Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α Promotes Liver Fibrosis by Inducing Hepatocellular Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HIF-2α Expression Is Upregulated in Acute Liver Injury and Fibrosis
2.2. Hepatocyte-Specific HIF-2α Inhibition Protects Against Liver Fibrosis
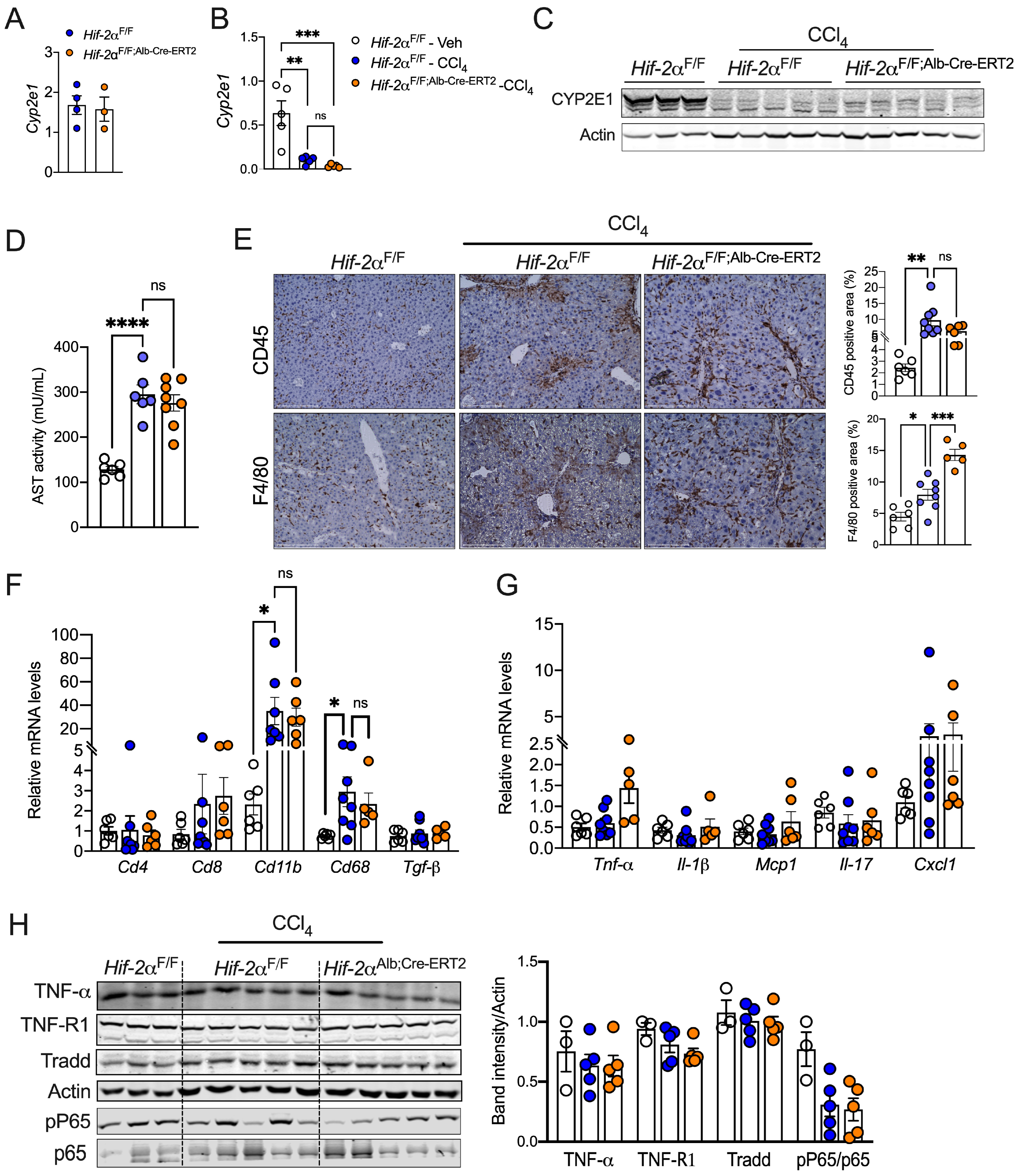
2.3. HIF-2α Induces Fibrosis Independent of Inflammation
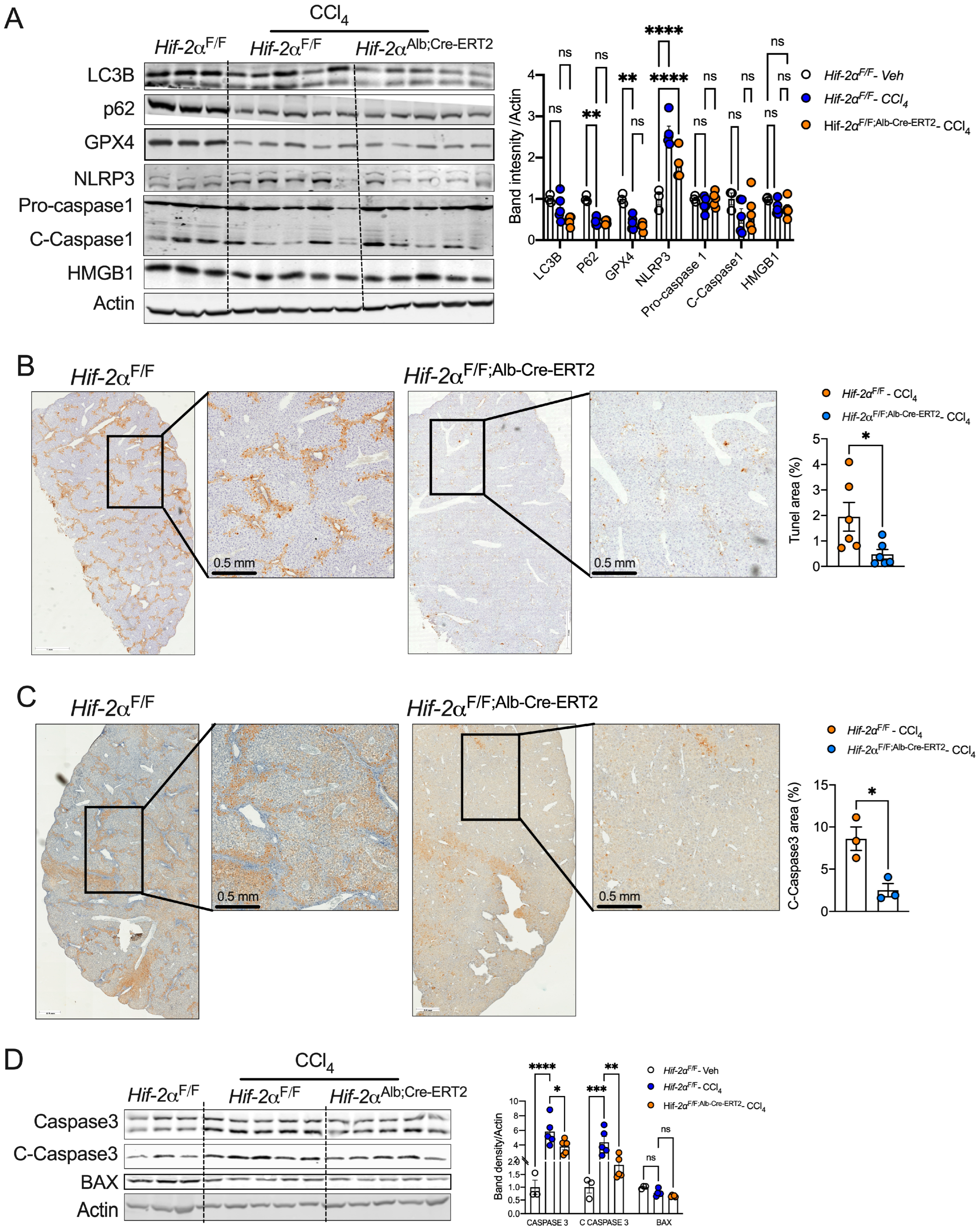
2.4. HIF-2α Deletion Prevents Hepatocyte Apoptosis in Fibrotic Livers
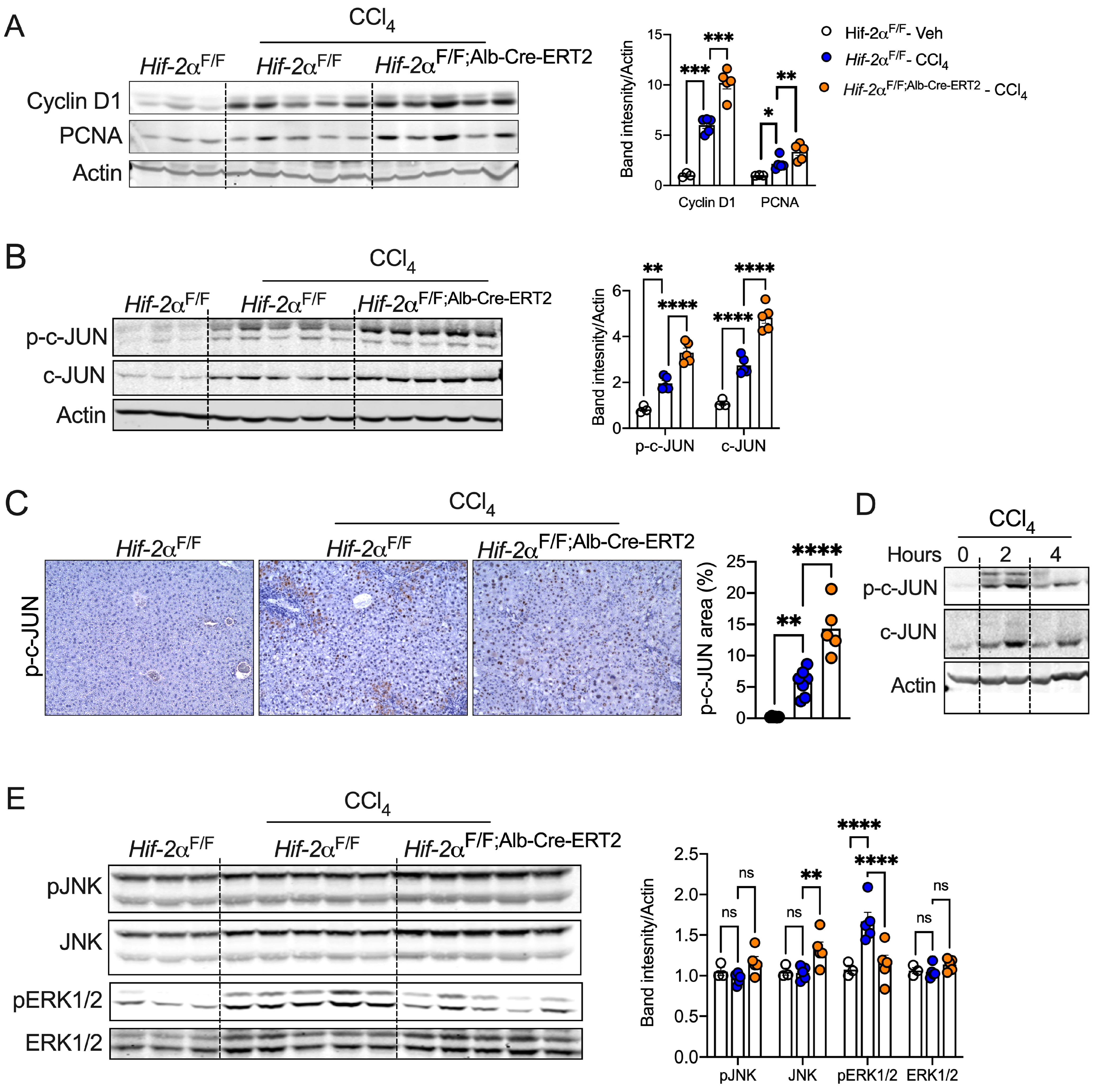
2.5. Disruption of HIF-2α Enhances Hepatocyte Survival and c-JUN Activation
2.6. HIF-2α Inhibition Promotes Hepatocyte Expansion and Preserves Cell Identity
3. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and qPCR Analysis
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. H&E, Sirius Red, and Masson’s Trichrome Staining
Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.7. Microscopy, Imaging, and Staining Quantification
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.Y.; Friedman, S.L. Fibrosis-dependent mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataller, R.; Brenner, D.A. Liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedde, T.; Kaplowitz, N.; Schwabe, R.F. Cell death and cell death responses in liver disease: Mechanisms and clinical relevance. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 765–783 e764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewidar, B.; Meyer, C.; Dooley, S.; Meindl-Beinker, A.N. TGF-beta in Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Liver Fibrogenesis-Updated 2019. Cells 2019, 8, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, A.; Pradhan-Sundd, T.; Singh, S.; Nagarajan, S.; Loizos, N.; Monga, S.P. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor alpha Contributes to Human Hepatic Stellate Cell Proliferation and Migration. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 2273–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.G.; Kruglov, E.; Dranoff, J.A. Autocrine release of TGF-beta by portal fibroblasts regulates cell growth. FEBS Lett. 2004, 559, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonzo, J.A.; Ferry, C.H.; Matsubara, T.; Kim, J.H.; Gonzalez, F.J. Suppression of hepatocyte proliferation by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha in adult mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7345–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yao, L.J.; Shen, W.; Ding, K.; Shi, P.M.; Chen, F.; He, J.; Ding, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, W.F. FOXA2 alleviates CCl(4)-induced liver fibrosis by protecting hepatocytes in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, P.; Wei, L.L.; Zhao, S.; Sverdlov, D.Y.; Vaid, K.A.; Miyamoto, M.; Kuramitsu, K.; Lai, M.; Popov, Y.V. Hepatocyte mitochondria-derived danger signals directly activate hepatic stellate cells and drive progression of liver fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, T.; Bell, A.; Brooks, J.M.; Setoyama, K.; Melis, M.; Han, B.; Fukumitsu, K.; Handa, K.; Tian, J.; Kaestner, K.H.; et al. Resetting the transcription factor network reverses terminal chronic hepatic failure. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicoro, A.; Ramachandran, P.; Iredale, J.P.; Fallowfield, J.A. Liver fibrosis and repair: Immune regulation of wound healing in a solid organ. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, B.; Apte, U. Liver Regeneration after Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratcliffe, P.J.; O’Rourke, J.F.; Maxwell, P.H.; Pugh, C.W. Oxygen sensing, hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and the regulation of mammalian gene expression. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201 Pt 3, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Fu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Luo, S.; Lu, H. Hypoxia exacerbates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the HIF-2alpha/PPARalpha pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E710–E722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Yagai, T.; Luo, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, Q.; Sun, D.; Zhao, J.; Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Sun, L.; et al. Activation of intestinal hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha during obesity contributes to hepatic steatosis. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marxsen, J.H.; Stengel, P.; Doege, K.; Heikkinen, P.; Jokilehto, T.; Wagner, T.; Jelkmann, W.; Jaakkola, P.; Metzen, E. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) promotes its degradation by induction of HIF-alpha-prolyl-4-hydroxylases. Biochem. J. 2004, 381, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, P.H.; Wiesener, M.S.; Chang, G.W.; Clifford, S.C.; Vaux, E.C.; Cockman, M.E.; Wykoff, C.C.; Pugh, C.W.; Maher, E.R.; Ratcliffe, P.J. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 1999, 399, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.S.J.; Nathan, J.A. Metabolic Regulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factors: The Role of Small Molecule Metabolites and Iron. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzen, E.; Zhou, J.; Jelkmann, W.; Fandrey, J.; Brune, B. Nitric oxide impairs normoxic degradation of HIF-1alpha by inhibition of prolyl hydroxylases. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 3470–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roychowdhury, S.; Chiang, D.J.; McMullen, M.R.; Nagy, L.E. Moderate, chronic ethanol feeding exacerbates carbon-tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis via hepatocyte-specific hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2014, 2, e00061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.O.; Welch, T.P.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Copple, B.L. Reduced liver fibrosis in hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-deficient mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G582–G592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Tian, P.; Miao, H.; Pan, S.; Song, R.; Sun, X.; Zhao, B.; Wang, D.; et al. Reduction of hepatic fibrosis by overexpression of von Hippel-Lindau protein in experimental models of chronic liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, A.; Taylor, M.; Xue, X.; Matsubara, T.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Shah, Y.M. Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 2alpha promotes steatohepatitis through augmenting lipid accumulation, inflammation, and fibrosis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Taylor, M.; Qu, A.; Ahn, S.H.; Suresh, M.V.; Raghavendran, K.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Shah, Y.M. Loss of von Hippel-Lindau protein (VHL) increases systemic cholesterol levels through targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha and regulation of bile acid homeostasis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, E.; Sutti, S.; Foglia, B.; Novo, E.; Cannito, S.; Bocca, C.; Rajsky, M.; Bruzzi, S.; Abate, M.L.; Rosso, C.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha drives nonalcoholic fatty liver progression by triggering hepatocyte release of histidine-rich glycoprotein. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2196–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Reeves, H.L.; Kotsiliti, E.; Govaere, O.; Heikenwalder, M. From NASH to HCC: Current concepts and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, S.; McCullough, S.S.; Hennings, L.; Letzig, L.; Simpson, P.M.; Hinson, J.A.; James, L.P. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and HIF-1alpha induction in acetaminophen toxicity in mice occurs without hypoxia. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 252, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Zhang, H.; Takahashi, S.; Centofanti, B.; Periyasamy, S.; Weisz, K.; Chen, Z.; Uhler, M.D.; Rui, L.; Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. HIF2alpha Is an Essential Molecular Brake for Postprandial Hepatic Glucagon Response Independent of Insulin Signaling. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressner, A.M. Transdifferentiation of hepatic stellate cells (Ito cells) to myofibroblasts: A key event in hepatic fibrogenesis. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1996, 54, S39–S45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Copple, B.L.; Bai, S.; Burgoon, L.D.; Moon, J.O. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha regulates the expression of genes in hypoxic hepatic stellate cells important for collagen deposition and angiogenesis. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.W.; Chan, W.Y.; Lee, S.S. Resistance to carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice which lack CYP2E1 expression. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998, 153, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradette, C.; Du Souich, P. Effect of hypoxia on cytochrome P450 activity and expression. Curr. Drug Metab. 2004, 5, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandrer, F.; Liebig, S.; Marhenke, S.; Vogel, A.; John, K.; Manns, M.P.; Teufel, A.; Itzel, T.; Longerich, T.; Maier, O.; et al. TNF-Receptor-1 inhibition reduces liver steatosis, hepatocellular injury and fibrosis in NAFLD mice. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. NF-kappaB in the liver—Linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Tang, H.; Mao, J. Programmed Cell Death in Liver Fibrosis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 3897–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Jia, X.; Ding, Z.; Wang, G.; Jiang, M.; Li, B.; Chen, S.; Xia, B.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; et al. Loss of MLKL ameliorates liver fibrosis by inhibiting hepatocyte necroptosis and hepatic stellate cell activation. Theranostics 2022, 12, 5220–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaul, S.; Leszczynska, A.; Alegre, F.; Kaufmann, B.; Johnson, C.D.; Adams, L.A.; Wree, A.; Damm, G.; Seehofer, D.; Calvente, C.J.; et al. Hepatocyte pyroptosis and release of inflammasome particles induce stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Shen, J.; Lin, S.; Xue, W.; Mao, C.; Tang, R.; Sun, H.; Qi, X.; et al. CD1d protects against hepatocyte apoptosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Ge, C.; Min, J.; Wang, F. The multifaceted role of ferroptosis in liver disease. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Yan, N.; Xia, Y.; Sawaswong, V.; Zhu, X.; Dias, H.B.; Aibara, D.; Takahashi, S.; Hamada, K.; Saito, Y.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha restricts liver fibrosis progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Lepe, J.; Cervantes-Alvarez, E.; Collin de l’Hortet, A.; Wang, Y.; Mars, W.M.; Oda, Y.; Bekki, Y.; Shimokawa, M.; Wang, H.; Yoshizumi, T.; et al. Liver-enriched transcription factor expression relates to chronic hepatic failure in humans. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisdom, R.; Johnson, R.S.; Moore, C. c-Jun regulates cell cycle progression and apoptosis by distinct mechanisms. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Bradham, C.A.; Uehara, T.; Hatano, E.; Bennett, B.L.; Schoonhoven, R.; Brenner, D.A. c-Jun-N-terminal kinase drives cyclin D1 expression and proliferation during liver regeneration. Hepatology 2003, 37, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulien, I.; Hockenjos, B.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Perdekamp, M.G.; Follo, M.; Thimme, R.; Hasselblatt, P. The transcription factor c-Jun/AP-1 promotes liver fibrosis during non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating Osteopontin expression. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselblatt, P.; Rath, M.; Komnenovic, V.; Zatloukal, K.; Wagner, E.F. Hepatocyte survival in acute hepatitis is due to c-Jun/AP-1-dependent expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17105–17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluwe, J.; Pradere, J.P.; Gwak, G.Y.; Mencin, A.; De Minicis, S.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Colmenero, J.; Bataller, R.; Schwabe, R.F. Modulation of hepatic fibrosis by c-Jun-N-terminal kinase inhibition. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosse, J.P.; Ronvaux, M.; Ninane, N.; Raes, M.J.; Michiels, C. Hypoxia-induced decrease in p53 protein level and increase in c-jun DNA binding activity results in cancer cell resistance to etoposide. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eferl, R.; Ricci, R.; Kenner, L.; Zenz, R.; David, J.P.; Rath, M.; Wagner, E.F. Liver tumor development. c-Jun antagonizes the proapoptotic activity of p53. Cell 2003, 112, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettinger, K.; Vikhanskaya, F.; Poh, M.K.; Lee, M.K.; de Belle, I.; Zhang, J.T.; Reddy, S.A.; Sabapathy, K. c-Jun promotes cellular survival by suppression of PTEN. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, M.M.; Bosch, D.E.; Daoud, S.S. Role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha in gastrointestinal and liver diseases. World, J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4074–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, W.; Hao, L.; Guo, W.; Yue, R.; Sun, X.; Sun, Z.; Bataller, R.; Zhou, Z. Loss of long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 1 promotes hepatocyte death in alcohol-induced steatohepatitis. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2023, 138, 155334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copple, B.L.; Bustamante, J.J.; Welch, T.P.; Kim, N.D.; Moon, J.O. Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent production of profibrotic mediators by hypoxic hepatocytes. Liver Int. 2009, 29, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Colgan, S.P.; Eltzschig, H.K. Hypoxia-inducible factors as molecular targets for liver diseases. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Minville, C.; Tordjman, J.; Levy, P.; Bouillot, J.L.; Basdevant, A.; Bedossa, P.; Clement, K.; Pepin, J.L. Chronic intermittent hypoxia is a major trigger for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in morbid obese. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, R.G.; Ji, S.; Matsumura, T.; Lemasters, J.J. Is Hypoxia Involved in the Mechanism of Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury? ☆ Toxicol. Sci. 1984, 4, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xu, X. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 promotes liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by activating PTEN/p65 signaling pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 14735–14744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strowitzki, M.J.; Kirchberg, J.; Tuffs, C.; Schiedeck, M.; Ritter, A.S.; Biller, M.; Harnoss, J.M.; Lasitschka, F.; Schmidt, T.; Radhakrishnan, P.; et al. Loss of Prolyl-Hydroxylase 1 Protects against Biliary Fibrosis via Attenuated Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 2826–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooli, R.G.R.; Rodriguez, J.; Takahashi, S.; Solanki, S.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Shah, Y.M. Hypoxia via ERK Signaling Inhibits Hepatic PPARalpha to Promote Fatty Liver. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foglia, B.; Sutti, S.; Cannito, S.; Rosso, C.; Maggiora, M.; Autelli, R.; Novo, E.; Bocca, C.; Villano, G.; Ramavath, N.N.; et al. Hepatocyte-Specific Deletion of HIF2alpha Prevents NASH-Related Liver Carcinogenesis by Decreasing Cancer Cell Proliferation. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 13, 459–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claveria-Cabello, A.; Avila, M.A. HIF2alpha Activation in NASH: A New Force Pushing Toward HCC. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 13, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorsy, E.A.; Saber, S.; Hamad, R.S.; Abdel-Reheim, M.A.; Nadwa, E.H.; Alibrahim, A.O.E.; Alkhamiss, A.S.; AlSalloom, A.A.; Mohamed, E.A.; Nour-El-Din, M.; et al. Modulating the HSP90 control over NFkappaB/NLRP3/Caspase-1 axis is a new therapeutic target in the management of liver fibrosis: Insights into the role of TAS-116 (Pimitespib). Life Sci. 2024, 354, 122966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Cai, T.; Wang, F.; Shao, F. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 2015, 526, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imtiyaz, H.Z.; Williams, E.P.; Hickey, M.M.; Patel, S.A.; Durham, A.C.; Yuan, L.J.; Hammond, R.; Gimotty, P.A.; Keith, B.; Simon, M.C. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha regulates macrophage function in mouse models of acute and tumor inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2699–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.L.; Yu, C.X.; Song, L.J. Programmed cell death in hepatic fibrosis: Current and perspectives. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.S.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Sola, S.; Castro, R.E.; Ramalho, R.M.; Baptista, A.; Moura, M.C.; Camilo, M.E.; Rodrigues, C.M. Hepatocyte apoptosis, expression of death receptors, and activation of NF-κB in the liver of nonalcoholic and alcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbay, A.; Friedman, S.; Gores, G.J. Apoptosis: The nexus of liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology 2004, 39, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapaliya, S.; Wree, A.; Povero, D.; Inzaugarat, M.E.; Berk, M.; Dixon, L.; Papouchado, B.G.; Feldstein, A.E. Caspase 3 inactivation protects against hepatic cell death and ameliorates fibrogenesis in a diet-induced NASH model. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, R.P.; Stone, W.C.; Karaca, F.G.; Syn, W.K.; Pereira, T.A.; Agboola, K.M.; Omenetti, A.; Jung, Y.; Teaberry, V.; Choi, S.S.; et al. Pan-caspase inhibitor VX-166 reduces fibrosis in an animal model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreyro, F.J.; Holod, S.; Finocchietto, P.V.; Camino, A.M.; Aquino, J.B.; Avagnina, A.; Carreras, M.C.; Poderoso, J.J.; Gores, G.J. The pan-caspase inhibitor Emricasan (IDN-6556) decreases liver injury and fibrosis in a murine model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.L.; Liu, L.P.; Niu, L.; Sun, Y.F.; Yang, X.R.; Fan, J.; Ren, J.W.; Chen, G.G.; Lai, P.B. Downregulation and pro-apoptotic effect of hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34571–34581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlapati, C.; Joshi, S.; Turaga, R.C.; Mishra, M.; Reid, M.D.; Kapoor, S.; Artinian, L.; Rehder, V.; Aneja, R. Monoethanolamine-induced glucose deprivation promotes apoptosis through metabolic rewiring in prostate cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 9089–9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, C.; Engelmann, J.C.; Saugspier, M.; Koch, A.; Hartmann, A.; Muller, M.; Spang, R.; Bosserhoff, A.; Hellerbrand, C. Increased expression of c-Jun in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lab. Investig. 2014, 94, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuest, M.; Willim, K.; MacNelly, S.; Fellner, N.; Resch, G.P.; Blum, H.E.; Hasselblatt, P. The transcription factor c-Jun protects against sustained hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress thereby promoting hepatocyte survival. Hepatology 2012, 55, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrabi, A.J.; Kao, D.; Nguyen, D.T.; Loscalzo, J.; Handy, D.E. Hypoxia-induced suppression of c-Myc by HIF-2alpha in human pulmonary endothelial cells attenuates TFAM expression. Cell. Signal. 2017, 38, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Poenisch, M.; Khanal, R.; Hu, Q.; Dai, Z.; Li, R.; Song, G.; Yuan, Q.; Yao, Q.; Shen, X.; et al. Therapeutic HNF4A mRNA attenuates liver fibrosis in a preclinical model. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1420–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.Y.; Yin, C.; Hou, J.L.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhong, W.; Hu, P.F.; Deng, X.; Tan, Y.X.; Zhang, J.P.; et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gut 2010, 59, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, E.B.; Rha, J.; Selak, M.A.; Unger, T.L.; Keith, B.; Liu, Q.; Haase, V.H. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2 regulates hepatic lipid metabolism. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 4527–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlapati, C.; Joshi, S.; Bhattarai, S.; Krishnamurthy, J.; Turaga, R.C.; Nguyen, T.; Li, X.; Aneja, R. PLK1 and AURKB phosphorylate survivin differentially to affect proliferation in racially distinct triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mooli, R.G.R.; Mukhi, D.; Watt, M.; Nagati, V.; Reed, S.M.; Gandhi, N.K.; Oertel, M.; Ramakrishnan, S.K. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α Promotes Liver Fibrosis by Inducing Hepatocellular Death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313114
Mooli RGR, Mukhi D, Watt M, Nagati V, Reed SM, Gandhi NK, Oertel M, Ramakrishnan SK. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α Promotes Liver Fibrosis by Inducing Hepatocellular Death. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):13114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313114
Chicago/Turabian StyleMooli, Raja Gopal Reddy, Dhanunjay Mukhi, Mikayla Watt, Veerababu Nagati, Sara M. Reed, Nikita K. Gandhi, Michael Oertel, and Sadeesh K. Ramakrishnan. 2024. "Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α Promotes Liver Fibrosis by Inducing Hepatocellular Death" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 13114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313114
APA StyleMooli, R. G. R., Mukhi, D., Watt, M., Nagati, V., Reed, S. M., Gandhi, N. K., Oertel, M., & Ramakrishnan, S. K. (2024). Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α Promotes Liver Fibrosis by Inducing Hepatocellular Death. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 13114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252313114






