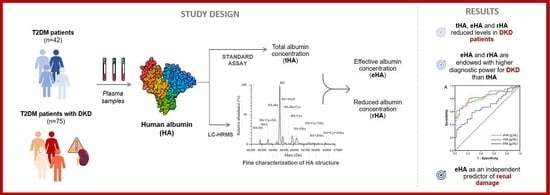
Association between Albumin Alterations and Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
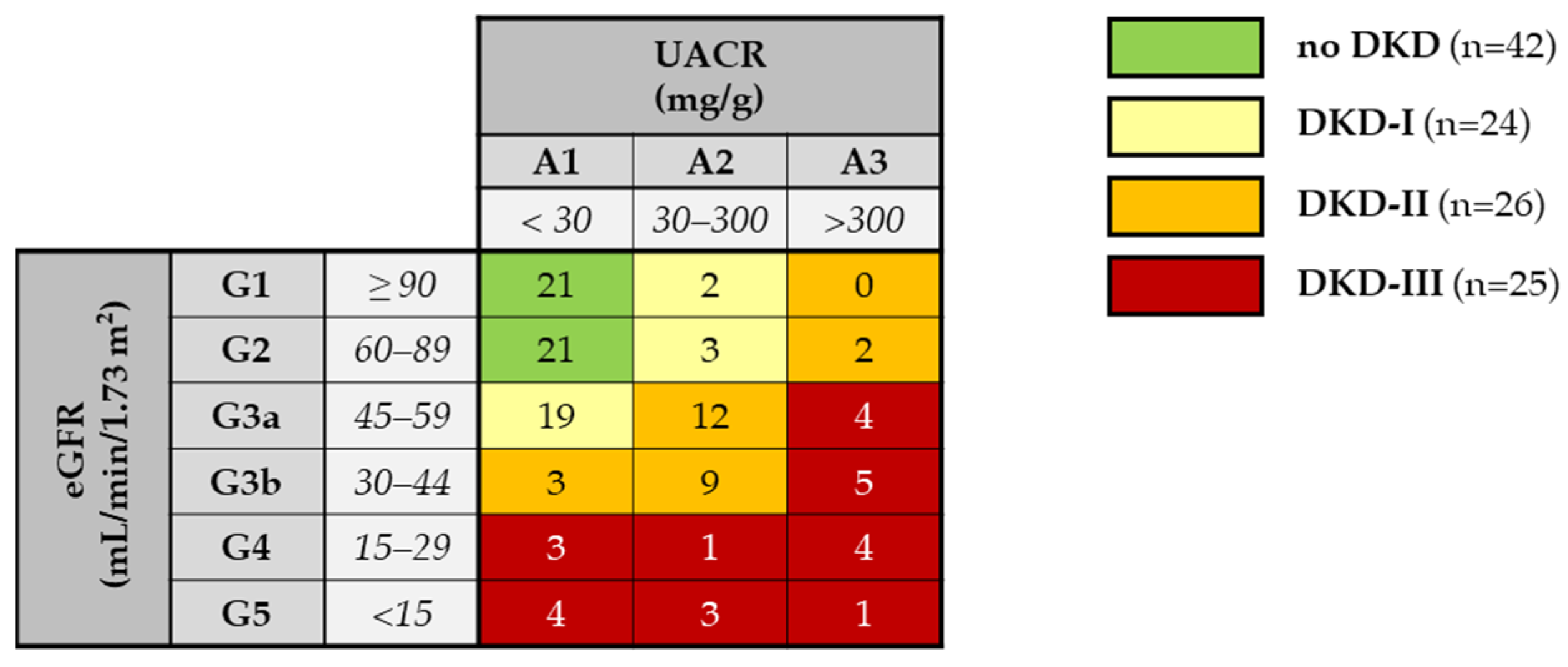
2.1. Subject Population
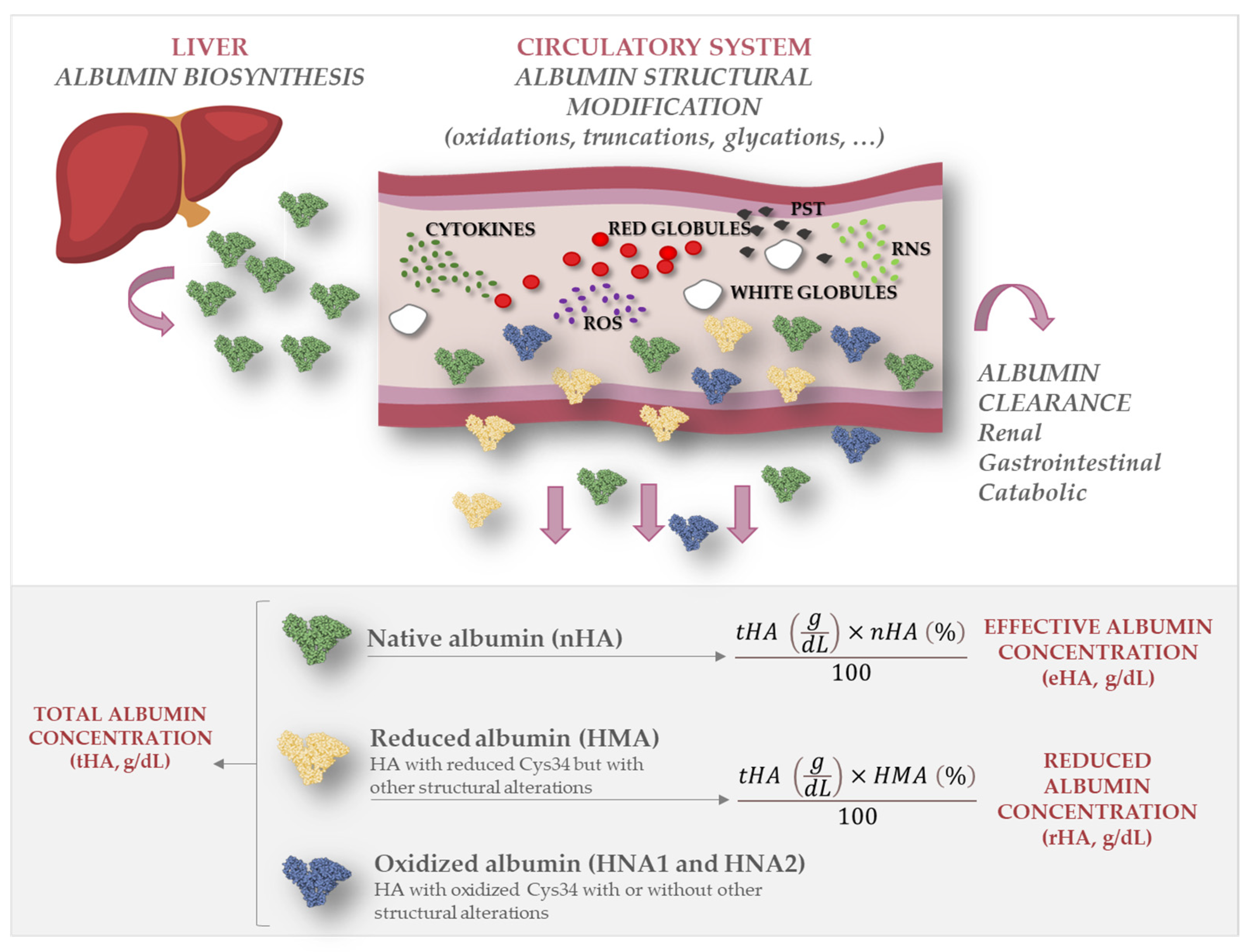
2.2. Evaluation of Albumin Structure
2.3. Total, Effective, and Reduced Albumin Concentrations
2.4. Correlation of tHA, rHA, and eHA with Biochemical Parameters
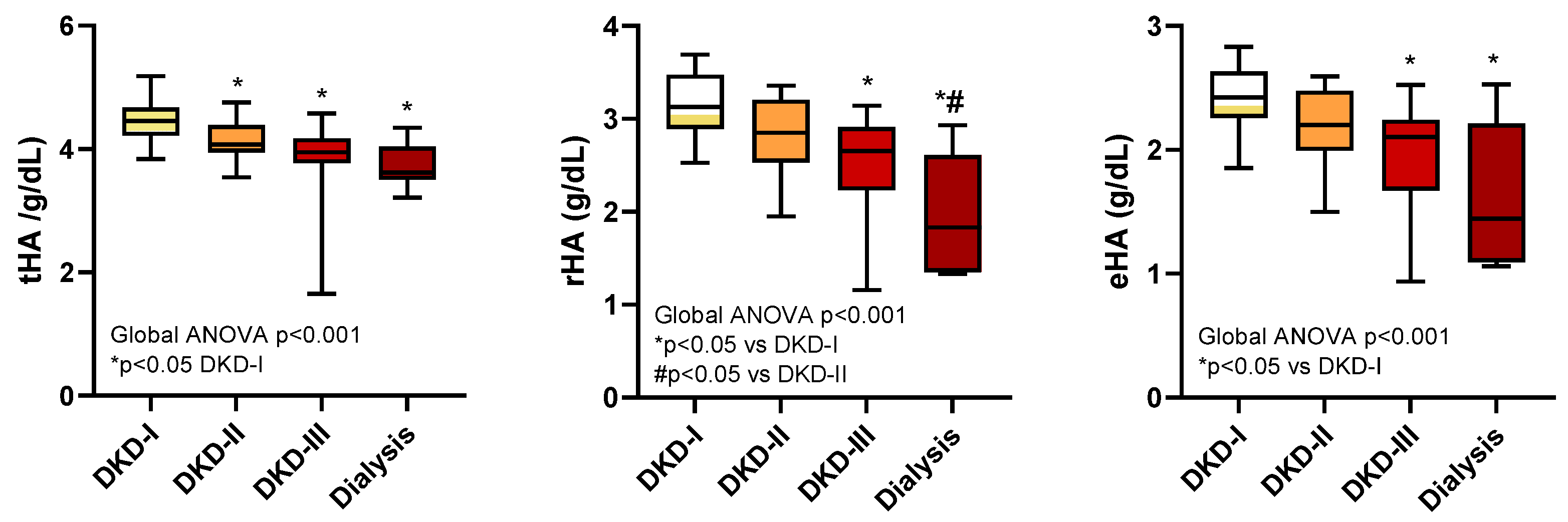
2.5. Albumin Levels and Severity of Diabetic Kidney Disease
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Study Design
4.2. Bromocresol Green (BCG) Colorimetric Assay
4.3. Liquid Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) Analysis
4.4. Assessment of eHA and rHA
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Persson, F.; Rossing, P. Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney Disease: State of the Art and Future Perspective. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2018, 8, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugahara, M.; Pak, W.L.W.; Tanaka, T.; Tang, S.C.W.; Nangaku, M. Update on Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Management of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nephrology 2021, 26, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanouchi, M.; Furuichi, K.; Hoshino, J.; Ubara, Y.; Wada, T. Nonproteinuric Diabetic Kidney Disease. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2020, 24, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogeveen, E.K. The Epidemiology of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Dial. 2022, 2, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, P.; Caramori, M.L.; Chan, J.C.; Heerspink, H.J.; Hurst, C.; Khunti, K.; Liew, A.; Michos, E.D.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Olowu, W.A.; et al. KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, S1–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Castelao, A.; Górriz, J.L.; Bover, J.; Segura-de la Morena, J.; Cebollada, J.; Escalada, J.; Esmatjes, E.; Fácila, L.; Gamarra, J.; Gràcia, S.; et al. Documento de Consenso Para La Detección y Manejo de La Enfermedad Renal Crónica. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2014, 61, e25–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KDOQI. Clinical Practice Guidelines and Clinical Practice Recommendations for Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, S62–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, S.; González, E.; López-Revuelta, K.; Ibernon, M.; López, D.; Martín-Gómez, A.; Garcia-Osuna, R.; Linares, T.; Diáz, M.; Martín, N.; et al. Risk Factors for Non-Diabetic Renal Disease in Diabetic Patients. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, S.; García-Carro, C.; Soler, M.J. Diabetes and Renal Disease-Should We Biopsy? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1384–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solini, A.; Penno, G.; Bonora, E.; Fondelli, C.; Orsi, E.; Arosio, M.; Trevisan, R.; Vedovato, M.; Cignarelli, M.; Andreozzi, F.; et al. Diverging Association of Reduced Glomerular Filtration Rate and Albuminuria with Coronary and Noncoronary Events in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The Renal Insufficiency and Cardiovascular Events (RIACE) Italian Multicenter Study. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, M.; Shimizu, M.; Yamanouchi, M.; Toyama, T.; Hara, A.; Furuichi, K.; Wada, T. Trajectories of Kidney Function in Diabetes: A Clinicopathological Update. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauriasari, R.; Safitri, D.D.; Azmi, N.U. Current Updates on Protein as Biomarkers for Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 12, 20420188211049612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.C.; Brownlee, M.; Susztak, K.; Sharma, K.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.A.M.; Zoungas, S.; Rossing, P.; Groop, P.H.; Cooper, M.E. Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, M.J.; Mischak, H.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Proteomics for Prediction of Disease Progression and Response to Therapy in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, G.; Shi, X. Advances in the Progression and Prognosis Biomarkers of Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piwkowska, A.; Zdrojewski, Ł.; Heleniak, Z.; Dębska-ślizień, A. Novel Markers in Diabetic Kidney Disease—Current State and Perspectives. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldi, M.; Baldassarre, M.; Domenicali, M.; Bartolini, M.; Caraceni, P. Structural and Functional Integrity of Human Serum Albumin: Analytical Approaches and Clinical Relevance in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 144, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terawaki, H.; Yoshimura, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Matsuyama, Y.; Negawa, T.; Yamada, K.; Matsushima, M.; Nakayama, M.; Hosoya, T.; Era, S. Oxidative Stress Is Enhanced in Correlation with Renal Dysfunction: Examination with the Redox State of Albumin. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassarre, M.; Domenicali, M.; Naldi, M.; Laggetta, M.; Giannone, F.A.; Biselli, M.; Patrono, D.; Bertucci, C.; Bernardi, M.; Caraceni, P. Albumin Homodimers in Patients with Cirrhosis: Clinical and Prognostic Relevance of a Novel Identified Structural Alteration of the Molecule. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenicali, M.; Baldassarre, M.; Giannone, F.A.; Naldi, M.; Mastroroberto, M.; Biselli, M.; Laggetta, M.; Patrono, D.; Bertucci, C.; Bernardi, M.; et al. Posttranscriptional Changes of Serum Albumin: Clinical and Prognostic Significance in Hospitalized Patients with Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, M.; Naldi, M.; Zacchierini, G.; Bartoletti, M.; Agnese, A.; Laggetta, M.; Gagliardi, M.; Tufoni, M.; Domenicali, M.; Waterstradt, K.; et al. Determination of Effective Albumin in Patients With Decompensated Cirrhosis: Clinical and Prognostic Implications. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2058–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, M.; Rondeau, P.; Singh, N.R.; Tarnus, E.; Bourdon, E. The Antioxidant Properties of Serum Albumin. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagdish, R.K.; Maras, J.S.; Sarin, S.K. Albumin in Advanced Liver Diseases: The Good and Bad of a Drug! John Wiley and Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; Volume 74, ISBN 0000000175. [Google Scholar]
- Michelis, R.; Kristal, B.; Zeitun, T.; Shapiro, G.; Fridman, Y.; Geron, R.; Sela, S. Albumin Oxidation Leads to Neutrophil Activation in Vitro and Inaccurate Measurement of Serum Albumin in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 60, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, A.N.; Fadem, S.Z. Reassessment of Albumin as a Nutritional Marker in Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Han, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, F. The Level of Serum Albumin Is Associated with Renal Prognosis in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Hao, J.; Hu, H.; Hao, L. The Level of Serum Albumin Is Associated with Renal Prognosis and Renal Function Decline in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramasivan, S.; Adav, S.S.; Ngan, S.F.C.; Dalan, R.; Leow, M.K.S.; Ho, H.H.; Sze, S.K. Serum Albumin Cysteine Trioxidation Is a Potential Oxidative Stress Biomarker of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H. Oxidized Albumin: Evaluation of Oxidative Stress as a Marker for the Progression of Kidney Disease. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International, K. KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, S1–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.H.; Drechsler, C.; Wenger, J.; Buccafusca, R.; Hod, T.; Kalim, S.; Ramma, W.; Parikh, S.M.; Steen, H.; Friedman, D.J.; et al. Carbamylation of Serum Albumin as a Risk Factor for Mortality in Patients with Kidney Failure. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 175ra29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akchurin, O.M.; Kaskel, F. Update on Inflammation in Chronic Kidney Disease. Blood Purif. 2015, 39, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Foresto-Neto, O.; Watanabe, I.K.M.; Zatz, R.; Câmara, N.O.S. Inflammation in Renal Diseases: New and Old Players. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, J.C.; Banal, C.; Chow, B.S.M.; Cooper, M.E.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K. Diabetes and Kidney Disease: Role of Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 25, 657–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.W.; Moon, J.Y. The Role of Inflammation in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico-Fontalvo, J.; Aroca, G.; Cabrales, J.; Daza-Arnedo, R.; Yánez-Rodríguez, T.; Martínez-Ávila, M.C.; Uparella-Gulfo, I.; Raad-Sarabia, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremese, E.; Bruno, D.; Varriano, V.; Perniola, S.; Petricca, L.; Ferraccioli, G. Serum Albumin Levels: A Biomarker to Be Repurposed in Different Disease Settings in Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S. Role of Human Serum Albumin and Oxidative Stress in Diabetes. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 3, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clària, J.; Stauber, R.E.; Coenraad, M.J.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Pavesi, M.; Amorós, À.; Titos, E.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Oettl, K.; et al. Systemic Inflammation in Decompensated Cirrhosis: Characterization and Role in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imafuku, T.; Watanabe, H.; Oniki, K.; Yoshida, A.; Kato, H.; Nakano, T.; Tokumaru, K.; Fujita, I.; Arimura, N.; Maeda, H.; et al. Cysteinylated Albumin as a Potential Biomarker for the Progression of Kidney Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, e115–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Care, D.; Suppl, S.S. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 517–538. [Google Scholar]
- Beng, C.G.; Rasanayagam, L.J.; Lim, K.L.; Lau, K.S. Solubility and Absorption Spectra of Complexes Resulting from Interaction among Human Albumin, Bromcresol Green and Detergents. Clin. Chim. Acta 1974, 52, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldi, M.; Baldassarre, M.; Domenicali, M.; Giannone, F.A.; Bossi, M.; Montomoli, J.; Sandahl, T.D.; Glavind, E.; Vilstrup, H.; Caraceni, P.; et al. Mass Spectrometry Characterization of Circulating Human Serum Albumin Microheterogeneity in Patients with Alcoholic Hepatitis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 122, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| No DKD n = 42 | DKD n = 75 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric data | |||
| Age (years) | 63 (56–67) | 70 (64–74) | <0.001 |
| Male sex (n, %) | 29 (69) | 52 (69) | 1.000 |
| BMI | 28.7 (25.8–34.4) | 32.3 (27.4–36.5) | 0.114 |
| Drug therapy | |||
| Anti-hypertensives (n, %) | 31 (74) | 62 (83) | 0.340 |
| ACE inhibitors (n, %) | 15 (48) | 29 (47) | 0.883 |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers (n, %) | 13 (42) | 27 (44) | 0.882 |
| Diuretics (n, %) | 6 (14) | 32 (43) | 0.002 |
| Metformin (n, %) | 29 (70) | 42 (56) | 0.175 |
| Insulin (n, %) | 15 (36) | 40 (53) | 0.083 |
| Other glucose-lowering therapies (n, %) | 22 (52) | 43 (57) | 0.699 |
| Sulfonylureas (n, %) | 4 (18) | 10 (23) | 0.222 |
| DPP-4 inhibitors (n, %) | 7 (32) | 13 (30) | 0.896 |
| GLP-1 Receptor agonists (n, %) | 8 (36) | 21 (49) | 0.298 |
| SGLT-2 Inhibitors (n, %) | 5 (12) | 3 (4) | 0.067 |
| Statin/fibrates (n, %) | 26 (62) | 50 (67) | 0.687 |
| Biochemical parameters | |||
| HbA1c (%) | 7.0 (6.4–7.6) | 7.1 (6.2–7.6) | 0.952 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 133 (110–155) | 123 (110–151) | 0.496 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 172 ± 35 | 149 ± 31 | 0.001 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 47 ± 9 | 41 ± 9 | 0.005 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 101 ± 31 | 79 ± 27 | 0.002 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 122 (87–177) | 166 (116–204) | 0.032 |
| Triglycerides/HDL ratio | 2.3 (1.5–3.7) | 3.7 (2.8–5.5) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.8 (0.8–0.9) | 1.4 (1.2–1.7) | <0.001 |
| UACR (mg/g) | 7 (5–10) | 66 (17–229) | <0.001 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 89 (77–97) | 48 (34–56) | <0.001 |
| HA Forms | Relative Abundance (%) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No DKD n = 42 | DKD n = 75 | ||
| nHA | 59.0 (57.1–60.6) | 52.5 (48.3–56.7) | <0.0001 |
| HMA | 75.7 (73.2–78.4) | 67.1 (62.5–72.7) | <0.0001 |
| HNA1 | 16.4 (13.7–19) | 25.7 (19.8–30.9) | <0.0001 |
| HNA2 | 8.9 (8.1–9.6) | 7.9 (7–8.6) | <0.0001 |
| Truncated | 6.5 (5.1–7.9) | 5.2 (4.4–7) | 0.0242 |
| Glycated | 10.8 (9.2–12.2) | 12.5 (10.5–14.7) | 0.0028 |
| HA Forms | Relative Abundance (%) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No DKD n = 42 | DKD (I–III) n = 75 | ||
| tHA (g/dL) | 4.3 (4.1–4.5) | 4.1 (3.9–4.4) | 0.001 |
| rHA (g/dL) | 3.3 (3.2–3.4) | 2.8 (2.5–3.1) | <0.001 |
| eHA (g/dL) | 2.5 (2.4–2.7) | 2.2 (1.9–2.4) | <0.001 |
| tHA | rHA | eHA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rho (p-Value) | Rho (p-Value) | Rho (p-Value) | ||
| Baseline | Creatinine (mg/dL) | −0.260 (0.006) | −0.567 (<0.001) | −0.548 (<0.001) |
| eGFR | 0.337 (<0.001) | 0.659 (<0.001) | 0.649 (<0.001) | |
| Albuminuria | −0.497 (<0.001) | −0.546 (<0.001) | −0.554 (<0.001) | |
| Follow-up | Creatinine (mg/dL) | −0.172 (0.077) | −0.508 (<0.001) | −0.509 (<0.001) |
| eGFR | 0.172 (0.076) | 0.562 (<0.001) | 0.584 (<0.001) | |
| Albuminuria | −0.363 (<0.001) | −0.461 (<0.001) | −0.407 (<0.001) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nugnes, M.; Baldassarre, M.; Ribichini, D.; Tedesco, D.; Capelli, I.; Vetrano, D.; Marchignoli, F.; Brodosi, L.; Pompili, E.; Petroni, M.L.; et al. Association between Albumin Alterations and Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063168
Nugnes M, Baldassarre M, Ribichini D, Tedesco D, Capelli I, Vetrano D, Marchignoli F, Brodosi L, Pompili E, Petroni ML, et al. Association between Albumin Alterations and Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(6):3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063168
Chicago/Turabian StyleNugnes, Marta, Maurizio Baldassarre, Danilo Ribichini, Daniele Tedesco, Irene Capelli, Daniele Vetrano, Francesca Marchignoli, Lucia Brodosi, Enrico Pompili, Maria Letizia Petroni, and et al. 2024. "Association between Albumin Alterations and Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 6: 3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063168
APA StyleNugnes, M., Baldassarre, M., Ribichini, D., Tedesco, D., Capelli, I., Vetrano, D., Marchignoli, F., Brodosi, L., Pompili, E., Petroni, M. L., La Manna, G., Marchesini, G., Naldi, M., & Bartolini, M. (2024). Association between Albumin Alterations and Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(6), 3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063168