Investigation into the Anti-Acne Effects of Castanea sativa Mill Leaf and Its Pure Ellagitannin Castalagin in HaCaT Cells Infected with Cutibacterium acnes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phytochemical Analysis
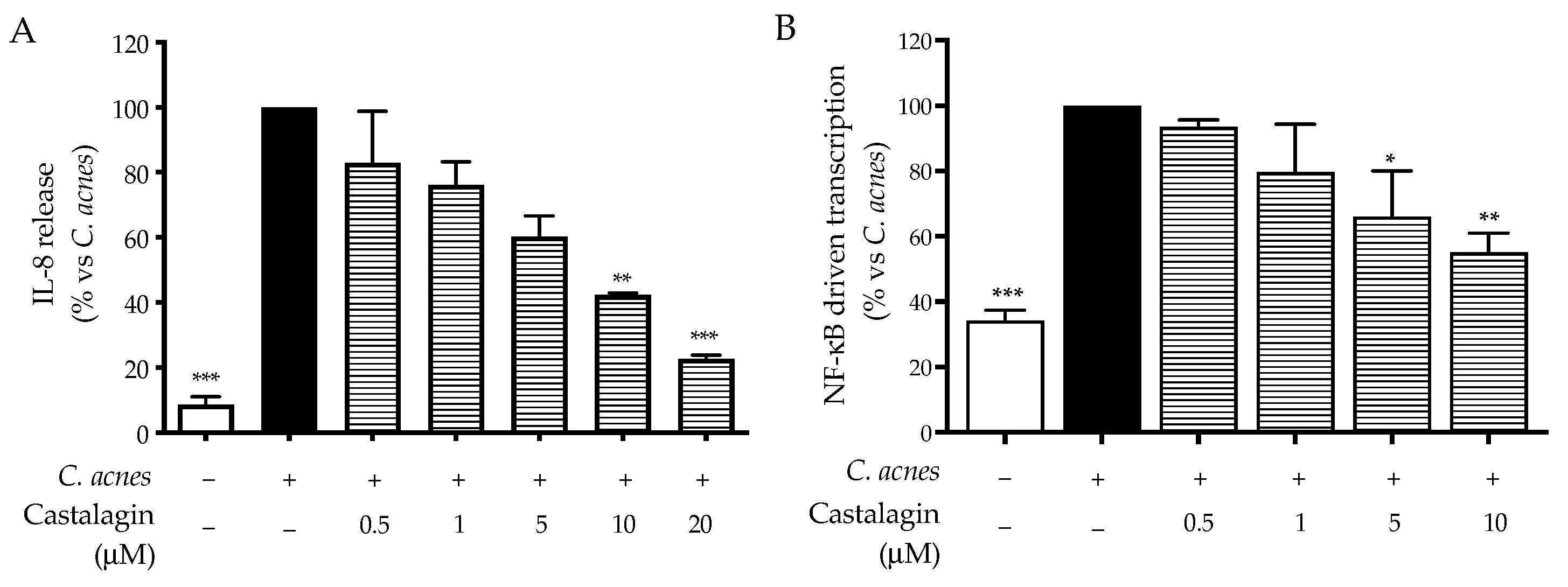
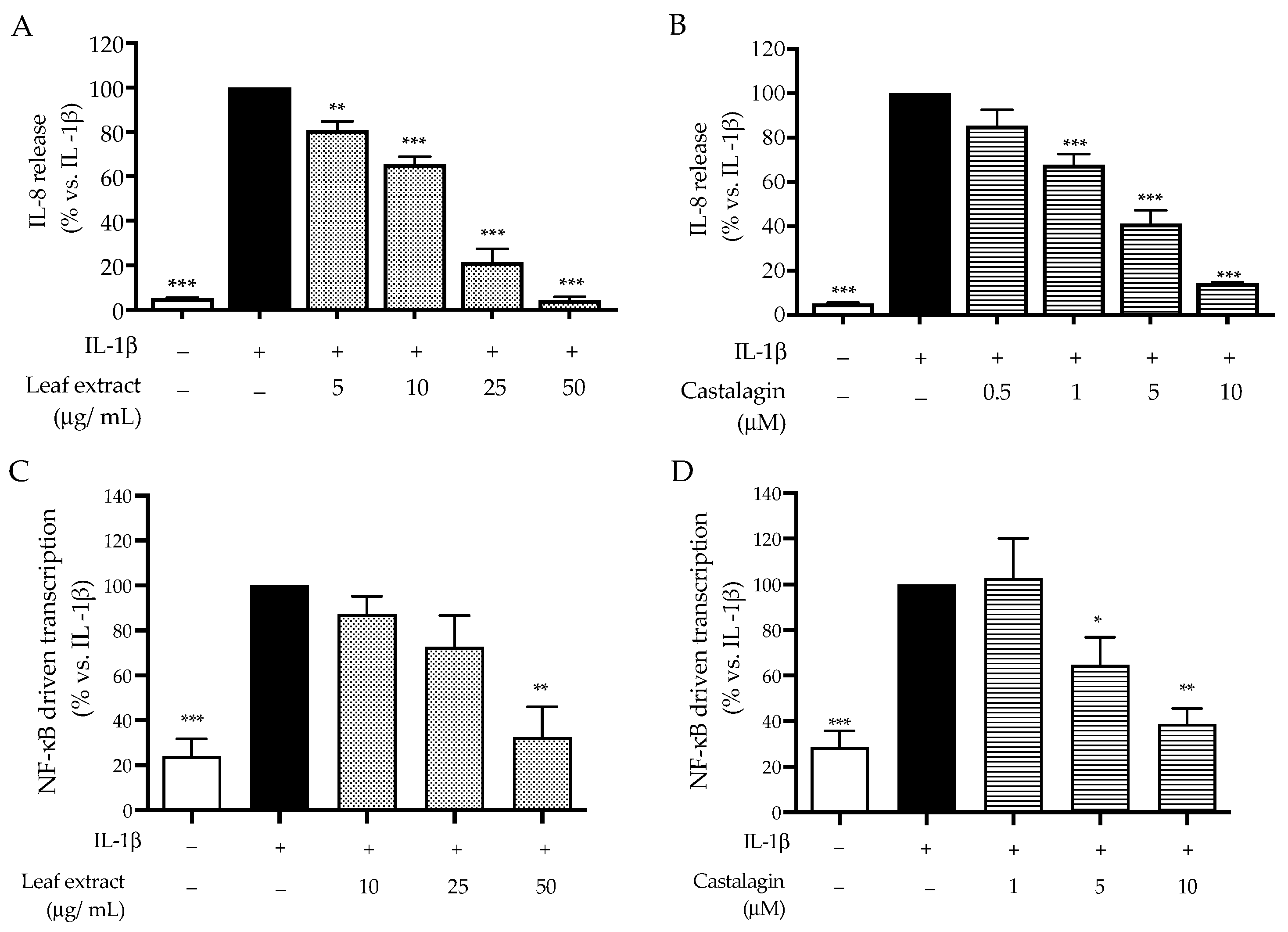
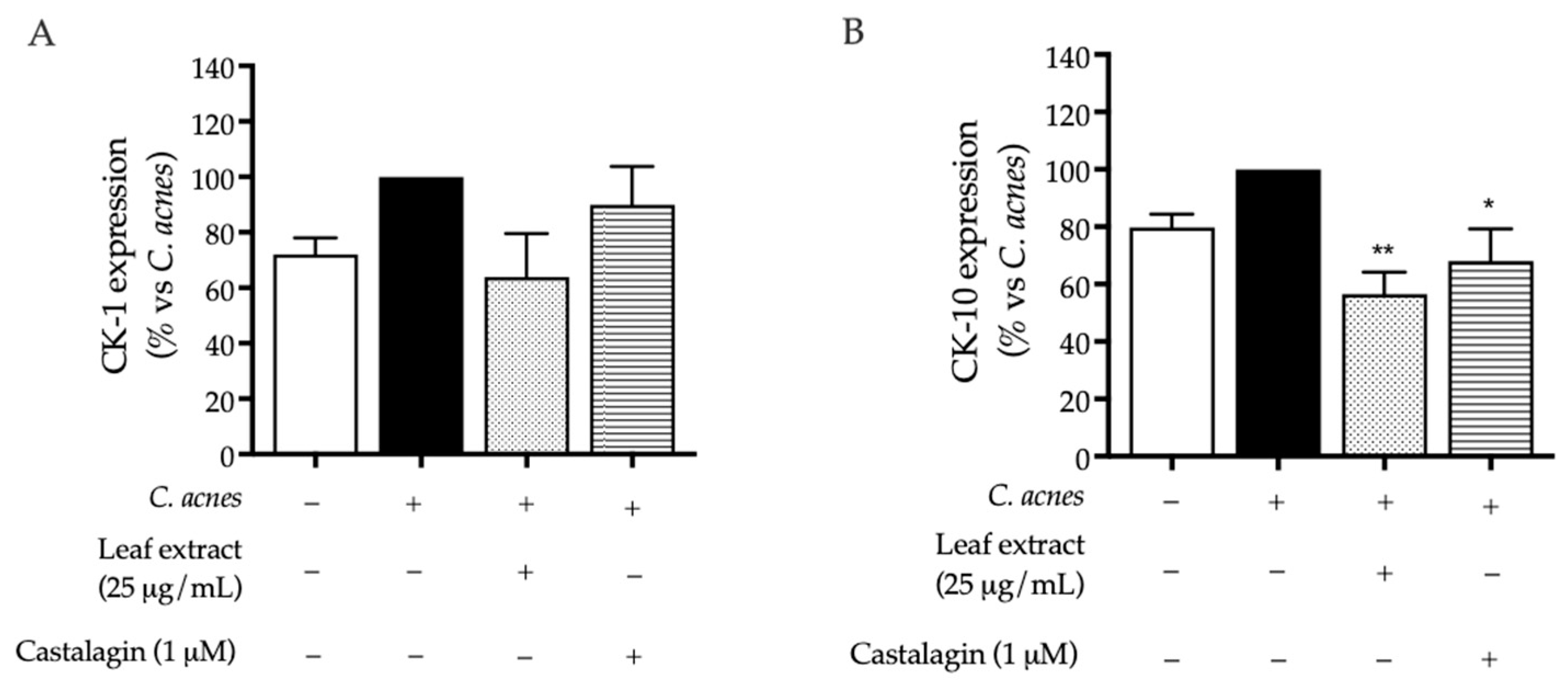
2.2. Bioactivity in HaCaT Cells
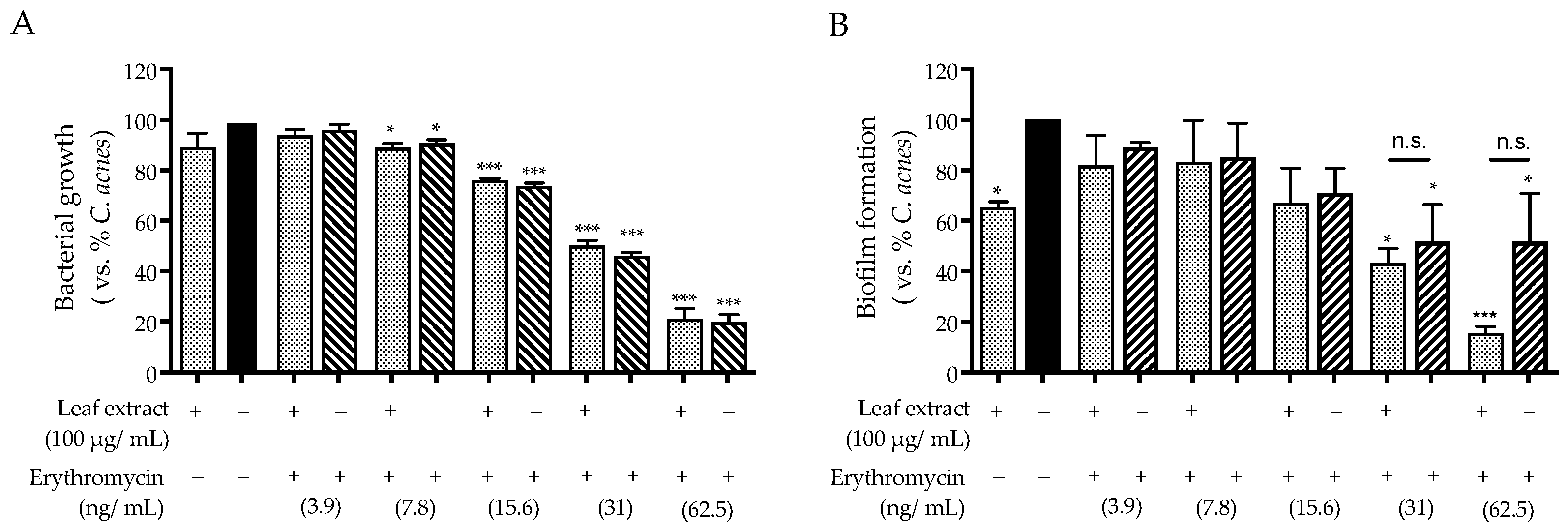
2.3. Antibacterial Activity against C. acnes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Extraction
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Treatment of HaCaT Cells and Co-Culture with C. acnes
4.4. Cell Viability
4.5. Immunoassays
4.5.1. ELISA Assay
4.5.2. Confocal Microscopy Analysis
4.6. NF-κB- and AP-1-Driven Transcription
4.7. Microbiological Assays
4.8. LC-MS
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, H.C.; Dellavalle, R.P.; Garner, S. Acne vulgaris. Lancet 2012, 379, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhate, K.; Williams, H.C. Epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 168, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayslich, C.; Grange, P.A.; Dupin, N. Cutibacterium acnes as an Opportunistic Pathogen: An Update of Its Virulence-Associated Factors. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreno, B.; Pecastaings, S.; Corvec, S.; Veraldi, S.; Khammari, A.; Roques, C. Cutibacterium acnes (Propionibacterium acnes) and acne vulgaris: A brief look at the latest updates. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32 (Suppl. S2), 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Review of the innate immune response in acne vulgaris: Activation of Toll-like receptor 2 in acne triggers inflammatory cytokine responses. Dermatology 2005, 211, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firlej, E.; Kowalska, W.; Szymaszek, K.; Rolinski, J.; Bartosinska, J. The Role of Skin Immune System in Acne. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, M.K.; Bosanac, S.S.; Sivamani, R.K.; Larsen, L.N. Emerging Therapies for Acne Vulgaris. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, S.; Fumagalli, M.; Khalilpour, S.; Martinelli, G.; Magnavacca, A.; Dell’Agli, M.; Sangiovanni, E. A Review of the Potential Benefits of Plants Producing Berries in Skin Disorders. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, S.; Fumagalli, M.; Martinelli, G.; Pozzoli, C.; Maranta, N.; Angarano, M.; Sangiovanni, E.; Dell’Agli, M. Hydrolyzable Tannins in the Management of Th1, Th2 and Th17 Inflammatory-Related Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatogawa, K.; Hayashi, S.; Shimomura, H.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Ito, H.; Hirai, Y. Antibacterial activity of hydrolyzable tannins derived from medicinal plants against Helicobacter pylori. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 48, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzini, P.; Arapitsas, P.; Goretti, M.; Branda, E.; Turchetti, B.; Pinelli, P.; Ieri, F.; Romani, A. Antimicrobial and antiviral activity of hydrolysable tannins. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseki, J.; Matsumoto, T.; Matsubara, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Mizuhara, Y.; Sekiguchi, K.; Nishimura, H.; Watanabe, J.; Kaneko, A.; Hattori, T.; et al. Inhibition of Rat 5alpha-Reductase Activity and Testosterone-Induced Sebum Synthesis in Hamster Sebocytes by an Extract of Quercus acutissima Cortex. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 853846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Hwang, I.H.; Lee, M.W. Anti-acne vulgaris effect including skin barrier improvement and 5alpha-reductase inhibition by tellimagrandin I from Carpinus tschonoskii. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Yin, J.; Hwang, I.H.; Park, D.H.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, M.W. Anti-Acne Vulgaris Effects of Pedunculagin from the Leaves of Quercus mongolica by Anti-Inflammatory Activity and 5alpha-Reductase Inhibition. Molecules 2020, 25, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Ji, H.; Roh, K.-B.; Cho, E.; Chajra, H.; Frechet, M.; Park, D.; Jung, E. Anti-acne effects of Castanea crenata bur extract and identification of active compound. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2022, 65, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comandini, P.; Lerma-Garcia, M.J.; Simo-Alfonso, E.F.; Toschi, T.G. Tannin analysis of chestnut bark samples (Castanea sativa Mill.) by HPLC-DAD-MS. Food Chem. 2014, 157, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, S.; Martinelli, G.; Fumagalli, M.; Pozzoli, C.; Maranta, N.; Giavarini, F.; Colombo, L.; Nicotra, G.; Vicentini, S.F.; Genova, F.; et al. Ellagitannins from Castanea sativa Mill. Leaf Extracts Impair H. pylori Viability and Infection-Induced Inflammation in Human Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, N.; Rodrigues, F.; Oliveira, M.B. Castanea sativa by-products: A review on added value and sustainable application. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formato, M.; Vastolo, A.; Piccolella, S.; Calabro, S.; Cutrignelli, M.I.; Zidorn, C.; Pacifico, S. Castanea sativa Mill. Leaf: UHPLC-HR MS/MS Analysis and Effects on In Vitro Rumen Fermentation and Methanogenesis. Molecules 2022, 27, 8662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, S.; Martinelli, G.; Vrhovsek, U.; Masuero, D.; Fumagalli, M.; Magnavacca, A.; Pozzoli, C.; Canilli, L.; Terno, M.; Angarano, M.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Acne Effects of Hamamelis virginiana Bark in Human Keratinocytes. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, P.A.; Raingeaud, J.; Calvez, V.; Dupin, N. Nicotinamide inhibits Propionibacterium acnes-induced IL-8 production in keratinocytes through the NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 56, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Kaczanowska, S.; Davila, E. IL-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase Signaling and Its Role in Inflammation, Cancer Progression, and Therapy Resistance. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, S.; Flori, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Ottaviani, M. Acne as an altered dermato-endocrine response problem. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessinioti, C.; Katsambas, A. Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Resistance in Acne: Epidemiological Trends and Clinical Practice Considerations. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2022, 95, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zaenglein, A.L.; Pathy, A.L.; Schlosser, B.J.; Alikhan, A.; Baldwin, H.E.; Berson, D.S.; Bowe, W.P.; Graber, E.M.; Harper, J.C.; Kang, S.; et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 945–973.e933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Martinez, R.; Zhang, W.; Estevez, M. Crosstalk between dietary pomegranate and gut microbiota: Evidence of health benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.J.; Kang, S.H.; Song, Y.J.; Jeon, Y.D.; Jin, J.S. Inhibitory Effect of Quercetin on Propionibacterium acnes-induced Skin Inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tax, G.; Urban, E.; Palotas, Z.; Puskas, R.; Konya, Z.; Biro, T.; Kemeny, L.; Szabo, K. Propionic Acid Produced by Propionibacterium acnes Strains Contri-butes to Their Pathogenicity. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2016, 96, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaza, N.; Akamatsu, H.; Kishi, M.; Mizutani, H.; Ishii, I.; Nakata, S.; Matsunaga, K. Effects of Propionibacterium acnes on various mRNA expression levels in normal human epidermal keratinocytes in vitro. J. Dermatol. 2009, 36, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrousse, V.; Castex-Rizzi, N.; Khammari, A.; Charveron, M.; Dreno, B. Modulation of integrins and filaggrin expression by Propionibacterium acnes extracts on keratinocytes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2007, 299, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.C.; Shafaee, S.; Lee, D.; Bikle, D.D. Requirement of an AP-1 site in the calcium response region of the involucrin promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24080–24088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukamp, P.; Petrussevska, R.T.; Breitkreutz, D.; Hornung, J.; Markham, A.; Fusenig, N.E. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 106, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerulli, A.; Napolitano, A.; Hosek, J.; Masullo, M.; Pizza, C.; Piacente, S. Antioxidant and In Vitro Preliminary Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Castanea sativa (Italian Cultivar “Marrone di Roccadaspide” PGI) Burs, Leaves, and Chestnuts Extracts and Their Metabolite Profiles by LC-ESI/LTQOrbitrap/MS/MS. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerulli, A.; Masullo, M.; Mari, A.; Balato, A.; Filosa, R.; Lembo, S.; Napolitano, A.; Piacente, S. Phenolics from Castanea sativa leaves and their effects on UVB-induced damage. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; Cadahia, E.; Esteruelas, E.; Munoz, A.M.; Fernandez de Simon, B.; Hernandez, T.; Estrella, I. Phenolic compounds in chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) heartwood. Effect of toasting at cooperage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9631–9640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Tentative Identification | R.T. | m/z [M-H]− | MS2 Fragments |
|---|---|---|---|
| HHDP acid | 5.31 | 337 | 293, 169.07 |
| Castalagin/vescalagin | 6.14 | 933 | 914.92, 897.21, 631.15, 612.90, 301.11, 924.05 |
| Quinic acid | 6.48 | 191 | 144.95, 129.03, 147.00, 152.86, 172.91 |
| Chesnatin | 7.39 | 637 | 593.23, 469.18, 467.07 |
| Cretanin | 7.79 | 469 | 169.04, 305.12, 303.88, 261.14, 306.02, 262.17, 243.22, 393.43 |
| Chestanin | 7.86 | 937 | 467.11, 469.07, 637.07 |
| Quercetin glucuronide | 9.05 | 477 | 315.08, 301.09 |
| Quercetin glucoside | 9.16 | 463 | 301.03, 300.03, 343.20, 151.05 |
| Ellagic acid | 9.61 | 301 | 301.00, 257.10, 185.02, 232.90, 229.07, 284.02 |
| Astragalin | 9.67 | 447 | 314.97, 316.07, 284.08, 285.17, 379.31 |
| Inflammatory Markers: IC50 Mean (CI 95%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| IL-8 Release | NF-κB Activity | |
| Leaf extract (μg/mL) | 18.37 (14.52 to 24.09) | 16.12 (10.13 to 25.75) |
| Castalagin (μM) | 3.66 (1.95 to 6.87) | 4.06 (1.46 to 11.29) |
| Inflammatory Markers: IC50 Mean (CI 95%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| IL-8 Release | NF-κB Activity | |
| Leaf extract (μg/mL) | 11.97 (10.13 to 14.14) | 34.71 (21.86 to 55.10) |
| Castalagin (μM) | 2.24 (1.55 to 3.24) | 5.49 (3.38 to 8.90) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piazza, S.; Martinelli, G.; Maranta, N.; Pozzoli, C.; Fumagalli, M.; Nicolaci, V.; Sonzogni, E.; Colombo, L.; Sangiovanni, E.; Dell’Agli, M. Investigation into the Anti-Acne Effects of Castanea sativa Mill Leaf and Its Pure Ellagitannin Castalagin in HaCaT Cells Infected with Cutibacterium acnes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094764
Piazza S, Martinelli G, Maranta N, Pozzoli C, Fumagalli M, Nicolaci V, Sonzogni E, Colombo L, Sangiovanni E, Dell’Agli M. Investigation into the Anti-Acne Effects of Castanea sativa Mill Leaf and Its Pure Ellagitannin Castalagin in HaCaT Cells Infected with Cutibacterium acnes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(9):4764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094764
Chicago/Turabian StylePiazza, Stefano, Giulia Martinelli, Nicole Maranta, Carola Pozzoli, Marco Fumagalli, Vincenzo Nicolaci, Elisa Sonzogni, Luca Colombo, Enrico Sangiovanni, and Mario Dell’Agli. 2024. "Investigation into the Anti-Acne Effects of Castanea sativa Mill Leaf and Its Pure Ellagitannin Castalagin in HaCaT Cells Infected with Cutibacterium acnes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 9: 4764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094764
APA StylePiazza, S., Martinelli, G., Maranta, N., Pozzoli, C., Fumagalli, M., Nicolaci, V., Sonzogni, E., Colombo, L., Sangiovanni, E., & Dell’Agli, M. (2024). Investigation into the Anti-Acne Effects of Castanea sativa Mill Leaf and Its Pure Ellagitannin Castalagin in HaCaT Cells Infected with Cutibacterium acnes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(9), 4764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094764







