Effect of High-Dose Vitamin C on Tendon Cell Degeneration—An In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Vitamin C Inhibits Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production Due to Oxidative Stress
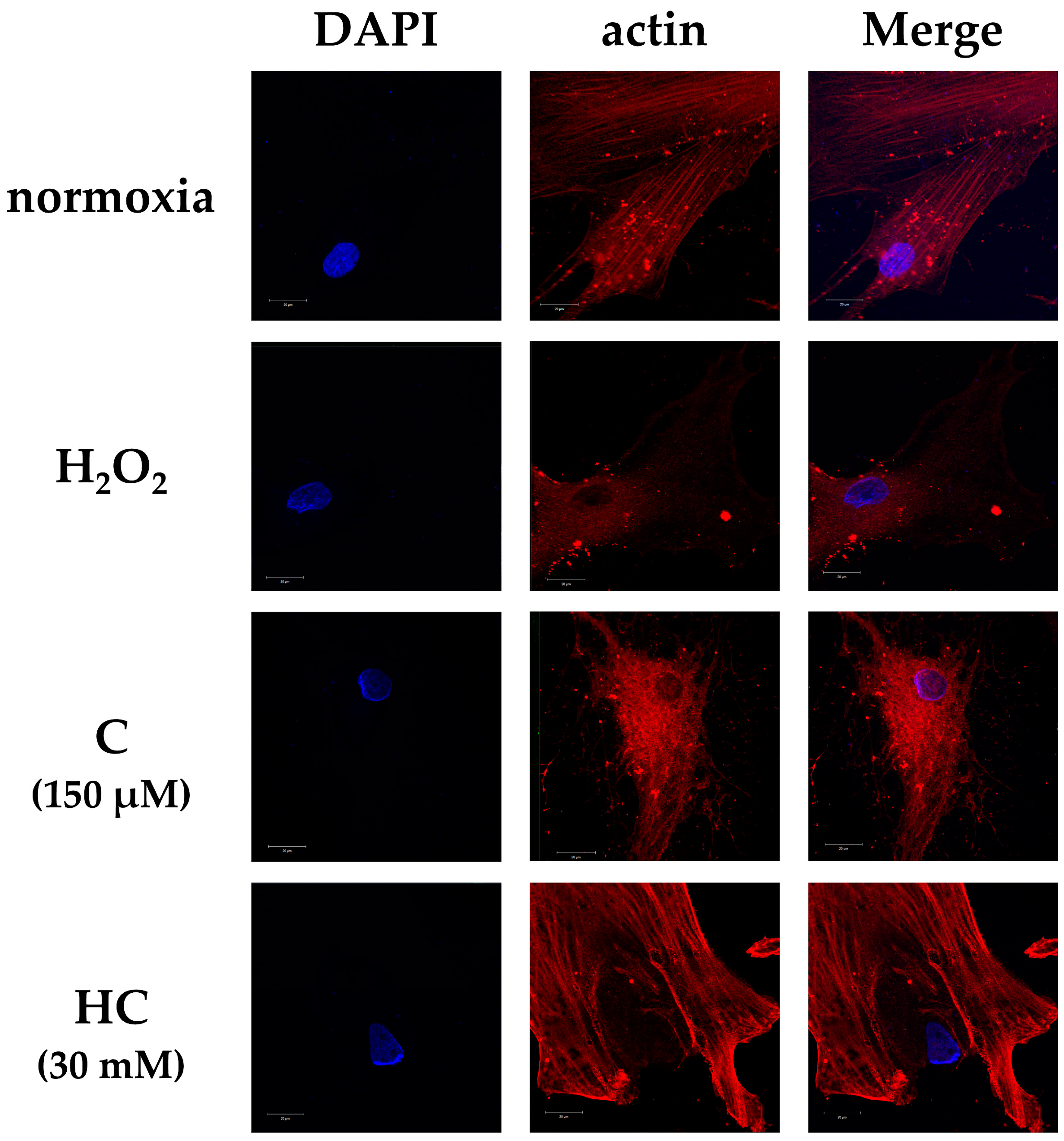
2.2. Vitamin C Protects Against Cytoskeletal Damage in Tendon Cells Due to Oxidative Stress
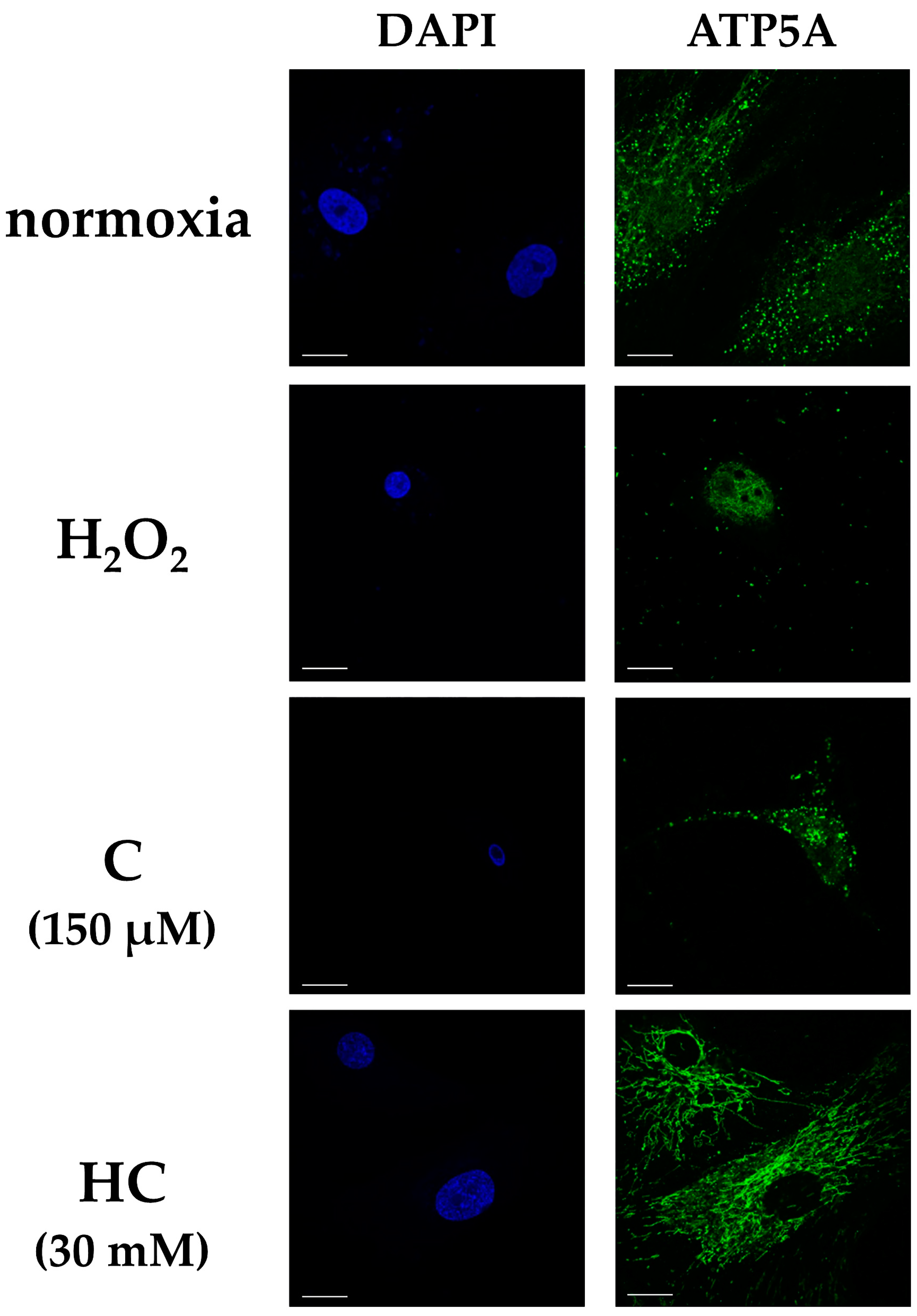
2.3. Vitamin C Maintains Mitochondrial Function, Energy Production, and the Extracellular Matrix from Cellular Damage Due to Oxidative Stress and Inhibits the Expression of Cellular Senescence-Related Genes
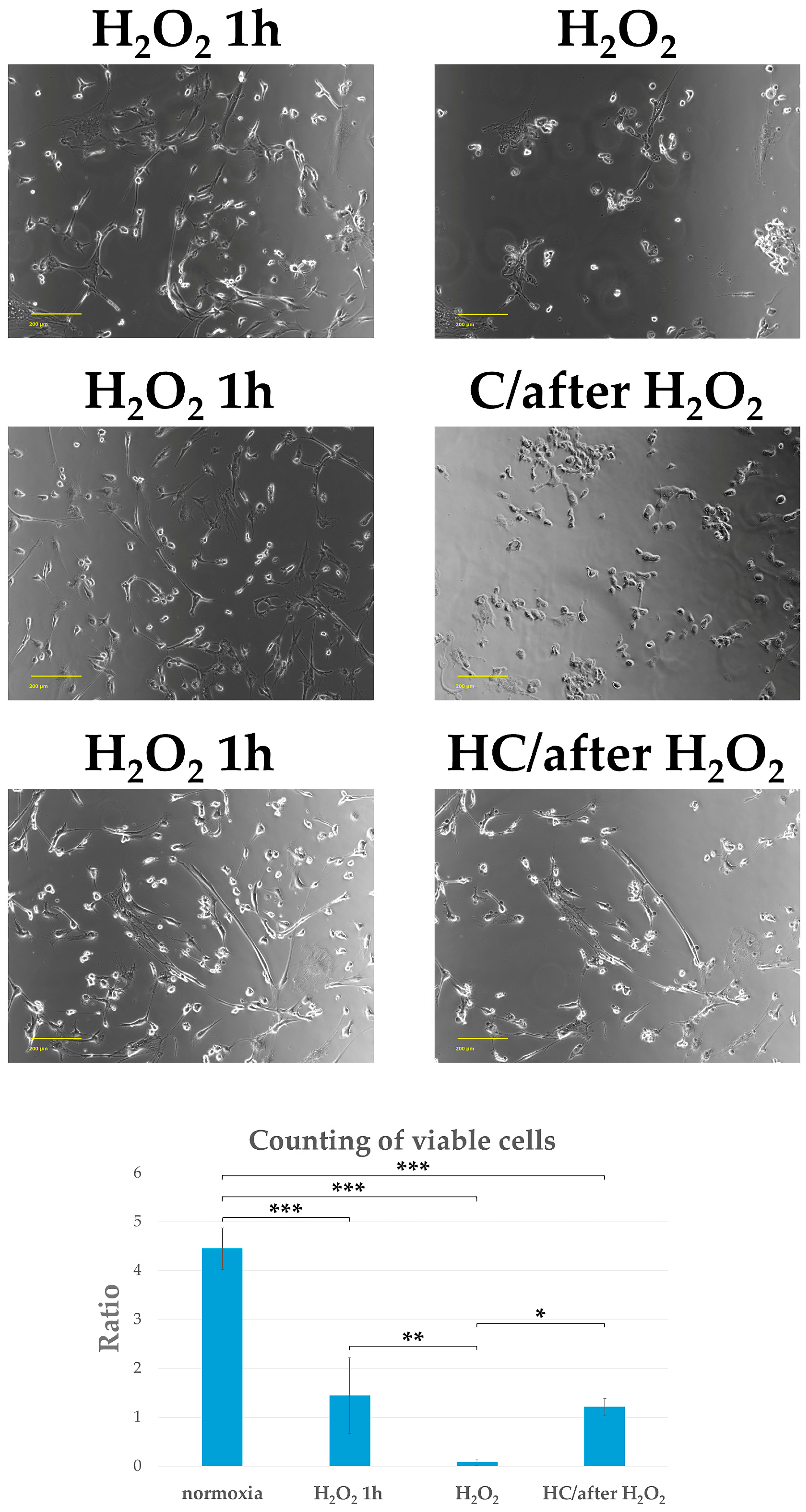
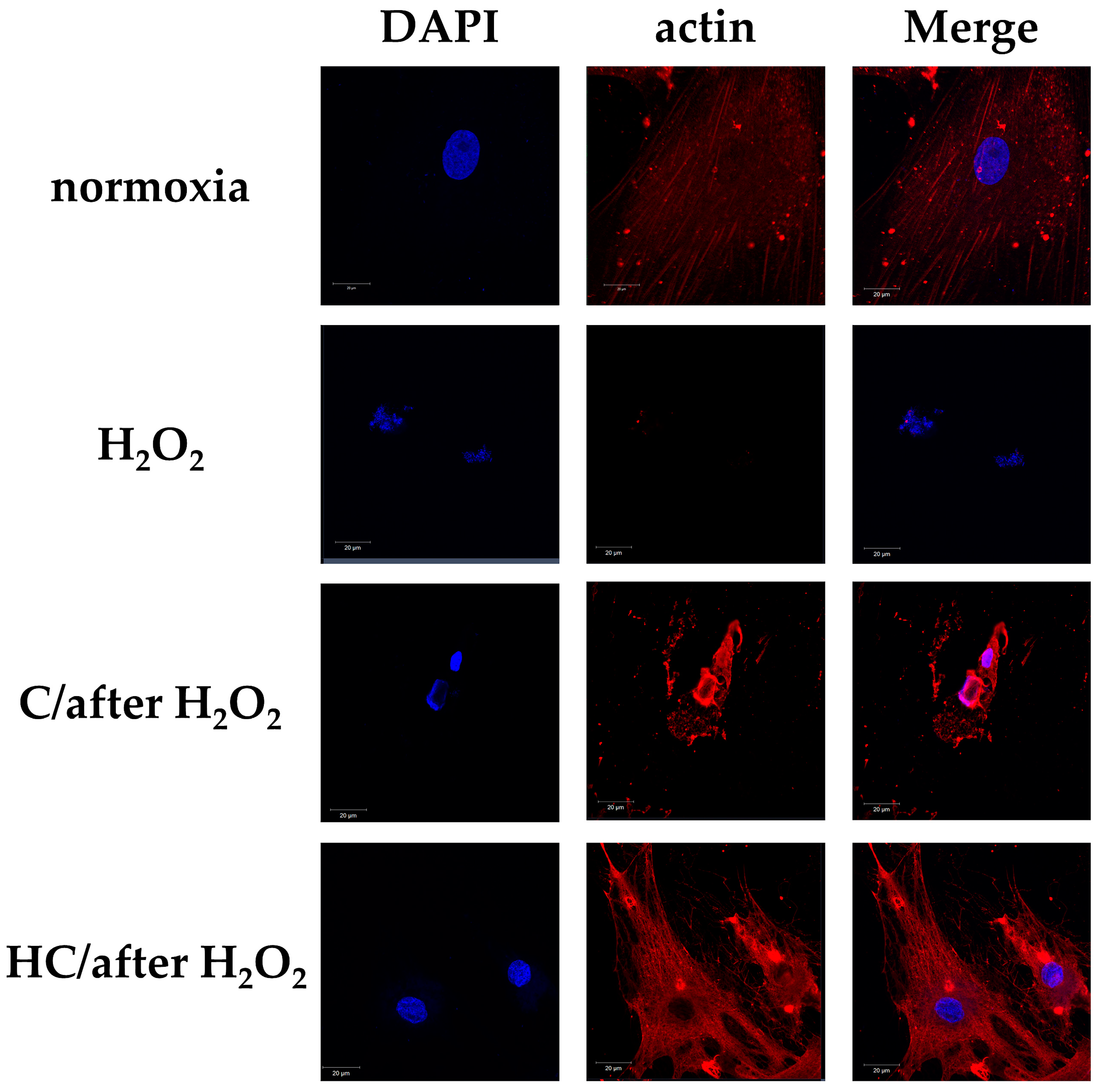
2.4. High-Dose Vitamin C Maintains Cell Viability by Protecting the Cytoskeleton from Cell Damage in Tendon Cells Previously Exposed to Oxidative Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Analysis of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
4.3. Detection of Intracellular ROS Generation
4.4. Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
4.5. Immunostaining for F-Actin and ATP Synthase (ATP5A)
4.6. Determination of Cell Viability
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lui, P.P.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yao, S.; Sun, H.; Huang, C. Roles of oxidative stress in acute tendon injury and degenerative tendinopathy-A target for intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, H.; Morya, V.K.; Oh, J.U.; Kim, J.H.; Noh, K.C. Hypoxia-inducible factor and oxidative stress in tendon degeneration: A molecular perspective. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhou, H.; Tu, T.; Lu, H. Dynamic exacerbation in inflammation and oxidative stress during the formation of peritendinous adhesion resulted from acute tendon injury. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, D.A.; Wallace, C.; Murphy, M.P.; Webster, N.R.; Galley, H.F. The mitochondria targeted antioxidant MitoQ protects against fluoroquinolone-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial membrane damage in human Achilles tendon cells. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Qian, H.; Yu, X.; Meng, J.; Lai, C.T.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, J.N.; Bao, N.R. Proteomic analysis reveals rotator cuff injury caused by oxidative stress. Ther. Adv. Chronic. Dis. 2021, 12, 2040622320987057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Itoigawa, Y.; Wada, T.; Maruyama, Y.; Nojiri, H.; Kawasaki, T.; Kaneko, K. Association of superoxide-induced oxidative stress with rotator cuff tears in human patients. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, J.; Yang, L. Advanced glycation end products impair the repair of injured tendon: A study in rats. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovgaard, D.; Svensson, R.B.; Scheijen, J.; Eliasson, P.; Mogensen, P.; Hag, A.M.; Kjær, M.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Schjerling, P.; Magnusson, S.P.; et al. An advanced glycation endproduct (AGE)-rich diet promotes accumulation of AGEs in Achilles tendon. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mifune, Y.; Inui, A.; Muto, T.; Nishimoto, H.; Kataoka, T.; Kurosawa, T.; Yamaura, K.; Mukohara, S.; Niikura, T.; Kokubu, T.; et al. Influence of advanced glycation end products on rotator cuff. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 1490–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, R.T.; McDonnell, S.M.; Knowles, H.J.; Rees, J.L.; Carr, A.J.; Hulley, P.A. Tendinopathy and tears of the rotator cuff are associated with hypoxia and apoptosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2010, 92, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, J.M.; Harrison, F.E. Role of vitamin C in the function of the vascular endothelium. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 2068–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.C.; Maggini, S. Vitamin C and immune function. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padayatty, S.J.; Katz, A.; Wang, Y.; Eck, P.; Kwon, O.; Lee, J.H.; Chen, S.; Corpe, C.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, S.K.; et al. Vitamin C as an antioxidant: Evaluation of its role in disease prevention. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2003, 22, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, D.; Nojiri, H.; Itoigawa, Y.; Ozawa, Y.; Kaneko, K.; Shimizu, T. Antioxidant treatment with vitamin C attenuated rotator cuff degeneration caused by oxidative stress in Sod1-deficient mice. JSES Open Access 2018, 2, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noriega-González, D.C.; Drobnic, F.; Caballero-García, A.; Roche, E.; Perez-Valdecantos, D.; Córdova, A. Effect of vitamin C on tendinopathy recovery: A scoping review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, H.; Itoigawa, Y.; Morikawa, D.; Koga, A.; Tsurukami, H.; Maruyama, Y.; Ishijima, M. The effect of vitamin C and N-acetylcysteine on tendon-to-bone healing in a rodent model of rotator cuff repair. Am. J. Sports Med. 2023, 51, 1596–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, S.; Tatsumi, T.; Shiraishi, J.; Mano, A.; Keira, N.; Matoba, S.; Asayama, J.; Fushiki, S.; Fliss, H.; Nakagawa, M. Amlodipine inhibits doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, J.A. Antioxidants and coronary artery disease: From pathophysiology to preventive therapy. Coron. Artery Dis. 2015, 26, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, S.; Ichiseki, T.; Shimasaki, M.; Hirata, H.; Kawahara, N.; Ueda, Y. Inhibitory effect of taurine on rotator cuff degeneration via mitochondrial protection. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 6286–6294. [Google Scholar]
- Böttger, F.; Vallés-Martí, A.; Cahn, L.; Jimenez, C.R. High-dose intravenous vitamin C, a promising multi-targeting agent in the treatment of cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.H.; Jun, J.H.; Oh, J.E.; Shin, E.; Kwak, Y.L.; Shim, J.K. Effect of high-dose vitamin C on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.N.; Tian, N.; Luo, Y.H.; Zhao, J.J.; Bi, C.F.; Gou, Y.; Liu, J.; Feng, K.; Zhang, J.F. High-dose Vitamin C injection ameliorates against sepsis-induced myocardial injury by anti-apoptosis, anti-inflammatory and pro-autophagy through regulating MAPK, NF-κB and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways in rats. Aging 2024, 16, 6937–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Baek, S.M.; Kang, K.K.; Kim, T.U.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Han, S.H.; Choi, S.K.; Park, S.J.; et al. Mega-dose vitamin C ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a mouse fast-food diet model. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Lim, S.M.; Yoo, J.A.; Woo, M.J.; Cho, K.H. Consumption of high-dose vitamin C (1250 mg per day) enhances functional and structural properties of serum lipoprotein to improve anti-oxidant, anti-atherosclerotic, and anti-aging effects via regulation of anti-inflammatory microRNA. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3604–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, S.; Stockert, J.C.; Moreno, V.L.; Gamez, A.; Pacheco, M.; Juarranz, A.; Canete, M.; Villanueva, A. Morphological criteria to distinguish cell death induced by apoptotic and necrotic treatments. Apoptosis 2005, 10, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lei, H.; Zhou, L.; Tang, M.; Liu, Q.; Long, F.; Li, Q.; Su, J. Effect of Fumonisin B1 on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Intestinal Porcine Epithelial Cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukas, J.; Parry, D.; Aagaard, L.; Mann, D.J.; Bartkova, J.; Strauss, M.; Peters, G.; Bartek, J. Retinoblastoma-protein-dependent cell-cycle inhibition by the tumour suppressor p16. Nature 1995, 375, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, F.J.; Bates, S.; James, M.C.; McConnell, B.B.; Starborg, M.; Brookes, S.; Palmero, I.; Ryan, K.; Hara, E.; Vousden, K.H.; et al. The alternative product from the human CDKN2A locus, p14(ARF), participates in a regulatory feedback loop with p53 and MDM2. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5001–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.J.; Wijshake, T.; Tchkonia, T.; LeBrasseur, N.K.; Childs, B.G.; van de Sluis, B.; Kirkland, J.L.; van Deursen, J.M. Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive senescent cells delays ageing-associated disorders. Nature 2011, 479, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, T.; Deng, B.; Bao, Y.; Gu, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. P16INK4a regulates ROS-related autophagy and CDK4/6-mediated proliferation: A new target of myocardial regeneration therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2023, 2023, 1696190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Youle, R.J.; Finkel, T. The mitochondrial basis of aging. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, T.; Li, T.Y.; Mottis, A.; Auwerx, J. Pleiotropic effects of mitochondria in aging. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, H. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 646354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Zheng, Q.; Qiu, K.; Elmer Ker, D.F.; Chen, X.; Yin, Z. Mitochondrial destabilization in tendinopathy and potential therapeutic strategies. J. Orthop. Translat. 2024, 49, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.S.; Sampat, V.; Espey, M.G.; Sitapara, R.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Ashby, C.R.; Thomas, D.D.; Mantell, L.L. Ascorbic acid attenuates hyperoxia-compromised host defense against pulmonary bacterial infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldogh, I.R.; Pon, L.A. Interactions of mitochondria with the actin cytoskeleton. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1763, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Seo, D.Y.; Sohn, T.S. Mitochondrial TFAM as a Signaling Regulator between Cellular Organelles: A Perspective on Metabolic Diseases. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Sehrawat, A.; Mastana, S.S.; Kandimalla, R.; Sharma, P.K.; Bhatti, G.K.; Bhatti, J.S. Targeting calcium homeostasis and impaired inter-organelle crosstalk as a potential therapeutic approach in Parkinson’s disease. Life Sci. 2023, 330, 121995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padayatty, S.J.; Sun, A.Y.; Chen, Q.; Espey, M.G.; Drisko, J.; Levine, M. Vitamin C: Intravenous use by complementary and alternative medicine practitioners and adverse effects. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurm, H.; Sheta, M.A.; Nivera, N.; Tunkel, A. Vitamin C-induced oxalate nephropathy: A case report. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2012, 2, 17718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melin, A.M.; Perromat, A.; Déléris, G. Pharmacologic application of FTIR spectroscopy: Effect of ascorbic acid-induced free radicals on Deinococcus radiodurans. Biospectroscopy 1999, 5, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ueda, S.; Ichiseki, T.; Shimasaki, M.; Soma, D.; Sakurai, M.; Kaneuji, A.; Kawahara, N. Effect of High-Dose Vitamin C on Tendon Cell Degeneration—An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413358
Ueda S, Ichiseki T, Shimasaki M, Soma D, Sakurai M, Kaneuji A, Kawahara N. Effect of High-Dose Vitamin C on Tendon Cell Degeneration—An In Vitro Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(24):13358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413358
Chicago/Turabian StyleUeda, Shusuke, Toru Ichiseki, Miyako Shimasaki, Daisuke Soma, Masaru Sakurai, Ayumi Kaneuji, and Norio Kawahara. 2024. "Effect of High-Dose Vitamin C on Tendon Cell Degeneration—An In Vitro Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 24: 13358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413358
APA StyleUeda, S., Ichiseki, T., Shimasaki, M., Soma, D., Sakurai, M., Kaneuji, A., & Kawahara, N. (2024). Effect of High-Dose Vitamin C on Tendon Cell Degeneration—An In Vitro Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413358









