Mutations in the FOXO3 Gene and Their Effects on Meat Traits in Gannan Yaks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genetic Characteristics of the FOXO3 Gene SNPs in Gannan Yaks
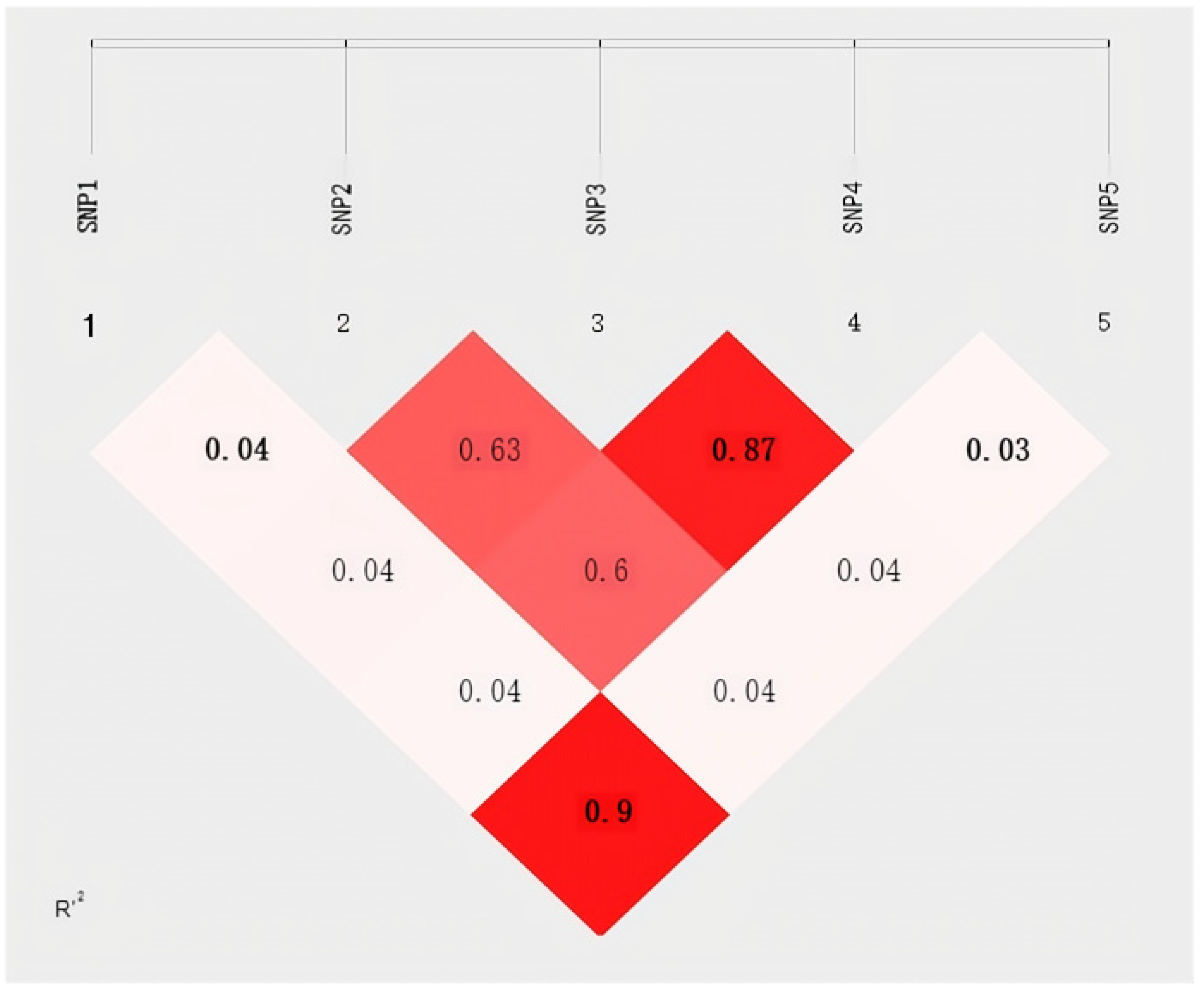
2.2. Gene Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis and Haplotype Construction in Gannan Yak’s FOXO3
2.3. Association of FOXO3 Genotypes with Meat Traits in Gannan Yaks
2.4. Effects of Haplotype Combinations on the Meat Traits of Gannan Yak Meat
2.5. Expression Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Selection
4.2. DNA Extraction and PCR
4.3. Genotype Testing
4.4. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, J.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z. Study on Genetic Diversity and Classification of the Yak. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2006, 39, 389–397. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Feng, T. Developing green yak meat industries in Datong Yak Breeding Farm of Qinghai province. In Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Yak, Chengdu, China, 20–26 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, B.; Yu, Q.; Ji, Q.; Xie, P.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. The Breed and Sex Effect on the Carcass Size Performance and Meat Quality of Yak in Different Muscles. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2016, 36, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzinger, C.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Rudnicki, M.A. Building Muscle: Molecular Regulation of Myogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Lai, X.; Xue, J.; Lan, X.; Lei, C.; Jia, Y.; Chen, H. Associations between polymorphisms in the NICD domain of bovine NOTCH1 gene and growth traits in Chinese Qinchuan cattle. J. Appl. Genet. 2016, 58, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, R.; Ruo, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J.; et al. Variation in the HSL Gene and Its Association with Carcass and Meat Quality Traits in Yak. Animals 2023, 13, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Chai, Z.-X.; Cao, H.-W.; Zhang, C.-F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xin, J.-W. Genome-wide identification of SNPs associated with body weight in yak. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hribal, M.L.; Nakae, J.; Kitamura, T.; Shutter, J.R. Regulation of insulin-like growth facto-dependent myoblast differentiation by Foxo forkhead transcription factors. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stitt, T.N.; Drujan, D.; Clarke, B.A.; Panaro, F.; Timofeyva, Y.; Kline, W.O.; Gonzalez, M.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Glass, D.J. The IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway prevents expression of muscle atrophy-induced ubiquitin ligases by inhibiting FOXO transcription factors. Mol. Cell 2004, 14, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamei, Y.; Mizukami, J.; Miura, S.; Suzuki, M.; Takahashi, N.; Kawada, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Ezaki, O. A forkhead transcription factor FKHR up-regulates lipoprotein lipase expression in skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 2003, 536, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-R.; Jung, H.S.; Bae, S.-W.; Kim, J.H.; Park, B.L.; Choi, Y.H.; Cho, H.Y.; Cheong, H.S.; Shin, H.D. Polymorphisms in FOXO gene family and association analysis with BMI. Obesity 2006, 14, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, J.; He, X.; Xu, H.; Li, G.; Du, H.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, X. A Genome-Wide mRNA Screen and Functional Analysis Reveal FOXO3 as a Candidate Gene for Chicken Growth. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.L.; Bridgham, J.T.; Swenson, J.A. Activation of the Akt/protein kinase B signaling pathway is associated with granulosa cell survival. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 64, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, C.; Su, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Hu, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L.; Jin, Y. Effect of dietary arginine supplementation on protein synthesis, meat quality and flavor in growing lambs. Meat Sci. 2023, 204, 109291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, K.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Chen, H. Differential expression of FOXO1 during development and myoblast differentiation of Qinchuan cattle and its association analysis with growth traits. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammucari, C.; Milan, G.; Romanello, V.; Masiero, E.; Rudolf, R.; Del Piccolo, P.; Burden, S.J.; Di Lisi, R.; Sandri, C.; Zhao, J.; et al. FoxO3 controls autophagy in skeletal muscle in vivo. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.C.; Wu, C.W.; Li, C.I.; Wu, F.Y.; Lin, C.C. Interactions among IGF-1, AKT2, FOXO1, and FOXO3 variations and between genes and physical activities on physical performance in community-dwelling elders. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soerensen, M.; Nygaard, M.; Dato, S.; Stevnsner, T.; Bohr, V.A.; Christensen, K.; Christiansen, L. Association study of FOXO3A SNPs and aging phenotypes in Danish oldest-old individuals. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdel, M.; Durairaj, J.; de Ridder, D.; van Dijk, A.D.J. Caretta—A multiple protein structure alignment and feature extraction suite. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Vignato, B.; Cesar, A.S.M.; Afonso, J.; Moreira, G.C.M.; Poleti, M.D.; Petrini, J.; Garcia, I.S.; Clemente, L.G.; Mourao, G.B.; Regitano, L.C.D.; et al. Integrative Analysis Between Genome-Wide Association Study and Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Reveals Bovine Muscle Gene Expression Regulatory Polymorphisms Associated with Intramuscular Fat and Backfat Thickness. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 935238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ni, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, X. Tissue Expression and Polymorphism of Jiangquhai Pig FoxO3 Gene and Their Associationswith Meat Quality. Henan Agric. Sci. 2021, 50, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.W.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.X. Yak FOXO1 and FOXO3 SNPs and association with production traits, and their promotes cells apoptosis via RNAi. Gene 2020, 743, 144592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco, G.; Hinks, A.; Eyre, S.; Ke, X.; Worthington, J. Combined effects of three independent SNPs greatly increase the risk estimate for RA at 6q23. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, B.D.; Camp, N.J. Principal component analysis for selection of optimal SNP-sets that capture intragenic genetic variation. Genet. Epidemiol. 2004, 26, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Gao, X.; Shi, B.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Luo, Y. Sequence and haplotypes of ankyrin 1 gene (ANK1) and their association with carcass and meat quality traits in yak. Mamm. Genome 2021, 32, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eelen, G.; Verlinden, L.; Maes, C.; Beullens, I.; Gysemans, C.; Paik, J.H.; Depinho, R.A.; Bouillon, R.; Carmeliet, G.; Verstuyf, A. Forkhead box O transcription factors in chondrocytes regulate endochondral bone formation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 164, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodine, S.C.; Stitt, T.N.; Gonzalez, M.; Kline, W.O.; Stover, G.L.; Bauerlein, R.; Zlotchenko, E.; Scrimgeour, A.; Lawrence, J.C.; Glass, D.J.; et al. Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle atrophy in vivo. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodine, S.C.; Latres, E.; Baumhueter, S.; Lai, V.K.; Nunez, L.; Clarke, B.A.; Poueymirou, W.T.; Panaro, F.J.; Na, E.; Dharmarajan, K.; et al. Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 2001, 294, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuyama, T.; Kitayama, K.; Yamashita, H.; Mori, N. Forkhead transcription factor FOXO1 (FKHR)-dependent induction of PDK4 gene expression in skeletal muscle during energy deprivation. Biochem. J. 2003, 375, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imae, M.; Fu, Z.; Yoshida, A.; Noguchi, T.; Kato, H. Nutritional and hormonal factors control the gene expression of FoxOs, the mammalian homologues of DAF-16. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 30, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, M.; Sandri, C.; Gilbert, A.; Skurk, C.; Calabria, E.; Picard, A.; Walsh, K.; Schiaffino, S.; Lecker, S.H.; Goldberg, A.L. Foxo Transcription Factors Induce the Atrophy-Related Ubiquitin Ligase Atrogin-1 and Cause Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. Cell 2004, 117, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W. Regulation of Muscle Protein Degradation: Coordinated Control of Apoptotic and Ubiquitin-Proteasome Systems by Phosphatidylinositol 3 Kinase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, B.; Vergani, L.; Sorarù, G.; Hespel, P.; Russell, A.P. Human skeletal muscle atrophy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis reveals a reduction in Akt and an increase in atrogin-1. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Peng, J.; Xu, D.Q.; Zheng, R.; Li, F.E.; Li, J.L.; Zuo, B.; Lei, M.G.; Xiong, Y.Z.; Deng, C.Y.; et al. Association of MYF5 and MYOD1 gene polymorphisms and meat quality traits in Large White x Meishan F2 pig populations. Biochem. Genet. 2008, 46, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, S.D.; Wheeler, T.L.; Koohmaraie, M. Evaluation of slice shear force as an objective method of assessing beef longissimus tenderness. J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 77, 2693–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honikel, K.O. Reference methods for the assessment of physical characteristics of meat. Meat Sci. 1998, 49, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| SNP | Genotype Frequency | Allele Frequency | HWE | Genetic Polymorphism | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype | Number | Frequency | Allele | Frequency | PIC | He | Ne | HO | ||
| SNP1 | CC | 476 | 88.80 | C | 94.41 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 1.16 | 0.85 |
| GC | 57 | 10.63 | G | 5.87 | ||||||
| GG | 3 | 0.559 | ||||||||
| SNP2 | CC | 164 | 30.59 | C | 54.94 | 0.69 | 0.37 | 0.49 | 1.99 | 0.50 |
| TC | 261 | 48.69 | T | 45.06 | ||||||
| TT | 111 | 20.70 | ||||||||
| SNP3 | AA | 159 | 29.66 | A | 54.19 | 0.68 | 0.37 | 0.49 | 1.96 | 0.50 |
| AG | 263 | 49.06 | G | 45.81 | ||||||
| GG | 114 | 21.26 | ||||||||
| SNP4 | CC | 183 | 34.14 | C | 57.46 | 0.67 | 0.36 | 0.48 | 1.92 | 0.52 |
| CG | 250 | 46.64 | G | 42.54 | ||||||
| GG | 103 | 19.21 | ||||||||
| SNP5 | CC | 481 | 89.73 | C | 94.68 | 0.21 | 0.098 | 0.10 | 1.11 | 0.89 |
| CG | 53 | 9.88 | G | 5.32 | ||||||
| GG | 2 | 0.37 | ||||||||
| Haplotype | Tag SNP | Frequency/% |
|---|---|---|
| H1 | CTACC | 44.2% |
| H2 | CCGGC | 42.2% |
| H3 | GCACG | 4.8% |
| H4 | CCACC | 4.7% |
| SNP | Genotype | Meat Traits | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | WBSF/kg | CMP/% | WHC/% | REA/cm2 | ||
| SNP1 | CC | 476 | 5.51 ± 0.10 | 65.95 ± 0.40 | 21.31 ± 0.39 a | 31.31 ± 0.59 |
| CG | 57 | 5.48 ± 0.20 | 66.07 ± 0.81 | 19.69 ± 0.78 b | 31.68 ± 1.19 | |
| GG | 3 | |||||
| p | 0.845 | 0.382 | 0.030 | 0.739 | ||
| SNP2 | CC | 164 | 5.47 ± 0.13 | 67.15 ± 0.53 | 21.58 ± 0.51 | 31.27 ± 0.78 |
| TC | 261 | 5.44 ± 0.12 | 66.35 ± 0.48 | 20.82 ± 0.47 | 31.10 ± 0.71 | |
| TT | 111 | 5.69 ± 0.14 | 66.68 ± 0.59 | 21.31 ± 0.57 | 31.83 ± 0.86 | |
| p | 0.259 | 0.335 | 0.335 | 0.725 | ||
| SNP3 | AA | 159 | 5.68 ± 0.13 a | 66.37 ± 0.54 | 21.04 ± 0.52 | 31.56 ± 0.80 |
| AG | 263 | 5.35 ± 0.11 b | 66.50 ± 0.47 | 20.81 ± 0.45 | 31.53 ± 0.69 | |
| GG | 114 | 5.63 ± 0.14 a | 67.43 ± 0.59 | 22.08 ± 0.57 | 30.70 ± 0.87 | |
| p | 0.031 | 0.232 | 0.098 | 0.614 | ||
| SNP4 | CC | 183 | 5.65 ± 0.1 3 | 66.33 ± 0.51 | 21.06 ± 0.50 | 31.57 ± 0.76 |
| CG | 250 | 5.37 ± 0.12 | 66.54 ± 0.48 | 20.78 ± 0.46 | 31.45 ± 0.70 | |
| GG | 103 | 5.58 ± 0.15 | 67.50 ± 0.61 | 22.15 ± 0.59 | 30.76 ± 0.90 | |
| p | 0.084 | 0.205 | 0.086 | 0.697 | ||
| SNP5 | CC | 481 | 5.52 ± 0.10 | 66.72 ± 0.40 | 21.30 ± 0.39 | 31.32 ± 0.59 |
| GC | 53 | 5.42 ± 0.21 | 66.27 ± 0.84 | 19.78 ± 0.81 | 31.51 ± 1.23 | |
| GG | 2 | |||||
| p | 0.605 | 0.569 | 0.049 | 0.876 | ||
| Diplotypes | Meat Traits | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | WBSF/kg | CMP/% | WHC/% | REA/cm2 | |
| H1H1 | 101 | 5.55 ± 0.16 a | 67.53 ± 0.64 | 22.19 ± 0.62 | 30.78 ± 0.90 |
| H1H2 | 203 | 5.46 ± 0.14 a | 66.41 ± 0.54 | 20.77 ± 0.52 | 30.92 ± 0.76 |
| H2H2 | 119 | 5.10 ± 0.16 b | 66.85 ± 0.60 | 21.59 ± 0.59 | 31.78 ± 0.85 |
| H2H3 | 32 | 4.89 ± 0.26 b | 66.56 ± 1.05 | 21.10 ± 1.03 | 30.46 ± 1.47 |
| p | 0.014 | 0.422 | 0.170 | 0.666 | |
| Trait (Unit)2 | Haplotype | n | Single-Haplotype Model | p | Multi-Haplotype Model | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present | Absent | Present | Absent | Other Haplotypes in Model | Present | Absent | ||||
| WBSF/kg·f | H1 | 345 | 149 | 5.58 ± 0.13 | 5.53 ± 0.15 | 0.715 | H2, H3 | 5.42 ± 0.15 | 5.50 ± 0.16 | 0.563 |
| H2 | 338 | 156 | 5.45 ± 0.12 | 5.84 ± 0.15 | 0.009 | H3 | 5.32 ± 0.15 | 5.59 ± 0.16 | 0.041 | |
| H3 | 47 | 447 | 5.19 ± 0.25 | 5.60 ± 0.12 | 0.079 | H2 | 5.34 ± 0.22 | 5.56 ± 0.11 | 0.290 | |
| H4 | 46 | 448 | 5.70 ± 0.25 | 5.56 ± 0.12 | 0.550 | H2, H3 | 5.19 ± 0.25 | 5.46 ± 0.14 | 0.220 | |
| CMP/% | H1 | 345 | 149 | 66.49 ± 0.46 | 67.09 ± 0.56 | 0.270 | ||||
| H2 | 338 | 156 | 66.87 ± 0.46 | 66.27 ± 0.57 | 0.262 | |||||
| H3 | 47 | 447 | 65.66 ± 0.90 | 66.69 ± 0.43 | 0.974 | |||||
| H4 | 46 | 448 | 65.36 ± 0.90 | 66.80 ± 0.43 | 0.096 | |||||
| WHC/% | H1 | 345 | 149 | 21.04 ± 0.78 | 20.19 ± 0.65 | 0.262 | ||||
| H2 | 338 | 156 | 20.86 ± 0.64 | 19.62 ± 0.79 | 0.100 | |||||
| H3 | 47 | 447 | 21.18 ± 1.25 | 20.42 ± 0.60 | 0.524 | |||||
| H4 | 46 | 448 | 18.45 ± 1.26 | 20.64 ± 0.61 | 0.070 | |||||
| REA/cm2 | H1 | 345 | 149 | 31.08 ± 0.84 | 30.82 ± 0.71 | 0.752 | ||||
| H2 | 338 | 156 | 30.84 ± 0.86 | 30.95 ± 0.70 | 0.889 | |||||
| H3 | 47 | 447 | 30.79 ± 0.65 | 32.44 ± 1.36 | 0.200 | |||||
| H4 | 46 | 448 | 31.62 ± 1.37 | 30.86 ± 0.66 | 0.558 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, C.; Mi, B.; Cui, C.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Mutations in the FOXO3 Gene and Their Effects on Meat Traits in Gannan Yaks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25041948
Qi Y, Wang X, Zhu C, Mi B, Cui C, Chen S, Zhao Z, Zhao F, Liu X, Wang J, et al. Mutations in the FOXO3 Gene and Their Effects on Meat Traits in Gannan Yaks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(4):1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25041948
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Youpeng, Xiangyan Wang, Chune Zhu, Baohong Mi, Changze Cui, Shaopeng Chen, Zhidong Zhao, Fangfang Zhao, Xiu Liu, Jiqing Wang, and et al. 2024. "Mutations in the FOXO3 Gene and Their Effects on Meat Traits in Gannan Yaks" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 4: 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25041948
APA StyleQi, Y., Wang, X., Zhu, C., Mi, B., Cui, C., Chen, S., Zhao, Z., Zhao, F., Liu, X., Wang, J., Shi, B., & Hu, J. (2024). Mutations in the FOXO3 Gene and Their Effects on Meat Traits in Gannan Yaks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(4), 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25041948






