Serotypes, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Potential Mechanisms of Resistance Gene Transfer in Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strains from Waterfowl in Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of E. rhusiopathiae Isolates
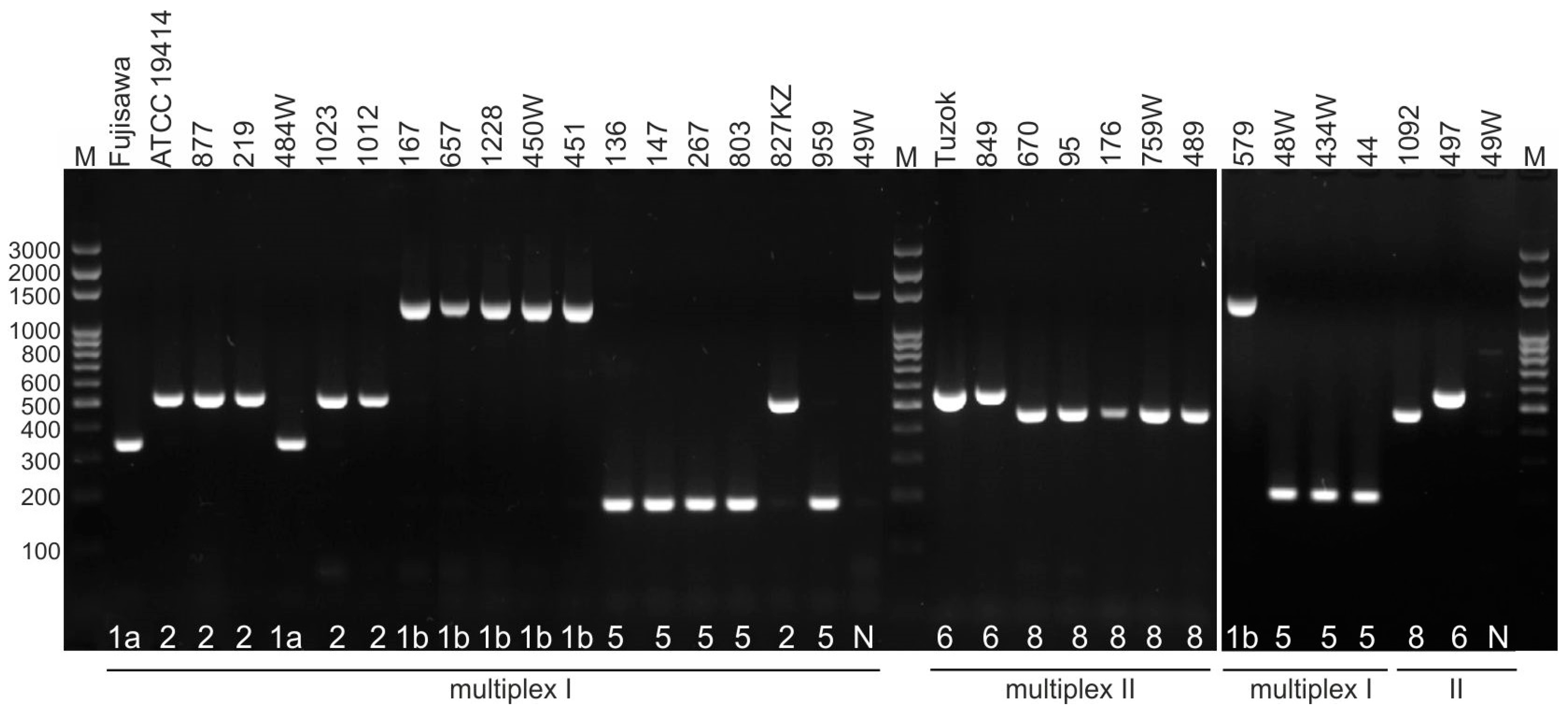
2.2. Serotyping
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
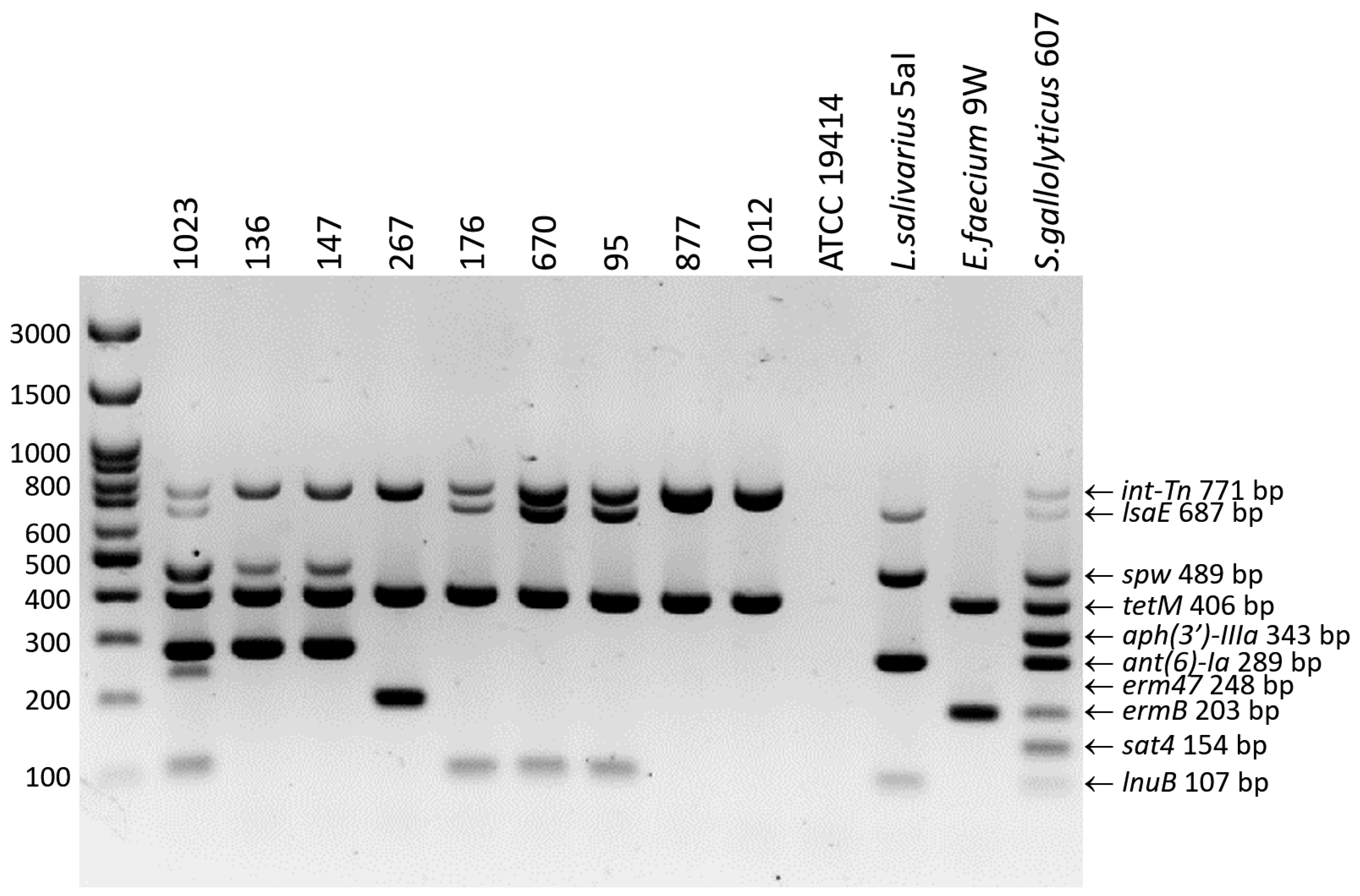
2.4. Genotypic Resistance Profiles
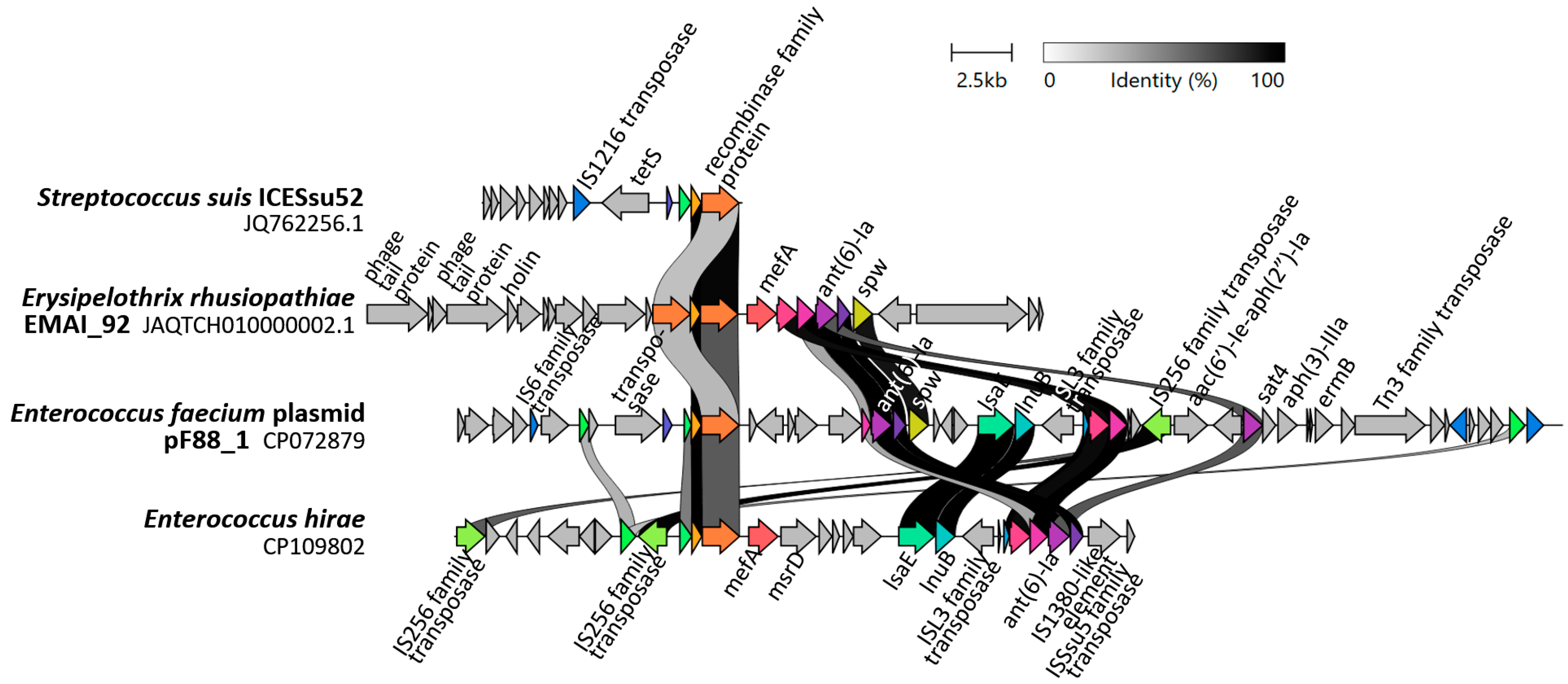
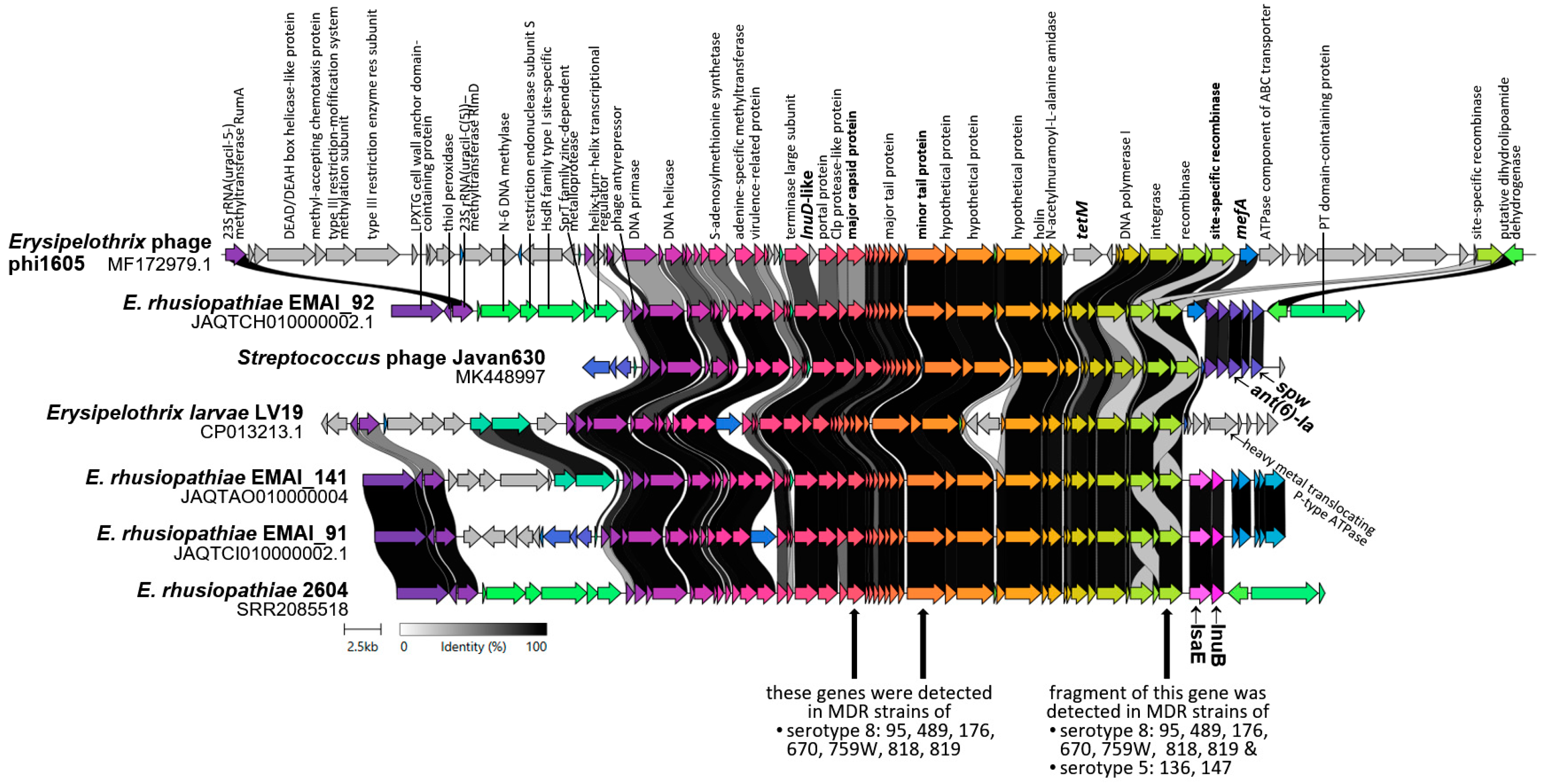
2.5. Detection of ICE-Specific Genes and Prophage Regions
2.6. MLST Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Serotypes of E. rhusiopathiae Strains
3.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility and Genotypic Resistance Profiles
3.3. Potential Mechanisms of Resistance Gene Transfer
3.4. Sequence Types of E. rhusiopathiae Isolates
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of E. rhusiopathiae Strains
4.2. Identification of E. rhusiopathiae Strains
4.3. Serotyping of E. rhusiopathiae Strains
4.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
4.5. Detection of Resistance Genes and Development of 10-Plex PCR
4.6. Sequence Analysis of the gyrA and parC Genes
4.7. Detection of ICE-Specific Genes and Prophage DNA
4.8. Multilocus Sequence Typing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Isolate | Ser. | AMP | PEN | AMX | AMC | CEF | ERY | TYL | LIN | CLI | TIA | TET | ENR | STR | SPE | GEN | NEO | TR/S | FLO | Resistance Genes | ICE-Specific Genes | Prophage Encoded Genes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 484W | 1a | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 1 | ≤0.06 | 4 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.125 | 128 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | |||
| 2 | 219 | 2 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | ≤0.125 | 64 | 16 | >512 | >512 | 512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 3 | 877 | 2 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | ≤0.125 | 128 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn, mobL | |
| 4 | 827KZ | 2 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 5 | 827NW | 2 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 6 | 1012 | 2 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 2 | 1 | 0.125 | 1 | 16 | ≤0.125 | 64 | 128 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn, mobL | |
| 7 | 1023 | 2 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 32 | 1 | >64 | 2 | >64 | 32 | 16 | >512 | 256 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE, ant(6)-Ia, spw, erm47 | int-Tn, virB, mobL | |
| 8 | 267 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | >32 | >32 | >64 | >16 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 32 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM, ermB | int-Tn | |
| 9 | 86 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | >64 | 4 | >64 | 64 | 8 | >512 | >512 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE, ant(6)-Ia, spw | int-Tn, mobL | ND |
| 10 | 136 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | 4 | 0.125 | 0.5 | 64 | 8 | >512 | 256 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM, ant(6)-Ia, spw | int-Tn, mobL | rec * |
| 11 | 147 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 8 | ≤0.06 | 0.5 | 32 | 8 | >512 | 512 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM, ant(6)-Ia, spw | int-Tn, mobL | rec |
| 12 | 413 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 1 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 13 | 512 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 14 | 652 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 1 | 32 | 8 | 32 | 32 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 15 | 815 | 5 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 1 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 64 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn, mobL | |
| 16 | 1154 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 1 | 0.125 | 4 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 64 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 2 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 17 | 43 | 5 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 1 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 16 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 18 | 44 | 5 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 19 | 1173 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 0.5 | 32 | 8 | 32 | 16 | 256 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 20 | 13 | 5 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn, mobL | |
| 21 | 48W | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 32 | 16 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 8 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 22 | 51W | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 2 | 16 | 8 | 32 | 16 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 23 | 89W | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 4 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 24 | 90W | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 4 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 25 | 936W | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.5 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 1 | 16 | 8 | 32 | 16 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 26 | 434W | 5 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 0.5 | 32 | 8 | 32 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 27 | 959 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 8 | 1 | ≤0.125 | 128 | 32 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | |||
| 28 | 584 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 1 | ≤0.125 | 64 | 32 | 512 | 512 | >512 | 2 | |||
| 29 | 803 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1 | ≤0.06 | 1 | 1 | ≤0.125 | 128 | 64 | >512 | 512 | >512 | 2 | |||
| 30 | 155 | 5 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 4 | 16 | 16 | 32 | 16 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 31 | 95 | 8 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | >64 | 1 | >64 | 32 | 16 | 64 | 32 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 8 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn | rec, mcp **, mtp *** |
| 32 | 489 | 8 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | >64 | 1 | 64 | 32 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn | rec, mcp, mtp |
| 33 | 176 | 8 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | >64 | 4 | >64 | 64 | 8 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn | rec, mcp, mtp |
| 34 | 670 | 8 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | >64 | 2 | >64 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 8 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn | rec, mcp, mtp |
| 35 | 759W | 8 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | >64 | 2 | 64 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 8 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn | rec, mcp, mtp |
| 36 | 818 | 8 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | >64 | 2 | >64 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn | rec, mcp, mtp |
| 37 | 819 | 8 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | >64 | 2 | >64 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn | rec, mcp, mtp |
| 38 | 1092 | 8 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 4 | 32 | 16 | 64 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 39 | 53 | 8 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 8 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 8 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 40 | 579 | 1b | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 41 | 167 | 1b | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 32 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 42 | 395 | 1b | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 4 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 8 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 43 | 784 | 1b | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 32 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 44 | 1042 | 1b | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 45 | 1228 | 1b | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.5 | 0.125 | 1 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 16 | 8 | 128 | 64 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 46 | 439W | 1b | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 47 | 450W | 1b | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 1 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 16 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 48 | 195 | 1b | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 2 | 0.125 | 4 | 1 | ≤0.125 | 128 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | |||
| 49 | 657 | 1b | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.125 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | |||
| 50 | 1083 | 1b | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.125 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | |||
| 51 | 202 | 1b | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 1 | 0.125 | 4 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 8 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 52 | 525 | 1b | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 4 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 53 | 526 | 1b | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 1 | ≤0.06 | 4 | 16 | 16 | 128 | 64 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 54 | 783 | 1b | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 1 | 0.125 | 8 | 64 | 16 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 55 | 633 | 1b | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 8 | 64 | 32 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 56 | 451 | 1b | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 16 | 128 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 57 | 49W | N | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 1 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.125 | 64 | 32 | 512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | |||
| 58 | 320 | N | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 4 | 32 | 8 | 128 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 59 | 497 | 6 | 0.125 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | ≤0.06 | 2 | 32 | 16 | 128 | 64 | >512 | >512 | >512 | 4 | tetM | int-Tn | |
| 60 | 849 | 6 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | 0.125 | 0.25 | ≤0.06 | 1 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.125 | 32 | 16 | 512 | 512 | >512 | 4 | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 3.3% | 3 5% | 10 16.7% | 10 16.7% | 9 15% | 51 85% | 48 80% | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
References
- Wang, Q.; Chang, B.J.; Riley, T.V. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoji, Y.; Shiraiwa, K.; Tominaga, H.; Nishikawa, S.; Eguchi, M.; Hikono, H.; Ogawa, Y. Development of a Multiplex PCR-Based Assay for Rapid Serotyping of Erysipelothrix Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00315-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, T.; Mühldorfer, K.; Erhard, M.; Fawzy, A.; Kehm, S.; Ewers, C.; Semmler, T.; Blom, J.; Lipski, A.; Rau, J.; et al. Erysipelothrix anatis sp. nov., Erysipelothrix aquatica sp. nov. and Erysipelothrix urinaevulpis sp. nov., three novel species of the genus, and emended description of Erysipelothrix. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Medvecky, M.; Tornos, J.; Clessin, A.; Le Net, R.; Gantelet, H.; Gamble, A.; Forde, T.L.; Boulinier, T. Erysipelothrix amsterdamensis sp. nov., associated with mortalities among endangered seabirds. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 006264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.K.; Miller, M.A.; Tekedar, H.C.; Rose, D.; García, J.C.; LaFrentz, B.R.; Older, C.E.; Waldbieser, G.C.; Pomaranski, E.; Shahin, K.; et al. Pathology, microbiology, and genetic diversity associated with Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae and novel Erysipelothrix spp. infections in southern sea otters (Enhydra lutris nereis). Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1303235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Huang, W.; Li, J. The First Report of Erysipelothrix muris sp. nov. Unpublished. 2006. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=380638 (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Stackebrandt, E. Erysipelothrix. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria, 1st ed.; Whitman, W.B., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Bergey’s Manual Trust: Glasgow, UK, 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Zarkasie, K.; Mariana, S.; Sumadi; Ogata, M. Serological and pathogenic characterization of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolates from tonsils of slaughter pigs in Indonesia. Vet. Microbiol. 1989, 21, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dec, M.; Łagowski, D.; Nowak, T.; Pietras-Ożga, D.; Herman, K. Serotypes, Antibiotic Susceptibility, Genotypic Virulence Profiles and SpaA Variants of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strains Isolated from Pigs in Poland. Pathogens 2023, 12, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, T.; Wódz, K.; Kwiecieński, P.; Kwieciński, A.; Dec, M. Incidence of erysipelas in waterfowl in Poland–clinical & pathological investigations. Br. Poult. Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrek, K.; Nowak, M.; Borkowska, J.; Bobusia, K.; Gaweł, A. An outbreak of erysipelas in commercial geese. Pak. Vet. J. 2016, 36, 372–374. [Google Scholar]
- Żbikowski, A.; Karpińska, E.; Rzewuska, M.; Szeleszczuk, P. Różyca u drobiu [Erysipelas in poultry]. Życie Weterynaryjne 2011, 86, 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Bobrek, K.; Gaweł, A. Antimicrobial Resistance of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strains Isolated from Geese to Antimicrobials Widely Used in Veterinary Medicine. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dec, M.; Zomer, A.; Webster, J.; Nowak, T.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Urban-Chmiel, R. Integrative and Conjugative Elements and Prophage DNA as Carriers of Resistance Genes in Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strains from Domestic Geese in Poland. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Com/2017/0339-Communication from the Commission to the Council and the European Parliament A European One Health Action Plan Against Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A52017DC0339 (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Gu, J.; Li, Y.X.; Xu, C.W.; Xie, X.J.; Li, P.; Ma, G.X.; Lei, C.W.; Liu, J.X.; Zhang, A.Y. Genome sequence of multidrug-resistant Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae ZJ carrying several acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Hu, Y.; Wu, H.; Feng, Z.; Hu, C.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.; Yu, X. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of a Highly Virulent Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strain. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases. Transpoundary Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 5401707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Javan, R.; Ramos-Sevillano, E.; Akter, A.; Brown, J.; Brueggemann, A.B. Prophages and satellite prophages are widespread in Streptococcus and may play a role in pneumococcal pathogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Bowring, B.; Stroud, L.; Marsh, I.; Sales, N.; Bogema, D. Population Structure and Genomic Characteristics of Australian Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Reveals Unobserved Diversity in the Australian Pig Industry. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.; Bilic, I.; Jandreski-Cvetkovic, D.; Hess, M. Antimicrobial Dilution Susceptibility Testing of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae According to CLSI Document VET06 Reveals High Resistance against Penicillin G, Erythromycin and Enrofloxacin. Poultry 2023, 2, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janßen, T.; Voss, M.; Kühl, M.; Semmler, T.; Philipp, H.-C.; Ewers, C. A Combinational Approach of Multilocus Sequence Typing and Other Molecular Typing Methods in Unravelling the Epidemiology of Erysipelothrix Rhusiopathiae Strains from Poultry and Mammals. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, M.; Gerber, P.F.; Thomson, J.; Williamson, S.; Opriessnig, T. Serotypes and Spa Types of Erysipelothrix Rhusiopathiae Isolates from British Pigs (1987 to 2015). Vet. J. 2017, 225, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imada, Y.; Takase, A.; Kikuma, R.; Iwamaru, Y.; Akachi, S.; Hayakawa, Y. Serotyping of 800 Strains of Erysipelothrix Isolated from Pigs Affected with Erysipelas and Discrimination of Attenuated Live Vaccine Strain by Genotyping. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhu, X.; Muhammad, H.M.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y. Characterization of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae strains isolated from acute swine erysipelas outbreaks in Eastern China. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Tan, C. Virulence determinants, antimicrobial susceptibility, and molecular profiles of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae strains isolated from China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2015, 4, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuma, T.; Kawamoto, T.; Shahada, F.; Fujimoto, H.; Okamoto, K. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolated from pigs in Southern Japan with a modified agar dilution method. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 643–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidalgo, S.G.; Longbottom, C.J.; Rjley, T.V. Susceptibility of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae to antimicrobial agents and home disinfectants. Pathology 2002, 34, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Ghany, W. A review article on avian Erysipelas infection: An occupational disease of one health importance. Vet. Integr. Sci. 2023, 21, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Lv, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, T.; Kang, C.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Characterization of Erysipelothrix Rhusiopathiae Isolates from Diseased Pigs in 15 Chinese Provinces from 2012 to 2018. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, F.; Isnard, C.; Bucquet, F.; Fines-Guyon, M.; Giard, J.C.; Burrus, V.; Cattoir, V. Novel chromosome-encoded erm(47) determinant responsible for constitutive MLSB resistance in Helcococcus kunzii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 3046–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uruén, C.; Gimeno, J.; Sanz, M.; Fraile, L.; Marín, C.M.; Arenas, J. Invasive Streptococcus suis isolated in Spain contain a highly promiscuous and dynamic resistome. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 13, 1329632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Lei, C.; Liu, B.; Guan, Z.; Yang, C.; Yang, Y.; Peng, L. Presence and new genetic environment of pleuromutilin-lincosamide-streptogramin A resistance gene lsa(E) in Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae of swine origin. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kijima, M.; Yoshimura, H.; Takahashi, T. Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Erysipelothrix Rhusiopathiae Isolated from Pigs with Swine Erysipelas in Japan, 1988–1998. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2001, 48, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, T.A.; Imada, Y.; Barcellos, D.E.S.N.; Oliveira, S.J.; Moreno, A.M. Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of Recent and Archived Erysipelothrix Spp. Isolated from Brazilian Swine. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 69, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R.L. A selective liquid medium utilizing antibiotics for isolation of Erysipelothrix insidiosa. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1965, 26, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Sawada, T.; Muramatsu, M.; Tamura, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Benno, Y.; Mitsuoka, T. Serotype, antimicrobial susceptibility, and pathogenicity of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolates from tonsils of apparently healthy slaughter pigs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.M.; Grossman, A.D. Integrative and Conjugative Elements (ICEs): What They Do and How They Work. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2015, 49, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Nishikawa, S.; Eguchi, M.; Shimoji, Y. Identification of serovar 1a, 1b, 2, and 5 strains of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae by a conventional gel-based PCR. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 225, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI Supplement M100. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI Supplement Vet06. Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 1st ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dec, M.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Gnat, S.; Fratini, F.; Urban-Chmiel, R.; Cerri, D.; Winiarczyk, S.; Turchi, B. Antibiotic Susceptibility and Virulence Genes in Enterococcus Isolates from Wild Mammals Living in Tuscany, Italy. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dec, M.; Stępien-Pyśniak, D.; Puchalski, A.; Hauschild, T.; Pietras-Ozga, D.; Ignaciuk, S.; Urban-Chmiel, R. Biodiversity of Ligilactobacillus salivarius Strains from Poultry and Domestic Pigeons. Animals 2021, 11, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, C.L.M.; Chooi, Y.H. Clinker & clustermap.js: Automatic generation of gene cluster comparison figures. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2473–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.B.; Xie, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Wu, J. Complete genome sequence of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae strain GXBY-1 isolated from acute swine erysipelas outbreaks in south China. Genom. Data 2016, 8, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Ooka, T.; Shi, F.; Ogura, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Hayashi, T.; Shimoji, Y. The genome of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, the causative agent of swine erysipelas, reveals new insights into the evolution of firmicutes and the organism’s intracellular adaptations. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 2959–2971. Available online: https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/jb.01500-10 (accessed on 1 October 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, A.H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, P.; Leung, F.C. Complete genome assembly and characterization of an outbreak strain of the causative agent of swine erysipelas—Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae SY1027. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Ding, Y.; Jie, K.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; et al. Comparative Genome Analysis of a Pathogenic Erysipelothrix Rhusiopathiae Isolate WH13013 from Pig Reveals Potential Genes Involve in Bacterial Adaptions and Pathogenesis. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Park, S.Y.; Seo, H.W.; Cho, Y.; Choi, S.G.; Seo, S.; Han, W.; Lee, N.K.; Kwon, H.; Han, J.E.; et al. Pathological and Genomic Findings of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Isolated from a Free-Ranging Rough-Toothed Dolphin Steno bredanensis (Cetacea: Delphinidae) Stranded in Korea. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 774836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalchuk, S.; Babii, A. Draft genome sequence data of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae vaccine strain VR-2. Data Brief 2020, 33, 106352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, K.; Bloodgood, J.; Mullis, M.M.; Deming, A.C.; Colegrove, K.; Kiel Reese, B. Draft Genome Sequences of Erysipelothrix sp. Strains Isolated from Stranded Septic Bottlenose Dolphins in Alabama, USA. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 11, e0027322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zautner, A.E.; Tersteegen, A.; Schiffner, C.J.; Ðilas, M.; Marquardt, P.; Riediger, M.; Delker, A.M.; Mäde, D.; Kaasch, A.J. Human Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae infection via bath water—Case report and genome announcement. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 981477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IJsseldijk, L.L.; Begeman, L.; Duim, B.; Gröne, A.; Kik, M.J.L.; Klijnstra, M.D.; Lakemeyer, J.; Leopold, M.; Munnink, B.B.O.; Ten Doeschate, M.; et al. Harbor Porpoise Deaths Associated with Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, the Netherlands, 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileto, I.; Merla, C.; Corbella, M.; Gaiarsa, S.; Kuka, A.; Ghilotti, S.; De Cata, P.; Baldanti, F.; Cambieri, P. Bloodstream Infection Caused by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in an Immunocompetent Patient. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlund, R.; Formenti, N.; Caló, S.; Chiari, M.; Zoric, M.; Alborali, G.L.; Sørensen Dalgaard, T.; Wattrang, E.; Eriksson, H. Comparative genome analysis of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolated from domestic pigs and wild boars suggests host adaptation and selective pressure from the use of antibiotics. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, mgen000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, T.L.; Kollanandi Ratheesh, N.; Harvey, W.T.; Thomson, J.R.; Williamson, S.; Biek, R.; Opriessnig, T. Genomic and Immunogenic Protein Diversity of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Isolated from Pigs in Great Britain: Implications for Vaccine Protection. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Lammens, C.; Piessens, J.; Goossens, H. Multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection of macrolide and tetracycline resistance determinants in streptococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4798–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakulenko, S.B.; Donabedian, S.M.; Voskresenskiy, A.M.; Zervos, M.J.; Lerner, S.A.; Chow, J.W. Multiplex PCR for detection of aminoglycoside resistance genes in enterococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1423–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Alam, M.; Nishimoto, Y.; Urasawa, S.; Uehara, N.; Watanabe, N. Distribution of aminoglycoside resistance genes in recent clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus avium. Epidemiol. Infect. 2001, 126, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
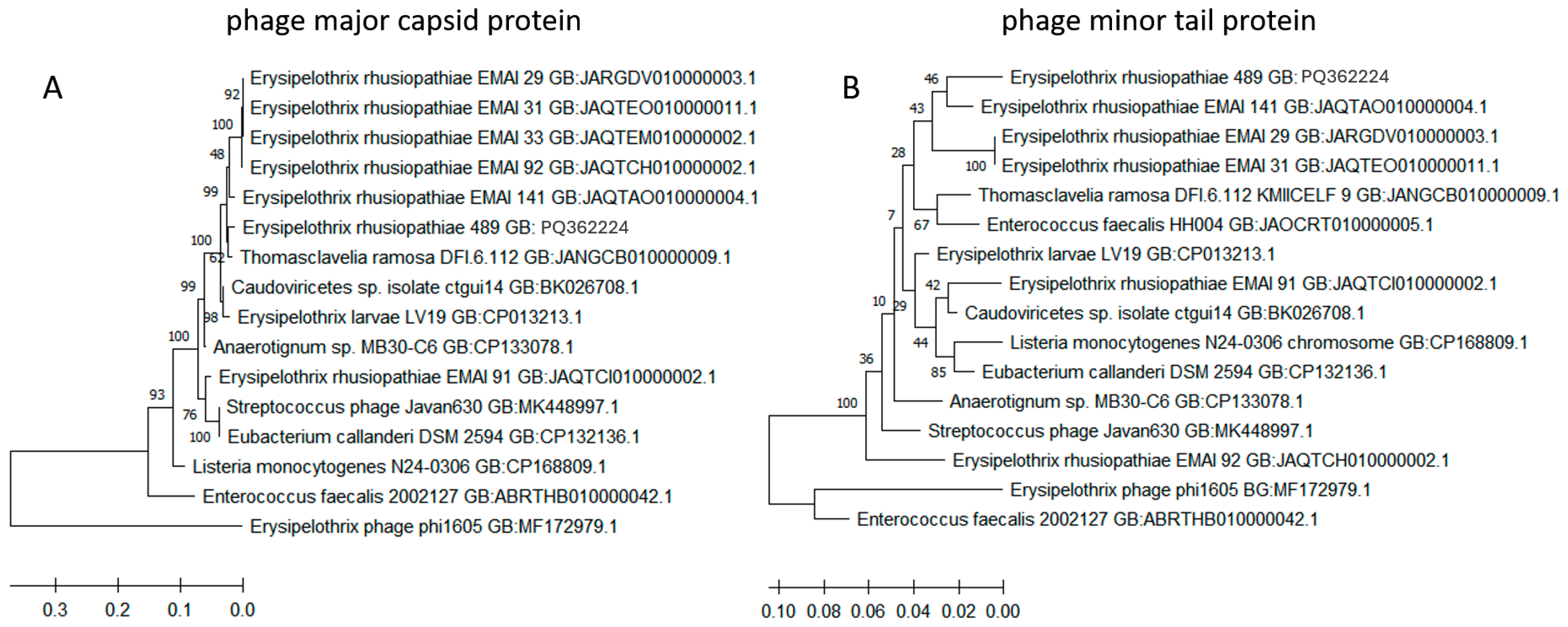
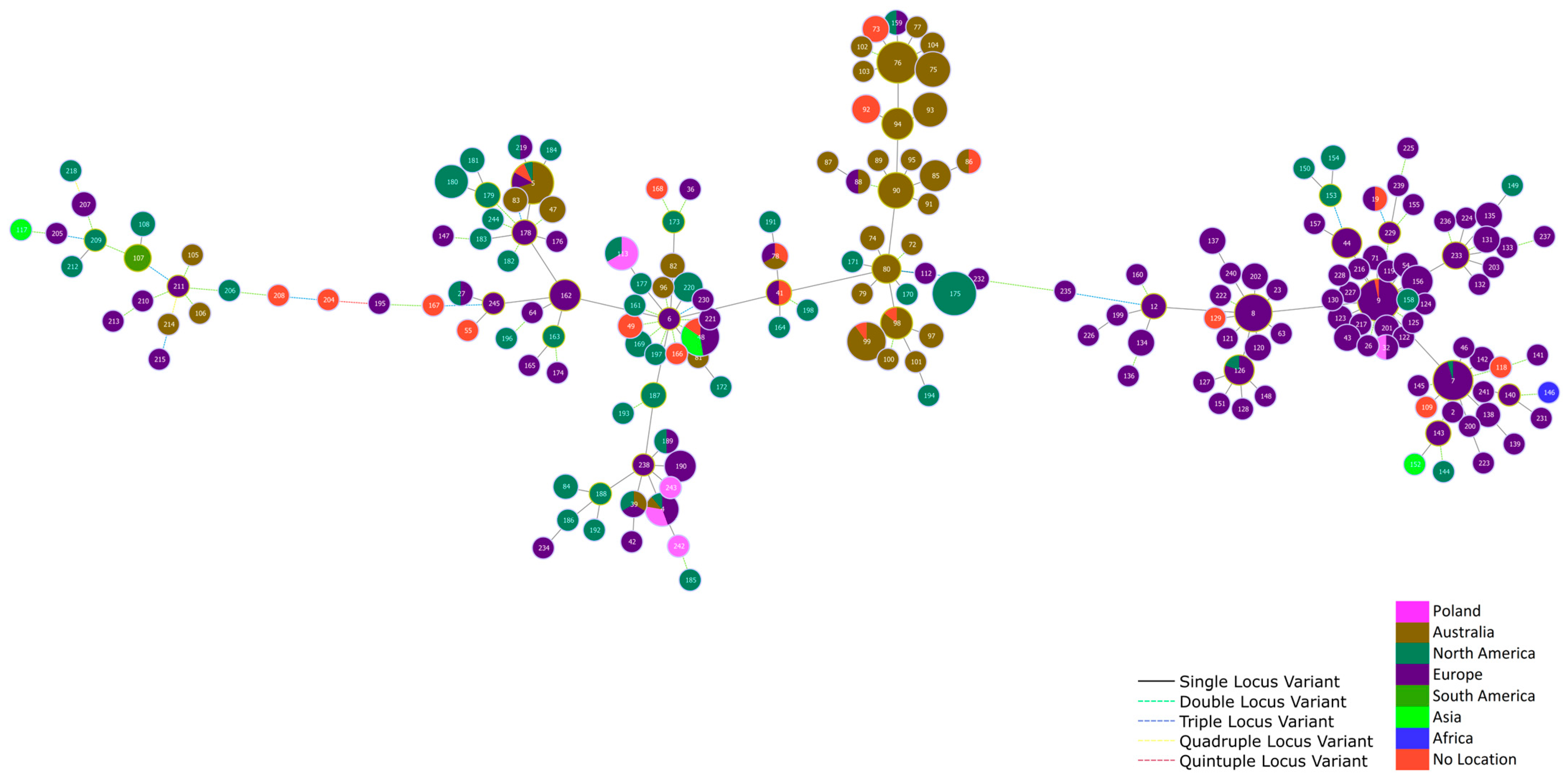
| Serotype | E. rhusiopathiae Strains Tested in This Work (n = 60) | E. rhusiopathiae Strains Whose WGS Were Derived from GenBank (n = 260) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 1 [1.7%] | 92 [35.4%] | |
| 1b | 17 [28.3%] | 57 [21.9%] | |
| 2 | 6 [10.0%] | 56 [21.5%] | |
| 1a/2 | 0 | 22 [8.5%] | |
| 1a/1b | 0 | 1 [0.4%] | |
| 2/15 | 0 | 1 [0.4%] | |
| 5 | 23 [38.3%] | 7 [2.7%] | all strains from birds * |
| 6 | 2 [3.3%] | 2 [0.8%] | all strains from birds * |
| 8 | 9 [15.0%] | 0 | all strains from birds * |
| 9 | 0 | 3 [1.1%] | |
| 11 | 0 | 1 [0.4%] | |
| 15 | 0 | 1 [0.4%] | |
| 16 | 0 | 1 [0.4%] | |
| 17 | 0 | 2 [0.8%] | |
| 19 | 0 | 1 [0.4%] | |
| 21 | 0 | 11 [4.2%] | |
| 23 | 0 | 1 [0.4%] | |
| N | 2 [3.3%] | 1 [0.4%] |
| ≤0.06 | ≤0.125 | ≤0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | ≥16 | 32 | ≥64 | 128 | 256 | ≥512 | Number (%) of Resistant Isolates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEN | 60 | 0 | |||||||||||||
| AMP | 37 | 22 | 1 | 0 | |||||||||||
| AMX | 60 | 0 | |||||||||||||
| AMC | 60 | 0 | |||||||||||||
| CEF | 59 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||||
| TET | 1 | 2 | 6 | 2tetM | 22tetM | 27tetM | 51 (85%) | ||||||||
| ENR | 12 | 29 | 19 | 48 (80%) | |||||||||||
| ERY | 2 | 34 | 21 | 1 | 1erm47 | 1ermB | 2 (3.3%) | ||||||||
| TYL | 2 | 49 | 5 | 1 | 1erm47 | 1 | 1ermB | 3 (5.0%) | |||||||
| CLI | 42 | 7 | 1 | 2lnuB | 5lnuB | 2lnuB | 1 | 10 (16.7%) | |||||||
| LIN | 15 | 24 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10lnuB(9) ermB (1) | 10 (16.7%) | |||||||
| TIA | 4 | 10 | 22 | 12 | 3 | 9lsaE | 9 (15%) | ||||||||
| FLO | 3 | 50 | 7 | NA | |||||||||||
| STR | 2 | 9 | 23 | 22 | 4ant(6)-Ia spw | NA | |||||||||
| SPE | 9 | 28 | 18 | 1 | 2ant(6)-Ia, spw | 2ant(6)-Ia, spw | NA | ||||||||
| GEN | 1 | 59 | NA | ||||||||||||
| NEO | 60 | NA | |||||||||||||
| TR/S | 60 | NA |
| Isolate | Serotype | Enrofloxacin MIC [µg/mL] | Mutation at Position 257 of the gyrA Gene | GB or ENA Acc. No. | Mutation at Position 242 of the parC Gene | GB or ENA Acc. No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 19414 | 2 | ≤0.25 | S | Thr86 (ACA) | LR134439.1 | Ser81 (AGT) | LR134439.1 |
| 1012 | 2 | ≤0.125 | S | Thr86 (ACA) | OP921306 | Ser81 (AGT) | ERR12736636 |
| 1023 | 2 | 16 | R | Ile86 (ATA) | OP921307 | Ile81 (ATT) | ERR12736637 |
| 827KZ | 2 | 8 | R | Lys86 (AAA) | PQ015304 | Ile81 (ATT) | PQ015313 |
| 584 | 5 | ≤0.125 | S | Thr86 (ACA) | ERR1273663 | Ser81 (AGT) | ERR1273663 |
| 267 | 5 | 8 | R | Lys86 (AAA) | OQ625325 | Ile81 (ATT) | ERR12736634 |
| 136 | 5 | 8 | R | Lys86 (AAA) | PQ015305 | Ile81 (ATT) | PQ015314 |
| 434W | 5 | 8 | R | Lys86 (AAA) | PQ015306 | Ile81 (ATT) | PQ015315 |
| 95 | 8 | 16 | R | Ile86 (ATA) | OP921308 | Ile81 (ATT) | PQ015321 |
| 759W | 8 | 8 | R | Ile86 (ATA) | PQ015307 | Ile81 (ATT) | PQ015318 |
| 1092 | 8 | 16 | R | Ile86 (ATA) | PQ015308 | Ile81 (ATT) | PQ015319 |
| 849 | 6 | ≤0.125 | S | Thr86 (ACA) | PQ015309 | Ser81 (AGT) | PQ015322 |
| 497 | 6 | 16 | R | Ile86 (ATA) | PQ015310 | Ile81 (ATT) | PQ015320 |
| 657 | 1b | ≤0.125 | S | Thr86 (ACA) | OP921309 | Ser81 (AGT) | PQ015323 |
| 167 | 1b | 16 | R | Ile86 (ATA) | PQ015311 | Ile81 (ATT) | PQ015317 |
| 526 | 1b | 16 | R | Ile86 (ATA) | PQ015312 | Ile81 (ATT) | PQ015316 |
| Isolate | Serotype | Host | Year of Isolation | Resistance Genes | ICE- and Phage-Specific Genes | gpsA | recA | purA | pta | prsA | galK | ldhA | ST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95 | 8 | goose | 2020 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn, rec 1, mcp 2, mtp 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 113 |
| 759W | 8 | goose | 2019 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn, rec, mcp, mtp | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 113 |
| 176 | 8 | goose | 2020 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn, rec, mcp, mtp | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 113 |
| 489 | 8 | goose | 2020 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn, rec, mcp, mtp | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 113 |
| 8S | 8 | pig | 2019 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE | int-Tn, rec, mcp, mtp | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 113 |
| 1092 | 8 | goose | 2021 | tetM | int-Tn | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 113 |
| 451 | 1b | duck | 2021 | tetM | int-Tn | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 4 |
| 136 | 5 | goose | 2020 | tetM, ant(6)-Ia, spw | int-Tn, mobL, rec | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 4 |
| 1023 * | 2 | goose | 2021 | tetM, lnuB, lsaE, spw, ant(6)-Ia, erm47 | int-Tn, mobL, virB4 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 4 |
| 1012 * | 2 | goose | 2020 | tetM | int-Tn | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 242 |
| 267 * | 5 | goose | 2021 | tetM, ermB | int-Tn, prophage detected 4 | 2 | 24 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 243 |
| 584 * | 5 | goose | 2021 | none | none | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 32 |
| Antimicrobial Agent | Breakpoints | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | I | R | ||
| Penicillin | ≤0.12 | – | – | CLSI VET06 [40] |
| Ampicillin | ≤0.25 | – | – | CLSI VET06 [40] |
| Amoxicillin | – | – | – | No recommendations |
| Amoxicillin + ca | – | – | – | No recommendations |
| Ceftiofur | ≤2 | 4 | ≥8 | CLSI VET06 [40] |
| Erythromycin | ≤0.25 | 0.5 | ≥1 | CLSI VET06 [40] |
| Tylosin | ≤0.25 | 0.5 | ≥1 | Dec et al. [9] |
| Clindamycin | ≤0.25 | 0.5 | ≥1 | CLSI VET06 [40] |
| Lincomycin | ≤2 | 4 -8 | ≥16 | Dec et al. [9] |
| Tiamulin | ≤16 | – | ≥32 | Dec et al. [9] |
| Enrofloxacin | ≤0.5 | 1 | ≥2 | CLSI VET06 [40] |
| Tetracycline | ≤4 | 8 | ≥16 | Dec et al. [9] |
| Florfenicol | – | – | – | No recommendations |
| Gentamicin | – | – | – | No recommendations |
| Neomycin | – | – | – | No recommendations |
| Streptomycin | – | – | – | No recommendations |
| Spectinomycin | – | – | – | No recommendations |
| Trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole | – | – | – | No recommendations |
| Genotypic Resistance Profile | Acc. No. | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. rhusiopathiae 1023 | tetM, lsaE, lnuB, spw, ant(6)-Ia, erm47; int-Tn | ENA: ERR12736637 | [14] |
| E. rhusiopathiae 267 | tetM, ermB; int-Tn | ENA: ERR12736634 | [14] |
| E. rhusiopathiae 1012 | tetM; int-Tn | ENA: ERR12736636 | [14] |
| E. rhusiopathiae ATCC 19414 | none | GB: NZ_LR134439.1 | unpublished |
| Streptococcus gallolyticus 607 | tetM, lsaE, lnuB, spw, ant(6)-Ia, sat4 aph(3′)-IIIa; int-Tn, | Not applicable | unpublished |
| Enterococcus faecium 9W | tetM, ermB | Not applicable | [41] |
| Ligilactobacillus salivarius 5aI | ant(6)-Ia, spw, lsaE, lnuB | GB: MK091478.1; MK091477.1 | [42] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dec, M.; Nowak, T.; Webster, J.; Wódz, K. Serotypes, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Potential Mechanisms of Resistance Gene Transfer in Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strains from Waterfowl in Poland. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212192
Dec M, Nowak T, Webster J, Wódz K. Serotypes, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Potential Mechanisms of Resistance Gene Transfer in Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strains from Waterfowl in Poland. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(22):12192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212192
Chicago/Turabian StyleDec, Marta, Tomasz Nowak, John Webster, and Karolina Wódz. 2024. "Serotypes, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Potential Mechanisms of Resistance Gene Transfer in Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strains from Waterfowl in Poland" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 22: 12192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212192
APA StyleDec, M., Nowak, T., Webster, J., & Wódz, K. (2024). Serotypes, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Potential Mechanisms of Resistance Gene Transfer in Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Strains from Waterfowl in Poland. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(22), 12192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212192







