Bone Morphogenic Proteins in Pediatric Diffuse Midline Gliomas: How to Make New Out of Old?
Abstract
1. Introduction
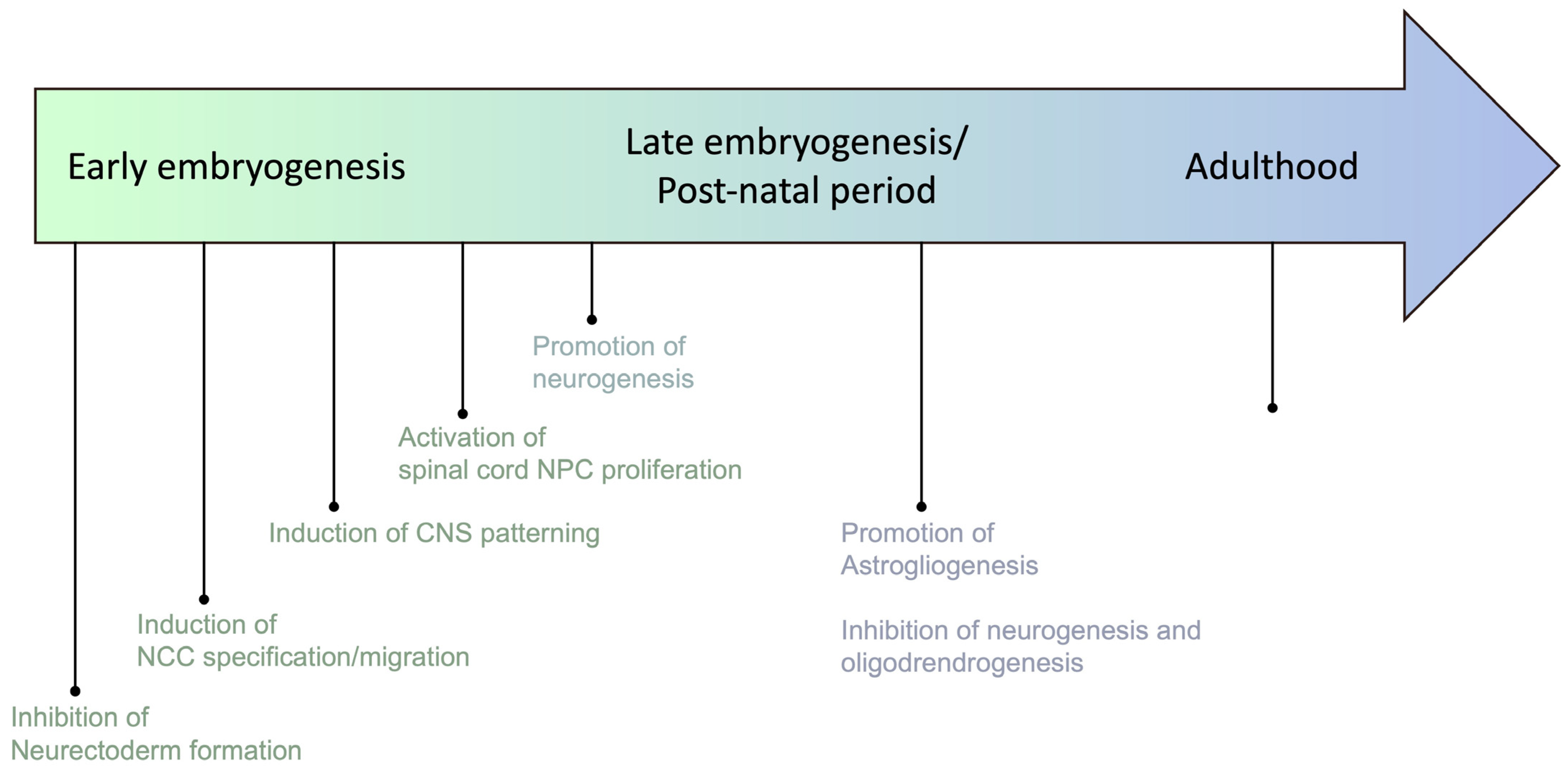
2. BMP Family: An Old Hand in Embryonic Development
3. Beyond Development: The Well-Known Complex Role of BMP in Cancers
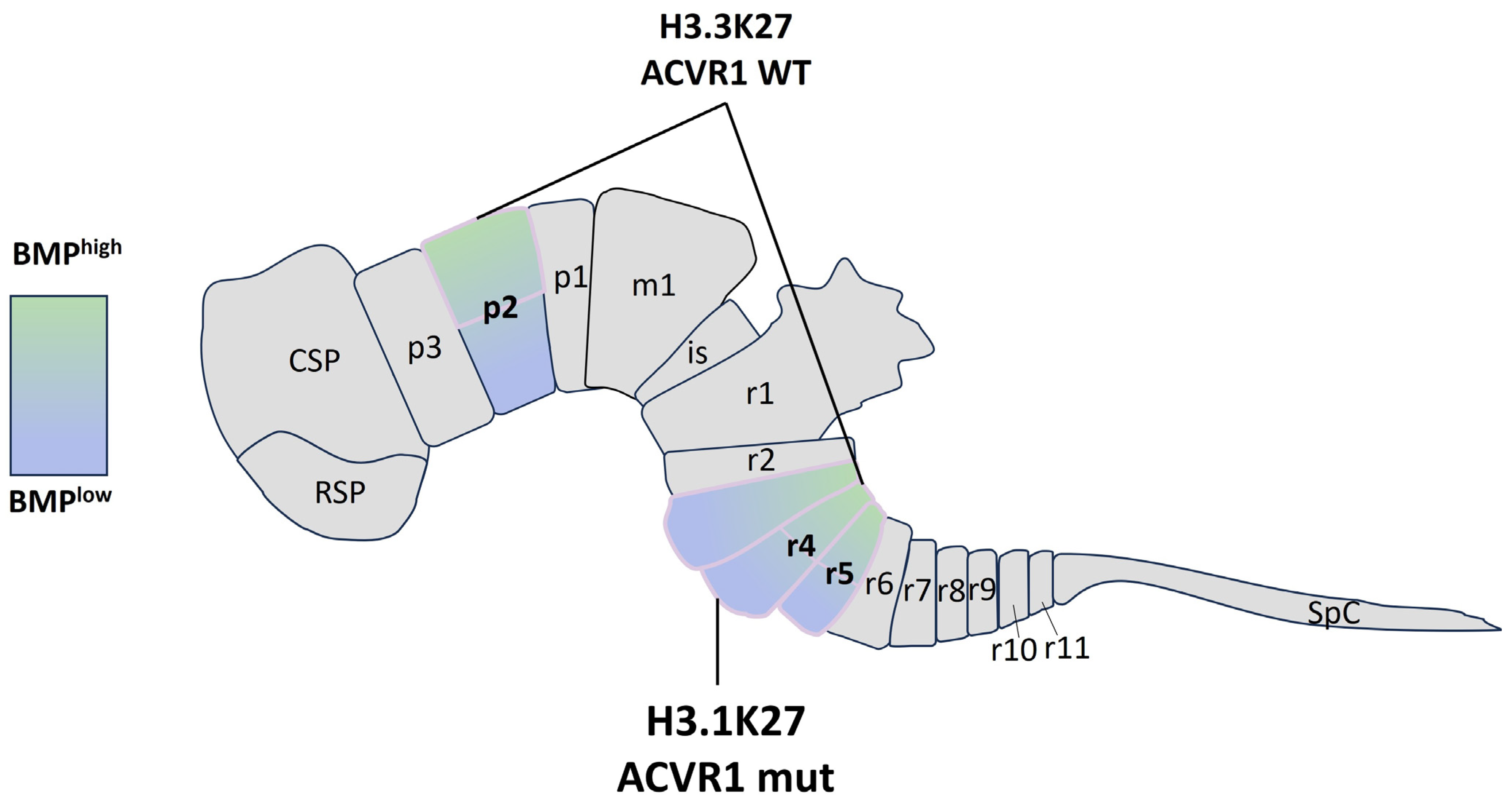
4. When Development Meets Tumorigenesis: Emerging Roles of BMP Pathway in pDMG
5. What Is Next? Therapeutic Potential of Targeting the BMP Pathway in pDMG
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, M.E. Epidemiology and Overview of Gliomas. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2018, 34, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, A.; Burford, A.; Carvalho, D.; Izquierdo, E.; Fazal-Salom, J.; Taylor, K.R.; Bjerke, L.; Clarke, M.; Vinci, M.; Nandhabalan, M.; et al. Integrated Molecular Meta-Analysis of 1000 Pediatric High-Grade and Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 520–537.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castel, D.; Kergrohen, T.; Tauziède-Espariat, A.; Mackay, A.; Ghermaoui, S.; Lechapt, E.; Pfister, S.M.; Kramm, C.M.; Boddaert, N.; Blauwblomme, T.; et al. Histone H3 wild-type DIPG/DMG overexpressing EZHIP extend the spectrum diffuse midline gliomas with PRC2 inhibition beyond H3-K27M mutation. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzi, S.; Michaeli, O.; Ramaswamy, V.; Huang, A.; Stephens, D.; Maguire, B.; Tabori, U.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U. Causes of death in pediatric neuro-oncology: The sickkids experience from 2000 to 2017. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 149, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, A.; Bandopadhayay, P.; Cooney, T.M. Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: Insights into oncogenesis and opportunities for targeted therapy. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. J. 2023, 8, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocito, C.; Martin, B.; Giantini-Larsen, A.M.; Valcarce-Aspegren, M.; Souweidane, M.M.; Szalontay, L.; Dahmane, N.; Greenfield, J.P. Leptomeningeal dissemination in pediatric brain tumors. Neoplasia 2023, 39, 100898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Benesch, M.; Berthold, F.; Gnekow, A.K.; Rutkowski, S.; Sträter, R.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Kortmann, R.-D.; Pietsch, T.; Wolff, J.E.A. Secondary dissemination in children with high-grade malignant gliomas and diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbin, M.G.; Tirosh, I.; Hovestadt, V.; Shaw, M.L.; Escalante, L.E.; Mathewson, N.D.; Neftel, C.; Frank, N.; Pelton, K.; Hebert, C.M.; et al. Developmental and oncogenic programs in H3K27M gliomas dissected by single-cell RNA-seq. Science 2018, 360, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, S.; Vitanza, N.A.; Woo, P.J.; Taylor, K.R.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Meng, W.; Ponnuswami, A.; Sun, W.; et al. Transcriptional Dependencies in Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 635–652.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuong-Quang, D.-A.; Buczkowicz, P.; Rakopoulos, P.; Liu, X.-Y.; Fontebasso, A.M.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U.; Albrecht, S.; Schwartzentruber, J.; Letourneau, L.; et al. K27M mutation in histone H3.3 defines clinically and biologically distinct subgroups of pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzentruber, J.; Korshunov, A.; Liu, X.-Y.; Jones, D.T.W.; Pfaff, E.; Jacob, K.; Sturm, D.; Fontebasso, A.M.; Quang, D.-A.K.; Tönjes, M.; et al. Driver mutations in histone H3.3 and chromatin remodelling genes in paediatric glioblastoma. Nature 2012, 482, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, D.; Witt, H.; Hovestadt, V.; Khuong-Quang, D.-A.; Jones, D.T.W.; Konermann, C.; Pfaff, E.; Tönjes, M.; Sill, M.; Bender, S.; et al. Hotspot Mutations in H3F3A and IDH1 Define Distinct Epigenetic and Biological Subgroups of Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikbakht, H.; Panditharatna, E.; Mikael, L.G.; Li, R.; Gayden, T.; Osmond, M.; Ho, C.-Y.; Kambhampati, M.; Hwang, E.I.; Faury, D.; et al. Spatial and temporal homogeneity of driver mutations in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinci, M.; Burford, A.; Molinari, V.; Kessler, K.; Popov, S.; Clarke, M.; Taylor, K.R.; Pemberton, H.; Lord, C.J.; Gutteridge, A.; et al. Functional diversity and co-operativity between subclonal populations of paediatric glioblastoma and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma cells. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpaz, N.; Mittelman, T.; Beresh, O.; Griess, O.; Furth, N.; Salame, T.-M.; Oren, R.; Fellus-Alyagor, L.; Harmelin, A.; Alexandrescu, S.; et al. Single-cell epigenetic analysis reveals principles of chromatin states in H3.3-K27M gliomas. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2696–2713.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.; Jiang, L.; Samuelsson, E.R.; Marco Salas, S.; Beck, A.; Hack, O.A.; Jeong, D.; Shaw, M.L.; Englinger, B.; LaBelle, J.; et al. The landscape of tumor cell states and spatial organization in H3-K27M mutant diffuse midline glioma across age and location. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathania, M.; De Jay, N.; Maestro, N.; Harutyunyan, A.S.; Nitarska, J.; Pahlavan, P.; Henderson, S.; Mikael, L.G.; Richard-Londt, A.; Zhang, Y.; et al. H3.3K27M Cooperates with Trp53 Loss and PDGFRA Gain in Mouse Embryonic Neural Progenitor Cells to Induce Invasive High-Grade Gliomas. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 684–700.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, D.; Mack, N.; Benites Goncalves da Silva, P.; Statz, B.; Clark, J.; Tanabe, K.; Sharma, T.; Jäger, N.; Jones, D.T.W.; Kawauchi, D.; et al. H3.3-K27M drives neural stem cell-specific gliomagenesis in a human iPSC-derived model. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 407–422.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, R.B.; Southgate, B.; Ferguson, K.M.; Blin, C.; Grant, V.; Alfazema, N.; Wills, J.C.; Marques-Torrejon, M.A.; Morrison, G.M.; Ashmore, J.; et al. Regional identity of human neural stem cells determines oncogenic responses to histone H3.3 mutants. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 877–893.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urist, M.R. Bone: Formation by Autoinduction. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2002, 395, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishigami, S.; Mishina, Y. BMP signaling and early embryonic patterning. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Cao, X. BMP signaling in skeletal development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 328, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.Q. Consequences of knocking out BMP signaling in the mouse. Genesis 2003, 35, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Duffhues, G.; Hiepen, C.; Knaus, P.; Ten Dijke, P. Bone morphogenetic protein signaling in bone homeostasis. Bone 2015, 80, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, P.; Vukicevic, S. Bone morphogenetic proteins in development and homeostasis of kidney. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, L.M.; Hill, C.S. Beyond TGFβ: Roles of Other TGFβ Superfamily Members in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 328–341. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nrc3500 (accessed on 6 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Zhang, Y.E. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-b family signalling. Nature 2003, 425, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massagué, J. TGF-β Signal Transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 753–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrana, J.L. TGFp Signals through a Heteromeric Protein Kinase Receptor Complex. Cell 1992, 71, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, T.D.; Nickel, J. Promiscuity and specificity in BMP receptor activation. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1846–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrana, J.L. Regulation of Smad Activity. Cell 2000, 100, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldin, C.H.; Miyazono, K. TGF-β signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature 1997, 390, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikov, A.; Zehorai, E.; Procaccia, S.; Seger, R. The MAPK cascades: Signaling components, nuclear roles and mechanisms of nuclear translocation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouahoud, S.; Hardwick, J.C.H.; Hawinkels, L.J.A.C. Extracellular BMP Antagonists, Multifaceted Orchestrators in the Tumor and Its Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.W.; Godson, C.; Brazil, D.P.; Martin, F. Extracellular BMP-antagonist regulation in development and disease: Tied up in knots. Trends Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iemura, S.; Yamamoto, T.S.; Takagi, C.; Uchiyama, H.; Natsume, T.; Shimasaki, S.; Sugino, H.; Ueno, N. Direct binding of follistatin to a complex of bone-morphogenetic protein and its receptor inhibits ventral and epidermal cell fates in early Xenopus embryo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9337–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, L.Z.; Bardot, B.; Zhang, Q.; Resau, J.; Huillard, E.; Marx, M.; Calothy, G.; Blair, D.G. Biosynthesis, Post-translation Modification, and Functional Characterization of Drm/Gremlin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 8785–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, E.; De Robertis, E.M. Embryo Development. BMP gradients: A paradigm for morphogen-mediated developmental patterning. Science 2015, 348, aaa5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A.M.; Bhalala, O.G.; Kessler, J.A. The dynamic role of bone morphogenetic proteins in neural stem cell fate and maturation. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 1068–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spemann, H.; Mangold, H. über Induktion von Embryonalanlagen durch Implantation artfremder Organisatoren. Arch. Mikrosk. Anat. Entwicklungsmechanik 1924, 100, 599–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaguidi, M.A.; Peng, C.-Y.; McGuire, T.; Falciglia, G.; Gobeske, K.T.; Czeisler, C.; Kessler, J.A. Noggin expands neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9194–9204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeske, K.T.; Das, S.; Bonaguidi, M.A.; Weiss, C.; Radulovic, J.; Disterhoft, J.F.; Kessler, J.A. BMP signaling mediates effects of exercise on hippocampal neurogenesis and cognition in mice. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oboti, L.; Savalli, G.; Giachino, C.; De Marchis, S.; Panzica, G.C.; Fasolo, A.; Peretto, P. Integration and sensory experience-dependent survival of newly-generated neurons in the accessory olfactory bulb of female mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaune, E.; Lemaire, P.; Kodjabachian, L. Neural induction in Xenopus requires early FGF signalling in addition to BMP inhibition. Development 2005, 132, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccolo, S.; Sasai, Y.; Lu, B.; De Robertis, E.M. Dorsoventral Patterning in Xenopus: Inhibition of Ventral Signals by Direct Binding of Chordin to BMP-4. Cell 1996, 86, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, L.B.; De Jesús-Escobar, J.M.; Harland, R.M. The Spemann Organizer Signal noggin Binds and Inactivates Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4. Cell 1996, 86, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimura, A.; Maeda, R.; Takeda, M.; Kikkawa, M.; Daar, I.O.; Maéno, M. Involvement of BMP-4/msx-1 and FGF pathways in neural induction in the Xenopus embryo. Dev. Growth Differ. 2000, 42, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.I.; Graziano, E.; Harland, R.; Jessell, T.M.; Edlund, T. An early requirement for FGF signalling in the acquisition of neural cell fate in the chick embryo. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, R.E.; Mehler, M.F.; Mabie, P.C.; Zang, Z.; Santschi, L.; Kessler, J.A. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins Promote Astroglial Lineage Commitment by Mammalian Subventricular Zone Progenitor Cells. Neuron 1996, 17, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehler, M.F.; Mabie, P.C.; Zhu, G.; Gokhan, S.; Kessler, J.A. Developmental changes in progenitor cell responsiveness to bone morphogenetic proteins differentially modulate progressive CNS lineage fate. Dev. Neurosci. 2000, 22, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viñals, F.; Reiriz, J.; Ambrosio, S.; Bartrons, R.; Rosa, J.L.; Ventura, F. BMP-2 decreases Mash1 stability by increasing Id1 expression. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3527–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, M.; Takizawa, T.; Ochiai, W.; Uemura, A.; Nakashima, K.; Taga, T. Fate alteration of neuroepithelial cells from neurogenesis to astrocytogenesis by bone morphogenetic proteins. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 41, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Abematsu, M.; Mori, H.; Yanagisawa, M.; Kagawa, T.; Nakashima, K.; Yoshimura, A.; Taga, T. Potentiation of astrogliogenesis by STAT3-mediated activation of bone morphogenetic protein-Smad signaling in neural stem cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 4931–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Yanagisawa, M.; Arakawa, H.; Kimura, N.; Hisatsune, T.; Kawabata, M.; Miyazono, K.; Taga, T. Synergistic signaling in fetal brain by STAT3-Smad1 complex bridged by p300. Science 1999, 284, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, J.; Zhang, X.; Eraydin, N.; Mun, S.-B.; Mamontov, P.; Golden, J.A.; Grinspan, J.B. Oligodendrocyte maturation is inhibited by bone morphogenetic protein. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2004, 26, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.R.; Yuk, D.; Alberta, J.A.; Zhu, Z.; Pawlitzky, I.; Chan, J.; McMahon, A.P.; Stiles, C.D.; Rowitch, D.H. Sonic hedgehog—Regulated oligodendrocyte lineage genes encoding bHLH proteins in the mammalian central nervous system. Neuron 2000, 25, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, S.; Anderson, D.J. Identification of a Novel Family of Oligodendrocyte Lineage-Specific Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Transcription Factors. Neuron 2000, 25, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, J.; Kessler, J.A. Interactions between ID and OLIG proteins mediate the inhibitory effects of BMP4 on oligodendroglial differentiation. Development 2004, 131, 4131–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reversade, B.; Kuroda, H.; Lee, H.; Mays, A.; De Robertis, E.M. Depletion of Bmp2, Bmp4, Bmp7 and Spemann organizer signals induces massive brain formation in Xenopus embryos. Development 2005, 132, 3381–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschmidt, M.; Mullins, M.C. Dorsoventral patterning in the zebrafish: Bone morphogenetic proteins and beyond. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2002, 40, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manzo, G. Phylogenesis—ontogenesis—oncogenesis. Med. Hypotheses 1989, 30, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzo, G. Similarities Between Embryo Development and Cancer Process Suggest New Strategies for Research and Therapy of Tumors: A New Point of View. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkell, R.; Beddington, R.S.P. BMP-7 influences pattern and growth of the developing hindbrain of mouse embryos. Development 1997, 124, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polevoy, H.; Gutkovich, Y.E.; Michaelov, A.; Volovik, Y.; Elkouby, Y.M.; Frank, D. New roles for Wnt and BMP signaling in neural anteroposterior patterning. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e45842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Gutin, G.; Alcorn, H.; McConnell, S.K.; Hébert, J.M. Mutations in the BMP pathway in mice support the existence of two molecular classes of holoprosencephaly. Development 2007, 134, 3789–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, J.M.; Mishina, Y.; McConnell, S.K. BMP Signaling Is Required Locally to Pattern the Dorsal Telencephalic Midline. Neuron 2002, 35, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, M.; Agnihotri, N.; Sen, J. Perturbation of canonical and non-canonical BMP signaling affects migration, polarity and dendritogenesis of mouse cortical neurons. Development 2018, 145, dev147157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selleck, M.A.J.; García-Castro, M.I.; Artinger, K.B.; Bronner-Fraser, M. Effects of Shh and Noggin on neural crest formation demonstrate that BMP is required in the neural tube but not ectoderm. Development 1998, 125, 4919–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansod, S.; Kageyama, R.; Ohtsuka, T. Hes5 regulates the transition timing of neurogenesis and gliogenesis in mammalian neocortical development. Development 2017, 144, 3156–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, W.; Martinowich, K.; Wu, X.; He, F.; Miyamoto, A.; Fan, G.; Weinmaster, G.; Sun, Y.E. Notch signaling promotes astrogliogenesis via direct CSL-mediated glial gene activation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 69, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akizu, N.; Estarás, C.; Guerrero, L.; Martí, E.; Martínez-Balbás, M.A. H3K27me3 regulates BMP activity in developing spinal cord. Development 2010, 137, 2915–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maegdefrau, U.; Bosserhoff, A.K. BMP activated Smad signaling strongly promotes migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2012, 92, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothhammer, T.; Poser, I.; Soncin, F.; Bataille, F.; Moser, M.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Bone Morphogenic Proteins Are Overexpressed in Malignant Melanoma and Promote Cell Invasion and Migration. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothhammer, T.; Wild, P.J.; Meyer, S.; Bataille, F.; Pauer, A.; Klinkhammer-Schalke, M.; Hein, R.; Hofstaedter, F.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP7) expression is a potential novel prognostic marker for recurrence in patients with primary melanoma1. Cancer Biomark. 2007, 3, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, K.J.; Kirkbride, K.C.; How, T.; Blobe, G.C. Bone morphogenetic proteins induce pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness through a Smad1-dependent mechanism that involves matrix metalloproteinase-2. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothhammer, T.; Braig, S.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Bone morphogenetic proteins induce expression of metalloproteinases in melanoma cells and fibroblasts. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushige, S.; Furukawa, T.; Satoh, K.; Sunamura, M.; Kobari, M.; Koizumi, M.; Horii, A. Loss of chromosome 18q is an early event in pancreatic ductal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4222–4226. [Google Scholar]
- Schleger, C.; Arens, N.; Zentgraf, H.; Bleyl, U.; Verbeke, C. Identification of frequent chromosomal aberrations in ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas by comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). J. Pathol. 2000, 191, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangkumpha, K.; Techasen, A.; Loilome, W.; Namwat, N.; Thanan, R.; Khuntikeo, N.; Yongvanit, P. BMP-7 blocks the effects of TGF-β-induced EMT in cholangiocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 9667–9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Wang, J.; Lu, P.; Si, X.; Han, K.; Ruan, T.; Lu, J. BMP10 inhibited the growth and migration of gastric cancer cells. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2016, 37, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, K.; Preca, B.T.; Brummer, T.; Brabletz, S.; Stemmler, M.P.; Brabletz, T. The EMT-activator ZEB1 induces bone metastasis associated genes including BMP-inhibitors. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14399–14412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawani, J.P.; Wang, A.C.; Than, K.D.; Lin, C.Y.; La Marca, F.; Park, P. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and Cancer: Review of the Literature. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, Y.; Long, X.; Xiao, P.; Ren, X.; Yu, J. BMP signaling and its paradoxical effects in tumorigenesis and dissemination. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78206–78218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanpierre, S.; Arizkane, K.; Thongjuea, S.; Grockowiak, E.; Geistlich, K.; Barral, L.; Voeltzel, T.; Guillemin, A.; Gonin-Giraud, S.; Gandrillon, O.; et al. The quiescent fraction of chronic myeloid leukemic stem cells depends on BMPR1B, Stat3 and BMP4-niche signals to persist in patients in remission. Haematologica 2021, 106, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, R.; Wu, M.; Johnson, K.; Kim, H.; Celebre, A.; Shahzad, U.; Graham, M.S.; Kessler, J.A.; Chuang, J.H.; Karamchandani, J.; et al. BMP signaling mediates glioma stem cell quiescence and confers treatment resistance in glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caja, L.; Tzavlaki, K.; Dadras, M.S.; Tan, E.-J.; Hatem, G.; Maturi, N.P.; Morén, A.; Wik, L.; Watanabe, Y.; Savary, K.; et al. Snail regulates BMP and TGFβ pathways to control the differentiation status of glioma-initiating cells. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2515–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirasani, S.R.; Sternjak, A.; Wend, P.; Momma, S.; Campos, B.; Herrmann, I.M.; Graf, D.; Mitsiadis, T.; Herold-Mende, C.; Besser, D.; et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 release from endogenous neural precursor cells suppresses the tumourigenicity of stem-like glioblastoma cells. Brain 2010, 133, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, A.; Waerzeggers, Y.; Monfared, P.; Vukicevic, S.; Kaijzel, E.L.; Winkeler, A.; Wickenhauser, C.; Löwik, C.W.G.M.; Jacobs, A.H. Imaging Bone Morphogenetic Protein 7 Induced Cell Cycle Arrest in Experimental Gliomas. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 276-IN22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, S.G.M.; Reynolds, B.A.; Zanetti, N.; Lamorte, G.; Binda, E.; Broggi, G.; Brem, H.; Olivi, A.; Dimeco, F.; Vescovi, A.L. Bone morphogenetic proteins inhibit the tumorigenic potential of human brain tumour-initiating cells. Nature 2006, 444, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzo, E.; Dettin, M.; Maule, F.; Scabello, A.; Calvanese, L.; D’Auria, G.; Falcigno, L.; Porcù, E.; Zamuner, A.; Della Puppa, A.; et al. A synthetic BMP-2 mimicking peptide induces glioblastoma stem cell differentiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, C.M.; Pallini, R.; Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Dowless, M.; Shiyanova, T.; D’Alessandris, G.Q.; Morgante, L.; Giannetti, S.; Larocca, L.M.; di Martino, S.; et al. A BMP7 variant inhibits the tumorigenic potential of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 1644–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hover, L.D.; Owens, P.; Munden, A.L.; Wang, J.; Chambless, L.B.; Hopkins, C.R.; Hong, C.C.; Moses, H.L.; Abel, T.W. Bone morphogenetic protein signaling promotes tumorigenesis in a murine model of high-grade glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczkowicz, P.; Hoeman, C.; Rakopoulos, P.; Pajovic, S.; Letourneau, L.; Dzamba, M.; Morrison, A.; Lewis, P.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U.; et al. Genomic analysis of diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas identifies three molecular subgroups and recurrent activating ACVR1 mutations. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontebasso, A.M.; Papillon-Cavanagh, S.; Schwartzentruber, J.; Nikbakht, H.; Gerges, N.; Fiset, P.-O.; Bechet, D.; Faury, D.; De Jay, N.; Ramkissoon, L.A.; et al. Recurrent somatic mutations in ACVR1 in pediatric midline high-grade astrocytoma. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.R.; Mackay, A.; Truffaux, N.; Butterfield, Y.S.; Morozova, O.; Philippe, C.; Castel, D.; Grasso, C.S.; Vinci, M.; Carvalho, D.; et al. Recurrent activating ACVR1 mutations in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, D.; Taylor, K.R.; Olaciregui, N.G.; Molinari, V.; Clarke, M.; Mackay, A.; Ruddle, R.; Henley, A.; Valenti, M.; Hayes, A.; et al. ALK2 inhibitors display beneficial effects in preclinical models of ACVR1 mutant diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessa, S.; Mohammadnia, A.; Harutyunyan, A.S.; Hulswit, M.; Varadharajan, S.; Lakkis, H.; Kabir, N.; Bashardanesh, Z.; Hébert, S.; Faury, D.; et al. K27M in canonical and noncanonical H3 variants occurs in distinct oligodendroglial cell lineages in brain midline gliomas. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1865–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, K.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Zhou, W.; Guo, S.; Han, Y.; Tang, L.; Shao, Y.; et al. Context-dependent tumor-suppressive BMP signaling in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma regulates stemness through epigenetic regulation of CXXC5. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 1105–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huchedé, P.; Meyer, S.; Berthelot, C.; Hamadou, M.; Bertrand-Chapel, A.; Rakotomalala, A.; Manceau, L.; Tomine, J.; Lespinasse, N.; Lewandowski, P.; et al. BMP2 and BMP7 cooperate with H3.3K27M to promote quiescence and invasiveness in pediatric diffuse midline gliomas. eLife 2023, 12, RP91313. Available online: https://elifesciences.org/reviewed-preprints/91313 (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Bruschi, M.; Midjek, L.; Ajlil, Y.; Vairy, S.; Lancien, M.; Ghermaoui, S.; Kergrohen, T.; Verreault, M.; Idbaih, A.; De Biagi, C.A.O., Jr.; et al. Diffuse Midline Glioma Invasion and Metastasis Rely on Cell-autonomous Signaling. Neuro-Oncology 2023, 26, noad161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, W.P.; Yang, S.N.; Lai, C.H.; Tang, C.H. Hypoxia induces BMP-2 expression via ILK, Akt, mTOR, and HIF-1 pathways in osteoblasts. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 223, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, E.M.; Binda, E.; Verploegh, I.S.C.; Wembacher, E.; Hoefnagel, D.; Balvers, R.K.; Korporaal, A.L.; Conidi, A.; Warnert, E.A.H.; Trivieri, N.; et al. Local delivery of hrBMP4 as an anticancer therapy in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: A first-in-human phase 1 dose escalation trial. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemgen. A Dose Escalation Phase I Study of Human- Recombinant Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 Administrated via Convection-Enhanced Delivery in Patients with Progressive and/or Multiple Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme. Nov Report No.: NCT02869243. 2020. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02869243 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
| Tumor Type | Gene/Molecular Alterations |
|---|---|
| Pediatric-type diffuse low-grade gliomas | |
| Diffuse astrocytoma | MYB, MYBL1 |
| Angiocentric glioma | MYB |
| Polymorphous low-grade neuroepithelial tumor | BRAF, FGFR family |
| Diffuse low-grade glioma | MAPK pathway-altered (FGFR1, BRAF) |
| Pediatric-type diffuse high-grade gliomas | |
| Diffuse midline glioma, | H3 K27-altered, TP53, ACVR1, PDGFRA, EGFR, EZHIP |
| Diffuse hemispheric glioma, | H3 G34-mutant, TP53, ATRX |
| Diffuse pediatric-type high-grade glioma, | H3-wildtype and IDH-wildtype, PDGFRA, MYCN, EGFR |
| Infant-type hemispheric glioma | NTRK family, ALK, ROS, MET |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berthelot, C.; Huchedé, P.; Bertrand-Chapel, A.; Beuriat, P.-A.; Leblond, P.; Castets, M. Bone Morphogenic Proteins in Pediatric Diffuse Midline Gliomas: How to Make New Out of Old? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063361
Berthelot C, Huchedé P, Bertrand-Chapel A, Beuriat P-A, Leblond P, Castets M. Bone Morphogenic Proteins in Pediatric Diffuse Midline Gliomas: How to Make New Out of Old? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(6):3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063361
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerthelot, Clément, Paul Huchedé, Adrien Bertrand-Chapel, Pierre-Aurélien Beuriat, Pierre Leblond, and Marie Castets. 2024. "Bone Morphogenic Proteins in Pediatric Diffuse Midline Gliomas: How to Make New Out of Old?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 6: 3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063361
APA StyleBerthelot, C., Huchedé, P., Bertrand-Chapel, A., Beuriat, P.-A., Leblond, P., & Castets, M. (2024). Bone Morphogenic Proteins in Pediatric Diffuse Midline Gliomas: How to Make New Out of Old? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(6), 3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063361





