4-Alkyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline Derivatives as New Heterocyclic Analogues of Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines: Synthesis and Antitubercular Activity
Abstract
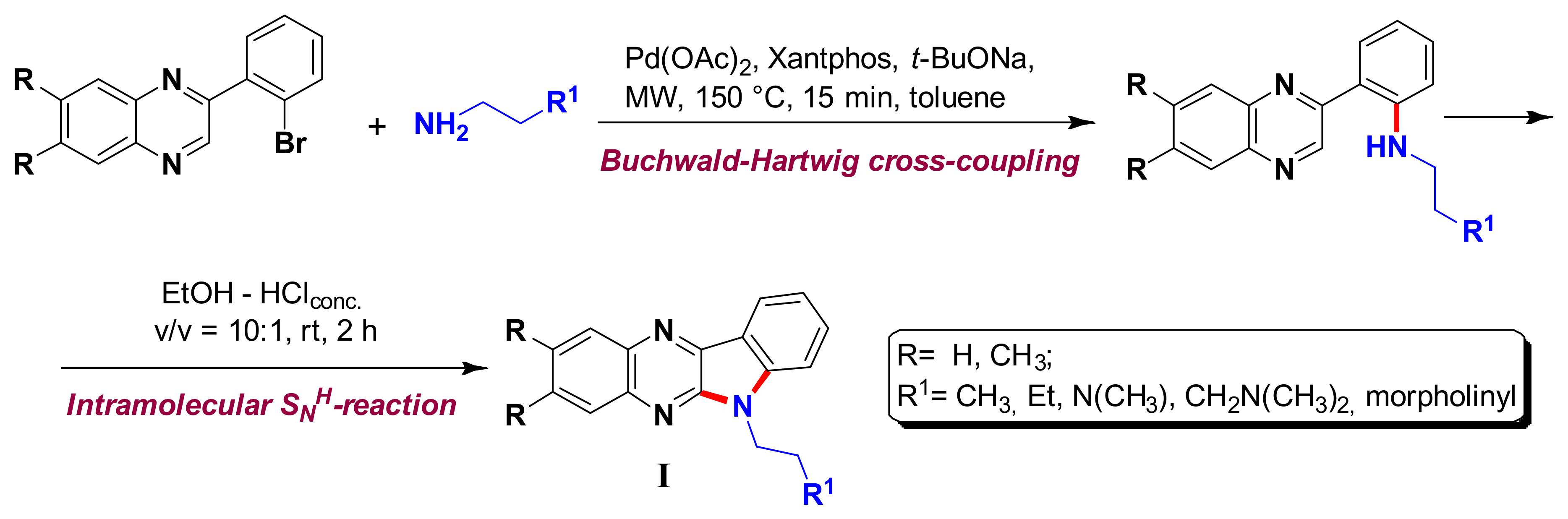
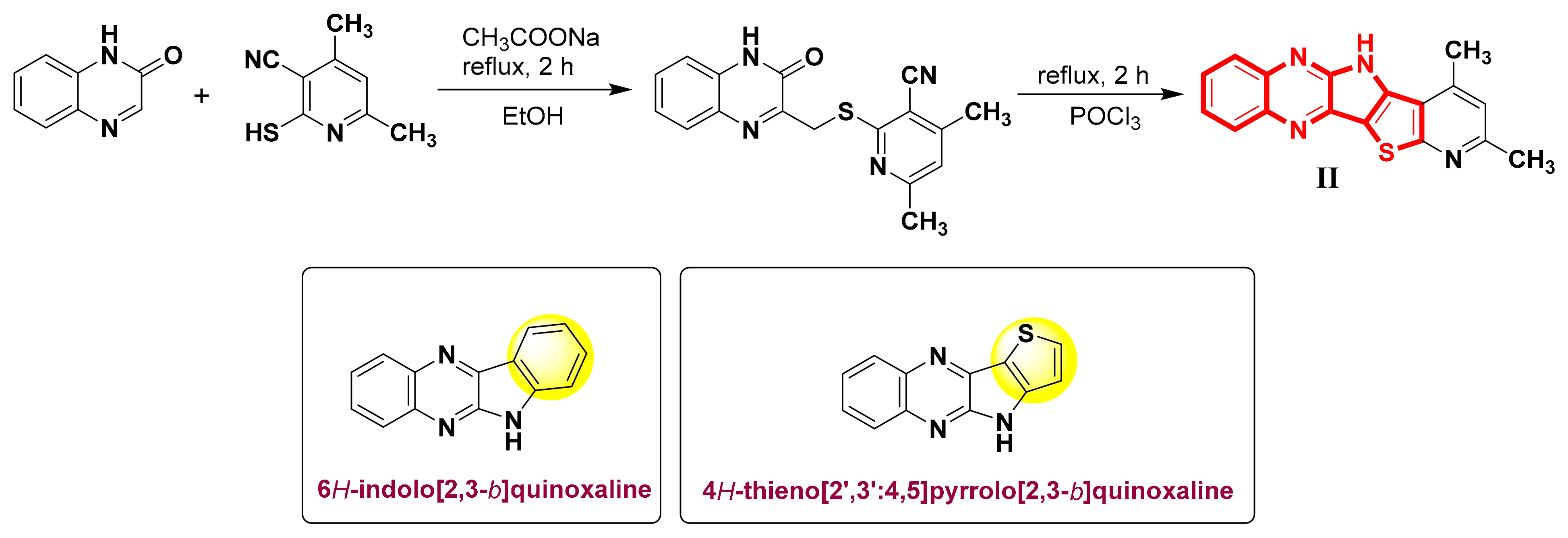
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
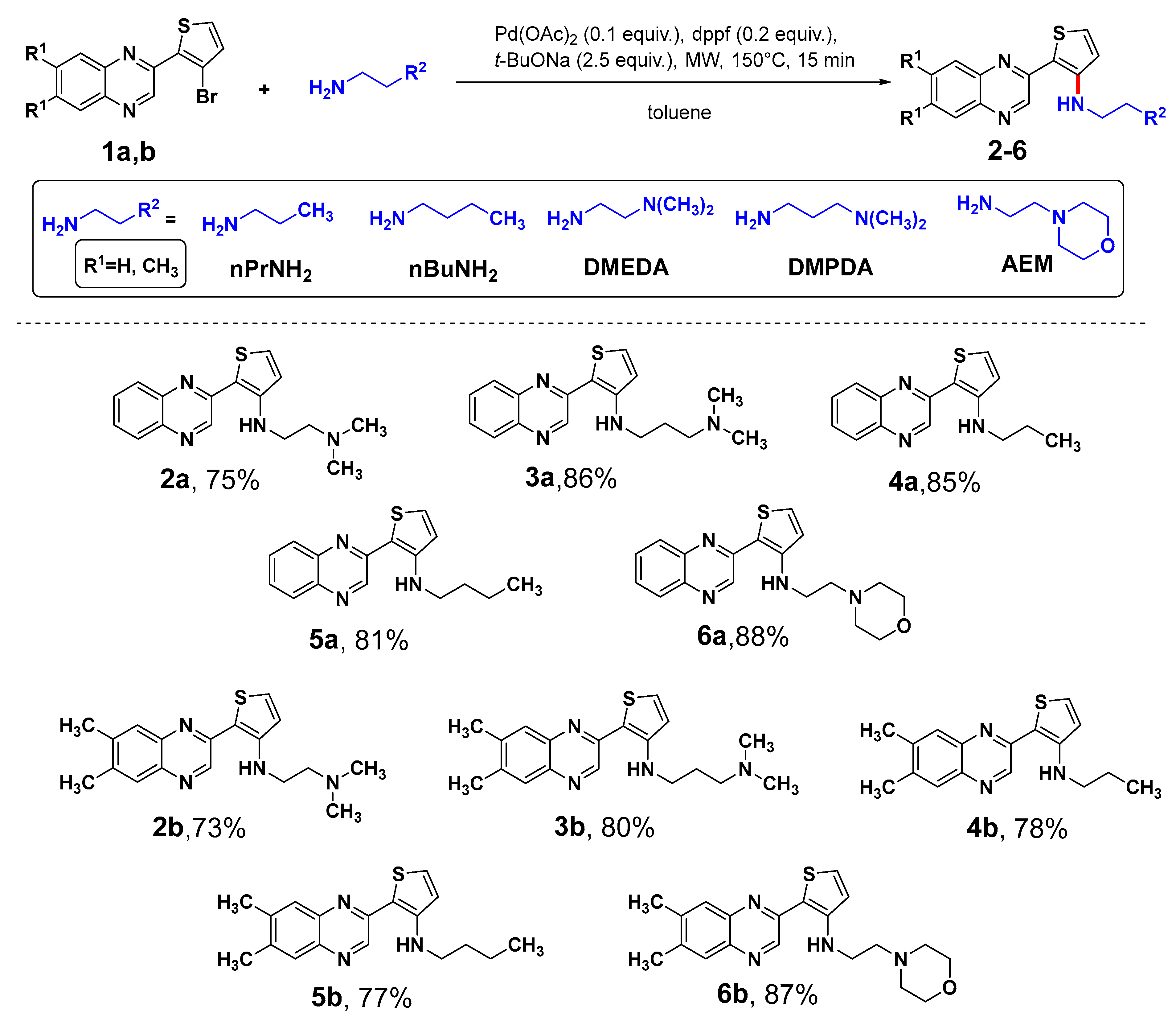
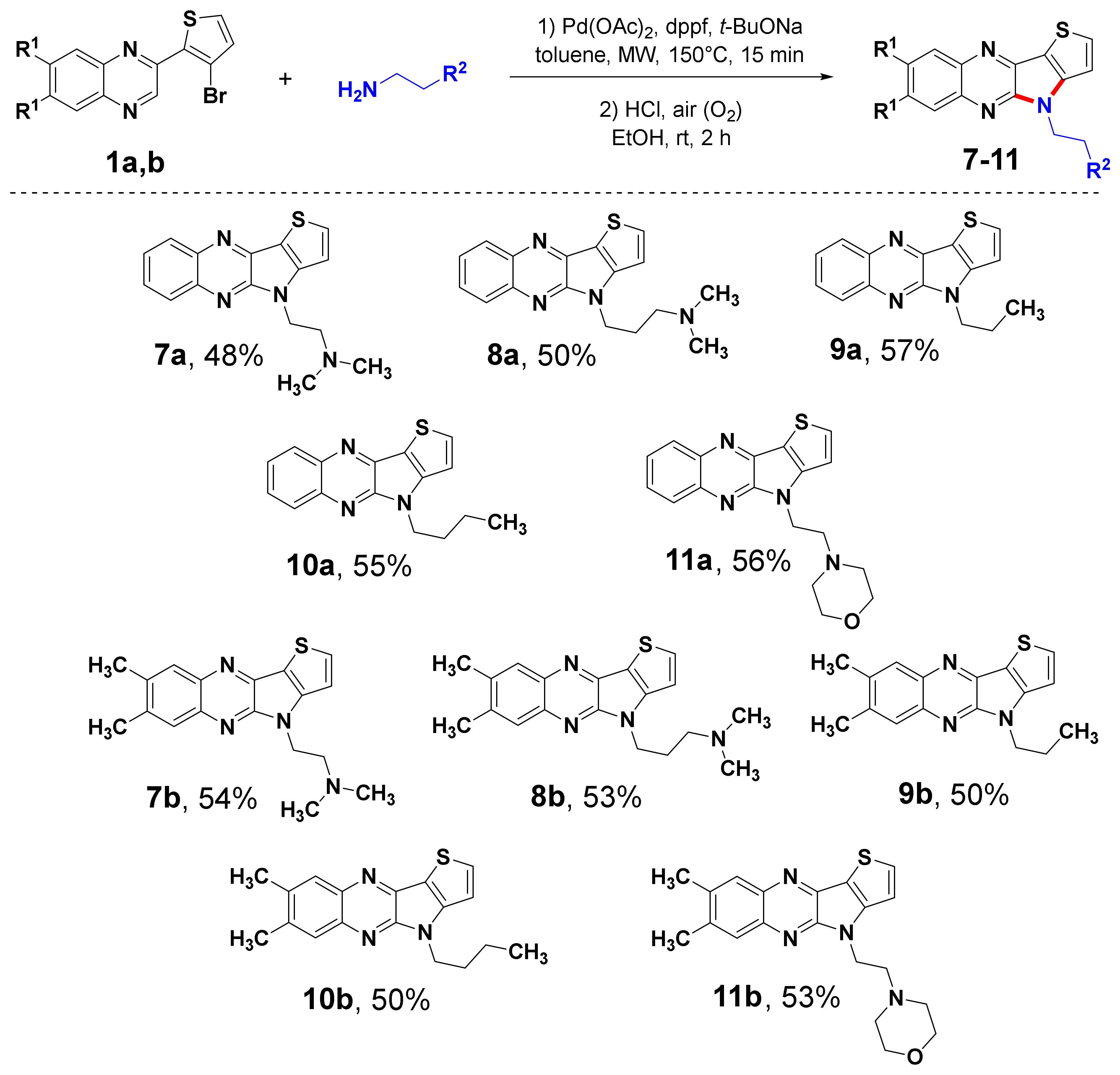
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Antimycobacterial Activity
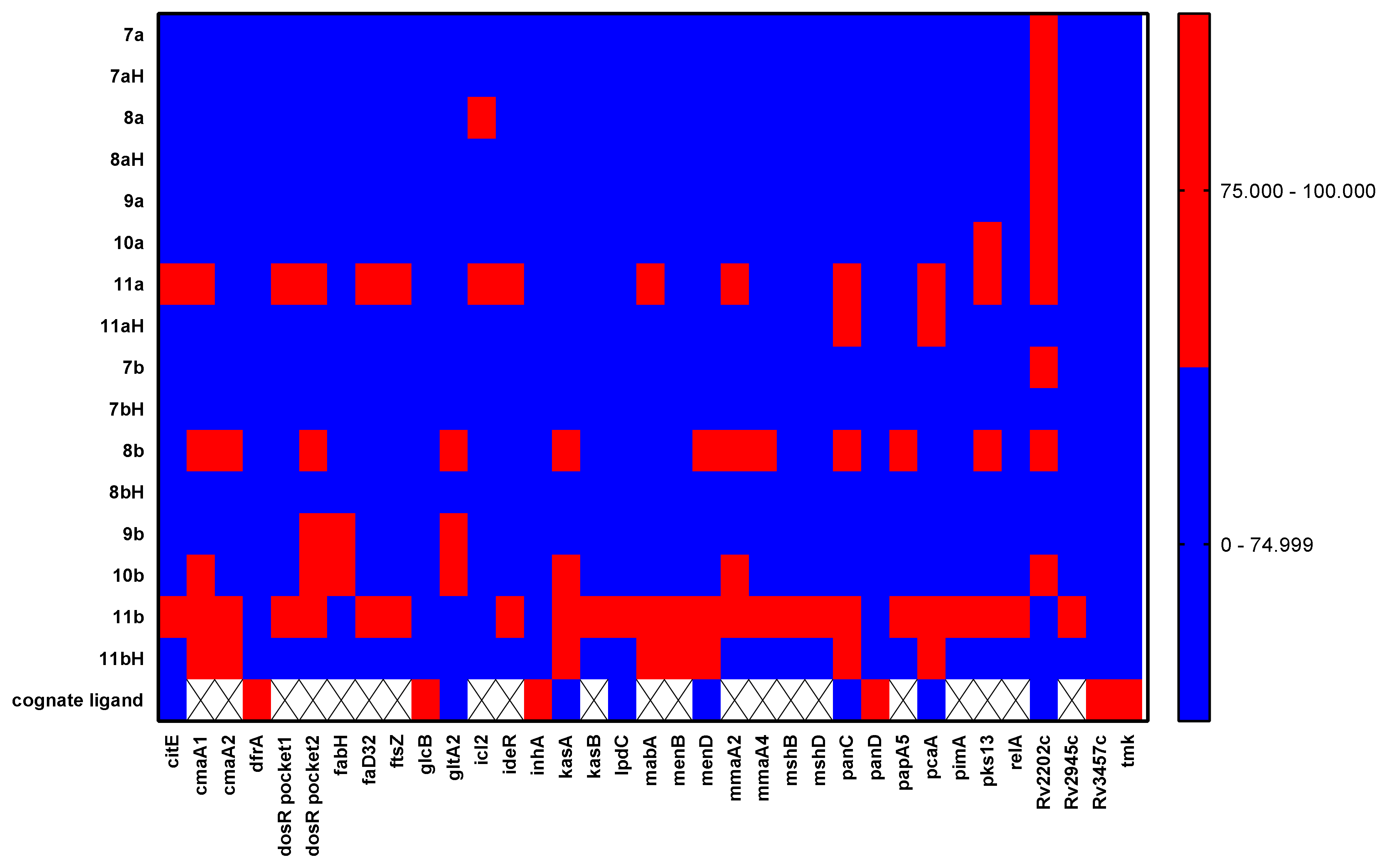
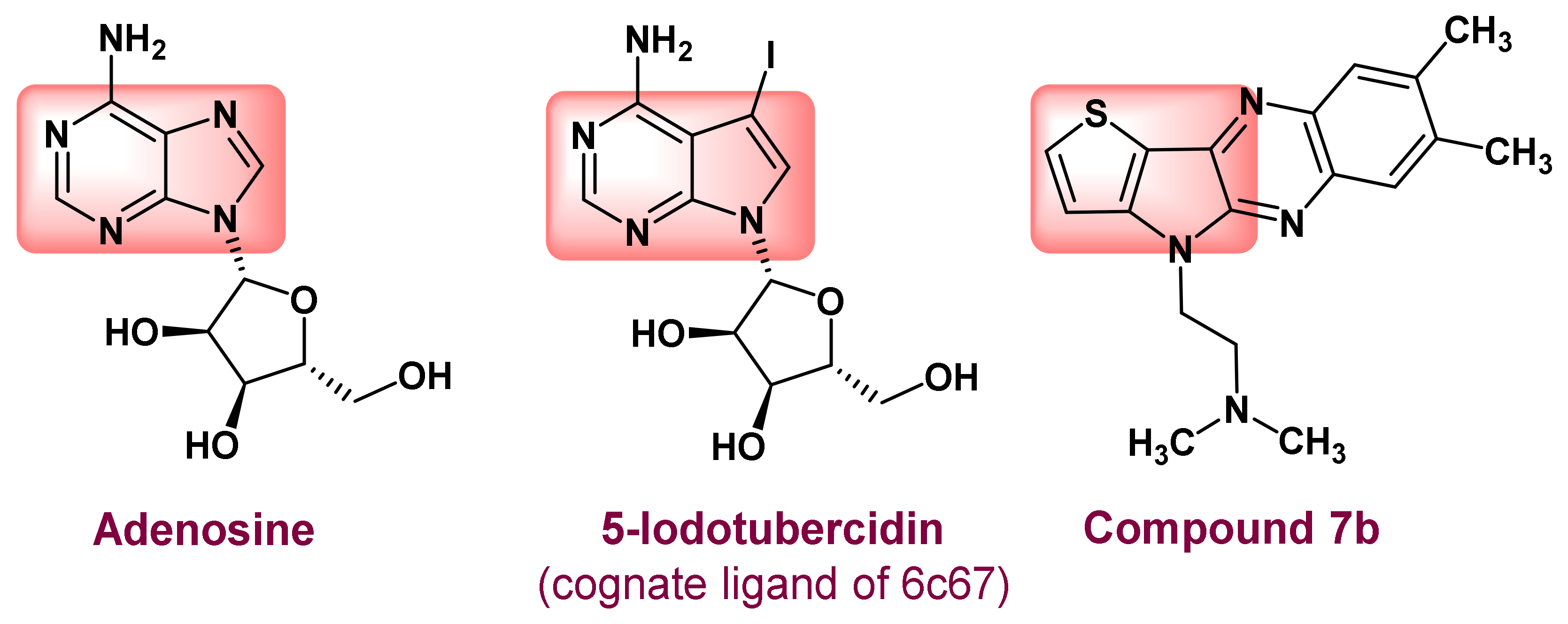
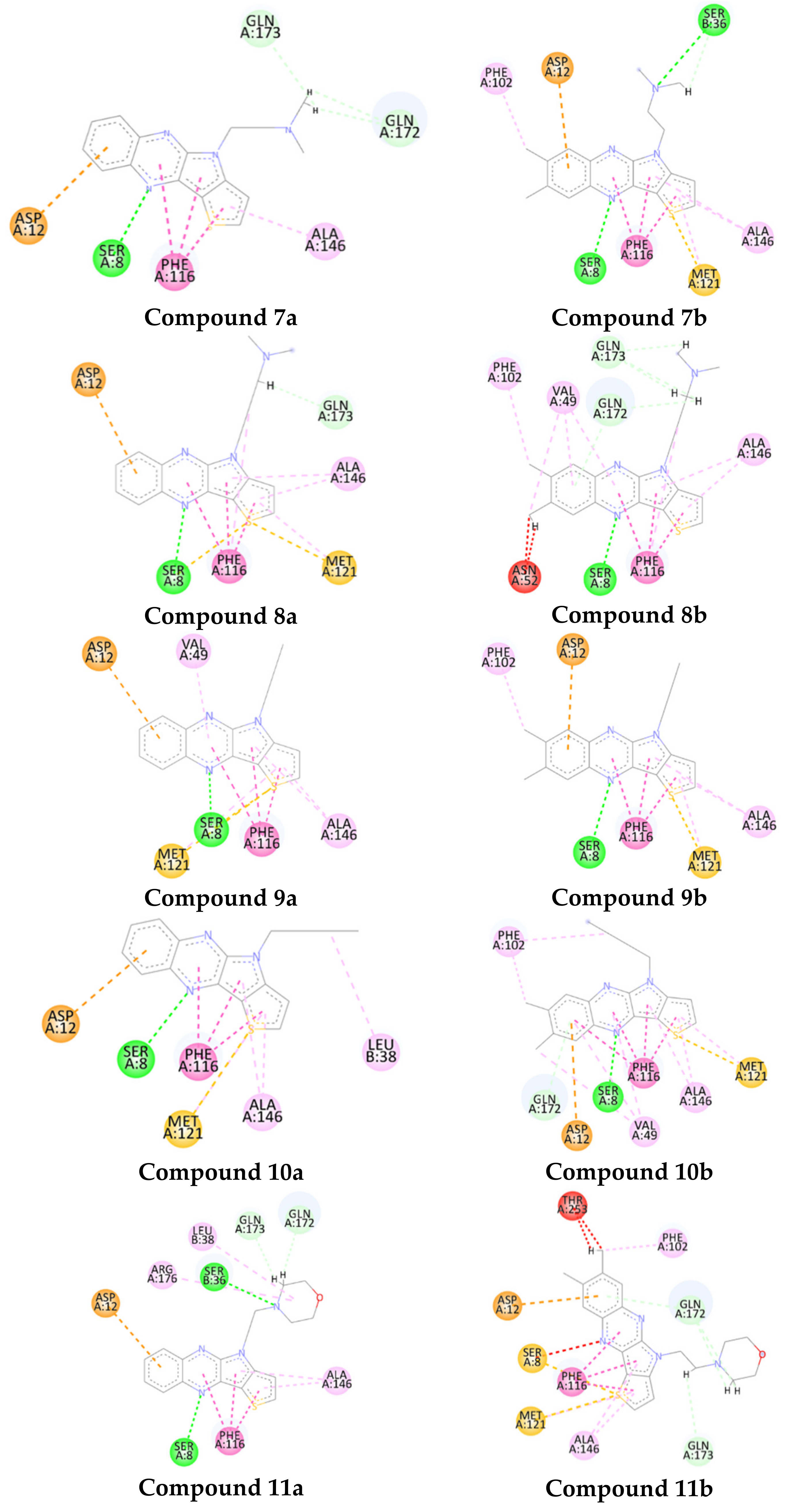
2.3. Molecular Docking of Antitubercular Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.1.1. Synthesis of 2-(3-Bromothiophen-2-yl)-6,7-dimethylquinoxaline (1b)
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of N-Alkyl-2-(quinoxaline-2-yl)thiophen-3-amines (2a–6a) and N-Alkyl-2-(6,7-dimethylquinoxalin-2-yl)thiophen-3-amines (2b–6b)
3.1.3. N1,N1-Dimethyl-N2-(2-(quinoxalin-2-yl)thiophen-3-yl)ethane-1,2-diamine (2a)
3.1.4. N1,N1-Dimethyl-N3-(2-(quinoxalin-2-yl)thiophen-3-yl)propane-1,3-diamine (3a)
3.1.5. N-Propyl-2-(quinoxalin-2-yl)thiophen-3-amine (4a)
3.1.6. N-Butyl-2-(quinoxalin-2-yl)thiophen-3-amine (5a)
3.1.7. N-(2-Morpholinoethyl)-2-(quinoxalin-2-yl)thiophen-3-amine (6a)
3.1.8. N1-(2-(6,7-Dimethylquinoxalin-2-yl)thiophen-3-yl)-N2,N2-dimethylethane-1,2-diamine (2b)
3.1.9. N1-(2-(6,7-Dimethylquinoxalin-2-yl)thiophen-3-yl)-N3,N3-dimethylpropane-1,3-diamine (3b)
3.1.10. 2-(6,7-Dimethylquinoxalin-2-yl)-N-propylthiophen-3-amine (4b)
3.1.11. N-Butyl-2-(6,7-dimethylquinoxalin-2-yl)thiophen-3-amine (5b)
3.1.12. 2-(6,7-Dimethylquinoxalin-2-yl)-N-(2-morpholinoethyl)thiophen-3-amine (6b)
3.1.13. General Procedure for Syntheses of 4-Alkyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline Derivatives (7–11)
3.1.14. N,N-Dimethyl-2-(4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-4-yl)ethan-1-amine (7a)
3.1.15. N,N-Dimethyl-3-(4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-4-yl)propan-1-amine (8a)
3.1.16. 4-Propyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline (9a)
3.1.17. 4-Butyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline (10a)
3.1.18. 4-(2-(4H-Thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-4-yl)ethyl)morpholine (11a)
3.1.19. 2-(7,8-Dimethyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-4-yl)-N,N-dimethylethan-1-amine (7b)
3.1.20. 3-(7,8-Dimethyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-4-yl)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine (8b)
3.1.21. 7,8-Dimethyl-4-propyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline (9b)
3.1.22. 4-Butyl-7,8-dimethyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline (10b)
3.1.23. 4-(2-(7,8-Dimethyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-4-yl)ethyl)morpholine (11b)
3.2. Evaluation of Antimycobacterial Activity and Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moorthy, N.S.H.N.; Manivannan, E.; Karthikeyan, C.; Trivedi, P. 6H-Indolo[2,3-b]Quinoxalines: DNA and Proteins Interacting Scaffold for Pharmacological Activities. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimenko, K.; Lyakhov, S.; Shibinskaya, M.; Karpenko, A.; Marcou, G.; Horvath, D.; Zenkova, M.; Goncharova, E.; Amirkhanov, R.; Krysko, A.; et al. Virtual screening, synthesis and biological evaluation of DNA intercalating antiviral agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3915–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avula, S.; Komsani, J.R.; Koppireddi, S.; Yadla, R.; Kanugula, A.K.R.; Kotamraju, S. Synthesis and cytotoxicity of novel 6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 3712–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, S.; Zhou, G.; Ding, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, C. Synthesis, cytotoxic evaluation and DNA binding study of 9-fluoro-6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline derivatives. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41869–41879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Santiago, M.; Santiago, Á.; Pastor, N.; Alvarez, L.; Razo-Hernández, R.S. Isatin derivatives as DNA minor groove-binding agents: A structural and theoretical study. Struct. Chem. 2020, 31, 1289–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Malah, T.; El-Rashedy, A.A.; Hegab, M.I.; Awad, H.M.; Shamroukh, A.H. Click synthesis of novel 6-((1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines for in vitro anticancer evaluation and docking studies. New J. Chem. 2024, 48, 11064–11078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Malah, T.; El-Mageid, E.-S.A.; Shamroukh, A.H.; Rashad, A.E.; El-Rashedy, A.A.; Awad, H.M.; Abdel-Megeid, F.M.E.; Hegab, M.I. Click synthesis, anticancer and molecular docking evaluation of some hexahydro-6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines incorporated triazole moiety. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1303, 137573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, S.; Raza, A.; Seboletswe, P.; Cele, N.; Sharma, A.K.; Singh, P.; Kumar, V. Cu-promoted synthesis of Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline-Mannich adducts via three-component reaction and their anti-proliferative evaluation on colorectal and ovarian cancer cells. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1275, 134627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibinskaya, M.O.; Lyakhov, S.A.; Mazepa, A.V.; Andronati, S.A.; Turov, A.V.; Zholobak, N.M.; Spivak, N.Y. Synthesis, cytotoxicity, antiviral activity and interferon inducing ability of 6-(2-aminoethyl)-6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunjiappan, S.; Theivendren, P.; Pavadai, P.; Govindaraj, S.; Sankaranarayanan, M.; Somasundaram, B.; Arunachalam, S.; Pandian, S.R.K.; Ammunje, D.N. Design and in silico modeling of Indoloquinoxaline incorporated keratin nanoparticles for modulation of glucose metabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biotechnol. Prog. 2020, 36, e2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhed, A.M.; Patel, D.V.; Patel, N.R.; Sinha, A.; Thakor, P.S.; Patel, K.B.; Prajapati, N.K.; Patel, K.V.; Yadav, M.R. Indoloquinoxaline derivatives as promising multi-functional anti-Alzheimer agents. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 40, 2498–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Zhao, Q.; Ling, H.; Li, J.; Lin, J.; Xie, L.; Lin, Z.; Yi, M.; et al. Synthesis, characterization and charge storage properties of π-biindolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline for solution processing organic transistor memory. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 167, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Badani, P.M.; Kamble, R.M. Impact of the donor substituent on the optoelectrochemical properties of 6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline amine derivatives. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 19379–19396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K.; Shaikh, A.M.; Chacko, A.; Kamble, R.M. Synthesis, Spectral, Electrochemical and Theoretical Investigation of indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline dyes derived from Anthraquinone for n–type materials. J. Chem. Sci. 2017, 129, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Shirgaonkar, A.J.; Chawathe, B.K.; Kamble, R.M. Opto-electrochemistry of pyridopyrazino[2,3-b]indole Derivatives. J. Chem. Sci. 2020, 132, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Ghadiyali, M.; Chacko, S.; Kamble, R.M. D–A–D based pyrido-pyrazino[2,3-b]indole amines as blue-red fluorescent dyes: Photophysical, aggregation-induced emission, electrochemical and theoretical studies. J. Lumin. 2022, 242, 118568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswararao, A.; Tyagi, P.; Thomas, K.R.J.; Chen, P.-W.; Ho, K.-C. Organic dyes containing indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline as a donor: Synthesis, optical and photovoltaic properties. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 6318–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Fang, D.; Li, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Jin, L.; Xie, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; et al. C–H Direct Arylated 6H-Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline Derivative as Thickness-Dependent Hole Injection Layer. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Walser-Kuntz, R.; Tracy, J.S.; Schramm, T.K.; Shee, J.; Head-Gordon, M.; Chen, G.; Helms, B.A.; Sanford, M.S.; Toste, F.D. Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline as a Low Reduction Potential and High Stability Anolyte Scaffold for Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 18877–18887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Ashraf, S.; Lyu, L.; El-Shafei, A. Tailoring dual-channel anchorable organic sensitizers with indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline moieties: Correlation between structure and DSSC performance. Sol. Energy 2020, 206, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Gao, H.-H.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Lu, L.; Zheng, J.-Y. 6H-Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline-based organic dyes containing different electron-rich conjugated linkers for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 280, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandhare, R.J.; Badani, P.M.; Kamble, R.M. Synthesis of D–A based violet–red light emitting indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-2-yl(phenyl)methanone amine dyes: Opto-electrochemical, AIE, and theoretical properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1298, 137080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, M.; Bhattacharjee, B.; Ramesh, A.; Das, G. Self-assembled quinoxaline derivative: Insight into disaggregation induced selective detection of nitro-aromatics in aqueous medium and live cell imaging. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 196, 109779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Basak, M.; Deka, D.; Das, G. Fabrication and photophysical assessment of quinoxaline based chemosensor: Selective determination of picric acid in hydrogel and aqueous medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 363, 119816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadykhov, G.A.o.; Verbitskiy, E.V. Modern methods for the synthesis of indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines (microreview). Chem. Heterocycl. Comp. 2022, 58, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, S.V.; Singh, B.; Pradeepa, N.; Peruncheralathan, S. PIFA-mediated intramolecular N-arylation of 2-aminoquinoxalines to afford indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline derivatives. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 5803–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.M.; Ansari, G.M.; Karbari, Z.Z.; Babre, A.A.; Borge, V.V.; Bangade, V.M.; Kommi, D.N.; Popatkar, B.B. [EMIM]AlCl4-ionic liquid catalyzed mechanochemically assisted green approach towards the synthesis of quinoxaline, 6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline and benzimidazole derivatives. Results Chem. 2024, 12, 101884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandia, A.; Parewa, V.; Maheshwari, S.; Rathore, K.S. Cu doped CdS nanoparticles: A versatile and recoverable catalyst for chemoselective synthesis of indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline derivatives under microwave irradiation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 394, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadykhov, G.A.; Belyaev, D.V.; Vakhrusheva, D.V.; Eremeeva, N.I.; Khramtsova, E.E.; Pervova, M.G.; Rusinov, G.L.; Verbitskiy, E.V.; Chupakhin, O.N.; Charushin, V.N. New Approach to Biologically Active Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline Derivatives through Intramolecular Oxidative Cyclodehydrogenation. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202200497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charushin, V.N.; Varaksin, M.V.; Verbitskiy, E.V.; Chupakhin, O.N. Metal free C(sp2)–H functionalization of nitrogen heterocycles. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 2024, 144, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charushin, V.N.; Verbitskiy, E.V.; Chupakhin, O.N.; Vorobyeva, D.V.; Gribanov, P.S.; Osipov, S.N.; Ivanov, A.V.; Martynovskaya, S.V.; Sagitova, E.F.; Dyachenko, V.D.; et al. The chemistry of heterocycles in the 21st century. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2024, 93, RCR5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasov, A.A.; Fedorova, O.V.; Rasputin, N.A.; Ovchinnikova, I.G.; Ishmetova, R.I.; Ignatenko, N.K.; Gorbunov, E.B.; Sadykhov, G.A.o.; Kucheryavenko, A.F.; Gaidukova, K.A.; et al. Novel Substituted Azoloazines with Anticoagulant Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Dean, A.M.K. Synthesis of new pyridyl quinoxalinemethyl sulfides. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1995, 105, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino, J.-C.; Martin, A.; Camacho, M.; Guerra, H.; Swings, J.; Portaels, F. Resazurin Microtiter Assay Plate: Simple and Inexpensive Method for Detection of Drug Resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2720–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, N.K.; Tyagi, J.S. Resazurin reduction assays for screening of anti-tubercular compounds against dormant and actively growing Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium bovis BCG and Mycobacterium smegmatis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpeleva, T.; Chetverikova, E.; Belyaev, D.; Eremeeva, N.; Boteva, T.; Golubeva, L.; Vakhrusheva, D.; Vasilieva, I. Identification of genetic determinants of bedaquiline resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Ural region, Russia. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e03749-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, E.E.; Balandina, S.Y.; Drobkova, V.A.; Dmitriev, M.V.; Mashevskaya, I.V.; Maslivets, A.N. Synthesis, in vitro antibacterial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, reverse docking-based target fishing of 1,4-benzoxazin-2-one derivatives. Arch. Pharm. 2021, 354, E2000199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomioka, H.; Tatano, Y.; Yasumoto, K.; Shimizu, T. Recent advances in antituberculous drug development and novel drug targets. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2008, 2, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, R.A.; Dang, Q.; Zhou, N.E.; Guthrie, L.M.; Snavely, T.C.; Dong, W.; Loesch, K.A.; Suzuki, T.; You, L.; Wang, W.; et al. Structure-Guided Drug Design of 6-Substituted Adenosine Analogues as Potent Inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Adenosine Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4483–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boison, D. Adenosine kinase: Exploitation for therapeutic gain. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 906–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvashnin, Y.A.; Verbitskiy, E.V.; Zhilina, E.F.; Rusinov, G.L.; Chupakhin, O.N.; Charushin, V.N. Synthesis of Heteroannulated Indolopyrazines through Domino N–H Palladium-Catalyzed/Metal-Free Oxidative C–H Bond Activation. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 15681–15690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| № | Pd Catalyst (0.1 Equiv.) | Ligand (0.2 Equiv.) | Base (2.5 Equiv.) | Solvent | Reaction Time, Temperature | Reaction Mixtures a GC–MS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pd(OAc)2 | Xantphos | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—91 1a—0 2-ThioQx—9 |
| 2 | Pd(OAc)2 | PCy3 | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—0 1a—0 2-ThioQx—100 |
| 3 | Pd(PPh3)4 | - | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—0 1a—0 2-ThioQx—100 |
| 4 | Pd(OAc)2 | PPh3 | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—0 1a—0 2-ThioQx—100 |
| 5 | Pd(OAc)2 | DPEPhos | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—4 1a—90 2-ThioQx—2 |
| 6 | Pd(OAc) | BrettPhos | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—2.4 1a—94.4 2-ThioQx—3.2 |
| 7 | Pd(OAc)2 | P(o-Tol)3 | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—2.7 1a—86.5 2-ThioQx—10.8 |
| 8 | Pd(OAc)2 | XPhos | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—3.4 1a—82.5 2-ThioQx—14.1 |
| 9 | Pd(dba)2 | - | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—7.7 1a—72.0 2-ThioQx—20.3 |
| 10 | Pd2(dba)3 | - | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—9.8 1a—52.3 2-ThioQx—37.9 |
| 11 | Pd(OAc)2 | rac-BINAP | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—90.3 1a—0 2-ThioQx—9.3 |
| 12 | Pd(OAc)2 | dppf | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—94,4 1a—0 2-ThioQx—5.6 |
| 13 | Pd(OAc)2 | dppf | KF | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—0 1a—98,3 2-ThioQx—1.7 |
| 14 | Pd(OAc)2 | dppf | K2CO3 | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—0 1a—100 2-ThioQx—0 |
| 15 | Pd(OAc)2 | dppf | DABCO | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—0 1a—89.3 2-ThioQx—10.7 |
| 16 | Pd(OAc)2 | dppf | K3PO4 | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—8.7 1a—91.3 2-ThioQx—0 |
| 17 | Pd(OAc)2 | dppf | t-BuOK | toluene | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—40.9 1a—0 2-ThioQx—59.1 |
| 18 | Pd(OAc)2 | dppf | t-BuONa | dioxane | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—80.3 1a—0 2-ThioQx—19.7 |
| 19 | Pd(OAc)2 | dppf | t-BuONa | THF | 15 min, 150 °C | 2a—81.7 1a—0 2-ThioQx—18.3 |
| 20 | Pd(OAc)2 | dppf | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 120 °C | 2a—94.9 1a—0 2-ThioQx—5.1 |
| 21 | Pd(OAc)2 | dppf | t-BuONa | toluene | 15 min, 100 °C | 2a—90.6 1a—6.2 2-ThioQx—3.2 |
| Entry | Compound | Antimycobacterial Activity Against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (MIC) a | IC50 (μg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg/mL | μM | |||
| 1 | 7a | 25 | 84.35 | n.d |
| 2 | 8a | >25 | >80.54 | n.d. |
| 3 | 9a | 25 | 93.51 | n.d. |
| 4 | 10a | >25 | >88.85 | n.d. |
| 5 | 11a | >25 | 73.87 | n.d. |
| 6 | 7b | 12.5 | 38.53 | 11.8 ± 1.4 |
| 7 | 8b | 25 | 73.86 | n.d |
| 8 | 9b | >25 | >84.63 | n.d. |
| 9 | 10b | >25 | 80.79 | n.d. |
| 10 | 11b | >25 | 68.22 | n.d. |
| 13 | INH | 0.06 | 4.38 | n.d. |
| Entry | PDB ID | Protein (Gene) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1z6k | Citrate lyase (citE) |
| 2 | 1kpg, 1kph | Cyclopropane synthase (cmaA1) |
| 3 | 1kpi | Cyclopropane synthase (cmaA2) |
| 4 | 6ddp, 6nnh, 6nni | Dihydrofolate reductase (dfrA) |
| 5 | 1zlj | DosR regulator protein (DosR) |
| 6 | 2qo1 | β-Ketoacyl-ACP synthase (fabH) |
| 7 | 5hm3 | Acyl-AMP ligase (fadD32) |
| 8 | 5zue | Filamentation temperature-sensitive protein (ftsZ) |
| 9 | 5ecv, 5h8u, 5t8g | Malate synthase (glcB) |
| 10 | 4tvm | Citrate synthase (gltA2) |
| 11 | 5dql | Isocitrate lyase (icl1) |
| 12 | 6ee1 | Isocitrate lyase (icl2) |
| 13 | 2isy | Iron-dependent regulator (IdeR) |
| 14 | 4ohu, 4tzk, 5g0t | Enoyl-ACP reductase (inhA) |
| 15 | 5ld8, 6p9l, 6p9m | β-Ketoacyl-ACP synthase (kasA) |
| 16 | 2gp6 | β-Ketoacyl-ACP synthase (kasB) |
| 17 | 2a8x, 4m52 | Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (lpdC) |
| 18 | 1uzn | β-Ketoacyl-ACP reductase (mabA) |
| 19 | 4qij | 1,4-Dihydroxy-2-naphthoate-coenzyme A synthase (menB) |
| 20 | 6o0j | 2-Succinyl-5-enolpyruvyl-6-hydroxy-3-cyclohexene-1-carboxylate synthase (menD) |
| 21 | 1tpy | Cyclopropane synthase (mmaA2) |
| 22 | 3ha5 | S-Adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase (mmaA4) |
| 23 | 4ewl | N-Acetyl-1-D-myo-inosityl-2-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranoside deacetylase (mshB) |
| 24 | 1ozp, 1p0h | Mycothiol synthase (mshD) |
| 25 | 1mop, 1n2h, 4fzj | Pantothenate synthetase (panC) |
| 26 | 6p02, 6oyy, 6oz8 | Aspartate decarboxylase (panD) |
| 27 | 1q9j | Phthiocerol dimycocerosyl transferase (papA5) |
| 28 | 1l1e | Cyclopropane synthase (pcaA) |
| 29 | 4n9w, 4nc9 | Phosphatidyl mannosyltransferase (pimA) |
| 30 | 6c4q | Polyketide synthase (pks13) |
| 31 | 5xnx | RelA protein (relA) |
| 32 | 6c67 | Adenosine kinase (Rv2202c) |
| 33 | 2byo | Lipoprotein LppX (Rv2945c) |
| 34 | 5uhb | Transcription initiation complex (Rv3457c) |
| 35 | 4unr | Thymidylate kinase (tmk) |
| Ligand | Scores | ΔGbind, kJ/mol |
|---|---|---|
| 7a | 33.44 | −34.49 |
| 8a | 33.53 | −34.81 |
| 9a | 34.14 | −34.01 |
| 10a | 34.62 | −34.90 |
| 11a | 33.48 | −37.41 |
| 7b | 34.09 | −36.81 |
| 8b | 34.53 | −37.53 |
| 9b | 29.5 | −36.01 |
| 10b | 32,23 | −36.71 |
| 11b | 30.14 | −30.47 |
| Cognate ligand (6c67) | 21.46 | −26.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadykhov, G.A.; Belyaev, D.V.; Khramtsova, E.E.; Vakhrusheva, D.V.; Krasnoborova, S.Y.; Dianov, D.V.; Pervova, M.G.; Rusinov, G.L.; Verbitskiy, E.V.; Charushin, V.N. 4-Alkyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline Derivatives as New Heterocyclic Analogues of Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines: Synthesis and Antitubercular Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010369
Sadykhov GA, Belyaev DV, Khramtsova EE, Vakhrusheva DV, Krasnoborova SY, Dianov DV, Pervova MG, Rusinov GL, Verbitskiy EV, Charushin VN. 4-Alkyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline Derivatives as New Heterocyclic Analogues of Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines: Synthesis and Antitubercular Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010369
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadykhov, Gusein A., Danila V. Belyaev, Ekaterina E. Khramtsova, Diana V. Vakhrusheva, Svetlana Yu. Krasnoborova, Dmitry V. Dianov, Marina G. Pervova, Gennady L. Rusinov, Egor V. Verbitskiy, and Valery N. Charushin. 2025. "4-Alkyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline Derivatives as New Heterocyclic Analogues of Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines: Synthesis and Antitubercular Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010369
APA StyleSadykhov, G. A., Belyaev, D. V., Khramtsova, E. E., Vakhrusheva, D. V., Krasnoborova, S. Y., Dianov, D. V., Pervova, M. G., Rusinov, G. L., Verbitskiy, E. V., & Charushin, V. N. (2025). 4-Alkyl-4H-thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline Derivatives as New Heterocyclic Analogues of Indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines: Synthesis and Antitubercular Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010369







