Current Approaches to Worsening Heart Failure: Pathophysiological and Molecular Insights
Abstract
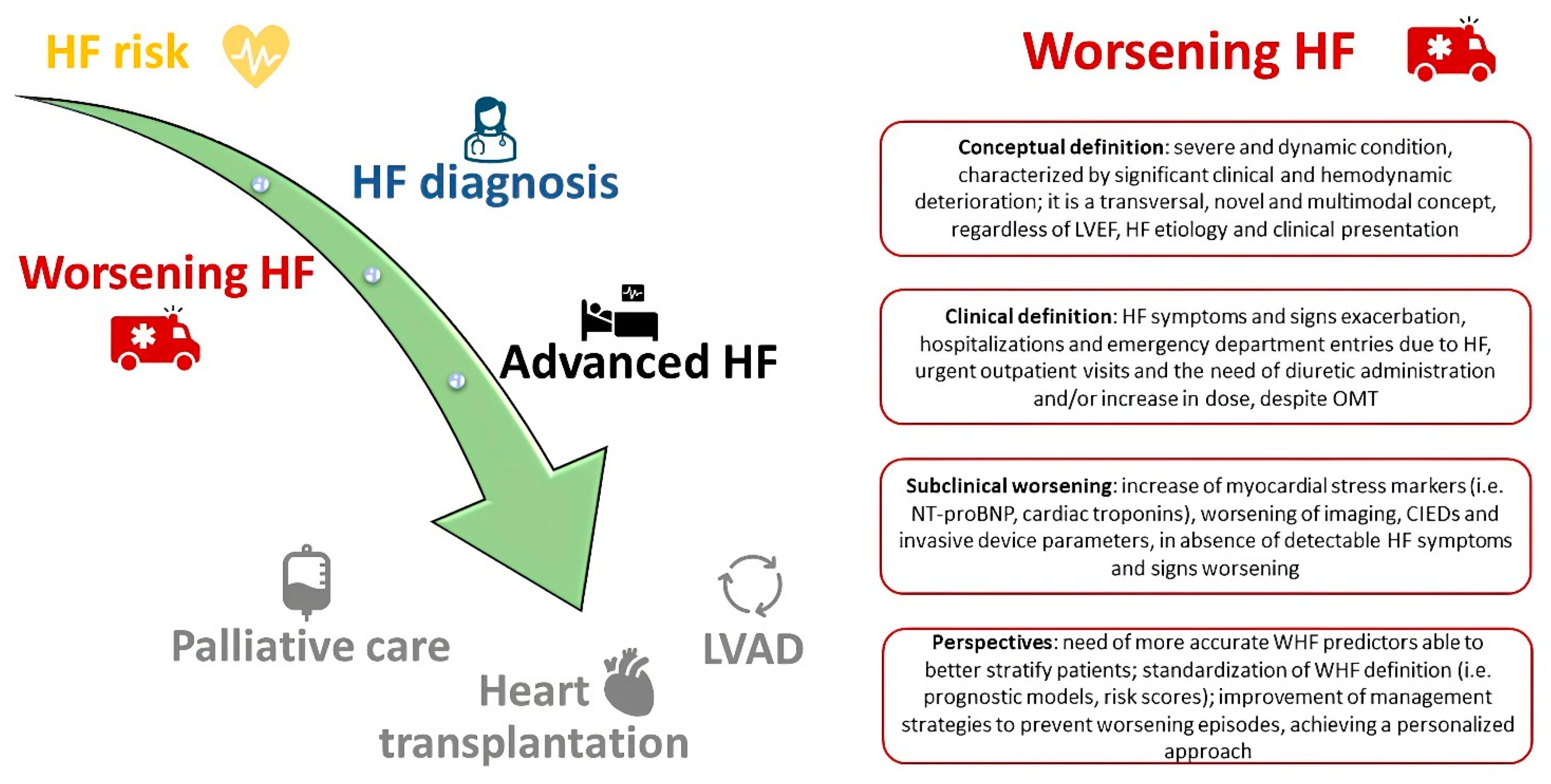
:1. Introduction
2. Repetitive Levosimendan Infusion in Worsening Heart Failure: The Achievement of Haemodynamic Stabilization
3. Innovative Pharmacological Targets in Worsening Heart Failure
4. The Management of Congestion: The Use of Diuretics and Some Innovative Combinations
5. Advances in Remote Monitoring Technologies for Heart Failure Management: Insights from CardioMEMS and Other Emerging Devices
6. When Pharmacological Therapy Is Not Enough: Cardiac Contractility Modulation and Baroceptor Activation Therapy
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, e263–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, S.J.; Bauersachs, J.; Brugts, J.J.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lund, L.H.; Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Zannad, F.; Zieroth, S.; et al. Worsening Heart Failure: Nomenclature, Epidemiology, and Future Directions: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metra, M.; Tomasoni, D.; Adamo, M.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Filippatos, G.; Abdelhamid, M.; Adamopoulos, S.; Anker, S.D.; Antohi, L.; Böhm, M.; et al. Worsening of chronic heart failure: Definition, epidemiology, management and prevention. A clinical consensus statement by the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 776–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Butler, J. The Importance of Worsening Heart Failure: Hiding in Plain Sight. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosy, A.P.; Parikh, R.V.; Sung, S.H.; Tan, T.C.; Narayanan, A.; Masson, R.; Lam, P.Q.; Kheder, K.; Iwahashi, A.; Hardwick, A.B.; et al. Analysis of Worsening Heart Failure Events in an Integrated Health Care System. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, A.S.; Fonarow, G.C.; Greene, S.J. Prioritizing prevention of de novo and worsening chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, P.; D’Amato, A.; Prosperi, S.; Dei Cas, A.; Mattioli, A.V.; Cevese, A.; Novo, G.; Prat, M.; Pedrinelli, R.; Raddino, R.; et al. Do the Current Guidelines for Heart Failure Diagnosis and Treatment Fit with Clinical Complexity? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, P.; D’Amato, A.; Prosperi, S.; Myftari, V.; Canuti, E.S.; Labbro Francia, A.; Cestiè, C.; Maestrini, V.; Lavalle, C.; Badagliacca, R.; et al. Heart Failure Pharmacological Management: Gaps and Current Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi, G.; Mariani, M.V.; Filomena, D.; Poscia, R.; Severino, P.; Iaconelli, A.; Recchioni, T.; Madonna, R.; Vizza, C.D.; Badagliacca, R. Biobanks: The unmet need in heart failure management. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2023, 150, 107179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; D’Amato, A.; Prosperi, S.; Fanisio, F.; Birtolo, L.I.; Costi, B.; Netti, L.; Chimenti, C.; Lavalle, C.; Maestrini, V.; et al. Myocardial Tissue Characterization in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: From Histopathology and Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Findings to Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebazaa, A.; Davison, B.; Chioncel, O.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Diaz, R.; Filippatos, G.; Metra, M.; Ponikowski, P.; Sliwa, K.; Voors, A.A.; et al. Safety, tolerability and efficacy of up-titration of guideline-directed medical therapies for acute heart failure (STRONG-HF): A multinational, open-label, randomised, trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 1938–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarese, G.; Kishi, T.; Vardeny, O.; Adamsson Eryd, S.; Bodegård, J.; Lund, L.H.; Thuresson, M.; Bozkurt, B. Heart Failure Drug Treatment-Inertia, Titration, and Discontinuation: A Multinational Observational Study (EVOLUTION HF). JACC Heart Fail. 2023, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2023 Focused Update of the 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3627–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, K.; Butler, J.; Fonarow, G.C. Residual risk in heart failure and the need for simultaneous implementation and innovation. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniades, C.; Tousoulis, D.; Koumallos, N.; Marinou, K.; Stefanadis, C. Levosimendan: Beyond its simple inotropic effect in heart failure. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 114, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, Z.; Édes, I.; Fruhwald, S.; De Hert, S.G.; Salmenperä, M.; Leppikangas, H.; Mebazaa, A.; Landoni, G.; Grossini, E.; Caimmi, P.; et al. Levosimendan: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications: Consensus of experts on the mechanisms of action of levosimendan. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 159, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.B.; Grossini, E.; Silva Cardoso, J.C.; Édes, I.; Fedele, F.; Pollesello, P.; Kivikko, M.; Harjola, V.P.; Hasslacher, J.; Mebazaa, A.; et al. Renal effects of levosimendan: A consensus report. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2013, 27, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heringlake, M.; Alvarez, J.; Bettex, D.; Bouchez, S.; Fruhwald, S.; Girardis, M.; Grossini, E.; Guarracino, F.; Herpain, A.; Toller, W.; et al. An update on levosimendan in acute cardiac care: Applications and recommendations for optimal efficacy and safety. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2021, 19, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altenberger, J.; Parissis, J.T.; Costard-Jaeckle, A.; Winter, A.; Ebner, C.; Karavidas, A.; Sihorsch, K.; Avgeropoulou, E.; Weber, T.; Dimopoulos, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the pulsed infusions of levosimendan in outpatients with advanced heart failure (LevoRep) study: A multicentre randomized trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comín-Colet, J.; Manito, N.; Segovia-Cubero, J.; Delgado, J.; García Pinilla, J.M.; Almenar, L.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Sionis, A.; Blasco, T.; Pascual-Figal, D.; et al. Efficacy and safety of intermittent intravenous outpatient administration of levosimendan in patients with advanced heart failure: The LION-HEART multicentre randomised trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, M.J.; de Mora-Martín, M.; López-Fernández, S.; López-Díaz, J.; Martínez-Sellés, M.; Romero-García, J.; Cordero, M.; Lara-Padrón, A.; Marrero-Rodríguez, F.; del Mar García-Saiz, M.; et al. Rationale and design of a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled multicenter trial to study efficacy, security, and long term effects of intermittent repeated levosimendan administration in patients with advanced heart failure: LAICA study. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2013, 27, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pölzl, G.; Altenberger, J.; Comín-Colet, J.; Delgado, J.F.; Fedele, F.; García-González, M.J.; Gustafsson, F.; Masip, J.; Papp, Z.; Störk, S.; et al. Repetitive levosimendan infusions for patients with advanced chronic heart failure in the vulnerable post-discharge period: The multinational randomized LeoDOR trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarone, D.; Kittleson, M.M.; Martucci, M.L.; Valente, F.; Gravino, R.; Verrengia, M.; Ammendola, E.; Contaldi, C.; Di Palma, V.; Caiazzo, A.; et al. Levosimendan as a “Bridge to Optimization” in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection—A Single-Center Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Juanatey, J.R.; Anguita-Sánchez, M.; Bayes-Genís, A.; Comín-Colet, J.; García-Quintana, A.; Recio-Mayoral, A.; Zamorano-Gómez, J.L.; Cepeda-Rodrigo, J.M.; Manzano, L. Vericiguat in heart failure: From scientific evidence to clinical practice. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2022, 222, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminiti, G.; Sposato, B.; Volterrani, M. Chronic heart failure: The role of di vericiguat. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2023, 25, C316–C318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, P.W.; Pieske, B.; Anstrom, K.J.; Ezekowitz, J.; Hernandez, A.F.; Butler, J.; Lam, C.S.P.; Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Jia, G.; et al. Vericiguat in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, S.J.; Bauersachs, J.; Brugts, J.J.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Filippatos, G.; Gustafsson, F.; Lam, C.S.-P.; Lund, L.H.; Mentz, R.J.; Pieske, B.; et al. Management of Worsening Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: JACC Focus Seminar 3/3. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senni, M.; Lopez-Sendon, J.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Ponikowski, P.; Nkulikiyinka, R.; Freitas, C.; Vlajnic, V.M.; Roessig, L.; Pieske, B. Vericiguat and NT-proBNP in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Analyses from the VICTORIA trial. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 3791–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planelles-Herrero, V.J.; Hartman, J.J.; Robert-Paganin, J.; Malik, F.I.; Houdusse, A. Mechanistic and structural basis for activation of cardiac myosin force production by omecamtiv mecarbil. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesJardin, J.T.; Teerlink, J.R. Inotropic therapies in heart failure and cardiogenic shock: An educational review. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2021, 10, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ráduly, A.P.; Tóth, A.; Sárkány, F.; Horváth, B.; Szentandrássy, N.; Nánási, P.P.; Csanádi, Z.; Édes, I.; Papp, Z.; Borbély, A. Omecamtiv mecarbil augments cardiomyocyte contractile activity both at resting and systolic Ca2+ levels. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teerlink, J.R.; Felker, G.M.; McMurray, J.J.; Solomon, S.D.; Adams, K.F., Jr.; Cleland, J.G.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Goudev, A.; Macdonald, P.; Metra, M.; et al. Chronic Oral Study of Myosin Activation to Increase Contractility in Heart Failure (COSMIC-HF): A phase 2, pharmacokinetic, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2895–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teerlink, J.R.; Diaz, R.; Felker, G.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Metra, M.; Solomon, S.D.; Legg, J.C.; Büchele, G.; Varin, C.; Kurtz, C.E.; et al. Omecamtiv Mecarbil in Chronic Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: Rationale and Design of GALACTIC-HF. JACC Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.D.; Voors, A.A.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Metra, M.; Whellan, D.J.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Böhm, M.; Teerlink, J.R.; Docherty, K.F.; Lopes, R.D.; et al. Effect of Omecamtiv Mecarbil on Exercise Capacity in Chronic Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: The METEORIC-HF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 328, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felker, G.M.; Solomon, S.D.; Claggett, B.; Diaz, R.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Metra, M.; Anand, I.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Dahlström, U.; Goncalvesova, E.; et al. Assessment of Omecamtiv Mecarbil for the Treatment of Patients with Severe Heart Failure: A Post Hoc Analysis of Data From the GALACTIC-HF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, M.G.; Walther, N.; Ferrannini, E.; Powell, D.R.; Banks, P.; Wason, S.; Dahmen, R. Metabolic, Intestinal, and Cardiovascular Effects of Sotagliflozin Compared with Empagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2118–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Szarek, M.; Steg, P.G.; Cannon, C.P.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Lewis, J.B.; Riddle, M.C.; Voors, A.A.; Metra, M.; et al. Sotagliflozin in Patients with Diabetes and Recent Worsening Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, P.; D’Amato, A.; Prosperi, S.; Costi, B.; Angotti, D.; Birtolo, L.I.; Chimenti, C.; Lavalle, C.; Maestrini, V.; Mancone, M.; et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and heart failure: The best timing for the right patient. Heart Fail. Rev. 2023, 28, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosperi, S.; D’Amato, A.; Severino, P.; Myftari, V.; Monosilio, S.; Marchiori, L.; Zagordi, L.M.; Filomena, D.; Di Pietro, G.; Birtolo, L.I.; et al. Sizing SGLT2 Inhibitors Up: From a Molecular to a Morpho-Functional Point of View. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Szarek, M.; Pitt, B.; Cannon, C.P.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Lewis, J.B.; Riddle, M.C.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; et al. Sotagliflozin in Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Pocock, S.J.; Carson, P.; Januzzi, J.; Verma, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Brueckmann, M.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, K.F.; McMurray, J.J.V. SOLOIST-WHF and updated meta-analysis: Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors should be initiated in patients hospitalized with worsening heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullens, W.; Damman, K.; Harjola, V.P.; Mebazaa, A.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Martens, P.; Testani, J.M.; Tang, W.H.W.; Orso, F.; Rossignol, P.; et al. The use of diuretics in heart failure with congestion—A position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiernan, M.S.; Stevens, S.R.; Tang, W.H.W.; Butler, J.; Anstrom, K.J.; Birati, E.Y.; Grodin, J.L.; Gupta, D.; Margulies, K.B.; LaRue, S.; et al. Determinants of Diuretic Responsiveness and Associated Outcomes During Acute Heart Failure Hospitalization: An Analysis From the NHLBI Heart Failure Network Clinical Trials. J. Card. Fail. 2018, 24, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.S.; Testani, J.M.; Pitt, B. Pathophysiology of Diuretic Resistance and Its Implications for the Management of Chronic Heart Failure. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Testani, J.; Collins, S. Diuretic Resistance in Heart Failure. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2019, 16, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felker, G.M.; Lee, K.L.; Bull, D.A.; Redfield, M.M.; Stevenson, L.W.; Goldsmith, S.R.; LeWinter, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Rouleau, J.L.; Ofili, E.O.; et al. Diuretic strategies in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentz, R.J.; Anstrom, K.J.; Eisenstein, E.L.; Sapp, S.; Greene, S.J.; Morgan, S.; Testani, J.M.; Harrington, A.H.; Sachdev, V.; Ketema, F.; et al. Effect of Torsemide vs. Furosemide After Discharge on All-Cause Mortality in Patients Hospitalized with Heart Failure: The TRANSFORM-HF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 329, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Braunwald, E. Mechanisms of Cardiorenal Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, P.C.; Bogoviku, J.; Westphal, J.; Aftanski, P.; Haertel, F.; Grund, S.; von Haehling, S.; Schumacher, U.; Möbius-Winkler, S.; Busch, M. Effects of Early Empagliflozin Initiation on Diuresis and Kidney Function in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (EMPAG-HF). Circulation 2022, 146, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damman, K.; Beusekamp, J.C.; Boorsma, E.M.; Swart, H.P.; Smilde, T.D.J.; Elvan, A.; van Eck, J.W.M.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Voors, A.A. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre pilot study on the effects of empagliflozin on clinical outcomes in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (EMPA-RESPONSE-AHF). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biegus, J.; Voors, A.A.; Collins, S.P.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Teerlink, J.R.; Angermann, C.E.; Tromp, J.; Ferreira, J.P.; Nassif, M.E.; Psotka, M.A.; et al. Impact of empagliflozin on decongestion in acute heart failure: The EMPULSE trial. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emara, A.N.; Wadie, M.; Mansour, N.O.; Shams, M.E.E. The clinical outcomes of dapagliflozin in patients with acute heart failure: A randomized controlled trial (DAPA-RESPONSE-AHF). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 961, 176179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullens, W.; Dauw, J.; Martens, P.; Verbrugge, F.H.; Nijst, P.; Meekers, E.; Tartaglia, K.; Chenot, F.; Moubayed, S.; Dierckx, R.; et al. Acetazolamide in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure with Volume Overload. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trullàs, J.C.; Morales-Rull, J.L.; Casado, J.; Carrera-Izquierdo, M.; Sánchez-Marteles, M.; Conde-Martel, A.; Dávila-Ramos, M.F.; Llácer, P.; Salamanca-Bautista, P.; Pérez-Silvestre, J.; et al. Combining loop with thiazide diuretics for decompensated heart failure: The CLOROTIC trial. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trullàs, J.C.; Morales-Rull, J.L.; Casado, J.; Freitas Ramírez, A.; Manzano, L.; Formiga, F.; CLOROTIC Investigators. Rationale and Design of the “Safety and Efficacy of the Combination of Loop with Thiazide-type Diuretics in Patients with Decompensated Heart Failure (CLOROTIC) Trial:” A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study to Determine the Effect of Combined Diuretic Therapy (Loop Diuretics with Thiazide-Type Diuretics) Among Patients with Decompensated Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2016, 22, 529–536. [Google Scholar]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, G.; Anker, S.D.; Agarwal, R.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Schloemer, P.; Tornus, I.; Joseph, A.; et al. Finerenone and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. Circulation 2021, 143, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, G.; Anker, S.D.; Agarwal, R.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G.L.; Tasto, C.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Lage, A.; et al. Finerenone Reduces Risk of Incident Heart Failure in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: Analyses From the FIGARO-DKD Trial. Circulation 2022, 145, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, G.; Anker, S.D.; Böhm, M.; Gheorghiade, M.; Køber, L.; Krum, H.; Maggioni, A.P.; Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Zannad, F.; et al. A randomized controlled study of finerenone vs. eplerenone in patients with worsening chronic heart failure and diabetes mellitus and/or chronic kidney disease. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugts, J.J.; Radhoe, S.P.; Aydin, D.; Theuns, D.A.; Veenis, J.F. Clinical Update of the Latest Evidence for CardioMEMS Pulmonary Artery Pressure Monitoring in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Promising System for Remote Heart Failure Care. Sensors 2021, 21, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, P.; Prosperi, S.; D’Amato, A.; Cestiè, C.; Myftari, V.; Maestrini, V.; Birtolo, L.I.; Filomena, D.; Mariani, M.V.; Lavalle, C.; et al. Telemedicine: An Effective and Low-Cost Lesson From the COVID-19 Pandemic for the Management of Heart Failure Patients. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2023, 20, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmbhatt, D.H.; Cowie, M.R. Remote Management of Heart Failure: An Overview of Telemonitoring Technologies. Card. Fail. Rev. 2019, 5, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, P.; D’Amato, A.; Prosperi, S.; Magnocavallo, M.; Maraone, A.; Notari, C.; Papisca, I.; Mancone, M.; Fedele, F. Clinical Support through Telemedicine in Heart Failure Outpatients during the COVID-19 Pandemic Period: Results of a 12-Months Follow Up. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.T.; Stevenson, L.W.; Bourge, R.C.; Lindenfeld, J.A.; Bauman, J.G.; Adamson, P.B. Sustained efficacy of pulmonary artery pressure to guide adjustment of chronic heart failure therapy: Complete follow-up results from the CHAMPION randomised trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavelle, D.M.; Desai, A.S.; Abraham, W.T.; Bourge, R.C.; Raval, N.; Rathman, L.D.; Heywood, J.T.; Jermyn, R.A.; Pelzel, J.; Jonsson, O.T.; et al. Lower Rates of Heart Failure and All-Cause Hospitalizations During Pulmonary Artery Pressure-Guided Therapy for Ambulatory Heart Failure: One-Year Outcomes from the CardioMEMS Post-Approval Study. Circ. Heart Fail. 2020, 13, e006863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugts, J.J.; Radhoe, S.P.; Clephas, P.R.D.; Aydin, D.; van Gent, M.W.F.; Szymanski, M.K.; Rienstra, M.; van den Heuvel, M.H.; da Fonseca, C.A.; Linssen, G.C.M.; et al. Remote haemodynamic monitoring of pulmonary artery pressures in patients with chronic heart failure (MONITOR-HF): A randomised clinical trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, M.E.; Qintar, M.; Windsor, S.L.; Jermyn, R.; Shavelle, D.M.; Tang, F.; Lamba, S.; Bhatt, K.; Brush, J.; Civitello, A.; et al. Empagliflozin Effects on Pulmonary Artery Pressure in Patients with Heart Failure: Results From the EMBRACE-HF Trial. Circulation 2021, 143, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amario, D.; Meerkin, D.; Restivo, A.; Ince, H.; Sievert, H.; Wiese, A.; Schaefer, U.; Trani, C.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Leyva, F.; et al. Safety, usability, and performance of a wireless left atrial pressure monitoring system in patients with heart failure: The VECTOR-HF trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restivo, A.; D’Amario, D.; Paglianiti, D.A.; Laborante, R.; Princi, G.; Cappannoli, L.; Iaconelli, A.; Galli, M.; Aspromonte, N.; Locorotondo, G.; et al. A 3-Year Single Center Experience with Left Atrial Pressure Remote Monitoring: The Long and Winding Road. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 899656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, W.S.; Wetterling, F.; Testani, J.M.; Borlaug, B.A.; Fudim, M.; Damman, K.; Gray, A.; Gaines, P.; Poloczek, M.; Madden, S.; et al. Safety and performance of a novel implantable sensor in the inferior vena cava under acute and chronic intravascular volume modulation. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glikson, M.; Nielsen, J.C.; Kronborg, M.B.; Michowitz, Y.; Auricchio, A.; Barbash, I.M.; Barrabés, J.A.; Boriani, G.; Braunschweig, F.; Brignole, M.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3427–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappannoli, L.; Scacciavillani, R.; Rocco, E.; Perna, F.; Narducci, M.L.; Vaccarella, M.; D’Amario, D.; Pelargonio, G.; Massetti, M.; Crea, F.; et al. Cardiac contractility modulation for patient with refractory heart failure: An updated evidence-based review. Heart Fail Rev. 2021, 26, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, A.R.; Samara, M.A.; Feldman, D.S. Cardiac contractility modulation therapy in advanced systolic heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2013, 10, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, A.R. Calcium cycling proteins and heart failure: Mechanisms and therapeutics. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunckhorst, C.B.; Shemer, I.; Mika, Y.; Ben-Haim, S.A.; Burkhoff, D. Cardiac contractility modulation by non-excitatory currents: Studies in isolated cardiac muscle. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2006, 8, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahwash, R.; Burkhoff, D.; Abraham, W.T. Cardiac contractility modulation in patients with advanced heart failure. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2013, 11, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figgitt, D.P.; Gillies, P.S.; Goa, K.L. Levosimendan. Drugs 2001, 61, 613–627, discussion 628–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.T.; Kuck, K.H.; Goldsmith, R.L.; Lindenfeld, J.; Reddy, V.Y.; Carson, P.E.; Mann, D.L.; Saville, B.; Parise, H.; Chan, R.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Cardiac Contractility Modulation. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borggrefe, M.M.; Lawo, T.; Butter, C.; Schmidinger, H.; Lunati, M.; Pieske, B.; Misier, A.R.; Curnis, A.; Böcker, D.; Remppis, A.; et al. Randomized, double blind study of non-excitatory, cardiac contractility modulation electrical impulses for symptomatic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallauria, F.; Cuomo, G.; Parlato, A.; Raval, N.Y.; Kuschyk, J.; Stewart Coats, A.J. A comprehensive individual patient data meta-analysis of the effects of cardiac contractility modulation on functional capacity and heart failure-related quality of life. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 2922–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, P.; Gennaro, F.; Mazzotta, G.; Acciarri, C.; Amabili, S.; Bonanni, C.; D’Antonio, A.; Delfino, D.; Di Vito, L.; Partemi, M.; et al. Cardiac Contractility Modulation Therapy in Patients with Amyloid Cardiomyopathy and Heart Failure, Case Report, Review of the Biophysics of CCM Function, and AMY-CCM Registry Presentation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierucci, N.; La Fazia, V.M.; Gianni, C.; Mohanty, S.; Lavalle, C.; Cishek, M.B.; Canby, R.C.; Natale, A. Cardiac contractility modulation in a patient with refractory systolic heart failure following orthotopic heart transplant. Heart Rhythm. Case Rep. 2024, 10, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, M.; Wu, M.; Lin, L. Advances in device-based treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Evidence from clinical trials. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, C.; Madej, T.; Mangner, N.; Hommel, J.; Grimm, S.; Knaut, M.; Linke, A.; Winzer, E.B. Baroreflex activation therapy in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: A single-centre experience. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 3373–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zile, M.R.; Lindenfeld, J.A.; Weaver, F.A.; Zannad, F.; Galle, E.; Rogers, T.; Abraham, W.T. Baroreflex Activation Therapy in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W.T.; Zile, M.R.; Weaver, F.A.; Butter, C.; Ducharme, A.; Halbach, M.; Klug, D.; Lovett, E.G.; Müller-Ehmsen, J.; Schafer, J.E.; et al. Baroreflex Activation Therapy for the Treatment of Heart Failure with a Reduced Ejection Fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2015, 3, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, P.; Mancone, M.; D’Amato, A.; Mariani, M.V.; Prosperi, S.; Alunni Fegatelli, D.; Birtolo, L.I.; Angotti, D.; Milanese, A.; Cerrato, E.; et al. Heart failure ‘the cancer of the heart’: The prognostic role of the HLM score. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, S.J.; Butler, J.; Fonarow, G.C. In-hospital initiation of quadruple medical therapy for heart failure: Making the post-discharge vulnerable phase far less vulnerable. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Drug | Trials and Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Levosimendan | LevoRep trial: Intermittent Levosimendan infusion did not significantly improve patients’ functional capacity and quality of life. | [20] |
| LION-HEART trial: Intermittent Levosimendan administration was effective in decreasing the serum concentration of NT-proBNP and was associated with improvement in clinical symptoms. | [21] | |
| LAICA study: Repetitive Levosimendan infusion is effective in reducing the HF hospitalization rate and HF worsening in patients with advanced HF. | [22] | |
| LeoDOR trial: Repetitive Levosimendan administration in patients with a recent HF hospitalization did not result in post-hospitalization clinical stability. | [23] | |
| Vericiguat | VICTORIA trial: The primary composite of death from cardiovascular causes or first hospitalization for HF was lower in those who received Vericiguat. | [27] |
| Omecamtiv Mecarbil | GALACTIC-HF trial: The primary composite endpoint of hospitalization or urgent visit for HF and death from cardiovascular causes is reduced in patients treated with OM. | [34] |
| METEORIC-HF trial: OM did not increase exercise capacity after 20 weeks of treatment. | [35] | |
| COSMIC-HF trial: Guiding the administration of OM through drug pharmacokinetic is associated with reduction in ventricular diameter and cardiac function improvement. | [33] | |
| Sotagliflozin | SOLOIST-WHF trial: The primary endpoint, a combination of total number of cardiovascular deaths, hospitalizations and urgent visits for HF, resulted lower, and the benefits of an early initiation of Sotagliflozin, before or immediately after hospital discharge, was highlighted. | [38] |
| SCORED trial: Sotagliflozin reduced the composite endpoint of HF hospitalization, urgent ambulatory visit and cardiovascular death, along with major incidence of adverse events. | [41] |
| Drug | Trials and Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| SGLT2i | EMPAG-HF: In patients with acute decompensated HF, the early initiation of Empagliflozin on top of standard diuretic improves urinary output. | [52] |
| EMPA-RESPONSE-AHF: In acute HF patients, the use of Empagliflozin is associated with reduction in WHF, death and rehospitalization, and increased urinary output. | [53] | |
| EMPULSE trial: Starting Empagliflozin in patients admitted for AHF is associated with early and effective decongestion. | [54] | |
| DAPA-RESPONSE-AHF: In patients with acute HF, Dapagliflozin is associated with diuresis and symptoms improvement. | [55] | |
| Acetazolamide | ADVOR trial: In patients with acute decompensated HF, the addition of Acetazolamide on top of furosemide is associated with increased rate of decongestion. | [56] |
| HCTZ | CLOROTIC trial: Patients treated with HCTZ on top of intravenous furosemide show significant weight loss and better 24-h urinary output, but no difference in terms of dyspnoea. | [57,58] |
| Finerenone | FIDELIO-DKD: Finerenone reduces the risk of kidney disease progression and cardiovascular events, including HF hospitalization, in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. | [59] |
| FIGARO-DKD: Finerenone reduces the incidence of new HF and improved HF outcomes in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease, regardless of HF presence. | [61] | |
| ARTS-HF: Finerenone determines a significant reduction in NT proBNP levels in patients with WHF and diabetes mellitus and/or chronic kidney disease. | [62] |
| Device | Trials and Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CardioMEMS | CHAMPION trial: Significant reduction in HF hospital admissions in patients with daily PAP monitoring through CardioMEMS was observed. | [67] |
| MONITOR-HF trial: CardioMEMS improves the QoL of HF patients with a significant increase in KCCQ-12 score. | [69] | |
| EMBRACE-HF trial: A prompt reduction in PAP in patients treated with Empagliflozin and monitored with CardioMEMS was observed. | [70] | |
| V-LAP | VECTOR-HF study: A significant correlation was found between the mean LA pressure and mean PCWP. | [71] |
| CCM | FIX-HF-4 study and FIX-HF-5: CCM is safe and effective in improving exercise tolerance and QoL, while reducing HF hospitalizations. | [81,82] |
| BAT | BeAT-HF study and HOPE4HF study: BAT therapy significantly improves QoL, exercise capacity and reduced NT-proBNP levels. | [88,89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Amato, A.; Prosperi, S.; Severino, P.; Myftari, V.; Labbro Francia, A.; Cestiè, C.; Pierucci, N.; Marek-Iannucci, S.; Mariani, M.V.; Germanò, R.; et al. Current Approaches to Worsening Heart Failure: Pathophysiological and Molecular Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031574
D’Amato A, Prosperi S, Severino P, Myftari V, Labbro Francia A, Cestiè C, Pierucci N, Marek-Iannucci S, Mariani MV, Germanò R, et al. Current Approaches to Worsening Heart Failure: Pathophysiological and Molecular Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031574
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Amato, Andrea, Silvia Prosperi, Paolo Severino, Vincenzo Myftari, Aurora Labbro Francia, Claudia Cestiè, Nicola Pierucci, Stefanie Marek-Iannucci, Marco Valerio Mariani, Rosanna Germanò, and et al. 2024. "Current Approaches to Worsening Heart Failure: Pathophysiological and Molecular Insights" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031574
APA StyleD’Amato, A., Prosperi, S., Severino, P., Myftari, V., Labbro Francia, A., Cestiè, C., Pierucci, N., Marek-Iannucci, S., Mariani, M. V., Germanò, R., Fanisio, F., Lavalle, C., Maestrini, V., Badagliacca, R., Mancone, M., Fedele, F., & Vizza, C. D. (2024). Current Approaches to Worsening Heart Failure: Pathophysiological and Molecular Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031574







