Effects of a Combination of Polynucleotide and Hyaluronic Acid for Treating Osteoarthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
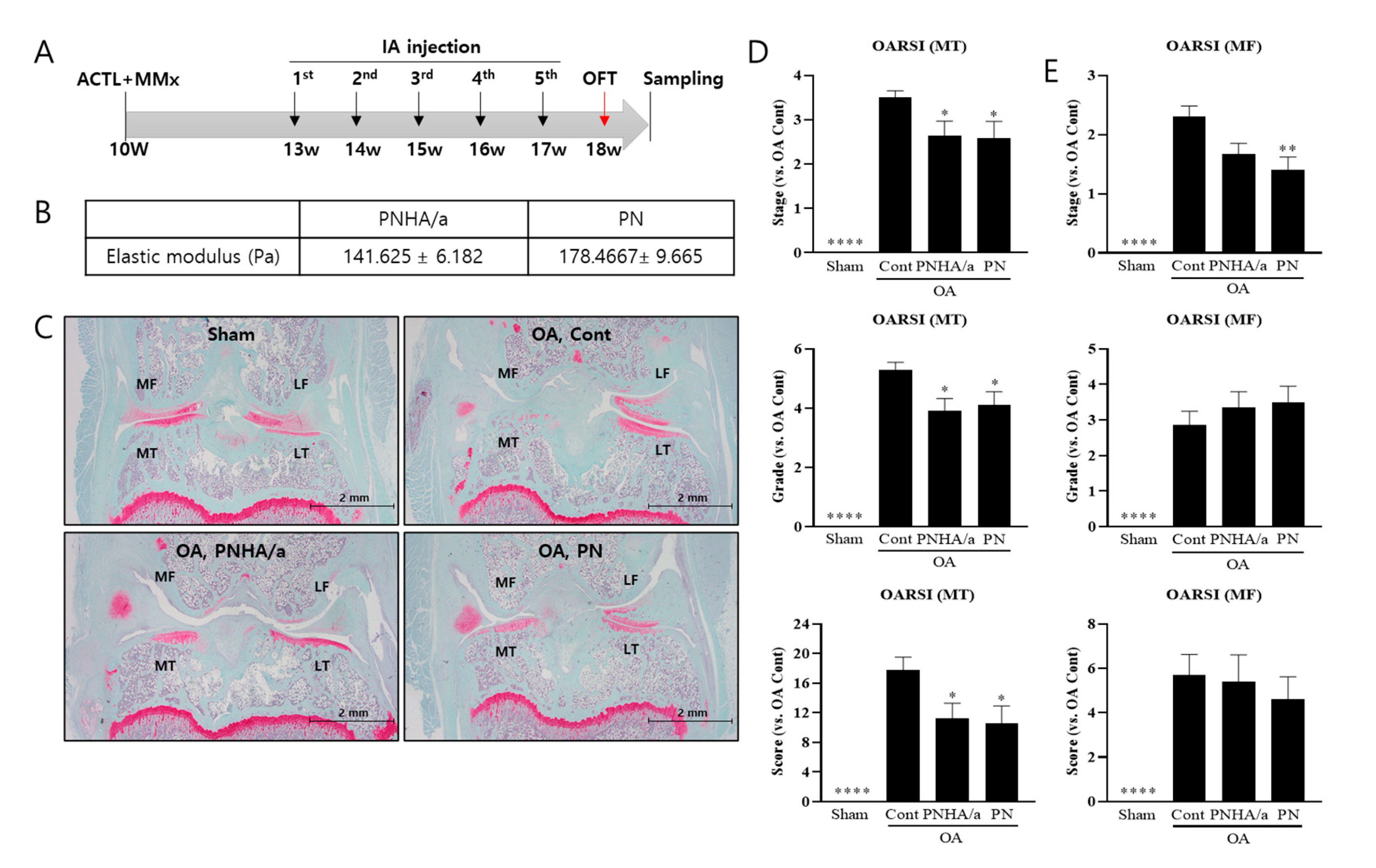
2.1. IA injection of PNHA/a Delays Cartilage Degeneration
2.2. PNHA/a Rescues Locomotor Activity in the OA Rat Model
2.3. IA Injection of PNHA/b Suppresses MMP13 Expression
2.4. IA Injection of PNHA/b Reduces TNFα Levels in OA Cartilage
2.5. PNHA/b Rescued Locomotor Activity in the OA Rat Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Manufacturing
4.2. Animal OA Models
4.3. OFT for Locomotor Activity
4.4. Histological Staining
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lohmander, L.S. What can we do about osteoarthritis? Arthritis Res. 2000, 2, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozeki, N.; Koga, H.; Sekiya, I. Degenerative Meniscus in Knee Osteoarthritis: From Pathology to Treatment. Life 2022, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WWang, M.; Tan, G.; Jiang, H.; Liu, A.; Wu, R.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.; Lv, Z.; Sun, W.; Shi, D. Molecular crosstalk between articular cartilage, meniscus, synovium, and subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res. 2022, 11, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, L.A.; Ahmed, G.; Dakin, S.G.; Kendrick, B.; Price, A. Osteoarthritis: A narrative review of molecular approaches to disease management. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, N.; Yan, Z.P.; Chen, X.Y.; Ni, G.X. Infrapatellar Fat Pad and Knee Osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanella, C.G.; Belluzzi, E.; Pozzuoli, A.; Scioni, M.; Olivotto, E.; Reale, D.; Ruggieri, P.; De Caro, R.; Ramonda, R.; Carniel, E.L.; et al. Exploring Anatomo-Morphometric Characteristics of Infrapatellar, Suprapatellar Fat Pad, and Knee Ligaments in Osteoarthritis Compared to Post-Traumatic Lesions. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, Y.A.; Ju, J.H. The Role of Fibrosis in Osteoarthritis Progression. Life 2020, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, V.; Matišić, V.; Kodvanj, I.; Bjelica, R.; Jeleč, Ž.; Hudetz, D.; Rod, E.; Čukelj, F.; Vrdoljak, T.; Vidović, D.; et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wu, Y.-L.; Li, C.; Wang, M.-L.; Ma, X.-X.; Liu, J.-W.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Yang, L. Warming moxibustion attenuates inflammation and cartilage degradation in experimental rabbit knee osteoarthriti. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 41, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sampson, E.R.; Jin, H.; Li, J.; Ke, Q.H.; Im, H.J.; Chen, D. MMP13 is a critical target gene during the progression of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, W.H.; Lepus, C.M.; Wang, Q.; Raghu, H.; Mao, R.; Lindstrom, T.M.; Sokolove, J. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, M.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Lajeunesse, D.; Pelletier, J.P.; Fahmi, H. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.C.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Pelletier, J.P. The role of cytokines in osteoarthritis pathophysiology. Biorheology 2002, 39, s237–s246. [Google Scholar]
- Kloppenburg, M. Inflammation is a relevant treatment target in osteoarthritis. Lancet 2023, 402, 1725–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Sun, Y.T.; Chen, J.J.; Chiu, K.T. TNF-alpha-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human lung epithelial cells: Involvement of the phospholipase C-gamma 2, protein kinase C-alpha, tyrosine kinase, NF-kappa B-inducing kinase, and I-kappa B kinase 1/2 pathway. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2719–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, F.; Fan, C.; Wang, C.; Ruan, H. Analysis of isoform specific ERK signaling on the effects of interleukin-1β on COX-2 expression and PGE2 production in human chondrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 402, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.L.; Berry, H.; Capell, H.; Coppock, J.; Daymond, T.; Doyle, D.V.; Fernandes, L.; Hazleman, B.; Hunter, J.; Huskisson, E.C.; et al. The long-term effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in osteoarthritis of the knee: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatology 2000, 39, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, B.R.; Reichenbach, S.; Keller, N.; Nartey, L.; Wandel, S.; Jüni, P.; Trelle, S. Effectiveness of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of pain in knee and hip osteoarthritis: A network meta-analysis. Lancet 2017, 390, e21–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruyère, O.; Cooper, C.; Pelletier, J.P.; Maheu, E.; Rannou, F.; Branco, J.; Luisa Brandi, M.; Kanis, J.A.; Altman, R.D.; Hochberg, M.C.; et al. A consensus statement on the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO) algorithm for the management of knee osteoarthritis-From evidence-based medicine to the real-life setting. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 45 (Suppl. S4), S3–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruyère, O.; Cooper, C.; Pelletier, J.P.; Branco, J.; Luisa Brandi, M.; Guillemin, F.; Hochberg, M.C.; Kanis, J.A.; Kvien, T.K.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; et al. An algorithm recommendation for the management of knee osteoarthritis in Europe and internationally: A report from a task force of the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO). Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 44, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannitti, T.; Lodi, D.; Palmieri, B. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis: Focus on the clinical use of hyaluronic acid. Drugs 2011, 11, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trelle, S.; Reichenbach, S.; Wandel, S.; Hildebrand, P.; Tschannen, B.; Villiger, P.M.; Egger, M.; Jüni, P. Cardiovascular safety of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Network meta-analysis. BMJ 2011, 342, c7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliore, A.; Procopio, S. Effectiveness and utility of hyaluronic acid in osteoarthritis. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2015, 12, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasin, A.; Ren, Y.; Li, J.; Sheng, Y.; Cao, C.; Zhang, K. Advances in Hyaluronic Acid for Biomedical Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 910290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalczyk, M.; Humeniuk, E.; Adamczuk, G.; Korga-Plewko, A. Hyaluronic Acid as a Modern Approach in Anticancer Therapy-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, M.G.; Nanau, R.M.; Oruña-Sanchez, L.; Coto, G. Hyaluronic acid and wound healing. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 18, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowman, M.K.; Schmidt, T.A.; Raghavan, P.; Stecco, A. Viscoelastic Properties of Hyaluronan in Physiological Conditions. F1000Res 2015, 4, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iaconisi, G.N.; Lunetti, P.; Gallo, N.; Cappello, A.R.; Fiermonte, G.; Dolce, V.; Capobianco, L. Hyaluronic Acid: A Powerful Biomolecule with Wide-Ranging Applications—A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Q.; Chou, P.-L.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chiang, C.-C.; Wei, M.-T.; Chuang, C.-T.; Chen, Y.-L.S.; Chiou, A. Microrheology of human synovial fluid of arthritis patients studied by diffusing wave spectroscopy. J. Biophotonics 2012, 5, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, R.D.; Bedi, A.; Karlsson, J.; Sancheti, P.; Schemitsch, E. Product Differences in Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acids for Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Am. J. Sports Med. 2016, 44, 2158–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, R.D.; Manjoo, A.; Fierlinger, A.; Niazi, F.; Nicholls, M. The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanelli, R.; Costa, P.; Rossi, S.M.; Benazzo, F. Efficacy of intra-articular polynucleotides in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2010, 18, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saggini, R.; Di Stefano, A.; Cavezza, T.; Saladino, G.; Bellomo, R.G. Intrarticular treatment of osteoartropaty knee with polynucleotides: A pilot study with medium-term follow-up. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2013, 27, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giarratana, L.S.; Marelli, B.M.; Crapanzano, C.; De Martinis, S.E.; Gala, L.; Ferraro, M.; Marelli, N.; Albisetti, W. A randomized double-blind clinical trial on the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: The efficacy of polynucleotides compared to standard hyaluronian viscosupplementation. Knee 2014, 21, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.N.; Lee, Y.J.; Sim, S.E.; Ko, Y.R.; Shim, J.W.; Lee, K.S.; Joo, M.; Park, H.J. Pilot Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of Polynucleotide Sodium Compared to Sodium Hyaluronate and Crosslinked Sodium Hyaluronate in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.W.; Chang, M.J.; Shin, C.Y.; Chang, C.B.; Kang, S.B. A randomized controlled trial for comparing efficacy and safety between intraarticular polynucleotide and hyaluronic acid for knee osteoarthritis treatment. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Huh, C.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, M.Y. Histologic study of bone-forming capacity on polydeoxyribonucleotide combined with demineralized dentin matrix. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 38, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, F.; Dallari, D.; Sabbioni, G.; Carubbi, C.; Martini, L.; Fini, M. Polydeoxyribonucleotides (PDRNs) from Skin to Musculoskeletal Tissue Regeneration via Adenosine A. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitto, A.; Polito, F.; Irrera, N.; D’Ascola, A.; Avenoso, A.; Nastasi, G.; Campo, G.M.; Micali, A.; Bagnato, G.; Minutoli, L.; et al. Polydeoxyribonucleotide reduces cytokine production and the severity of collagen-induced arthritis by stimulation of adenosine A2A receptor. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3364–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallari, D.; Sabbioni, G.; Del Piccolo, N.; Carubbi, C.; Veronesi, F.; Torricelli, P.; Fini, M. Efficacy of Intra-Articular Polynucleotides Associated with Hyaluronic Acid versus Hyaluronic Acid Alone in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. J. Sport. Med. 2020, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.W.; Kim, S.H.; Yong, S.Y. Study of the Efficacy of Artificial Intelligence Algorithm-Based Analysis of the Functional and Anatomical Improvement in Polynucleotide Treatment in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: A Prospective Case Series. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagni, C.; Rocchi, M.; Mazzotta, A.; Del Piccolo, N.; Rani, N.; Govoni, M.; Vivarelli, L.; Veronesi, F.; Fini, M.; Dallari, D. Randomised, double-blind comparison of a fixed co-formulation of intra-articular polynucleotides and hyaluronic acid versus hyaluronic acid alone in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: Two-year follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, T.; Pickarski, M.; Zhuo, Y.; Wesolowski, G.A.; Rodan, G.A.; Duong, L.T. Characterization of articular cartilage and subchondral bone changes in the rat anterior cruciate ligament transection and meniscectomized models of osteoarthritis. Bone 2006, 38, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, G.; Giardina, S.M.C.; Culmone, A.; Vescio, A.; Turchetta, M.; Cannavò, S.; Pavone, V. Intra-Articular Injections in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review of Literature. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2021, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis, A.; Miralles, A.; Schmidt, R.F.; Belmonte, C. Intra-articular injections of hyaluronan solutions of different elastoviscosity reduce nociceptive nerve activity in a model of osteoarthritic knee joint of the guinea pig. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2009, 17, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwin, N.; Bendele, A.M.; Glasson, S.; Carlson, C.S. The OARSI histopathology initiative–recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rat. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18 (Suppl. S3), S24–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevet, S.; Favier, B.; Brun, E.; Gavazzi, G.; Lardy, B. Mouse Models of Osteoarthritis: A Summary of Models and Outcomes Assessment. Comp. Med. 2022, 72, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, B.Y.; Allen, K.D. Factors affecting the reliability of behavioral assessments for rodent osteoarthritis models. Lab. Anim. 2020, 54, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, H.J.; Oh, M.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Eom, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.-N.; Chung, K.S.; Jang, H.J. Effects of salmon DNA fraction. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 22, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambamurthy, N.; Nguyen, V.; Smalley, R.; Xiao, R.; Hankenson, K.; Gan, J.; Miller, R.E.; Malfait, A.; Dodge, G.R.; Scanzello, C.R. Chemokine receptor-7 (CCR7) deficiency leads to delayed development of joint damage and functional deficits in a murine model of osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.E.; Tran, P.B.; Das, R.; Ghoreishi-Haack, N.; Ren, D.; Miller, R.J.; Malfait, A.-M. CCR2 chemokine receptor signaling mediates pain in experimental osteoarthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20602–20607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, M.Z.; Patel, R.M.; Dawson, B.C.; Jiang, M.M.; Lee, B.H. Pain, motor and gait assessment of murine osteoarthritis in a cruciate ligament transection model. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.J.; Couto, M.; Sousa, D.M.; Magalhães, A.; Neto, E.; Leitão, L.; Conceição, F.; Monteiro, A.C.; Ribeiro-Da-Silva, M.; Lamghari, M. Nociceptive mechanisms driving pain in a post-traumatic osteoarthritis mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, A.S.; Kumari, R.R.; Gupta, G.; Lingaraju, M.C.; Balaganur, V.; Pathak, N.N.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, D.; Sharma, A.K.; Tandan, S.K. Effect of iNOS inhibitor S-methylisothiourea in monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoathritic pain: Implication for osteoarthritis therapy. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 103, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsalem, M.; Haddad, M.; Altarifi, A.; Aldossary, S.A.; Kalbouneh, H.; Abojaradeh, A.M.; El-Salem, K. Impairment in locomotor activity as an objective measure of pain and analgesia in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, A.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, S.R.; Kim, H.J. Anti-inflammatory Effect of DNA Polymeric Molecules in a Cell Model of Osteoarthritis. Inflammation 2018, 41, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wagner, E.S.; Yu, D.; Chen, K.J.; Keel, T.J.; Pownder, S.L.; Koff, M.F.; Cheetham, J.; Samaroo, K.J.; Reesink, H.L. Assessment of osteoarthritis functional outcomes and intra-articular injection volume in the rat anterior cruciate ligament transection model. J. Orthop. Res. 2022, 40, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, D.; Yang, H. Protocatechuic acid attenuates anterior cruciate ligament transection-induced osteoarthritis by suppressing osteoclastogenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugasawa, T.; Kuji, T.; Aoki, K.; Yanazawa, K.; Takenouchi, A.; Watanabe, M.; Tome, Y.; Takeuchi, Y.; Aita, Y.; Yahagi, N.; et al. Characterization of Osteoarthritis in a Medial Meniscectomy-Induced Animal Model Using Contrast-Enhanced X-ray Microtomography. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubomura, D.; Ueno, T.; Yamada, M.; Nagaoka, I. Evaluation of the chondroprotective action of N-acetylglucosamine in a rat experimental osteoarthritis model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb.prot4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custers, R.J.; Creemers, L.B.; Verbout, A.J.; van Rijen, M.H.; Dhert, W.J.; Saris, D.B. Reliability, reproducibility and variability of the traditional Histologic/Histochemical Grading System vs the new OARSI Osteoarthritis Cartilage Histopathology Assessment System. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2007, 15, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritzker, K.P.H.; Gay, S.; Jimenez, S.A.; Ostergaard, K.; Pelletier, J.-P.; Revell, P.A.; Salter, D.; van den Berg, W.B. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: Grading and staging. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2006, 14, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Stage | % Involvement (Surface, Area, Volume) |
| Stage 0 | No OA activity |
| Stage 1 | <10% |
| Stage 2 | 11–25% |
| Stage 3 | 26–50% |
| Stage 4 | >50% |
| Grade | Associated Criteria (Tissue Reaction) |
| Grade 0: Surface, cartilage intact | Matrix: normal architecture Cells: intact, appropriate orientation |
| Grade 1: Surface intact | Matrix: superficial zone intact, oedema and/or superficial fibrillation (abrasion), focal superficial matrix condensation Cells: death, proliferation (clusters), hypertrophy, superficial zone Reaction must be more than superficial fibrillation only |
| Grade 2: Surface discontinuity | As above +Matrix discontinuity at superficial zone (deep fibrillation) ±Cationic stain matrix depletion (Safranin O or Toluidine Blue) upper 1/3 of cartilage ±Focal peri-chondronal increased stain (mid zone) ±Disorientation of chondron columns Cells: death, proliferation (clusters), hypertrophy |
| Grade 3: Vertical fissures (clefts) | As above +Matrix vertical fissures into mid zone, branched fissures ±Cationic stain depletion (Safranin O or Toluidine Blue) into lower 2/3 of cartilage (deep zone) ±New collagen formation (polarized light microscopy, Picro Sirius Red stain) Cells: death, regeneration (clusters), hypertrophy, cartilage domains adjacent to fissures |
| Grade 4: Erosion | Cartilage matrix loss: delamination of superficial layer, mid layer cyst formation Excavation: matrix loss superficial layer and mid zone |
| Grade 5: Denudation | Sclerotic bone or reparative tissue including fibrocartilage within denuded surface. Microfracture with repair limited to bone surface |
| Grade 6: Deformation | Bone remodeling (more than osteophyte formation only). Includes: microfracture with fibrocartilaginous and osseous repair extending above the previous surface |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.C.; Jang, S.G.; Lee, Y.J.; Heo, J.Y.; Kweon, G.R.; Ryu, M.J. Effects of a Combination of Polynucleotide and Hyaluronic Acid for Treating Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031714
Choi SH, Kim HC, Jang SG, Lee YJ, Heo JY, Kweon GR, Ryu MJ. Effects of a Combination of Polynucleotide and Hyaluronic Acid for Treating Osteoarthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031714
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Seung Hee, Hyun Chul Kim, Seul Gi Jang, Yeon Jae Lee, Jun Young Heo, Gi Ryang Kweon, and Min Jeong Ryu. 2024. "Effects of a Combination of Polynucleotide and Hyaluronic Acid for Treating Osteoarthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031714
APA StyleChoi, S. H., Kim, H. C., Jang, S. G., Lee, Y. J., Heo, J. Y., Kweon, G. R., & Ryu, M. J. (2024). Effects of a Combination of Polynucleotide and Hyaluronic Acid for Treating Osteoarthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031714






