KiSS-1 Modulation by Epigenetic Agents Improves the Cisplatin Sensitivity of Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sensitivity of NSCLC Cell Lines to Cisplatin, SAHA and AZA
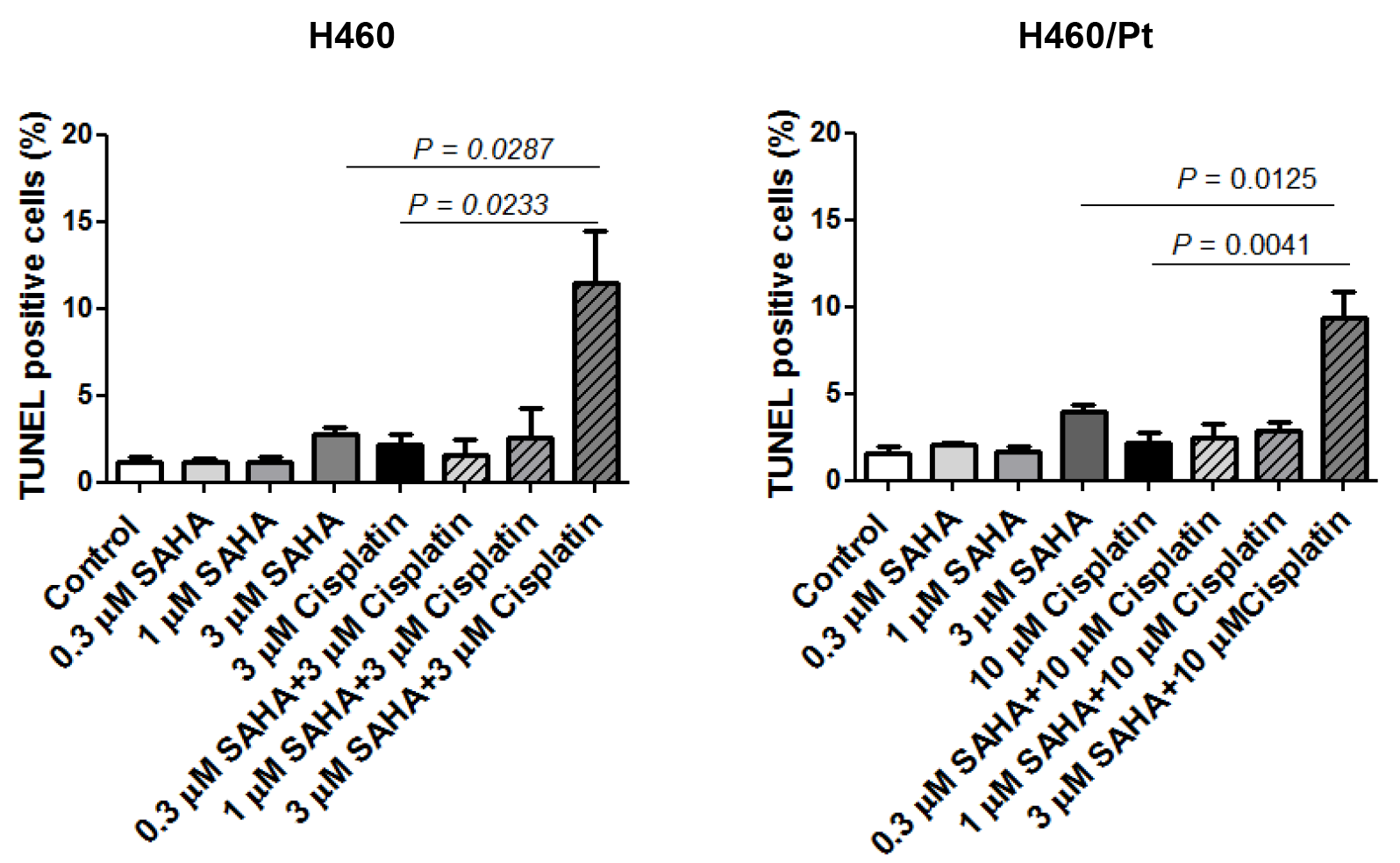
2.2. Drug Combination Studies
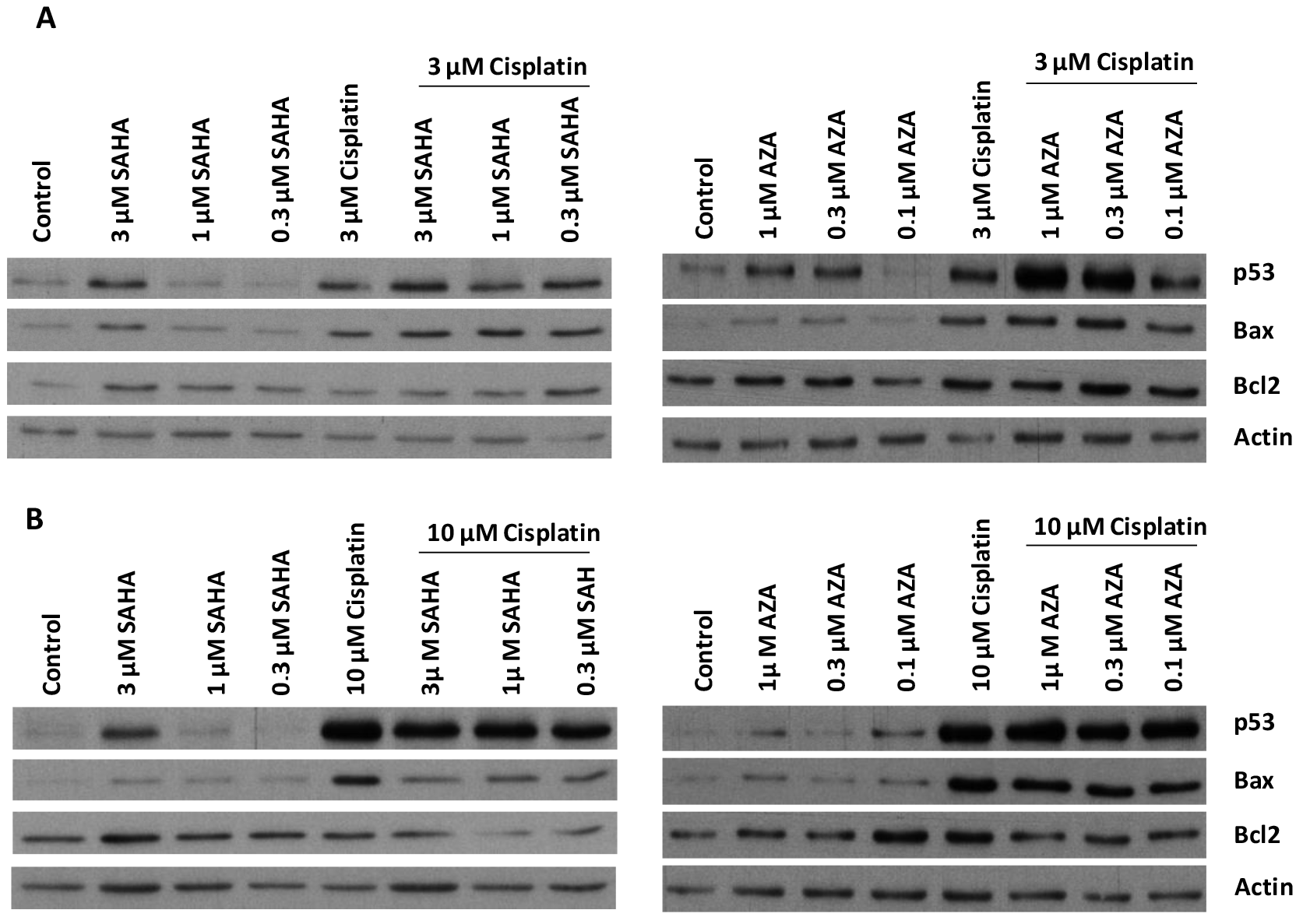
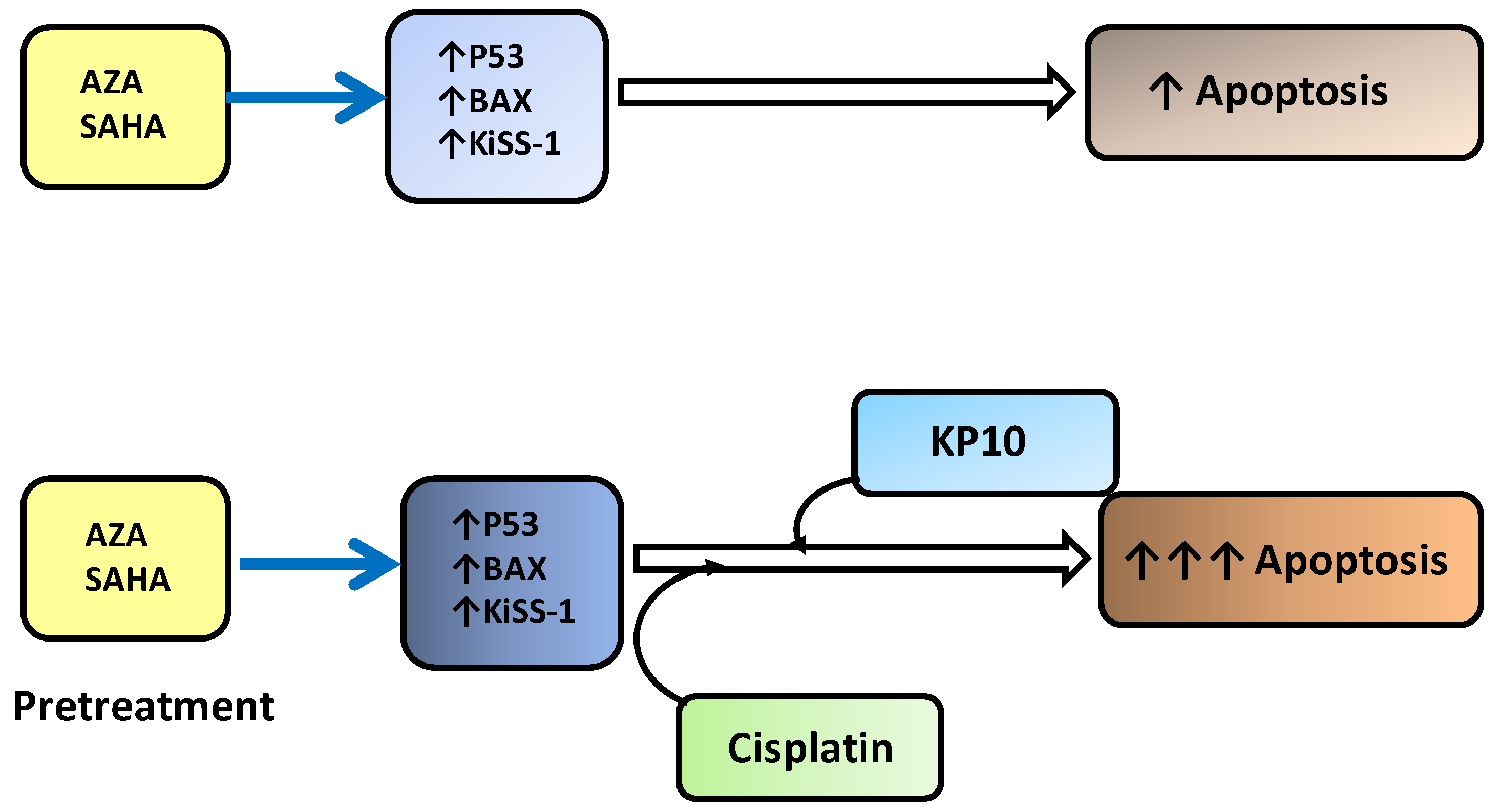
2.3. Modulation of Proteins Involved in Apoptosis Induction
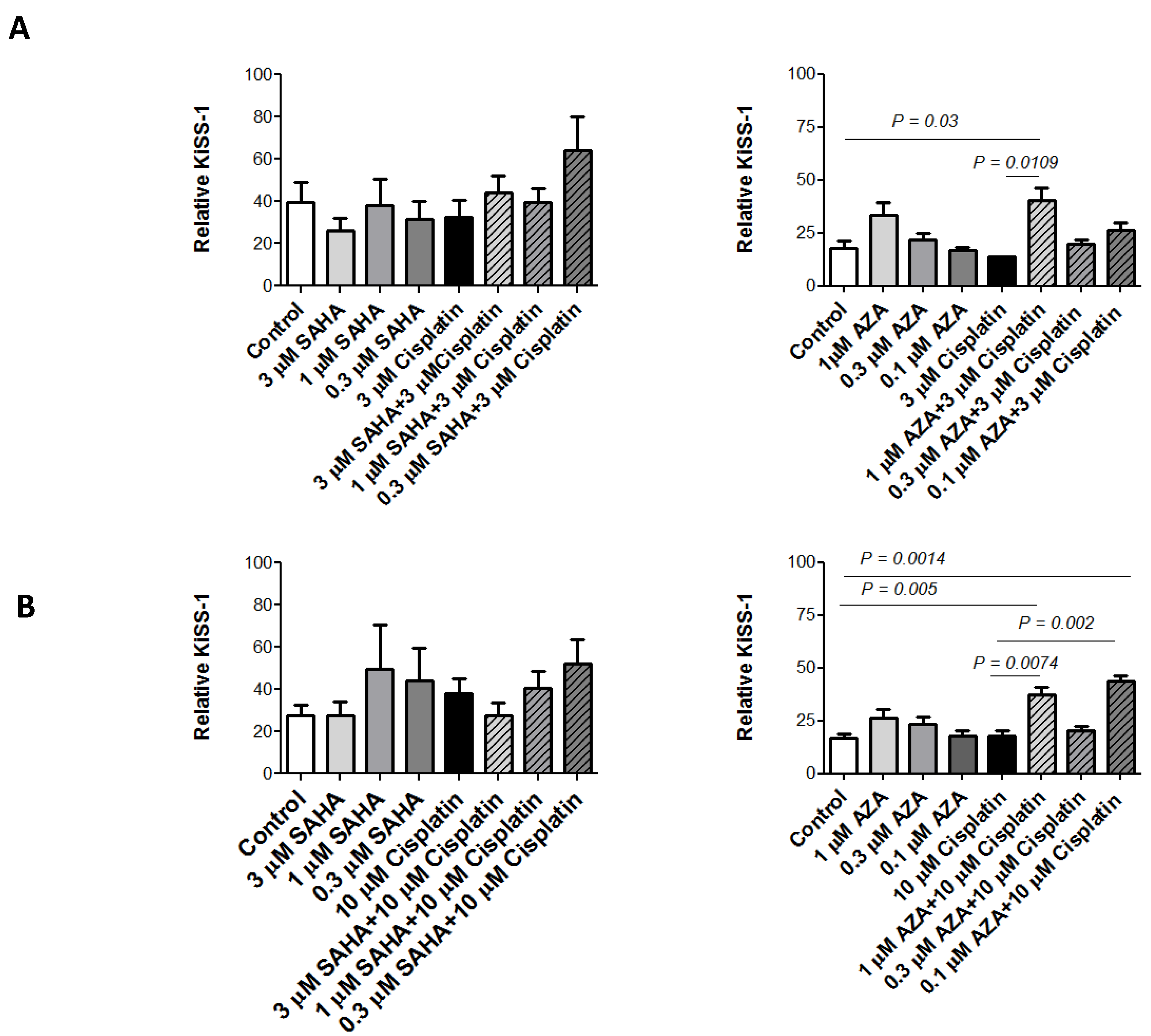
2.4. KiSS-1 Modulation upon Drug Treatment
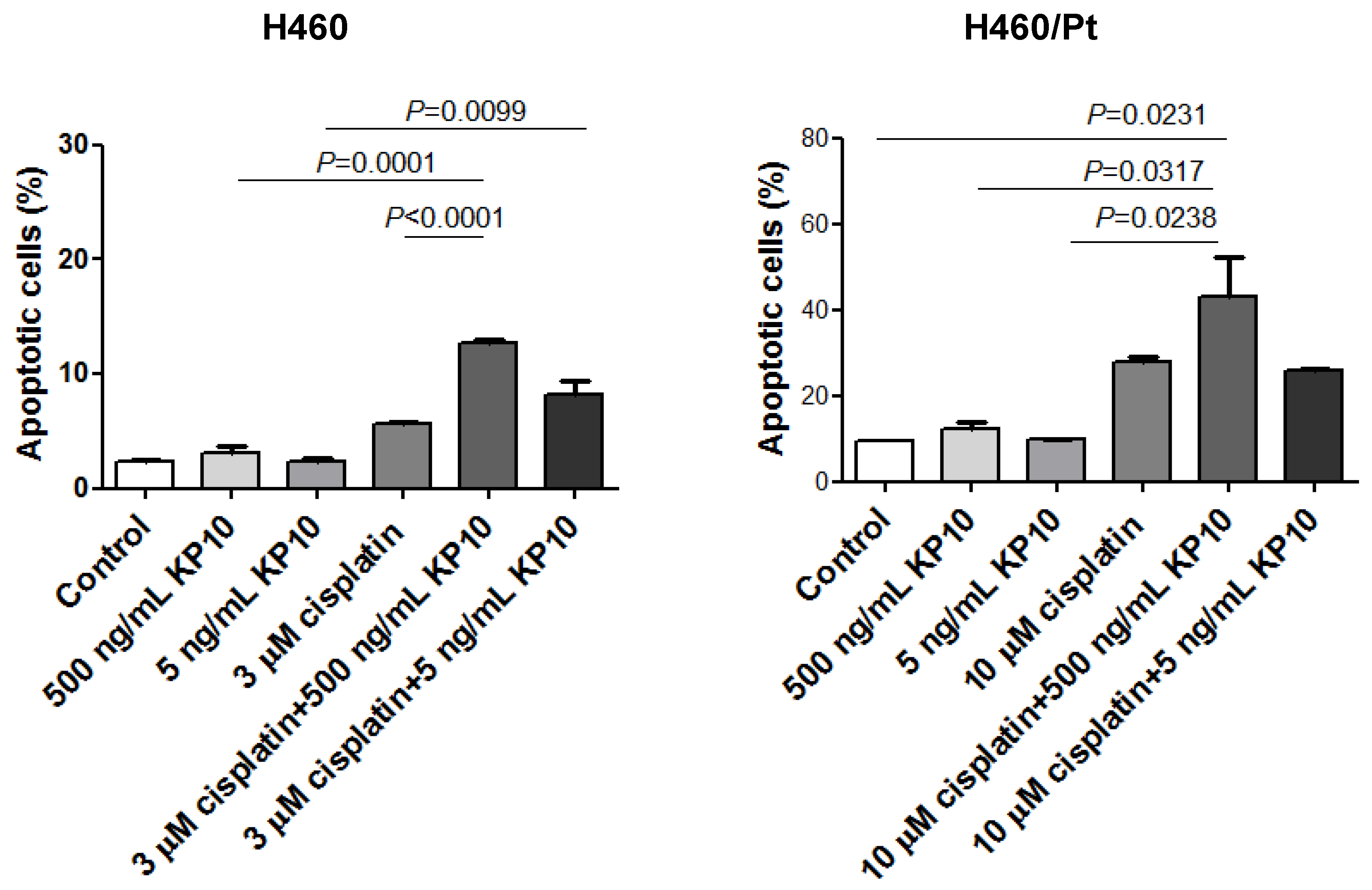
2.5. Effect of Exogenous KiSS-1 on Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis
2.6. Antitumor Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs, Cell Lines, Culture Conditions
4.2. Growth Inhibition Assay and Drug Interaction Studies
4.3. Western Blot Assays
4.4. Apoptosis Analysis
4.5. ELISA
4.6. Antitumor Activity Studies
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reungwetwattana, T.; Weroha, S.J.; Molina, J.R. Oncogenic pathways, molecularly targeted therapies, and highlighted clinical trials in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin. Lung Cancer 2012, 13, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Heymach, J.V.; Lippman, S.M. Lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westcott, P.M.; To, M.D. The genetics and biology of KRAS in lung cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2013, 32, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, W.A.; Lam, D.C.; O’Toole, S.A.; Minna, J.D. Molecular biology of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5 (Suppl. S5), S479–S490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, D.; Yuan, M.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Ma, W.; Xin, J. Prognostic value of K-RAS mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2013, 81, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fojo, T. Multiple paths to a drug resistance phenotype: Mutations, translocations, deletions and amplification of coding genes or promoter regions, epigenetic changes and microRNAs. Drug Resist. Updates 2007, 10, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zeng, J.; Huang, L.; Peng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, S.; et al. RNA adenosine modifications related to prognosis and immune infiltration in osteosarcoma. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Shen, F.; Long, D.; Yu, T.; Wu, M.; Lin, X. In vitro neutralization of autocrine IL-10 affects Op18/stathmin signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, P.M.; Brahmer, J.R.; Kelly, R.J. New strategies in lung cancer: Epigenetic therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2244–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topper, M.J.; Vaz, M.; Chiappinelli, K.B.; DeStefano Shields, C.E.; Niknafs, N.; Yen, R.C.; Wenzel, A.; Hicks, J.; Ballew, M.; Stone, M.; et al. Epigenetic Therapy Ties MYC Depletion to Reversing Immune Evasion and Treating Lung Cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 1284–1300.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajbouj, K.; Al-Ali, A.; Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Saber-Ayad, M.; Hamid, Q. Histone Modification in NSCLC: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulukuri, S.M.; Rao, J.S. Activation of p53/p21Waf1/Cip1 pathway by 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine inhibits cell proliferation, induces pro-apoptotic genes and mitogen-activated protein kinases in human prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 26, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaumik, S.R.; Smith, E.; Shilatifard, A. Covalent modifications of histones during development and disease pathogenesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenuwein, T.; Allis, C.D. Translating the histone code. Science 2001, 293, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damaskos, C.; Tomos, I.; Garmpis, N.; Karakatsani, A.; Dimitroulis, D.; Garmpi, A.; Spartalis, E.; Kampolis, C.F.; Tsagkari, E.; Loukeri, A.A.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as a Novel Targeted Therapy Against Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Where Are We Now and What Should We Expect? Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S.; Grant, S. Endogenous modulators and pharmacological inhibitors of histone deacetylases in cancer therapy. Oncogene 2012, 31, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Feng, F.; Wu, J.; Fan, S.; Han, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Xu, K. Demethylzeylasteral targets lactate by inhibiting histone lactylation to suppress the tumorigenicity of liver cancer stem cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 181, 106270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perego, P.; Zuco, V.; Gatti, L.; Zunino, F. Sensitization of tumor cells by targeting histone deacetylases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.S.; Kaye, S.B.; Brown, R. The promises and pitfalls of epigenetic therapies in solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuco, V.; Cassinelli, G.; Cossa, G.; Gatti, L.; Favini, E.; Tortoreto, M.; Cominetti, D.; Scanziani, E.; Castiglioni, V.; Cincinelli, R.; et al. Targeting the invasive phenotype of cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells by a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 94, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Seto, E. Deacetylation of nonhistone proteins by HDACs and the implications in cancer. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 206, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tredan, O.; Galmarini, C.M.; Patel, K.; Tannock, I.F. Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnyszka, A.; Jastrzebski, Z.; Flis, S. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors and their emerging role in epigenetic therapy of cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 2989–2996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pechalrieu, D.; Etievant, C.; Arimondo, P.B. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors in cancer: From pharmacology to translational studies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 129, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hascher, A.; Haase, A.K.; Hebestreit, K.; Rohde, C.; Klein, H.U.; Rius, M.; Jungen, D.; Witten, A.; Stoll, M.; Schulze, I.; et al. DNA methyltransferase inhibition reverses epigenetically embedded phenotypes in lung cancer preferentially affecting polycomb target genes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Füller, M.; Klein, M.; Schmidt, E.; Rohde, C.; Göllner, S.; Schulze, I.; Qianli, J.; Berdel, W.E.; Edemir, B.; Müller-Tidow, C.; et al. 5-azacytidine enhances efficacy of multiple chemotherapy drugs in AML and lung cancer with modulation of CpG methylation. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, S.J.; Kauffman, A.S. Emerging concepts on the epigenetic and transcriptional regulation of the Kiss1 gene. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2013, 31, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Miele, M.E.; Hicks, D.J.; Phillips, K.K.; Trent, J.M.; Weissman, B.E.; Welch, D.R. KiSS-1, a novel human malignant melanoma metastasis-suppressor gene. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1996, 88, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, S.; Brackstone, M.; Radovick, S.; Babwah, A.V.; Bhattacharya, M.M. KISS1/KISS1R in Cancer: Friend or Foe? Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, K.T.; Phadke, P.A.; Navenot, J.M.; Hurst, D.R.; Accavitti-Loper, M.A.; Sztul, E.; Vaidya, K.S.; Frost, A.R.; Kappes, J.C.; Peiper, S.C.; et al. Requirement of KISS1 secretion for multiple organ metastasis suppression and maintenance of tumor dormancy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, S.; Tang, X.Y.; Umemura, S.; Itoh, J.; Takekoshi, S.; Shima, M.; Usui, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Uchida, T.; Osamura, R.Y.; et al. Metastin inhibits migration and invasion of renal cell carcinoma with overexpression of metastin receptor. Eur. Urol. 2009, 55, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, M.; Kokuryo, T.; Yokoyama, Y.; Senga, T.; Nagino, M. α-Bisabolol Inhibits Invasiveness and Motility in Pancreatic Cancer Through KISS1R Activation. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.N.; Kim, T.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Cho, S.G. Kisspeptin Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Invasiveness by Activating PKR and PP2A. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 5791–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciaramella, V.; Della Corte, C.M.; Ciardiello, F.; Morgillo, F. Kisspeptin and Cancer: Molecular Interaction, Biological Functions, and Future Perspectives. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratangelo, F.; Carriero, M.V.; Motti, M.L. Controversial Role of Kisspeptins/KiSS-1R Signaling System in Tumor Development. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossa, G.; Gatti, L.; Cassinelli, G.; Lanzi, C.; Zaffaroni, N.; Perego, P. Modulation of sensitivity to antitumor agents by targeting the MAPK survival pathway. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzetti, C.; Corno, C.; Vergani, E.; Mirra, L.; Ciusani, E.; Rodolfo, M.; Perego, P.; Beretta, G.L. Kisspeptin-mediated improvement of sensitivity to BRAF inhibitors in vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cells. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1182853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, L.; Rolli, L.; Corno, C.; Carenini, N.; Corna, E.; Ciusani, E.; Frigerio, S.; Pogliani, S.; Guarino, C.; Ravagnani, F.; et al. Increased serum levels of KiSS1-derived peptides in non-small cell lung cancer patient liquid biopsies and biological relevance. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiffar, T.; Yilmaz, T.; Lee, J.; Hanna, E.; El-Naggar, A.; Yu, D.; Myers, J.N.; Kupferman, M.E. KiSS1 mediates platinum sensitivity and metastasis suppression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3163–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, F.; Long, D.; Yu, T.; Lin, X. Introduction of exogenous wild-type p53 mediates the regulation of oncoprotein 18/stathmin signaling via nuclear factor-kappaB in non-small cell lung cancer NCI-H1299 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebrian, V.; Fierro, M.; Orenes-Piñero, E.; Grau, L.; Moya, P.; Ecke, T.; Alvarez, M.; Gil, M.; Algaba, F.; Bellmunt, J.; et al. KISS1 methylation and expression as tumor stratification biomarkers and clinical outcome prognosticators for bladder cancer patients. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, L.; Cossa, G.; Tinelli, S.; Carenini, N.; Arrighetti, N.; Pennati, M.; Cominetti, D.; De Cesare, M.; Zunino, F.; Zaffaroni, N.; et al. Improved apoptotic cell death in drug-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer cells by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-based treatment. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 348, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Cell Line | Cisplatin (µM, 1 h) | RI | Cisplatin (µM, 72 h) | RI | SAHA (µM, 72 h) | R | AZA (µM, 72 h) | RI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H460 | 15.46 ± 5.0 | 1.02 ± 0.4 | 1.36 ± 0.5 | 0.50 ± 0.1 | ||||
| H460/Pt | 49.4 ± 11.0 | 3 | 2.4 ± 0.9 | 2.4 | 1.07 ± 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.85 ± 0.1 | 1.7 |
| Cisplatin | 0.1 µM | 0.3 µM | 1 µM | 3 µM | 10 µM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAHA | |||||
| 0.3 µM | - | 1.32 ± 0.6 | 1.15 ± 0.4 | 0.67 ± 0.1 | 1.44 ± 0.1 |
| 1 µM | - | 1.52 ± 0.5 | 0.68 ± 0.1 | 0.56 ± 0.1 | 1.56 ± 0.3 |
| 3 µM | - | 0.71 ± 0.2 | 0.58 ± 0.1 | 0.82 ± 0.1 | 1.46 ± 0.6 |
| AZA | |||||
| 0.3 µM | 0.98 ± 083 | 1.02 ± 0.43 | 0.49 ± 0.10 | 0.44 ± 0.03 | 0.51 ± 0.13 |
| 1 µM | 0.79 ± 0.50 | 0.58 ± 0.38 | 0.38 ± 0.16 | 0.39 ± 0.06 | 0.91 ± 0.09 |
| Cisplatin | 0.1 µM | 0.3 µM | 1 µM | 3 µM | 10 µM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAHA | |||||
| 0.3 µM | - | 0.98 ± 0.1 | 1.44 ± 0.6 | 0.81 ± 0.3 | 1.06 ± 0.1 |
| 1 µM | - | 1.41 ± 0.7 | 1.27 ± 0.8 | 0.56 ± 0.1 | 0.83 ± 0.1 |
| 3 µM | - | 0.65 ± 0.3 | 0.63 ± 0.3 | 0.63 ± 0.3 | 0.82 ± 0.4 |
| AZA | |||||
| 0.3 µM | 0.83 ± 0.13 | 0.83 ± 0.07 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.07 |
| 1 µM | 0.71 ± 0.03 | 0.49 ± 0.09 | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 0.25 ± 0.07 | 0.27 ± 0.05 |
| Cisplatin | 0.1 µM | 0.3 µM | 1 µM | 3 µM | 10 µM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAHA | |||||
| 0.3 µM | - | 1.42 ± 0.5 | 2.34 ± 0.9 | 1.42 ± 0.3 | 1.33 ± 0.2 |
| 1 µM | - | 1.39 ± 0.4 | 1.31 ± 0.1 | 1.37 ± 0.7 | 1.42 ± 0.2 |
| 3 µM | - | 1.45 ± 0.2 | 1.24 ± 0.3 | 1.07 ± 0.2 | 1.39 ± 0.2 |
| AZA | |||||
| 0.3 µM | 1.11 ± 0.5 | 1.48 ± 1.1 | 0.97 ± 0.2 | 0.46 ± 0.1 | 0.42 ± 0.2 |
| 1 µM | 1.06 ± 0.1 | 0.96 ± 0.3 | 0.64 ± 0.1 | 0.23 ± 0.1 | 0.58 ± 0.2 |
| Cisplatin | 0.1 µM | 0.3 µM | 1 µM | 3 µM | 10 µM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAHA | |||||
| 0.3 µM | - | 4.56 ± 4.2 | 2.18 ± 0.6 | 1.01 ± 0.1 | 1.15 ± 0.5 |
| 1 µM | - | 2.67 ± 2.1 | 2.03 ± 0.9 | 1.02 ± 0.5 | 0.81 ± 0.2 |
| 3 µM | - | 1.79 ± 0.7 | 1.16 ± 0.2 | 0.92 ± 0.1 | 0.94 ± 0.1 |
| AZA | |||||
| 0.3 µM | 1.06 ± 0.3 | 1.62 ± 1.7 | 0.64 ± 0.3 | 0.30 ± 0.1 | 0.27 ± 0.1 |
| 1 µM | 0.65 ± 0.1 | 0.59 ± 0.1 | 0.32 ± 0.1 | 0.28 ± 0.1 | 0.16 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beretta, G.L.; Alampi, D.; Corno, C.; Carenini, N.; Corna, E.; Perego, P. KiSS-1 Modulation by Epigenetic Agents Improves the Cisplatin Sensitivity of Lung Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25095048
Beretta GL, Alampi D, Corno C, Carenini N, Corna E, Perego P. KiSS-1 Modulation by Epigenetic Agents Improves the Cisplatin Sensitivity of Lung Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(9):5048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25095048
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeretta, Giovanni Luca, Desirè Alampi, Cristina Corno, Nives Carenini, Elisabetta Corna, and Paola Perego. 2024. "KiSS-1 Modulation by Epigenetic Agents Improves the Cisplatin Sensitivity of Lung Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 9: 5048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25095048
APA StyleBeretta, G. L., Alampi, D., Corno, C., Carenini, N., Corna, E., & Perego, P. (2024). KiSS-1 Modulation by Epigenetic Agents Improves the Cisplatin Sensitivity of Lung Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(9), 5048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25095048






