Sustainable Silk-Based Particulate Systems for the Controlled Release of Pharmaceuticals and Bioactive Agents in Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration
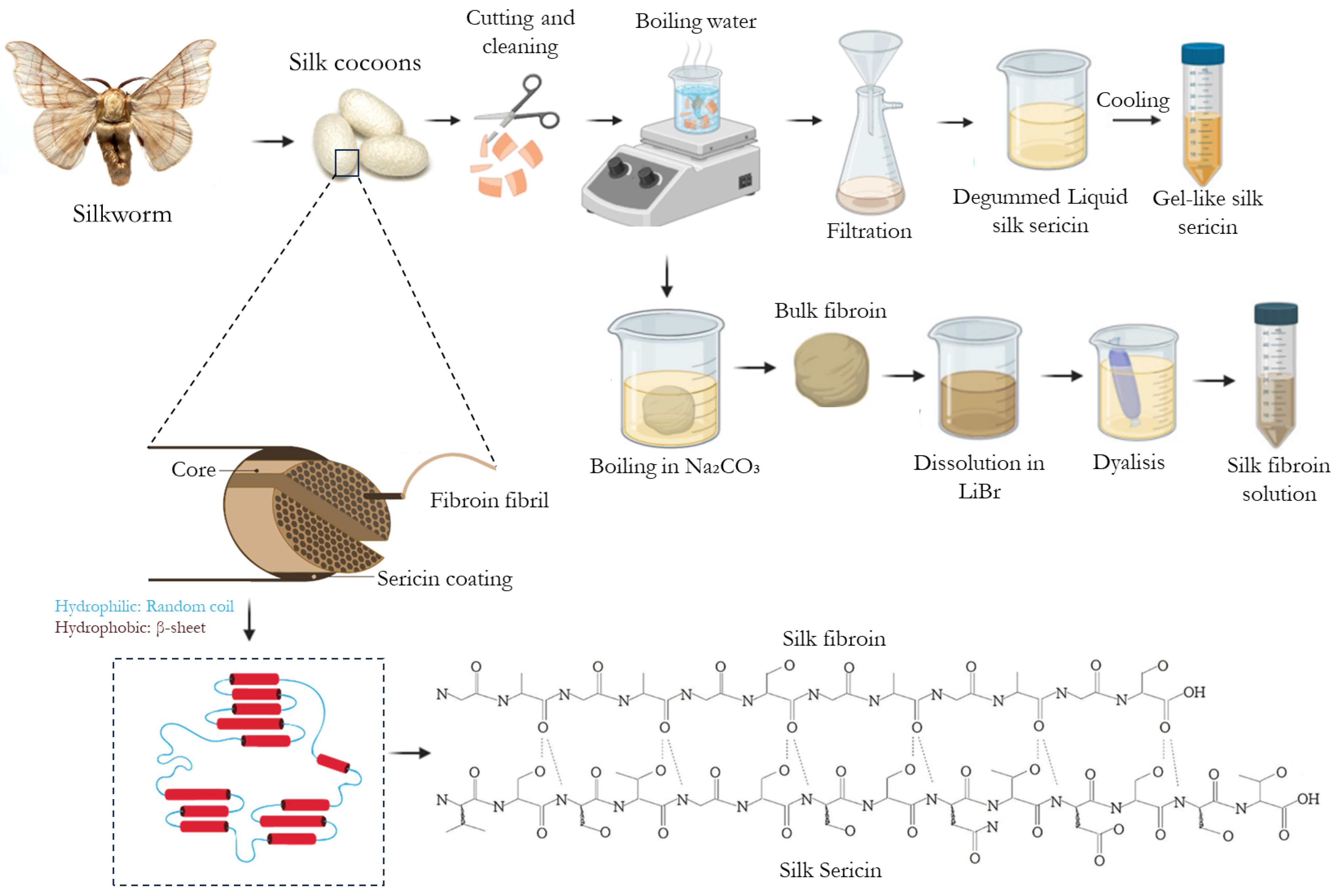
1.2. Silk Proteins as a Drug Carrier on Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration
1.2.1. Silk Fibroin
1.2.2. Silk Sericin
1.3. Overcoming Challenges in Scaling up Silk-Based Materials for Industrial Applications
2. Particulate Drug Delivery Systems in Wound and Skin Regeneration
2.1. Silk-Based Microparticles
2.1.1. Silk Sericin Micro-Systems
2.1.2. SF Micro-Systems
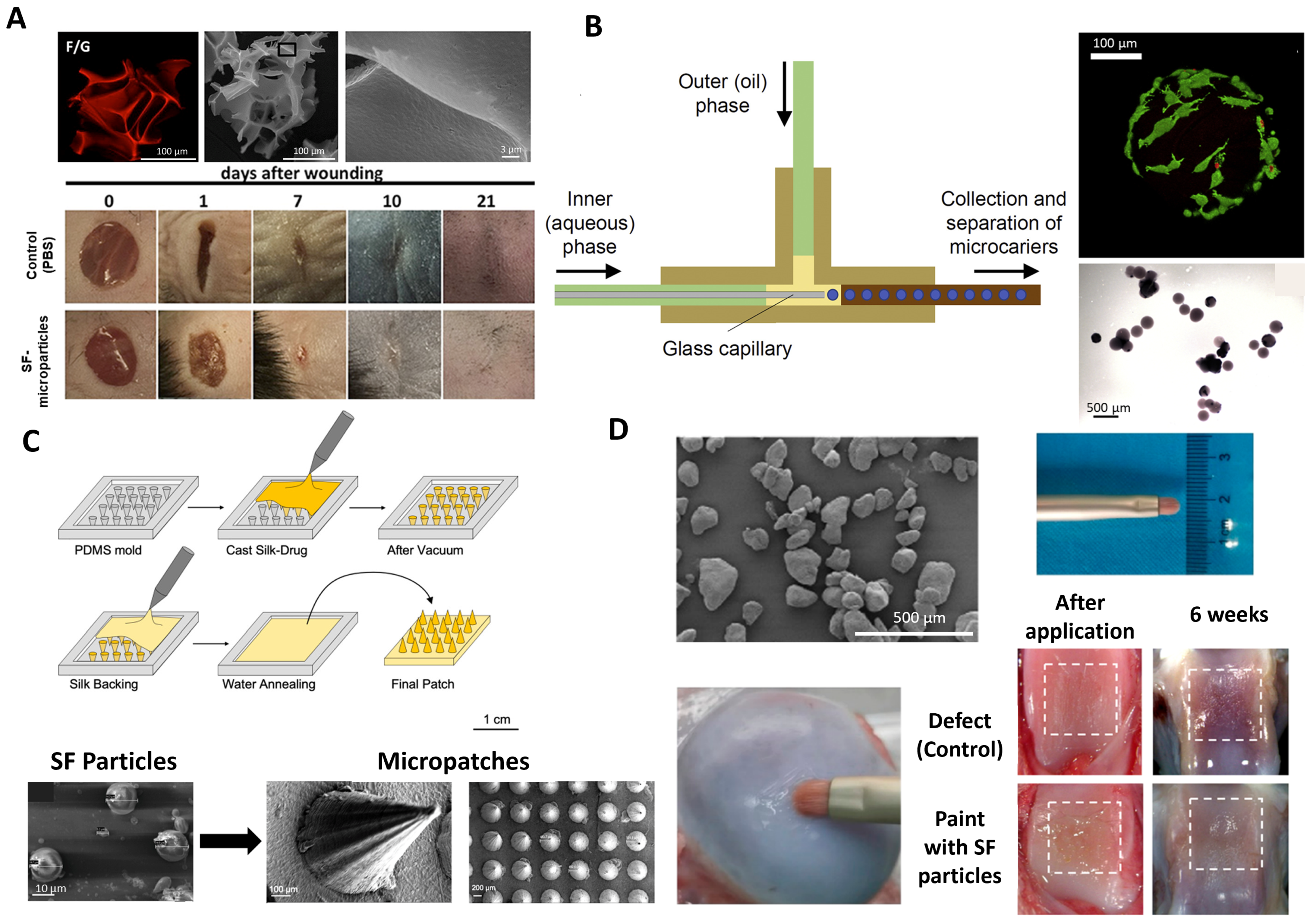
2.2. Silk-Based Nanoparticles
2.2.1. Physiochemical Properties Govern Nanoparticle Uptake
2.2.2. Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles for Delivery to the Skin
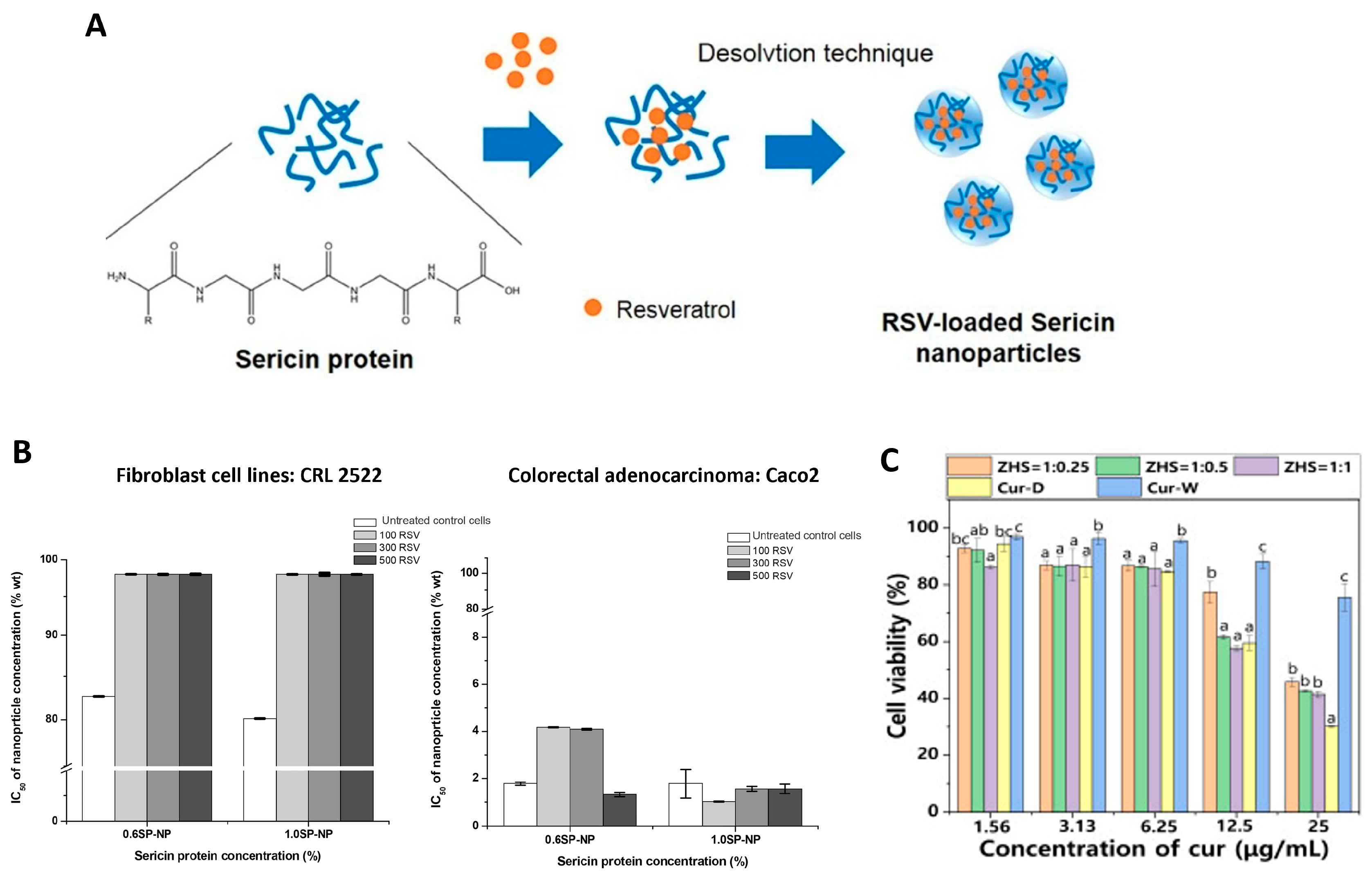
2.2.3. Silk Sericin Nanoparticles for Delivery to the Skin
2.2.4. Protein Corona Is Still Unexplored in Skin-Related Particle Systems
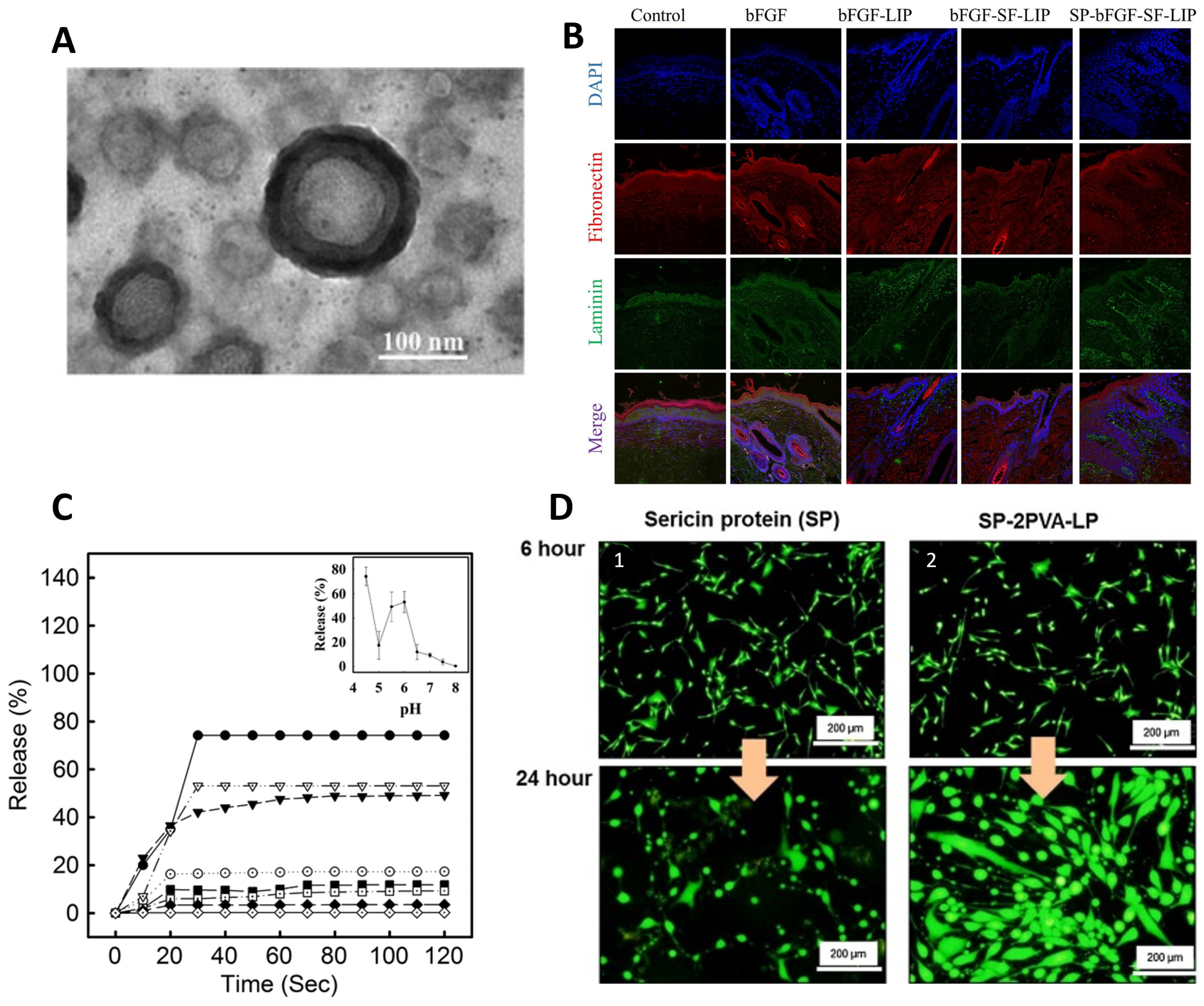
2.3. Silk-Based Liposomes
2.4. Silk-Based Aerogel Microparticle Systems

3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trucillo, P. Drug Carriers: Classification, Administration, Release Profiles, and Industrial Approach. Processes 2021, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, B.G.; Del Gaudio, P.; Alves, P.; Costa, R.; García-Gonzaléz, C.A.; Oliveira, A.L. Bioaerogels: Promising Nanostructured Materials in Fluid Management, Healing and Regeneration of Wounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezike, T.C.; Okpala, U.S.; Onoja, U.L.; Nwike, C.P.; Ezeako, E.C.; Okpara, O.J.; Okoroafor, C.C.; Eze, S.C.; Kalu, O.L.; Odoh, E.C.; et al. Advances in Drug Delivery Systems, Challenges and Future Directions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Romani, M.; Acharya, A.B.; Rahman, B.; Verron, E.; Badran, Z. Drug Delivery Systems in Regenerative Medicine: An Updated Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.S.; Cheruvu, H.S.; Mangion, S.E.; Alinaghi, A.; Benson, H.A.E.; Mohammed, Y.; Holmes, A.; van der Hoek, J.; Pastore, M.; Grice, J.E. Topical Drug Delivery: History, Percutaneous Absorption, and Product Development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 177, 113929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vepari, C.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a Biomaterial. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, D.; Mandal, B.B. Silk Biomaterials in Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration Therapeutics: From Bench to Bedside. Acta Biomater. 2020, 103, 24–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.; Wang, Y. Drug Delivery Systems for Wound Healing. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Pathak, K. Local Drug Delivery Strategies towards Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, X. Stem Cell-Based Drug Delivery Strategy for Skin Regeneration and Wound Healing: Potential Clinical Applications. Inflamm. Regen. 2023, 43, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matei, A.M.; Caruntu, C.; Tampa, M.; Georgescu, S.R.; Matei, C.; Constantin, M.M.; Constantin, T.V.; Calina, D.; Ciubotaru, D.A.; Badarau, I.A.; et al. Applications of Nanosized-Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Wound Care. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeo, M.; Lee, W.; Ito, M. Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a023267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, T.; Murtaza, B.N.; Shah, M.; Iqbal, S.; Rehman, M.; Jaber, F.; Dera, A.A.; Awwad, N.S.; Ibrahium, H.A. Recent Developments in Natural Biopolymer Based Drug Delivery Systems. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 23087–23121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Obeso, C.; Jane Hartzell, E.; Albert Scheel, R.; Kaplan, D.L. Delivering on the Promise of Recombinant Silk-Inspired Proteins for Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 192, 114622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.; Dan, A.K.; Sengupta, A.; Das, M.; Bindhani, B.K.; Das, D.; Parhi, P.K. Extraction of Silk Fibroin with Several Sericin Removal Processes and Its Importance in Tissue Engineering: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 2222–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, A.; Castro, F.; Rocha, F.; Oliveira, A.L. Protein-Based Hydroxyapatite Materials: Tuning Composition toward Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 3441–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardes, B.G.; Baptista-Silva, S.; Illanes-Bordomás, C.; Magalhães, R.; Dias, J.R.; Alves, N.M.F.; Costa, R.; García-González, C.A.; Oliveira, A.L. Expanding the Potential of Self-Assembled Silk Fibroin as Aerogel Particles for Tissue Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.S.; Costa, E.C.; Reis, S.; Spencer, C.; Calhelha, R.C.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Barros, L.; Vaz, J.A.; Coutinho, P. Silk Sericin: A Promising Sustainable Biomaterial for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonesi, M.; Garcia-Nieto, M.; Guinea, G.V.; Panetsos, F.; Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; González-Nieto, D. Silk Fibroin: An Ancient Material for Repairing the Injured Nervous System. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.H.; Liu, L.; Mitryashkin, A.; Wang, Y.; Goh, J.C.H. Silk Fibroin as a Bioink—A Thematic Review of Functionalization Strategies for Bioprinting Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 3242–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Gregory, D.A.; Tomeh, M.A.; Zhao, X. Silk Fibroin as a Functional Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkrongsak, S.; Tangthong, T.; Pasanphan, W. Electron Beam Induced Water-Soluble Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles as a Natural Antioxidant and Reducing Agent for a Green Synthesis of Gold Nanocolloid. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 118, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Lozano-Pérez, A.A.; Aznar-Cervantes, S.D.; Algieri, F.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Garrido-Mesa, N.; Vezza, T.; Utrilla, M.P.; Cenis, J.L.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, M.E.; et al. Effect of Aqueous and Particulate Silk Fibroin in a Rat Model of Experimental Colitis. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Hwang, H.-S.; Kim, D.-S.; Sheen, S.-H.; Heo, D.-H.; Hwang, G.-J.; Kang, S.-H.; Kweon, H.-Y.; Jo, Y.-Y.; Kang, S.-W.; et al. Effect of Silk Fibroin Peptide Derived from Silkworm Bombyx mori on the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Tat-SOD in a Mice Edema Model. BMB Rep. 2011, 44, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancheewa, B.; Buranapraditkun, S.; Laomeephol, C.; Rerknimitr, P.; Kanokpanont, S.; Damrongsakkul, S.; Klaewsongkram, J. In Vitro Immune Responses of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells to Silk Fibroin: IL-10 Stimulated Anti-Inflammatory and Hypoallergenic Properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-C.; Chen, C.-T.; Cherng, J.-H.; Li, M.-C.; Wen, C.-C.; Hu, S.-I.; Wang, Y.-W. Cutaneous Regeneration Mechanism of β-Sheet Silk Fibroin in a Rat Burn Wound Healing Model. Polymers 2021, 13, 3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalei, S.; Handa, H. A Review on Antibacterial Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials: Current State and Prospects. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 23, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalamak, S.; Erdoğdu, C.; Özalp, M.; Ulubayram, K. Silk Fibroin Based Antibacterial Bionanotextiles as Wound Dressing Materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 43, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, S.-G.; Park, J.-H.; Nam, H.; Kim, J.-B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Oh, Y.-S.; Suh, J.-G. Silk Fibroin Hydrolysate Exerts an Anti-Diabetic Effect by Increasing Pancreatic β Cell Mass in C57BL/KsJ-Db/Db Mice. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Jin, B.R. Spider Silk Fibroin Enhances Insulin Secretion and Reduces Blood Glucose Levels in Diabetic Mice. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2014, 17, 907–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Kojima, K.; Tamada, Y. Higher Gene Expression Related to Wound Healing by Fibroblasts on Silk Fibroin Biomaterial than on Collagen. Molecules 2020, 25, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, V.P.; Costa, J.B.; Carneiro, S.M.; Pina, S.; Veloso, A.C.A.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J.M. Bioinspired Silk Fibroin-Based Composite Grafts as Bone Tunnel Fillers for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Bai, T.; Li, C.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhou, W. Biomimetic Inorganic Nanoparticle-Loaded Silk Fibroin-Based Coating with Enhanced Antibacterial and Osteogenic Abilities. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30027–30039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, Ł.; Szudzik, M.; Rybka, M.; Konop, M. Silk Fibroin Biomaterials and Their Beneficial Role in Skin Wound Healing. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, E.-B.; Sung, N.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, J.; Matsui, T.; Byun, M.-W.; Lee, J.-W. Enhancement of Anti-Tumor Activity of Gamma-Irradiated Silk Fibroin via Immunomodulatory Effects. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 186, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yücel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials Fabrication from Bombyx mori Silk Fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, B. Biodegradation of Silk Biomaterials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horan, R.L.; Antle, K.; Collette, A.L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Moreau, J.E.; Volloch, V.; Kaplan, D.L.; Altman, G.H. In Vitro Degradation of Silk Fibroin. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3385–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Nguyen, V.-H.; Le, T.-H.; Huynh, V.Q.N.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Trinh, Q.T.; Kim, S.Y.; Le, Q. Van Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.H.; Tan, W.; Zhu, C.C.; Shang, X.; Zhang, L. Properties of a Stable and Sustained-Release Formulation of Recombinant Human Parathyroid Hormone (RhPTH) with Chitosan and Silk Fibroin Microparticles. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 7532–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luetchford, K.A.; Chaudhuri, J.B.; De Bank, P.A. Silk Fibroin/Gelatin Microcarriers as Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 106, 110116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.L.; Sun, L.; Kim, H.J.; Hu, X.; Rice, W.; Kluge, J.; Reis, R.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Aligned Silk-Based 3-D Architectures for Contact Guidance in Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1530–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Zuo, B. Effect of Sodium Carbonate Concentrations on the Degumming and Regeneration Process of Silk Fibroin. J. Text. Inst. 2015, 106, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, E.M.; Hu, X.; Finley, V.; Kuo, C.K.; Kaplan, D.L. Effect of Silk Protein Processing on Drug Delivery from Silk Films. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coburn, J.M.; Na, E.; Kaplan, D.L. Modulation of Vincristine and Doxorubicin Binding and Release from Silk Films. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, S.; Jabbari, H.; Yousofi, H.; Fathi, A.; Mahmoodi, S.; Jafarian, M.J.; Shomali, N.; Shotorbani, S.S. Regulatory Effect of Sericin Protein in Inflammatory Pathways; A Comprehensive Review. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 243, 154369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, R.I.; Brancalhão, R.M.C.; Ribeiro, L.d.F.C.; Natali, M.R.M. Silkworm Sericin: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8175701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, S.; Nishimura, T.; Sasaki, M.; Yamada, H.; Miki, M. Sericin, a Protein Derived from Silkworms, Accelerates the Proliferation of Several Mammalian Cell Lines Including a Hybridoma. Cytotechnology 2002, 40, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, L.; Deng, Y.; Zou, M.; Cai, B.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Silk Sericin-Based Materials for Biomedical Applications. Biomaterials 2022, 287, 121638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaviria, A.; Jaramillo-Quiceno, N.; Motta, A.; Restrepo-Osorio, A. Silk Wastes and Autoclaved Degumming as an Alternative for a Sustainable Silk Process. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.R.; Ribani, M.; Gimenes, M.L.; Scheer, A.P. High Molecular Weight Sericin Obtained by High Temperature and Ultrafiltration Process. Procedia. Eng. 2012, 42, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, A.; Castro, F.; Oliveira, A.; Rocha, F. High Efficient Strategy for the Production of Hydroxyapatite/Silk Sericin Nanocomposites. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, A.; Castro, F.; Reis, C.C.; Sousa, A.; Oliveira, A.L.; Rocha, F. Hydroxyapatite/Sericin Composites: A Simple Synthesis Route under near-Physiological Conditions of Temperature and PH and Preliminary Study of the Effect of Sericin on the Biomineralization Process. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Yao, S.; He, L.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, P.; Qin, G. Safety Assessment of Water-Extract Sericin from Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Cocoons Using Different Model Approaches. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 9689386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista-Silva, S.; Borges, S.; Costa-Pinto, A.R.; Costa, R.; Amorim, M.; Dias, J.R.; Ramos, Ó.; Alves, P.; Granja, P.L.; Soares, R.; et al. In Situ Forming Silk Sericin-Based Hydrogel: A Novel Wound Healing Biomaterial. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1573–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, T.L.; Da Silva, A.C.; Ribani, M.; Vieira, M.G.A.; Gimenes, M.L.; Da Silva, M.G.C. Evaluation of Molecular Weight Distribution of Sericin in Solutions Concentrated via Precipitation by Ethanol and Precipitation by Freezing/Thawing. Chem. Eng. Trans 2014, 38, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, F.; Mahmood, T.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Usmani, S.; Bagga, P.; Shamim, A.; Srivastav, R.K. Diligent Profiling of Preclinical Safety of the Silk Protein Sericin. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 32, 20190272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, P.; Qin, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, P.; Ye, Y. Toxicological Evaluation of Water-Extract Sericin from Silkworm (Bombyx mori) in Pregnant Rats and Their Fetus during Pregnancy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 982841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.P.; Mandal, B.B. Antioxidant Potential of Mulberry and Non-Mulberry Silk Sericin and Its Implications in Biomedicine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manesa, K.C.; Kebede, T.G.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M. Profiling of Silk Sericin from Cocoons of Three Southern African Wild Silk Moths with a Focus on Their Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takechi, T.; Wada, R.; Fukuda, T.; Harada, K.; Takamura, H. Antioxidant Activities of Two Sericin Proteins Extracted from Cocoon of Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Measured by DPPH, Chemiluminescence, ORAC and ESR Methods. Biomed. Rep. 2014, 2, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramwit, P.; Towiwat, P.; Srichana, T. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Silk Sericin. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1934578X1300800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramwit, P.; Towiwat, P.; Srichana, T. An Investigation of the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Silk Sericin. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2013, 19, 3615–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahaliloglu, Z.; Kilicay, E.; Denkbas, E.B. Antibacterial Chitosan/Silk Sericin 3D Porous Scaffolds as a Wound Dressing Material. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, G.; Cai, R.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, H.; He, H. Fabrication of Antibacterial Sericin Based Hydrogel as an Injectable and Mouldable Wound Dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapru, S.; Ghosh, A.K.; Kundu, S.C. Non-Immunogenic, Porous and Antibacterial Chitosan and Antheraea Mylitta Silk Sericin Hydrogels as Potential Dermal Substitute. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.P.; Alam, S.; Jain, A.K.; Ansari, K.M.; Mandal, B.B. Protective Activity of Silk Sericin against UV Radiation-Induced Skin Damage by Downregulating Oxidative Stress. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2018, 1, 2120–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaorigetu, S.; Yanaka, N.; Sasaki, M.; Watanabe, H.; Kato, N. Inhibitory Effects of Silk Protein, Sericin on UVB-Induced Acute Damage and Tumor Promotion by Reducing Oxidative Stress in the Skin of Hairless Mouse. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2003, 71, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhao, S.-X.; Yin, X.-L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wei, Z.-G.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Silk Sericin Has Significantly Hypoglycaemic Effect in Type 2 Diabetic Mice via Anti-Oxidation and Anti-Inflammation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramwit, P.; Kanokpanont, S.; De-Eknamkul, W.; Kamei, K.; Srichana, T. The Effect of Sericin with Variable Amino-Acid Content from Different Silk Strains on the Production of Collagen and Nitric Oxide. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2009, 20, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramwit, P.; Kanokpanont, S.; Nakpheng, T.; Srichana, T. The Effect of Sericin from Various Extraction Methods on Cell Viability and Collagen Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 2200–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, A.; Magalhães, R.; Castro, F.; Oliveira, A.L. Fabrication of Highly Tuned Calcium Phosphate/Silk Sericin Composites: Exploring New Pathways on Skin Regeneration. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the European Society for Biomaterials, Porto, Portugal, 5–9 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, S.C.; Dash, B.C.; Dash, R.; Kaplan, D.L. Natural Protective Glue Protein, Sericin Bioengineered by Silkworms: Potential for Biomedical and Biotechnological Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 998–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padamwar, M.N.; Pawar, A.P.; Daithankar, A.V.; Mahadik, K.R. Silk Sericin as a Moisturizer: An in Vivo Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2005, 4, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, M.; Kimura, T.; Murakami, M.; Katayama, K.; Terada, S.; Yamaguchi, A. Rat Islet Culture in Serum-Free Medium Containing Silk Protein Sericin. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2009, 16, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Duan, S.; Chen, L.; Xiang, H.; Dong, Y.; Wang, W. Systematic Evaluation of Sericin Protein as a Substitute for Fetal Bovine Serum in Cell Culture. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, T.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Q. The Potential of Silk Sericin Protein as a Serum Substitute or an Additive in Cell Culture and Cryopreservation. Amino. Acids 2017, 49, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, T.T.; Wei, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.Q. Silk Sericin Hydrolysate Is a Potential Candidate as a Serum-Substitute in the Culture of Chinese Hamster Ovary and Henrietta Lacks Cells. J. Insect Sci. 2019, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubouchi, K.; Igarashi, Y.; Takasu, Y.; Yamada, H. Sericin Enhances Attachment of Cultured Human Skin Fibroblasts. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sheng, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; et al. Silk Fibroin and Sericin Differentially Potentiate the Paracrine and Regenerative Functions of Stem Cells Through Multiomics Analysis. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2210517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Sato, S.; Yamanaka, A.; Yamada, H.; Fuwa, N.; Nomura, M. Silk Protein, Sericin, Inhibits Lipid Peroxidation and Tyrosinase Activity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, C.; Numata, K.; Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Seib, F.P. The Biomedical Use of Silk: Past, Present, Future. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1800465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Ling, S.; Li, C.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Silkworm Silk-Based Materials and Devices Generated Using Bio-Nanotechnology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6486–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathumpai, W.; Promboon, A.; Werapan, B.; Nutaratat, P.; Chim-Anek, P.; Ninpetch, U. Pilot-Scale Protease Production by Bacillus Sp. C4 for Silk Degumming Processes. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, A.; Castro, F.; Rocha, F.; Oliveira, A.L. Recent Advances in Silk Sericin/Calcium Phosphate Biomaterials. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverri-Correa, E.; Grajales-Lopera, D.O.; Gutiérrez-Restrepo, S.; Ossa-Orozco, C.P. Effective Sericin-Fibroin Separation from Bombyx mori Silkworms Fibers and Low-Cost Salt Removal from Fibroin Solution. Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Antioq. 2019, 94, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capar, G.; Pilevneli, T.; Yetis, U.; Dilek, F.B. Life Cycle Assessment of Sericin Recovery from Silk Degumming Wastewaters. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 30, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q. Applications of Natural Silk Protein Sericin in Biomaterials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2002, 20, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.L.; Veiga, A.; Bernardes, B.G.; Costa, J.B.; Rojo del Olmo, L. Off-The-Shelf Silk Sericin. Methods and Uses Thereof. Patent No. 2023231000146, 7 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sherstneva, A.A.; Demina, T.S.; Monteiro, A.P.F.; Akopova, T.A.; Grandfils, C.; Ilangala, A.B. Biodegradable Microparticles for Regenerative Medicine: A State of the Art and Trends to Clinical Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, A.; Castro, F.; Rocha, F.; Bernardes, B.; Duarte, M.M.; Oliveira, A.L. Opening New Avenues for Bioceramics: Oscillatory Flow Reactors and Upcoming Technologies in Skin-Tissue Engineering. Solid State Phenom. 2022, 339, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, A.; Magalhães, R.; Duarte, M.M.; Dias, J.R.; Alves, N.M.; Costa-Pinto, A.R.; Castro, F.; Rocha, F.; Oliveira, A.L. Continuous Production of Highly Tuned Silk/Calcium-Based Composites: Exploring New Pathways for Skin Regeneration. Molecules 2022, 27, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdown, A.B.G. Calcium: A Potential Central Regulator in Wound Healing in the Skin. Wound Repair Regen. 2002, 10, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, E.; Arciola, C.; Vigani, B.; Crivelli, B.; Moro, P.; Marrubini, G.; Sorrenti, M.; Catenacci, L.; Bruni, G.; Chlapanidas, T.; et al. In Vitro Effectiveness of Microspheres Based on Silk Sericin and Chlorella Vulgaris or Arthrospira Platensis for Wound Healing Applications. Materials 2017, 10, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, E.; Perteghella, S.; Rassu, G.; Gavini, E.; Petretto, G.L.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Giunchedi, P.; Torre, M.L. Sericin/Crocetin Micro/Nanoparticles for Nucleus Pulposus Cells Regeneration: An “Active” Drug Delivery System. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1129882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, E.; Perteghella, S.; Marrubini, G.; Sorrenti, M.; Catenacci, L.; Tripodo, G.; Mastrogiacomo, M.; Mandracchia, D.; Trapani, A.; Faragò, S.; et al. In Vitro Efficacy of Silk Sericin Microparticles and Platelet Lysate for Intervertebral Disk Regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, E.; Perteghella, S.; Faragò, S.; Torre, M.L. Association of Silk Sericin and Platelet Lysate: Premises for the Formulation of Wound Healing Active Medications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phromsopha, T.; Baimark, Y. Chitosan/Silk Sericin Blend Microparticles Prepared by Water-in-Oil Emulsification-Diffusion for Controlled Release of Silk Sericin Antioxidant. Int. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2017, 7, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Feng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Gao, W.; Miao, Q.; Wu, H. Microparticles of Sericin-Dextran Conjugate for Improving the Solubility of Antiviral Drug. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosenko, M.A.; Moysenovich, A.M.; Zvartsev, R.V.; Arkhipova, A.Y.; Zhdanova, A.S.; Agapov, I.I.; Vasilieva, T.V.; Bogush, V.G.; Debabov, V.G.; Nedospasov, S.A.; et al. Novel Biodegradable Polymeric Microparticles Facilitate Scarless Wound Healing by Promoting Re-Epithelialization and Inhibiting Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisenovich, M.M.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Moysenovich, A.M.; Silachev, D.N.; Danilina, T.I.; Savchenko, E.S.; Bobrova, M.M.; Safonova, L.A.; Tatarskiy, V.V.; Kotliarova, M.S.; et al. Effect of Silk Fibroin on Neuroregeneration After Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Yang, X.; Zheng, F.; Shi, J.; Huo, C.; Wang, Z.; Reis, R.L.; Kundu, S.C.; Xiao, B.; Duan, L. Facilely Printed Silk Fibroin Hydrogel Microparticles as Injectable Long-Lasting Fillers. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 12, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T.; Huynh, Q.C.; Lieu, R.; Nguyen, V.B.; Tran, V.D.; Thuy, B.T.P. Controlled-Release Wedelia Trilobata L. Flower Extract Loaded Fibroin Microparticles as Potential Anti-Aging Preparations for Cosmetic Trade Commercialization. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ji, W.; Ren, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y. Silk Fibroin Microparticles with Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers Encapsulation for Abdominal Wall Repair. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1801005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavuz, B.; Chambre, L.; Harrington, K.; Kluge, J.; Valenti, L.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Fibroin Microneedle Patches for the Sustained Release of Levonorgestrel. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 5375–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Hong, Y.; Fu, Q.; He, Q.; Mechakra, A.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, F.; Liang, R.; Li, C.; et al. Tissue-Adhesive Paint of Silk Microparticles for Articular Surface Cartilage Regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 22467–22478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, R.; Shukla, S.; Kale, A.; Deshmukh, N.; Nisal, A.; Venugopalan, P. Silk Fibroin Microparticle Scaffold for Use in Bone Void Filling: Safety and Efficacy Studies. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, N.A.; Deshpande, R.V.; Shukla, S.G.; Nisal, A.A. Silk Fibroin 3D Microparticle Scaffolds with Bioactive Ceramics: Chemical, Mechanical, and Osteoregenerative Characteristics. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2000458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisal, A.; Sayyad, R.; Dhavale, P.; Khude, B.; Deshpande, R.; Mapare, V.; Shukla, S.; Venugopalan, P. Silk Fibroin Micro-Particle Scaffolds with Superior Compression Modulus and Slow Bioresorption for Effective Bone Regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.-L.; Fan, Z.-L.; Yuan, J.-D.; Chen, P.-P.; Yang, J.-J.; Xu, J.; ZhuGe, D.-L.; Jin, B.-H.; Zhu, Q.-Y.; Shen, B.-X.; et al. Skin-Penetrating Polymeric Nanoparticles Incorporated in Silk Fibroin Hydrogel for Topical Delivery of Curcumin to Improve Its Therapeutic Effect on Psoriasis Mouse Model. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, I.; Shimamura, Y.; Kakami, Y.; Kameda, T.; Hattori, K.; Miura, S.; Shirai, H.; Okumura, M.; Inagi, T.; Terada, H.; et al. Transdermal Delivery of 40-Nm Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2019, 175, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yucel, T.; Lu, Q.; Hu, X.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Nanospheres and Microspheres from Silk/Pva Blend Films for Drug Delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Naskar, D.; Kundu, S.C.; Bishop, D.P.; Doble, P.A.; Boddy, A.V.; Chan, H.-K.; Wall, I.B.; Chrzanowski, W. Formulation of Biologically-Inspired Silk-Based Drug Carriers for Pulmonary Delivery Targeted for Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Lu, G.; Lu, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. Direct Formation of Silk Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongpinyochit, T.; Johnston, B.F.; Philipp Seib, F. Manufacture and Drug Delivery Applications of Silk Nanoparticles. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 2016, e54669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatin, S.; Barar, J.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Adibkia, K.; Kiafar, F.; Jelvehgari, M. Development of a Nanoprecipitation Method for the Entrapment of a Very Water Soluble Drug into Eudragit RL Nanoparticles. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A.; Esendagli, G.; Yerlikaya, F.; Caban-Toktas, S.; Yoyen-Ermis, D.; Horzum, U.; Aktas, Y.; Khan, M.; Couvreur, P.; Capan, Y. A Small Variation in Average Particle Size of PLGA Nanoparticles Prepared by Nanoprecipitation Leads to Considerable Change in Nanoparticles’ Characteristics and Efficacy of Intracellular Delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, A.; Peng, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, N. Size-Dependent Absorption through Stratum Corneum by Drug-Loaded Liposomes. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, T.; Vaughn, A.E.; Seal, S.; Liechty, K.W.; Zgheib, C. Silk Fibroin-Based Therapeutics for Impaired Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, S.; Mitragotri, S. Challenges Associated with Penetration of Nanoparticles across Cell and Tissue Barriers: A Review of Current Status and Future Prospects. Nano Today 2014, 9, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, T. Nanoparticle-Mediated Cytoplasmic Delivery of Messenger RNA Vaccines: Challenges and Future Perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Xia, Y. Killing Cancer Cells by Rupturing Their Lysosomes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 252–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seib, F.P.; Jones, G.T.; Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Lin, Y.; Kaplan, D.L. PH-Dependent Anticancer Drug Release from Silk Nanoparticles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaidani, S.; Jacobus, C.; Sahoo, J.K.; Harrington, K.; Johnson, H.; Foster, O.; Cui, S.; Hasturk, O.; Falcucci, T.; Chen, Y.; et al. Silk Nanoparticle Synthesis: Tuning Size, Dispersity, and Surface Chemistry for Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 18967–18977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoujia, J.; Faizan, M.; Parashar, P.; Singh, N.; Saraf, S.A. Curcumin Loaded Sericin Nanoparticles: Assessment for Biomedical Application. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2021, 1, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Xu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Hu, B.; Yang, M.; Zhu, L. PH-Triggered Charge-Reversal Silk Sericin-Based Nanoparticles for Enhanced Cellular Uptake and Doxorubicin Delivery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Dey, T.; Kundu, S.C. Fabrication of Sericin Nanoparticles for Controlled Gene Delivery. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 2137–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Román, R.; Naik, A.; Kalia, Y.N.; Guy, R.H.; Fessi, H. Skin Penetration and Distribution of Polymeric Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.-Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zha, J. Study of Magnetic Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles for Massage-like Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Teichmann, A.; Otberg, N.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Luengo, J.; Weiß, B.; Schaefer, U.F.; Lehr, C.-M.; Wepf, R. Nanoparticles—An Efficient Carrier for Drug Delivery into the Hair Follicles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 66, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, I.; Suzuki, T.; Makino, K. Skin Permeability and Transdermal Delivery Route of 50-Nm Indomethacin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Fu, S.; Wu, X.; Xiao, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Q. Silk Nanocarrier with Tunable Size to Improve Transdermal Capacity for Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Drugs. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2023, 6, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaly, A.H.; Sarhan, W.A.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Development of a Silk Fibroin-Based Multitask Aerosolized Nanopowder Formula for Efficient Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweiker, D.; Horn, S.; Hoell, A.; Seitz, S.; Walter, D.; Trop, M. Semi-Permanent Skin Staining Associated with Silver-Coated Wound Dressing Acticoat. Ann. Burns Fire Disasters 2014, 27, 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, J.; Kanoujia, J.; Parashar, P.; Tripathi, C.B.; Saraf, S.A. Wound Healing Applications of Sericin/Chitosan-Capped Silver Nanoparticles Incorporated Hydrogel. Drug. Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelminiak-Dudkiewicz, D.; Smolarkiewicz-Wyczachowski, A.; Mylkie, K.; Wujak, M.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Nowak, P.; Bocian, S.; Goslinski, T.; Ziegler-Borowska, M. Chitosan-Based Films with Cannabis Oil as a Base Material for Wound Dressing Application. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiarajan, J.; Balaji, S.; Revathy, K.; Palanikumar, S. Fabrication and Validation of Silver Nanoparticles from Cocoon Extract of Silk Worm Bombyx mori. L. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suktham, K.; Koobkokkruad, T.; Wutikhun, T.; Surassmo, S. Efficiency of Resveratrol-Loaded Sericin Nanoparticles: Promising Bionanocarriers for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 537, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.J.; Tang, C.H.; Luo, F.C.; Yin, S.W.; Yang, X.Q. Topical Application of Zein-Silk Sericin Nanoparticles Loaded with Curcumin for Improved Therapy of Dermatitis. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 24, 100802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandra, F.; Khaliq, N.U.; Sunna, A.; Care, A. Developing Protein-Based Nanoparticles as Versatile Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy and Imaging. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champion, J.A.; Pustulka, S.M.; Ling, K.; Pish, S.L. Protein Nanoparticle Charge and Hydrophobicity Govern Protein Corona and Macrophage Uptake. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 48284–48295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasturk, O.; Sahoo, J.K.; Kaplan, D.L. Synthesis and Characterization of Silk Ionomers for Layer-by-Layer Electrostatic Deposition on Individual Mammalian Cells. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2829–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain, J.N.; Hawker, M.J.; Hartle, L.; Wu, J.; Montanari, V.; Sahoo, J.K.; Davis, L.M.; Kaplan, D.L.; Kumar, K. Towards Non-stick Silk: Tuning the Hydrophobicity of Silk Fibroin Protein. ChemBioChem 2022, 23, e202200429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guan, J.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Hua, W.; Mao, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, W.; Qian, J.; et al. Brain-Targeted Drug Delivery by Manipulating Protein Corona Functions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobin, A.S.; Rhea, R.; Newman, R.A.; Mathur, A.B. Silk-Fibroin-Coated Liposomes for Long-Term and Targeted Drug Delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2006, 1, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyamud, C.; Phetdee, C.; Jaimalai, T.; Prangkio, P. Silk Fibroin-Coated Liposomes as Biomimetic Nanocarrier for Long-Term Release Delivery System in Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2021, 26, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.-J.; Pyo, C.G.; Kim, J.-C. Liposomes Incorporating Hydrophobically Modified Silk Fibroin: PH-Dependent Release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Chen, P.; ZhuGe, D.; Zhu, Q.; Jin, B.; Shen, B.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Y. Liposomes with Silk Fibroin Hydrogel Core to Stabilize BFGF and Promote the Wound Healing of Mice with Deep Second-Degree Scald. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.-L.; Chen, P.-P.; Wang, L.-F.; Tong, M.-Q.; Ou, Z.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Xiao, J.; Fu, T.-L. Wei-Xue Skin-Permeable Liposome Improved Stability and Permeability of BFGF against Skin of Mice with Deep Second Degree Scald to Promote Hair Follicle Neogenesis through Inhibition of Scar Formation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-L.; Chen, P.-P.; Wang, L.; Xue, W.; Fu, T.-L. Hair Regenerative Effect of Silk Fibroin Hydrogel with Incorporation of FGF-2-Liposome and Its Potential Mechanism in Mice with Testosterone-Induced Alopecia Areata. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-C. Complexation-Triggerable Liposome Mixed with Silk Protein and Chitosan. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2015, 26, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laomeephol, C.; Ferreira, H.; Kanokpanont, S.; Neves, N.M.; Kobayashi, H.; Damrongsakkul, S. Dual-Functional Liposomes for Curcumin Delivery and Accelerating Silk Fibroin Hydrogel Formation. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suktham, K.; Koobkokkruad, T.; Saesoo, S.; Saengkrit, N.; Surassmo, S. Physical and Biological Characterization of Sericin-Loaded Copolymer Liposomes Stabilized by Polyvinyl Alcohol. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamikamkar, S.; Yalcintas, E.P.; Haghniaz, R.; de Barros, N.R.; Mecwan, M.; Nasiri, R.; Davoodi, E.; Nasrollahi, F.; Erdem, A.; Kang, H.; et al. Aerogel-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications: From Fabrication Methods to Disease-Targeting Applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2204681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, C.A.; Barros, J.; Rey-Rico, A.; Redondo, P.; Gómez-Amoza, J.L.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Monteiro, F.J. Antimicrobial Properties and Osteogenicity of Vancomycin-Loaded Synthetic Scaffolds Obtained by Supercritical Foaming. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3349–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Iglesias, C.; Barros, J.; Ardao, I.; Monteiro, F.J.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Gómez-Amoza, J.L.; García-González, C.A. Vancomycin-Loaded Chitosan Aerogel Particles for Chronic Wound Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 204, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-González, C.A.; Sosnik, A.; Kalmár, J.; De Marco, I.; Erkey, C.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Aerogels in Drug Delivery: From Design to Application. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, S.; Ying, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, F. Engineering of Aerogel-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2363–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista-Silva, S.; Bernardes, B.G.; Borges, S.; Rodrigues, I.; Fernandes, R.; Gomes-Guerreiro, S.; Pinto, M.T.; Pintado, M.; Soares, R.; Costa, R.; et al. Exploring Silk Sericin for Diabetic Wounds: An In Situ-Forming Hydrogel to Protect against Oxidative Stress and Improve Tissue Healing and Regeneration. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Li, X.-W.; Xu, W.; Yu, Q.-Y.; Fang, S.-M. Advances of Regenerated and Functionalized Silk Biomaterials and Application in Skin Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 128024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-Y.; Um, I.C.; Kim, M.-K.; Kwon, K.-J.; Kim, S.-G.; Park, Y.-W. Effectiveness of Woven Silk Dressing Materials on Full-Skin Thickness Burn Wounds in Rat Model. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 36, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallepally, R.R.; Marin, M.A.; Surampudi, V.; Subia, B.; Rao, R.R.; Kundu, S.C.; McHugh, M.A. Silk Fibroin Aerogels: Potential Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.A.; Mallepally, R.R.; McHugh, M.A. Silk Fibroin Aerogels for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2014, 91, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jawuschi, N.; Chen, S.; Abie, N.; Fischer, T.; Fare, S.; Maleki, H.H. Self-Assembly-Driven Bi2S3 Nanobelts Integrated a Silk-Fibroin-Based 3D-Printed Aerogel-Based Scaffold with a Dual-Network Structure for Photothermal Bone Cancer Therapy. Langmuir 2023, 39, 4326–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, A.; Castro, F.; Rocha, F.; Oliveira, A. Silk-based Microcarriers: Current Developments and Future Perspectives. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamboni, L.; Gauthier, M.; Yang, G.; Wang, Q. Silk Sericin: A Versatile Material for Tissue Engineering and Drug Delivery. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Properties | Observations | References |
|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant activity | SF exhibits significant antioxidant activity due to the presence of specific amino acids and an abundance of other chemical groups (hydroxyl and carboxyl). | [17,22] |
| Anti-inflammatory | Suppression of the elevated levels of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α; stimulation of IL-10. | [23,24,25,26] |
| Antibacterial | SF naturally lacks inherent antibacterial activity, requiring the combination of anti-bacterial agents. | [27,28] |
| Metabolic regulation activity (anti-diabetic) | SF exerts anti-diabetic effects by increasing pancreatic β cell mass in a non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus mouse model and enhances insulin secretion. | [29,30] |
| Collagen production | SF promotes type-III collagen. | [31] |
| Mimic the organic component in bone-like systems | Scaffold-based frameworks made of SF can be employed to recreate the biomineralization process of bone tissue. SF serves as a supportive structure for the proliferation of osteoblasts. | [32,33] |
| Moisturizing | SF shows great promise as a natural moisturizing agent. | [26] |
| Promotion of cell behavior | SF promotes cell growth and migration of keratinocytes and fibroblasts, enhances pro-angiogenic activity, and considerably expedites the healing of skin wounds. | [17,34] |
| Anti-tumor | Gamma-irradiated SF reduces the tumor growth in B16BL6 (mouse melanoma cancer). | [35] |
| Biodegradability | SF is susceptible to biological degradation by proteolytic enzymes (e.g., chymotrypsin, actinase, protease XIV, carboxylase). | [36,37,38] |
| Properties | Observations | References |
|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant and Photoprotective Activity | SS exhibits ROS scavenging activity protects cells from oxidative stress and shows suppression of lipid peroxidation. The antioxidant activity of SS benefits from its high serine and threonine content. | [59,60,61] |
| Anti-inflammatory | Suppression of the COX-2 enzyme and nitric oxide production. | [62,63] |
| Antibacterial | Inhibitory effects on Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtilis. The reason is that SS has a positive amino acid side-chain due to its carboxyl group being protonated under acidic conditions, thus having antibacterial activity. | [60,64,65,66] |
| UV protection | SS reduces UVA and UVB radiation-induced skin damage. | [67,68] |
| Metabolic regulation activity (anti-diabetic) | As a dietary additive, SS is demonstrated to regulate glycolipid metabolism. | [69] |
| Collagen production | SS from all strains promotes type-I collagen production in a concentration-dependent manner. | [70,71] |
| Mimic the organic component in bone-like systems | It can be used to study the biomineralization process of bone tissue or to develop bone-like structures for bone-TE. | [52,72] |
| Moisturizing | SS has a hygroscopic (water-attracting) nature, which allows it to attract and retain moisture. | [73,74] |
| Supplement | SS can be used as a cell culture medium supplement or substitute due to its nutrient content and reduced immune response. | [75,76,77,78] |
| Promotion of cell behavior | Promote cell growth of different mammalian cell lines. | [48,79,80] |
| Anti-tumor | Inhibition of tyrosinase and polyphenol oxidase activities. | [46,81] |
| Biodegradability | Ability to be broken down: degradation is mediated both in vitro and in vivo by proteolytic enzymes (e.g., protease XIV, α-chymotrypsin, proteinase K, papain, matrix metalloproteinases, and collagenase) which act on the amorphous hydrophilic segments. | [37,82] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernardes, B.G.; Veiga, A.; Barros, J.; García-González, C.A.; Oliveira, A.L. Sustainable Silk-Based Particulate Systems for the Controlled Release of Pharmaceuticals and Bioactive Agents in Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063133
Bernardes BG, Veiga A, Barros J, García-González CA, Oliveira AL. Sustainable Silk-Based Particulate Systems for the Controlled Release of Pharmaceuticals and Bioactive Agents in Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(6):3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063133
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernardes, Beatriz G., Anabela Veiga, Joana Barros, Carlos A. García-González, and Ana Leite Oliveira. 2024. "Sustainable Silk-Based Particulate Systems for the Controlled Release of Pharmaceuticals and Bioactive Agents in Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 6: 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063133
APA StyleBernardes, B. G., Veiga, A., Barros, J., García-González, C. A., & Oliveira, A. L. (2024). Sustainable Silk-Based Particulate Systems for the Controlled Release of Pharmaceuticals and Bioactive Agents in Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(6), 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063133










