Identification of Serum Interleukin-22 as Novel Biomarker in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Translational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Right Ventricular Function and Right Ventricular Pressure in the Rat Model
2.2. PH Associated Lung and Right Ventricular Tissue Damage
2.3. Immunofluorescence Based Detection of Interleukins 17a and 22 in Lung and Right Ventricular Tissue
2.3.1. Interleukin 17a
2.3.2. Interleukin 22
2.4. Serum Concentrations of Interleukins 17a and 22 in the Rat Model Using ELISA
2.5. Correlations of Tissue and Circulating Interleukins, Laboratory Values and Clinical Data in the Rat Model
2.6. Human Subjects Clinical Data
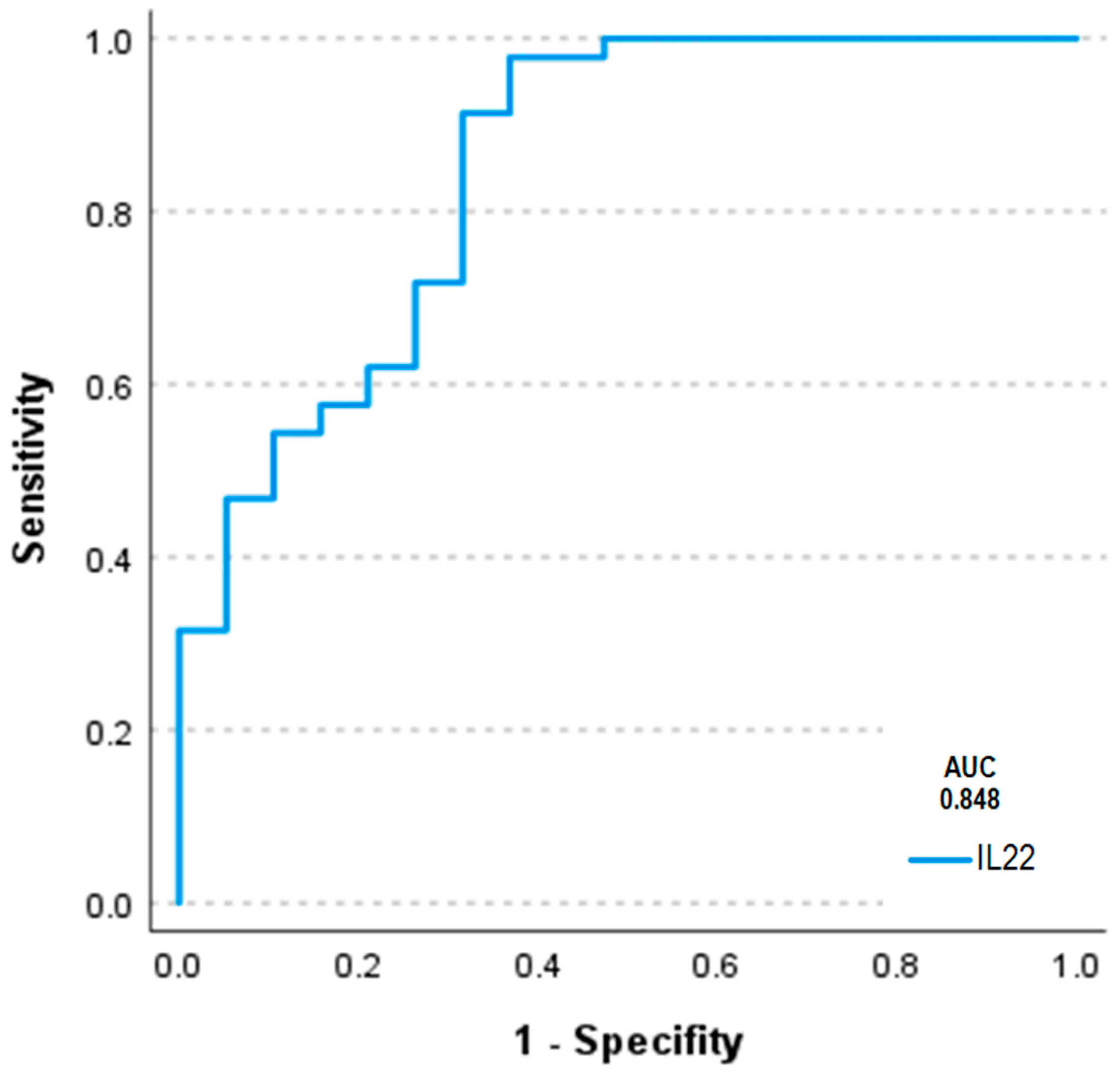
2.7. Serum Concentrations of Interleukins 17a and 22 in Humans Using ELISA and Correlations of Circulating Interleukins, Laboratory Values and Clinical Data
3. Methods
3.1. Animal Model of PH
3.1.1. Echocardiographic and Hemodynamic Assessment
3.1.2. Histological Assessment of PH-Induced Lung and Right Ventricular Tissue Damage
3.1.3. Immunofluorescence Based Detection of Interleukins in Lung and Right Ventricular Tissue
3.1.4. Quantification of Circulating Interleukins by ELISA
3.2. Human Subjects
Assessment of Circulating Interleukins by ELISA in Human Subjects
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koudstaal, T.; Boomars, K.A.; Kool, M. Pulmonal-arterielle Hypertonie und chronisch-thromboembolische pulmonale Hypertonie: Eine immunologische Perspektive. Kompass Pneumol. 2020, 8, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Adatia, I.; Celermajer, D.; Denton, C.; Ghofrani, A.; Sanchez, M.A.G.; Kumar, R.K.; Landzberg, M.; Machado, R.F.; et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62 (Suppl. 25), D34–D41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, V.V.; Shah, S.J.; Souza, R.; Humbert, M. Management of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1976–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Desai, A.A.; Black, S.M.; Tang, H. Cytokines, Chemokines, and Inflammation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. In Lung Inflammation in Health and Disease, Volume I; Wang, Y.-X., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 275–303. [Google Scholar]
- Price, L.C.; Wort, S.J.; Perros, F.; Dorfmüller, P.; Huertas, A.; Montani, D.; Cohen-Kaminsky, S.; Humbert, M. Inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 2012, 141, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perros, F.; Dorfmüller, P.; Montani, D.; Hammad, H.; Waelput, W.; Girerd, B.; Raymond, N.; Mercier, O.; Mussot, S.; Cohen-Kaminsky, S.; et al. Pulmonary lymphoid neogenesis in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolenc, J.; Šebeštjen, M.; Vrtovec, B.; Koželj, M.; Haddad, F. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with advanced heart failure is associated with increased levels of interleukin-6. Biomarkers 2014, 19, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, N.; Paulin, R. Epigenetics, inflammation and metabolism in right heart failure associated with pulmonary hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2017, 7, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohm, I.; Grün, K.; Müller, L.M.; Bäz, L.; Förster, M.; Schrepper, A.; Kretzschmar, D.; Pistulli, R.; Yilmaz, A.; Bauer, R.; et al. Cellular inflammation in pulmonary hypertension: Detailed analysis of lung and right ventricular tissue, circulating immune cells and effects of a dual endothelin receptor antagonist. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2019, 73, 497–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stracher, E.; Graham, B.B.; Hunt, J.M.; Gandjeva, A.; Groshong, S.D.; McLaughlin, V.; Jessup, M.; Grizzle, W.; Cool, C.; Tuder, R.M. Modern age pathology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amatya, N.; Garg, A.V.; Gaffen, S.L. IL-17 Signaling: The Yin and the Yang. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miossec, P.; Kolls, J.K. Targeting IL-17 and TH17 cells in chronic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudakov, J.A.; Hanash, A.M.; Brink, M.R.M.V.D. Interleukin-22: Immunobiology and pathology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 747–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, H.; Olsson, T. Interleukin-22 Influences the Th1/Th17 Axis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 618110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.-H.; Aggarwal, S.; Ho, W.-H.; Foster, J.; Zhang, Z.; Stinson, J.; Wood, W.I.; Goddard, A.D.; Gurney, A.L. Interleukin (IL)-22, a novel human cytokine that signals through the interferon receptor-related proteins CRF2–4 and IL-22R. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 31335–31339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenberg, G.F.; Nair, M.G.; Kirn, T.J.; Zaph, C.; Fouser, L.A.; Artis, D. Pathological versus protective functions of IL-22 in airway inflammation are regulated by IL-17A. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenewicz, L.A. IL-22: There Is a Gap in Our Knowledge. Immunohorizons 2018, 2, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenmark, K.R.; Meyrick, B.; Galie, N.; Mooi, W.J.; McMurtry, I.F. Animal models of pulmonary arterial hypertension: The hope for etiological discovery and pharmacological cure. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L1013–L1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonnert, F.A.; Recknagel, P.; Seidel, M.; Jbeily, N.; Dahlke, K.; Bockmeyer, C.L.; Winning, J.; Lösche, W.; Claus, R.A.; Bauer, M. Characteristics of clinical sepsis reflected in a reliable and reproducible rodent sepsis model. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 170, e123–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, M.; Grün, K.; Betge, S.; Rohm, I.; Ndongson-Dongmo, B.; Bauer, R.; Schulze, P.C.; Lichtenauer, M.; Petersen, I.; Neri, D.; et al. Lung tissue remodelling in MCT-induced pulmonary hypertension: A proposal for a novel scoring system and changes in extracellular matrix and fibrosis associated gene expression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 81241–81254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiely, D.G.; Lawrie, A.; Humbert, M. Screening strategies for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Hear. J. Suppl. 2019, 21 (Suppl. K), K9–K20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorè, N.I.; Bragonzi, A.; Cigana, C. The IL-17A/IL-17RA axis in pulmonary defence and immunopathology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 30, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konya, C.; Paz, Z.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Tsokos, G.C. Update on the role of Interleukin 17 in rheumatologic autoimmune diseases. Cytokine 2015, 75, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweatt, A.J.; Hedlin, H.K.; Balasubramanian, V.; Hsi, A.; Blum, L.K.; Robinson, W.H.; Haddad, F.; Hickey, P.M.; Condliffe, R.; Lawrie, A.; et al. Discovery of Distinct Immune Phenotypes Using Machine Learning in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circ Res. 2019, 124, 904–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, E.; Witte, K.; Warszawska, K.; Sabat, R.; Wolk, K. Interleukin-22: A cytokine produced by T, NK and NKT cell subsets, with importance in the innate immune defense and tissue protection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aujla, S.J.; Alcorn, J.F. T(H)17 cells in asthma and inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1810, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Ji, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Feng, Y.; et al. Interleukin 22 Promotes Blood Pressure Elevation and Endothelial Dysfunction in Angiotensin II–Treated Mice. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2017, 6, e005875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Yang, G.; Xiao, F.; Xie, J.; Wang, S.; Lu, L.; Cui, D. Role of Th22 Cells in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 688066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, G.; Das, D.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Gilmore, B.A.; Wong, C.-M.; Suzuki, Y.J. IL-22 activates oxidant signaling in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandegar, M.; Fung, Y.-C.B.; Huang, W.; Remillard, C.V.; Rubin, L.J.; Yuan, J.X.-J. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pulmonary vascular remodeling: Role in the development of pulmonary hypertension. Microvasc. Res. 2004, 68, 75–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, L.C.; Bye, H.; Brock, M. Swiss Society of Pulmonary H. The pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension—An update. Swiss. Med. Wkly. 2015, 145, w14202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.; Farkas, L. Epigenetic Regulation of Endothelial Dysfunction and Inflammation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAleer, J.P.; Kolls, J.K. Directing traffic: IL-17 and IL-22 coordinate pulmonary immune defense. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; O’garra, A. IL-10 Family Cytokines IL-10 and IL-22: From Basic Science to Clinical Translation. Immunity 2019, 50, 871–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachiery, J.L.; Adir, Y.; Barbera, J.A. Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart diseases. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, D100–D108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Rouzic, O.; Pichavant, M.; Frealle, E.; Guillon, A.; Si-Tahar, M.; Gosset, P. Th17 cytokines: Novel potential therapeutic targets for COPD pathogenesis and exacerbations. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1602434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkey, M.R.; Plank, M.W.; Casolari, P.; Papi, A.; Pavlidis, S.; Guo, Y.; Cameron, G.J.; Haw, T.J.; Tam, A.; Obiedat, M.; et al. IL-22 and its receptors are increased in human and experimental COPD and contribute to pathogenesis. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1800174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Jin, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, D.; Zhang, S.; Gao, P.; Liu, D. Increased Levels of Cytokines Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and IL-22 in Deep Vein Thrombosis. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2016, 13, 2763–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, E.; Holmes, A.M.; Treacy, C.M.; Doughty, N.J.; Southgate, L.; Machado, R.D.; Trembath, R.C.; Jennings, S.; Barker, L.; Nicklin, P.; et al. Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines predict survival in idiopathic and familial pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 2010, 122, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, F.; Schramm, R.; Bauer, M.; Tscholl, D.; Kunihara, T.; Scha¨fers, H.-J. Cytokine response to pulmonary thromboendarterectomy. Chest 2004, 126, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, S.; Nagaya, N.; Satoh, T.; Kyotani, S.; Sakamaki, F.; Fujita, M.; Nakanishi, N.; Miyatake, K. Clinical correlates and prognostic significance of six-minute walk test in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Comparison with cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161 Pt 1, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarck, R.; Nawrot, T.; Meyns, B.; Delcroix, M. C-Reactive Protein: A New Predictor of Adverse Outcome in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzen, J.M.; Nickel, N.; Krämer, R.; Golpon, H.; Westerkamp, V.; Olsson, K.M.; Haller, H.; Hoeper, M.M. Osteopontin in patients with idiopathic pulmonary hypertension. Chest 2011, 139, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, R.; Paskin-Flerlage, S.; Zamanian, R.T.; Zimmerman, P.; Schmidt, J.W.; Deng, D.Y.; Southwood, M.; Spencer, R.; Lai, C.S.; Parker, W.; et al. Circulating angiogenic modulatory factors predict survival and functional class in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohm, I.; Grun, K.; Muller, L.M.; Kretzschmar, D.; Fritzenwanger, M.; Yilmaz, A.; Lauten, A.; Jung, C.; Schulze, P.C.; Berndt, A.; et al. Increased Serum Levels of Fetal Tenascin-C Variants in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension: Novel Biomarkers Reflecting Vascular Remodeling and Right Ventricular Dysfunction? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Marques, J.; Martins, S.R.; Calisto, C.; Goncalves, S.; Almeida, A.G.; de Sousa, J.C.; Pinto, F.J.; Diogo, A.N. An exploratory panel of biomarkers for risk prediction in pulmonary hypertension: Emerging role of CT-proET-1. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2013, 32, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Souza, R.; Bogossian, H.B.; Humbert, M.; Jardim, C.; Rabelo, R.; Amato, M.B.P.; Carvalho, C.R.R. N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide as a haemodynamic marker in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 25, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allanore, Y.; Borderie, D.; Meune, C.; Cabanes, L.; Weber, S.; Ekindjian, O.G.; Kahan, A. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide as a diagnostic marker of early pulmonary artery hypertension in patients with systemic sclerosis and effects of calcium-channel blockers. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3503–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzycki, B.; Pietrzak, A.; Grywalska, E.; Krasowska, D.; Chodorowska, G.; Roliński, J. Interleukin-22 and Its Correlation with Disease Activity in Plaque Psoriasis. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2019, 67, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grapsa, J.; Pereira Nunes, M.C.; Tan, T.C.; Cabrita, I.Z.; Coulter, T.; Smith, B.C.; Dawson, D.; Gibbs, J.S.; Nihoyannopoulos, P. Echocardiographic and Hemodynamic Predictors of Survival in Precapillary Pulmonary Hypertension: Seven-Year Follow-Up. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8, e002107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, R.J.; Hinderliter, A.L.; Willis, P.W.; Ralph, D.; Caldwell, E.J.; Williams, W.; Ettinger, N.A.; Hill, N.S.; Summer, W.R.; de Boisblanc, B.; et al. Echocardiographic predictors of adverse outcomes in primary pulmonary hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogaard, H.J.; Abe, K.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Voelkel, N.F. The right ventricle under pressure: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of right-heart failure in pulmonary hypertension. Chest 2009, 135, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Siebenthal, C.; Aubert, J.-D.; Mitsakis, P.; Yerly, P.; Prior, J.O.; Nicod, L.P. Pulmonary Hypertension and Indicators of Right Ventricular Function. Front. Med. 2016, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galie, N.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Rubin, L.J.; Simonneau, G. An overview of the 6th World Symposium on Pulmonary Hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1802148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Okada, O.; Tanabe, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Terai, M.; Takiguchi, Y.; Masuda, M.; Nakajima, N.; Hiroshima, K.; Inadera, H.; et al. Plasma monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and pulmonary vascular resistance in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
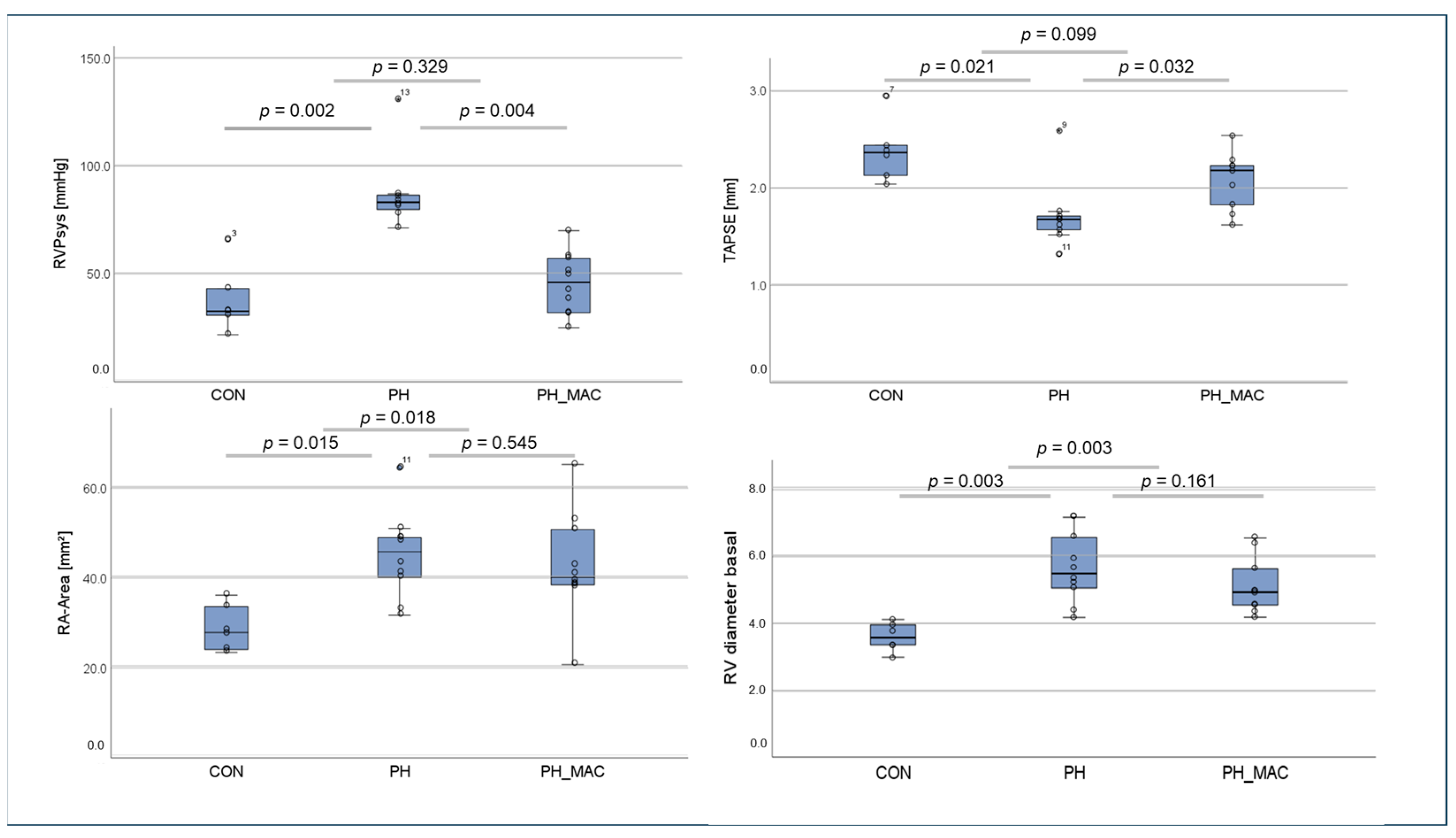
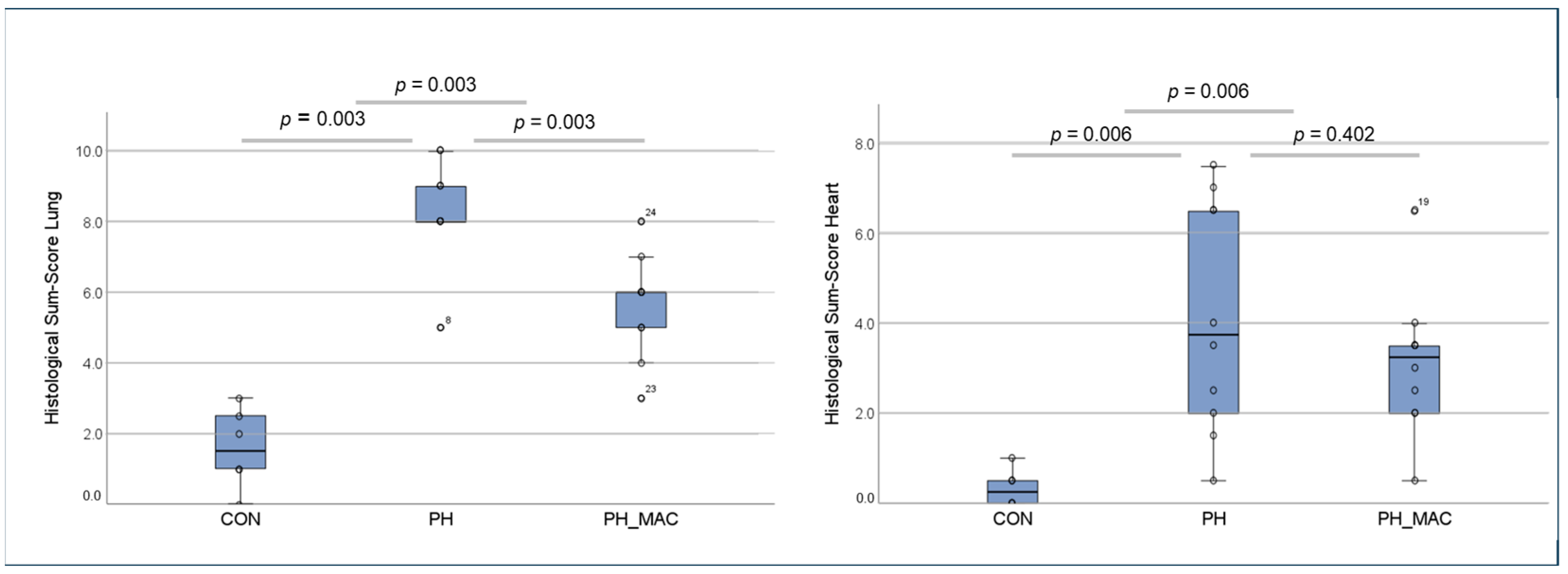



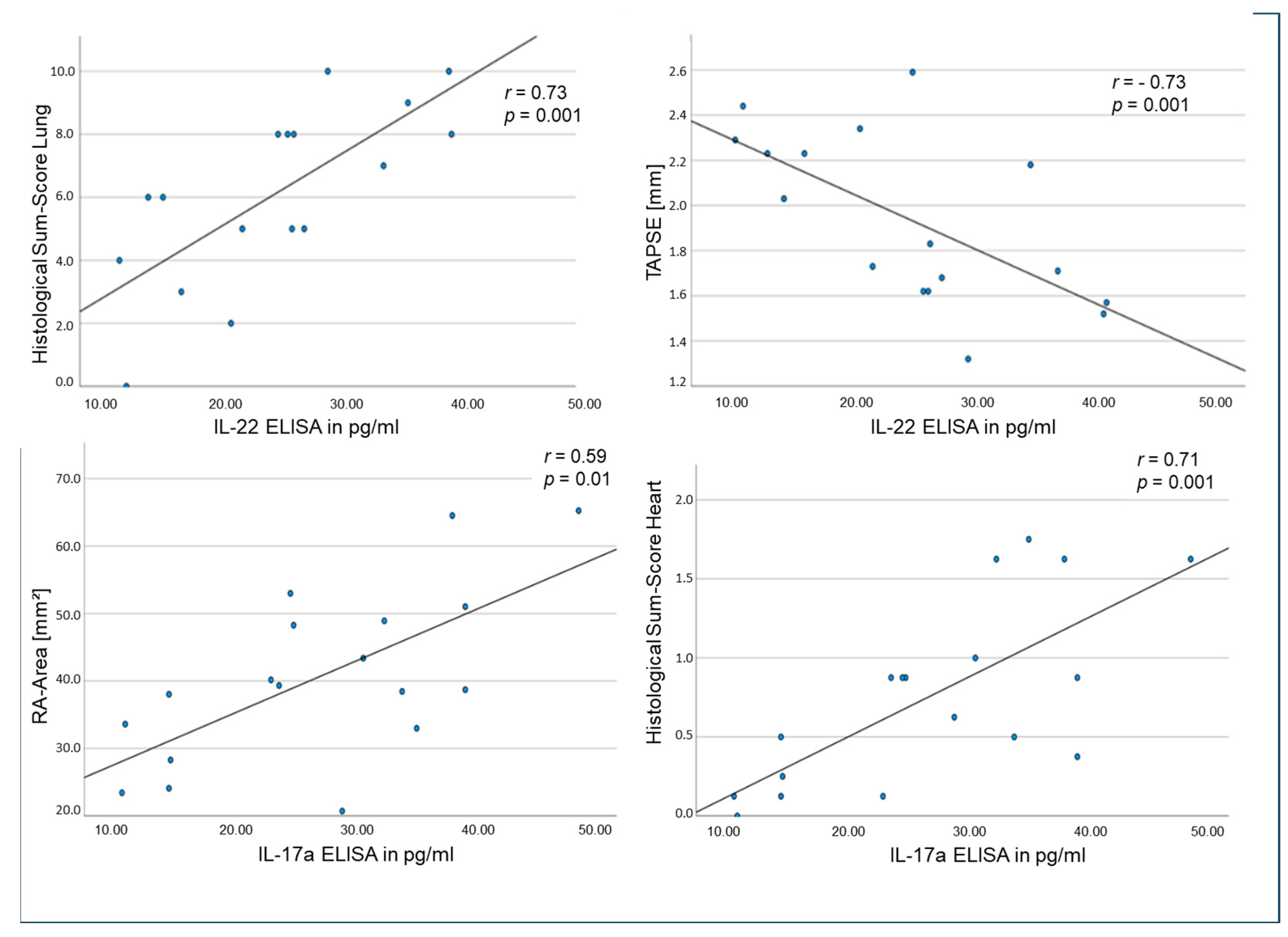
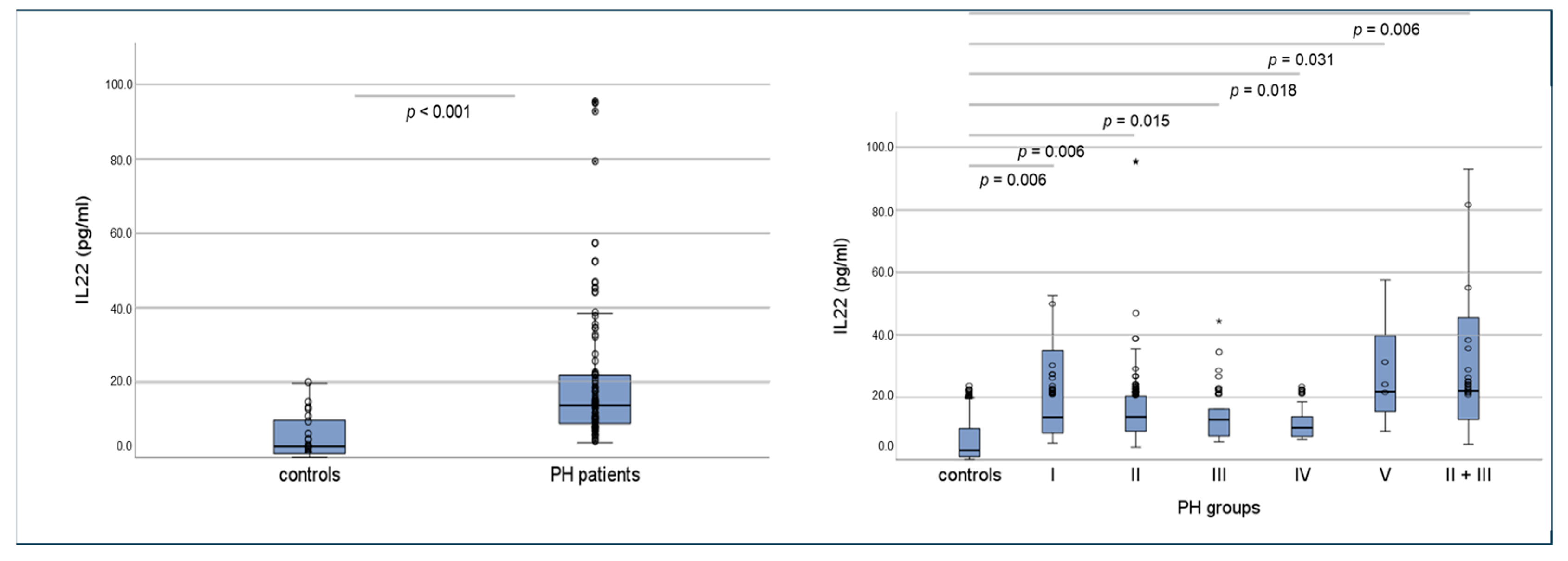
| Immunohistochemical/ ELISA Result | Echocardiographic/Hemodynamic/ Histologic Parameter | r-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-17a ELISA | Histological Sum-Score Lung | 0.580 | 0.012 |
| IL-17a ELISA | Histological Sum-Score Heart | 0.711 | 0.001 |
| IL-17a ELISA | RA-Area [mm2] | 0.592 | 0.010 |
| IL-17a ELISA | TAPSE [mm] | −0.535 | 0.022 |
| IL-17a ELISA | RVOT [mm] | 0.696 | 0.001 |
| IL-22 ELISA | Histological Sum-Score Lung | 0.731 | 0.001 |
| IL-22 ELISA | Histological Sum-Score Heart | 0.497 | 0.042 |
| IL-22 ELISA | RV-Catheter RVPsys [mmHg] | 0.550 | 0.034 |
| IL-22 ELISA | TAPSE [mm] | −0.730 | 0.001 |
| Control Group (n = 30) | PH Patients (n = 92) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical parameters | |||
| Age (years) | 65 ± 7 | 75 ± 12 | <0.001 |
| Male gender (%) | 37 | 30 | n.s. |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.4 ± 4.3 | 29.5 ± 6.7 | n.s. |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 153.6 ± 28.4 | 141.9 ± 27.0 | 0.026 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 87.6 ± 12.6 | 79.5 ± 14.5 | 0.011 |
| Heart rate (beats per min) | 70.3 ± 11.5 | 76.7 ± 13.8 | 0.026 |
| Functional class | 1.4 ± 0.5 (NYHA) | 2.4 ± 0.8 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Arterial hypertension (%) | 87 | 86 | n.s. |
| Coronary artery disease (%) | 10 | 28 | 0.042 |
| Hypertensive heart disease (%) | 66 | 63 | n.s. |
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 13 | 50 | <0.001 |
| Lung diseases (%) | 17 | 52 | 0.001 |
| COPD (%) | 3 | 23 | 0.015 |
| Pulmonary fibrosis (%) | 0 | 14 | 0.029 |
| Chronic kidney disease (GFR < 50 mL/min) (%) | 3 | 55 | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia (%) | 63 | 61 | n.s. |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 13 | 44 | 0.003 |
| Obesity (BMI > 30 kg/m2) (%) | 33 | 48 | n.s. |
| Autoimmune diseases (%) | 0 | 21 | 0.007 |
| Smoking (%) | 37 | 34 | n.s. |
| Medication (%) | |||
| ASA(%) | 40 | 20 | 0.031 |
| Beta blocker (%) | 53 | 65 | n.s. |
| ACE inhibitor/Sartan (%) | 73 | 62 | n.s. |
| Calcium channel blocker (%) | 37 | 33 | n.s. |
| Diuretic (%) | 33 | 83 | <0.001 |
| Statin (%) | 50 | 66 | n.s. |
| Prednisolone (%) | 7 | 14 | n.s. |
| Inhaled glucocorticoid (%) | 13 | 20 | n.s. |
| Laboratory parameters | |||
| BNP (pg/mL) | 38 ± 33.1 | 199.0 ± 782.5 | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 2.0 ± 4.6 | 5.7 ± 17.1 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 75.5 ± 10.1 | 104.0 ± 78.7 | <0.001 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.7 ± 1.4 | 2.4 ± 1.0 | 0.003 |
| Hemoglobin (mmol/L) | 8.6 ± 0.8 | 7.9 ± 1.2 | 0.001 |
| Leukocytes (Gpt/L) | 6.9 ± 2.3 | 7.0 ± 2.3 | n.s. |
| Platelets (Gpt/L) | 258 ± 51.8 | 223.0 ± 67.0 | 0.006 |
| Parameter | Control Group | PHall_groups | p-Value * | PH l | PH ll | PH lll | PH lV | PH V | PH ll/lll | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAPsys (mmHg) | 25.5 ± 4.1 | 52 ± 17.8 | <0.001 | 53.2 ± 19.9 | 51.6 ± 15.7 | 55.5 ± 17.7 | 37.8 ± 20.1 | 35.0 ± 6.2 | 57.4 ± 17.1 | n.s. |
| TAPSE (mm) | 24.7 ± 4.0 | 18 ± 5.3 | <0.001 | 17.6 ± 6.6 | 16.7 ± 4.2 | 20.1 ± 6.6 | 19.2 ± 4.3 | (32; n = 1) | 16.0 ± 3.6 | n.s. |
| RAA (cm2) | 16 ± 2.6 | 26 ± 10.7 | <0.001 | 23 ± 10.9 | 29.6 ± 11.1 | 22.3 ± 7.4 | 18.7 ± 5.3 | (16; n = 1) | 30.3 ± 11.3 | 0.03 |
| Relevant Vitium (%) | 3 | 66 | 0.001 | 77 | 87 | 11 | 44 | 33 | 65 | 0.001 |
| IVSd (mm) | 11.6 ± 2.5 | 13 ± 9.2 | n.s. | 11.8 ± 3.2 | 12.4 ± 3.0 | 13.8 ± 3.0 | 11.4 ± 2.6 | (10; n = 1) | 12.0 ± 2.3 | n.s. |
| LVEF (%) | 65.2 ± 9.5 | 59 ± 11 | 0.015 | 59.9 ± 8.8 | 56.3 ± 12.9 | 62.6 ± 8.2 | 63.3 ± 5.6 | 70 ± 6.4 | 56.2 ± 11.4 | n.s. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klein, F.; Dinesh, S.; Fiedler, D.; Grün, K.; Schrepper, A.; Bogoviku, J.; Bäz, L.; Pfeil, A.; Kretzschmar, D.; Schulze, P.C.; et al. Identification of Serum Interleukin-22 as Novel Biomarker in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Translational Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073985
Klein F, Dinesh S, Fiedler D, Grün K, Schrepper A, Bogoviku J, Bäz L, Pfeil A, Kretzschmar D, Schulze PC, et al. Identification of Serum Interleukin-22 as Novel Biomarker in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Translational Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(7):3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073985
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlein, Friederike, Sandesh Dinesh, Desiree Fiedler, Katja Grün, Andrea Schrepper, Jürgen Bogoviku, Laura Bäz, Alexander Pfeil, Daniel Kretzschmar, P. Christian Schulze, and et al. 2024. "Identification of Serum Interleukin-22 as Novel Biomarker in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Translational Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 7: 3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073985
APA StyleKlein, F., Dinesh, S., Fiedler, D., Grün, K., Schrepper, A., Bogoviku, J., Bäz, L., Pfeil, A., Kretzschmar, D., Schulze, P. C., Möbius-Winkler, S., & Franz, M. (2024). Identification of Serum Interleukin-22 as Novel Biomarker in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Translational Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(7), 3985. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25073985






