Ameliorative Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Chemotherapeutic Intestinal Mucositis via the PI3K-AKT/NF-κB Signaling Pathway: In Vivo and In Vitro Evaluations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
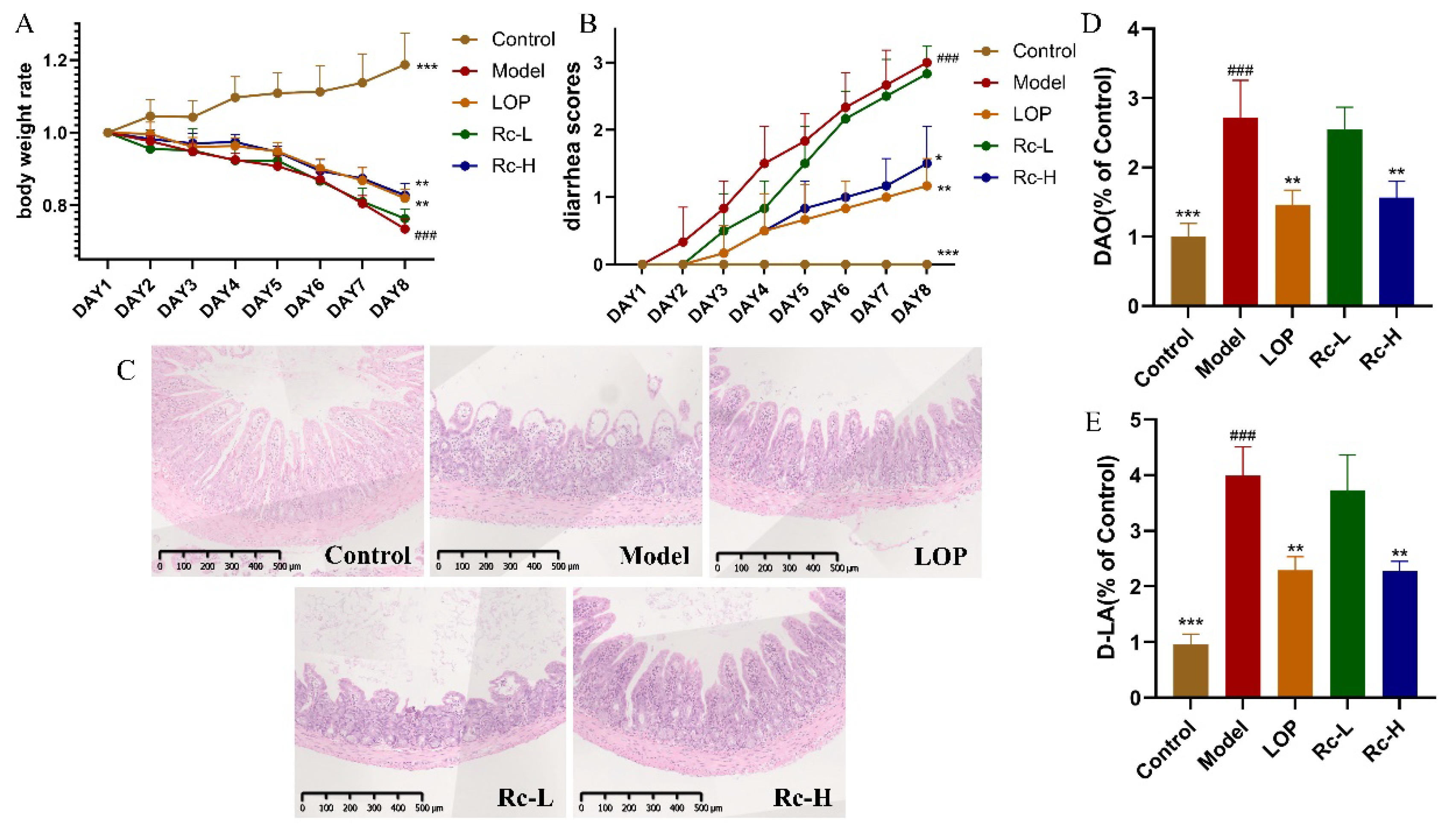
2.1. Therapeutic Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on 5-Fu-Induced Chemotherapeutic Intestinal Mucositis in Mice
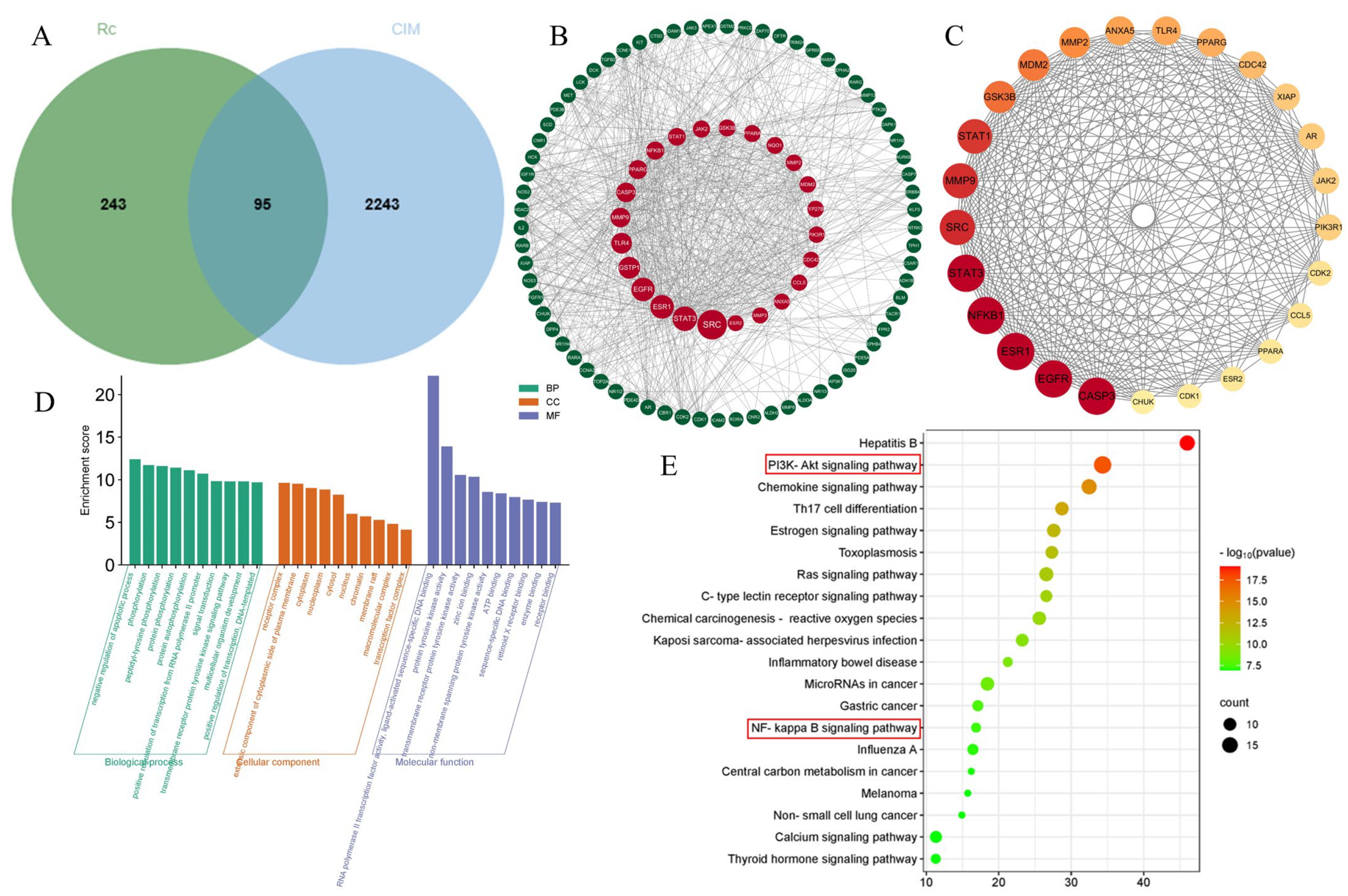
2.2. Potential Targets of Ginsenoside Rc and Chemotherapeutic Intestinal Mucositis
2.3. Construction of the PPI Network
2.4. GO Enrichment and KEGG Pathway Analyses
2.5. Molecular Docking Validation Results
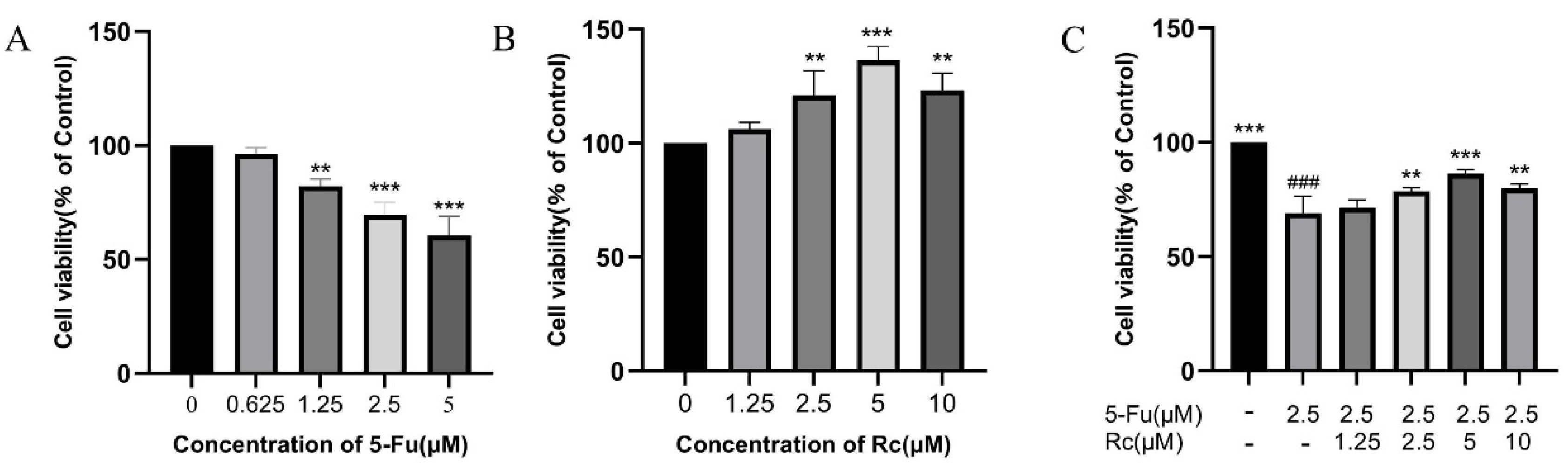
2.6. Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on Proliferation of IEC-6 Treated by 5-Fu
2.7. Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on Permeability of IEC-6 Cells Treated by 5-Fu
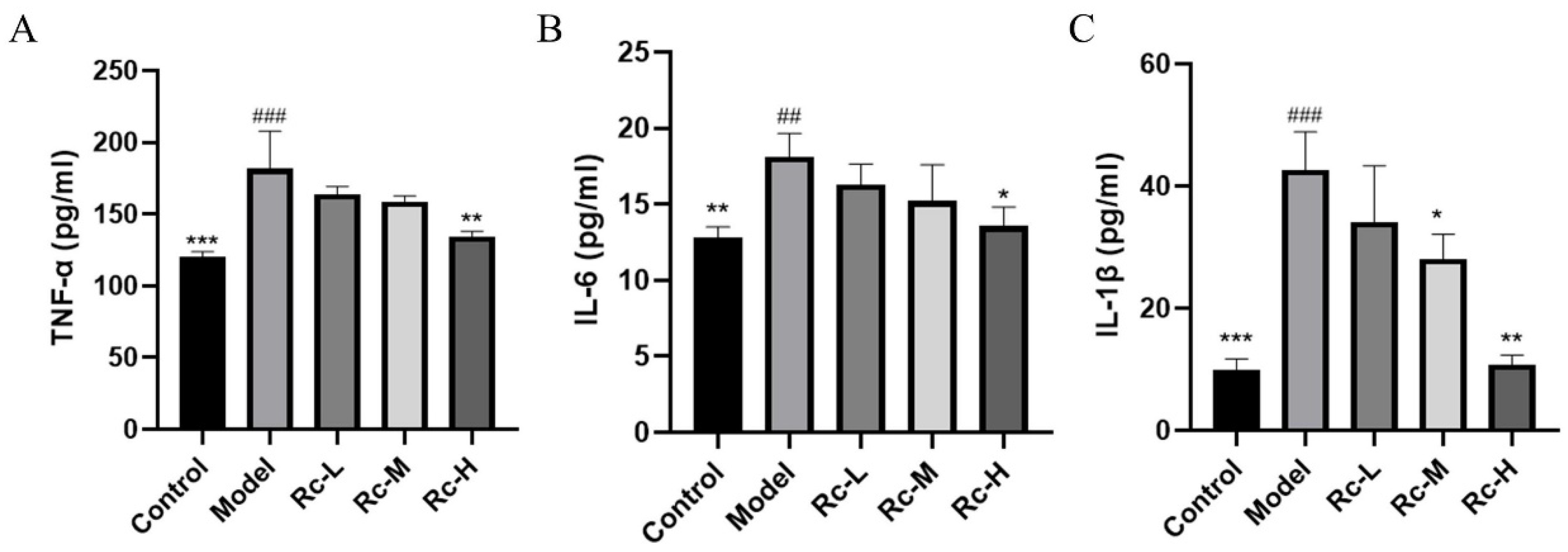
2.8. Ameliorative Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on 5-Fu-Induced Inflammation
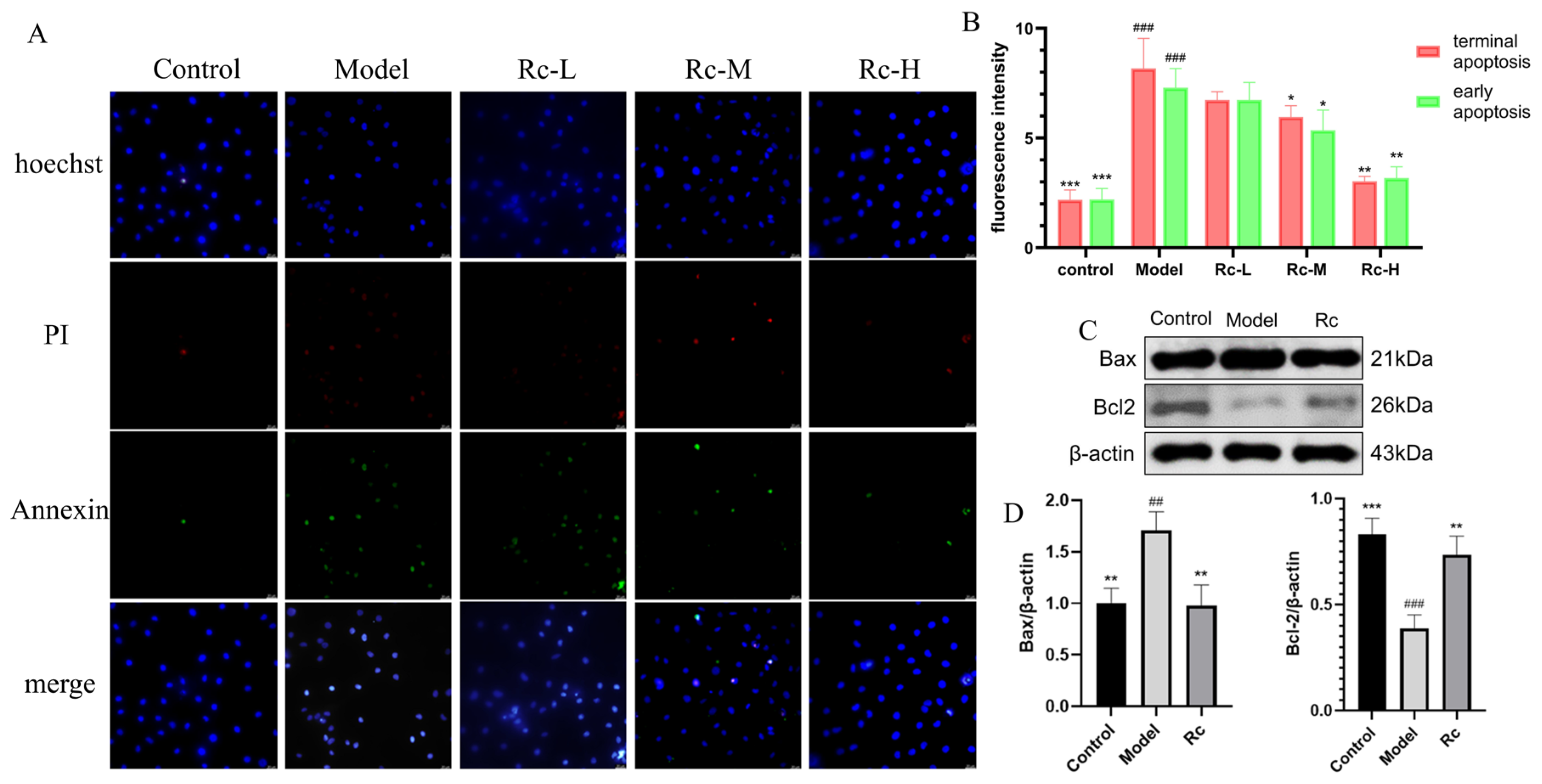
2.9. Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on IEC-6 Apoptosis
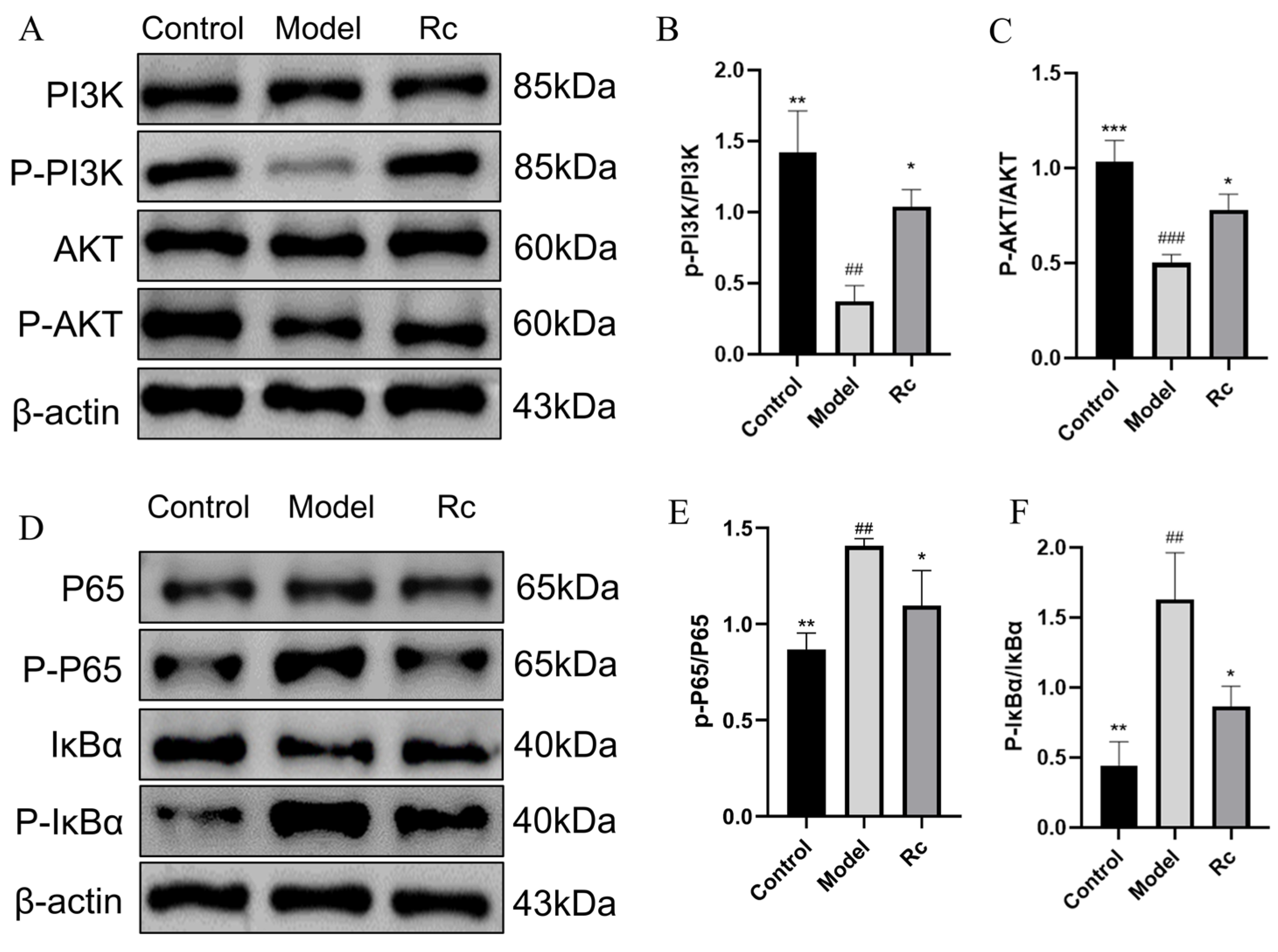
2.10. Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on Protein Expressions of PI3K/AKT and NF-κB Pathway
2.11. Effects of Ginsenoside Rc on mRNA Expressions of PI3K-AKT/NF-κB Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. In Vivo Experiments on Animals
4.2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2.2. Recording Weight and Diarrhea Extent
4.2.3. Histopathologic Evaluation
4.2.4. Detection of Intestinal Permeability in Mice
4.3. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
4.3.1. Ginsenoside Rc Target Prediction
4.3.2. Screening of CIM-Related Targets
4.3.3. Construction of a Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
4.3.4. GO Enrichment and KEGG Pathway Analysis
4.3.5. Molecular Docking Validation
4.4. In Vitro Experimental Validation
4.4.1. Cell Culture
4.4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.4.3. Measurement of LDH Release
4.4.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.4.5. Apoptosis Assay
4.4.6. Western Blotting (WB)
4.4.7. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-PCR)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dual Protective and Cytotoxic Benefits of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in Combination with Chemotherapy/Radiotherapy for Cancer Patients. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26558944/ (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Shahid, S. Review of Hematological Indices of Cancer Patients Receiving Combined Chemotherapy & Radiotherapy or Receiving Radiotherapy Alone. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 105, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doxorubicin-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Drug Delivery System for Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Monitoring Magnet-Enhancing Tumor Chemotherapy. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27274233/ (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- Martinel Lamas, D.J.; Carabajal, E.; Prestifilippo, J.P.; Rossi, L.; Elverdin, J.C.; Merani, S.; Bergoc, R.M.; Rivera, E.S.; Medina, V.A. Protection of Radiation-Induced Damage to the Hematopoietic System, Small Intestine and Salivary Glands in Rats by JNJ7777120 Compound, a Histamine H4 Ligand. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalla, R.V.; Bowen, J.; Barasch, A.; Elting, L.; Epstein, J.; Keefe, D.M.; McGuire, D.B.; Migliorati, C.; Nicolatou-Galitis, O.; Peterson, D.E.; et al. MASCC/ISOO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Mucositis Secondary to Cancer Therapy. Cancer 2014, 120, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Frontiers in the Pathobiology and Treatment of Cancer Regimen-Related Mucosal Injury. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28642709/ (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Management of Oral and Gastrointestinal Mucosal Injury: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, and Follow-Up. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26142468/ (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Wang, J.; Feng, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Sheng, Y.; Tang, F.; He, J.; Xu, X.; Ao, H.; Peng, C. Ameliorative Effect of Atractylodes Macrocephala Essential Oil Combined with Panax Ginseng Total Saponins on 5-Fluorouracil Induced Diarrhea Is Associated with Gut Microbial Modulation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 238, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.-Y.; Zeng, J.-Z.; Wong, A.S.T. Chemical Structures and Pharmacological Profiles of Ginseng Saponins. Molecules 2019, 24, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A SIRT1 Activator, Ginsenoside Rc, Promotes Energy Metabolism in Cardiomyocytes and Neurons. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33439015/ (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Ginsenoside Rc: A Potential Intervention Agent for Metabolic Syndrome. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38223453/ (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Tang, K.; Kong, D.; Peng, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhong, Y.; Yu, H.; Mai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cui, T.; et al. Ginsenoside Rc Attenuates DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis, Intestinal Inflammatory, and Barrier Function by Activating the Farnesoid X Receptor. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1000444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Martinez, M.; Cabail, M.Z. The PI3K/Akt Pathway in Meta-Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atiq, A.; Shal, B.; Naveed, M.; Khan, A.; Ali, J.; Zeeshan, S.; Al-Sharari, S.D.; Kim, Y.S.; Khan, S. Diadzein Ameliorates 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Intestinal Mucositis by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Mediators in Rodents. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 843, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsenoside Rc from Korean Red Ginseng (Panax Ginseng C.A. Meyer) Attenuates Inflammatory Symptoms of Gastritis, Hepatitis and Arthritis. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27109153/ (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Gao, F.; Wu, S.; Zhang, K.; Xu, Z.; Quan, F. Goat Milk Exosomal microRNAs Alleviate LPS-Induced Intestinal Inflammation in Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 131698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yin, L.; Dong, R. Inhibition of IEC-6 Cell Proliferation and the Mechanism of Ulcerative Colitis in C57BL/6 Mice by Dandelion Root Polysaccharides. Foods 2023, 12, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, D.; Li, Q.; Tong, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, T. Trans-Anethole Ameliorates LPS-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of TLR4/NF-κB Pathway in IEC-6 Cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlgren, D.; Lennernäs, H. Review on the Effect of Chemotherapy on the Intestinal Barrier: Epithelial Permeability, Mucus and Bacterial Translocation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Gao, K.; Zhang, H.; Takeda, M.; Yao, J. Suppression of Cell Membrane Permeability by Suramin: Involvement of Its Inhibitory Actions on Connexin 43 Hemichannels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3448–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protective Effects of Baicalin on LPS-Induced Injury in Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Intercellular Tight Junctions. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25665915/ (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists Ameliorate 5-fluorouracil-induced Intestinal Mucositis by Suppression of Apoptosis in Murine Intestinal Crypt Cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 168, 1388–1400.
- The Serotoninergic Receptors of Human Dendritic Cells: Identification and Coupling to Cytokine Release. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15128784/ (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- Akt Signaling Pathway in Macrophage Activation and M1/M2 Polarization. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28115590/ (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Kulik, G.; Klippel, A.; Weber, M.J. Antiapoptotic Signalling by the Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptor, Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, and Akt. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A.; Rodriguez-Viciana, P.; Wennström, S.; Warne, P.H.; Downward, J. Matrix Adhesion and Ras Transformation Both Activate a Phosphoinositide 3-OH Kinase and Protein Kinase B/Akt Cellular Survival Pathway. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 2783–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toll-like Receptors, Signaling Adapters and Regulation of the pro-Inflammatory Response by PI3K. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22895011/ (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Cotargeting BCL-2 and PI3K Induces BAX-Dependent Mitochondrial Apoptosis in AML Cells. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29559471/ (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Li, R.; Zhao, L.; Qin, S.-G.; Pan, L.-F.; Gao, Y.-X. MiR-217 Inhibits Apoptosis of Atherosclerotic Endothelial Cells via the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 12867–12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Dai, H.; Wei, Q.; Jin, S.; Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, D.; Shi, F. Dietary Genistein Supplementation Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Intestinal Injury through Altering Transcriptomic Profile. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3411–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wogonin Suppresses Inflammatory Response and Maintains Intestinal Barrier Function via TLR4-MyD88-TAK1-Mediated NF-κB Pathway In Vitro. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25917044/ (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Inflammatory Mechanisms in Obesity. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21219177/ (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Engelman, J.A.; Luo, J.; Cantley, L.C. The Evolution of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinases as Regulators of Growth and Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.D.; Toker, A. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell 2017, 169, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Phosphorylation Meets Ubiquitination: The Control of NF-[Kappa]B Activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 621–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, C.H.; Park, D.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, M.H.; Chung, K.W.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, J.S.; Chung, H.Y. Ginsenoside Rc Modulates Akt/FoxO1 Pathways and Suppresses Oxidative Stress. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modified Irinotecan Hydrochloride (CPT-11) Administration Schedule Improves Induction of Delayed-Onset Diarrhea in Rats. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11021738/ (accessed on 27 September 2024).
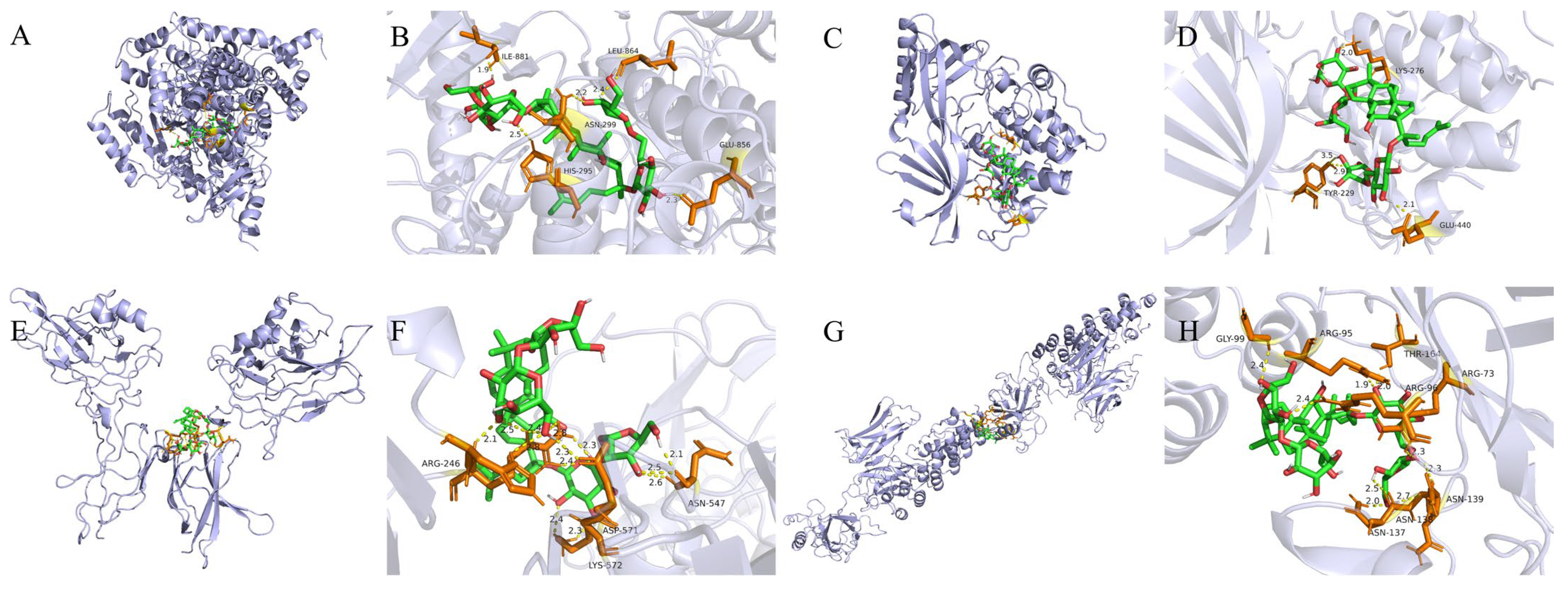




| Target | PDB ID | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Center_x | Center_y | Center_z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI3K | 3APD | −9.7 | 32.458 | 3.119 | 25.71 |
| AKT | 6HHG | −7.8 | 14.305 | −13.778 | −14.633 |
| NF-κB p65 | 1VKX | −7.1 | 1.153 | 40.241 | 56.792 |
| IκBα | 1NFI | −9.2 | −5.372 | 62.732 | 45.296 |
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| PI3K | AACCGGGACAGCTAAGCAAC | TCCCGGCTTCATTCACCTCC ACTCGTTCATGGTCACACGG |
| AKT | GAGACGATGGACTTCCGGTC | |
| NF-κB p65 | TTCAACATGGCAGACGACGA | AGGTATGGGCCATCTGTTGAC |
| IκBα | GAATCCTGACCTGGTCTCGC | CAGTCATCGTAGGGCAACTCA |
| β-actin | CCTTCCTGGGCATGGAGTC | TGATCTTCATTGTGCTGGGTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Zhao, X.; Tang, F.; Zhang, J.; Peng, C.; Ao, H. Ameliorative Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Chemotherapeutic Intestinal Mucositis via the PI3K-AKT/NF-κB Signaling Pathway: In Vivo and In Vitro Evaluations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313085
Xu L, Zhao X, Tang F, Zhang J, Peng C, Ao H. Ameliorative Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Chemotherapeutic Intestinal Mucositis via the PI3K-AKT/NF-κB Signaling Pathway: In Vivo and In Vitro Evaluations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):13085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313085
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Liyue, Xiaolan Zhao, Fei Tang, Jingnan Zhang, Cheng Peng, and Hui Ao. 2024. "Ameliorative Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Chemotherapeutic Intestinal Mucositis via the PI3K-AKT/NF-κB Signaling Pathway: In Vivo and In Vitro Evaluations" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 13085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313085
APA StyleXu, L., Zhao, X., Tang, F., Zhang, J., Peng, C., & Ao, H. (2024). Ameliorative Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Chemotherapeutic Intestinal Mucositis via the PI3K-AKT/NF-κB Signaling Pathway: In Vivo and In Vitro Evaluations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 13085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313085







