Can Mammalian Reproductive Health Withstand Massive Exposure to Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastic Derivatives? A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Bibliographic Search Methods
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Results
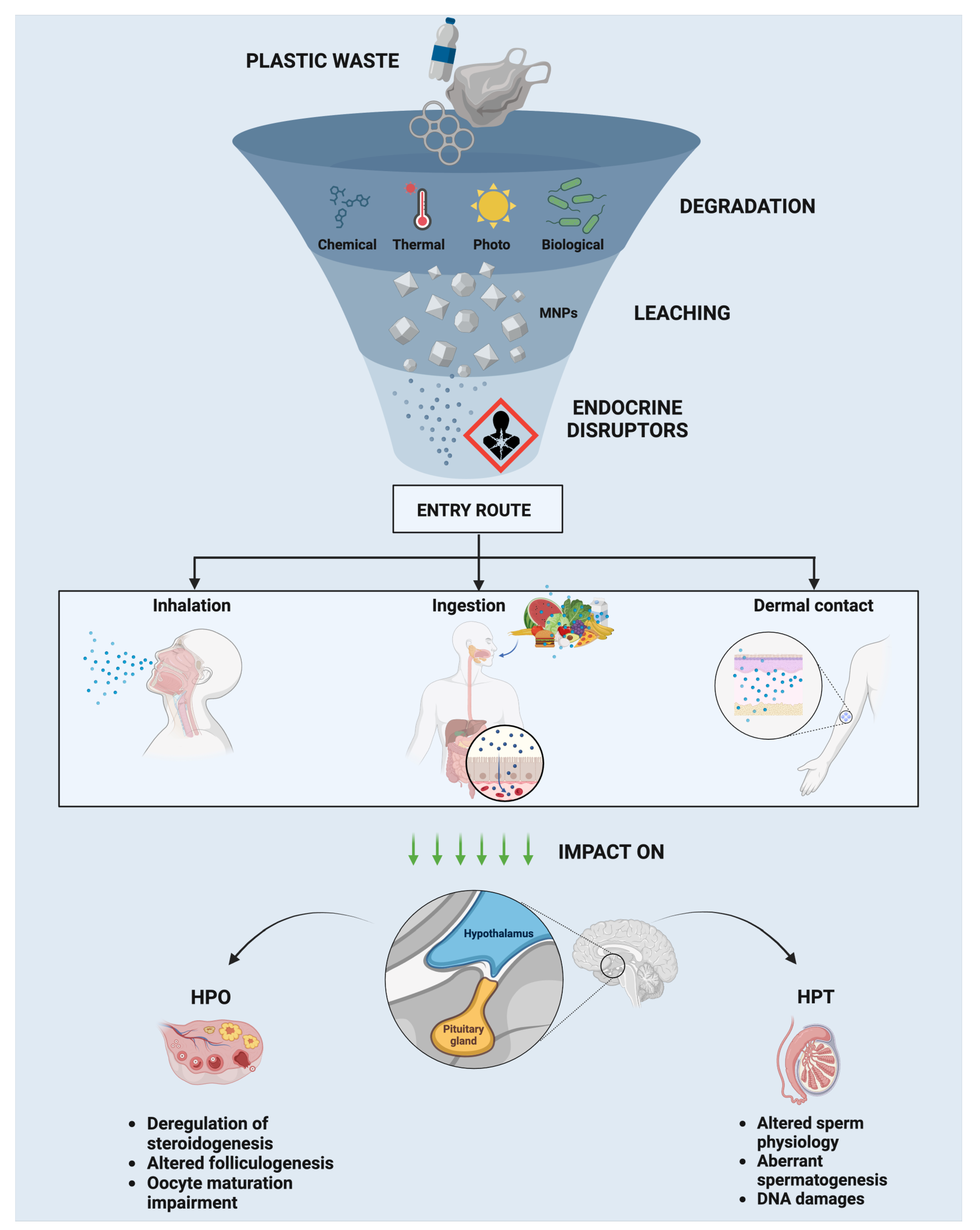
3. Increased Usage of Plastic Materials, Micro- and Nanoplastic (MNPs), Sources, and Environmental Pollution
3.1. Plastic Degradation Processes
3.2. MNP Composition
3.3. Reproductive Health: Interference on Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonad (HPG) Axis
3.3.1. Endocrine Effects in Males: HP–Testis (HPT) Axis
3.3.2. Endocrine Effects in Females: HP–Ovary (HPO) Axis
3.4. A Journey Along the Reproductive Effects of Polystyrene PS-MNP Exposure of Mammalian Organisms
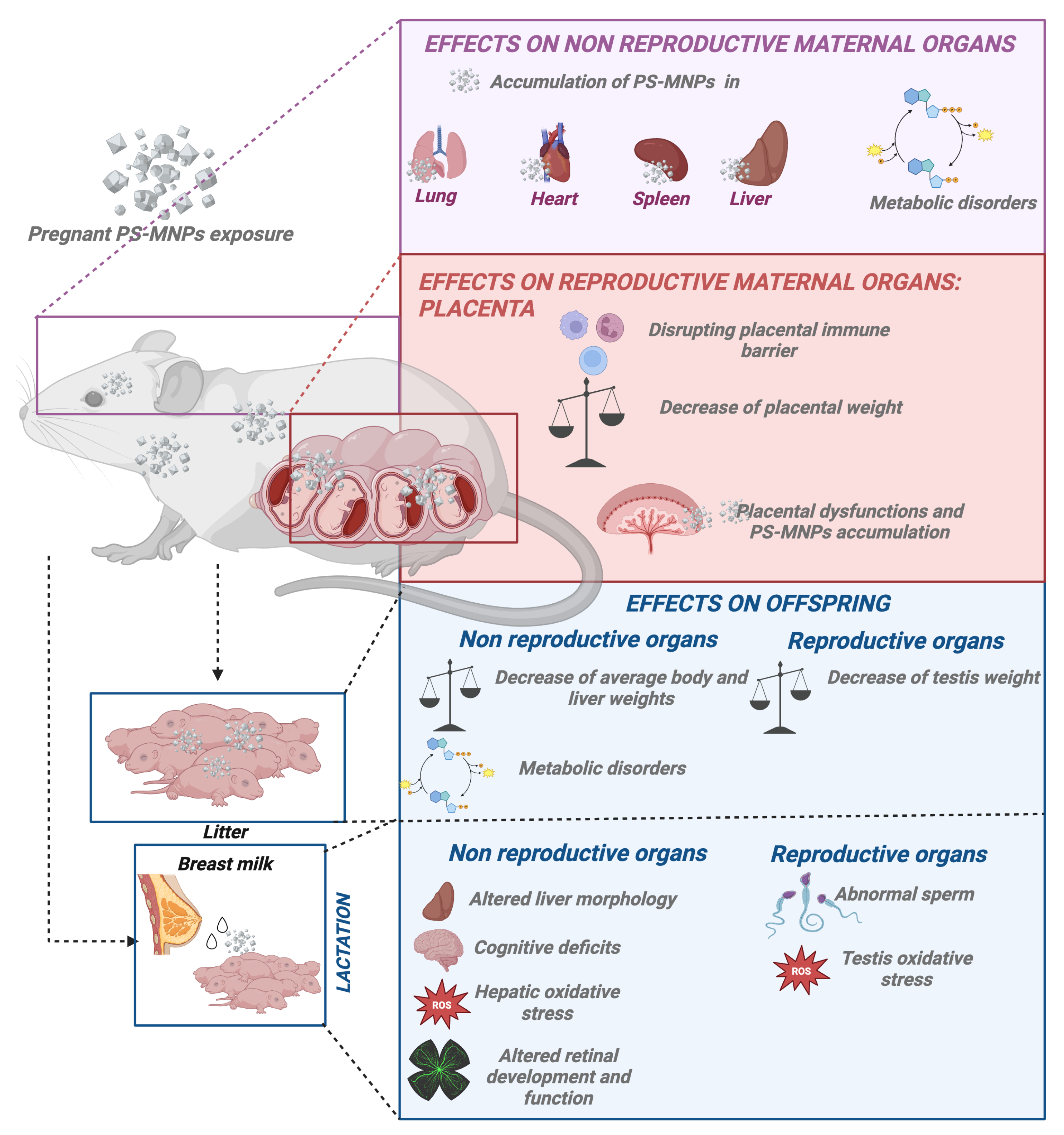
3.4.1. Gestational Influence of PS-MNPs
Impact of PS-MNPs on Pregnancy and Placental Function
3.4.2. Offspring Effects Derived from PS-MNP Maternal Exposure
Maternal Exposure to PS-MPs Causes Decreased Offspring Weight
Maternal Exposure to PS-MNPs Causes Fatty Acid Metabolic Disorders in Offspring
3.5. Post Natal PS-MNP Influence: Effects on Offspring During Lactation
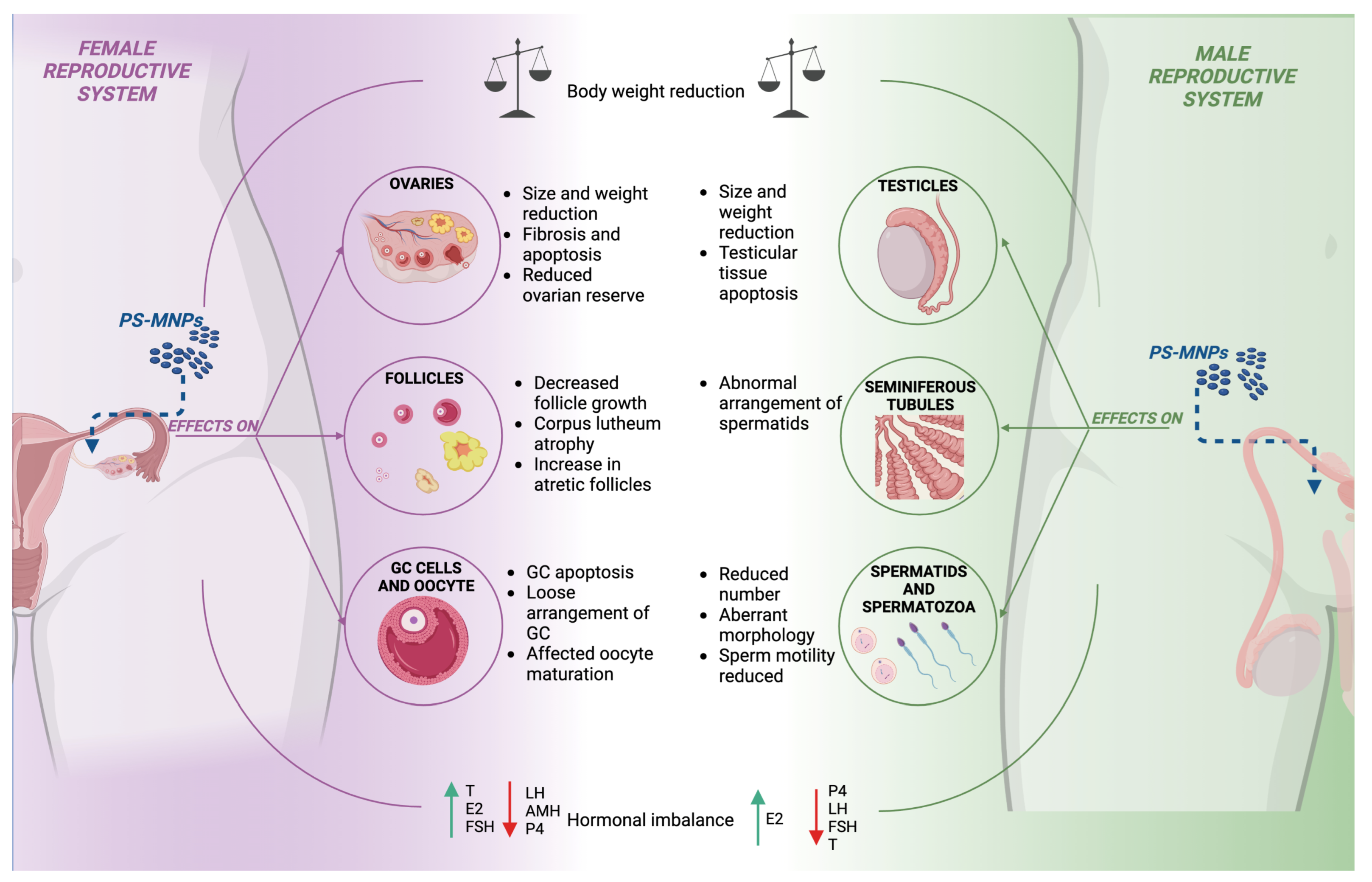
3.6. PS-MNPs on Adult Reproductive Health
3.6.1. Effects of PS-MNP Exposure on the Female Mammalian Reproductive System
3.6.2. Effects of PS-MNP Exposure on the Male Mammalian Reproductive System
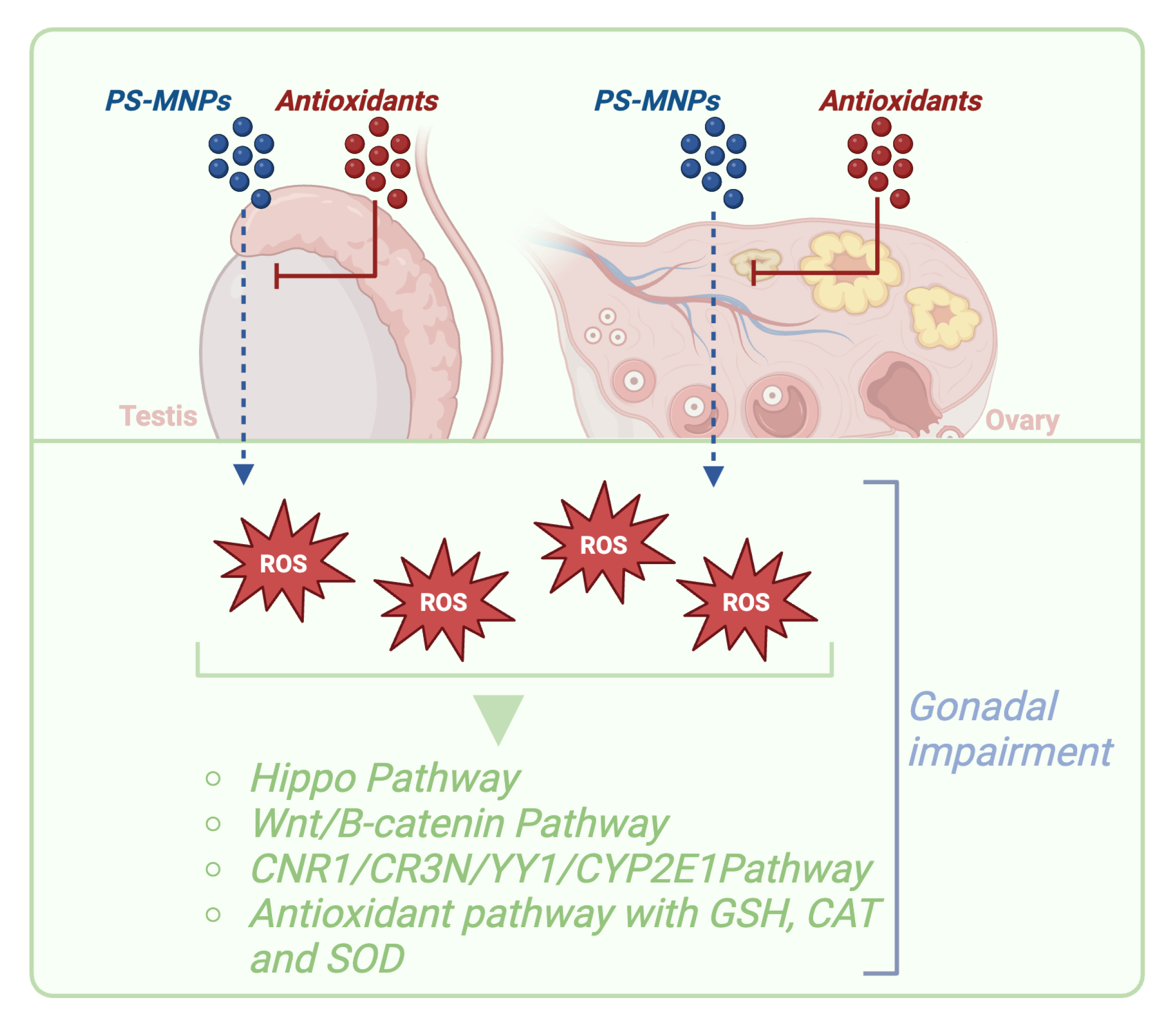
3.7. Mechanism of Action of PS-MNPs in Reproduction Systems
3.7.1. The Role of Signaling Pathways of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in PS-MNP-Mediated Male and Female Reproductive Function Failures
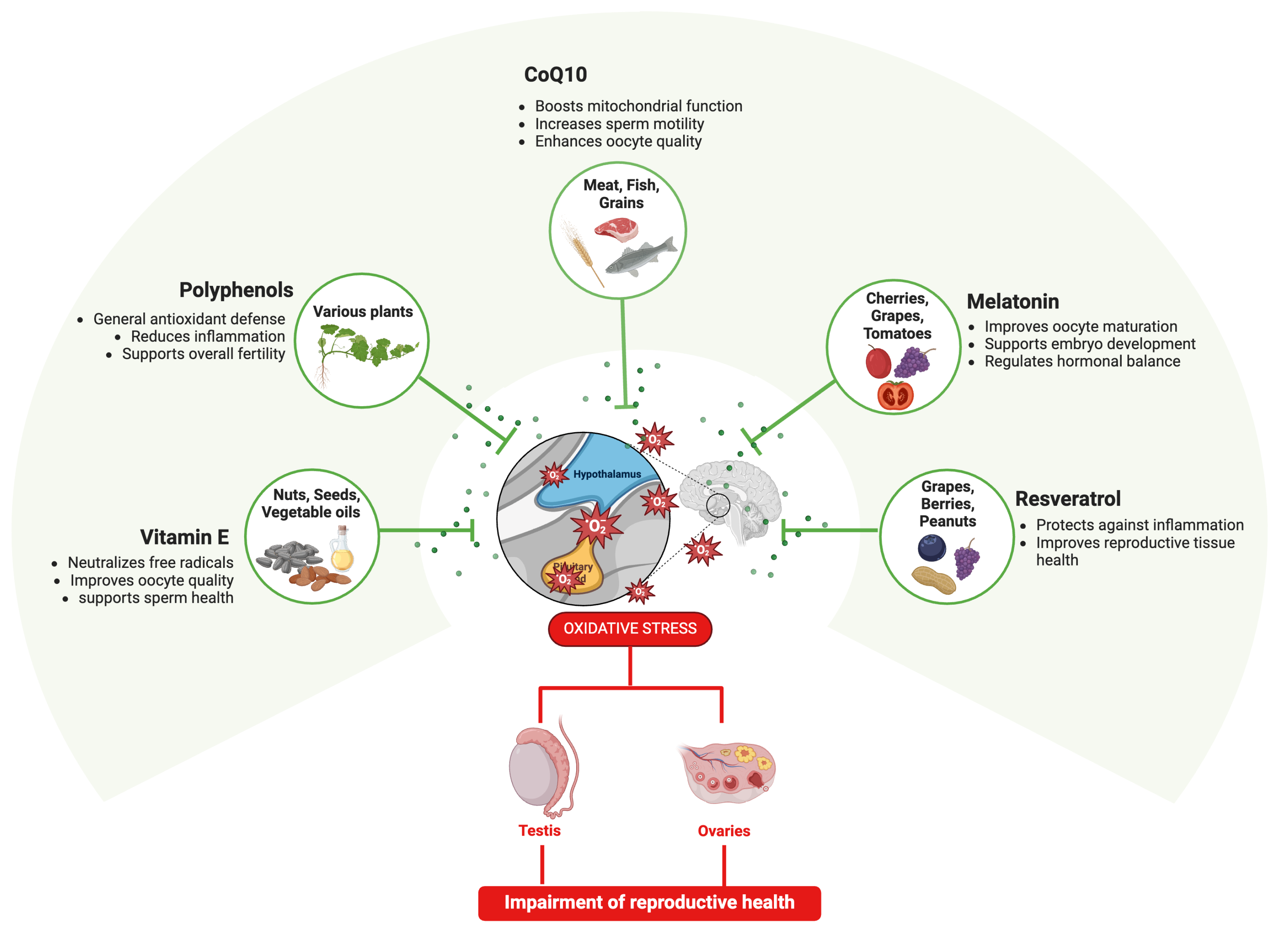
3.7.2. Are Antioxidants the Key to Prevent PS-MNP Effects on Reproductive Systems?
Beneficial Reproductive Effects of Antioxidants Derived from Biological Matrices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eliso, M.C.; Billè, B.; Cappello, T.; Maisano, M. Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastics (PS MNPs): A Review of Recent Advances in the Use of -Omics in PS MNP Toxicity Studies on Aquatic Organisms. Fishes 2024, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, M.; Jiang, J.; Dai, M.; Wang, B.; et al. Underestimated Health Risks: Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastics Jointly Induce Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction by ROS-Mediated Epithelial Cell Apoptosis. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüst, M.; Meijer, J.; Westerink, R.H.S. The Plastic Brain: Neurotoxicity of Micro- and Nanoplastics. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithner, D.; Larsson, Å.; Dave, G. Environmental and Health Hazard Ranking and Assessment of Plastic Polymers Based on Chemical Composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3309–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amobonye, A.; Bhagwat, P.; Raveendran, S.; Singh, S.; Pillai, S. Environmental Impacts of Microplastics and Nanoplastics: A Current Overview. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 768297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Savino, I.; Locaputo, V.; Uricchio, V.F. A Detailed Review Study on Potential Effects of Microplastics and Additives of Concern on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddela, N.R.; Kakarla, D.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M. Additives of Plastics: Entry into the Environment and Potential Risks to Human and Ecological Health. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotou, E.M.; Ojasalo, V.; Damdimopoulou, P. Phthalates, Ovarian Function and Fertility in Adulthood. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 35, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, R.; Huang, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced Reproductive Toxicities Induced by Phthalates Contaminated Microplastics in Male Mice (Mus musculus). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Sharma, S.; Afjal, M.A.; Habib, H.; Akhter, J.; Goswami, P.; Parvez, S.; Akhtar, M.; Raisuddin, S. mRNA Expression and Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis of Adrenal Steroidogenesis in Response to Exposure to Phthalates in Rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 89, 103780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, M.J.; Neff, A.M.; Brehm, E.; Warner, G.R.; Flaws, J.A. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals and Reproductive Disorders in Women, Men, and Animal Models. Adv. Pharmacol. 2021, 92, 151–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human Exposure to Bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLoid, G.M.; Yang, Z.; Bazina, L.; Kharaghani, D.; Sadrieh, F.; Demokritou, P. Mechanisms of Ingested Polystyrene Micro-Nanoplastics (MNPs) Uptake and Translocation in an in Vitro Tri-Culture Small Intestinal Epithelium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 473, 134706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, T.; Ge, Y.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Liang, G. Inhalation Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics Induces Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease-like Lung Injury in Mice through Multi-Dimensional Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 347, 123633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, T.; Gong, S.; Wan, X.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Hu, C.; Yang, F.; Yin, L.; et al. Ferroptosis Participated in Inhaled Polystyrene Nanoplastics-Induced Liver Injury and Fibrosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhuan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Fu, X.; Hou, Y. Polystyrene Microplastics Induced Female Reproductive Toxicity in Mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Lei, Z.; Cui, L.; Hou, Y.; Yang, L.; An, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene Microplastics Lead to Pyroptosis and Apoptosis of Ovarian Granulosa Cells via NLRP3/Caspase-1 Signaling Pathway in Rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 112012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zou, L.; Bao, M.; Feng, Q.; Xia, W.; Zhu, C. Toxicity of Polystyrene Nanoparticles for Mouse Ovary and Cultured Human Granulosa Cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Deng, T.; Duan, J.; Xie, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M. Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics Causes Reproductive Toxicity through Oxidative Stress and Activation of the P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Ma, T.; Sha, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Ding, J. Polystyrene Microplastics Induced Male Reproductive Toxicity in Mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Ahmad, S.; Guo, X.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, S.; Nabi, G.; Wanghe, K. A Review of the Endocrine Disrupting Effects of Micro and Nano Plastic and Their Associated Chemicals in Mammals. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1084236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoye, C.O.; Addey, C.I.; Oderinde, O.; Okoro, J.O.; Uwamungu, J.Y.; Ikechukwu, C.K.; Okeke, E.S.; Ejeromedoghene, O.; Odii, E.C. Toxic Chemicals and Persistent Organic Pollutants Associated with Micro-and Nanoplastics Pollution. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, A.H.; Yesilay, G.; Hazeem, L.; Rashdan, S.; AlMealla, R.; Kilinc, Z.; Ali, F.; Abdulrasool, F.; Kamel, A.H. Micro- and Nano-Plastics Contaminants in the Environment: Sources, Fate, Toxicity, Detection, Remediation, and Sustainable Perspectives. Water 2023, 15, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Verma, A.; Shome, A.; Sinha, R.; Sinha, S.; Jha, P.K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Shubham; Das, S.; et al. Impacts of Plastic Pollution on Ecosystem Services, Sustainable Development Goals, and Need to Focus on Circular Economy and Policy Interventions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.E.; Hamann, M.; Kroon, F.J. Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification of Microplastics in Marine Organisms: A Review and Meta-Analysis of Current Data. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afreen, V.; Hashmi, K.; Nasir, R.; Saleem, A.; Khan, M.I.; Akhtar, M.F. Adverse Health Effects and Mechanisms of Microplastics on Female Reproductive System: A Descriptive Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 76283–76296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Yan, M.; Pan, C.; Liu, Z.; Sha, X.; Jiang, C.; Li, L.; Pan, M.; Li, D.; Han, X.; et al. Chronic Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics Induced Male Reproductive Toxicity and Decreased Testosterone Levels via the LH-Mediated LHR/cAMP/PKA/StAR Pathway. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yin, R. The Reproductive and Transgenerational Toxicity of Microplastics and Nanoplastics: A Threat to Mammalian Fertility in Both Sexes. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 66–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Xu, F.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene Microplastics Cause Granulosa Cells Apoptosis and Fibrosis in Ovary through Oxidative Stress in Rats. Toxicology 2021, 449, 152665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Xie, J.; Han, Q.; Chen, M. Comparing the Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics Exposure on Reproduction and Fertility in Male and Female Mice. Toxicology 2022, 465, 153059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Zhou, C.; Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Hu, L.; Xue, Y.; et al. The Ovarian-Related Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Human Ovarian Granulosa Cells and Female Mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 257, 114941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.; Akhtar, M.F.; Saleem, A.; Akhtar, B.; Sharif, A. Reproductive and Metabolic Toxic Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics in Adult Female Wistar Rats: A Mechanistic Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 63185–63199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Yang, N.; Xu, S. Polystyrene-Microplastics and DEHP Co-Exposure Induced DNA Damage, Cell Cycle Arrest and Necroptosis of Ovarian Granulosa Cells in Mice by Promoting ROS Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Reproductive Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics: In Vivo Experimental Study on Testicular Toxicity in Mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabò, N.; Di Berardino, C.; Capacchietti, G.; Peserico, A.; Buoncuore, G.; Tosi, U.; Crociati, M.; Monaci, M.; Barboni, B. In Vitro Folliculogenesis in Mammalian Models: A Computational Biology Study. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 737912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.T.; Rangel-Buitrago, N. The Past, Present, and Future of Plastic Pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrady, A.L.; Neal, M.A. Applications and Societal Benefits of Plastics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Swan, S.H. Plastics, the Environment and Human Health: Current Consensus and Future Trends. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, V.; Chatterjee, S. Contribution of Plastic and Microplastic to Global Climate Change and Their Conjoining Impacts on the Environment—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, E.; Okuthe, G.E. Plastics and Micro/Nano-Plastics (MNPs) in the Environment: Occurrence, Impact, and Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-J.; Kang, Y.-D.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chiang, C.-W.; Lee, W.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Liao, L.-D.; et al. Multitheragnostic Multi-GNRs Crystal-Seeded Magnetic Nanoseaurchin for Enhanced In Vivo Mesenchymal-Stem-Cell Homing, Multimodal Imaging, and Stroke Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6488–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahney, J.; Hallerud, M.; Heim, E.; Hahnenberger, M.; Sukumaran, S. Plastic Rain in Protected Areas of the United States. Science 2020, 368, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Dixit, P.; Rathore, K.S.; Sharma, N. Detrimental Impact of Plastic Outcome on Agriculture: Biggest Threat to Environment. In Advances in Environmental Engineering and Green Technologies; Wani, K.A., Ariana, L., Zuber, S.M., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 122–141. ISBN 978-1-5225-9452-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for Degradation of Plastic Polymers Floating in the Marine Environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, J.F.; López-Ordaz, A.; Hernández, A.J.; Catarí, E.; Sabino, M.A.; Ramos, R. Synthetic Microfiber Emissions from Denim Industrial Washing Processes: An Overlooked Microplastic Source within the Manufacturing Process of Blue Jeans. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Wei, R.; Luo, W.; Hu, L.; Li, B.; Di, Y.; Shi, H. Microplastic Pollution in Water and Sediment in a Textile Industrial Area. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, F.; Forestieri, B.; Papa, G.; Bandini, F.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Boughattas, I.; Missawi, O.; Banni, M.; Negri, I.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; et al. Effects of Micro and Nanoplastics on Soil Fauna Gut Microbiome: An Emerging Ecological Risk for Soil Health. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 30, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.D.; Vyazovkin, S.; Wight, C.A. Kinetics of the Thermal and Thermo-Oxidative Degradation of Polystyrene, Polyethylene and Poly(Propylene). Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2001, 202, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, G.; Ahmad, S.; Ullah, S.; Zada, S.; Sarfraz, M.; Guo, X.; Ismail, M.; Wanghe, K. The Adverse Health Effects of Increasing Microplastic Pollution on Aquatic Mammals. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Marine Pollution. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrera, M.C.; Aragona, M.; Porcino, C.; Fazio, F.; Laurà, R.; Levanti, M.; Montalbano, G.; Germanà, G.; Abbate, F.; Germanà, A. Micro and Nano Plastics Distribution in Fish as Model Organisms: Histopathology, Blood Response and Bioaccumulation in Different Organs. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; Lowe, D.M.; Thompson, R.C. Ingested Microscopic Plastic Translocates to the Circulatory System of the Mussel, Mytilus edulis (L). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, P.; Nelson, K. Trophic Level Transfer of Microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic Ingestion by Zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziani, K.; Ioniță-Mîndrican, C.-B.; Mititelu, M.; Neacșu, S.M.; Negrei, C.; Moroșan, E.; Drăgănescu, D.; Preda, O.-T. Microplastics: A Real Global Threat for Environment and Food Safety: A State of the Art Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, W.-M.; Bolan, N.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Li, Y.; Qin, M.; Hou, D. Environmental Fate, Toxicity and Risk Management Strategies of Nanoplastics in the Environment: Current Status and Future Perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.C.; Rosenberg, M.; Cheng, L. Increased Oceanic Microplastic Debris Enhances Oviposition in an Endemic Pelagic Insect. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Spatial Patterns of Plastic Debris along Estuarine Shorelines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3404–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Kauffman, A.E.; Li, L.; McFee, W.; Cai, B.; Weinstein, J.; Lead, J.R.; Chatterjee, S.; Scott, G.I.; Xiao, S. Health Impacts of Environmental Contamination of Micro- and Nanoplastics: A Review. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2020, 25, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, L.M.; Xu, E.G.; Larsson, H.C.E.; Tahara, R.; Maisuria, V.B.; Tufenkji, N. Plastic Teabags Release Billions of Microparticles and Nanoparticles into Tea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12300–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimi, O.S.; Farner Budarz, J.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: Aggregation, Deposition, and Enhanced Contaminant Transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, N. Mechanistic Implications of Plastic Degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Lettieri, P.; Baeyens, J. Recycling and Recovery Routes of Plastic Solid Waste (PSW): A Review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa, I.O.; Auta, H.S.; Ilyasu, U.S.; Aransiola, S.A.; Makun, H.A.; Adabara, N.U.; Abioye, O.P.; Aziz, A.; Jayanthi, B.; Maddela, N.R.; et al. Micro- and Nanoplastics in Environment: Degradation, Detection, and Ecological Impact. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2024, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpia, A.A.; Chen, W.-H.; Ubando, A.T.; Naqvi, S.R.; Culaba, A.B. Microplastic Degradation as a Sustainable Concurrent Approach for Producing Biofuel and Obliterating Hazardous Environmental Effects: A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yin, L.; Wang, H.; He, P. Pyrolysis Technologies for Municipal Solid Waste: A Review. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2466–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marturano, V.; Cerruti, P.; Ambrogi, V. Polymer Additives. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2017, 2, 20160130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirilo, G.; Iemma, F. (Eds.) Antioxidant Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications, 1st ed.; John and Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-118-20854-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, S.; Untereker, D. Degradability of Polymers for Implantable Biomedical Devices. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4033–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, L.N.; Grunlan, M.A. Hydrolytic Degradation and Erosion of Polyester Biomaterials. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Sinclair, C.; Boxall, A. Occurrence, Degradation, and Effect of Polymer-Based Materials in the Environment. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 227, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, N.; Bienaime, C.; Belloy, C.; Queneudec, M.; Silvestre, F.; Nava-Saucedo, J.-E. Polymer Biodegradation: Mechanisms and Estimation Techniques. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, C.; Huang, W.; Dang, Z. Aggregation Kinetics of UV Irradiated Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, L.; Groven, A.S.; Hovsbakken, I.A.; Del Puerto, O.; Krause, D.F.; Sarno, A.; Booth, A.M. UV Degradation of Natural and Synthetic Microfibers Causes Fragmentation and Release of Polymer Degradation Products and Chemical Additives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.; Shim, W.J. The Fragmentation of Nano- and Microplastic Particles from Thermoplastics Accelerated by Simulated-Sunlight-Mediated Photooxidation. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Jayanthi, B.; Fauziah, S.H. Growth Kinetics and Biodeterioration of Polypropylene Microplastics by Bacillus sp. and Rhodococcus sp. Isolated Mangrove Sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Screening of Bacillus Strains Isolated from Mangrove Ecosystems in Peninsular Malaysia for Microplastic Degradation. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. A Bacterium That Degrades and Assimilates Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Stemple, B.; Kumar, M.; Wei, N. Cell Surface Display Fungal Laccase as a Renewable Biocatalyst for Degradation of Persistent Micropollutants Bisphenol A and Sulfamethoxazole. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8799–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.R.; Huang, J.; Anand, P.; Kucera, K.; Sandoval, A.G.; Dantzler, K.W.; Hickman, D.; Jee, J.; Kimovec, F.M.; Koppstein, D.; et al. Biodegradation of Polyester Polyurethane by Endophytic Fungi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6076–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, F. Microbial Degradation and Other Environmental Aspects of Microplastics/Plastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijchavengkul, T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Ngouajio, M.; Fernandez, R.T. Assessment of Aliphatic-Aromatic Copolyester Biodegradable Mulch Films. Part I: Field Study. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alijagic, A.; Suljević, D.; Fočak, M.; Sulejmanović, J.; Šehović, E.; Särndahl, E.; Engwall, M. The Triple Exposure Nexus of Microplastic Particles, Plastic-Associated Chemicals, and Environmental Pollutants from a Human Health Perspective. Environ. Int. 2024, 188, 108736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Velis, C.A.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An Overview of Chemical Additives Present in Plastics: Migration, Release, Fate and Environmental Impact during Their Use, Disposal and Recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Hentschel, B.T.; Kaye, S. Long-Term Field Measurement of Sorption of Organic Contaminants to Five Types of Plastic Pellets: Implications for Plastic Marine Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 130109073312009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halden, R.U. Plastics and Health Risks. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2010, 31, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsness, C.E.; Andrade, A.J.M.; Kuriyama, S.N.; Taylor, J.A.; vom Saal, F.S. Components of Plastic: Experimental Studies in Animals and Relevance for Human Health. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2079–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, Z.; Zang, Y.; Jia, H.; Teraguchi, M.; Kaneko, T.; Aoki, T. Macromolecular Design for Oxygen/Nitrogen. Permselective Membranes—Top-Performing Polymers in 2020—. Polymers 2021, 13, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanishima, M.; Goto, A.; Lei, L.; Ohtsuki, A.; Kaji, H.; Nomura, A.; Tsujii, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Komatsu, H.; Miyamoto, M. Macromolecular Architectures Designed by Living Radical Polymerization with Organic Catalysts. Polymers 2014, 6, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröter, L.; Ventura, N. Nanoplastic Toxicity: Insights and Challenges from Experimental Model Systems. Small 2022, 18, e2201680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, X.; Sheng, D.; Xu, Z.; Rong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylene Microplastics Affect the Distribution of Gut Microbiota and Inflammation Development in Mice. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.-J.; Han, J.-S.; Park, E.-J.; Seong, E.; Lee, G.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Son, H.-Y.; Han, H.-Y.; Lee, B.-S. Repeated-Oral Dose Toxicity of Polyethylene Microplastics and the Possible Implications on Reproduction and Development of the next Generation. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 324, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. An Assessment of the Toxicity of Polypropylene Microplastics in Human Derived Cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sökmen, T.Ö.; Sulukan, E.; Türkoğlu, M.; Baran, A.; Özkaraca, M.; Ceyhun, S.B. Polystyrene Nanoplastics (20 Nm) Are Able to Bioaccumulate and Cause Oxidative DNA Damages in the Brain Tissue of Zebrafish Embryo (Danio Rerio). Neurotoxicology 2020, 77, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Park, S.-B.; Tran, Q.-G.; Cho, D.-H.; Choi, D.-Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.-S. Functional Expression of Polyethylene Terephthalate-Degrading Enzyme (PETase) in Green Microalgae. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Sun, M.; Zhou, M.; Chang, Z.; Li, L. Polyvinyl Chloride Microplastics Induce Growth Inhibition and Oxidative Stress in Cyprinus carpio var. Larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, N.; Kawasaki, N.; Ida, S.; Nakayama, A. Biodegradation of Polyamide 4 in Seawater. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 166, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latini, G.; De Felice, C.; Verrotti, A. Plasticizers, Infant Nutrition and Reproductive Health. Reprod. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Jung, S.Y.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. Potential Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastic Particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, S.; Takizawa, R.; Okuda, K.; Takada, H.; Chiba, K.; Kanehiro, H.; Ogi, H.; Yamashita, R.; Date, T. Concentration of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Beached Resin Pellets: Variability among Individual Particles and Regional Differences. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-W.; Shim, W.J.; Kwon, O.Y.; Kang, J.-H. Size-Dependent Effects of Micro Polystyrene Particles in the Marine Copepod Tigriopus Japonicus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11278–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic Resin Pellets as a Transport Medium for Toxic Chemicals in the Marine Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Takada, H.; Ogata, Y.; Yamashita, R.; Mizukawa, K.; Saha, M.; Kwan, C.; Moore, C.; Gray, H.; Laursen, D.; et al. Organic Micropollutants in Marine Plastics Debris from the Open Ocean and Remote and Urban Beaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, L.M.; Moore, C.; Jones, P.R. Persistent Organic Pollutants Carried by Synthetic Polymers in the Ocean Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Ibarra, A.; Cerbón, M.; Martínez-Razo, L.D.; Morales-Pacheco, M.; Torre-Villalvazo, I.; Kawa, S.; Rodríguez-Dorantes, M. Impact of DEHP Exposure on Female Reproductive Health: Insights into Uterine Effects. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 107, 104391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnini, B.G.; Forcato, S.; Pernoncine, K.V.; Monteiro, M.C.; Pereira, M.R.F.; Costa, N.O.; Moreira, E.G.; Anselmo-Franci, J.A.; Gerardin, D.C.C. Developmental and Reproductive Outcomes in Male Rats Exposed to Triclosan: Two-Generation Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 738980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioccarelli, T.; Manfrevola, F.; Migliaccio, M.; Altucci, L.; Porreca, V.; Fasano, S.; Cobellis, G. Fetal-Perinatal Exposure to Bisphenol-A Affects Quality of Spermatozoa in Adulthood Mouse. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 2750501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmakar, P.C.; Kang, H.-G.; Kim, Y.-H.; Jung, S.-E.; Rahman, M.S.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Pang, M.-G.; Ryu, B.-Y. Bisphenol A Affects on the Functional Properties and Proteome of Testicular Germ Cells and Spermatogonial Stem Cells in Vitro Culture Model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert da Silva, G.; Zauer Curi, T.; Lima Tolouei, S.E.; Tapias Passoni, M.; Sari Hey, G.B.; Marino Romano, R.; Martino-Andrade, A.J.; Dalsenter, P.R. Effects of Diisopentyl Phthalate Exposure during Gestation and Lactation on Hormone-Dependent Behaviours and Hormone Receptor Expression in Rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 31, e12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, R.; Seymore, T.; Lin, P.-C.P.; Park, C.J.; Ko, C.J. Prenatal Exposure to an Environmentally Relevant Phthalate Mixture Disrupts Testicular Steroidogenesis in Adult Male Mice. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howdeshell, K.L.; Furr, J.; Lambright, C.R.; Rider, C.V.; Wilson, V.S.; Gray, L.E. Cumulative Effects of Dibutyl Phthalate and Diethylhexyl Phthalate on Male Rat Reproductive Tract Development: Altered Fetal Steroid Hormones and Genes. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnotta, V.; Amodei, R.; Frasca, F.; Aversa, A.; Giordano, C. Impact of Chemical Endocrine Disruptors and Hormone Modulators on the Endocrine System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, P.; D’Auria, R.; Viggiano, A.; Ciaglia, E.; Meccariello, R.; Russo, R.D.; Puca, A.A.; Vecchione, C.; Nori, S.L.; Santoro, A. Bisphenol A Induces DNA Damage in Cells Exerting Immune Surveillance Functions at Peripheral and Central Level. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hafner, K.S.; Flaws, J.A. In Utero Bisphenol A Exposure Disrupts Germ Cell Nest Breakdown and Reduces Fertility with Age in the Mouse. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 276, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, S.; Ther, L.; Gao, L.; Wang, W.; Ziv-Gal, A.; Flaws, J.A. The Effects of in Utero Bisphenol A Exposure on Ovarian Follicle Numbers and Steroidogenesis in the F1 and F2 Generations of Mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 74, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Zhu, J.; Weng, S.; Xiao, S.; Wu, T. Prepubertal Bisphenol A Exposure Interferes with Ovarian Follicle Development and Its Relevant Gene Expression. Reprod. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rodríguez, D.; Franssen, D.; Sevrin, E.; Gérard, A.; Balsat, C.; Blacher, S.; Noël, A.; Parent, A.-S. Persistent vs. Transient Alteration of Folliculogenesis and Estrous Cycle After Neonatal vs. Adult Exposure to Bisphenol A. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2558–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Osuga, Y.; Yano, T.; Morita, Y.; Tang, X.; Fujiwara, T.; Takai, Y.; Matsumi, H.; Koga, K.; Taketani, Y.; et al. Bisphenol A Induces Apoptosis and G2-to-M Arrest of Ovarian Granulosa Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 292, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Hua, R.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Xu, X.; Yu, Z.; Quan, S. Bisphenol A Promotes Autophagy in Ovarian Granulosa Cells by Inducing AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 Signalling Pathway. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Huang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Fu, L.; Jiang, X.; Yang, M. Bisphenol A Induces Apoptosis through GPER-Dependent Activation of the ROS/Ca2+-ASK1-JNK Pathway in Human Granulosa Cell Line KGN. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, A.; Semiz, O.; Cinar, O. Bisphenol-A Induces Cell Cycle Delay and Alters Centrosome and Spindle Microtubular Organization in Oocytes during Meiosis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2005, 11, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenlaub-Ritter, U.; Vogt, E.; Cukurcam, S.; Sun, F.; Pacchierotti, F.; Parry, J. Exposure of Mouse Oocytes to Bisphenol A Causes Meiotic Arrest but Not Aneuploidy. Mutat. Res. 2008, 651, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machtinger, R.; Combelles, C.M.H.; Missmer, S.A.; Correia, K.F.; Williams, P.; Hauser, R.; Racowsky, C. Bisphenol-A and Human Oocyte Maturation in Vitro. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brieño-Enríquez, M.A.; Robles, P.; Camats-Tarruella, N.; García-Cruz, R.; Roig, I.; Cabero, L.; Martínez, F.; Caldés, M.G. Human Meiotic Progression and Recombination Are Affected by Bisphenol A Exposure during in Vitro Human Oocyte Development. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 26, 2807–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B.E.; Ventura, S.J. Fertility and Abortion Rates in the United States, 1960–2002. Int. J. Androl. 2006, 29, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, P.R.; Brannick, K.E.; Wang, W.; Flaws, J.A. Mono(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Accelerates Early Folliculogenesis and Inhibits Steroidogenesis in Cultured Mouse Whole Ovaries and Antral Follicles. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 92, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, J.-A.; Qiu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, J.; Yang, L.; Zeng, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; et al. Ovotoxicity and PPAR-Mediated Aromatase Downregulation in Female Sprague-Dawley Rats Following Combined Oral Exposure to Benzo[a]Pyrene and Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 199, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meling, D.D.; Warner, G.R.; Szumski, J.R.; Gao, L.; Gonsioroski, A.V.; Rattan, S.; Flaws, J.A. The Effects of a Phthalate Metabolite Mixture on Antral Follicle Growth and Sex Steroid Synthesis in Mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 388, 114875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gao, L.; Flaws, J.A. Prenatal Exposure to an Environmentally Relevant Phthalate Mixture Disrupts Reproduction in F1 Female Mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 318, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacruz-Márquez, R.; Safar, A.M.; Laws, M.J.; Meling, D.D.; Liu, Z.; Kumar, T.R.; Nowak, R.A.; Raetzman, L.T.; Flaws, J.A. The Effects of Short-Term and Long-Term Phthalate Exposures on Ovarian Follicle Growth Dynamics and Hormone Levels in Female Mice. Biol. Reprod. 2024, 110, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.; Lewis, L.R.; Borkowski, G.; Flaws, J.A. Late-Life Consequences of Short-Term Exposure to Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate and Diisononyl Phthalate during Adulthood in Female Mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2020, 93, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.; Flaws, J.A. Subchronic Exposure to Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate and Diisononyl Phthalate During Adulthood Has Immediate and Long-Term Reproductive Consequences in Female Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 168, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannon, P.R.; Niermann, S.; Flaws, J.A. Acute Exposure to Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate in Adulthood Causes Adverse Reproductive Outcomes Later in Life and Accelerates Reproductive Aging in Female Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 150, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-P.; Hsieh, P.C.H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, T.-Y.; Chen, P.-C.; Liu, C.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, C.-P. Nanoparticles Can Cross Mouse Placenta and Induce Trophoblast Apoptosis. Placenta 2015, 36, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusza, H.M.; Katrukha, E.A.; Nijmeijer, S.M.; Akhmanova, A.; Vethaak, A.D.; Walker, D.I.; Legler, J. Uptake, Transport, and Toxicity of Pristine and Weathered Micro- and Nanoplastics in Human Placenta Cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 97006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibbon, K.C.; Mercer, G.V.; Maekawa, A.S.; Hanrahan, J.; Steeves, K.L.; Ringer, L.C.M.; Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J.; Baschat, A.A.; Kingdom, J.C.; et al. Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastics Cause Placental Dysfunction in Mice†. Biol. Reprod. 2024, 110, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Hu, W.; Chao, L.; Chu, X.; Qian, M.; Wang, R.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; et al. Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastic Gestational Exposure on Mice. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Bu, W.; Hu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, L.; Luo, C.; Wang, R.; Fan, S.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; et al. Ferroptosis Is Involved in Sex-Specific Small Intestinal Toxicity in the Offspring of Adult Mice Exposed to Polystyrene Nanoplastics during Pregnancy. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 2440–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, P.; Malek, A.; Manser, P.; Meili, D.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Diener, L.; Diener, P.-A.; Zisch, A.; Krug, H.F.; von Mandach, U. Barrier Capacity of Human Placenta for Nanosized Materials. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Duru, C.E.; Ovuoraye, P.E.; Wang, Q. Evaluation of Nanoplastics Toxicity to the Human Placenta in Systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, L.; Weng, J.; Jin, Z.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z. Detection and Characterization of Microplastics in the Human Testis and Semen. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Baek, J.Y.; Koo, J.; Park, S.; Ryu, Y.-K.; Kim, K.-S.; Zhang, S.; Chung, C.; Dogan, R.; Choi, H.-S.; et al. Maternal Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics Causes Brain Abnormalities in Progeny. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basini, G.; Bussolati, S.; Andriani, L.; Grolli, S.; Ramoni, R.; Bertini, S.; Iemmi, T.; Menozzi, A.; Berni, P.; Grasselli, F. Nanoplastics Impair in Vitro Swine Granulosa Cell Functions. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2021, 76, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.B.; D’Errico, J.N.; Adler, D.S.; Kollontzi, S.; Goedken, M.J.; Fabris, L.; Yurkow, E.J.; Stapleton, P.A. Nanopolystyrene Translocation and Fetal Deposition after Acute Lung Exposure during Late-Stage Pregnancy. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, W.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X. Polystyrene Microplastics Disturb Maternal-Fetal Immune Balance and Cause Reproductive Toxicity in Pregnant Mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafmueller, S.; Manser, P.; Diener, L.; Diener, P.-A.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Maurizi, L.; Jochum, W.; Krug, H.F.; Buerki-Thurnherr, T.; von Mandach, U.; et al. Bidirectional Transfer Study of Polystyrene Nanoparticles across the Placental Barrier in an Ex Vivo Human Placental Perfusion Model. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Yu, R.; Liu, J.; Su, J. Reproductive Toxicity of Microplastics in Female Mice and Their Offspring from Induction of Oxidative Stress. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Shen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Maternal Exposure to Different Sizes of Polystyrene Microplastics during Gestation Causes Metabolic Disorders in Their Offspring. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, R.; Mi, C.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, H. Exposure to High Dose of Polystyrene Nanoplastics Causes Trophoblast Cell Apoptosis and Induces Miscarriage. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Wang, C.; Pan, Z.; Jin, C.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Maternal Polystyrene Microplastic Exposure during Gestation and Lactation Altered Metabolic Homeostasis in the Dams and Their F1 and F2 Offspring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10978–10992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; He, J.; Qiu, H.; van Gestel, C.A.M.; He, E.; Qiao, Z.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Chen, G. Maternal Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics Causes Defective Retinal Development and Function in Progeny Mice by Disturbing Metabolic Profiles. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, W.; Lin, T.; Liu, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, F.; Yuan, Y.; Xiang, X.; Kuang, H.; Yang, B.; et al. Maternal Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics during Gestation and Lactation Induces Hepatic and Testicular Toxicity in Male Mouse Offspring. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 160, 112803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.; Kim, J.S.; Kwon, A.R.; Lee, J.; Park, S.; Koo, J.; Lee, W.S.; Baek, J.Y.; Shin, W.H.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Maternal nanoplastic ingestion induces an increase in offspring body weight through altered lipid species and microbiota. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurub, R.E.; Cariaco, Y.; Wade, M.G.; Bainbridge, S.A. Microplastics Exposure: Implications for Human Fertility, Pregnancy and Child Health. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1330396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Cho, J.; Sohn, J.; Kim, C. Health Effects of Microplastic Exposures: Current Issues and Perspectives in South Korea. Yonsei Med. J. 2023, 64, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, P.J.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.A.J.; Ragas, A.M.J. Wear and Tear of Tyres: A Stealthy Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kamstra, J.; Legler, J.; Aardema, H. The Impact of Microplastics on Female Reproduction and Early Life. Anim. Reprod. 2023, 20, e20230037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.F.; Kreitner, K.J.; Starling, A.P.; Martenies, S.E.; Magzamen, S.; Clark, M.; Dabelea, D. Early-life Exposure to Tobacco and Childhood Adiposity: Identifying Windows of Susceptibility. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, L.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Bennett, R.T.; Cowen, M.; Tentzeris, V.; Sadofsky, L.R. Detection of Microplastics in Human Lung Tissue Using μFTIR Spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Berardino, C.; Peserico, A.; Capacchietti, G.; Zappacosta, A.; Bernabò, N.; Russo, V.; Mauro, A.; El Khatib, M.; Gonnella, F.; Konstantinidou, F.; et al. High-Fat Diet and Female Fertility across Lifespan: A Comparative Lesson from Mammal Models. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohos, N.M.; Skaznik-Wikiel, M.E. High-Fat Diet and Female Fertility. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2407–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarghouei, S.; Hedayati, A.; Raeisi, M.; Hadavand, B.S.; Rezaei, H.; Abed-Elmdoust, A. Size-Dependent Effects of Microplastic on Uptake, Immune System, Related Gene Expression and Histopathology of Goldfish (Carassius auratus). Chemosphere 2021, 276, 129977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhou, W.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, H. Size-Dependent Toxicological Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics in the Shrimp Litopenaeus Vannamei Using a Histomorphology, Microbiome, and Metabolic Approach. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongaerts, E.; Nawrot, T.S.; Van Pee, T.; Ameloot, M.; Bové, H. Translocation of (Ultra)Fine Particles and Nanoparticles across the Placenta; a Systematic Review on the Evidence of in Vitro, Ex Vivo, and in Vivo Studies. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wan, Z.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene Microplastics Induce Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Disorder in Mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Aponte-Mellado, A.; Premkumar, B.J.; Shaman, A.; Gupta, S. The Effects of Oxidative Stress on Female Reproduction: A Review. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2012, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltsas, A. Oxidative Stress and Male Infertility: The Protective Role of Antioxidants. Medicina 2023, 59, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.-R.; Jiang, Y.-S.; Sun, J.-Y.; Li, H.-H.; Luo, X.-L.; Zhao, M.-M. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism Involved in 4-Ethylguaiacol-Mediated Inhibition of LPS-Induced Inflammation in THP-1 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1230–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lee, W.; Lee, B.-S.; Lee, C.; Park, E.K.; Ku, S.-K.; Bae, J.-S. Aloin Reduces HMGB1-Mediated Septic Responses and Improves Survival in Septic Mice by Activation of the SIRT1 and PI3K/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Axis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 613–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-M.; Guo, Z.-X.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Wang, Q.-J.; Gao, Y.-S.; Yu, T.; Chen, Y.-K.; Chen, X.-M.; Wang, G.-Q. L-Carnitine Regulated Nrf2/Keap1 Activation in Vitro and in Vivo and Protected Oxidized Fish Oil-Induced Inflammation Response by Inhibiting the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Rhynchocypris lagowski Dybowski. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 93, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Zou, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Geng, J. Toxicological Effects of Nano- and Micro-Polystyrene Plastics on Red Tilapia: Are Larger Plastic Particles More Harmless? J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Size-Dependent Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Cytotoxicity and Efflux Pump Inhibition in Human Caco-2 cells. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Khalil, A.A.; Awadallah, S.; Khan, S.A.; Abu-Izneid, T.; Kamran, M.; Hemeg, H.A.; Mubarak, M.S.; Khalid, A.; Wilairatana, P. Reactive Oxygen Species in Biological Systems: Pathways, Associated Diseases, and Potential Inhibitors-A Review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of Apoptosis Signalling Pathways by Reactive Oxygen Species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.K. Does the Interdependence between Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Explain the Antioxidant Paradox? Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 5698931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparacio, S.M.; Zhang, Y.; Vilcek, J.; Benveniste, E.N. Cytokine Regulation of Interleukin-6 Gene Expression in Astrocytes Involves Activation of an NF-Kappa B-like Nuclear Protein. J. Neuroimmunol. 1992, 39, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadjeva, M.; Tomczak, M.F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Dull, K.; Rogers, A.B.; Erdman, S.E.; Fox, J.G.; Carroll, M.; Horwitz, B.H. A Role for NF-Kappa B Subunits P50 and P65 in the Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Shock. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 5786–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-D.; Shen, X.-Y.; Machado, J.; Luo, J.-F.; Dai, Y.; Lio, C.-K.; Yu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Luo, P.; Liu, J.-X.; et al. Nardochinoid B Inhibited the Activation of RAW264.7 Macrophages Stimulated by Lipopolysaccharide through Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, T.S.; Lee, I.; Hüttemann, M.; Kumar, A.; Nantwi, K.D.; Singh, L.P. TXNIP Links Innate Host Defense Mechanisms to Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Retinal Muller Glia under Chronic Hyperglycemia: Implications for Diabetic Retinopathy. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 438238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, O.; Thomas, C.J.; Guarda, G.; Tschopp, J. The Inflammasome: An Integrated View. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 243, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strowig, T.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Flavell, R. Inflammasomes in Health and Disease. Nature 2012, 481, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, S.L.; Cookson, B.T. Apoptosis, Pyroptosis, and Necrosis: Mechanistic Description of Dead and Dying Eukaryotic Cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tian, M.; Ding, N.; Yan, X.; Chen, S.-J.; Mo, Y.-Z.; Yang, W.-Q.; Bi, X.-H.; Wang, X.-M.; Mai, B.-X. Semivolatile Organic Compounds (SOCs) in Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) during Clear, Fog, and Haze Episodes in Winter in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5199–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Mahapatra, A.; Suman, A.; Ray, S.S.; Malafaia, G.; Singh, R.K. Polystyrene Microplastics Disrupt Female Reproductive Health and Fertility via Sirt1 Modulation in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, D.; Berger Eberhardt, A. Climate Change, Microplastics, and Male Infertility. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2024, 34, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, S.; Meccariello, R. Microplastics: A Threat for Male Fertility. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Berardino, C.; Barceviciute, U.; Camerano Spelta Rapini, C.; Peserico, A.; Capacchietti, G.; Bernabò, N.; Russo, V.; Gatta, V.; Konstantinidou, F.; Donato, M.; et al. High-Fat Diet-Negative Impact on Female Fertility: From Mechanisms to Protective Actions of Antioxidant Matrices. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1415455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.I.; May, L.; Roik, L.J.; Fuda, M.R.; Luo, A.; Hettinga, B.P.; Bujak, A.L.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. A Multi-Ingredient Supplement Protects against Obesity and Infertility in Western Diet-Fed Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Ge, J.; Reiter, R.J.; Wang, Q. Melatonin Protects against Maternal Obesity-Associated Oxidative Stress and Meiotic Defects in Oocytes via the SIRT3-SOD2-Dependent Pathway. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63, e12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Feng, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, D.; Zhao, X.; Feng, D.; Feng, X. Resveratrol Reverses the Adverse Effects of a Diet-Induced Obese Murine Model on Oocyte Quality and Zona Pellucida Softening. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCance, D.R.; Holmes, V.A.; Maresh, M.J.A.; Patterson, C.C.; Walker, J.D.; Pearson, D.W.M.; Young, I.S.; Diabetes and Pre-eclampsia Intervention Trial (DAPIT) Study Group. Vitamins C and E for Prevention of Pre-Eclampsia in Women with Type 1 Diabetes (DAPIT): A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| In Vivo/In Vitro Studies | Species | Sample Typology for In Vitro Investigation | PS-MNP Size | PS-MNP Dose | In Vivo Exposure Time | In Vivo Exposure Way | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro/in vivo | Mouse | Human granulosa cell line KGN | 20 nm | 100 μg/mL in vitro 1 mg/d in vivo | 48 h in vivo | Oral gavage | [32] |
| In vivo | Rat | / | 800 nm | From 2.5 to 10 mg/kg/day | 45 days | Oral administration | [33] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 50 nm and 5 μm | 100 ng/L | All gestation (20 days) | Drinking water | [139] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 80 nm | From 1 to 25 μg/µL | All gestation (20 days) | Inhalation | [140] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 80 nm | From 1 to 25 μg/µL | All gestation (20 days), 3 times per week | Oropharyngeal aspiration | [141] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 50 nm and 500 nm | From 0.5 to 1000 µg/day | From embryonic day 8 (E8) until 2 weeks after birth | Oral administration | [145] |
| In vitro | Human | BeWo b30 choriocarcinoma cell line (placental cells) | 200 nm, 500 nm, 1 µM, and 10 µM | 100 µg/mL | / | / | [138] |
| In vitro | Swine | Granulosa cells | 100 nm | From 5 to 75 µg/mL | / | / | [146] |
| In vivo | Rat | / | 20 nm | 300 μL (2.64 × 1014 particles) | On gestational day 19 for 24 h | Intratracheal instillation | [147] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 5 µm | From 100 µg/L to 10 mg/L | 35 days | Drinking water | [35] |
| In vivo | Rat | Granulosa cells | 500 nm | From 0.015 to 1.5 mg/kg/day | 90 days | Drinking water | [18] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 5 μm | From 0.01 to 1 mg/day | 42 days | Oral gavage | [20] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 10 μm | 250 μg in a 200 μL saline solution | On days 5.5 and 7.5 of gestation | Intraperitoneally injected | [148] |
| In vivo/in vitro | Rat | Granulosa cells | 500 nm | From 0.015 to 1.5 mg/day In vivo From 1 to 25 μg/mL in vitro | 90 days (in vivo); 24 h (in vitro) | Drinking water | [30] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 5 μm | 0.1 mg/day | 20 days | Oral gavage | [31] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 700 nm | 30 mg/kg | 35 days | Oral gavage | [17] |
| In vivo | Mouse | Granulosa cells | 5 μm and 10 µm | 100 mg/L | 35 days | Drinking water | [34] |
| In vivo/in vitro | Mouse | Germ cells (GC), Leydig cells (LC), and Sertoli cells (SC) | 500 nm, 4 μm, and 10 μm | 10 mg/mL | 28 days (in vivo); 24 h (in vitro) | Oral gavage | [21] |
| In vitro | Human | BeWo b30 choriocarcinoma cell line (placental cells) | 50 nm and 300 nm | 25 μg/mL | Perfusion for 6 h | / | [149] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 10 μm and 150 μm | From 0.4 to 40 mg/kg/day | 30 days | Oral gavage | [150] |
| In vitro/in vivo | Mouse | Mouse ovarian tissue and human ovarian granulosa cell lines | 50 nm | From 5 mg/Kg to 25 mg/Kg in vivo; from 50 to 200 μg/mL in vitro | 8 weeks | Oral administration | [19] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 500 nm and 5 µm | 100 µg/L and 1000 µg/L | All gestation (20 days) | Drinking water | [151] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 50 nm | From 50 to 200 µg/mL | 35 days | Oral gavage | [152] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 5 µm | 100 and 1000 µg/L | During pregnancy and lactation (6 weeks) | Drinking water | [153] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 100 nm | 2.07 × 1010 particles mL−1 | From the first day of pregnancy until the end of lactation (21 days after birth) | Drinking water | [154] |
| In vitro/in vivo | Mouse | Trophoblast cells | From 20 nm to 500 nm | 300 μg | 4 h | Injection through jugular vein | [137] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 100 nm | From 0.1 mg/mL to 10 mg/mL | 21 days | Drinking water | [155] |
| In vivo | Mouse | / | 80 nm | 0.5 µg/µL and 1 µg/µL | 21 days | Inhalation | [156] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camerano Spelta Rapini, C.; Di Berardino, C.; Peserico, A.; Capacchietti, G.; Barboni, B. Can Mammalian Reproductive Health Withstand Massive Exposure to Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastic Derivatives? A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212166
Camerano Spelta Rapini C, Di Berardino C, Peserico A, Capacchietti G, Barboni B. Can Mammalian Reproductive Health Withstand Massive Exposure to Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastic Derivatives? A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(22):12166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212166
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamerano Spelta Rapini, Chiara, Chiara Di Berardino, Alessia Peserico, Giulia Capacchietti, and Barbara Barboni. 2024. "Can Mammalian Reproductive Health Withstand Massive Exposure to Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastic Derivatives? A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 22: 12166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212166
APA StyleCamerano Spelta Rapini, C., Di Berardino, C., Peserico, A., Capacchietti, G., & Barboni, B. (2024). Can Mammalian Reproductive Health Withstand Massive Exposure to Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastic Derivatives? A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(22), 12166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212166








