Integrative Epigenetic and Molecular Analysis Reveals a Novel Promoter for a New Isoform of the Transcription Factor TEAD4
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
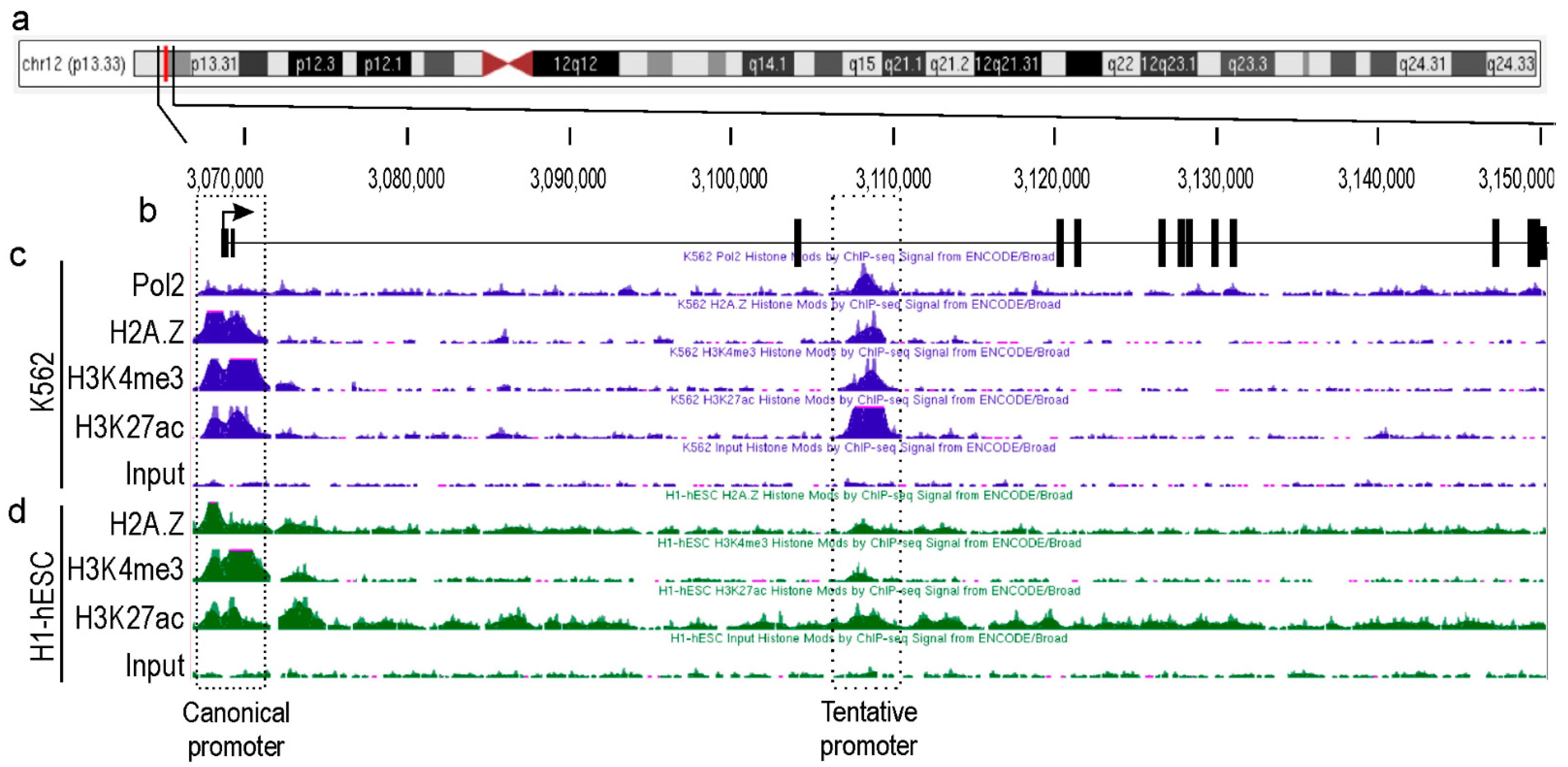
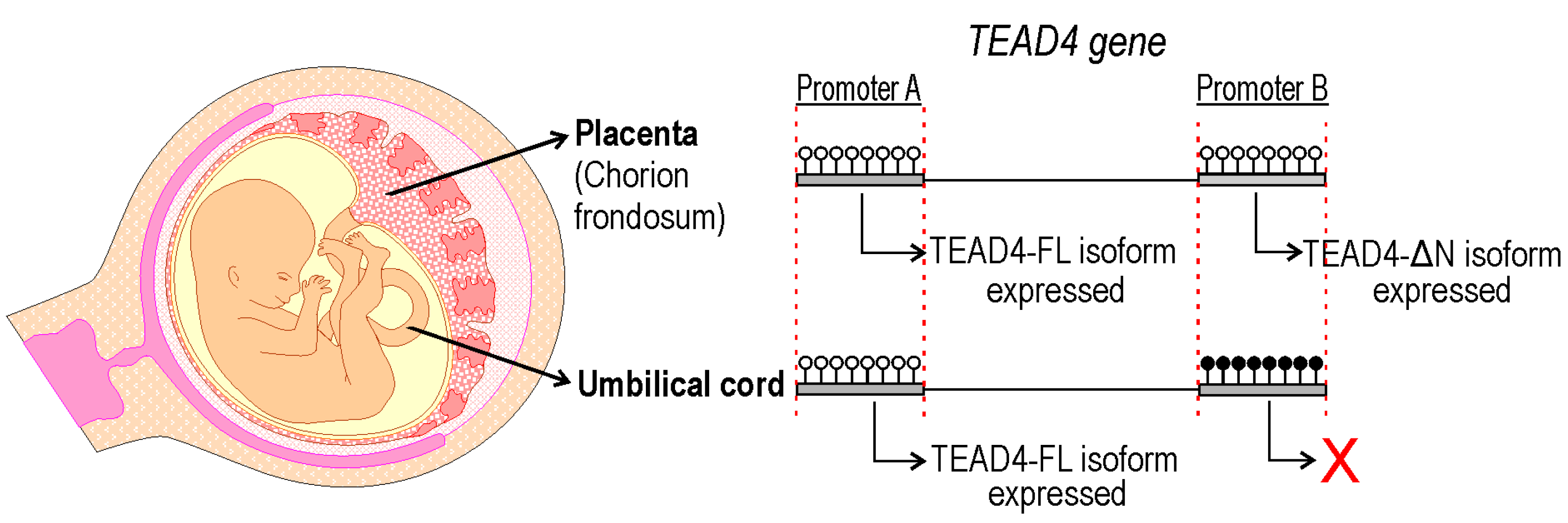
2.1. Identification of a Novel Promoter for TEAD4
2.2. Identification of a Novel TEAD4-Isoform-Encoding Transcript
2.3. The Novel TEAD4 Isoform Encodes a DNA-Binding-Domainless Protein
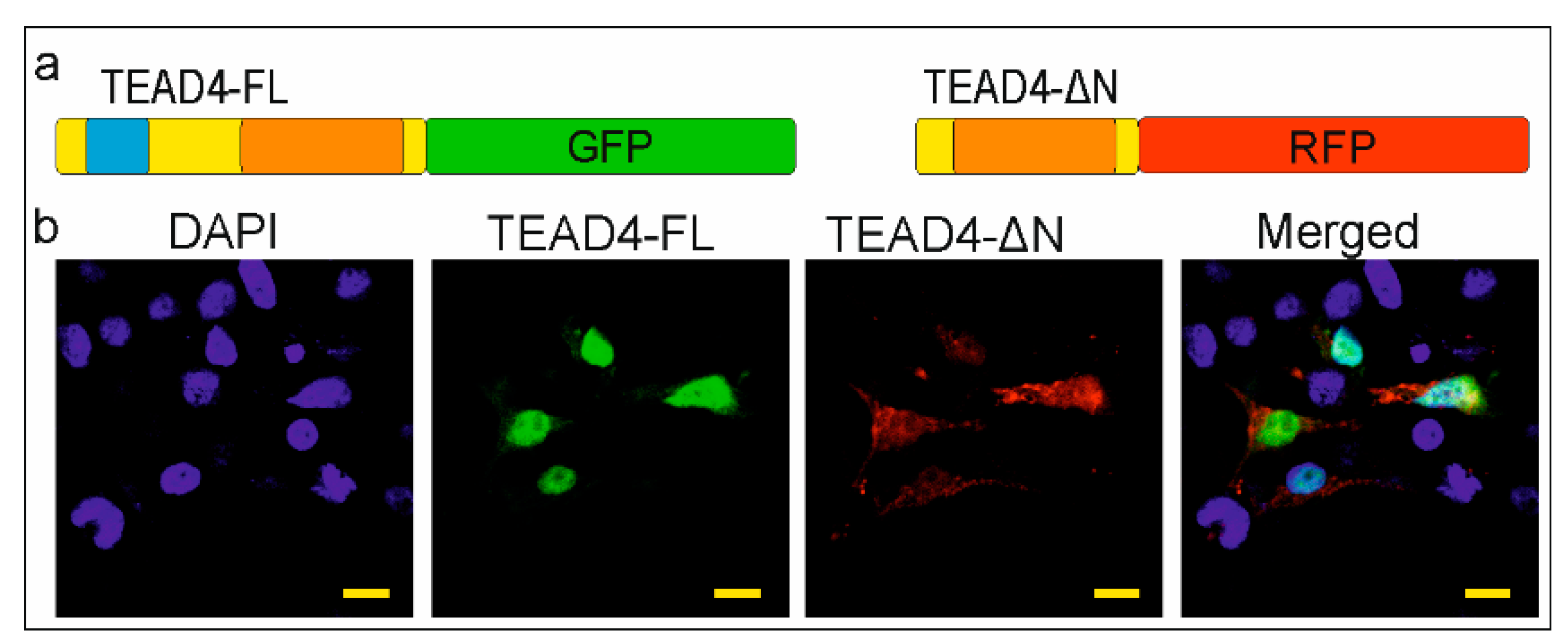
2.4. The TEAD-ΔN Isoform Is Excluded from the Nucleus
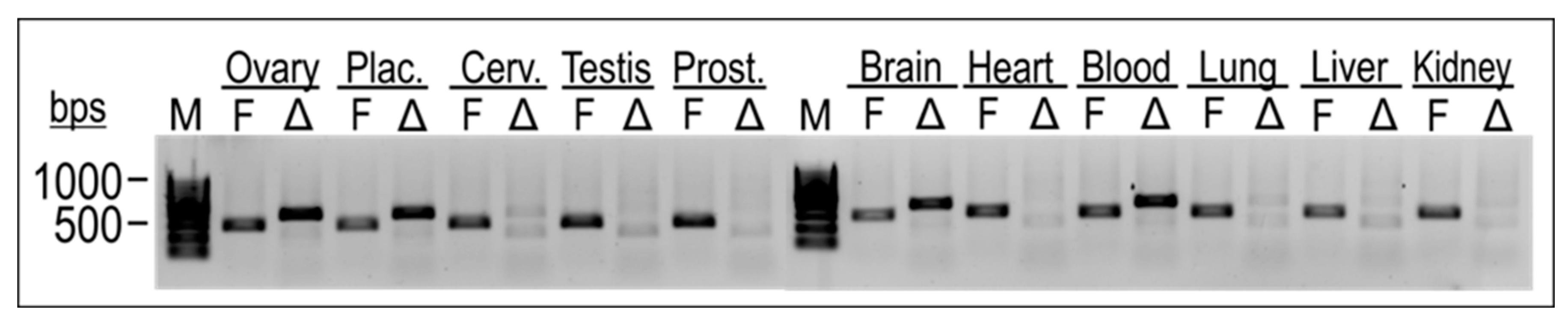
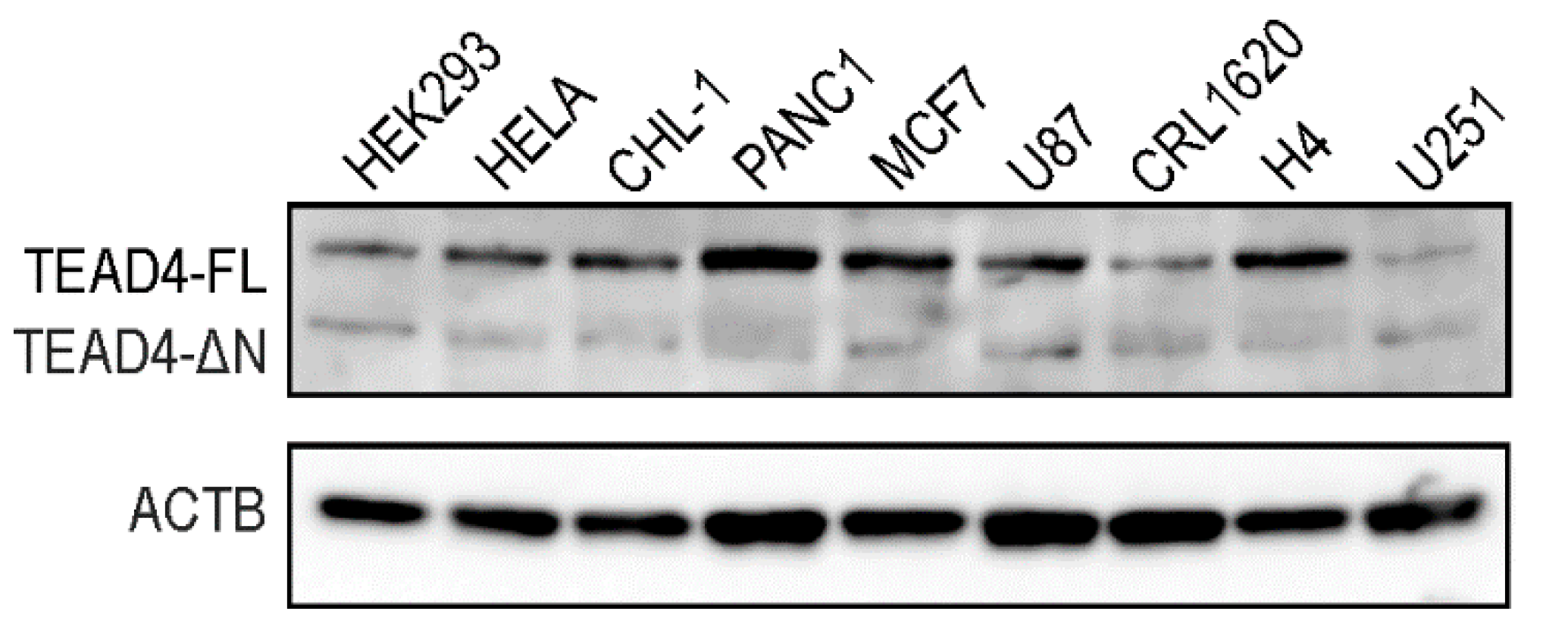
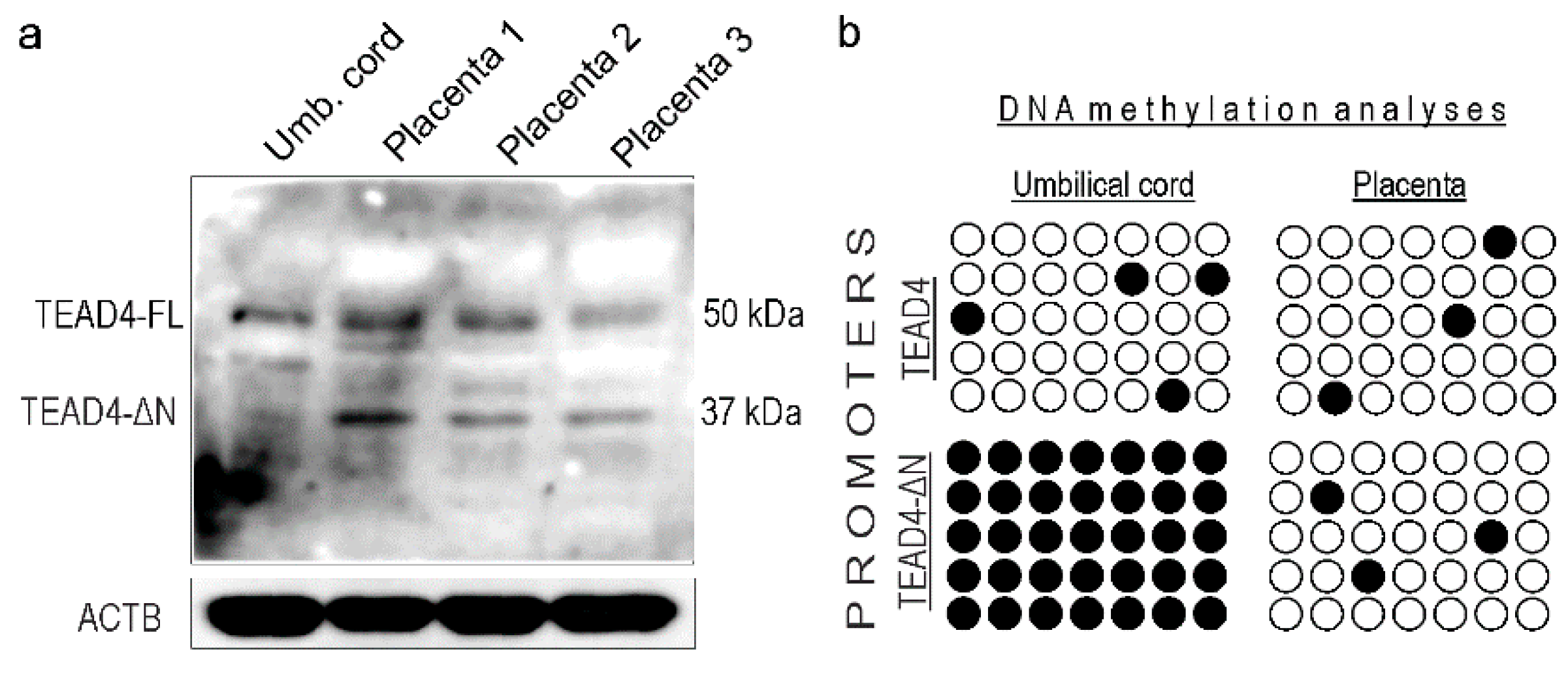
2.5. TEAD4-ΔN Expression Is Cell-Type-Specific
2.6. In Vitro Analysis of the Alternative TEAD4 Promoter
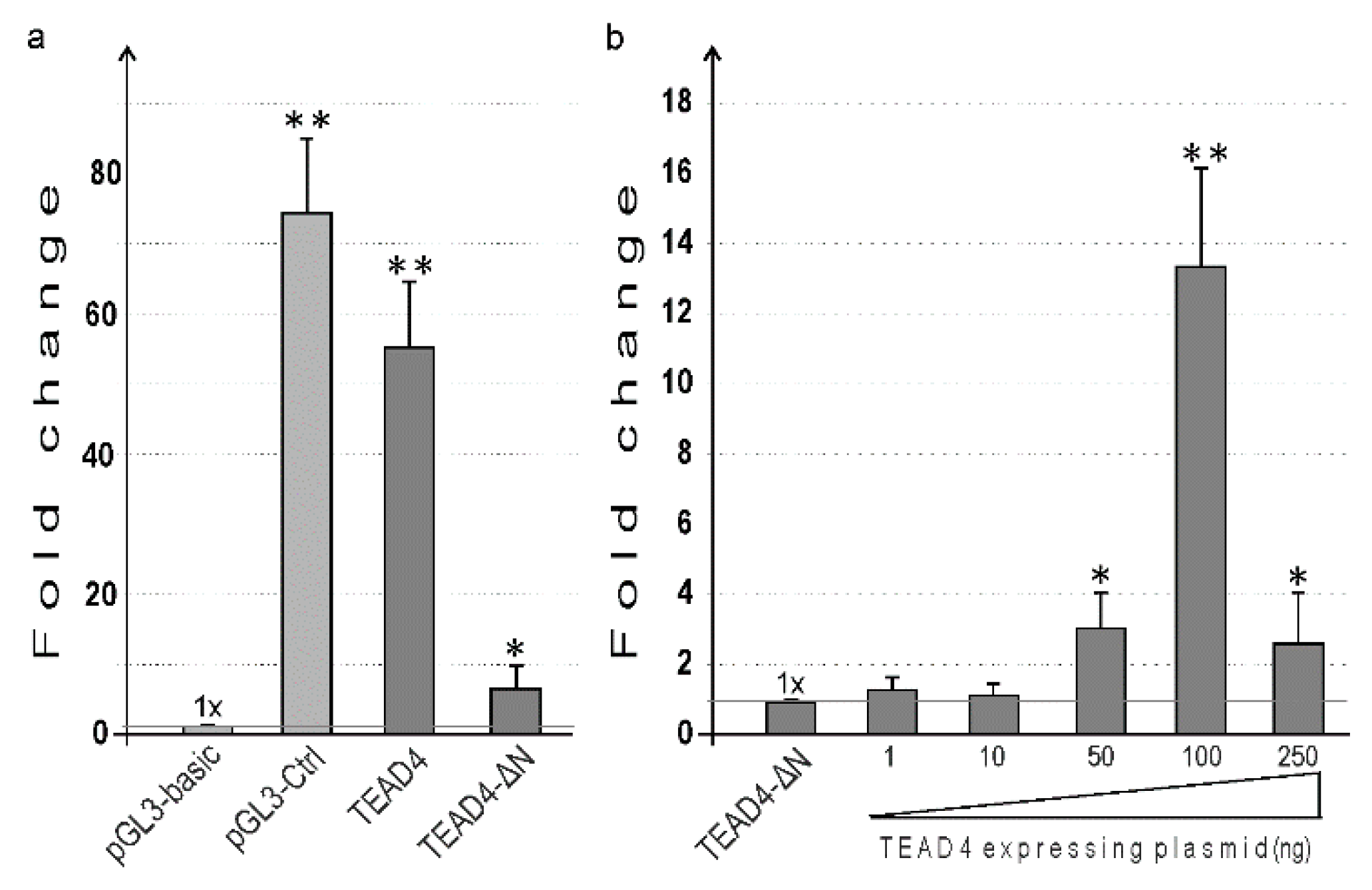
2.7. Functional Characterization of TEAD4 Promoter(s) in Transient Transfection Studies
2.8. TEAD4-ΔN Expression in Human Placenta Is Regulated by DNA Methylation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Epigenetic Data Analysis
4.2. Cell Culturing
4.3. Total RNA Isolation
4.4. 5′RACE (5′ Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends)
4.5. Nucleotide Sequence Analysis
4.6. Confocal Fluorescent Microscopy
4.7. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.8. DNA Methylation Analysis—Bisulfite Sequencing (BS) [42]
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. Electrophoretic-Shift Essay (EMSA)
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harvey, K.F.; Pfleger, C.M.; Hariharan, I.K. The Drosophila Mst ortholog, hippo, restricts growth and cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell 2003, 114, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Moroishi, T.; Guan, K.L. Mechanisms of Hippo pathway regulation. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snigdha, K.; Gangwani, K.S.; Lapalikar, G.V.; Singh, A.; Kango-Singh, M. Hippo signaling in cancer: Lessons from Drosophila models. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolma, A.; Yan, J.; Whitington, T.; Toivonen, J.; Nitta, K.R.; Rastas, P.; Morgunova, E.; Enge, M.; Taipale, M.; Wei, G.; et al. DNA-binding specificities of human transcription factors. Cell 2013, 152, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currey, L.; Thor, S.; Piper, M. TEAD family transcription factors in development and disease. Development 2021, 148, dev196675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, T.; Cheng, A.S.L.; Yu, J.; Kang, W.; To, K.F. The TEAD family and its oncogenic role in promoting tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.S.; Wang, Q.; Buxton, S.K.; Balasubramanyam, N.; Kim, J.J.; Dong, J.; Zhang, A.; Li, S.; et al. Tead1 is required for maintaining adult cardiomyocyte function, and its loss results in lethal dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 2, e93343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.J.; Kohn, M.J.; Liu, C.; DePamphilis, M.L. Transcription factor TEAD2 is involved in neural tube closure. Genesis 2007, 45, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, N.; Inoue, K.; Adachi, K.; Kiyonari, H.; Ota, M.; Ralston, A.; Yabuta, N.; Hirahara, S.; Stephenson, R.O.; Ogonuki, N.; et al. The Hippo Signaling Pathway Components Lats and Yap Pattern Tead4 Activity to Distinguish Mouse Trophectoderm from Inner Cell Mass. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Home, P.; Saha, B.; Ray, S.; Dutta, D.; Gunewardena, S.; Yoo, B.; Pal, A.; Vivian, J.L.; Larson, M.; Petroff, M.; et al. Altered subcellular localization of transcription factor TEAD4 regulates first mammalian cell lineage commitment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7362–7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Kiyonari, H.; Sato, H.; Sawada, A.; Ota, M.; Nakao, K.; Sasaki, H. Tead4 is required for specification of trophectoderm in pre-implantation mouse embryos. Mech. Dev. 2008, 125, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, K.J.; De Pamphilis, M.L. TEAD4 establishes the energy homeostasis essential for blastocoel formation. Development 2013, 140, 3680–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.; Ganguly, A.; Home, P.; Bhattacharya, B.; Ray, S.; Ghosh, A.; Karim Rumi, M.A.; Marsh, C.; French, V.A.; Gunewardena, S.; et al. TEAD4 ensures postimplantation development by promoting trophoblast self-renewal: An implication in early human pregnancy loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17864–17875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilev, A.; Kaneko, K.J.; Shu, H.; Zhao, Y.; DePamphilis, M.L. TEAD/TEF transcription factors utilize the activation domain of YAP65, a Src/Yes-associated protein localized in the cytoplasm. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.G.; Koh, E.; Chen, X.; Gumbiner, B.M. E-cadherin mediates contact inhibition of proliferation through Hippo signaling-pathway components. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11930–11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.X.; Zhao, B.; Panupinthu, N.; Jewell, J.L.; Lian, I.; Wang, L.H.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, H.; Tumaneng, K.; Li, H.; et al. Regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway by G-protein-coupled receptor signaling. Cell 2012, 150, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulshan, K.; Thommandru, B.; Moye-Rowley, W.S. Proteolytic degradation of the Yap1 transcription factor is regulated by subcellular localization and the E3 ubiquitin ligase Not4. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26796–26805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, K.E.; Gertz, J.; Bowling, K.M.; Parker, S.L.; Reddy, T.E.; Pauli-Behn, F.; Cross, M.K.; Williams, B.A.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.A.; Crawford, G.E.; et al. Dynamic DNA methylation across diverse human cell lines and tissues. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, M.; Lacey, M. DNA methylation and differentiation: Silencing, upregulation and modulation of gene expression. Epigenomics 2013, 5, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Baribault, C.; Lacey, M.; Ehrlich, M. Myogenic differential methylation: Diverse associations with chromatin structure. Biology 2014, 3, 426–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunakea, A.K.; Nagarajan, R.P.; Bilenky, M.; Ballinger, T.J.; Dsouza, C.; Fouse, S.D.; Johnson, B.E.; Hong, C.; Nielsen, C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Conserved role of intragenic DNA methylation in regulating alternative promoters. Nature 2010, 466, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeziorska, D.M.; Murray, R.J.S.; De Gobbi, M.; Gaentzsch, R.; Garrick, D.; Ayyub, H.; Chen, T.; Li, E.; Telenius, J.; Lynch, M.; et al. DNA methylation of intragenic CpG islands depends on their transcriptional activity during differentiation and disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7526–E7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, A.M.; Webb, S.; Kerr, A.R.W.; Illingworth, R.S.; Guy, J.; Andrews, R.; Bird, A. Cell type-specific DNA methylation at intragenic CpG islands in the immune system. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, R.D.; Hon, G.C.; Lee, L.K.; Ngo, Q.; Lister, R.; Pelizzola, M.; Edsall, L.E.; Kuan, S.; Luu, Y.; Klugman, S.; et al. Distinct epigenomic landscapes of pluripotent and lineage-committed human cells. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davuluri, R.V.; Suzuki, Y.; Sugano, S.; Plass, C.; Huang, T.H.M. The functional consequences of alternative promoter use in mammalian genomes. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Sin, H.S.; Lu, C.; Fuller, M.T. Developmental regulation of cell type-specific transcription by novel promoter-proximal sequence elements. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, I.M.; Stevenson, J.K.; Schwarz, E.M.; Van Antwerp, D.; Miyamoto, S. Rel/NF-κB/IκB family: Intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagotto, F.; Glück, U.; Gumbiner, B.M. Nuclear localization signal-independent and importin/karyopherin-independent nuclear import of β-catenin. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeitlinger, J. Seven myths of how transcription factors read the cis-regulatory code. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 2020, 23, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Wilder, S.P.; Johnson, N.; Juettemann, T.; Flicek, P.R. The Ensembl Regulatory Build. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yu, J.; Han, W.; Fan, X.; Qian, H.; Wei, H.; Tsai, Y.H.S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; et al. A splicing isoform of TEAD4 attenuates the Hippo-YAP signalling to inhibit tumour proliferation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, ncomms11840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Wu, Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, X.; et al. Tea domain transcription factor TEAD4 mitigates TGF-β signaling and hepatocellular carcinoma progression independently of YAP. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 15, mjad010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.V.C.; Bourc’his, D. The diverse roles of DNA methylation in mammalian development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 590–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.V.C. Get Out and Stay Out: New Insights Into DNA Methylation Reprogramming in Mammals. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 629068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.; Krueger, C.; Mellado-Lopez, M.; Hemberger, M.; Dean, W.; Perez-Garcia, V.; Hanna, C.W. Mechanisms and function of de novo DNA methylation in placental development reveals an essential role for DNMT3B. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyfer, N.; Magenheim, J.; Peretz, A.; Cann, G.; Bredno, J.; Klochendler, A.; Fox-Fisher, I.; Shabi-Porat, S.; Hecht, M.; Pelet, T.; et al. A DNA methylation atlas of normal human cell types. Nature 2023, 613, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckersley-Maslin, M.A.; Alda-Catalinas, C.; Reik, W. Dynamics of the epigenetic landscape during the maternal-to-zygotic transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Lei, D.; Xiang, J.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J. Recent progress in DNA methyltransferase inhibitors as anticancer agents. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1072651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplánek, R.; Kejík, Z.; Hajduch, J.; Veselá, K.; Kučnirová, K.; Skaličková, M.; Venhauerová, A.; Hosnedlová, B.; Hromádka, R.; Dytrych, P.; et al. TET protein inhibitors: Potential and limitations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soncin, F.; Khater, M.; To, C.; Pizzo, D.; Farah, O.; Wakeland, A.; Rajan, K.A.N.; Nelson, K.K.; Chang, C.W.; Moretto-Zita, M.; et al. Comparative analysis of mouse and human placentae across gestation reveals species-specific regulators of placental development. Development 2018, 145, dev156273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, C.A.; Chan, E.T.; Davidson, J.M.; Malladi, V.S.; Strattan, J.S.; Hitz, B.C.; Gabdank, I.; Narayanan, A.K.; Ho, M.; Lee, B.T.; et al. ENCODE data at the ENCODE portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D726–D732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauluseviciute, I.; Drabløs, F.; Rye, M.B. DNA methylation data by sequencing: Experimental approaches and recommendations for tools and pipelines for data analysis. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, P.E.; Tang, S.-H.E.; Silva, F.J.; Tsark, W.M.K.; Mann, J.R. Role of CTCF Binding Sites in the Igf2/H19 Imprinting Control Region. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 4791–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashidiani, S.; Mamo, G.; Farkas, B.; Szabadi, A.; Farkas, B.; Uszkai, V.; Császár, A.; Brandt, B.; Kovács, K.; Pap, M.; et al. Integrative Epigenetic and Molecular Analysis Reveals a Novel Promoter for a New Isoform of the Transcription Factor TEAD4. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042223
Rashidiani S, Mamo G, Farkas B, Szabadi A, Farkas B, Uszkai V, Császár A, Brandt B, Kovács K, Pap M, et al. Integrative Epigenetic and Molecular Analysis Reveals a Novel Promoter for a New Isoform of the Transcription Factor TEAD4. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(4):2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042223
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashidiani, Shima, Gizaw Mamo, Benjámin Farkas, András Szabadi, Bálint Farkas, Veronika Uszkai, András Császár, Barbara Brandt, Kálmán Kovács, Marianna Pap, and et al. 2024. "Integrative Epigenetic and Molecular Analysis Reveals a Novel Promoter for a New Isoform of the Transcription Factor TEAD4" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 4: 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042223
APA StyleRashidiani, S., Mamo, G., Farkas, B., Szabadi, A., Farkas, B., Uszkai, V., Császár, A., Brandt, B., Kovács, K., Pap, M., & Rauch, T. A. (2024). Integrative Epigenetic and Molecular Analysis Reveals a Novel Promoter for a New Isoform of the Transcription Factor TEAD4. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(4), 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042223






