Lactoferrin Attenuates Pro-Inflammatory Response and Promotes the Conversion into Neuronal Lineages in the Astrocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
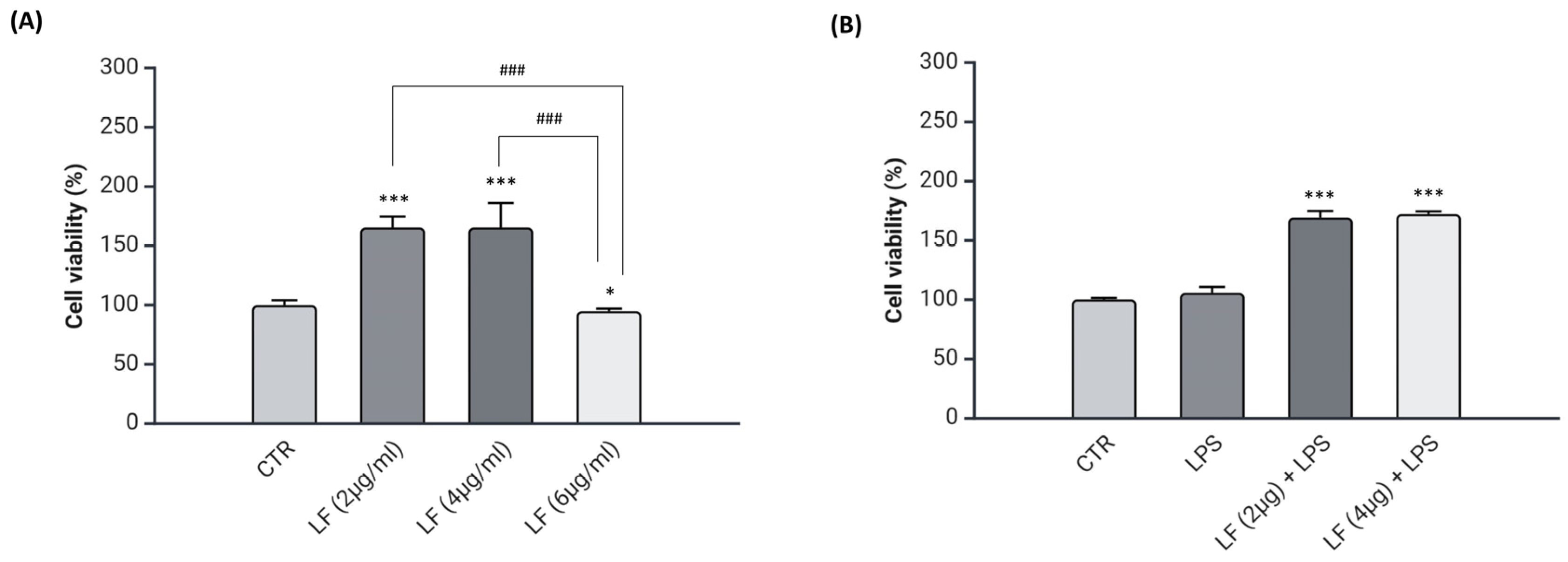
2.1. Effects of Lactoferrin on Viability of DI-TNC1 Cells
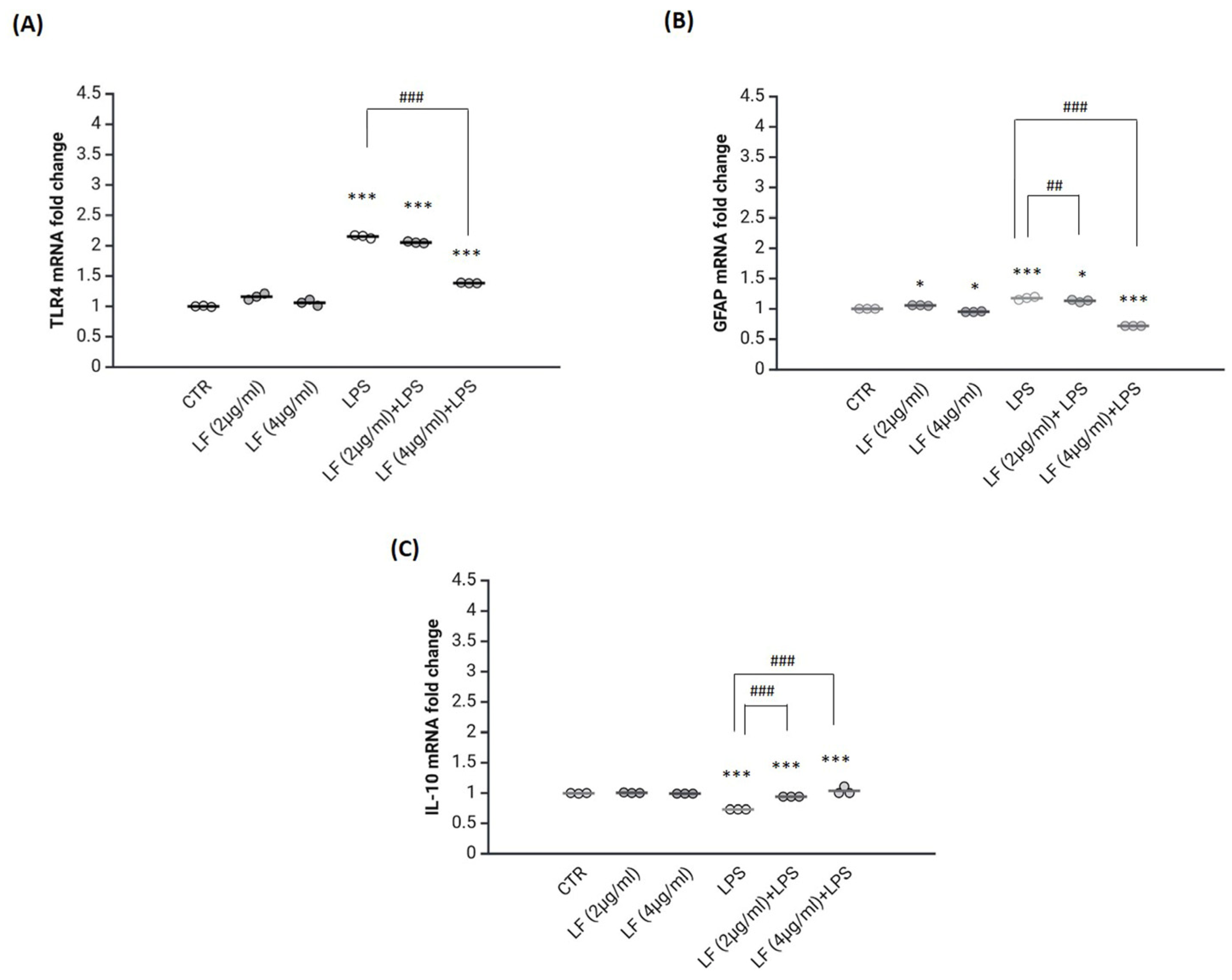
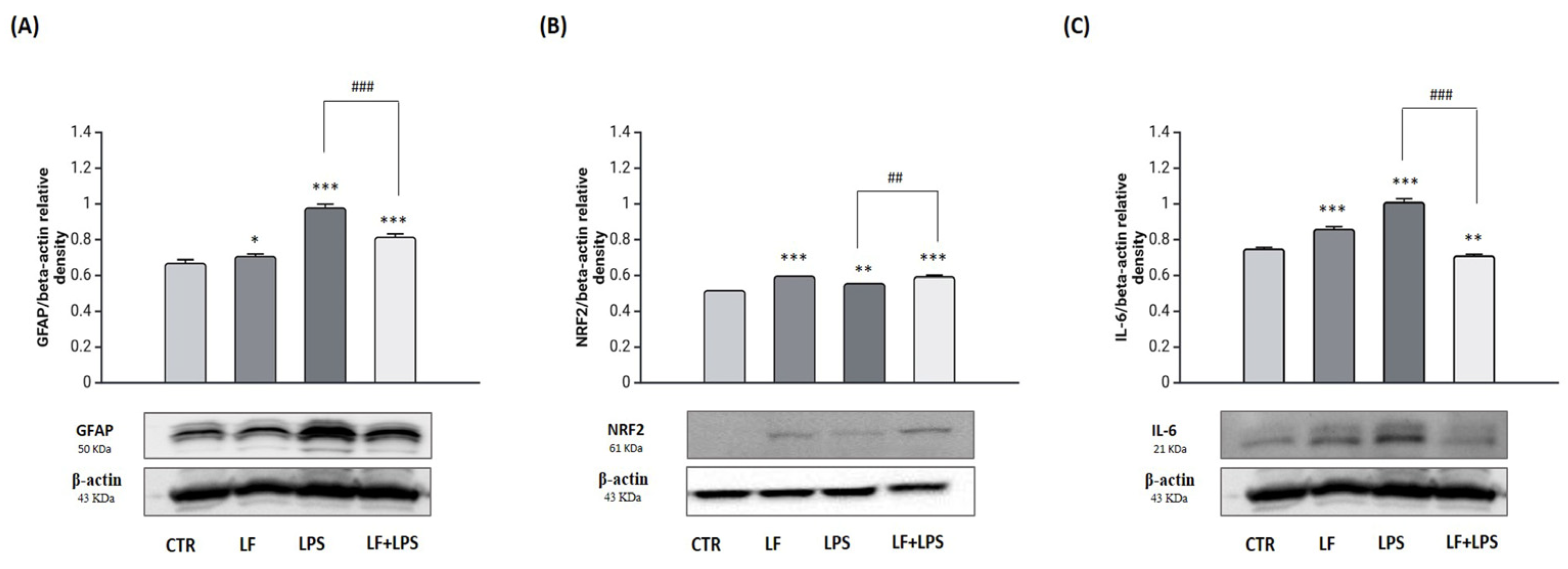
2.2. Lactoferrin Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Functions in the Astrocytes
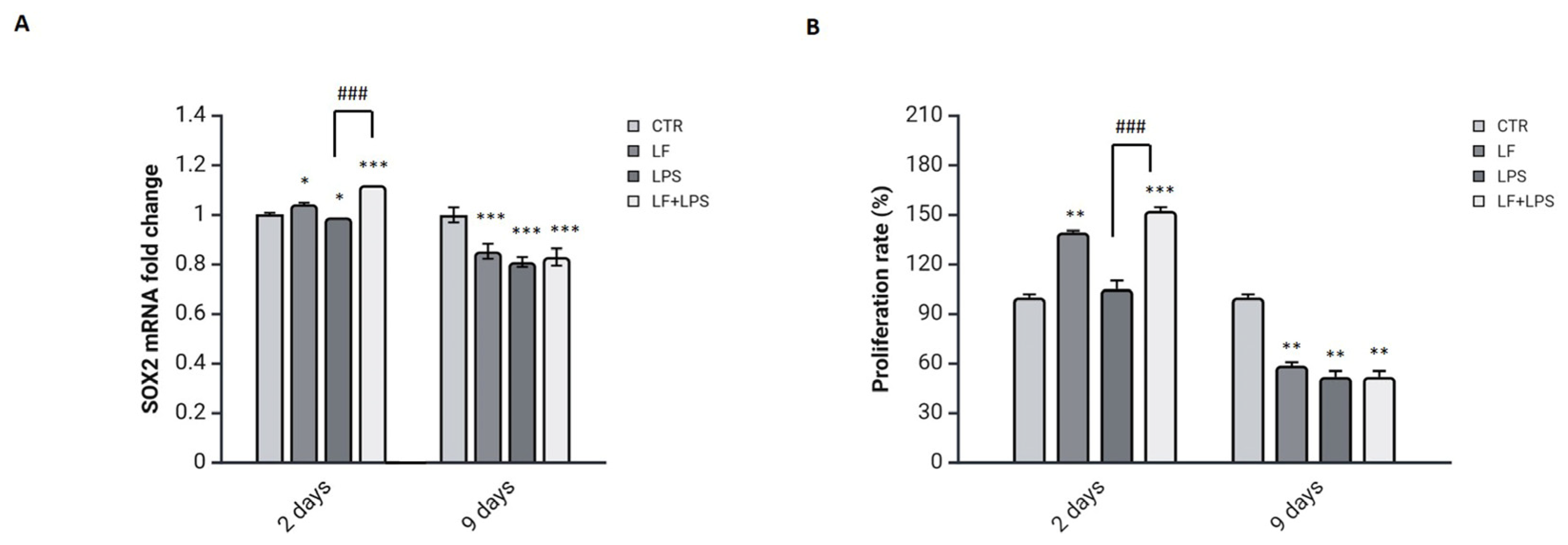
2.3. Lactoferrin Triggers the SOX2 Reprogramming Transcription Factor by Inducing a Proliferative State
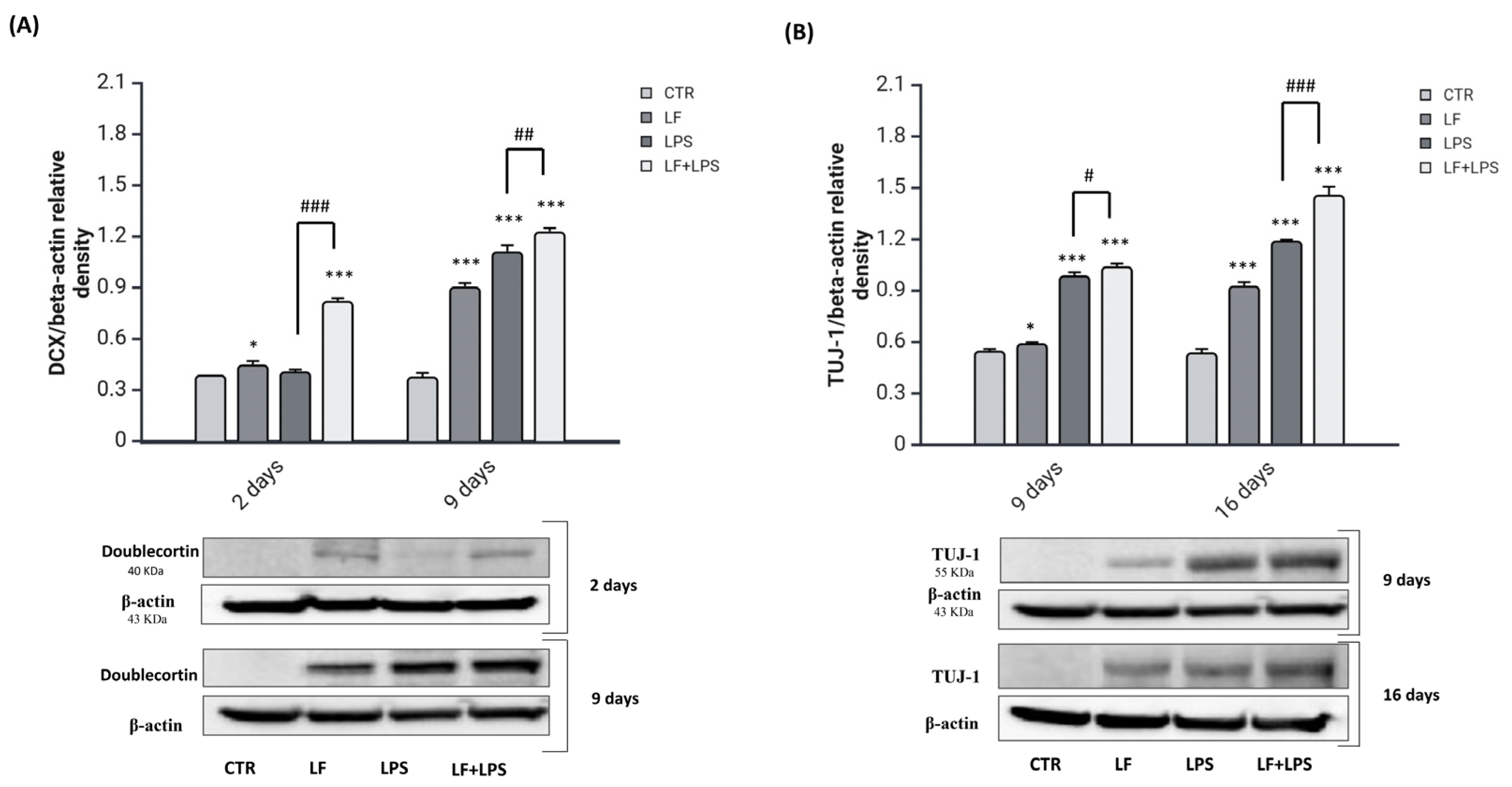
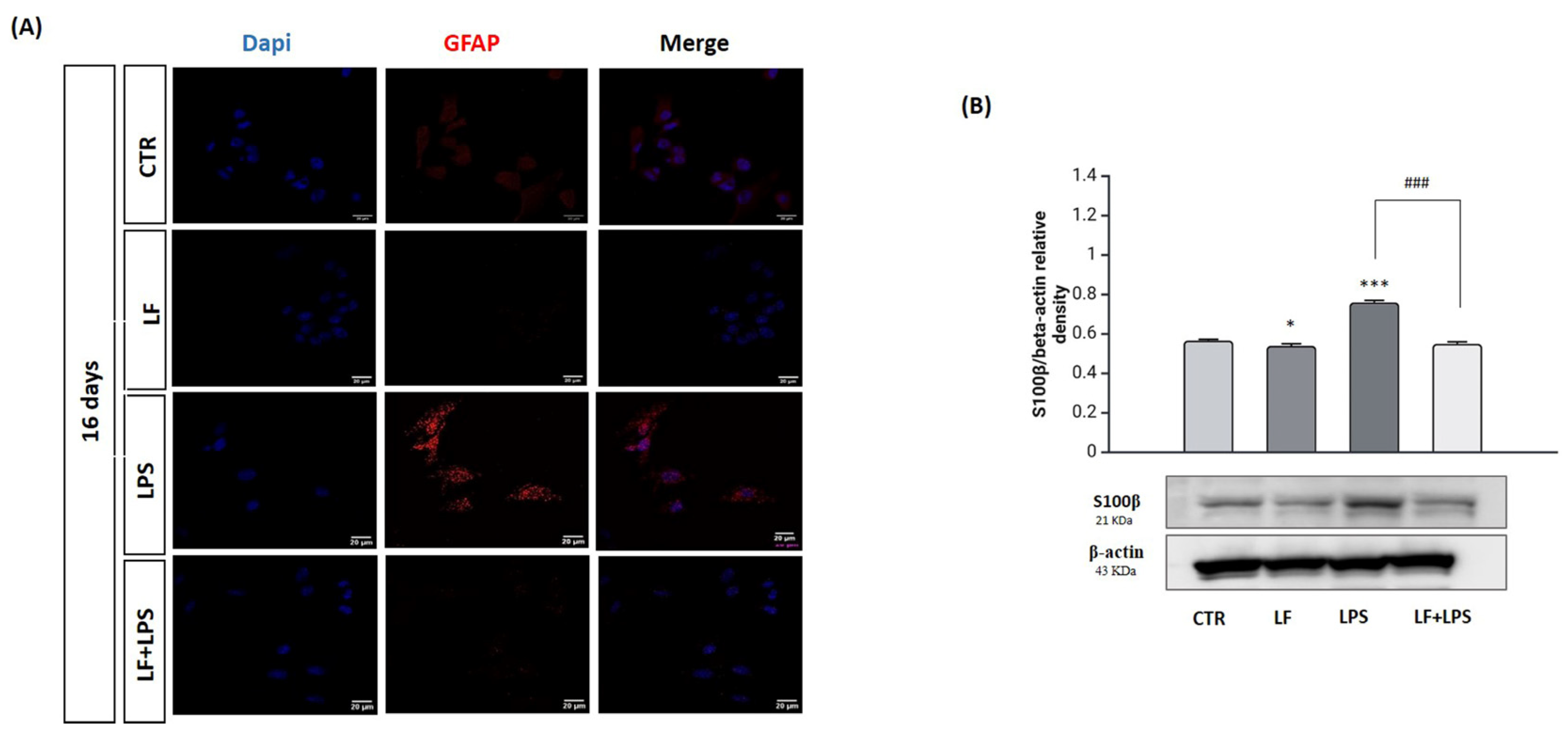
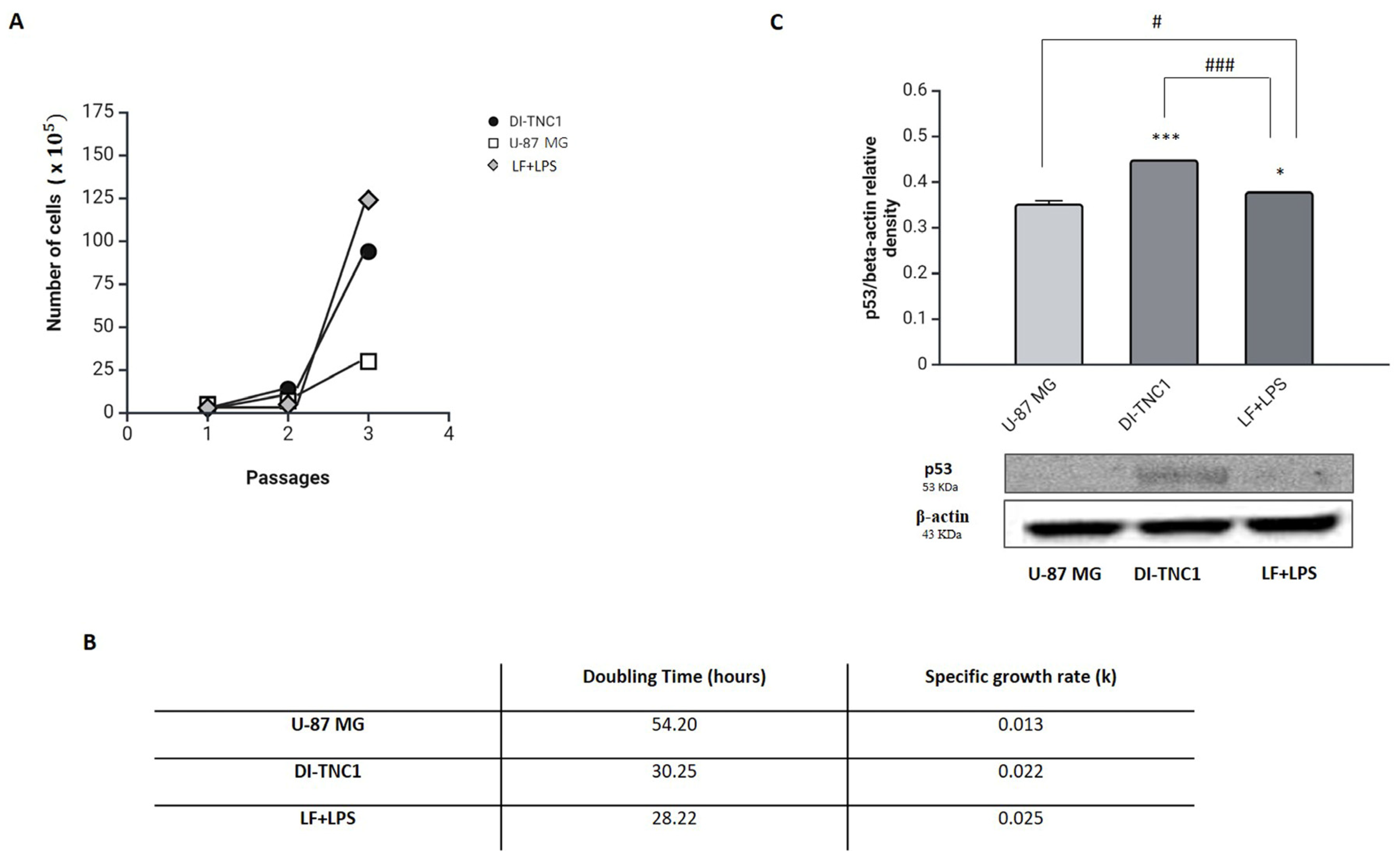
2.4. Lactoferrin Stimulates the Reprogramming of Reactive Astrocytes into Neuroblasts
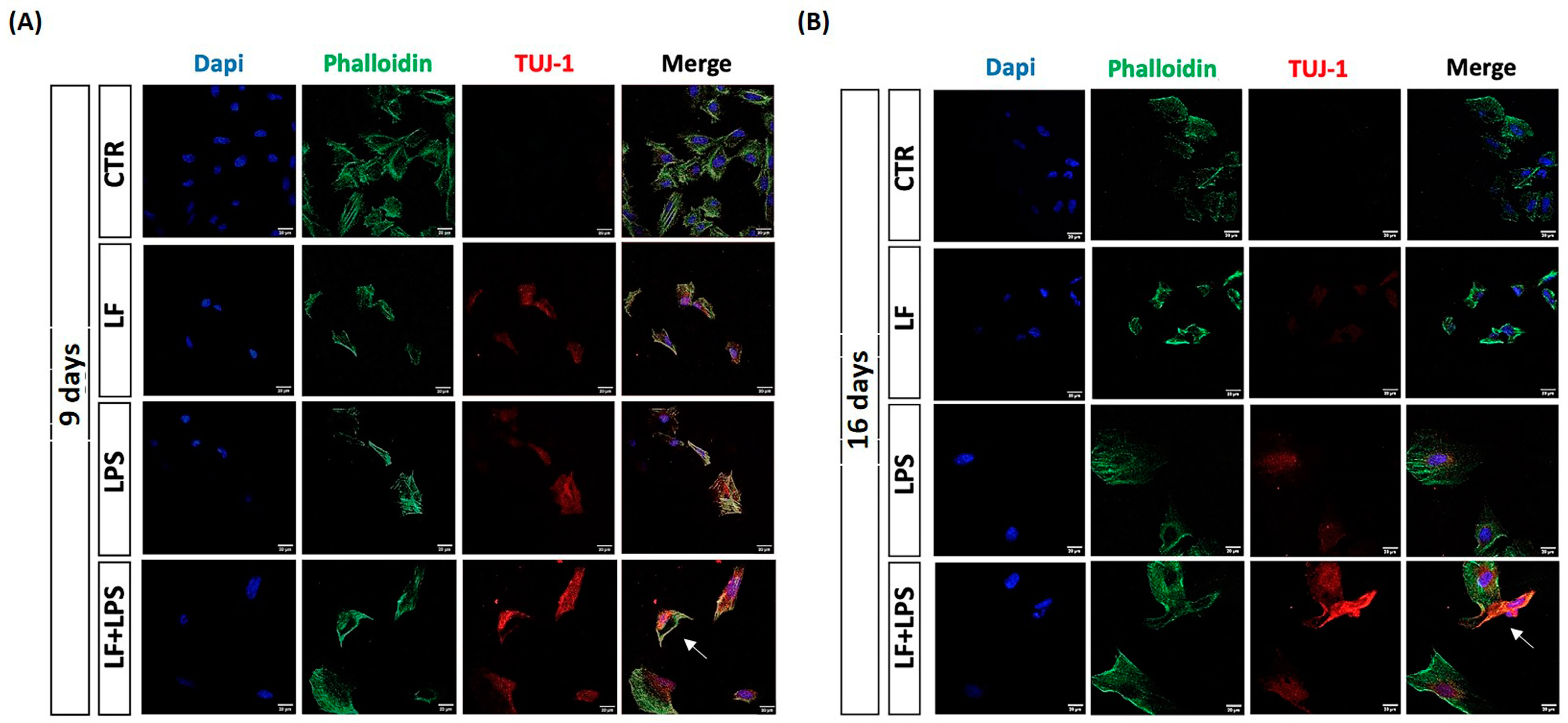
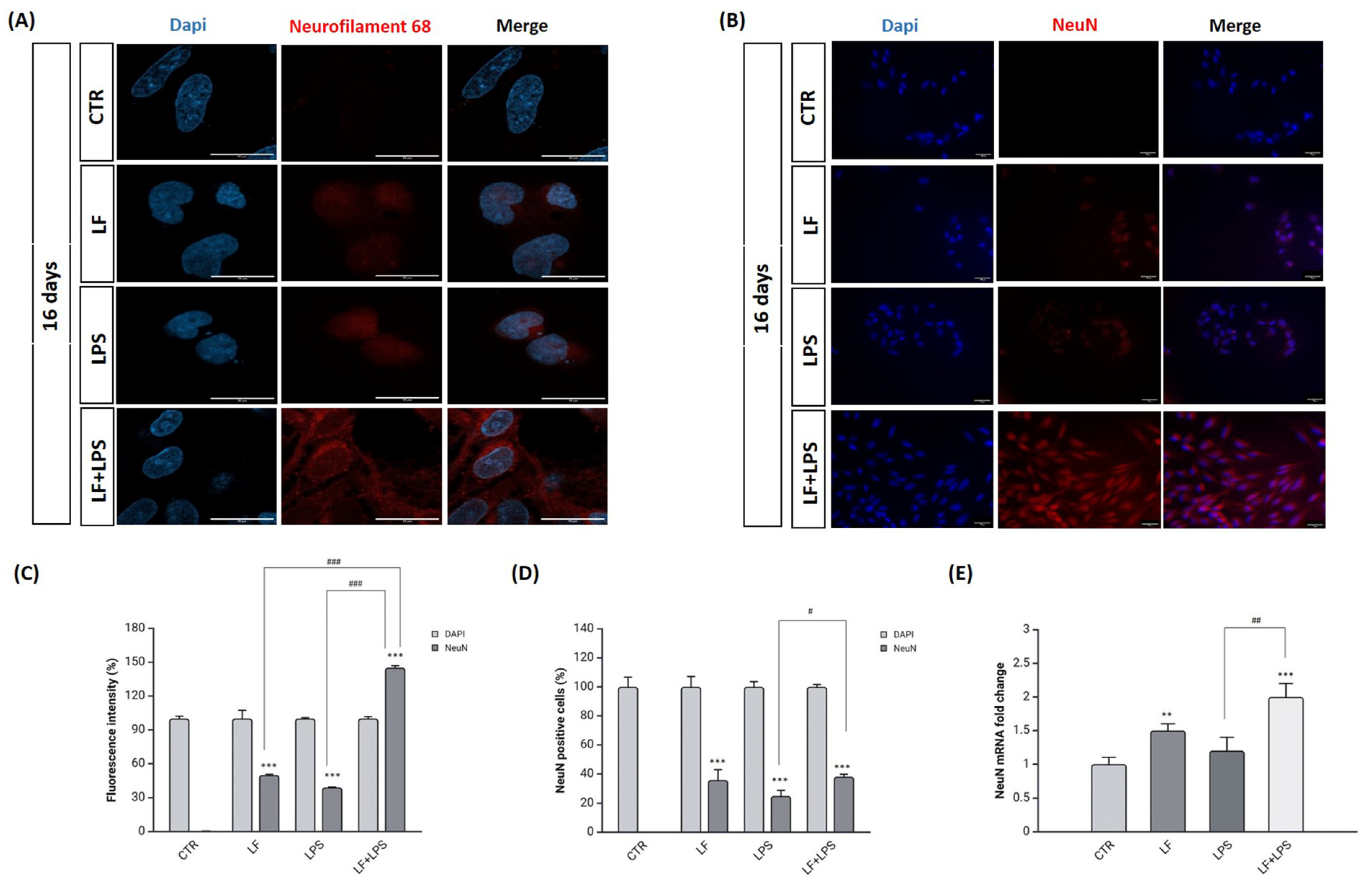
2.5. Lactoferrin Induces the Acquisition of Neuronal Features
2.6. Tumorigenicity Assessment for Reprogrammed Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.2. MTT Assay
4.3. Cell Lysates and Western Blotting
4.4. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. In Vitro Tumorigenicity Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.H. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.M., 3rd; Cookson, M.R.; Van Den Bosch, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Holtzman, D.M.; Dewachter, I. Hallmarks of neurodegenerative diseases. Cell 2023, 186, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, B.; Winkler, J. Adult neurogenesis in neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a021287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilgun-Sherki, Y.; Melamed, E.; Offen, D. Anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: Current state. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 3509–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phukan, B.C.; Roy, R.; Gahatraj, I.; Bhattacharya, P.; Borah, A. Therapeutic considerations of bioactive compounds in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: Dissecting the molecular pathways. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 5657–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianciulli, A.; Calvello, R.; Ruggiero, M.; Panaro, M.A. Inflammaging and Brain: Curcumin and Its Beneficial Potential as Regulator of Microglia Activation. Molecules 2022, 27, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nuccio, F.; Cianciulli, A.; Porro, C.; Kashyrina, M.; Ruggiero, M.; Calvello, R.; Miraglia, A.; Nicolardi, G.; Lofrumento, D.D.; Panaro, M.A. Inflammatory Response Modulation by Vitamin C in an MPTP Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Biology 2021, 10, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, M.; Cianciulli, A.; Calvello, R.; Porro, C.; De Nuccio, F.; Kashyrina, M.; Miraglia, A.; Lofrumento, D.D.; Panaro, M.A. Ser9p-GSK3β Modulation Contributes to the Protective Effects of Vitamin C in Neuroinflammation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, M.; Calvello, R.; Porro, C.; Messina, G.; Cianciulli, A.; Panaro, M.A. Neurodegenerative Diseases: Can Caffeine Be a Powerful Ally to Weaken Neuroinflammation? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvello, R.; Porro, C.; Lofrumento, D.D.; Ruggiero, M.; Panaro, M.A.; Cianciulli, A. Decoy Receptors Regulation by Resveratrol in Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Microglia. Cells 2023, 12, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Han, Y.; Li, M.; Nie, C. Curcumin Promotes Proliferation of Adult Neural Stem Cells and the Birth of Neurons in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice via Notch Signaling Pathway. Cell. Reprogram. 2019, 21, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Qian, L. Direct cell reprogramming: Approaches, mechanisms and progress. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Lai, X.; Liang, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Qin, Q.; Qin, R.; Huang, X.; Xie, M.; et al. A promise for neuronal repair: Reprogramming astrocytes into neurons in vivo. Biosci. Rep. 2024, 44, BSR20231717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Qin, S.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, H.; Pu, Y.; He, C.; Su, Z. NOTCH1 signaling regulates the latent neurogenic program in adult reactive astrocytes after spinal cord injury. Theranostics 2022, 12, 4548–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.A.F.; Fiadeiro, M.B.; Bernardino, L.I.; Fonseca, C.S.P.; Baltazar, G.M.F.; Cristóvão, A.C.B. Lipopolysaccharide-induced animal models for neuroinflammation—An overview. J. Neuroimmunol. 2024, 387, 578273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edison, P. Astroglial activation: Current concepts and future directions. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 3034–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Dai, Y.; Chen, G.; Cui, S. Dissecting the Dual Role of the Glial Scar and Scar-Forming Astrocytes in Spinal Cord Injury. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Kou, L.; Yin, S.; Chi, X.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zou, W.; et al. Astrocyte-to-neuron reprogramming and crosstalk in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 184, 106224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Zang, T.; Smith, D.K.; Vue, T.Y.; Zou, Y.; Bachoo, R.; Johnson, J.E.; Zhang, C.L. SOX2 reprograms resident astrocytes into neural progenitors in the adult brain. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 4, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Niu, W.; Liu, M.L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, C.L. In vivo conversion of astrocytes to neurons in the injured adult spinal cord. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, L.; Cutone, A.; Lepanto, M.S.; Paesano, R.; Valenti, P. Lactoferrin: A Natural Glycoprotein Involved in Iron and Inflammatory Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Timilsena, Y.P.; Blanch, E.; Adhikari, B. Lactoferrin: Structure, function, denaturation and digestion. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 59, 580–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embleton, N.; Berrington, J.; McGuire, W.; Stewart, C.J.; Cummings, S.P.; Stewart, C.J. Lactoferrin: Antimicrobial activity and therapeutic potential. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 18, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Ren, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wang, K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.S.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z. Lactoferrin: A glycoprotein that plays an active role in human health. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1018336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Q.; Guo, C. A Review on Lactoferrin and Central Nervous System Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essam, R.M.; Saadawy, M.A.; Gamal, M.; Abdelsalam, R.M.; El-Sahar, A.E. Lactoferrin averts neurological and behavioral impairments of thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in rats via modulating HGMB1/TLR-4/MyD88/Nrf2 pathway. Neuropharmacology 2023, 236, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczak-Wiercioch, A.; Sałat, K. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Model of Neuroinflammation: Mechanisms of Action, Research Application and Future Directions for Its Use. Molecules 2022, 27, 5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, T.E.; Wenzel, T.J.; Simtchouk, S.; Greuel, B.K.; Gibon, J.; Klegeris, A. Extracellular Cardiolipin Modulates Select Immune Functions of Astrocytes in Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) 4-Dependent Manner. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 9946439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Simtchouk, S.; Gibon, J.; Klegeris, A. Regulation of the phagocytic activity of astrocytes by neuroimmune mediators endogenous to the central nervous system. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbatenko, V.O.; Goriainov, S.V.; Babenko, V.A.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Sergeeva, M.G.; Chistyakov, D.V. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Metformin During Cultivation of Primary Rat Astrocytes in a Medium with High Glucose Concentration. Biochemistry 2022, 87, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, M.R.; Johnson, J.A. The Nrf2-ARE cytoprotective pathway in astrocytes. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009, 11, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, W.; Zang, T.; Zou, Y.; Fang, S.; Smith, D.K.; Bachoo, R.; Zhang, C.L. In vivo reprogramming of astrocytes to neuroblasts in the adult brain. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, K.; Lie, D.C. Evidence that Doublecortin is dispensable for the development of adult born neurons in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, E.; Dao, D.Q.; Wu, Z.Y.; Kandalam, S.M.; Camacho, F.M.; Tom, C.; Zhang, W.; Krencik, R.; Rauen, K.A.; Ullian, E.M.; et al. Patient-derived iPSCs show premature neural differentiation and neuron type-specific phenotypes relevant to neurodevelopment. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, S.M.; Jessberger, S. Adult neurogenesis: Mechanisms and functional significance. Development 2014, 141, 1983–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmbeck, G.H.; Sizonenko, S.; Sanches, E.F. Neuroprotective Role of Lactoferrin During Early Brain Development and Injury Through Lifespan. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Kruzel, M.; Ting, S.M.; Sun, G.; Savitz, S.I.; Aronowski, J. Optimized lactoferrin as a highly promising treatment for intracerebral hemorrhage: Pre-clinical experience. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2021, 41, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ting, S.M.; Sun, G.; Bautista Garrido, J.; Obertas, L.; Aronowski, J. Clearance of Neutrophils From ICH-Affected Brain by Macrophages Is Beneficial and Is Assisted by Lactoferrin and CD91. Stroke 2024, 55, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.G.; Guo, C.; Zhao, L.X.; Ge, R.L.; Pang, Z.Q.; He, D.L.; Ren, H.; Wu, T.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, Z.Y. Astrocyte-derived lactoferrin reduces β-amyloid burden by promoting the interaction between p38 kinase and PP2A phosphatase in male APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bi, M.; Liu, H.; Song, N.; Xie, J. The Protective Effect of Lactoferrin on Ventral Mesencephalon Neurons against MPP+ Is Not Connected with Its Iron Binding Ability. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Zhu, N.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Wang, J. Lactoferrin Protects Against Iron Dysregulation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis in 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-Induced Parkinson’s Disease in Mice. J. Neurochem. 2020, 152, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, E.; Michel, P.P.; Hirsch, E.C. The iron-binding protein lactoferrin protects vulnerable dopamine neurons from degeneration by preserving mitochondrial calcium homeostasis. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 84, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, S.; Pang, Z.Q.; Fan, Y.G.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Guo, C. Lactoferrin ameliorates dopaminergic neurodegeneration and motor deficits in MPTP-treated mice. Redox Biol. 2019, 21, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conneely, O.M. Antiinflammatory activities of lactoferrin. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2001, 20 (Suppl. 5), 389S–395S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; An, Q.; Huang, K.; Dai, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Unlocking the power of Lactoferrin: Exploring its role in early life and its preventive potential for adult chronic diseases. Food Res. Int. 2024, 182, 114143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopaeva, M.Y.; Cherepov, A.B.; Zaraiskaya, I.Y. Lactoferrin Has a Protective Effect on Mouse Brain Cells after Acute Gamma Irradiation of the Head. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 176, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallah, K.; Couch, C.; Borucki, D.M.; Toutonji, A.; Alshareef, M.; Tomlinson, S. Anti-inflammatory and Neuroprotective Agents in Clinical Trials for CNS Disease and Injury: Where Do We Go From Here? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.Q.; Yu, S.P.; Wei, Z.Z.; Zhong, W.; Cao, W.; Gu, X.; Wu, A.; McCrary, M.R.; Berglund, K.; Wei, L. Conversion of Reactive Astrocytes to Induced Neurons Enhances Neuronal Repair and Functional Recovery After Ischemic Stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 612856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Qin, S.; Liu, H.; Huang, X.; Pu, Y.; He, C.; Yuan, Y.; Su, Z. Small molecules reprogram reactive astrocytes into neuronal cells in the injured adult spinal cord. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 59, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurram, P.C.; Manandhar, S.; Satarker, S.; Mudgal, J.; Arora, D.; Nampoothiri, M. Dopaminergic Signaling as a Plausible Modulator of Astrocytic Toll-Like Receptor 4: A Crosstalk between Neuroinflammation and Cognition. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2023, 22, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Benito, D.; Paradela-Leal, C.; Ganchala, D.; de Castro-Molina, P.; Arevalo, M.A. IGF-1 regulates astrocytic phagocytosis and inflammation through the p110α isoform of PI3K in a sex-specific manner. Glia 2022, 70, 1153–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.B.; Bhutani, A.; Stary, C.M. Adult neurogenesis from reprogrammed astrocytes. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Xing, L.; Yu, W.; Cai, Y.; Cui, S.; Chen, G. Astrocytic reprogramming combined with rehabilitation strategy improves recovery from spinal cord injury. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 15504–15515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascón, S.; Murenu, E.; Masserdotti, G.; Ortega, F.; Russo, G.L.; Petrik, D.; Deshpande, A.; Heinrich, C.; Karow, M.; Robertson, S.P.; et al. Identification and Successful Negotiation of a Metabolic Checkpoint in Direct Neuronal Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez-David, I.; David, D.J.; Deloménie, C.; Tritschler, L.; Beaulieu, J.M.; Colle, R.; Corruble, E.; Gardier, A.M.; Hen, R. A complex relation between levels of adult hippocampal neurogenesis and expression of the immature neuron marker doublecortin. Hippocampus 2023, 33, 1075–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanovic, M.; Kovacevic-Grujicic, N.; Mojsin, M.; Milivojevic, M.; Drakulic, D. SOX transcription factors and glioma stem cells: Choosing between stemness and differentiation. World J. Stem Cells 2021, 13, 1417–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, J.P.; Zamboni, M.; Santopolo, G.; Mold, J.E.; Barrientos-Somarribas, M.; Talavera-Lopez, C.; Andersson, B.; Frisén, J. Activation of a neural stem cell transcriptional program in parenchymal astrocytes. eLife 2020, 9, e59733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Fan, H.; Fu, F.F.; Guo, B.L.; Huang, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, W.T.; Xing, J.L.; Hu, X.T.; Ding, Y.Q.; et al. Transient neurogenesis in ischemic cortex from Sox2+ astrocytes. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 1521–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.F.; Cui, J.H.; Liu, X.; Pang, Z.Q.; Bai, C.Y.; Jiang, C.; Luan, C.; Li, Y.P.; Zhao, Y.; You, Y.M.; et al. Astrocytic lactoferrin deficiency augments MPTP-induced dopaminergic neuron loss by disturbing glutamate/calcium and ER-mitochondria signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 225, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, E.; van de Looij, Y.; Ho, D.; Modernell, L.; da Silva, A.; Sizonenko, S. Early Neuroprotective Effects of Bovine Lactoferrin Associated with Hypothermia after Neonatal Brain Hypoxia-Ischemia in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Uto, T.; Mori, K.; Fujikawa, R. Integrin-linked kinase is involved in lactoferrin-induced anchorage-independent cell growth and survival in PC12 cells. Life Sci. 2009, 84, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, S.; Nizzardo, M.; Simone, C.; Falcone, M.; Donadoni, C.; Salani, S.; Rizzo, F.; Nardini, M.; Riboldi, G.; Magri, F.; et al. Direct reprogramming of human astrocytes into neural stem cells and neurons. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 1528–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Su, Z.; Tai, W.; Zou, Y.; Xu, X.M.; Zhang, C.L. The p53 Pathway Controls SOX2-Mediated Reprogramming in the Adult Mouse Spinal Cord. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Bando, H.; Di Piazza, M.; Gowing, G.; Herberts, C.; Jackman, S.; Leoni, G.; Libertini, S.; MacLachlan, T.; McBlane, J.W.; et al. Tumorigenicity assessment of cell therapy products: The need for global consensus and points to consider. Cytotherapy 2019, 21, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.J.; Xu, J.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Tong, X.; Yang, H.H.; Yang, J.; Yuan, L.X.; Qin, L.Q. Lactoferrin promotes bile acid metabolism and reduces hepatic cholesterol deposition by inhibiting the farnesoid X receptor (FXR)-mediated enterohepatic axis. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7299–7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernick, D.; Zhong, R.; Li, L. The Role of HDL and HDL Mimetic Peptides as Potential Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Button, E.B.; Robert, J.; Caffrey, T.M.; Fan, J.; Zhao, W.; Wellington, C.L. HDL from an Alzheimer’s disease perspective. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2019, 30, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.F.; Pang, Z.Q.; Fan, Y.G.; Zhang, Y.H.; Meng, Y.H.; Bai, C.Y.; Jia, M.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Guo, C. Astrocyte-specific loss of lactoferrin influences neuronal structure and function by interfering with cholesterol synthesis. Glia 2022, 70, 2392–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reseco, L.; Atienza, M.; Fernandez-Alvarez, M.; Carro, E.; Cantero, J.L. Salivary lactoferrin is associated with cortical amyloid-beta load, cortical integrity, and memory in aging. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, H.D.; Das, T.; Banerjee, S.; Venkatesh, M.; Vidyasagar, P.B.; Mishra, K.P. Studies on efficacy of a novel 177Lu-labeled porphyrin derivative in regression of tumors in mouse model. Curr. Radiopharm. 2011, 4, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrara, E.; Forssell-Aronsson, E.; Ahlman, H.; Bernhardt, P. Specific growth rate versus doubling time for quantitative characterization of tumor growth rate. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3970–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| cDNA Target | Sense Primer (5′–>3′) | Antisense Primer (3′–>5′) |
|---|---|---|
| TLR4 | CGCTTTCACCTCTGCCTCACTACAG | ACACTACCACAATAACCTTCCGGCTC |
| GFAP | CACGAACGAGTCCCTAGAGC | GAAGAAAACCGCATCACCAT |
| IL-10 | CTGTCATCGATTTCTCCCCTGT | CAGTAGATGCCGGGTGGTTC |
| SOX2 | ACTAATCACAACAATCGCGGCGGC | GACGGGCGAAGTGCAATTGGA |
| NeuN | TTACGGAGCGGTCGTGTATC | GCAGGGTAAACCTTGGGACA |
| GAPDH | ACCACAGTCCCTGCCATCAG | TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruggiero, M.; Cianciulli, A.; Calvello, R.; Lofrumento, D.D.; Saponaro, C.; Filannino, F.M.; Porro, C.; Panaro, M.A. Lactoferrin Attenuates Pro-Inflammatory Response and Promotes the Conversion into Neuronal Lineages in the Astrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010405
Ruggiero M, Cianciulli A, Calvello R, Lofrumento DD, Saponaro C, Filannino FM, Porro C, Panaro MA. Lactoferrin Attenuates Pro-Inflammatory Response and Promotes the Conversion into Neuronal Lineages in the Astrocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010405
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuggiero, Melania, Antonia Cianciulli, Rosa Calvello, Dario Domenico Lofrumento, Concetta Saponaro, Francesca Martina Filannino, Chiara Porro, and Maria Antonietta Panaro. 2025. "Lactoferrin Attenuates Pro-Inflammatory Response and Promotes the Conversion into Neuronal Lineages in the Astrocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010405
APA StyleRuggiero, M., Cianciulli, A., Calvello, R., Lofrumento, D. D., Saponaro, C., Filannino, F. M., Porro, C., & Panaro, M. A. (2025). Lactoferrin Attenuates Pro-Inflammatory Response and Promotes the Conversion into Neuronal Lineages in the Astrocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010405








