Effects of Bradykinin B2 Receptor Ablation from Tyrosine Hydroxylase Cells on Behavioral and Motor Aspects in Male and Female Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
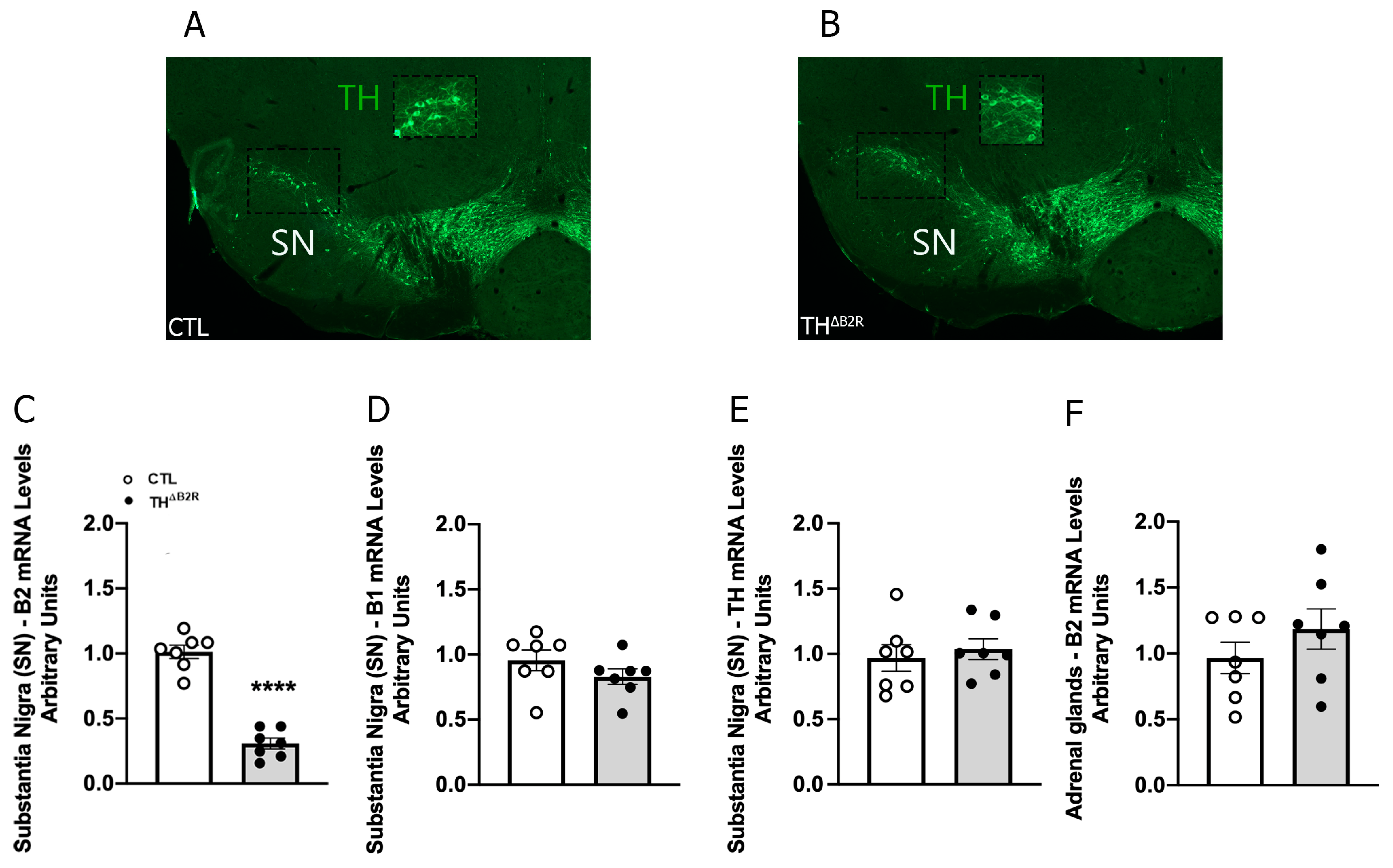
2.1. Generation of Mice Carrying Ablation of B2R in TH Neurons
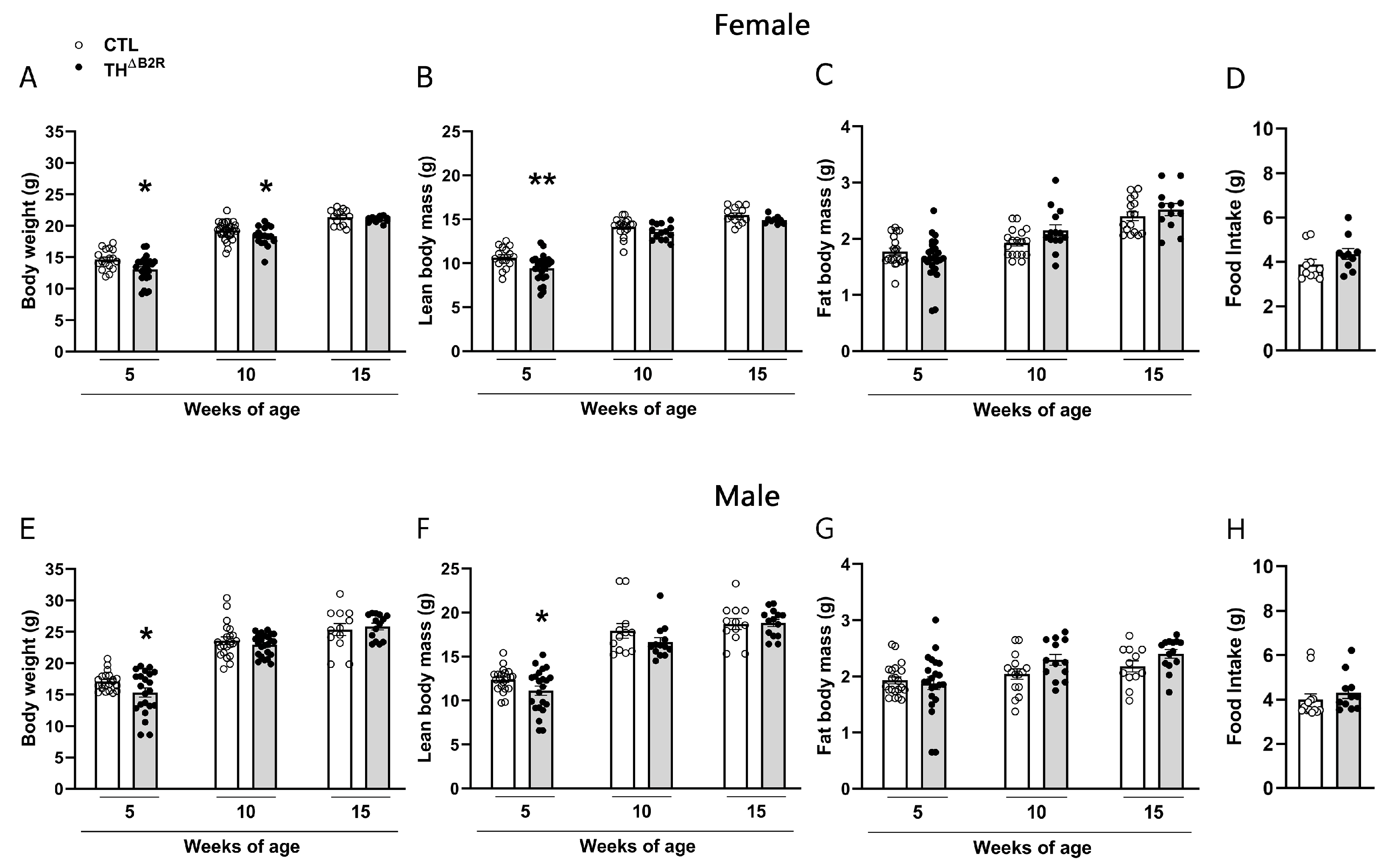
2.2. B2R Ablation in TH Cells Leads to a Transitory Reduction in Body Weight in Female and Male Mice
2.3. Impact of B2R Ablation in TH Cells on Metabolic Parameters
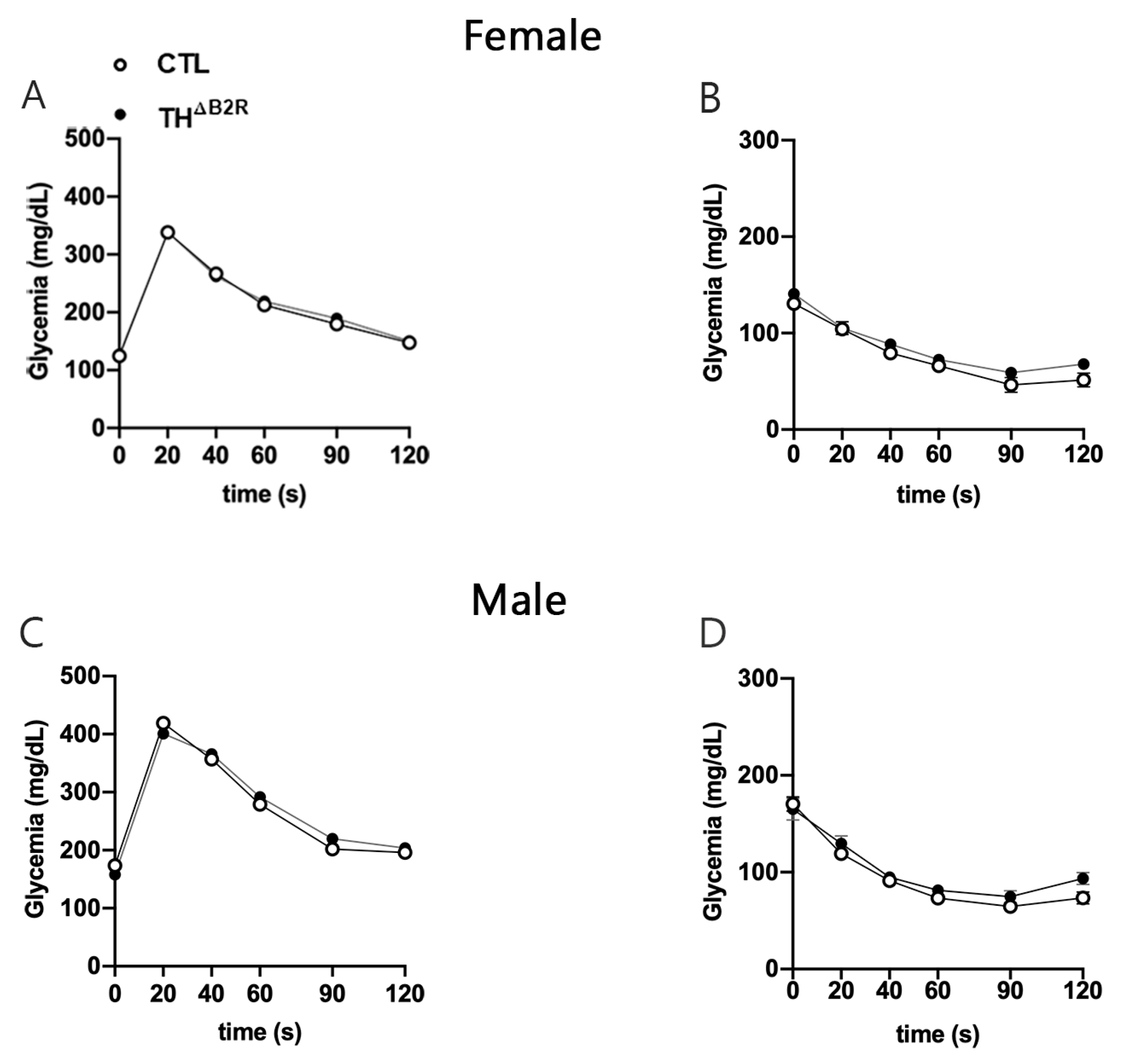
2.4. Glucose Homeostasis Is Unaltered by B2R Ablation from TH Cells
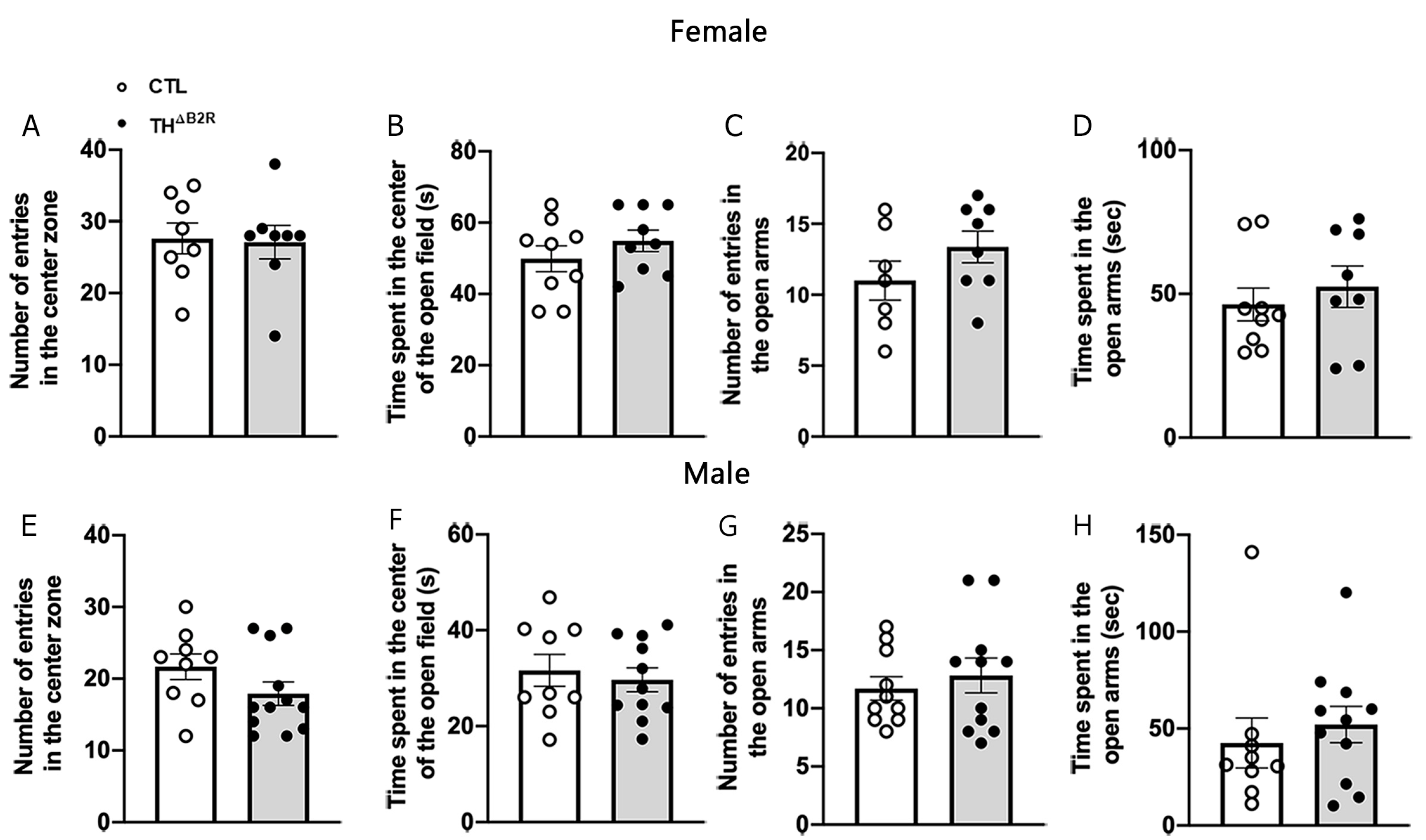
2.5. B2R Ablation in TH Cells Does Not Affect Anxiety
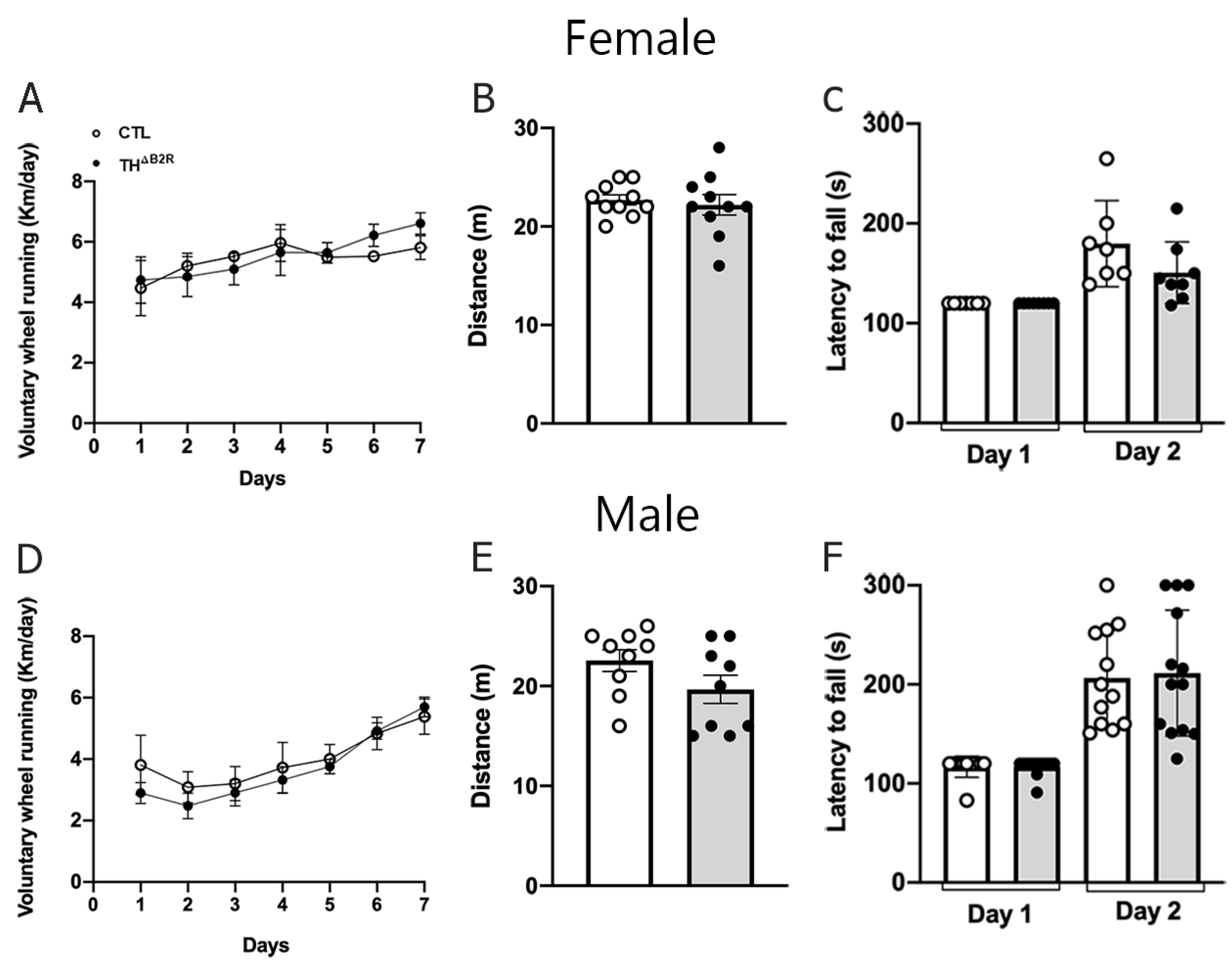
2.6. B2R Ablation in TH Cells Does Not Impair Physical Exercise Performance and Motor Coordination
2.7. Monoamine and Metabolite Concentrations Remain Unaltered Following B2R Ablation in TH Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Evaluation of Energy and Glucose Homeostasis
4.3. Metabolic Parameters
4.4. Behavioral Tests
4.4.1. Open Field (OFT) and Elevated Plus Maze Tests (EPM)
4.4.2. Voluntary Wheel Running and Incremental Treadmill Maximal Running Tests
4.4.3. Rotarod Test
4.5. HPLC-Electrochemical Detection and Sample Preparation
4.6. qRT-PCR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhoola, K.D.; Figueroa, C.D.; Worthy, K. Bioregulation of kinins: Kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol. Rev. 1992, 44, 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Dray, A.; Perkins, M. Bradykinin and inflammatory pain. Trends Neurosci. 1993, 16, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schölkens, B.A. Kinins in the cardiovascular system. Immunopharmacology 1996, 33, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsa Allogho, S.; Gobeil, F.; Pheng, L.H.; Nguyen-Le, X.K.; Neugebauer, W.; Regoli, D. Antagonists for kinin B1 and B2 receptors in the mouse. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1997, 75, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asraf, K.; Torika, N.; Danon, A.; Fleisher-Berkovich, S. Involvement of the Bradykinin B(1) Receptor in Microglial Activation: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, R.C. Kinin receptors: Key regulators of autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, F.; Bachvarov, D.R. Kinin receptors. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 1998, 16, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoli, D.; Barabé, J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol. Rev. 1980, 32, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg, L.M.; Marceau, F.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Pettibone, D.J.; Zuraw, B.L. International union of pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: From molecular mechanisms to pathophysiological consequences. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 27–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.K.; Zhang, H.T. Function and structure of bradykinin receptor 2 for drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, E.C.D.; Vieira, G.; Gonçalves, T.R.; Simões, R.R.; Brusco, I.; Oliveira, S.M.; Calixto, J.B.; Cola, M.; Santos, A.R.S.; Dutra, R.C. Bradykinin Receptors Play a Critical Role in the Chronic Post-ischaemia Pain Model. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 41, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.G.; Gitaí, D.L.; Paçó-Larson, M.L.; Pesquero, J.B.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Costa-Neto, C.M. Modulation of B1 and B2 kinin receptors expression levels in the hippocampus of rats after audiogenic kindling and with limbic recruitment, a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howl, J.; Payne, S.J. Bradykinin receptors as a therapeutic target. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2003, 7, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Emerich, D.F.; Bartus, R.T.; Kordower, J.H. B2 bradykinin receptor immunoreactivity in rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 427, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shughrue, P.J.; Ky, B.; Austin, C.P. Localization of B1 bradykinin receptor mRNA in the primate brain and spinal cord: An in situ hybridization study. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 465, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scicli, A.G.; Forbes, G.; Nolly, H.; Dujovny, M.; Carretero, O.A. Kallikrein-kinins in the central nervous system. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. A 1984, 6, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, J.B.; Medeiros, R.; Fernandes, E.S.; Ferreira, J.; Cabrini, D.A.; Campos, M.M. Kinin B1 receptors: Key G-protein-coupled receptors and their role in inflammatory and painful processes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, M.T.; Amaral, F.A.; Dong, K.E.; Bittencourt, M.F.; Caetano, A.L.; Pesquero, J.B.; Viel, T.A.; Buck, H.S. Role of kinin B1 and B2 receptors in memory consolidation during the aging process of mice. Neuropeptides 2010, 44, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, C.A.; Negraes, P.D.; Schwindt, T.T.; Lameu, C.; Carromeu, C.; Muotri, A.R.; Pesquero, J.B.; Cerqueira, D.M.; Pillat, M.M.; de Souza, H.D.; et al. Kinin-B2 receptor activity determines the differentiation fate of neural stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 44046–44061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.F.; Yin, H.; Yao, Y.Y.; Borlongan, C.V.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Kallikrein protects against ischemic stroke by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation and promoting angiogenesis and neurogenesis. Hum. Gene Ther. 2006, 17, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasinski, F.; Batista, R.O.; Bader, M.; Araujo, R.C.; Klempin, F. Bradykinin B2 receptor is essential to running-induced cell proliferation in the adult mouse hippocampus. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 3901–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, B.; Cheng, B.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Bai, B. Neuroprotection of bradykinin/bradykinin B2 receptor system in cerebral ischemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeler, J.A.; Faust, R.P.; Turkson, S.; Ye, H.; Zhuang, X. Low Dopamine D2 Receptor Increases Vulnerability to Obesity Via Reduced Physical Activity, Not Increased Appetitive Motivation. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knab, A.M.; Lightfoot, J.T. Does the difference between physically active and couch potato lie in the dopamine system? Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 6, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiarowska-Sendo, A.; Polit, A.; Piwowar, M.; Tworzydło, M.; Kozik, A.; Guevara-Lora, I. Bradykinin B2 and dopamine D2 receptors form a functional dimer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasinski, F.; Pedroso, J.A.B.; Dos Santos, W.O.; Furigo, I.C.; Garcia-Galiano, D.; Elias, C.F.; List, E.O.; Kopchick, J.J.; Szawka, R.E.; Donato, J., Jr. Tyrosine Hydroxylase Neurons Regulate Growth Hormone Secretion via Short-Loop Negative Feedback. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 4309–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, C.C.; Haro, A.; Russo, F.J.; Schadock, I.; Almeida, S.S.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Vanzela, E.C.; Lanzoni, V.P.; Barros, F.C.; Moraes, M.R.; et al. Altered glucose homeostasis and hepatic function in obese mice deficient for both kinin receptor genes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, K.V.; Kinyua, A.W.; Yang, D.J.; Ko, C.M.; Moh, S.H.; Shong, K.E.; Kim, H.; Park, S.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, I.; et al. FoxO1 in dopaminergic neurons regulates energy homeostasis and targets tyrosine hydroxylase. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.G.; Sales, V.M.; Ropelle, E.; Barros, C.C.; Oyama, L.; Ihara, S.S.; Saad, M.J.; Araújo, R.C.; Pesquero, J.B. Lack of kinin B1 receptor potentiates leptin action in the liver. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.; Tulloch, A.; Gold, M.S.; Avena, N.M. Hormonal and neural mechanisms of food reward, eating behaviour and obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, F.C.; Haro, A.S.; Bacurau, A.V.; Hirabara, S.M.; Wasinski, F.; Ormanji, M.S.; Moreira, J.B.; Kiyomoto, B.H.; Bertoncini, C.R.; Brum, P.C.; et al. Deletion of Kinin B2 Receptor Alters Muscle Metabolism and Exercise Performance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, R.L.; Silva, E.D.; Sales, V.M.; Filippelli-Silva, R.; Mori, M.A.; Bader, M.; Pesquero, J.B. Kinin B1 and B2 receptor deficiency protects against obesity induced by a high-fat diet and improves glucose tolerance in mice. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2015, 8, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.K.; Mohan Rao, P.J.; Sen, A.P. Anxiogenic activity of intraventricularly administered bradykinin in rats. J. Psychopharmacol. 1995, 9, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdin, T.A.; Graeff, F.G.; Pelá, I.R. Opioid mediation of the antiaversive and hyperalgesic actions of bradykinin injected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray of the rat. Physiol. Behav. 1992, 52, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhiainen, A.; Kulesskaya, N.; Mennesson, M.; Misiewicz, Z.; Sipilä, T.; Sokolowska, E.; Trontti, K.; Urpa, L.; McEntegart, W.; Saarnio, S.; et al. The bradykinin system in stress and anxiety in humans and mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.E.; Cirincione, A.B.; Jimenez-Torres, A.C.; Zhu, J. The Impact of Neurotransmitters on the Neurobiology of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, R.A. Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, B.; Mahesh, V.B.; Bhat, G.K.; Ping, L.; Brann, D.W. Evidence for a role of bradykinin neurons in the control of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion. Neuroendocrinology 1998, 67, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messager, S.; Chatzidaki, E.E.; Ma, D.; Hendrick, A.G.; Zahn, D.; Dixon, J.; Thresher, R.R.; Malinge, I.; Lomet, D.; Carlton, M.B.; et al. Kisspeptin directly stimulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone release via G protein-coupled receptor 54. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Candlish, M.; Periasamy, V.; Avcu, N.; Mayer, C.; Boehm, U. Specialized subpopulations of kisspeptin neurons communicate with GnRH neurons in female mice. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, S.J.; Murray, E.K.; Poling, M.C.; Dhamija, S.; Forger, N.G.; Kauffman, A.S. BAX-dependent and BAX-independent regulation of Kiss1 neuron development in mice. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5807–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, S.B.Z.; Rouse, M.L.; Tolson, K.P.; Liaw, R.B.; Parra, R.A.; Chahal, N.; Kauffman, A.S. Effects of Selective Deletion of Tyrosine Hydroxylase from Kisspeptin Cells on Puberty and Reproduction in Male and Female Mice. eNeuro 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregnani, M.F.; Hungaro, T.G.; Martins-Silva, L.; Bader, M.; Araujo, R.C. Bradykinin B2 Receptor Signaling Increases Glucose Uptake and Oxidation: Evidence and Open Questions. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, K.T.; Steinberg, E.E.; DeLoach, K.E.; Xie, S.; Miyamichi, K.; Schwarz, L.; Gao, X.J.; Kremer, E.J.; Malenka, R.C.; Luo, L. Circuit Architecture of VTA Dopamine Neurons Revealed by Systematic Input-Output Mapping. Cell 2015, 162, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwin Thanarajah, S.; Iglesias, S.; Kuzmanovic, B.; Rigoux, L.; Stephan, K.E.; Brüning, J.C.; Tittgemeyer, M. Modulation of midbrain neurocircuitry by intranasal insulin. Neuroimage 2019, 194, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, J.; Brouwers, B.; Pruniau, V.P.; Stijnen, P.; de Faudeur, G.; Tuand, K.; Meulemans, S.; Serneels, L.; Schraenen, A.; Schuit, F.; et al. Metabolic and Behavioural Phenotypes in Nestin-Cre Mice Are Caused by Hypothalamic Expression of Human Growth Hormone. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.D.; Münzberg, H. Capricious Cre: The devil is in the details. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1005–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, J.A.B.; Dos Santos, L.B.P.; Furigo, I.C.; Spagnol, A.R.; Wasinski, F.; List, E.O.; Kopchick, J.J.; Donato, J., Jr. Deletion of growth hormone receptor in hypothalamic neurons affects the adaptation capacity to aerobic exercise. Peptides 2021, 135, 170426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viollet, C.; Simon, A.; Tolle, V.; Labarthe, A.; Grouselle, D.; Loe-Mie, Y.; Simonneau, M.; Martel, G.; Epelbaum, J. Somatostatin-IRES-Cre Mice: Between Knockout and Wild-Type? Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorgason, J.T.; España, R.A.; Konstantopoulos, J.K.; Weiner, J.L.; Jones, S.R. Enduring increases in anxiety-like behavior and rapid nucleus accumbens dopamine signaling in socially isolated rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 37, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Zhang, P.; Li, T.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; He, F.; Zhang, L.; Cai, H.; Lv, X.; Qiao, H.; et al. NAc-VTA circuit underlies emotional stress-induced anxiety-like behavior in the three-chamber vicarious social defeat stress mouse model. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweifel, L.S.; Fadok, J.P.; Argilli, E.; Garelick, M.G.; Jones, G.L.; Dickerson, T.M.; Allen, J.M.; Mizumori, S.J.; Bonci, A.; Palmiter, R.D. Activation of dopamine neurons is critical for aversive conditioning and prevention of generalized anxiety. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Q.; Cui, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, S.; Huang, F.; Xiao, L. D1 receptor-expressing neurons in ventral tegmental area alleviate mouse anxiety-like behaviors via glutamatergic projection to lateral septum. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibenhener, M.L.; Wooten, M.C. Use of the Open Field Maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, e52434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walf, A.A.; Frye, C.A. The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, W.O.; Gusmao, D.O.; Wasinski, F.; List, E.O.; Kopchick, J.J.; Donato, J., Jr. Effects of Growth Hormone Receptor Ablation in Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.L.F.; Medeiros, P.O.S.; Pedrão, L.; Queiroz, V.C.; Oliveira, L.M.; Novaes, L.S.; Caetano, A.L.; Munhoz, C.D.; Takakura, A.C.; Falquetto, B. Oxidative Stress Inhibition Via Apocynin Prevents Medullary Respiratory Neurodegeneration and Respiratory Pattern Dysfunction in a 6-Hydroxydopamine Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroscience 2022, 502, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro-Neto, E.F.; da Cunha, R.H.; da Silveira, D.X.; Yonamine, M.; Gouveia, T.L.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Amado, D.; Naffah-Mazzacoratti Mda, G. Changes in aminoacidergic and monoaminergic neurotransmission in the hippocampus and amygdala of rats after ayahuasca ingestion. World J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 4, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| VMA | NA | LDOPA | DOPAC | DA | HVA | 5HIAA | 5HT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SN | Control | 0.795 ± 0.53 | 0.660 ± 0.24 | 0.020 ± 0.06 | 0.235 ± 0.14 | 0.170 ± 0.04 | 0.245 ± 0.16 | 2.815 ± 0.85 | 0.800 ± 0.30 |
| THΔB2R | 0.555 ± 0.33 | 0.580 ± 0.30 | 0.035 ± 0.33 | 0.180 ± 0.84 | 0.125 ± 0.55 | 0.240 ± 0.36 | 2.840 ± 0.56 | 0.710 ± 0.20 | |
| P (T test) | 0.368 | 0.933 | 0.455 | 0.434 | 0.345 | 0.503 | 0.504 | 0.780 | |
| Cortex | Control | 0.560 ± 0.07 | 0.780 ± 0.10 | 0.020 ± 0.10 | 0.080 ± 0.11 | 0.05 ± 0.08 | 0.190 ± 0.10 | 1.430 ± 0.65 | 0.530 ± 0.10 |
| THΔB2R | 0.655 ± 0.20 | 0.625 ± 0.35 | 0.015 ± 0.03 | 0.060 ± 0.04 | 0.030 ± 0.02 | 0.125 ± 0.03 | 1.305 ± 0.67 | 0.420 ± 0.18 | |
| P (T test) | 0.385 | 0.939 | 0.218 | 0.156 | 0.145 | 0.066 | 0.570 | 0.163 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco, T.M.; Tavares, M.R.; Novaes, L.S.; Munhoz, C.D.; Peixoto-Santos, J.E.; Araujo, R.C.; Donato, J., Jr.; Bader, M.; Wasinski, F. Effects of Bradykinin B2 Receptor Ablation from Tyrosine Hydroxylase Cells on Behavioral and Motor Aspects in Male and Female Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031490
Franco TM, Tavares MR, Novaes LS, Munhoz CD, Peixoto-Santos JE, Araujo RC, Donato J Jr., Bader M, Wasinski F. Effects of Bradykinin B2 Receptor Ablation from Tyrosine Hydroxylase Cells on Behavioral and Motor Aspects in Male and Female Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031490
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco, Thaina Maquedo, Mariana R. Tavares, Leonardo S. Novaes, Carolina D. Munhoz, Jose Eduardo Peixoto-Santos, Ronaldo C. Araujo, Jose Donato, Jr., Michael Bader, and Frederick Wasinski. 2024. "Effects of Bradykinin B2 Receptor Ablation from Tyrosine Hydroxylase Cells on Behavioral and Motor Aspects in Male and Female Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031490
APA StyleFranco, T. M., Tavares, M. R., Novaes, L. S., Munhoz, C. D., Peixoto-Santos, J. E., Araujo, R. C., Donato, J., Jr., Bader, M., & Wasinski, F. (2024). Effects of Bradykinin B2 Receptor Ablation from Tyrosine Hydroxylase Cells on Behavioral and Motor Aspects in Male and Female Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031490






