Targeting 5-HT Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
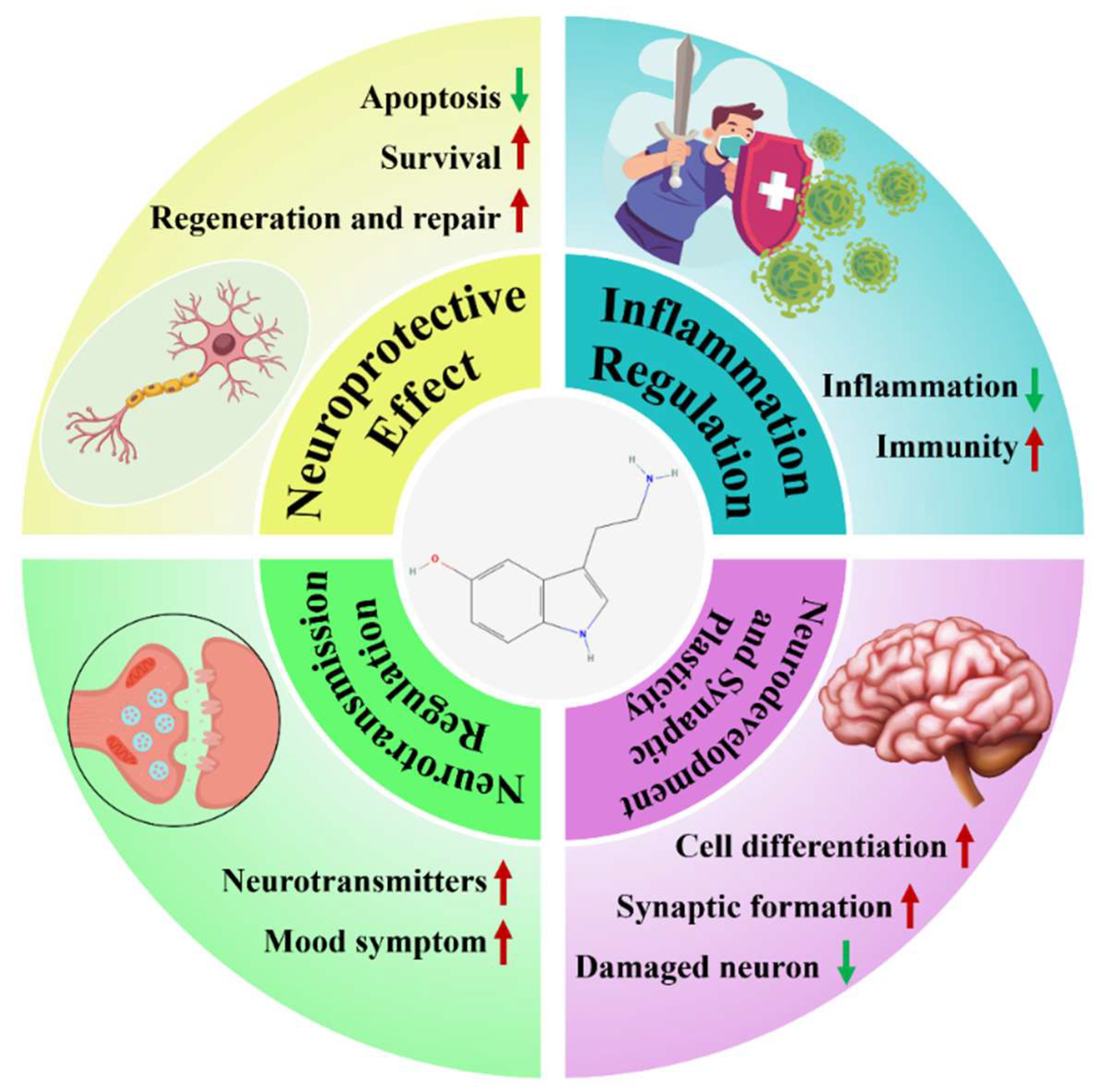
2. The System of 5-HT
2.1. Characteristics of the 5-HT System
2.2. 5-HT Receptor and Its Function
2.2.1. 5-HT1R
2.2.2. 5-HT2R
2.2.3. 5-HT3R
2.2.4. 5-HT4R
2.2.5. 5-HT5R
2.2.6. 5-HT6R
2.2.7. 5-HT7R
3. The Diagnostic and Therapeutic Potential of 5-HT in NDs
3.1. 5-HT Targeting AD Therapy
3.2. 5-HT Targeted PD Therapy
3.3. 5-HT Targeting ALS Therapy
3.4. 5-HT Targeted HD Therapy
3.5. 5-HT Targeted MS Therapy
3.6. The Potential of 5-HT as a Biomarker in Diagnosing NDs.
4. Progress of Clinical Research on Targeting 5-HT for NDs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | Serotonin |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| HD | Huntington’s disease |
| ALS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| ND | Neurodegenerative disease |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| AChE | acetylcholinesterase |
| Aβ | beta-amyloid |
| SNpc | substantia nigra pars compacta |
| BG | basal ganglia |
| SERT | 5-HT transporters |
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| LID | L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia |
| 5-HTP | 5-hydroxytryptophan |
| SSRIs | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors |
| PDP | PD psychosis |
| SDH | spinal dorsal horn |
| FALS | familial ALS |
| SALS | sporadic ALS |
| TDP-43 | TAR DNA-binding protein 43 |
| SOD1 | superoxide dismutase 1 |
| NAS | N-acetyl-5-HT |
| HLA | human leukocyte antigen |
| 5-HTTLPR | 5-HT transporter-linked polymorphic region |
| ICD | Impulse control disorder |
References
- Pentkowski, N.S.; Rogge-Obando, K.K.; Donaldson, T.N.; Bouquin, S.J.; Clark, B.J. Anxiety and Alzheimer’s disease: Behavioral analysis and neural basis in rodent models of Alzheimer’s-related neuropathology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 127, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Agarwal, P. Depression and Anxiety in Parkinson Disease. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2020, 36, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, M.; van Duijn, E. Anxiety in Huntington’s Disease. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 27, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, T.; Ziegler, A.C.; Dimitrion, P.; Zuo, L. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 2525967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachaturian, Z.S. Hypothesis on the regulation of cytosol calcium concentration and the aging brain. Neurobiol. Aging 1987, 8, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemels, M.T. Neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 2016, 539, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałużna-Czaplińska, J.; Gątarek, P.; Chirumbolo, S.; Chartrand, M.S.; Bjørklund, G. How important is tryptophan in human health? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Le, A.; Hong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Zang, W.; Jiang, C.; et al. Tryptophan Metabolism in Central Nervous System Diseases: Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 858–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, B.L.; Azmitia, E.C. Structure and function of the brain serotonin system. Physiol. Rev. 1992, 72, 165–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Gopalakrishnan, L.; Gaur, N.; Chatterjee, O.; Mol, P.; Modi, P.K.; Dagamajalu, S.; Advani, J.; Jain, S.; Keshava Prasad, T.S. The 5-Hydroxytryptamine signaling map: An overview of serotonin-serotonin receptor mediated signaling network. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppen, A.J.; Doogan, D.P. Serotonin and its place in the pathogenesis of depression. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1988, 49 (Suppl. S49), 4–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, D.; Rudge, S. The role of serotonin in depression and anxiety. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1995, 9 (Suppl. S4), 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursin, R. Serotonin and sleep. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2002, 6, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, D.J. Serotonin neurotransmission in anorexia nervosa. Behav. Pharmacol. 2012, 23, 478–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Villegas, A.; Valdés-Ferrer, S.I. Central nervous system effects of 5-HT(7) receptors: A potential target for neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsam, O.; Kohl, Z. Serotonin in synucleinopathies. Behav. Brain Res. 2023, 445, 114367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, P.; Sgambato-Faure, V.; Fox, S.H.; McCreary, A.C. Serotonergic Approaches in Parkinson’s Disease: Translational Perspectives, an Update. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremin, D.V.; Kondaurova, E.M.; Rodnyy, A.Y.; Molobekova, C.A.; Kudlay, D.A.; Naumenko, V.S. Serotonin Receptors as a Potential Target in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biochemistry 2023, 88, 2023–2042. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, Y.; Tatara, A.; Shimizu, S.; Sasa, M. Management of cognitive impairments in schizophrenia: The therapeutic role of 5-HT receptors. In Schizophrenia Research: Recent Advances; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 321–336. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Garcia, A.L.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Leonardo, E.D. P5-HT1A receptors in mood and anxiety: Recent insights into autoreceptor versus heteroreceptor function. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, J.P.; Fink, H. Serotonin controlling feeding and satiety. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, F. 5-Hydroxytryptamine in premature ejaculation: Opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, J.J.; Slade, P.D.; Gaster, L.; Jeffrey, P.; Hatcher, J.P.; Middlemiss, D.N. Stimulation of 5-HT1B receptors causes hypothermia in the guinea pig. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 331, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halberstadt, A.L. Recent advances in the neuropsychopharmacology of serotonergic hallucinogens. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.E.; Ettinger, D.S. 5-HT3 receptor antagonists for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. A comparison of their pharmacology and clinical efficacy. Drugs 1998, 55, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, M.; Goto, K.; Kawahara, I. The 5-hydroxytryptamine 4 Receptor Agonist-induced Actions and Enteric Neurogenesis in the Gut. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 20, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beglinger, C. Tegaserod: A novel, selective 5-HT4 receptor partial agonist for irritable bowel syndrome. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2002, 56, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, D.; Clarke, D.E.; Fozard, J.R.; Hartig, P.R.; Martin, G.R.; Mylecharane, E.J.; Saxena, P.R.; Humphrey, P.P. International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin). Pharmacol. Rev. 1994, 46, 157–203. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer, D.; Hannon, J.P.; Martin, G.R. Molecular, pharmacological and functional diversity of 5-HT receptors. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 71, 533–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, R.P.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Prickaerts, J.; Oliveira, R.M.W. The 5-HT(1A) receptor as a serotonergic target for neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 109, 110210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, P.R.; Vahid-Ansari, F. The 5-HT1A receptor: Signaling to behavior. Biochimie 2019, 161, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, P.R.; Lemonde, S. 5-HT1A receptors, gene repression, and depression: Guilt by association. Neuroscientist 2004, 10, 575–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massiou, H. Naratriptan. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2001, 17 (Suppl. S1), s51–s53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boers, P.M.; Donaldson, C.; Zagami, A.S.; Lambert, G.A. Naratriptan has a selective inhibitory effect on trigeminovascular neurones at central 5-HT1A and 5-HT(1B/1D) receptors in the cat: Implications for migraine therapy. Cephalalgia 2004, 24, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moen, M.D.; Keating, G.M. Sumatriptan fast-disintegrating/rapid-release tablets. Drugs 2006, 66, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, Y.N. Lasmiditan: First Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Maeso, J.; Weisstaub, N.V.; Zhou, M.; Chan, P.; Ivic, L.; Ang, R.; Lira, A.; Bradley-Moore, M.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Hallucinogens recruit specific cortical 5-HT(2A) receptor-mediated signaling pathways to affect behavior. Neuron 2007, 53, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukasiewicz, S.; Polit, A.; Kędracka-Krok, S.; Wędzony, K.; Maćkowiak, M.; Dziedzicka-Wasylewska, M. Hetero-dimerization of serotonin 5-HT(2A) and dopamine D(2) receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1803, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, S.; Remington, G. Serotonin-dopamine interaction and its relevance to schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 1996, 153, 466–476. [Google Scholar]
- Germann, D.; Kurylo, N.; Han, F. Risperidone. Profiles Drug Subst. Excip. Relat. Methodol. 2012, 37, 313–361. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, N.; Watanabe, K. [Olanzapine]. Nihon Rinsho 2013, 71, 666–672. [Google Scholar]
- Bonhaus, D.W.; Bach, C.; DeSouza, A.; Salazar, F.H.; Matsuoka, B.D.; Zuppan, P.; Chan, H.W.; Eglen, R.M. The pharmacology and distribution of human 5-hydroxytryptamine2B (5-HT2B) receptor gene products: Comparison with 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 115, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devroye, C.; Cathala, A.; Piazza, P.V.; Spampinato, U. The central serotonin(2B) receptor as a new pharmacological target for the treatment of dopamine-related neuropsychiatric disorders: Rationale and current status of research. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 181, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, G.A.; Fletcher, P.J.; Shanahan, W.R. Lorcaserin: A review of its preclinical and clinical pharmacology and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 205, 107417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Lummis, S.C. 5-HT3 receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 3615–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roila, F.; Del Favero, A. Ondansetron clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1995, 29, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, S.T.; Curran, M.P. Transdermal granisetron. Drugs 2009, 69, 2597–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celio, L.; Niger, M.; Ricchini, F.; Agustoni, F. Palonosetron in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: An evidence-based review of safety, efficacy, and place in therapy. Core Evid. 2015, 10, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Edwards, E.; Zhang, J.Y. The role of 5-HT3-like receptors in the action of clozapine. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1994, 55 (Suppl. B), 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Serotonin 5-HT4 Receptor Agonists. In LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012.
- Bockaert, J.; Claeysen, S.; Compan, V.; Dumuis, A. 5-HT4 receptors. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2004, 3, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclennan, S.; Augood, C.; Cash-Gibson, L.; Logan, S.; Gilbert, R.E. Cisapride treatment for gastro-oesophageal reflux in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2010, Cd002300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, M.P.; Robinson, D.M. Mosapride in gastrointestinal disorders. Drugs 2008, 68, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, R.; Castro, E.; Pilar-Cuéllar, F.; Pascual-Brazo, J.; Díaz, A.; Rojo, M.L.; Linge, R.; Martín, A.; Valdizán, E.M.; Pazos, A. Serotonin 5-HT4 receptors: A new strategy for developing fast acting antidepressants? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 3751–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, M.; Robert, S.J.; Lezoualc’h, F. New insights into serotonin 5-HT4 receptors: A novel therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease? Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2004, 1, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.L. 5-HT5 receptors. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2004, 3, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, M.L.; Marsden, C.A.; Fone, K.C. 5-ht6 receptors. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2004, 3, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivachtchenko, A.V.; Lavrovsky, Y.; Ivanenkov, Y.A. AVN-211, Novel and Highly Selective 5-HT6 Receptor Small Molecule Antagonist, for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Altamirano, J.L.; Olmos-Hernandez, A.; Jaime, H.B.; Carrillo-Mora, P.; Bandala, C.; Reyes-Long, S.; Alfaro-Rodríguez, A. Review: 5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT3 and 5-HT7 Receptors and their Role in the Modulation of Pain Response in the Central Nervous System. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasbarri, A.; Pompili, A. Serotonergic 5-HT7 receptors and cognition. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 25, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Popova, N.K.; Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Ponimaskin, E.G. Interplay between serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 receptors in depressive disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, J.M.; Jantos, H. The role of serotonin 5-HT7 receptor in regulating sleep and wakefulness. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 25, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, P.B.; Sutcliffe, J.G. The 5-HT7 receptor influences stereotypic behavior in a model of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 414, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Højer, A.M.; Areberg, J.; Nomikos, G. Vortioxetine: Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Drug Interactions. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, I.; Horikoshi, S.; Ichinose, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Watanabe, K. Lurasidone for the Treatment of Schizophrenia: Design, Development, and Place in Therapy. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2023, 17, 3023–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, P.; Cselényi, Z.; Andrée, B.; Borg, J.; Nag, S.; Halldin, C.; Farde, L. Decreased 5-HT(1A) binding in mild Alzheimer’s disease-A positron emission tomography study. Synapse 2022, 76, e22235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, M.; Wu, K.; Loane, C.; Quinn, N.P.; Brooks, D.J.; Oertel, W.H.; Björklund, A.; Lindvall, O.; Piccini, P. Serotonin neuron loss and nonmotor symptoms continue in Parkinson’s patients treated with dopamine grafts. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 128ra41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendland, J.R.; DeGuzman, T.B.; McMahon, F.; Rudnick, G.; Detera-Wadleigh, S.D.; Murphy, D.L. SERT Ileu425Val in autism, Asperger syndrome and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatr. Genet. 2008, 18, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemonde, S.; Turecki, G.; Bakish, D.; Du, L.; Hrdina, P.D.; Bown, C.D.; Sequeira, A.; Kushwaha, N.; Morris, S.J.; Basak, A.; et al. Impaired repression at a 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor gene polymorphism associated with major depression and suicide. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 8788–8799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pinilla, F.; Ying, Z.; Roy, R.R.; Molteni, R.; Edgerton, V.R. Voluntary exercise induces a BDNF-mediated mechanism that promotes neuroplasticity. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 88, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. Plasticity of the hippocampus: Adaptation to chronic stress and allostatic load. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 933, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.N. How to increase serotonin in the human brain without drugs. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2007, 32, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Alzheimer Disease: An Update on Pathobiology and Treatment Strategies. Cell 2019, 179, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duyckaerts, C.; Delatour, B.; Potier, M.C. Classification and basic pathology of Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 5–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledo, J.H.; Azevedo, E.P.; Beckman, D.; Ribeiro, F.C.; Santos, L.E.; Razolli, D.S.; Kincheski, G.C.; Melo, H.M.; Bellio, M.; Teixeira, A.L.; et al. Cross Talk Between Brain Innate Immunity and Serotonin Signaling Underlies Depressive-Like Behavior Induced by Alzheimer’s Amyloid-β Oligomers in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 12106–12116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Areosa, S.A.; Sherriff, F.; McShane, R. Memantine for dementia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 2, Cd003154. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, L.; Faustino, C. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 418–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Chu, F.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, J. Impact of Anti-amyloid-β Monoclonal Antibodies on the Pathology and Clinical Profile of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Focus on Aducanumab and Lecanemab. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 870517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa-Pacha, N.M.; Abdin, S.M.; Omar, H.A.; Alniss, H.; Al-Tel, T.H. BACE1 inhibitors: Current status and future directions in treating Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 339–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidowitz, E.J.; Krishnamurthy, P.K.; Lopez, P.; Jimenez, H.; Adrien, L.; Davies, P.; Moe, J.G. In Vivo Validation of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of Tau Self-Association in htau Mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 73, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Ahmad, R.; Khare, S.K. Alzheimer’s disease and its treatment by different approaches: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 216, 113320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Moreno, T.; González-Acedo, A.; Rivas-Domínguez, A.; García-Morales, V.; García-Cozar, F.J.; Ramos-Rodríguez, J.J.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L. Therapeutic Approach to Alzheimer’s Disease: Current Treatments and New Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshir, S.A.; Aadithsoorya, A.M.; Parveen, A.; Goh, S.S.L.; Hussain, N.; Menon, V.B. Aducanumab Therapy to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 2022, 9343514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehouse, P.; Gandy, S.; Saini, V.; George, D.R.; Larson, E.B.; Alexander, G.C.; Avorn, J.; Brownlee, S.; Camp, C.; Chertkow, H.; et al. Making the Case for Accelerated Withdrawal of Aducanumab. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 87, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawardena, I.P.C.; Retinasamy, T.; Shaikh, M.F. Is Aducanumab for LMICs? Promises and Challenges. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, S.; Shahidi, S.; Rohani, A.H.; Soleimani Asl, S.; Komaki, A. Protective effects of 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist and 5-HT(2A) receptor agonist on the biochemical and histological features in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2019, 96, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, C.; Lv, J.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, X.; Lu, W.; Lu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, J.; Shen, X. Antiallergic drug desloratadine as a selective antagonist of 5HT(2A) receptor ameliorates pathology of Alzheimer’s disease model mice by improving microglial dysfunction. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consolo, S.; Arnaboldi, S.; Giorgi, S.; Russi, G.; Ladinsky, H. 5-HT4 receptor stimulation facilitates acetylcholine release in rat frontal cortex. Neuroreport 1994, 5, 1230–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Hu, Y. Activation of 5-HT4 receptors inhibits secretion of beta-amyloid peptides and increases neuronal survival. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 203, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Romeu, A.; Darcy, S.; Jackson, H.; White, T.; Rosenberg, P. Psychedelics as Novel Therapeutics in Alzheimer’s Disease: Rationale and Potential Mechanisms. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 56, 287–317. [Google Scholar]
- Caraci, F.; Santagati, M.; Caruso, G.; Cannavò, D.; Leggio, G.M.; Salomone, S.; Drago, F. New antipsychotic drugs for the treatment of agitation and psychosis in Alzheimer’s disease: Focus on brexpiprazole and pimavanserin. F1000Res 2020, 9, F1000, Faculty Rev-686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, I.E.M.; Mørk, A. Antagonism of the 5-HT(6) receptor—Preclinical rationale for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2017, 125, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanthier, C.; Payan, H.; Liparulo, I.; Hatat, B.; Lecoutey, C.; Since, M.; Davis, A.; Bergamini, C.; Claeysen, S.; Dallemagne, P.; et al. Novel multi target-directed ligands targeting 5-HT(4) receptors with in cellulo antioxidant properties as promising leads in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Burton, E.A.; Ross, G.W.; Huang, X.; Savica, R.; Abbott, R.D.; Ascherio, A.; Caviness, J.N.; Gao, X.; Gray, K.A.; et al. Research on the premotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: Clinical and etiological implications. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Jansen Steur, E.N.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, J.P. The human raphe nuclei and the serotonergic system. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2003, 26, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Neuropathobiology of non-motor symptoms in Parkinson disease. J. Neural Transm. 2015, 122, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Natale, E.R.; Wilson, H.; Politis, M. Serotonergic imaging in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Brain Res. 2021, 261, 303–338. [Google Scholar]
- Rylander, D.; Parent, M.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Dovero, S.; Lees, A.J.; Bezard, E.; Descarries, L.; Cenci, M.A. Maladaptive plasticity of serotonin axon terminals in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijnders, J.S.; Ehrt, U.; Weber, W.E.; Aarsland, D.; Leentjens, A.F. A systematic review of prevalence studies of depression in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, J.; Ceravolo, R.; Qamhawi, Z.; Lee, J.Y.; Deuschl, G.; Brooks, D.J.; Bonuccelli, U.; Pavese, N. Progression of tremor in early stages of Parkinson’s disease: A clinical and neuroimaging study. Brain 2018, 141, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeso, J.A.; Stamelou, M.; Goetz, C.G.; Poewe, W.; Lang, A.E.; Weintraub, D.; Burn, D.; Halliday, G.M.; Bezard, E.; Przedborski, S.; et al. Past, present, and future of Parkinson’s disease: A special essay on the 200th Anniversary of the Shaking Palsy. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1264–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanow, C.W.; Stocchi, F. Levodopa: A new look at an old friend. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espay, A.J.; Morgante, F.; Merola, A.; Fasano, A.; Marsili, L.; Fox, S.H.; Bezard, E.; Picconi, B.; Calabresi, P.; Lang, A.E. Levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson disease: Current and evolving concepts. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y. Therapeutic role of 5-HT1A receptors in the treatment of schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2011, 17, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezard, E.; Gerlach, I.; Moratalla, R.; Gross, C.E.; Jork, R. 5-HT1A receptor agonist-mediated protection from MPTP toxicity in mouse and macaque models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 23, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, A.; Costa, G.; Serra, M.; Contu, L.; Morelli, M. Neuroinflammation and L-dopa-induced abnormal involuntary movements in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat model of Parkinson’s disease are counteracted by combined administration of a 5-HT(1A/1B) receptor agonist and A(2A) receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacology 2021, 196, 108693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholpa, N.E.; Lynn, M.K.; Corum, D.; Boger, H.A.; Schnellmann, R.G. 5-HT(1F) receptor-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, I.; Asanuma, M. Serotonin 1A Receptors on Astrocytes as a Potential Target for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grychowska, K.; Chaumont-Dubel, S.; Kurczab, R.; Koczurkiewicz, P.; Deville, C.; Krawczyk, M.; Pietruś, W.; Satała, G.; Buda, S.; Piska, K.; et al. Dual 5-HT(6) and D(3) Receptor Antagonists in a Group of 1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinolines with Neuroprotective and Procognitive Activity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3183–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar-Colocho, P.; Del Río, J.; Frechilla, D. Neuroprotective effects of serotonin 5-HT 1A receptor activation against ischemic cell damage in gerbil hippocampus: Involvement of NMDA receptor NR1 subunit and BDNF. Brain Res. 2008, 1199, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.K.; Kwatra, M.; Wang, J.; Ko, H.S. Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Emerging Treatment Strategies. Cells 2022, 11, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meloni, M.; Puligheddu, M.; Sanna, F.; Cannas, A.; Farris, R.; Tronci, E.; Figorilli, M.; Defazio, G.; Carta, M. Efficacy and safety of 5-Hydroxytryptophan on levodopa-induced motor complications in Parkinson’s disease: A preliminary finding. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 415, 116869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Huh, E.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, M.G.; Seo, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, M.S. 5-Hydroxytryptophan Reduces Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia via Regulating AKT/mTOR/S6K and CREB/ΔFosB Signals in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Biomol. Ther. 2023, 31, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.C.; Nayyar, T.; Deutch, A.Y.; Ansah, T.A. 5-HT2A receptor antagonists improve motor impairments in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2010, 59, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, C.; Frouni, I.; Bédard, D.; Hamadjida, A.; Huot, P. Ondansetron, a highly selective 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist, reduces L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the 6-OHDA-lesioned rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 871, 172914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinski, M.A.; Uchic, M.E.; Seifert, T.; Shaughnessy, T.K.; Miller, L.N.; Nakane, M.; Cox, B.F.; Brioni, J.D.; Moreland, R.B. Dopamine D2, but not D4, receptor agonists are emetogenic in ferrets. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 81, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, K.D.; Lu, Z.; Rudd, J.A. Looking beyond 5-HT(3) receptors: A review of the wider role of serotonin in the pharmacology of nausea and vomiting. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 722, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, M.R.; Fuchs, G.; Gemende, I.; Herting, B.; Oehlwein, C.; Reichmann, H.; Rieke, J.; Volkmann, J. Depression and Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2004; 251, (Suppl. S6), vi24–vi27. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, S.; Devadoss, T.; Manjula, S.N.; Rajangam, J. 5-HT(3) receptor antagonism a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of depression and other disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Asin, K.E.; Artigas, F. Vortioxetine, a novel antidepressant with multimodal activity: Review of preclinical and clinical data. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 145, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, T.R.; Ricci, L.A.; Melloni, R.H., Jr. Aggression and anxiety in adolescent AAS-treated hamsters: A role for 5HT3 receptors. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 134, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadjida, A.; Nuara, S.G.; Bédard, D.; Gaudette, F.; Beaudry, F.; Gourdon, J.C.; Huot, P. The highly selective 5-HT(2A) antagonist EMD-281,014 reduces dyskinesia and psychosis in the l-DOPA-treated parkinsonian marmoset. Neuropharmacology 2018, 139, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, K.; Price, D.L.; Bonhaus, D.W. Pimavanserin, a 5-HT2A inverse agonist, reverses psychosis-like behaviors in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav. Pharmacol. 2011, 22, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, S.H.; Ballard, C.G.; Kreitzman, D.L.; Coate, B.; Norton, J.C.; Fernandez, H.H.; Ilic, T.V.; Azulay, J.P.; Ferreira, J.J.; Abler, V.; et al. Efficacy results of pimavanserin from a multi-center, open-label extension study in Parkinson’s disease psychosis patients. Park. Relat. Disord. 2021, 87, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Altamirano, J.L.; Reyes-Long, S.; Bandala, C.; Morraz-Varela, A.; Bonilla-Jaime, H.; Alfaro-Rodriguez, A. Neuropathic Pain in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurol. India 2022, 70, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Zhang, L.G.; Liu, L.B.; An, M.Q.; Dong, L.G.; Gu, H.Y.; Dai, Y.P.; Wang, F.; Mao, C.J.; Liu, C.F. Inhibition of Spinal 5-HT3 Receptor and Spinal Dorsal Horn Neuronal Excitability Alleviates Hyperalgesia in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 7253–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, Z.; Huang, R.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Q.; Zhong, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, H. Electroacupuncture Modulates 5-HT(4R)-Mediated cAMP/PKA Signaling to Improve Intestinal Motility Disorders in a Thy1-αSyn Parkinson’s Mouse Model. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 8659462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Song, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Z.; Xia, T.; Gu, X. The role of 5-HT(7)R in the memory impairment of mice induced by long-term isoflurane anesthesia. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2022, 188, 107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, C.M.; Leger, M.; Freret, T. Memory Disorders Related to Hippocampal Function: The Interest of 5-HT(4)Rs Targeting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, S.; Shahidi, S.; Baooshi, H.; Hoseini, M.; Esmaeili, M.; Hashemi-Firouzi, N.; Komaki, A. The role of hippocampal 5-HT(1D) and 5-HT(1F) receptors on learning and memory in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardiman, O.; van den Berg, L.H.; Kiernan, M.C. Clinical diagnosis and management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandyk, R. Serotonergic mechanisms in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Int. J. Neurosci. 2006, 116, 775–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.; Cazenave, W.; Allain, A.E.; Cattaert, D.; Branchereau, P. Implication of 5-HT in the Dysregulation of Chloride Homeostasis in Prenatal Spinal Motoneurons from the G93A Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; He, B.; Li, S.; Chai, W.; Rao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Pan, H.; et al. Distribution Features and Potential Effects of Serotonin in the Cerebrum of SOD1 G93A Transgenic Mice. eNeuro 2022, 9, ENEURO.0001-22.2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, M.; Lapiz, M.D.; Tanaka, E.; Grenhoff, J. Serotonin inhibits synaptic glutamate currents in rat nucleus accumbens neurons via presynaptic 5-HT1B receptors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciranna, L. Serotonin as a modulator of glutamate- and GABA-mediated neurotransmission: Implications in physiological functions and in pathology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2006, 4, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Oussini, H.; Bayer, H.; Scekic-Zahirovic, J.; Vercruysse, P.; Sinniger, J.; Dirrig-Grosch, S.; Dieterlé, S.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Larmet, Y.; Müller, K.; et al. Serotonin 2B receptor slows disease progression and prevents degeneration of spinal cord mononuclear phagocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoux, A.; Ayme-Dietrich, E.; Dieterle, S.; Goy, M.A.; Schann, S.; Frauli, M.; Monassier, L.; Dupuis, L. Evaluation of a 5-HT(2B) receptor agonist in a murine model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.S.; Gong, M.N.; Rao, W.; Chai, W.; Chen, W.Z.; Zhang, X.; Nie, H.B.; Xu, R.S. 5-Hydroxytryptamine: A potential therapeutic target in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, L.; Halder, R.C.; Montoya, D.J.; Rubbi, L.; Rinaldi, A.; Sagong, B.; Weitzman, S.; Rubattino, R.; Singh, R.R.; Pellegrini, M.; et al. Anti-inflammatory therapies of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis guided by immune pathways. Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2015, 4, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guseva, D.; Holst, K.; Kaune, B.; Meier, M.; Keubler, L.; Glage, S.; Buettner, M.; Bleich, A.; Pabst, O.; Bachmann, O.; et al. Serotonin 5-HT7 receptor is critically involved in acute and chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 1516–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, B.J.; Lopes, E.C.; Cheema, S.S. The serotonin precursor 5-hydroxytryptophan delays neuromuscular disease in murine familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Mot. Neuron Disord. 2003, 4, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentel, C.; Palamiuc, L.; Henriques, A.; Lannes, B.; Spreux-Varoquaux, O.; Gutknecht, L.; René, F.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Gonzalez de Aguilar, J.L.; Lesch, K.P.; et al. Degeneration of serotonergic neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A link to spasticity. Brain 2013, 136 Pt. 2, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Oussini, H.; Scekic-Zahirovic, J.; Vercruysse, P.; Marques, C.; Dirrig-Grosch, S.; Dieterlé, S.; Picchiarelli, G.; Sinniger, J.; Rouaux, C.; Dupuis, L. Degeneration of serotonin neurons triggers spasticity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Yao, X.X.; Gao, S.H.; Li, R.; Li, B.J.; Yang, W.; Cui, R.J. Role of 5-HT receptors in neuropathic pain: Potential therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boentert, M. Sleep and Sleep Disruption in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, J.M. Serotonin control of sleep-wake behavior. Sleep Med. Rev. 2011, 15, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, M.M.; Sinnott, J.; Osman, K.L.; Deninger, I.; Andel, E.; Caywood, V.; Mok, A.; Ballenger, B.; Cummings, K.; Thombs, L.; et al. Mice Lacking Brain-Derived Serotonin Have Altered Swallowing Function. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2019, 161, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, L.; Spreux-Varoquaux, O.; Bensimon, G.; Jullien, P.; Lacomblez, L.; Salachas, F.; Bruneteau, G.; Pradat, P.F.; Loeffler, J.P.; Meininger, V. Platelet serotonin level predicts survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Li, X.J. Huntingtin-protein interactions and the pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.B. Huntingtin in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Suofu, Y.; Yablonska, S.; Wang, X.; Larkin, T.M.; Kim, J.; Carlisle, D.L.; Friedlander, R.M. Increased Serotonin Transporter Expression in Huntington’s Disease Patients Is Not Consistently Replicated in Murine Models. J. Huntingt. Dis. 2019, 8, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, G.P.; Pearson, S.J. Decreased glutamic acid and increased 5-hydroxytryptamine in Huntington’s disease brain. Neurosci. Lett. 1987, 78, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédard, C.; Wallman, M.J.; Pourcher, E.; Gould, P.V.; Parent, A.; Parent, M. Serotonin and dopamine striatal innervation in Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s chorea. Park. Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Montilla, P.; Padillo, F.J.; Bujalance, I.; Muñoz, M.C.; Muntané, J.; Túnez, I. Role of serotonin in cerebral oxidative stress in rats. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2006, 66, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.M.; Lee, B.D.; Sok, D.E.; Ma, J.Y.; Kim, M.R. Neuroprotective action of N-acetyl serotonin in oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the activation of both TrkB/CREB/BDNF pathway and Akt/Nrf2/Antioxidant enzyme in neuronal cells. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roppongi, T.; Togo, T.; Nakamura, S.; Asami, T.; Yoshimi, A.; Shiozaki, K.; Kato, D.; Kawanishi, C.; Hirayasu, Y. Perospirone in treatment of Huntington’s disease: A first case report. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, T.Y.; Du, X.; Zajac, M.S.; Howard, M.L.; Hannan, A.J. Altered serotonin receptor expression is associated with depression-related behavior in the R6/1 transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhamzeh, M.; Moravej, F.G.; Arabi, M.; Shahriari, E.; Mehrabi, S.; Ward, R.; Ahadi, R.; Joghataei, M.T. The Roles of Serotonin in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedic Erjavec, G.; Tudor, L.; Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Podobnik, J.; Dodig Curkovic, K.; Curkovic, M.; Svob Strac, D.; Cusek, M.; Bortolato, M.; Pivac, N. Serotonin 5-HT(2A) receptor polymorphisms are associated with irritability and aggression in conduct disorder. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 117, 110542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compston, A.; Coles, A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2008, 372, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffjan, S.; Akkad, D.A. The genetics of multiple sclerosis: An update 2010. Mol. Cell. Probes 2010, 24, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascherio, A.; Munger, K.L.; White, R.; Köchert, K.; Simon, K.C.; Polman, C.H.; Freedman, M.S.; Hartung, H.P.; Miller, D.H.; Montalbán, X.; et al. Vitamin D as an early predictor of multiple sclerosis activity and progression. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolders, J.; Peelen, E.; Thewissen, M.; Menheere, P.; Tervaert, J.W.; Hupperts, R.; Damoiseaux, J. The relevance of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms for vitamin D research in multiple sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009, 8, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidina, T.V.; Trushnikova, T.N.; Danilova, M.A. Interferon-induced depression and peripheral blood serotonin in patients with multiple sclerosis. Zh Nevrol. Psikhiatr Im. S S Korsakova 2018, 118, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverchon, F.; Guillard, C.; Mollet, L.; Auzou, P.; Gosset, D.; Madouri, F.; Valéry, A.; Menuet, A.; Ozsancak, C.; Pallix-Guyot, M.; et al. T Lymphocyte Serotonin 5-HT(7) Receptor Is Dysregulated in Natalizumab-Treated Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, P.; Lawler, A.; Chandran, S.; Mead, G. Potential disease-modifying effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in multiple sclerosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 709–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviridova, A.; Rogovskii, V.; Kudrin, V.; Pashenkov, M.; Boyko, A.; Melnikov, M. The role of 5-HT(2B)-receptors in fluoxetine-mediated modulation of Th17- and Th1-cells in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 356, 577608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannitti, T.; Kerr, B.J.; Taylor, B.K. Mechanisms and pharmacology of neuropathic pain in multiple sclerosis. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 20, 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Gurba, K.N.; Chaudhry, R.; Haroutounian, S. Central Neuropathic Pain Syndromes: Current and Emerging Pharmacological Strategies. CNS Drugs 2022, 36, 483–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, K.C.; Stephens, M.J.; Ballou, E.W.; Heckman, C.J.; Bennett, D.J. Motoneuron excitability and muscle spasms are regulated by 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptor activity. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 105, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, H.; Laursen, B.; Stenager, E.N.; Stenager, E. Psychiatric co-morbidity in multiple sclerosis: The risk of depression and anxiety before and after MS diagnosis. Mult. Scler. 2016, 22, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickards, H. Depression in neurological disorders: Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76 (Suppl. S1), i48–i52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saul, A.; Taylor, B.; Simpson, S., Jr.; Ponsonby, A.L.; Blizzard, L.; Dwyer, T.; McMorran, B.; Wood, B.; van der Mei, I.A. Polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms (5-HTTLPR) modifies the association between significant life events and depression in people with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2019, 25, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarali, A.J.; Reynolds, G.P. Monoamine neurotransmitters and their metabolites in brain regions in Alzheimer’s disease: A postmortem study. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 1992, 12, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić Leko, M.; Nikolac Perković, M.; Španić, E.; Švob Štrac, D.; Pleić, N.; Vogrinc, Ž.; Gunjača, I.; Bežovan, D.; Nedić Erjavec, G.; Klepac, N.; et al. Serotonin Receptor Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated with Cerebrospinal Fluid, Genetic, and Neuropsychological Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Q.; Ding, J.; Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, K. Reduced plasma serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid levels in Parkinson’s disease are associated with nonmotor symptoms. Park. Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M.; Boileau, I.; Warsh, J.; Saint-Cyr, J.A.; Ginovart, N.; McCluskey, T.; Houle, S.; Wilson, A.; Mundo, E.; Rusjan, P.; et al. Brain serotonin transporter binding in non-depressed patients with Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2007, 14, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.L.; Chang, K.H.; Wu, Y.R.; Chen, C.M. Metabolic disturbances in plasma as biomarkers for Huntington’s disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 31, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ” indicates that the activation of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom; “
” indicates that the activation of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom; “ ” indicates that inhibition of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom.
” indicates that inhibition of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom.
 ” indicates that the activation of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom; “
” indicates that the activation of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom; “ ” indicates that inhibition of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom.
” indicates that inhibition of this receptor contributes to the recovery of the symptom.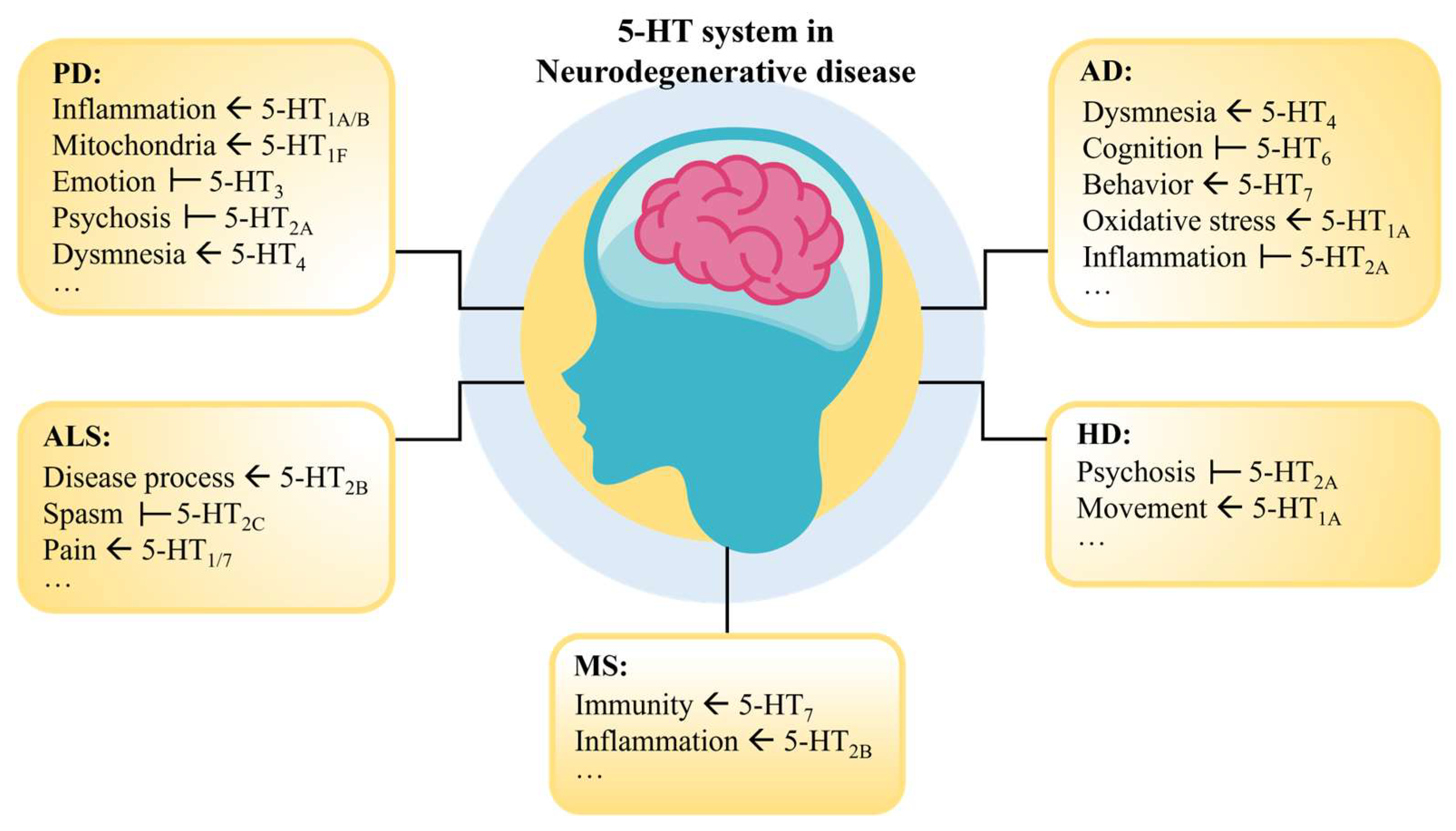
| 5-HT Receptors | Possible Functions | Known Agonist/Antagonist |
|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1A | anxiety, mood, cognition, suicidal tendencies, appetite, sleep, and pain perception | Buspirone |
| 5-HT1B/1D | stress responses, mood, and motor control | Naratriptan |
| Sumatriptan | ||
| 5-HT1F | pain | Lasmiditan |
| 5-HT2A | cognition, mood, perception, and behavior | Risperidone |
| Olanzapine | ||
| 5-HT2C | appetite regulation, weight control, mood, and behavior regulation | Lorcaserin |
| 5-HT3 | vomiting reflex, cognition, and anxiety | Ondansetron |
| Granisetron | ||
| Palonosetron | ||
| 5-HT4 | neurotransmission, gastrointestinal motility and secretion, and memory | Cisapride |
| Mosapride | ||
| Tegaserod | ||
| 5-HT6 | memory, energy metabolism, and mood | AVN-211 |
| 5-HT7 | learning and memory, mood regulation, sleep, addictive behaviors, and pain | SB-269970 |
| SB-656104-A |
| NCT Number | Stage | ND Type | Drug | Sample Size | Object | Mechanism | Year | Locations | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03652870 | III | Parkinson’s disease (PD) | Nortriptyline | 52 | Depression in PD | tricyclic antidepressants | 29-Aug-18 | Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom | + |
| Escitalopram | selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor | ||||||||
| NCT03947216 | II | Parkinson’s disease | Pimavanserin | 130 | Impulse control disorder (ICD) in PD | selective serotonin 5-HT2A inverse agonist | 13-May-19 | Service de Neurologie-CHU Besançon, Besançon, France | = |
| NCT04292223 | IV | Parkinson’s disease | Pimavanserin | 29 | Parkinson’s disease psychosis | selective serotonin 5-HT2A inverse agonist | 3-Mar-20 | Movement Disorders Center of Arizona, Scottsdale, Arizona, United States | + |
| NCT04373317 | IV | Parkinson’s disease | Pimavanserin | 358 | Parkinson’s disease psychosis | selective serotonin 5-HT2A inverse agonist | 4-May-20 | Southern Arizona VA Health Care System, Tucson, AZ, Tucson, Arizona, United States | = |
| Quetiapine | 5-HT2A receptor antagonist | ||||||||
| NCT05357612 | IV | Parkinson’s disease | Pimavanserin | 75 | measure baseline 5HT2A receptor density | selective serotonin 5-HT2A inverse agonist | 3-May-22 | Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, United States | = |
| NCT05590637 | IV | Parkinson’s disease | Pimavanserin | 94 | Parkinson’s disease psychosis, dementia with Lewy bodies | selective serotonin 5-HT2A inverse agonist | 21-Oct-22 | UT Health Science Center—San Antonio, San Antonio, Texas, United States | = |
| Quetiapine | 5-HT2A receptor antagonist | ||||||||
| NCT05796167 | Early I | Parkinson’s disease | Pimavanserin | 10 | sleep quality in patients with PD and visual hallucinations/delusions | selective serotonin 5-HT2A inverse agonist | 3-Apr-23 | − | − |
| NCT04167813 | II | Parkinson’s disease | Ondansetron | 306 | Parkinson’s hallucinations, dementia with Lewy bodies | 5-HT3 receptor antagonist | 19-Nov-19 | Grampian Aberdeen, United Kingdom | = |
| NCT04497168 | II | Parkinson’s disease | Citalopram | 58 | reduce visuospatial cortex Aβ plaque accrual | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors | 4-Aug-20 | University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States | = |
| NCT04932434 | II | Parkinson’s disease | Psilocybin | 10 | depression and anxiety in PD | 5-HT2A receptor agonist | 21-Jun-21 | University of California, San Francisco, United States | = |
| NCT05148884 | II | Parkinson’s disease | NLX-112 | 27 | L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in PD | high-efficacy selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist | 8-Dec-21 | Sahlgrenska Hospital, Gothenburg, Sweden | + |
| NCT03724942 | III | Alzheimer’s disease (AD) | Brexpiprazole | 164 | Agitation associated with dementia of the Alzheimer’s type | 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A receptor antagonists | 30-Oct-18 | Jisenkai Nanko Psychiatric Institute Shirakawa, Japan | + |
| NCT04123314 | I | Alzheimer’s disease | Psilocybin | 20 | depression in mild cognitive impairment and early AD | 5-HT2A receptor agonist | 10-Oct-19 | Behavioral Pharmacology Research Unit, Baltimore, Maryland, United States | = |
| NCT04341467 | − | Alzheimer’s disease | Olanzapine | 76 | Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia in AD | 5-HT2A receptor antagonist | 10-Apr-20 | Tianjin Anding Hospital, Tianjin, Tianjin, China | = |
| NCT05282550 | II | Alzheimer’s disease | Trazodone | 100 | Amnestic mild cognitive impairment | 5-HT2A receptor antagonist | 16-Mar-22 | Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, United States | = |
| NCT05397639 | III | Alzheimer’s disease | Masupirdine | 375 | Agitation, Alzheimer’s type dementia | 5-HT6 receptor antagonist | 31-May-22 | ATP Clinical Research, Inc. Costa Mesa, California, United States | = |
| NCT04071639 | I | Huntington’s disease (HD) | Risperidone | 60 | Huntington’s disease motor, MMSE, psychiatric, and functional domains | 5-HT2A receptor antagonist | 28-Aug-19 | Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China | = |
| Haloperidol | 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C receptor antagonists | ||||||||
| Zoloft | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors | ||||||||
| NCT04302870 | II/III | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | Trazodone | 800 | Motor neuron disease | 5-HT2A receptor antagonist | 10-Mar-20 | Southern Health and Social Care Trust, Craigavon Area Hospital, Portadown, County Armagh, United Kingdom | = |
| NCT04546698 | − | Multiple sclerosis (MS) | − | 78 | 5-HT7 receptor implication in inflammatory mechanisms in MS | 5-HT7 receptor | 14-Sep-20 | CHR Orléans, Orléans, France | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, C.; Chen, H.; Bi, W.; Lei, T.; Hang, Z.; Du, H. Targeting 5-HT Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413446
Xing C, Chen H, Bi W, Lei T, Hang Z, Du H. Targeting 5-HT Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(24):13446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413446
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Cencan, Hongyu Chen, Wangyu Bi, Tong Lei, Zhongci Hang, and Hongwu Du. 2024. "Targeting 5-HT Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Neurodegenerative Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 24: 13446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413446
APA StyleXing, C., Chen, H., Bi, W., Lei, T., Hang, Z., & Du, H. (2024). Targeting 5-HT Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413446





