Development and Validation of a Novel Four Gene-Pairs Signature for Predicting Prognosis in DLBCL Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
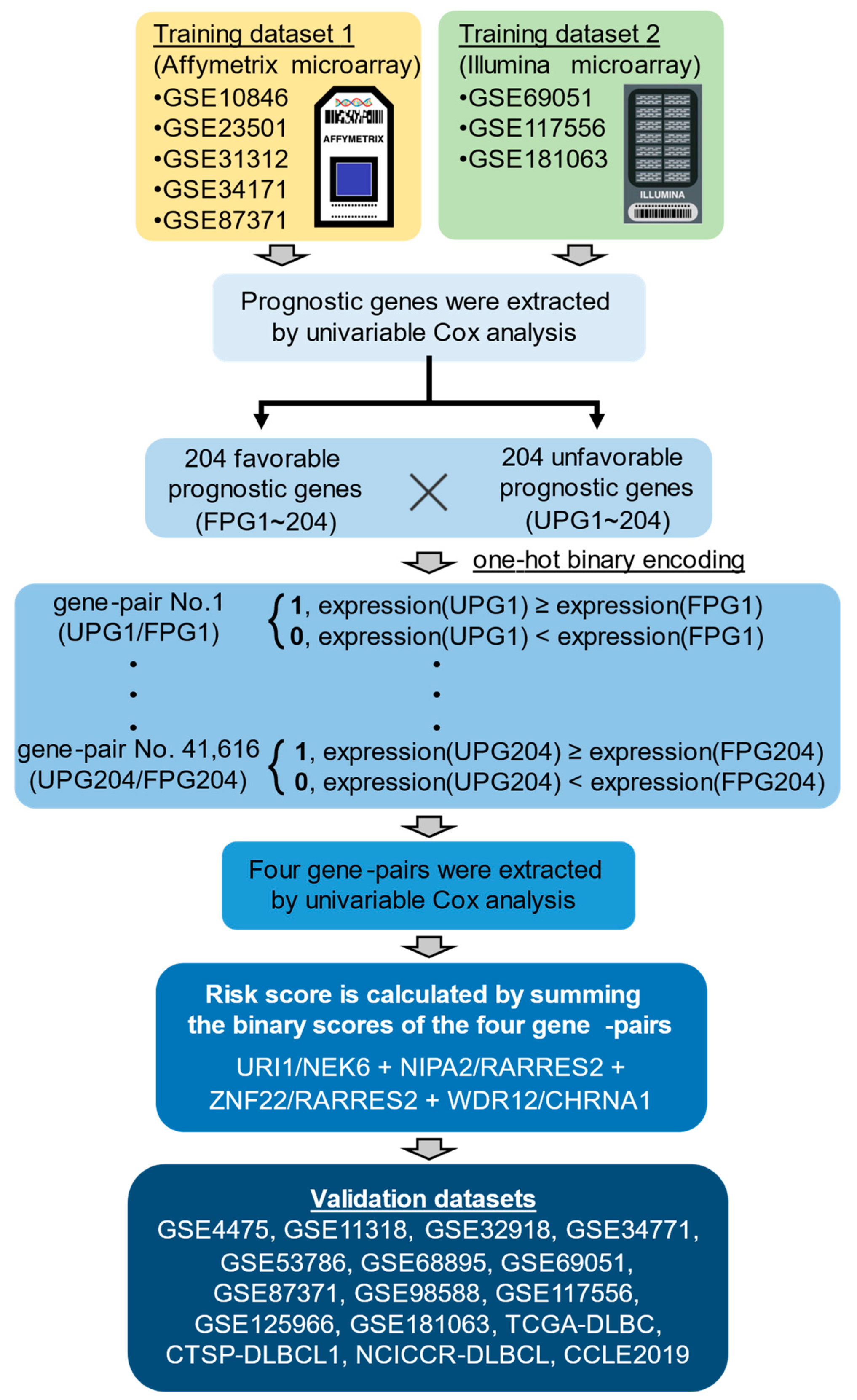
2.1. The Development of Four Gene-Pair Signature Model
2.2. Assessing the Performance of the Risk Score as a Prognostic Biomarker
2.3. Predictive Performance of the Risk Score in Conditions Stratified by Clinical Characteristics
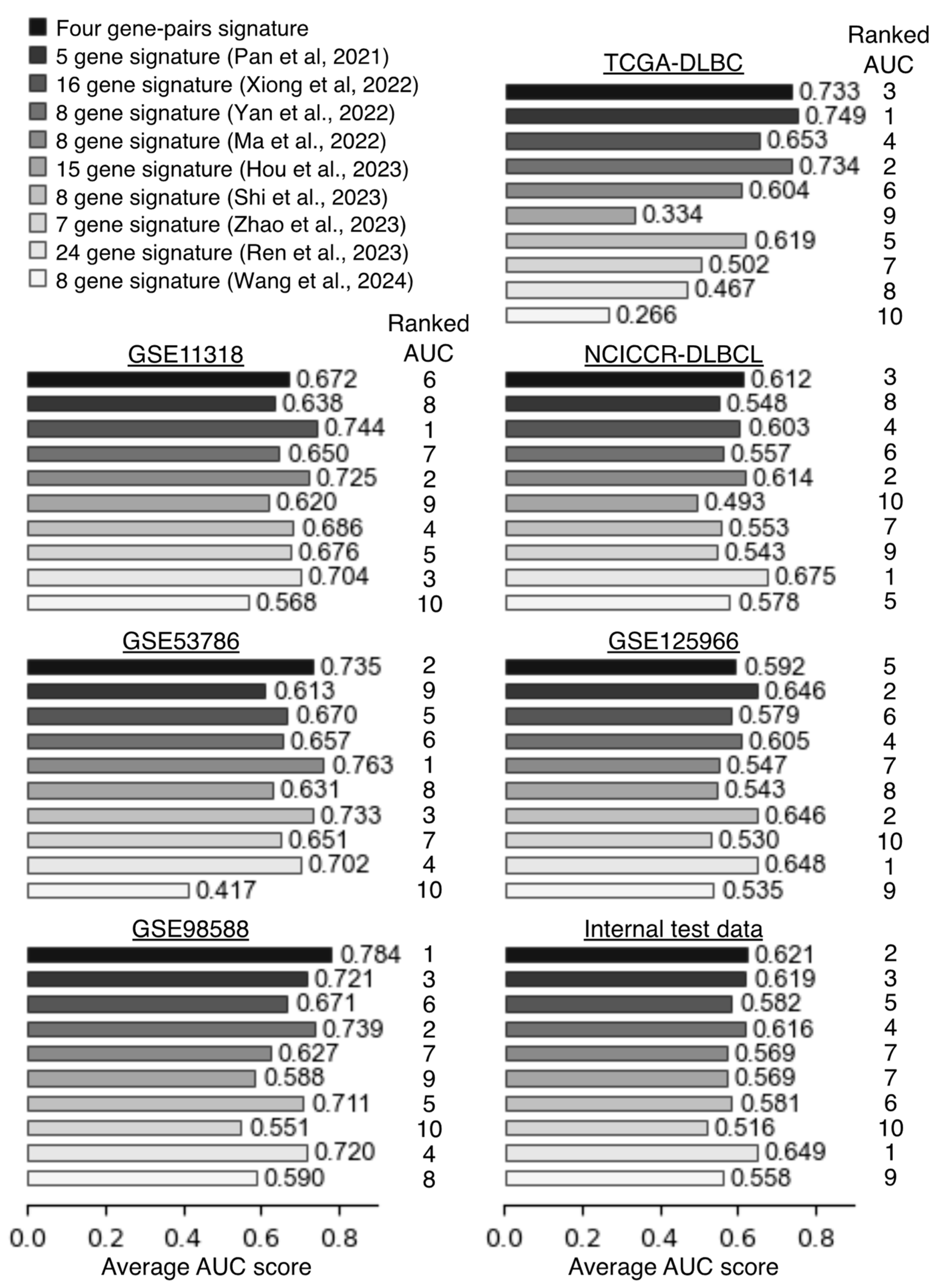
2.4. Comparison Predictive Performance of the Four Gene-Pair Signatures Against Other Signatures
2.5. Differential Signaling Pathways in Low- and High-Risk DLBCL
2.6. High-Risk DLBCL Cell Lines Are Resistant to Chemotherapy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Identification of Prognostic Genes Using a Univariable Cox Proportional Hazard Model
4.3. Selection of Four Gene-Pairs and Calculation of the Risk Score
4.4. Time-Dependent ROC Curves and GSVA Analysis
4.5. Data Analysis Environment and Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patriarca, A.; Gaidano, G. Investigational drugs for the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2021, 30, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coiffier, B.; Sarkozy, C. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: R-CHOP failure-what to do? Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Progr. 2016, 2016, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.J.; Ghesquières, H.; Jais, J.P.; Witzig, T.E.; Haioun, C.; Thompson, C.A.; Delarue, R.; Micallef, I.N.; Peyrade, F.; Macon, W.R.; et al. Event-free survival at 24 months is a robust end point for disease-related outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 987–994. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelicic, J.; Juul-Jensen, K.; Bukumiric, Z.; Roost Clausen, M.; Ludvigsen Al-Mashhadi, A.; Pedersen, R.S.; Poulsen, C.B.; Brown, P.; El-Galaly, T.C.; Stauffer Larsen, T. Prognostic indices in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A population-based comparison and validation study of multiple models. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Elsen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.L.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Beato, M.; Méndez, M.; Guirado, M.; Pedrosa, L.; Sequero, S.; Yanguas-Casás, N.; de la Cruz-Merino, L.; Gálvez, L.; Llanos, M.; García, J.F.; et al. A genetic profiling guideline to support diagnosis and clinical management of lymphomas. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 26, 1043–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlov, N.; Bagaev, A.; Revuelta, M.V.; Phillip, J.M.; Cacciapuoti, M.T.; Antysheva, Z.; Svekolkin, V.; Tikhonova, E.; Miheecheva, N.; Kuzkina, N.; et al. Clinical and biological subtypes of b-cell lymphoma revealed by microenvironmental signatures. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1468–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, C.B.; Luca, B.A.; Esfahani, M.S.; Azizi, A.; Sworder, B.J.; Nabet, B.Y.; Kurtz, D.M.; Liu, C.L.; Khameneh, F.; Advani, R.H.; et al. The landscape of tumor cell states and ecosystems in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1422–1437.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, A.L.; Wright, G.; Yang, L.; Powell, J.; Ngo, V.; Lamy, L.; Lam, L.T.; Davis, R.E.; Staudt, L.M. A library of gene expression signatures to illuminate normal and pathological lymphoid biology. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 210, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, F.A.; De Groen, R.A.L.; van den Berg, A.; Jansen, P.M.; Lam, K.H.; Mutsaers, P.G.N.J.; Van Noesel, C.J.M.; Chamuleau, M.E.D.; Stevens, W.B.C.; Plaça, J.R.; et al. Biological and Clinical Implications of Gene-Expression Profiling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Proposal for a Targeted BLYM-777 Consortium Panel as Part of a Multilayered Analytical Approach. Cancers 2022, 14, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Yang, P.; Wang, F.; Luo, X.; Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Lu, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xiu, B.; et al. Whole Transcriptome Data Analysis Reveals Prognostic Signature Genes for Overall Survival Prediction in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, D.; Li, M.; Zeng, C. Construction and validation of a risk scoring model for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma based on ferroptosis-related genes and its association with immune infiltration. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 16, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M. Identification and Validation of a Prognostic Prediction Model in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, W.; Ma, J.; Xu, Z. A Novel and Validated 8-Pyroptosis-Related Genes Based Risk Prediction Model for Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Guo, P.; Lu, Y.; Jin, X.; Liang, K.; Zhao, N.; Xue, S.; Zhou, C.; Wang, G.; Zhu, X.; et al. A prognostic 15-gene model based on differentially expressed genes among metabolic subtypes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2023, 29, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Pan, Y.; Xiang, G.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; He, L.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.; Li, L.; Liu, Z. A novel NET-related gene signature for predicting DLBCL prognosis. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shen, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, B. A novel telomere-related genes model for predicting prognosis and treatment responsiveness in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Aging 2023, 15, 12927–12951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Wan, H.; Own, S.A.; Berglund, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Ye, X.; Sonnevi, K.; et al. Genetic and transcriptomic analyses of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients with poor outcomes within two years of diagnosis. Leukemia 2024, 38, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Hori, M.; Iha, H. Disulfidptosis: A Novel Prognostic Criterion and Potential Treatment Strategy for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.; Tan, B.; Rosenwald, A.; Hurt, E.H.; Wiestner, A.; Staudt, L.M. A gene expression-based method to diagnose clinically distinct subgroups of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9991–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.; Dave, S.S.; Xiao, W.; Powell, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Tan, B.; Goldschmidt, N.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Stromal gene signatures in large-B-cell lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; He, L.; Zhu, J.; Brück, O.; Porkka, K.; Heckman, C.A.; Zhu, S.; Aittokallio, T. An immunity and pyroptosis gene-pair signature predicts overall survival in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2384–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.K.H.; Yu, L.; Maurel, P.; Waxman, D.J. Enhanced cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide activation in primary human hepatocyte cultures: Response to cytochrome P-450 inducers and autoinduction by oxazaphosphorines. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich, W.D.; Xiao, J.; Heyward, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Baer, M.R.; Hassan, H.E.; Wang, H. Activation of the constitutive androstane receptor increases the therapeutic index of CHOP in lymphoma treatment. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levstek, L.; Janžič, L.; Ihan, A.; Kopitar, A.N. Biomarkers for prediction of CAR T therapy outcomes: Current and future perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolley, E.R.; Lewinter, C.; Pedersen, L.M.; Nielsen, T.H. Efficacy of intravenous high-dose methotrexate in preventing relapse to the central nervous system in R-CHOP(-like)-treated, high-risk, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients and its effect on mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Haematologica 2024, 109, 3327–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durmaz, M.; Visser, O.; Posthuma, E.F.M.; Brouwer, R.E.; Issa, D.E.; de Jong, D.; Lam, K.H.; Blijlevens, N.M.A.; Zijlstra, J.M.; Chamuleau, M.E.D.; et al. Time trends in primary therapy and relative survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by stage: A nationwide, population-based study in the Netherlands, 1989–2018. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipp, M.A.; Ross, K.N.; Tamayo, P.; Weng, A.P.; Kutok, J.L.; Aguiar, R.C.T.; Gaasenbeek, M.; Angelo, M.; Reich, M.; Pinkus, G.S.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma outcome prediction by gene-expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, M.; Bentink, S.; Berger, H.; Klapper, W.; Wessendorf, S.; Barth, T.F.E.; Bernd, H.; Cogliatti, S.B.; Dierlamm, J.; Feller, A.C.; et al. A biologic definition of Burkitt’s lymphoma from transcriptional and genomic profiling. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, F.S.; Barker, A.D. Mapping the cancer genome. Pinpointing the genes involved in cancer will help chart a new course across the complex landscape of human malignancies. Sci. Am. 2007, 296, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.W.; Emre, N.C.T.; Kohlhammer, H.; Dave, S.S.; Davis, R.E.; Carty, S.; Lam, L.T.; Shaffer, A.L.; Xiao, W.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arise by distinct genetic pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13520–13525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaknovich, R.; Geng, H.; Johnson, N.A.; Tsikitas, L.; Cerchietti, L.; Greally, J.M.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Elemento, O.; Melnick, A. DNA methylation signatures define molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2010, 116, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visco, C.; Li, Y.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Miranda, R.N.; Green, T.M.; Li, Y.; Tzankov, A.; Wen, W.; Liu, W.; Kahl, B.S.; et al. Comprehensive gene expression profiling and immunohistochemical studies support application of immunophenotypic algorithm for molecular subtype classification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A report from the International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortiu. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2103–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, A.; Iwadate, Y.; Komohara, Y.; Sano, M.; Kajiwara, K.; Yajima, N.; Tsuchiya, N.; Homma, J.; Aoki, H.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Gene expression signature-based prognostic risk score in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5672–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrans, S.L.; Crouch, S.; Care, M.A.; Worrillow, L.; Smith, A.; Patmore, R.; Westhead, D.R.; Tooze, R.; Roman, E.; Jack, A.S. Whole genome expression profiling based on paraffin embedded tissue can be used to classify diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and predict clinical outcome. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 159, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, S.; Chapuy, B.; Takeyama, K.; Rodig, S.J.; Hao, Y.; Yeda, K.T.; Inguilizian, H.; Mermel, C.; Currie, T.; Dogan, A.; et al. Integrative Analysis Reveals an Outcome-Associated and Targetable Pattern of p53 and Cell Cycle Deregulation in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.W.; Wright, G.W.; Williams, P.M.; Lih, C.J.; Walsh, W.; Jaffe, E.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Campo, E.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Determining cell-of-origin subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using gene expression in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Blood 2014, 123, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, C.; Barrans, S.; Care, M.A.; Cunningham, D.; Tooze, R.M.; Jack, A.; Westhead, D.R. Transferring genomics to the clinic: Distinguishing Burkitt and diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, S.; Viailly, P.J.; Bohers, E.; Bertrand, P.; Ruminy, P.; Marchand, V.; Maingonnat, C.; Mareschal, S.; Picquenot, J.M.; Penther, D.; et al. Biological and clinical relevance of associated genomic alterations in MYD88 L265P and non-L265P-mutated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Analysis of 361 cases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2232–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, J.D.; Young, R.M.; Webster, D.E.; Roulland, S.; Wright, G.W.; Kasbekar, M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Ceribelli, M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; et al. A multiprotein supercomplex controlling oncogenic signalling in lymphoma. Nature 2018, 560, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, C.; Barrans, S.; Cucco, F.; Bentley, M.A.; Care, M.A.; Cummin, T.; Kennedy, H.; Thompson, J.S.; Uddin, R.; Worrillow, L.; et al. Molecular high-grade B-cell lymphoma: Defining a poor-risk group that requires different approaches to therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCord, R.; Bolen, C.R.; Koeppen, H.; Kadel, E.E.; Oestergaard, M.Z.; Nielsen, T.; Sehn, L.H.; Venstrom, J.M. PD-L1 and tumor-associated macrophages in de novo DLBCL. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, S.E.; Barrans, S.L.; Beer, P.A.; Painter, D.; Smith, A.G.; Roman, E.; Cooke, S.L.; Ruiz, C.; Glover, P.; Van Hoppe, S.J.L.; et al. Targeted sequencing in DLBCL, molecular subtypes, and outcomes: A Haematological Malignancy Research Network report. Blood 2020, 135, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets–Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.A.; Ferretti, V.; Grossman, R.L.; Staudt, L.M. The NCI Genomic Data Commons as an engine for precision medicine. Blood 2017, 130, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, M.; Huang, F.W.; Jané-Valbuena, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Lo, C.C.; McDonald, E.R.; Barretina, J.; Gelfand, E.T.; Bielski, C.M.; Li, H.; et al. Next-generation characterization of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. Nature 2019, 569, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal Complementary Data Sources and Analysis Options. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behdenna, A.; Colange, M.; Haziza, J.; Gema, A.; Appé, G.; Azencott, C.A.; Nordor, A. pyComBat, a Python tool for batch effects correction in high-throughput molecular data using empirical Bayes methods. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2013. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- VanRossum, G.; Drake, F.L. The Python Language Reference; Python Software Foundation: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kluyver, T.; Ragan-Kelley, B.; Pérez, F.; Granger, B.; Bussonnier, M.; Frederic, J.; Willing, C. Jupyter Notebooks—A publishing format for reproducible computational workflows. In Positioning and Power in Academic Publishing: Players, Agents and Agendas, Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Electronic Publishing, Göttingen, Germany, 7–9 June 2016; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 87–90. [Google Scholar]





| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Entrez ID | Probe ID | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HG-U133_Plus_2 | Illumina HumanHT-12 V4.0 | |||
| NEK6 | NIMA related kinase 6 | 10783 | 223158_s_at | ILMN_1660871 |
| RARRES2 | retinoic acid receptor responder 2 | 5919 | 209496_at | ILMN_1810844 |
| CHRNA1 | cholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 1 subunit | 1134 | 206633_at | ILMN_2361768 |
| URI1(C19orf2) | URI1 prefoldin like chaperone | 8725 | 214173_x_at | ILMN_2406892 |
| NIPA2 | NIPA magnesium transporter 2 | 81614 | 212129_at | ILMN_1720344 |
| ZNF22 | zinc finger protein 22 | 7570 | 218005_at | ILMN_1798533 |
| WDR12 | WD repeat domain 12 | 55759 | 218512_at | ILMN_1770692 |
| Study | Ranked AUC Scores | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE11318 | GSE53786 | GSE98588 | TCGA-DLBC | NCICCR-DLBCL | GSE125966 | Internal Test Data | Mean | |
| Four gene-pairs | 6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 3.14 |
| Pan et al., 2021 [13] | 8 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 2 | 3 | 4.86 |
| Xiong et al., 2022 [14] | 1 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 4.43 |
| Yan et al., 2022 [15] | 7 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4.43 |
| Ma et al. 2022 [16] | 2 | 1 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 4.57 |
| Hou et al., 2023 [17] | 9 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 8.57 |
| Shi et al., 2023 [18] | 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 4.57 |
| Zhao et al., 2023 [19] | 5 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 8.29 |
| Ren et al., 2023 [20] | 3 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3.14 |
| Wang et al., 2024 [21] | 10 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 9 | 8.71 |
| Drug | Description | LN_IC50_Mean | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Score: <3 | Risk Score: ≥3 | p Value | ||
| OSU-03012 | PDK1 (PDPK1) | 1.053 | 2.057 | 0.006 |
| GSK650394 | SGK2, SGK3 | 2.713 | 4.277 | 0.018 |
| Cisplatin | DNA crosslinker | 2.343 | 4.116 | 0.024 |
| Doxorubicin | Anthracycline | −2.945 | −1.070 | 0.027 |
| Mitomycin-C | DNA crosslinker | −1.648 | 0.197 | 0.031 |
| Bosutinib | SRC, ABL, TEC | 0.887 | 2.463 | 0.035 |
| SN-38 | TOP1 | −5.205 | −2.933 | 0.035 |
| XMD15-27 | CAMK2 | 3.414 | 4.391 | 0.040 |
| BX795 | TBK1, PDK1 (PDPK1), IKK, AURKB, AURKC | 0.973 | 2.161 | 0.042 |
| Lestaurtinib | FLT3, JAK2, NTRK1, NTRK2, NTRK3 | −1.929 | −0.734 | 0.048 |
| Ponatinib | ABL, PDGFRA, VEGFR2, FGFR1, SRC, TIE2,… | −1.324 | 0.860 | 0.045 |
| ZM447439 | AURKA, AURKB | 1.345 | 2.756 | 0.048 |
| Vorinostat | HDAC inhibitor Class I, IIa, IIb, IV | −0.091 | 0.715 | 0.057 |
| BAY-61-3606 | SYK | 0.728 | 2.431 | 0.057 |
| S-Trityl-L-cysteine | KIF11 | 0.043 | 1.467 | 0.066 |
| HG6-64-1 | BRAF | −0.219 | 1.562 | 0.069 |
| Pelitinib | EGFR | −0.033 | 1.315 | 0.078 |
| Gemcitabine | Pyrimidine antimetabolite | −3.887 | −0.723 | 0.080 |
| Tozasertib | AURKA, AURKB, AURKC, others | 0.007 | 2.448 | 0.083 |
| Tipifarnib | Farnesyl-transferase (FNTA) | 0.711 | 2.413 | 0.083 |
| ObatoclaxMesylate | BCL2, BCL-XL, BCL-W, MCL1 | −2.383 | −1.090 | 0.085 |
| Dasatinib | ABL, SRC, Ephrins, PDGFR, KIT | −1.112 | 1.782 | 0.091 |
| Etoposide | TOP2 | 0.163 | 2.373 | 0.094 |
| Piperlongumine | Induces reactive oxygen species | 1.503 | 2.614 | 0.097 |
| CGP-60474 | CDK1,CDK2,CDK5,CDK7,CDK9, PKC | −3.244 | −2.015 | 0.097 |
| Midostaurin | PKC, PPK, FLT1, c-FGR, others | −0.626 | 0.194 | 0.099 |
| Accession | Data Type | Platform | No. Samples | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE68895 | Microarray | Hu6800 | 77 | [30] |
| GSE4475 | Microarray | HG-U133A | 127 | [31] |
| TCGA-DLBC | RNA-seq | Illumina HiSeq 2000 | 47 | [32] |
| GSE11318 | Microarray | HG-U133_Plus_2 | 200 | [33] |
| GSE10846 | Microarray | HG-U133_Plus_2 | 414 | [23] |
| GSE23501 | Microarray | HG-U133_Plus_2 | 68 | [34] |
| GSE31312 | Microarray | HG-U133_Plus_2 | 470 | [35] |
| GSE34771 | Microarray | HG-U133_Plus_2 | 34 | [36] |
| GSE32918 | Microarray | Illumina HumanRef-8 v3.0 | 172 | [37] |
| GSE34171 | Microarray | HG-U133_Plus_2 | 68 | [38] |
| GSE53786 | Microarray | HG-U133_Plus_2 | 119 | [39] |
| GSE69051 | Microarray | Illumina HumanHT-12 V4.0 | 117 | [40] |
| GSE87371 | Microarray | HG-U133_Plus_2 | 223 | [41] |
| NCICCR-DLBCL | RNA-seq | Illumina HiSeq 2500 | 234 | [42] |
| GSE98588 | Microarray | HG-U133_Plus_2 | 105 | [43] |
| CTSP-DLBCL1 | RNA-seq | Illumina HiSeq 2500 | 18 | [44] |
| GSE117556 | Microarray | Illumina HumanHT-12 V4.0 | 928 | [45] |
| GSE125966 | RNA-seq | Illumina HiSeq 2500 | 553 | [46] |
| GSE181063 | Microarray | Illumina HumanHT-12 V4.0 | 1149 | [47] |
| CCLE 2019 | RNA-seq | Illumina HiSeq 2000 | 17 | [50] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanabe, A.; Ndzinu, J.; Sahara, H. Development and Validation of a Novel Four Gene-Pairs Signature for Predicting Prognosis in DLBCL Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312807
Tanabe A, Ndzinu J, Sahara H. Development and Validation of a Novel Four Gene-Pairs Signature for Predicting Prognosis in DLBCL Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312807
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanabe, Atsushi, Jerry Ndzinu, and Hiroeki Sahara. 2024. "Development and Validation of a Novel Four Gene-Pairs Signature for Predicting Prognosis in DLBCL Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312807
APA StyleTanabe, A., Ndzinu, J., & Sahara, H. (2024). Development and Validation of a Novel Four Gene-Pairs Signature for Predicting Prognosis in DLBCL Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312807







