The Effect of Diesel Exhaust Particles on Adipose Tissue Mitochondrial Function and Inflammatory Status
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
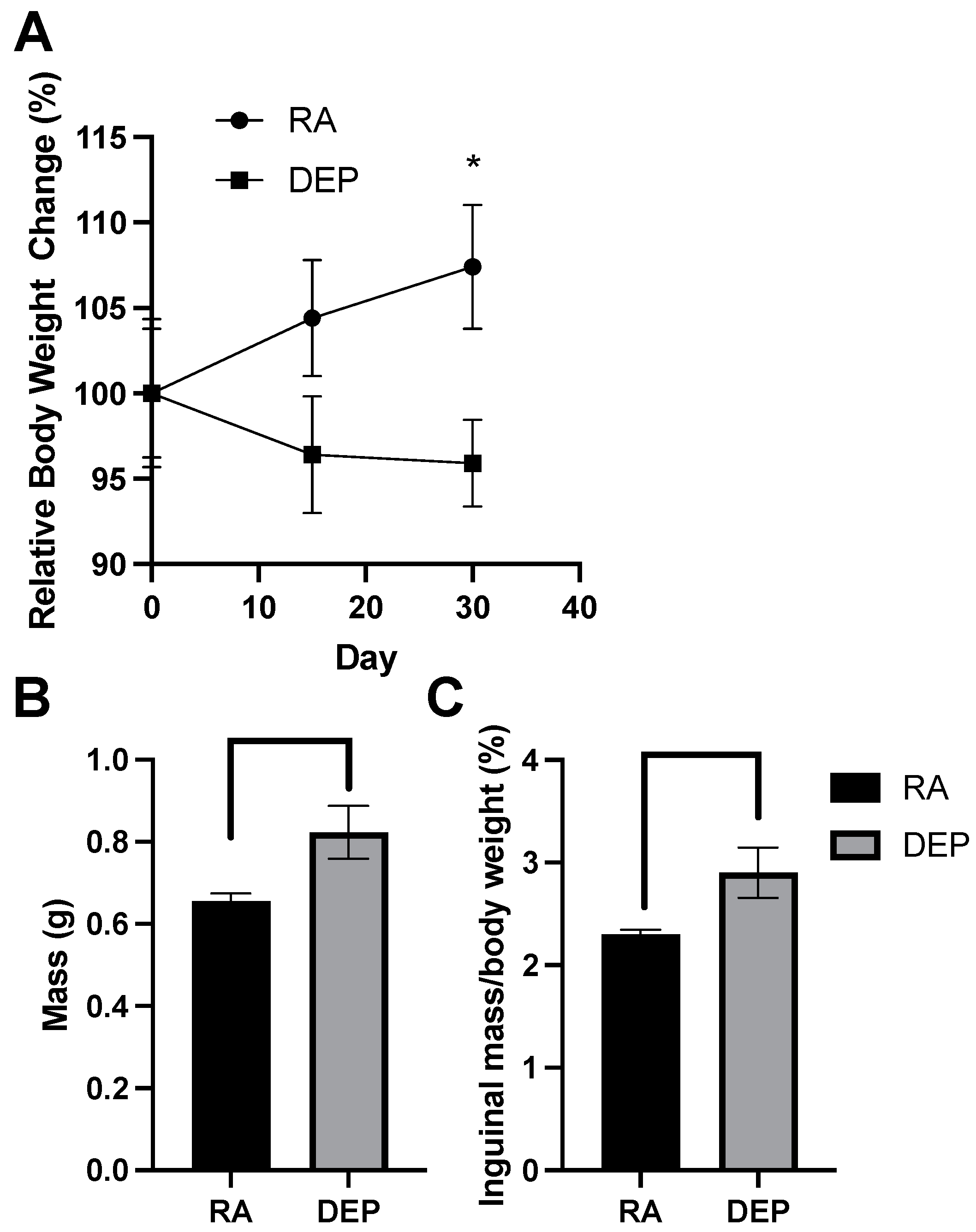
2.1. Body and Inguinal Adipose Tissue Weights
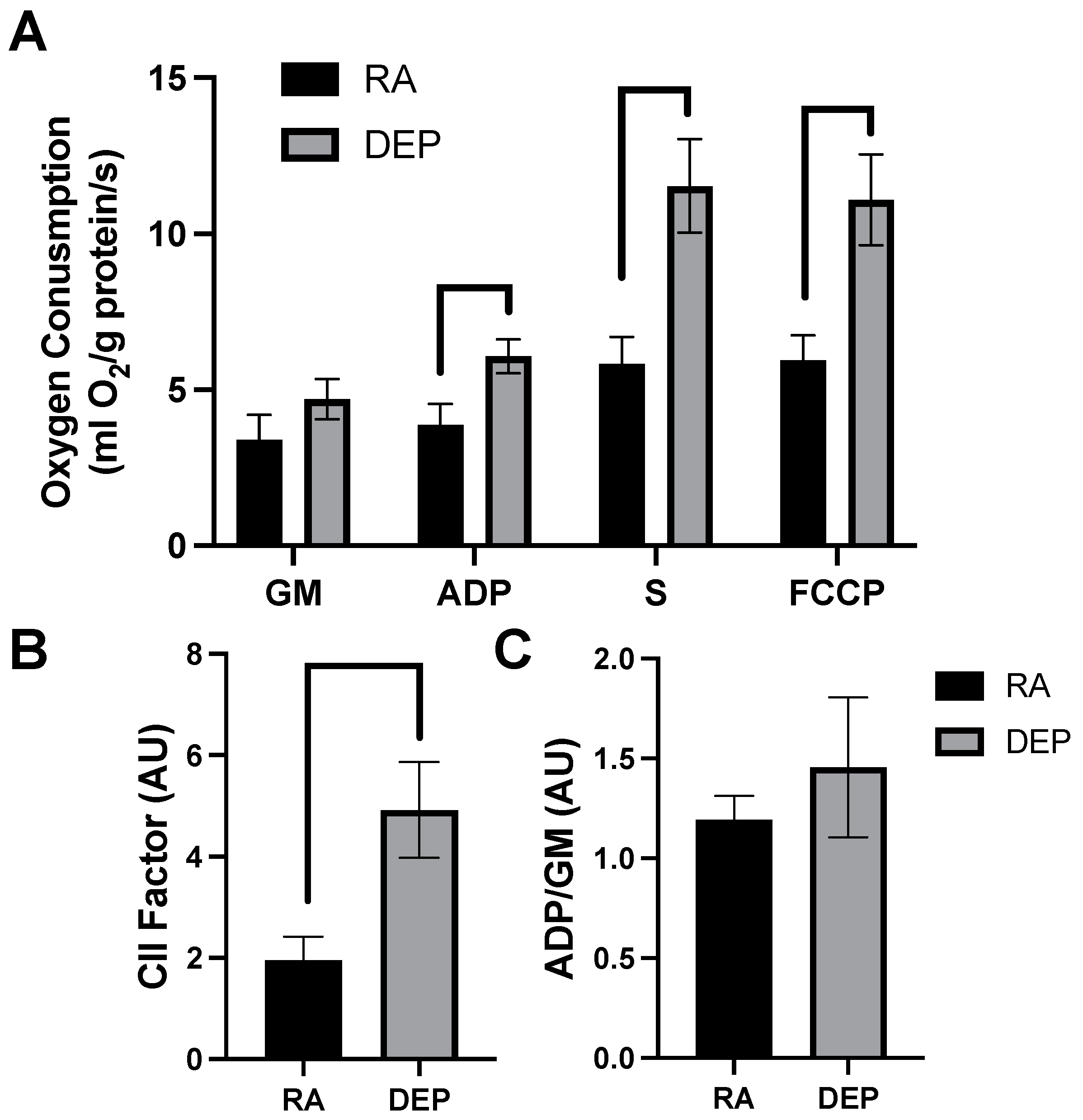
2.2. Mitochondrial Respiration
2.3. Inflammatory Marker Abundance following DEP Exposure
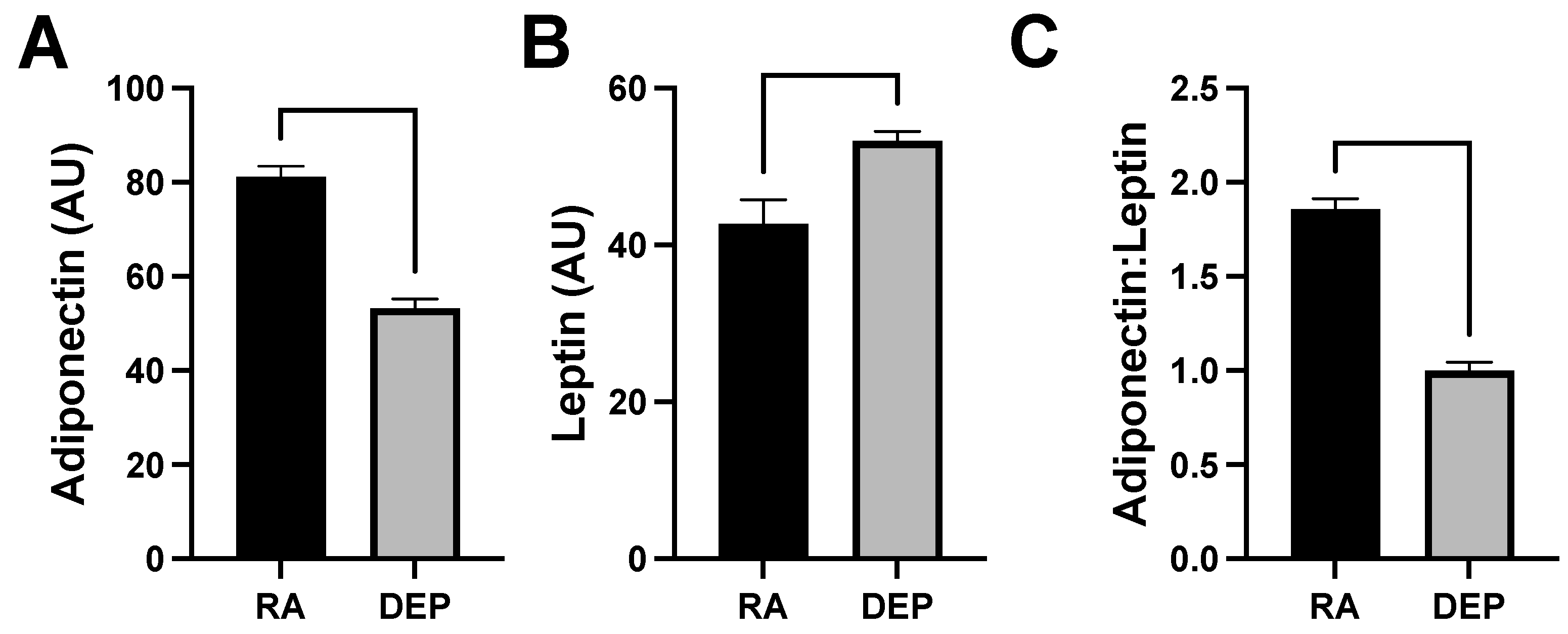
2.4. Adipokine Abundance following DEP Exposure
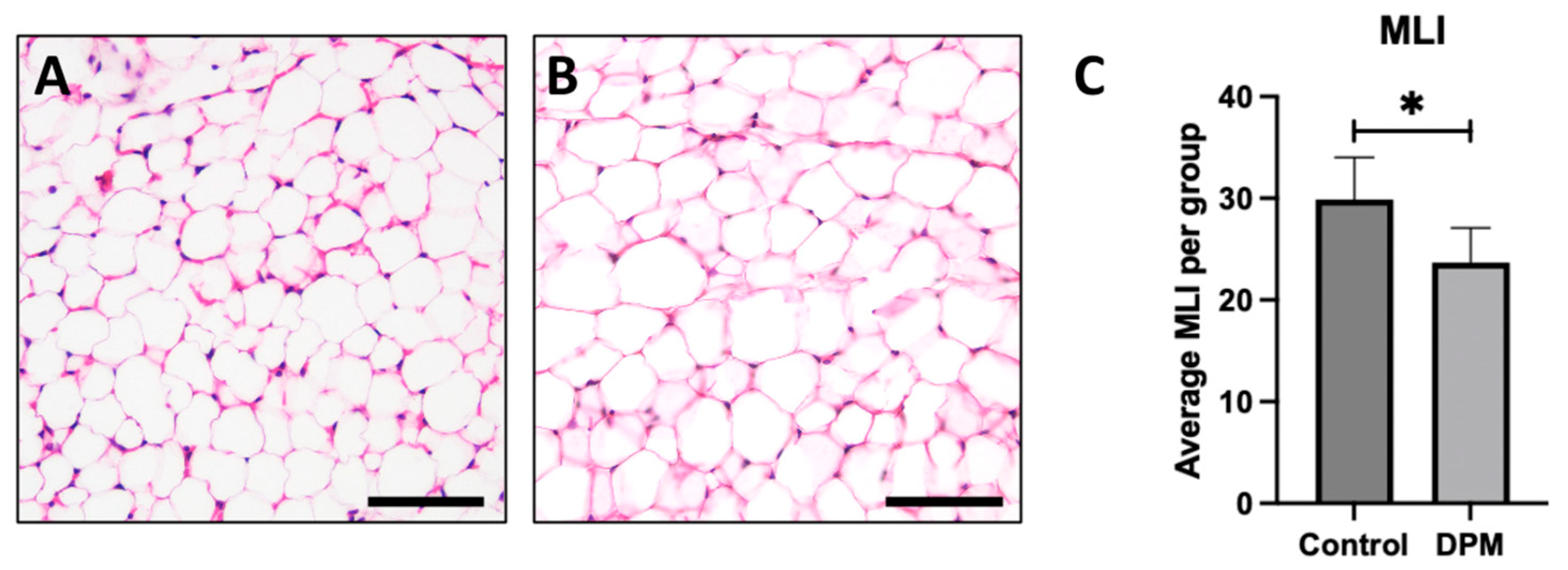
2.5. Histological Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Diesel Exhaust Particle Exposure
4.3. Mitochondrial Respirometry
4.4. Inflammatory Cytokine Analysis
4.5. Histology
4.6. Statistical Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Ambient (Outdoor) Air Pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Air pollution and public health: Emerging hazards and improved understanding of risk. Env. Geochem Health 2015, 37, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, J.L.; Dallon, B.W.; Lewis, J.B.; Walton, C.M.; Arroyo, J.A.; Reynolds, P.R.; Bikman, B.T. Diesel Exhaust Particle Exposure Compromises Alveolar Macrophage Mitochondrial Bioenergetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, L.; Foley, G.; Gill, I.; Gillmore, G.; Grigg, J.; Wertheim, D. Confocal microscopy 3D imaging of diesel particulate matter. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 30384–30389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Li, D.; Piao, J.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.; Pi, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, R.; et al. Real-ambient exposure to air pollution exaggerates excessive growth of adipose tissue modulated by Nrf2 signal. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munzel, T.; Sørensen, M.; Gori, T.; Schmidt, F.P.; Rao, X.; Brook, F.R.; Chen, L.C.; Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S. Environmental stressors and cardio-metabolic disease: Part II-mechanistic insights. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryar, C.C.M.; Afful, J. Prevalence of overweight, obesity, and severe obesity among adults aged 20 and over: United States, 1960–1962 through 2017–2018. CDC. 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db360-h.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Araujo, J.; Cai, J.; Stevens, J. Prevalence of Optimal Metabolic Health in American Adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2016. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2019, 17, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerrett, M.; McConnell, R.; Wolch, J.; Chang, R.; Lam, C.; Dunton, G.; Gilliland, F.; Lurmann, F.; Islam, T.; Berhane, K. Traffic-related air pollution and obesity formation in children: A longitudinal, multilevel analysis. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinchmann, B.C.; Holme, J.A.; Frerker, N.; Rambol, M.H.; Karlsen, T.; Brinchmann, J.E.; Kubatova, A.; Kukowski, K.; Skuland, T.; Ovrevik, J. Effects of organic chemicals from diesel exhaust particles on adipocytes differentiated from human mesenchymal stem cells. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 132, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.D.; Xu, X.; Bard, R.L.; Dvonch, J.T.; Morishita, M.; Kaciroti, N.; Sun, Q.; Harkema, J.; Rajagopalan, S. Reduced metabolic insulin sensitivity following sub-acute exposures to low levels of ambient fine particulate matter air pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 448, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.C.; Schwartz, J. Metabolic syndrome and inflammatory responses to long-term particulate air pollutants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Yue, P.; Deiuliis, J.A.; Lumeng, C.N.; Kampfrath, T.; Mikolaj, M.B.; Cai, Y.; Ostrowski, M.C.; Lu, B.; Parthasarathy, S.; et al. Ambient air pollution exaggerates adipose inflammation and insulin resistance in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. Circulation 2009, 119, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Shan, Z.; Teng, W.; Han, C. Association between air pollution and type 2 diabetes: An updated review of the literature. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 10, 2042018819897046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, J.F.; Bachireddy, C.; Shyamprasad, S.; Goldfine, A.B.; Brownstein, J.S. Association between fine particulate matter and diabetes prevalence in the U.S. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2196–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, L.; Pecht, T.; Goldstein, N.; Haim, Y.; Kloog, I.; Yarza, S.; Sarov, B.; Novack, V. The effects of ambient particulate matter on human adipose tissue. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Part A 2019, 82, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reina-Perez, I.; Artacho-Cordon, F.; Mustieles, V.; Castellano-Castillo, D.; Cardona, F.; Jimenez-Diaz, I.; Lopez-Medina, J.A.; Alcaide, J.; Ocana-Wilhelmi, L.; Iribarne-Duran, L.M.; et al. Cross-sectional associations of persistent organic pollutants measured in adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome in clinically diagnosed middle-aged adults. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A.E.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Ng, D.; Hiura, T.; Saxon, A. Enhancement of allergic inflammation by the interaction between diesel exhaust particles and the immune system. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 102, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, M.E.; Klein, A.D.; Stesniak, E.J. A Diesel Exhaust Filter System for Industrial Diesel Forklifts. SAE Tech. Pap. 1991, 911852. [Google Scholar]
- Cassee, F.R.; Héroux, M.-E.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Kelly, F.J. Particulate matter beyond mass: Recent health evidence on the role of fractions, chemical constituents and sources of emission. Inhal. Toxicol. 2013, 25, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, B.A.; Walton, C.; Carr, S.T.; Andrus, J.L.; Cheung, E.C.K.; Duplisea, M.J.; Wilson, E.K.; Draney, C.; Lathen, D.R.; Kenner, K.B.; et al. β-Hydroxybutyrate Elicits Favorable Mitochondrial Changes in Skeletal Muscle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, H.M.; Underkofler, C.; Kern, P.A.; Erickson, C.; Bredbeck, B.; Rasouli, N. Adipose Tissue Hypoxia, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Obese Insulin-Sensitive and Obese Insulin-Resistant Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trayhurn, P. Hypoxia and adipose tissue function and dysfunction in obesity. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruhbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin Ratio is a Functional Biomarker of Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Santibanez, G.; Singer, K.; Cho, K.W.; DelProposto, J.L.; Mergian, T.; Lumeng, C.N. Obesity-induced remodeling of the adipose tissue elastin network is independent of the metalloelastase MMP-12. Adipocyte 2015, 4, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, S.N.; Mantzke, K.A.; Kilgore, M.W.; Price, T.M. Relationship between adipose stromal-vascular cells and adipocytes in human adipose tissue. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 1996, 18, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, D.B.; Betteridge, B.; Earley, T.D.; Curtis, C.S.; Robinson, A.B.; Reynolds, P.R. Primary alveolar macrophages exposed to diesel particulate matter increase RAGE expression and activate RAGE signaling. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 358, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasband, W. ImageJ. U.S. National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, Maryland, USA. Available online: https://imagej.net/nih-image/ (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Reynolds, P.R.; Mucenski, M.; Le Cras, T.D.; Nichols, W.C.; Whitsett, J.A. Midkine is regulated by hypoxia and causes pulmonary vascular remodeling. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37124–37132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, A.M. Mechanistic links between COPD and lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Warren, C.E.; Campbell, K.M.; Kirkham, M.N.; Saito, E.R.; Remund, N.P.; Cayabyab, K.B.; Kim, I.J.; Heimuli, M.S.; Reynolds, P.R.; Arroyo, J.A.; et al. The Effect of Diesel Exhaust Particles on Adipose Tissue Mitochondrial Function and Inflammatory Status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084322
Warren CE, Campbell KM, Kirkham MN, Saito ER, Remund NP, Cayabyab KB, Kim IJ, Heimuli MS, Reynolds PR, Arroyo JA, et al. The Effect of Diesel Exhaust Particles on Adipose Tissue Mitochondrial Function and Inflammatory Status. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(8):4322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084322
Chicago/Turabian StyleWarren, Cali E., Kennedy M. Campbell, Madison N. Kirkham, Erin R. Saito, Nicole P. Remund, Kevin B. Cayabyab, Iris J. Kim, Micah S. Heimuli, Paul R. Reynolds, Juan A. Arroyo, and et al. 2024. "The Effect of Diesel Exhaust Particles on Adipose Tissue Mitochondrial Function and Inflammatory Status" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 8: 4322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084322
APA StyleWarren, C. E., Campbell, K. M., Kirkham, M. N., Saito, E. R., Remund, N. P., Cayabyab, K. B., Kim, I. J., Heimuli, M. S., Reynolds, P. R., Arroyo, J. A., & Bikman, B. T. (2024). The Effect of Diesel Exhaust Particles on Adipose Tissue Mitochondrial Function and Inflammatory Status. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(8), 4322. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084322







