Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Exosomal miR-99a Attenuate Silica-Induced Lung Fibrosis by Inhibiting Pulmonary Fibroblast Transdifferentiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
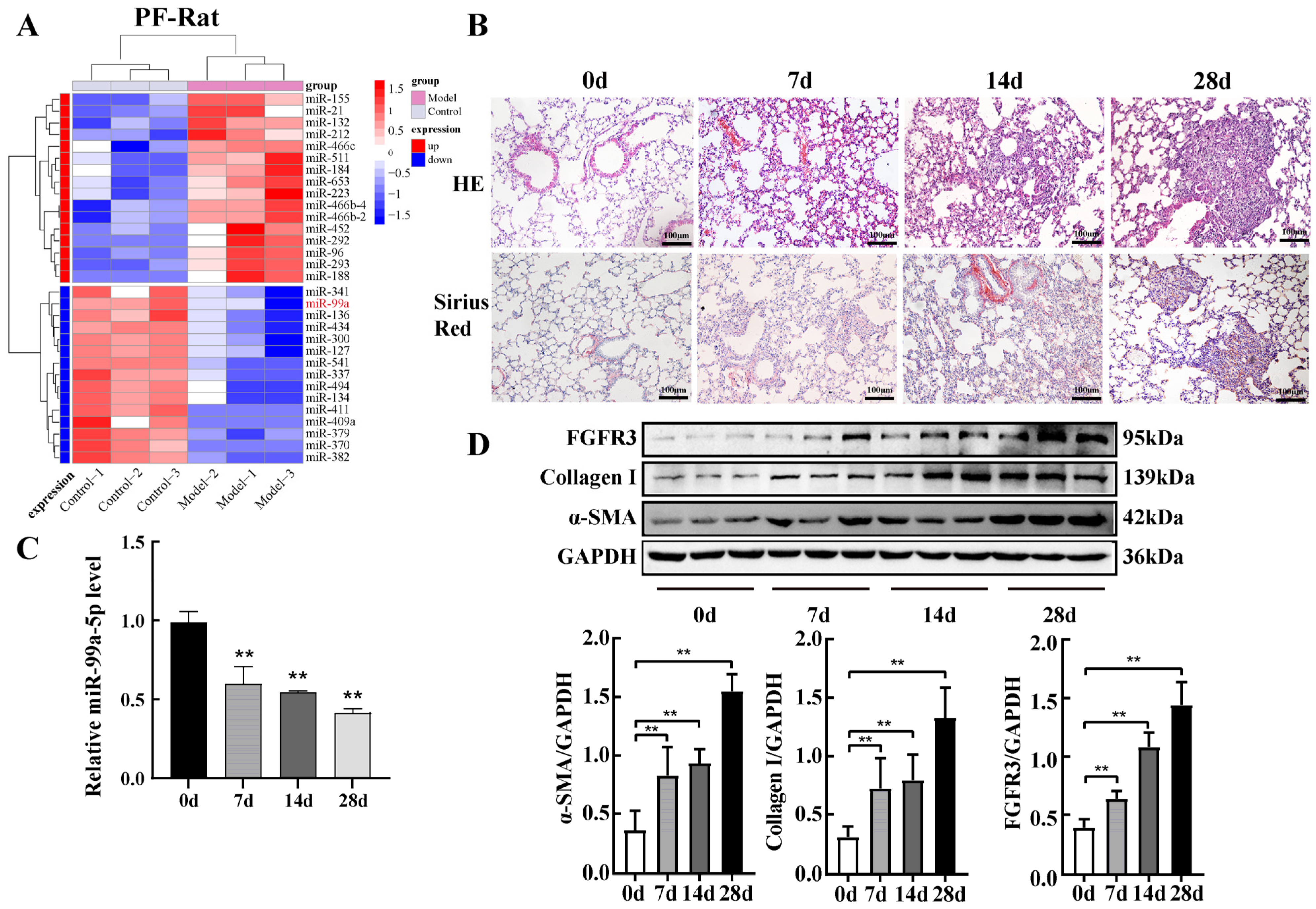
2.1. miR-99a-5p Was Significantly Downregulated and FGFR3 Was Upregulated in Pulmonary Fibrosis
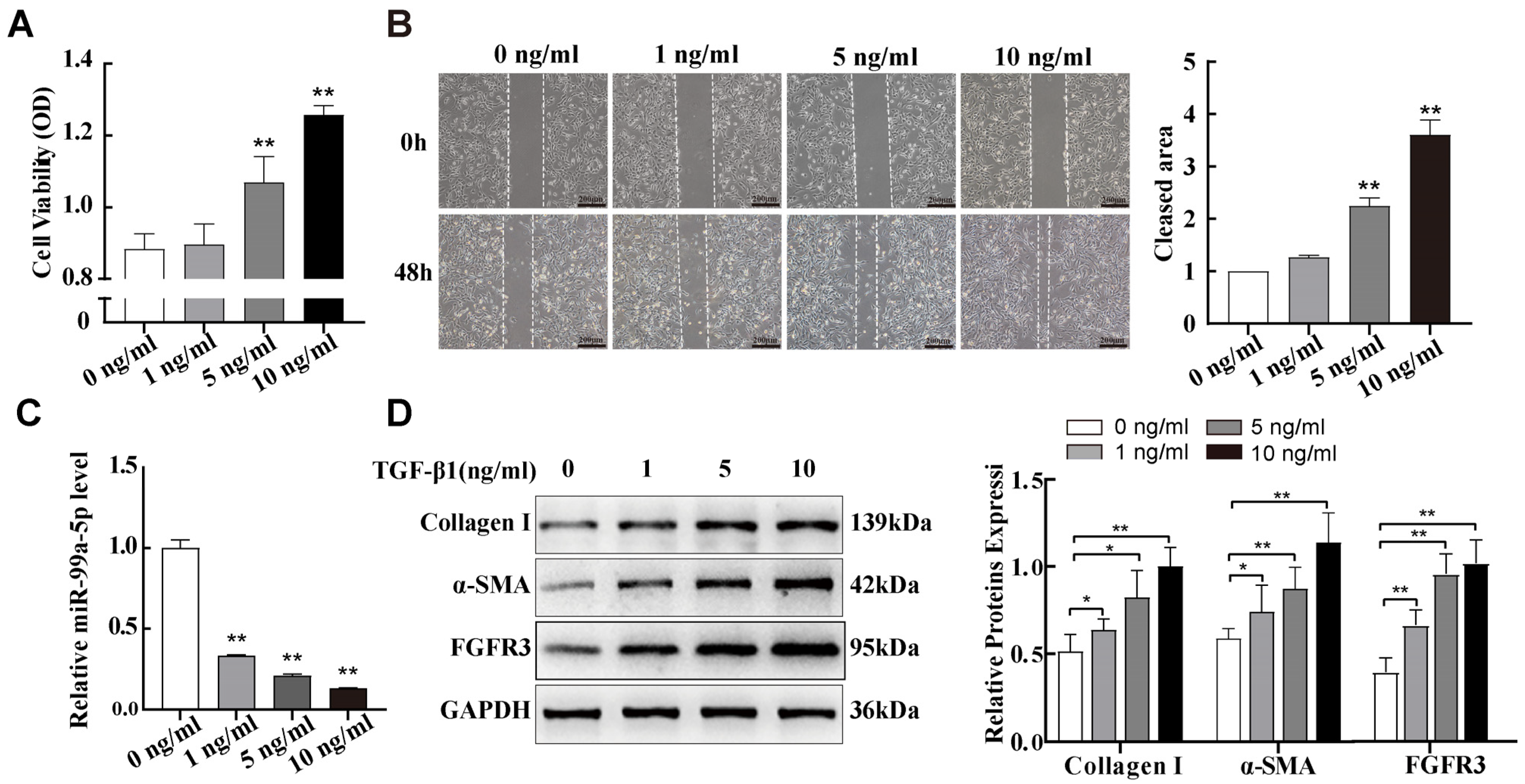
2.2. miR-99a-5p Was Significantly Downregulated and FGFR3 Was Upregulated in TGF-β1-Induced Pulmonary Fibroblast Transdifferentiation
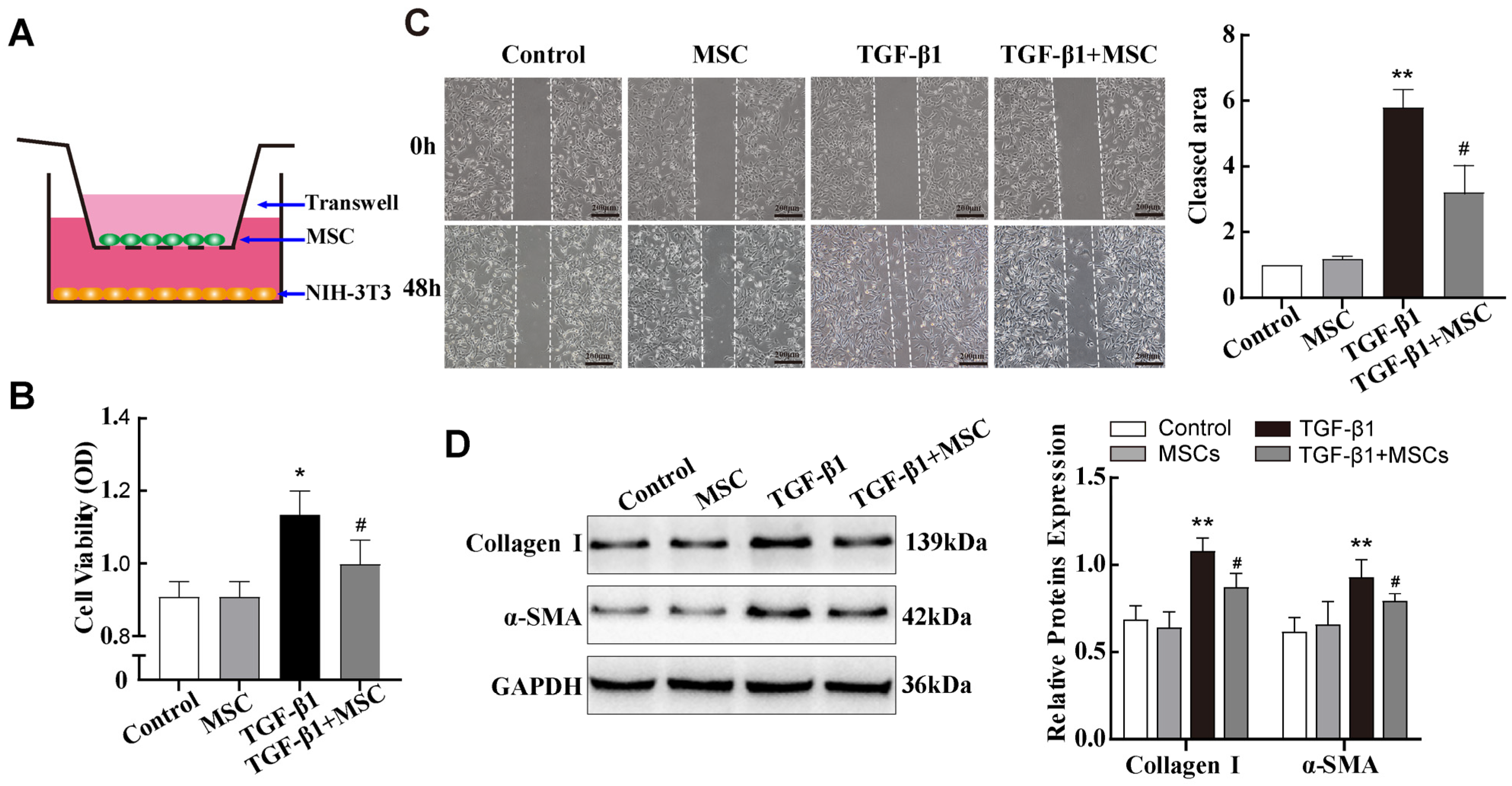
2.3. In Vitro Co-Culture with MSCs Reduced TGF-β1-Induced Pulmonary Fibroblast Transdifferentiation
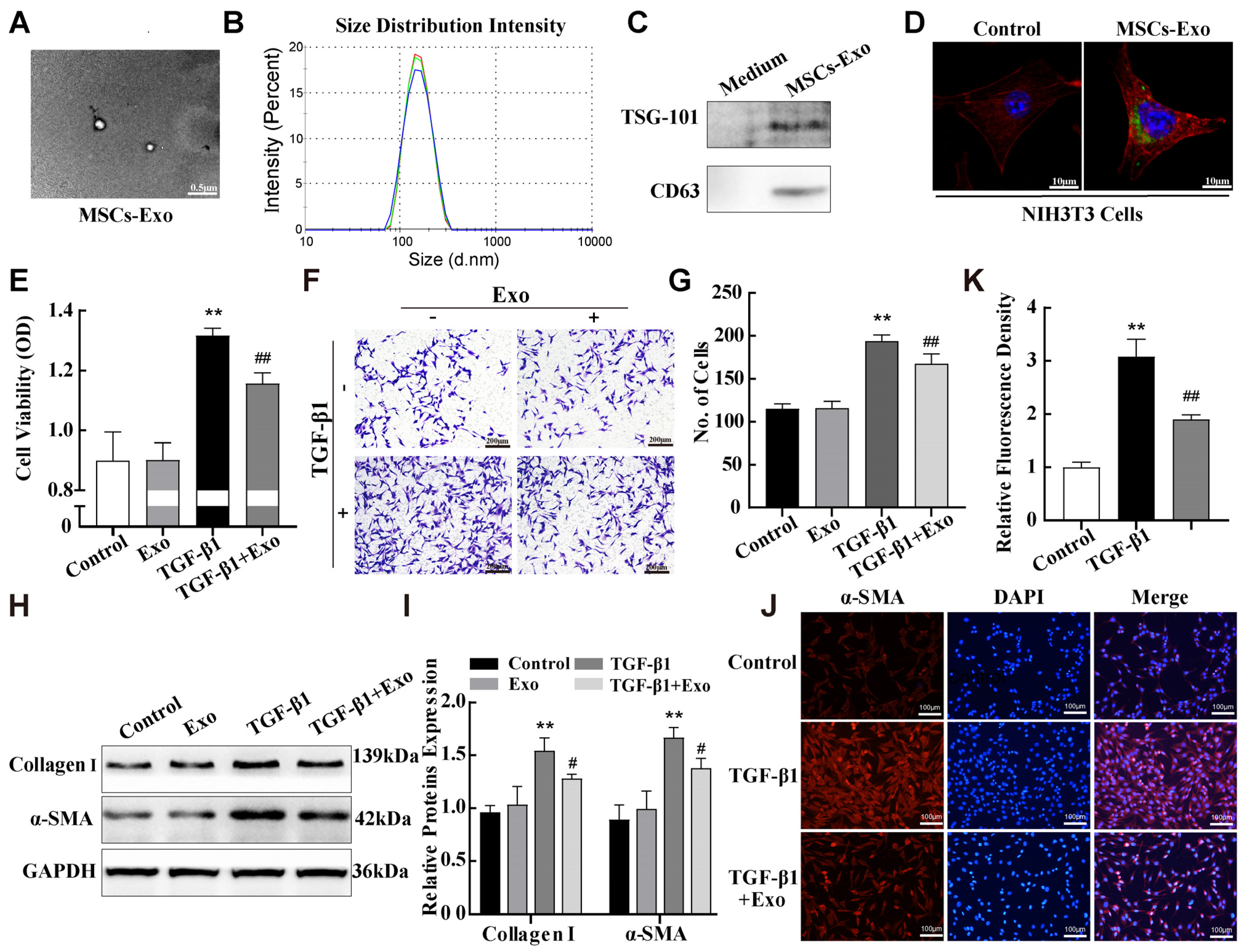
2.4. MSC-Exosomes Attenuated TGF-β1-Induced Pulmonary Fibroblast Transdifferentiation
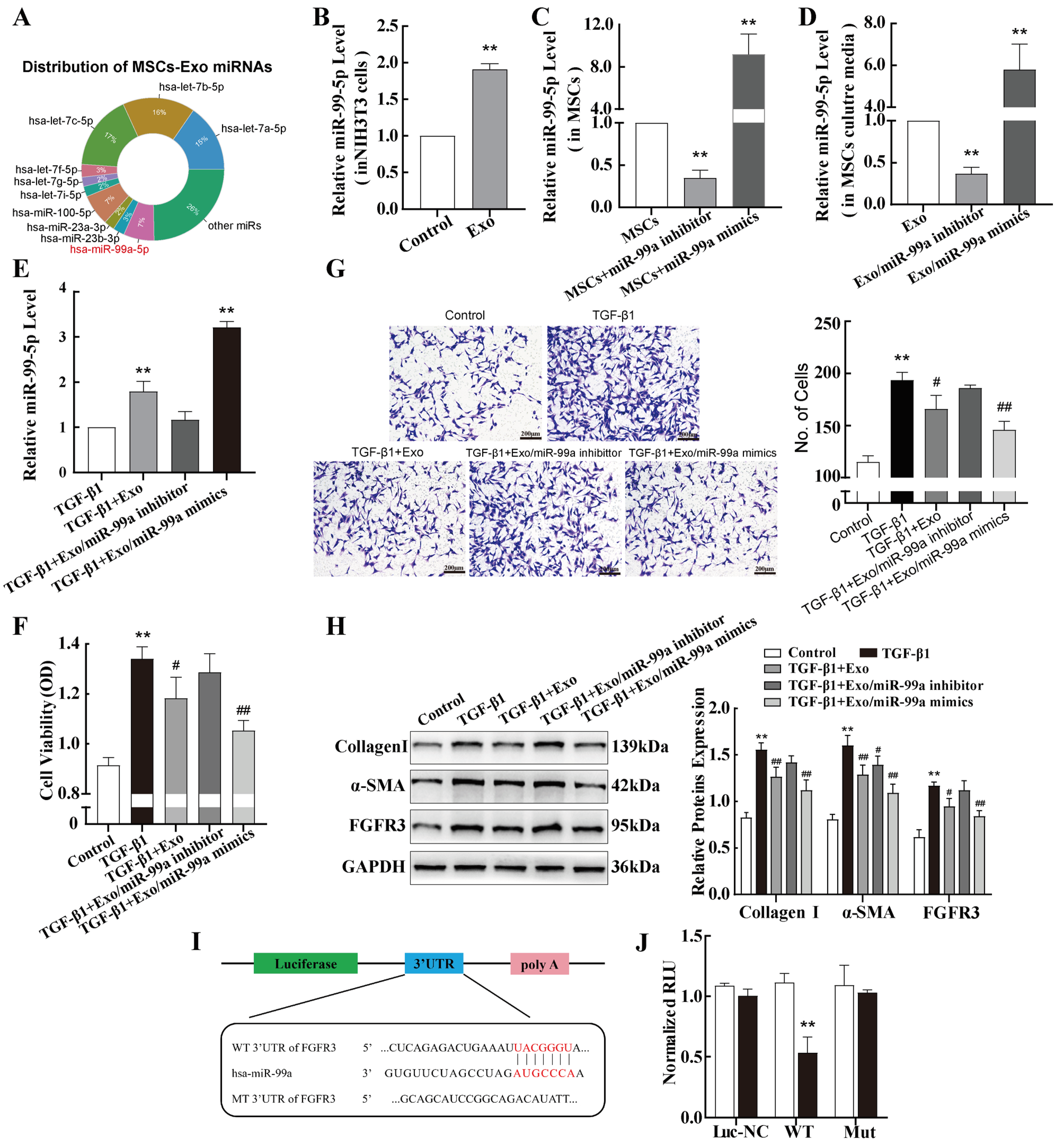
2.5. miR-99a-5p Transmitted by MSC-Derived Exosomes Inhibited TGF-β1-Induced Pulmonary Fibroblast Transdifferentiation by Directly Targeting FGFR3
2.6. FGFR3-Regulated TGF-β1-Induced Pulmonary Fibroblast Transdifferentiation Through the MAPK Signalling Pathway
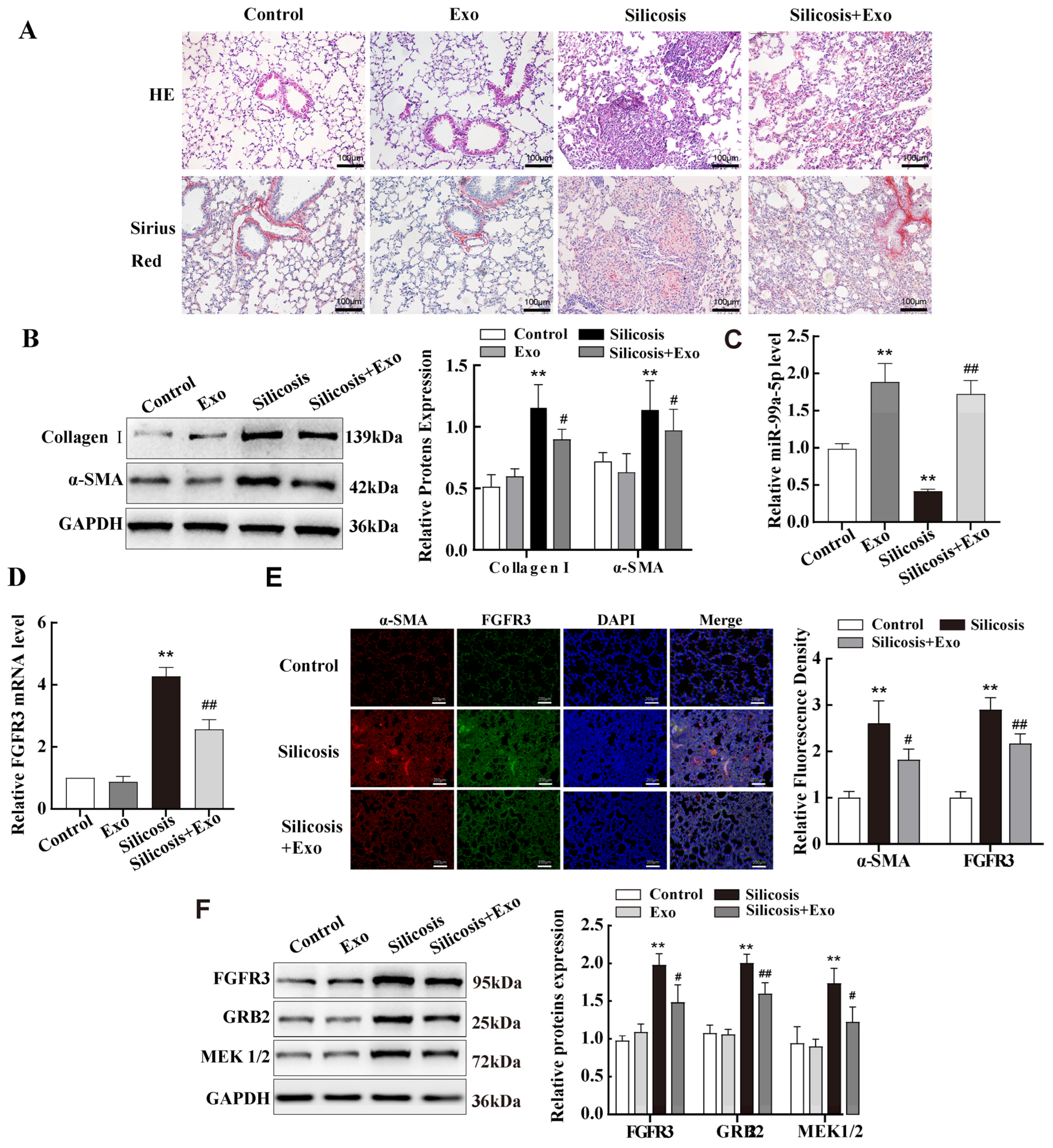
2.7. miR-99a-5p Transmitted by MSC-Derived Exosomes Inhibited MAPK Pathway by Targetting FGFR3 in Mouse Lung Tissue of Silicotic Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. Co-Culture Model of TGF-β1-Treated NIH-3T3 Cells with MSCs
4.3. Mouse Model of Silicosis and Group
4.4. Isolation, Characterisation, and NIH-3T3 Uptake of Exosomes
4.5. Histopathology (HE and Sirius Red Staining)
4.6. Cell Proliferation and Migration
4.7. Cell Transfection
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. RNA Extraction and Quantification
4.10. Immunofluorescence Assays
4.11. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, X.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Duan, M.; Qi, J.; Hao, C.; Yao, W. FAP expression dynamics and role in silicosis: Insights from epidemiological and experimental models. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 356, 124311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, R.F.; Chambers, D.C. Silica-related diseases in the modern world. Allergy 2020, 75, 2805–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Qi, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, X.; Shu, T.; Li, B.; Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Wei, D.; Chen, J.; et al. Multi-omics study of silicosis reveals the potential therapeutic targets PGD2 and TXA2. Theranostics 2021, 11, 2381–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, A.; Tian, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, C.; Wei, J.; Yao, W.; et al. PPARγ/LXRα axis mediated phenotypic plasticity of lung fibroblasts in silica-induced experimental silicosis. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecile, R.; Amy, H.; Ketki, P.; Coralynn, S.; Jenna, W.; Lauren, Z.; David, W.; Emily, H.; Robbie, S.; Ronda, B.; et al. Severe Silicosis in Engineered Stone Fabrication Workers—California, Colorado, Texas, and Washington, 2017–2019. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 813–818. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Chen, S.-Y.; Lerbs, T.; Lee, J.-W.; Domizi, P.; Gordon, S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Nolan, G.; Betancur, P.; Wernig, G. Activation of JUN in fibroblasts promotes pro-fibrotic programme and modulates protective immunity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Zeng, X.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J. Targeting Mechanics-Induced Fibroblast Activation through CD44-RhoA-YAP Pathway Ameliorates Crystalline Silica-Induced Silicosis. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4993–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younesi, F.S.; Miller, A.E.; Barker, T.H.; Rossi, F.M.V.; Hinz, B. Fibroblast and myofibroblast activation in normal tissue repair and fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Kim, T.J.; Peng, D.H.; Duan, D.; Gibbons, D.L.; Yamauchi, M.; Jackson, J.R.; Le Saux, C.J.; Calhoun, C.; Peters, J.; et al. Fibroblast-specific inhibition of TGF-β1 signaling attenuates lung and tumor fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3675–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, T.; Hu, W.; Zhen, C.; Wang, F.-S. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for severe COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; He, W.; Guan, W.; Hou, F.; Yan, P.; Xu, J.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L. Mesenchymal stem cells reverse EMT process through blocking the activation of NF-κB and Hedgehog pathways in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, S.; Hirsch, D.; Hermann, F.G. Cell therapy for lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Zhao, A. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome: From basic to clinics. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, G.R.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Anastas, J.; Vitali, S.H.; Liu, X.; Ericsson, M.; Kwong, A.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Kourembanas, S. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Exosomes Ameliorate Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Restore Lung Function through Macrophage Immunomodulation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourembanas, S. Exosomes: Vehicles of Intercellular Signaling, Biomarkers, and Vectors of Cell Therapy. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015, 77, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padinharayil, H.; Varghese, J.; Wilson, C.; George, A. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Characteristics and applications in disease pathology and management. Life Sci. 2024, 342, 122542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Du, Y.; Zhang, C.; Pan, F.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Peng, Q. Exosomes: The next generation of endogenous nanomaterials for advanced drug delivery and therapy. Acta Biomater. 2019, 86, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Hou, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, L. Exosomal let-7i-5p from three-dimensional cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells inhibits fibroblast activation in silicosis through targeting TGFBR1. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 233, 113302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Lv, H.; Lv, G.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Yu, L.; Su, B.; Guo, L.; Huang, S.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p induces cancer-associated fibroblast activation to foster lung metastasis of liver cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, D.; Li, S.; Wei, Z.; Li, S.; Cai, W.; Mao, N.; Jin, F.; Li, Y.; Yi, X.; et al. Pulmonary Silicosis Alters MicroRNA Expression in Rat Lung and miR-411-3p Exerts Anti-fibrotic Effects by Inhibiting MRTF-A/SRF Signaling. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Li, P.; Pan, H.; Xu, Q.; Xu, T.; Li, Y.; Wei, D.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. miR-770–5p inhibits the activation of pulmonary fibroblasts and silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis through targeting TGFBR1. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Zheng, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B. Exosome Theranostics: Biology and Translational Medicine. Theranostics 2018, 8, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.Z.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Sharma, T.; Kelley, S.; Oertling, E.; Zhu, H.; Corbitt, N. Pkd1l1-deficiency drives biliary atresia through ciliary dysfunction in biliary epithelial cells. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, J.-J.; Sun, Z.-L.; Liu, S.-Y.; Zou, M.-L.; Yuan, Z.-D.; Yu, S.; Lv, G.-Z.; Yuan, F.-L. Targeted apoptosis of myofibroblasts by elesclomol inhibits hypertrophic scar formation. EBioMedicine 2020, 54, 102715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, J.; Jia, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, H.; Xue, W.; Wang, Y.; Tian, L. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviated silica induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice via circPWWP2A/miR-223–3p/NLRP3 axis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 251, 114537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.Á.; Layrolle, P.; Mooney, D.J. Biomaterials Functionalized with MSC Secreted Extracellular Vesicles and Soluble Factors for Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Xie, L.; Lu, C.; Gu, C.; Xia, Y.; Lv, J.; Xuan, Z.; Fang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Gastric cancer-derived exosomal miR-519a-3p promotes liver metastasis by inducing intrahepatic M2-like macrophage-mediated angiogenesis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, P.-U.C.; Paudel, D.; Brochu, H.; Popowski, K.D.; Gracieux, M.C.; Cores, J.; Huang, K.; Hensley, M.T.; Harrell, E.; Vandergriff, A.C.; et al. Inhalation of lung spheroid cell secretome and exosomes promotes lung repair in pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, X.; Geng, M.; Huang, M. Targeting ERK, an Achilles’ Heel of the MAPK pathway, in cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, J.M.; Schleiff, P.L. Surveillance for Silicosis Deaths Among Persons Aged 15–44 Years—United States, 1999–2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmania, S. Deadly denim: Sandblasting-induced silicosis in the jeans industry. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, D.; Huang, Y.; Fanelli, V.; Delsedime, L.; Wu, S.; Khang, J.; Han, B.; Grassi, A.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; et al. Identification and Modulation of Microenvironment Is Crucial for Effective Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in Acute Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, N.; Willis, G.R.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Reis, M.; Nassiri, S.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Kourembanas, S. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes prevent and revert experimental pulmonary fibrosis through modulation of monocyte phenotypes. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e128060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollin, L.; Distler, J.H.W.; Redente, E.F.; Riches, D.W.H.; Stowasser, S.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Maher, T.M.; Kolb, M. Potential of nintedanib in treatment of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, L.; Zhang, P.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Miao, Q.; Niu, R.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y. Targeting STING-mediated pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic effects of alveolar macrophages and fibroblasts blunts silicosis caused by silica particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, J.; Sensébé, L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Shahzad, K.; Zheng, J. Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, S.; Zhao, R.C. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: A new therapeutic paradigm. Biomark. Res. 2019, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Su, C. Design strategies and application progress of therapeutic exosomes. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, Z.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Mao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, G.; Chen, H. Mouse mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-466f-3p reverses EMT process through inhibiting AKT/GSK3β pathway via c-MET in radiation-induced lung injury. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.-Y.; Wang, B.; Tang, T.-T.; Wen, Y.; Li, Z.-L.; Feng, S.-T.; Wu, M.; Liu, D.; Yin, D.; Ma, K.-L.; et al. Exosomal miR-125b-5p deriving from mesenchymal stem cells promotes tubular repair by suppression of p53 in ischemic acute kidney injury. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5248–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, V.; Sengupta, S.; Lazo, A.; Woods, P.; Nolan, A.; Bremer, N. Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Treatment for Severe COVID-19. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Talebi, S.F.; Shoorei, H.; Branicki, W.; Taheri, M.; Akbari Dilmaghani, N. Role of miRNA and lncRNAs in organ fibrosis and aging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiot, J.; Cambier, M.; Boeckx, A.; Henket, M.; Nivelles, O.; Gester, F.; Louis, E.; Malaise, M.; Dequiedt, F.; Louis, R.; et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes attenuate fibrosis in airway epithelial cells through delivery of antifibrotic miR-142-3p. Thorax 2020, 75, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yu, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, B.; Qian, F.; Cheng, Y.; He, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, L.; et al. miR-99a regulates CD4+ T cell differentiation and attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by mTOR-mediated glycolysis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, F.; Xiang, M. Engineered M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles with platelet membrane fusion for targeted therapy of atherosclerosis. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 35, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciano, A.; Garcia-Mayea, Y.; Jubierre, L.; Mir, C.; Hummel, M.; Castellvi, J.; Hernández-Losa, J.; Paciucci, R.; Sansano, I.; Sun, Y.; et al. miR-99a reveals two novel oncogenic proteins E2F2 and EMR2 and represses stemness in lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, N.J.; Nguyen, E.V.; Su, S.-P.; Novy, K.; Chan, H.C.; Nguyen, L.K.; Luu, J.; Simpson, K.J.; Lee, R.S.; Daly, R.J. FGFR3 signaling and function in triple negative breast cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Zhu, H.; Jüngel, A.; Summa, L.; Li, Y.N.; Matei, A.E.; Zhou, X.; Huang, J.; Trinh-Minh, T.; Chen, C.W.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 activates a network of profibrotic signaling pathways to promote fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Wilcox, W.R.; Chan, Y.Y.; Kawanami, A.; Bukulmez, H.; Balmes, G.; Krejci, P.; Mekikian, P.B.; Otani, K.; Yamaura, I.; et al. FGFR3 promotes synchondrosis closure and fusion of ossification centers through the MAPK pathway. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Deng, B.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Yan, T.; Yue, X.; An, Y.; et al. A novel and low-toxic peptide DR3penA alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by regulating the MAPK/miR-23b-5p/AQP5 signaling axis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 722–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, L. Exosomes in atherosclerosis: Performers, bystanders, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3996–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, X.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, F. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Exosomal miR-99a Attenuate Silica-Induced Lung Fibrosis by Inhibiting Pulmonary Fibroblast Transdifferentiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312626
Hao X, Li P, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Yang F. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Exosomal miR-99a Attenuate Silica-Induced Lung Fibrosis by Inhibiting Pulmonary Fibroblast Transdifferentiation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312626
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Xiaohui, Peiyuan Li, Yudi Wang, Qinxin Zhang, and Fang Yang. 2024. "Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Exosomal miR-99a Attenuate Silica-Induced Lung Fibrosis by Inhibiting Pulmonary Fibroblast Transdifferentiation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312626
APA StyleHao, X., Li, P., Wang, Y., Zhang, Q., & Yang, F. (2024). Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Exosomal miR-99a Attenuate Silica-Induced Lung Fibrosis by Inhibiting Pulmonary Fibroblast Transdifferentiation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312626





