Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differentially Expressed Serum Metabolites and Pathways in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with and without Cognitive Decline: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
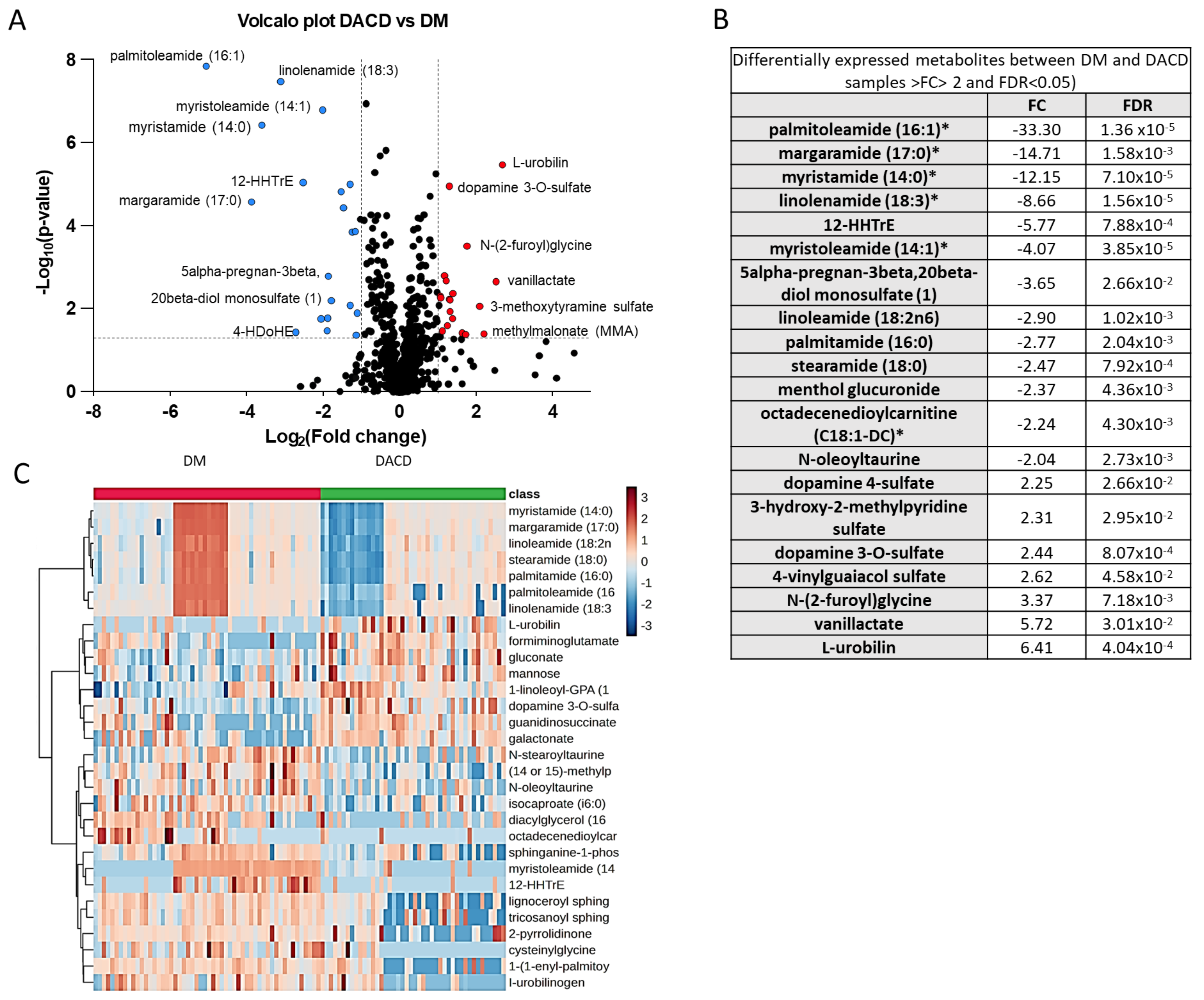
2.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed Metabolites between DM and DACD Samples
2.3. Chemometric Analysis
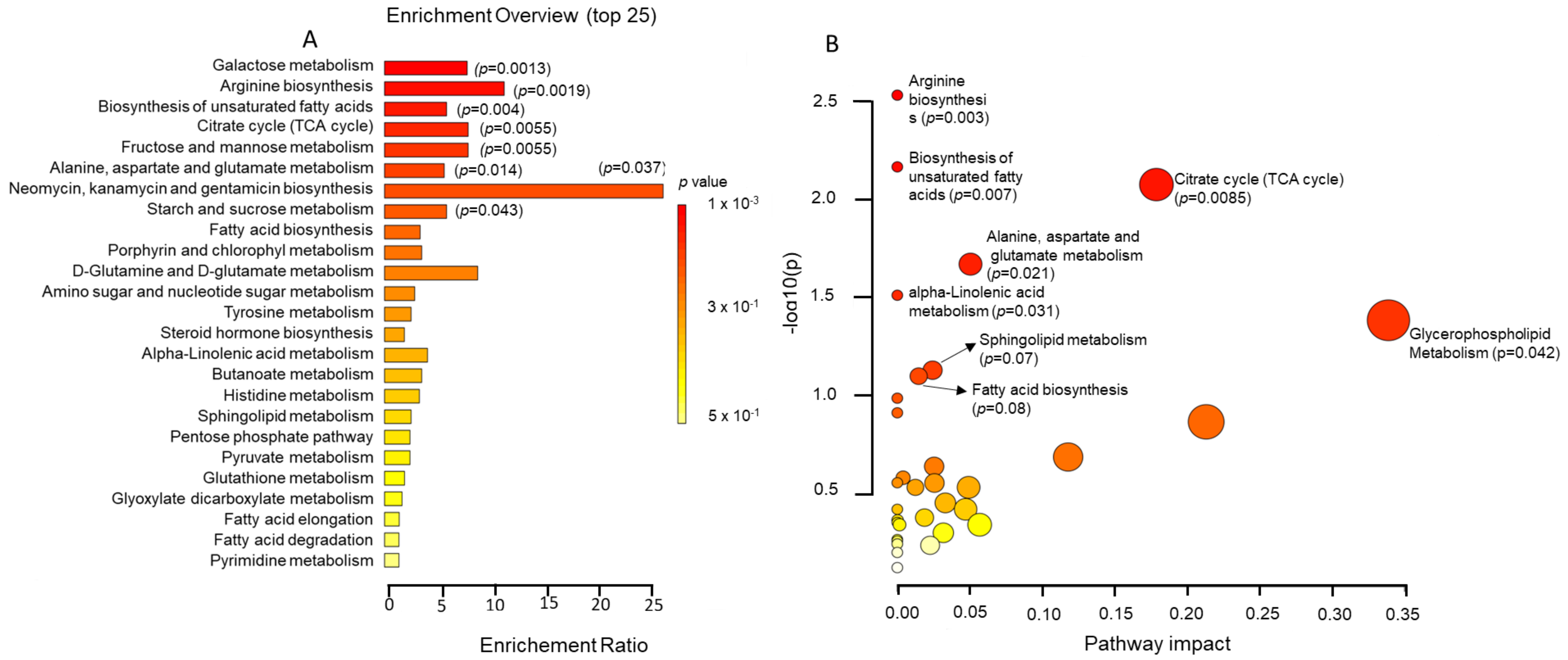
2.4. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
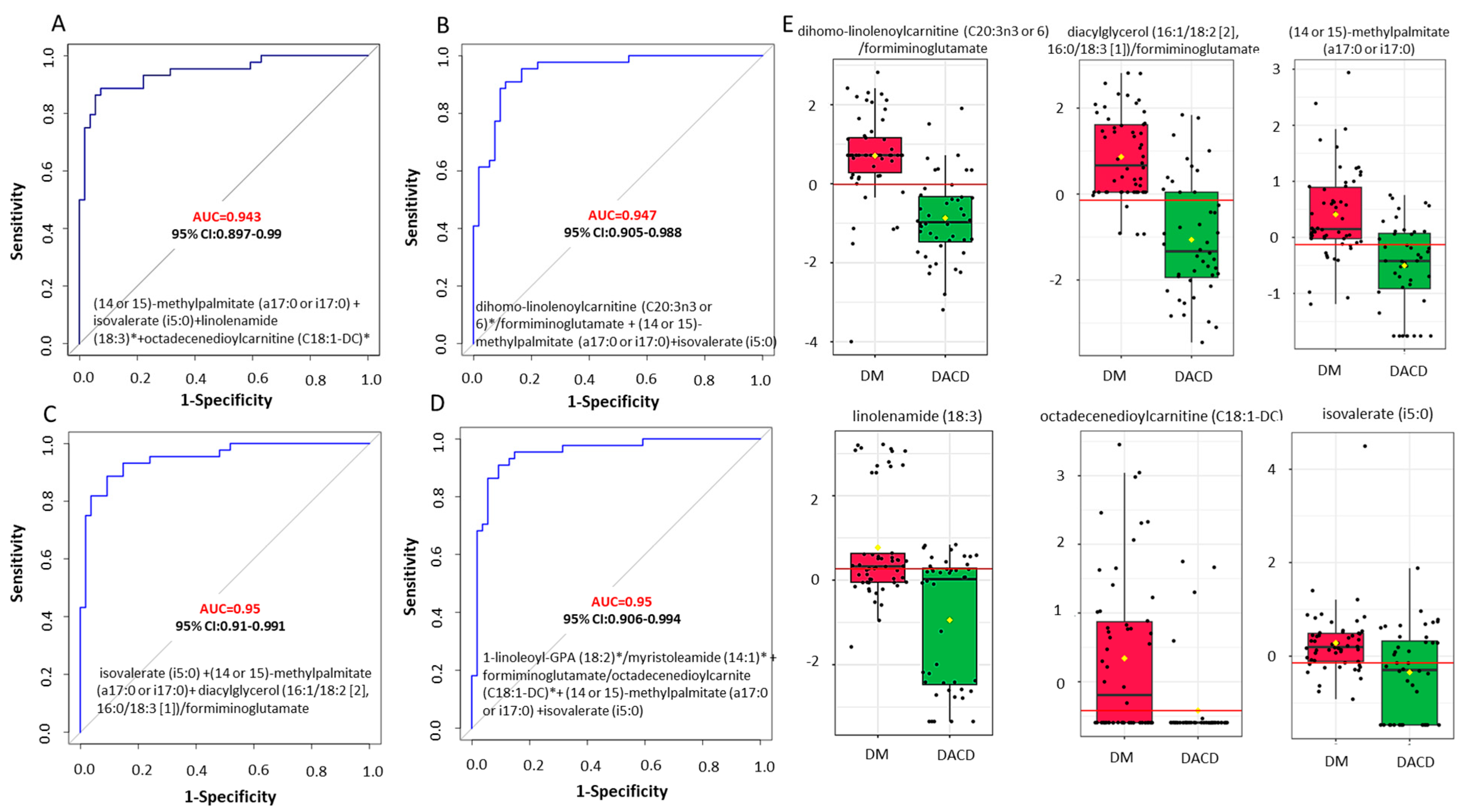
2.5. Biomarker Discovery
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Plasma Collection
4.3. Diagnostic Procedures
4.4. Cognitive Function Assessment
4.5. Functional Independence Assessment
4.6. Metabolomic Profiling
4.7. Statistical Analysis
4.8. Metabolomic Analysis
4.9. Ethical Approval
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clasen, F.; Nunes, P.M.; Bidkhori, G.; Bah, N.; Boeing, S.; Shoaie, S.; Anastasiou, D. Systematic diet composition swap in a mouse genome-scale metabolic model reveals determinants of obesogenic diet metabolism in liver cancer. iScience 2023, 26, 106040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, R.F.; Albert, M.S.; Alonso, A.; Coker, L.H.; Coresh, J.; Davis, S.M.; Deal, J.A.; McKhann, G.M.; Mosley, T.H.; Sharrett, A.R.; et al. Associations Between Midlife Vascular Risk Factors and 25-Year Incident Dementia in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Cohort. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Xu, W.; Ou, Y.N.; Cao, X.P.; Tan, M.S.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T. Diabetes mellitus and risks of cognitive impairment and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 144 prospective studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 55, 100944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Huang, C.; Deng, H.; Wang, H. Diabetes as a risk factor for dementia and mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 42, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, W.; Li, J.Q.; Cao, X.P.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. Midlife Modifiable Risk Factors for Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of 34 Prospective Cohort Studies. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 1254–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, K.; Mukadam, N.; Petersen, I.; Cooper, C. Mild cognitive impairment and progression to dementia in people with diabetes, prediabetes and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2018, 53, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuligenga, R.H.; Dugravot, A.; Tabák, A.G.; Elbaz, A.; Brunner, E.J.; Kivimäki, M.; Singh-Manoux, A. Midlife type 2 diabetes and poor glycaemic control as risk factors for cognitive decline in early old age: A post-hoc analysis of the Whitehall II cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbiellini Amidei, C.; Fayosse, A.; Dumurgier, J.; Machado-Fragua, M.D.; Tabak, A.G.; van Sloten, T.; Kivimäki, M.; Dugravot, A.; Sabia, S.; Singh-Manoux, A. Association between Age at Diabetes Onset and Subsequent Risk of Dementia. JAMA 2021, 325, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, N.N.; Austin, P.C.; Shah, B.R.; Wu, J.; Gill, S.S.; Booth, G.L. Risk of dementia in seniors with newly diagnosed diabetes: A population-based study. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, P.K.; Walker, R.; Hubbard, R.A.; Li, G.; Nathan, D.M.; Zheng, H.; Haneuse, S.; Craft, S.; Montine, T.J.; Kahn, S.E.; et al. Glucose levels and risk of dementia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehtewish, H.; Arredouani, A.; El-Agnaf, O. Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Mechanistic Biomarkers of Diabetes Mellitus-Associated Cognitive Decline. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.B.; Geng, N.; Li, Z.G.; Qiao, H.J.; Sun, H.R.; Li, F. Biomarkers of Renal Function in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Cognitive Impairment. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 610, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, C.; Tian, S.; Huang, R.; Guo, D.; Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, S. Higher Plasma Level of Nampt Presaging Memory Dysfunction in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 70, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, R.; Tian, S.; Wang, J.; Lin, H.; An, K.; Han, J.; Wang, S. Association between plasma adipsin level and mild cognitive impairment in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Cai, R.; Huang, R.; Tian, S.; Lin, H.; Guo, D.; Wang, S. Association between Plasma Levels of PAI-1, tPA/PAI-1 Molar Ratio, and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Tian, S.; An, K.; Cao, W.; Shi, J.; Tang, W.; Wang, S. Elevated Plasma Free Fatty Acid Susceptible to Early Cognitive Impairment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 82, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marioni, R.E.; Strachan, M.W.; Reynolds, R.M.; Lowe, G.D.; Mitchell, R.J.; Fowkes, F.G.; Frier, B.M.; Lee, A.J.; Butcher, I.; Rumley, A.; et al. Association between raised inflammatory markers and cognitive decline in elderly people with type 2 diabetes: The Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study. Diabetes 2010, 59, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorska-Ciebiada, M.; Saryusz-Wolska, M.; Borkowska, A.; Ciebiada, M.; Loba, J. Serum levels of inflammatory markers in depressed elderly patients with diabetes and mild cognitive impairment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorska-Ciebiada, M.; Saryusz-Wolska, M.; Borkowska, A.; Ciebiada, M.; Loba, J. C-Reactive Protein, Advanced Glycation End Products, and Their Receptor in Type 2 Diabetic, Elderly Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorska-Ciebiada, M.; Saryusz-Wolska, M.; Borkowska, A.; Ciebiada, M.; Loba, J. Adiponectin, Leptin and Il-1 B in Elderly Diabetic Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Metab Brain Dis 2016, 31, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.M.; Barzilay, J.I.; Lovato, J.F.; Williamson, J.D.; Miller, M.E.; Marcovina, S.; Launer, L.J. Biomarkers of renal function and cognitive impairment in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhen, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Fang, H.; Tian, L.B.; Zhou, D.H.; Kosten, T.R.; Zhang, X.Y. Low BDNF is associated with cognitive deficits in patients with type 2 diabetes. Psychopharmacology 2013, 227, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo Ortíz, B.; Ramírez Emiliano, J.; Ramos-Rodríguez, E.; Martínez-Garza, S.; Macías-Cervantes, H.; Solorio-Meza, S.; Pereyra-Nobara, T.A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor plasma levels and premature cognitive impairment/dementia in type 2 diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Metabolomics for Biomarker Discovery: Moving to the Clinic. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 354671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Raftery, D. Biomarker Discovery and Translation in Metabolomics. Curr. Metabolomics 2013, 1, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zheng, H.; Fan, K.; Xia, N.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y. NMR-based metabolomics characterizes metabolic changes in different brain regions of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice with cognitive decline. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Dong, M.; Ren, M.; Li, C.; Zheng, H.; Gao, H. Metabolomic Analysis Identifies Lactate as an Important Pathogenic Factor in Diabetes-associated Cognitive Decline Rats. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Zhai, C.; Li, X.; Gang, H.; Gao, X. Feature-Based Molecular Networking Facilitates the Comprehensive Identification of Differential Metabolites in Diabetic Cognitive Dysfunction Rats. Metabolites 2023, 13, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zeng, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, L.; Shu, Y. LC-MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals Early Biomarkers in STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats with Cognitive Impairment. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 665309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, L.; Feng, R.; Zhao, T.; Ren, W.; Hang, T.; Zhou, W.; Lu, X. Integrated Analyses of Microbiomics and Metabolomics Explore the Effect of Gut Microbiota Transplantation on Diabetes-Associated Cognitive Decline in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 913002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Zhan, L.; Lu, X.; Liang, L.; Su, B.; Sui, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Plasma metabolomic profiling of patients with diabetes-associated cognitive decline. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.K.; Piccolo, B.D.; John, C.S.; Green, Z.D.; Thyfault, J.P.; Adams, S.H. Oxylipin Profiling of Alzheimer’s Disease in Nondiabetic and Type 2 Diabetic Elderly. Metabolites 2019, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Diao, X.; Gang, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, G. Risk Factors for Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 4591938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koekkoek, P.S.; Kappelle, L.J.; van den Berg, E.; Rutten, G.E.; Biessels, G.J. Cognitive function in patients with diabetes mellitus: Guidance for daily care. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, M.A.; Chan, Q.L.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Hui, R.J.; Chong, S.S.; Chen, C.L.; Dong, Y. Risk Factors of Cognitive Impairment and Brief Cognitive Tests to Predict Cognitive Performance Determined by a Formal Neuropsychological Evaluation of Primary Health Care Patients. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qin, J.; Guo, S.; Huang, J.; Tao, J. The prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldana, S.L.; Guarnaccia, C.A. Comparing cognitive function in white Mexican & non-Hispanic white Americans with/without diabetes. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, X.; Han, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, J. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Is Associated with the Risk of Cognitive Impairment: A Meta-Analysis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 68, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Hua, S.; Liao, H.; Wang, M.; Xiong, Y.; Cao, F. An updated meta-analysis of cohort studies: Diabetes and risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 124, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassing, L.B.; Grant, M.D.; Hofer, S.M.; Pedersen, N.L.; Nilsson, S.E.; Berg, S.; McClearn, G.; Johansson, B. Type 2 diabetes mellitus contributes to cognitive decline in old age: A longitudinal population-based study. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2004, 10, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, P.A.; Schubert, D.R. Metabolic links between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areosa Sastre, A.; Vernooij, R.W.; González-Colaço Harmand, M.; Martínez, G. Effect of the treatment of Type 2 diabetes mellitus on the development of cognitive impairment and dementia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, CD003804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exalto, L.G.; Biessels, G.J.; Karter, A.J.; Huang, E.S.; Katon, W.J.; Minkoff, J.R.; Whitmer, R.A. Risk score for prediction of 10 year dementia risk in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinkohl, I.; Price, J.F.; Strachan, M.W.; Frier, B.M. The impact of diabetes on cognitive decline: Potential vascular, metabolic, and psychosocial risk factors. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2015, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geijselaers, S.L.C.; Sep, S.J.S.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Biessels, G.J. Glucose regulation, cognition, and brain MRI in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sredy, J.; Sawicki, D.R.; Notvest, R.R. Polyol pathway activity in nervous tissues of diabetic and galactose-fed rats: Effect of dietary galactose withdrawal or tolrestat intervention therapy. J. Diabet. Complicat. 1991, 5, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bril, V.; Ono, Y.; Buchanan, R.A. Sural nerve sorbitol in patients with diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1160–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Begley, P.; Church, S.J.; Patassini, S.; McHarg, S.; Kureishy, N.; Hollywood, K.A.; Waldvogel, H.J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; et al. Elevation of brain glucose and polyol-pathway intermediates with accompanying brain-copper deficiency in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: Metabolic basis for dementia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnuolo, M.S.; Iossa, S.; Cigliano, L. Sweet but Bitter: Focus on Fructose Impact on Brain Function in Rodent Models. Nutrients 2020, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.J.; Gomez-Pinilla, F.; Nagel, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, B.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Tolan, D.R.; Lanaspa, M.A. Cerebral Fructose Metabolism as a Potential Mechanism Driving Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 560865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Chen, S.; Ou, L.; Li, S.; Ye, Z.N.; Liu, H.F. Disrupted Alpha-Ketoglutarate Homeostasis: Understanding Kidney Diseases from the View of Metabolism and Beyond. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostiuchenko, O.; Lushnikova, I.; Kowalczyk, M.; Skibo, G. mTOR/α-ketoglutarate-mediated signaling pathways in the context of brain neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. BBA Adv. 2022, 2, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldendorf, W.H. Carrier-mediated blood-brain barrier transport of short-chain monocarboxylic organic acids. Am. J. Physiol. 1973, 224, 1450–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, A.R.; Steele, R.D. Transport of alpha-keto analogues of amino acids across blood-brain barrier in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1982, 243, E272–E277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; He, L.; Yao, K. The Antioxidative Function of Alpha-Ketoglutarate and Its Applications. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3408467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhre, K.; Shin, S.Y.; Petersen, A.K.; Mohney, R.P.; Meredith, D.; Wägele, B.; Altmaier, E.; Deloukas, P.; Erdmann, J.; Grundberg, E.; et al. Human metabolic individuality in biomedical and pharmaceutical research. Nature 2011, 477, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClay, J.L.; Vunck, S.A.; Batman, A.M.; Crowley, J.J.; Vann, R.E.; Beardsley, P.M.; van den Oord, E.J. Neurochemical Metabolomics Reveals Disruption to Sphingolipid Metabolism Following Chronic Haloperidol Administration. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, B.; Zhao, B.; Fan, Y.; He, X.; Yang, L.; Ma, Q.; Zheng, J.; Wang, W.; Bai, L.; et al. Assessing the Causal Effects of Human Serum Metabolites on 5 Major Psychiatric Disorders. Schizophr. Bull. 2020, 46, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.C.; Huang, W.Y.; Tang, H.Y.; Cheng, M.L.; Chen, K.H. The Differences of Serum Metabolites between Patients with Early-Stage Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.S.; Hung, C.F.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Chen, K.C.; Chen, N.C. Higher Serum DHA and Slower Cognitive Decline in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: Two-Year Follow-Up. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo van Lent, D.; Egert, S.; Wolfsgruber, S.; Kleineidam, L.; Weinhold, L.; Wagner-Thelen, H.; Maier, W.; Jessen, F.; Ramirez, A.; Schmid, M.; et al. Eicosapentaenoic Acid Is Associated with Decreased Incidence of Alzheimer’s Dementia in the Oldest Old. Nutrients 2021, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.Z.; Li, L.; Dong, C.W.; Tan, C.C.; Xu, W. The Relationship of Omega-3 Fatty Acids with Dementia and Cognitive Decline: Evidence from Prospective Cohort Studies of Supplementation, Dietary Intake, and Blood Markers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 1096–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, R.; Tange, C.; Nishita, Y.; Kato, Y.; Imai, T.; Ando, F.; Shimokata, H. Serum docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acid and risk of cognitive decline over 10 years among elderly Japanese. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardeshi, R.; Bolshette, N.; Gadhave, K.; Arfeen, M.; Ahmed, S.; Jamwal, R.; Hammock, B.D.; Lahkar, M.; Goswami, S.K. Docosahexaenoic Acid Increases the Potency of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor in Alleviating Streptozotocin-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Complications of Diabetes. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liao, H.; Zhang, X.; Kiburg, K.V.; Shang, X.; Bulloch, G.; Huang, Y.; et al. Plasma metabolomic profiles of dementia: A prospective study of 110,655 participants in the UK Biobank. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, F.A.; Karamujić-Čomić, H.; Tijms, B.M.; Peeters, C.F.W.; Kester, M.I.; Scheltens, P.; Ahmad, S.; Vojinovic, D.; Adams, H.H.H.; Hankemeier, T.; et al. Circulating metabolites are associated with brain atrophy and white matter hyperintensities. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021, 17, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, L.; Shen, Y.; Miao, Y.; Wei, M.; Qian, N.; Liu, Y.; Min, W. Spectral tracing of deuterium for imaging glucose metabolism. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Ren, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Zhao, L.; Gao, H. Analysis of Metabolic Alterations Related to Pathogenic Process of Diabetic Encephalopathy Rats. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate uptake. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 65, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.M. Glutamate: The Master Neurotransmitter and Its Implications in Chronic Stress and Mood Disorders. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 722323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, R.; Oliveira, N.; Morais, E.; Amaral, A.P.; Sousa, A.; Graça, G.; Verde, I. NMR analysis seeking for cognitive decline and dementia metabolic markers in plasma from aged individuals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 238, 115815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Dong, B.; Zheng, H.; Lin, X.; Du, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Gao, H. Metabonomic profiles delineate potential role of glutamate-glutamine cycle in db/db mice with diabetes-associated cognitive decline. Mol. Brain 2016, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoli, R.; Pessione, E. The Neuro-Endocrinological Role of Microbial Glutamate and Gaba Signaling. Front Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Gao, W. Cerebrospinal Fluid Amino Acid Metabolite Signatures of Diabetic Cognitive Dysfunction Based on Targeted Mass Spectrometry. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 86, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Picard, G.; Sarazin, M. Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease: New diagnostic criteria. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 11, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, G.C.; Tatemichi, T.K.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Cummings, J.L.; Masdeu, J.C.; Garcia, J.H.; Amaducci, L.; Orgogozo, J.M.; Brun, A.; Hofman, A.; et al. Vascular dementia: Diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN International Workshop. Neurology 1993, 43, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Nakatsuka, M.; Ishii, H.; Nakayama, R.; Hosaka, R.; Meguro, K. Clinical utility of the functional independence measure for assessment of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Psychogeriatrics 2013, 13, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.M.; DeHaven, C.D.; Barrett, T.; Mitchell, M.; Milgram, E. Integrated, nontargeted ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry platform for the identification and relative quantification of the small-molecule complement of biological systems. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6656–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Diabetes without DACD (n = 54) | Diabetes with DACD (n = 46) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 63 (±5) | 72 (±7) | <0.001 |
| Female | 24 (44%) | 18 (39%) | 0.59 |
| BMI | 31 (±7) | 29 (±7) | 0.12 |
| HbA1c mmol | 63 (±15) | 55 (±13) | 0.006 |
| HbA1c % | 8 (±1) | 7 (±1) | 0.006 |
| FIM score | 125 (±2) | 113 (±18) | 0.032 |
| MoCA score | 29 (±1) | 21 (±8) | <0.001 |
| VPT | 15 (±11) | 17 (±10) | 0.49 |
| SBP | 131 (±17) | 131 (±19) | 0.90 |
| DBP | 70 (±10) | 69 (±10) | 0.50 |
| TYG | 2 (±1) | 2 (±1) | 0.32 |
| HDL | 1 (±0) | 1 (±0) | 0.066 |
| LDL | 2 (±1) | 2 (±1) | 0.85 |
| TC | 4 (±1) | 4 (±1) | 0.22 |
| Creatinine | 75 (±22) | 91 (±33) | 0.004 |
| Vit D | 26 (±13) | 28 (±12) | 0.43 |
| TSH | 2 (±1) | 2 (±1) | 0.28 |
| FT4 | 14 (±2) | 14 (±3) | 0.080 |
| B12 | 316 (±113) | 307 (±129) | 0.73 |
| Hgb | 14 (±2) | 13 (±2) | 0.52 |
| MCV | 82 (±6) | 86 (±7) | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Akl, N.S.; Khalifa, O.; Ponirakis, G.; Parray, A.; Ramadan, M.; Khan, S.; Chandran, M.; Ayadathil, R.; Elsotouhy, A.; Own, A.; et al. Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differentially Expressed Serum Metabolites and Pathways in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with and without Cognitive Decline: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042247
Al-Akl NS, Khalifa O, Ponirakis G, Parray A, Ramadan M, Khan S, Chandran M, Ayadathil R, Elsotouhy A, Own A, et al. Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differentially Expressed Serum Metabolites and Pathways in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with and without Cognitive Decline: A Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(4):2247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042247
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Akl, Neyla S., Olfa Khalifa, Georgios Ponirakis, Aijaz Parray, Marwan Ramadan, Shafi Khan, Mani Chandran, Raheem Ayadathil, Ahmed Elsotouhy, Ahmed Own, and et al. 2024. "Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differentially Expressed Serum Metabolites and Pathways in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with and without Cognitive Decline: A Cross-Sectional Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 4: 2247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042247
APA StyleAl-Akl, N. S., Khalifa, O., Ponirakis, G., Parray, A., Ramadan, M., Khan, S., Chandran, M., Ayadathil, R., Elsotouhy, A., Own, A., Al Hamad, H., Decock, J., Alajez, N. M., Albagha, O., Malik, R. A., El-Agnaf, O. M. A., & Arredouani, A. (2024). Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differentially Expressed Serum Metabolites and Pathways in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with and without Cognitive Decline: A Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(4), 2247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25042247







