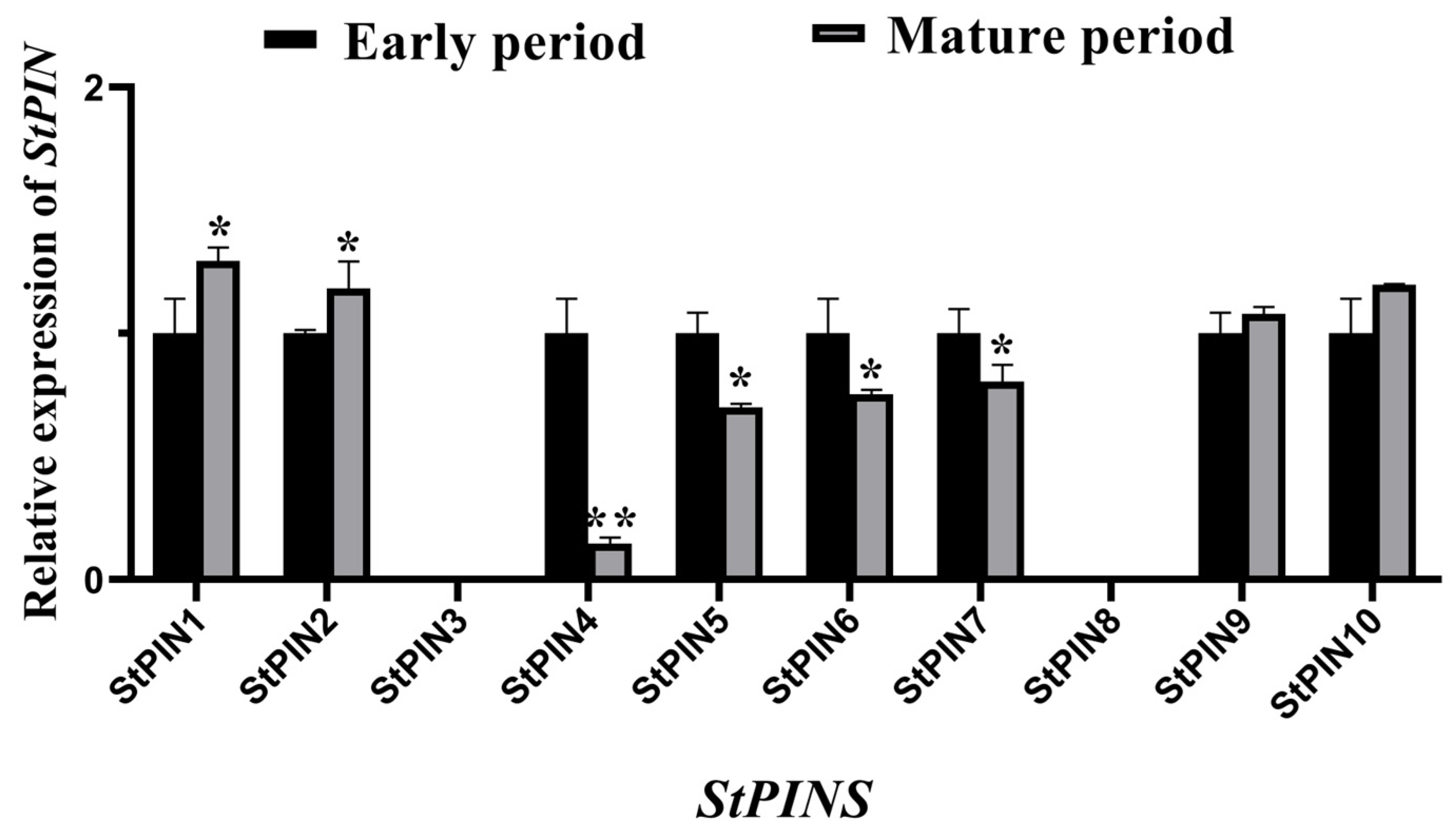

| Name | Gene ID | Number of AA | Molecular Weight | pI | Instability Coefficient | Hydrophilicity Index | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| StPIN1 | Soltu.DM.01G025960.1 | 235 | 25,398.31 | 9.22 | 42.42 | 0.793 | Plasma Membrane |
| StPIN2 | Soltu.DM.01G025980.1 | 355 | 39,264.82 | 9.13 | 36.26 | 0.762 | Plasma Membrane |
| StPIN3 | Soltu.DM.02G032050.1 | 358 | 39,084.99 | 9.18 | 34.90 | 0.793 | Plasma Membrane |
| StPIN4 | Soltu.DM.03G033110.1 | 614 | 67,134.08 | 9.08 | 37.51 | 0.030 | Plasma Membrane |
| StPIN5 | Soltu.DM.04G002690.1 | 622 | 68,279.87 | 6.57 | 39.89 | 0.141 | Plasma Membrane |
| StPIN6 | Soltu.DM.04G020760.1 | 349 | 38,620.75 | 6.58 | 35.82 | 0.681 | Plasma Membrane |
| StPIN7 | Soltu.DM.05G004900.1 | 745 | 81,967.28 | 7.05 | 41.95 | 0.085 | Plasma Membrane |
| StPIN8 | Soltu.DM.06G016050.1 | 531 | 57,957.83 | 8.85 | 33.17 | 0.408 | Plasma Membrane |
| StPIN9 | Soltu.DM.07G002230.1 | 631 | 68,666.48 | 9.14 | 42.51 | 0.166 | Plasma Membrane |
| StPIN10 | Soltu.DM.10G026500.1 | 587 | 63,906.07 | 8.81 | 34.67 | 0.233 | Plasma Membrane |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, N.; Si, H. Identification of Potato StPIN Gene Family and Regulation of Root Development by StPIN4. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111517
Zhang Q, Liu Q, Yang J, Zhang N, Si H. Identification of Potato StPIN Gene Family and Regulation of Root Development by StPIN4. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(21):11517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111517
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qian, Qing Liu, Jiangwei Yang, Ning Zhang, and Huaijun Si. 2024. "Identification of Potato StPIN Gene Family and Regulation of Root Development by StPIN4" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 21: 11517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111517
APA StyleZhang, Q., Liu, Q., Yang, J., Zhang, N., & Si, H. (2024). Identification of Potato StPIN Gene Family and Regulation of Root Development by StPIN4. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(21), 11517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111517






