Identification of Advantaged Genes for Low-Nitrogen-Tolerance-Related Traits in Rice Using a Genome-Wide Association Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
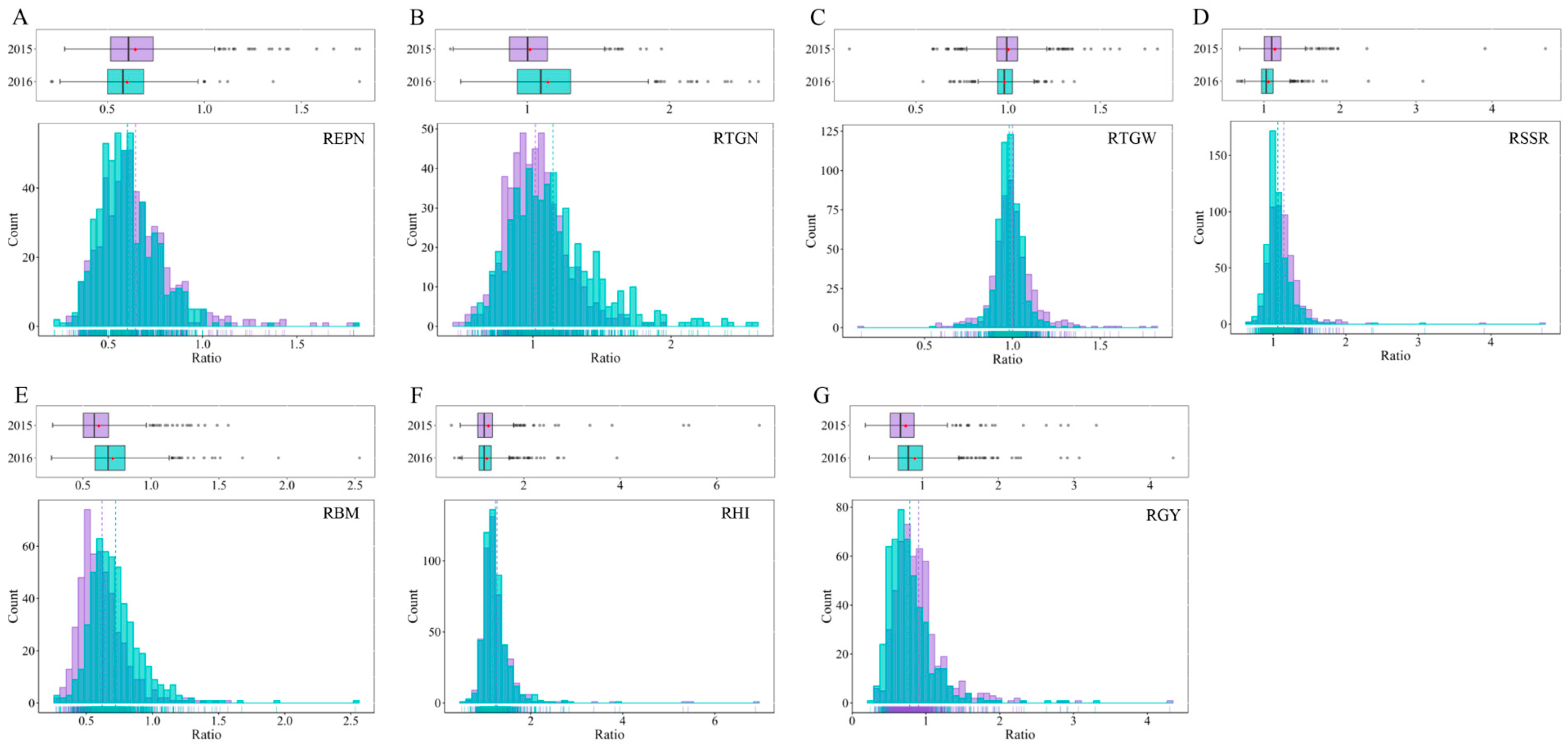
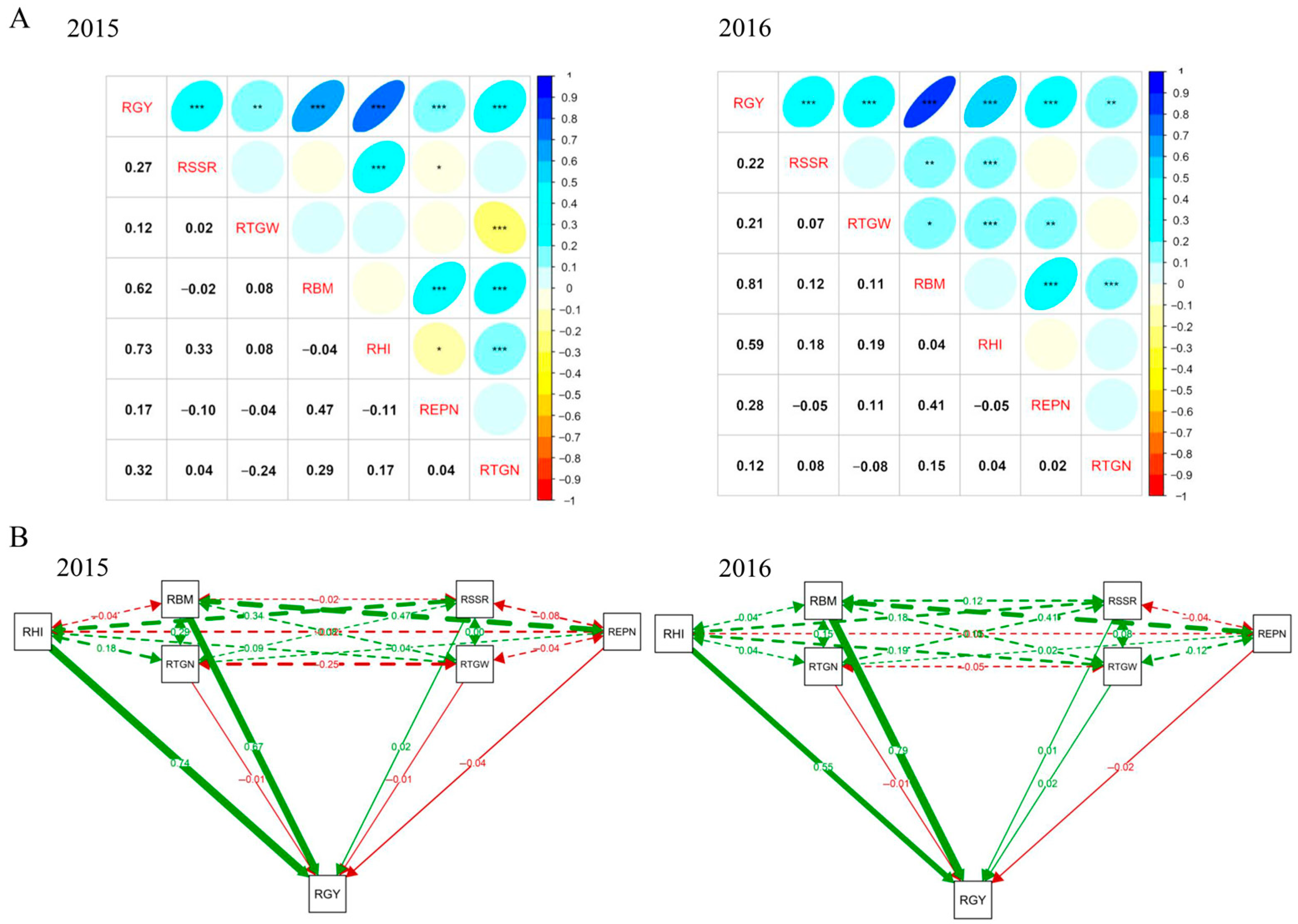
2.1. Phenotypic Variation
2.2. Genotype Analysis of the MAGIC Population in This Study
2.3. Genome-Wide Association Identifies Significant QTLs Using MAGIC Population
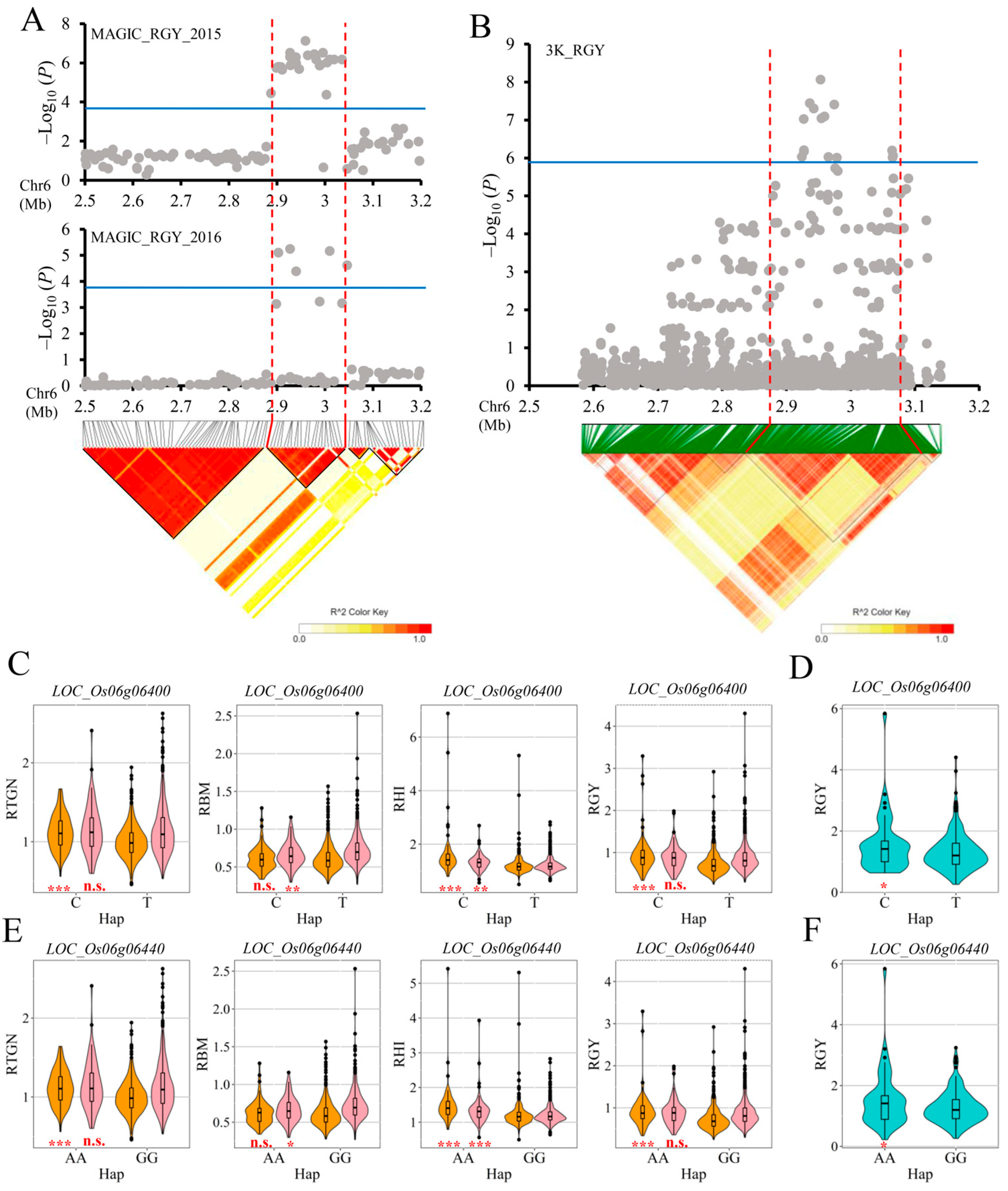
2.4. Important QTLs Were Further Identified Combined with the Result of Genome-Wide Association Analysis Using Germplasm Accessions
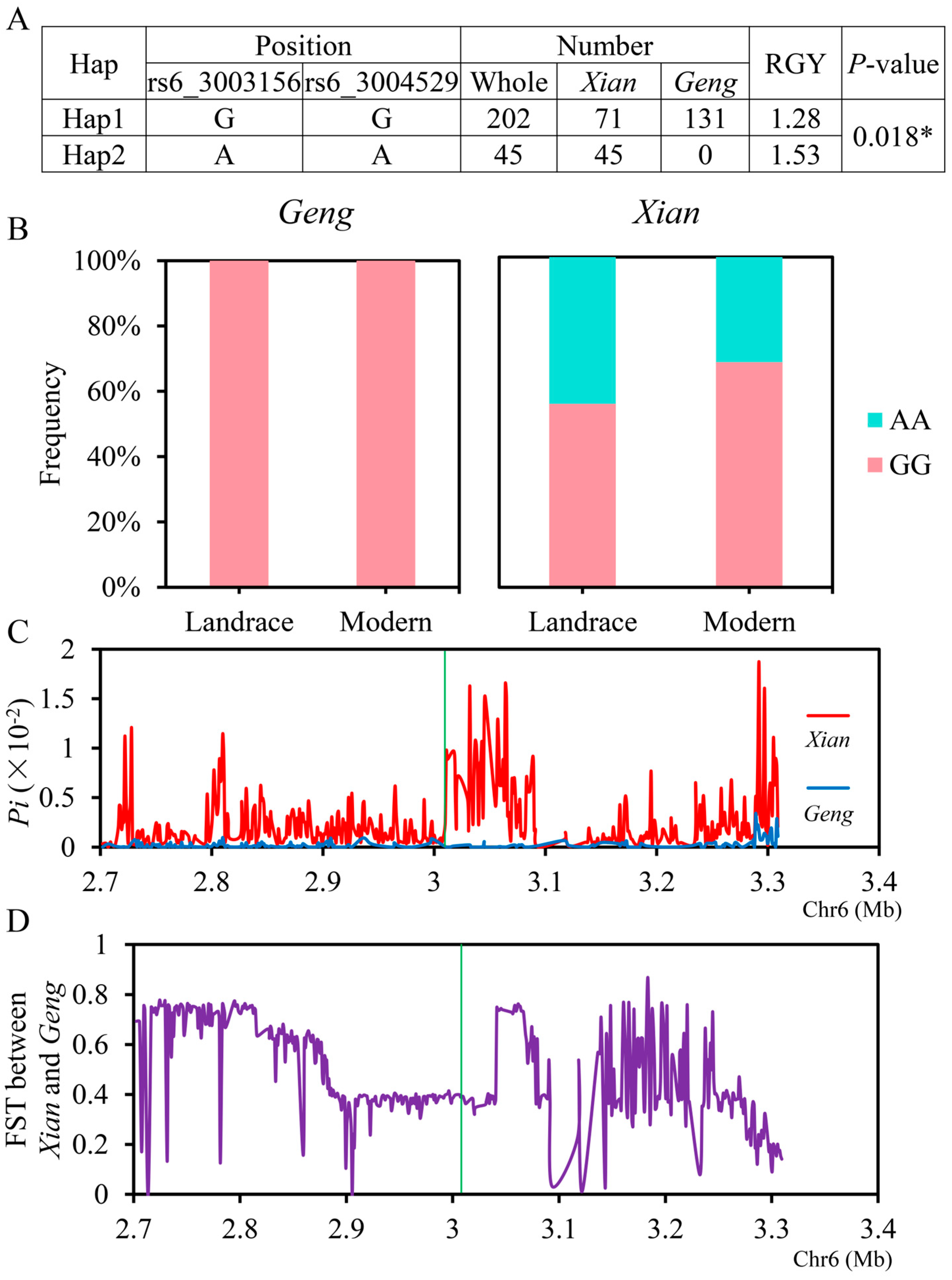
2.5. Candidate Genes Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Field Trial and Phenotypic Investigation
4.3. Genotyping Data Analysis
4.4. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) of QTL
4.5. Candidate Gene Identification for the Important QTL
4.6. Statistical Analysis of Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GWAS | genome-wide association study |
| LD | linkage disequilibrium |
| QTL | quantitative trait loci |
| MAGIC | multiparent advanced generation intercross |
| LN | low nitrogen conditions |
| NN | normal nitrogen conditions |
| EPN | effective spike number per plant |
| TGN | total number of grains per panicle |
| SSR | seed setting rate |
| TGW | thousand grains weight |
| BM | biomass |
| HI | harvest index |
| GY | grain yield per plant |
| MAF | minor allele frequency |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| K | kinship matrix |
| MLM | mixed linear model |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
References
- Qi, Z.; Ling, F.; Jia, D.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.; Yu, L.; Guan, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; et al. Effects of low nitrogen on seedling growth, photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant system of rice varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCouch, S.R.; Wright, M.H.; Tung, C.W.; Maron, L.G.; McNally, K.L.; Fitzgerald, M.; Singh, N.; DeClerck, G.; Agosto-Perez, F.; Korniliev, P.; et al. Open access resources for genome-wide association mapping in rice. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Chi, W.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Chen, G.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X.; Wang, S.; Lin, Z.; et al. Alternative splicing of OsGS1;1 affects nitrogen-use efficiency, grain development, and amylose content in rice. Plant J. 2022, 110, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, A.; Liang, Y.; Ou, S.; et al. Genomic basis of geographical adaptation to soil nitrogen in rice. Nature 2021, 590, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Ye, J.; Yao, X.; Zhao, P.; Xuan, W.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; An, H.; Chen, G.; et al. Genome-wide associated study identifies NAC42-activated nitrate transporter conferring high nitrogen use efficiency in rice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xuan, W.; Tian, Y.; Fan, L.; Sun, J.; Tang, W.; Chen, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; et al. Enhanced OsNLP4-OsNiR cascade confers nitrogen use efficiency by promoting tiller number in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Chu, C. Genetic improvement toward nitrogen-use efficiency in rice: Lessons and perspectives. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Ma, T.; Xia, S.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Qu, G.; Liu, H.; Zheng, H.; Yang, L.; et al. Mapping of candidate genes for nitrogen uptake and utilization in Japonica rice at seedling stage. Genes 2024, 15, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, B.; Chu, C. Nitrogen use efficiency in crops: Lessons from Arabidopsis and rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, W.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Zheng, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Chen, J.; et al. Candidate gene analysis for nitrogen absorption and utilization in Japonica Rice at the seedling stage based on a genome-wide association study. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 670861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xin, W.; Wang, W.; Zhao, S.; Xu, L.; Jiang, X.; Duan, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; et al. Mapping of candidate genes in response to low nitrogen in rice seedlings. Rice 2022, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Nian, J.; Xie, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Bai, J.; Dong, G.; Hu, J.; Bai, B.; Chen, L.; et al. Genetic variations in ARE1 mediate grain yield by modulating nitrogen utilization in rice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Lai, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, J. Overexpression of Nitrate Transporter 1/Peptide Gene OsNPF7.6 Increases Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Life 2022, 12, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, N.; Hu, B.; Jin, T.; Xu, H.; Qin, Y.; Yan, P.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; et al. NRT1.1B is associated with root microbiota composition and nitrogen use in field-grown rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hu, R.; Xia, K.; Duan, J.; Wang, Y.; Tsay, Y.F.; Zhang, M. Disruption of the rice nitrate transporter OsNPF2.2 hinders root-to-shoot nitrate transport and vascular development. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, N.; Ma, J.F. Three polarly localized ammonium transporter 1 members are cooperatively responsible for ammonium uptake in rice under low ammonium condition. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 1778–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Silim, S.N.; Okamoto, M.; Siddiqi, M.Y.; Glass, A.D. Differential expression of three members of the AMT1 gene family encoding putative high-affinity NH4+ transporters in roots of Oryza sativa subspecies indica. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranathunge, K.; El-Kereamy, A.; Gidda, S.; Bi, Y.M.; Rothstein, S.J. AMT1;1 transgenic rice plants with enhanced NH4(+) permeability show superior growth and higher yield under optimal and suboptimal NH4(+) conditions. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, Z.; Wei, J.; Qu, H.; Xie, Y.; Xu, G. The OsAMT1.1 gene functions in ammonium uptake and ammonium-potassium homeostasis over low and high ammonium concentration ranges. J. Genet. Genom. 2016, 43, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusano, M.; Tabuchi, M.; Fukushima, A.; Funayama, K.; Diaz, C.; Kobayashi, M.; Hayashi, N.; Tsuchiya, Y.N.; Takahashi, H.; Kamata, A.; et al. Metabolomics data reveal a crucial role of cytosolic glutamine synthetase 1;1 in coordinating metabolic balance in rice. Plant J. 2011, 66, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, M.; Suzuki, R.; Yamazaki, T.; Miyao, M. Comparison of plant-type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylases from rice: Identification of two plant-specific regulatory regions of the allosteric enzyme. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Mauleon, R.; Hu, Z.; Chebotarov, D.; Tai, S.; Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Zheng, T.; Fuentes, R.R.; Zhang, F.; et al. Genomic variation in 3010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice. Nature 2018, 557, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Guo, L.; Ponce, K.; Zhao, X.; Ye, G. Characterization of three indica rice multiparent advanced generation intercross (MAGIC) populations for quantitative trait loci identification. Plant Genome 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.F.; Yamaji, N.; Chen, Z.; Ma, J.F. A tonoplast-localized half-size ABC transporter is required for internal detoxification of aluminum in rice. Plant J. 2012, 69, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Yamaji, N.; Mitani, N.; Yano, M.; Nagamura, Y.; Ma, J.F. A bacterial-type ABC transporter is involved in aluminum tolerance in rice. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Guo, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Li, C.; Qian, Q.; Chen, F.; Geisler, M.; Qi, Y.; et al. OsABCB14 functions in auxin transport and iron homeostasis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant J. 2014, 79, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Tang, R.; Guo, H.; Ke, S.; Teng, B.; Hung, Y.H.; Xu, Z.; Xie, X.M.; Hsieh, T.F.; Zhang, X.Q. A naturally occurring conditional albino mutant in rice caused by defects in the plastid-localized OsABCI8 transporter. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 94, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhang, M.; Ye, H. Mitochondrial, ABC, transporter, ATM3, is, essential, for, cytosolic, iron-sulfur, cluster, assembly. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 2096–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, P.M.; Wray, N.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sklar, P.; McCarthy, M.I.; Brown, M.A.; Yang, J. 10 years of GWAS discovery: Biology, function, and translation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.C.M.; Carrijo, J.; Anjos, R.M.; Cunha, N.B.; Grynberg, P.; Aragão, F.J.L.; Vianna, G.R. The role of microRNAs in NBS-LRR gene expression and its implications for plant immunity and crop development. Transgenic Res. 2024, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Ponce, K.; Qian, Q.; Ye, G. Association mapping of ferrous, zinc, and aluminum tolerance at the seedling stage in Indica Rice using MAGIC populations. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The 3000 Rice Genomes Project. The 3000 rice genomes project. Gigascience 2014, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xin, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, C.; Zhai, L.; Feng, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, W. Genome-wide association analysis of effective tillers in rice under different nitrogen gradients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.X.; Yeung, J.M.Y.; Cherny, S.S.; Sham, P.C. Evaluating the effective numbers of independent tests and significant p-value thresholds in commercial genotyping arrays and public imputation reference datasets. Hum. Genet. 2011, 131, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, K.; Yamamoto, E.; Aya, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Lo, P.C.; Hu, L.; Yamasaki, M.; Yoshida, S.; Kitano, H.; Hirano, K.; et al. Genome-wide association study using whole-genome sequencing rapidly identifies new genes influencing agronomic traits in rice. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Lee, S.S.; Tanaka, T.; Numa, H.; Kim, J.; Kawahara, Y.; Wakimoto, H.; Yang, C.C.; Iwamoto, M.; Abe, T.; et al. Rice Annotation Project Database (RAP-DB): An integrative and interactive database for rice genomics. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilella, A.J.; Blanco-Garcia, A.; Hutter, S.; Rozas, J. VariScan: Analysis of evolutionary patterns from large-scale DNA sequence polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2791–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Traits | QTL | Year | Peak SNP | Allele a | QTL Region (Mb) | p-Value | R2 (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGY | qRGY1 | 2016 | rs1_38797291 | C/A | 38.65–38.95 | 5.19 × 10−5 | 3.25 |
| qRGY6 | 2015 | rs6_2959067 | G/A | 2.81–3.11 | 7.42 × 10−8 | 6.00 | |
| 2016 | rs6_2926939 | A/G | 2.78–3.08 | 5.68 × 10−6 | 6.36 | ||
| qRGY9 | 2016 | rs9_22349187 | G/A | 22.20–22.50 | 2.88 × 10−5 | 3.47 | |
| qRGY11 | 2015 | rs11_9235660 | G/A | 9.09–9.39 | 1.18 × 10−8 | 6.77 | |
| RBM | qRBM6.1 | 2016 | rs6_2123411 | C/T | 1.97–2.27 | 3.72 × 10−6 | 1.95 |
| qRBM6.2 | 2015 | rs6_2945886 | A/G | 2.80–3.10 | 3.17 × 10−6 | 1.98 | |
| RHI | qRHI2.1 | 2015 | rs2_26804244 | T/C | 26.65–26.95 | 5.62 × 10−5 | 3.45 |
| qRHI2.2 | 2015 | rs2_27601760 | A/C | 27.45–27.75 | 7.92 × 10−5 | 3.31 | |
| qRHI3 | 2016 | rs3_2221169 | G/A | 2.07–2.371 | 9.75 × 10−5 | 3.10 | |
| qRHI4 | 2016 | rs4_1056244 | T/C | 0.91–1.21 | 9.82 × 10−5 | 3.09 | |
| qRHI5.1 | 2015 | rs5_26492799 | C/T | 26.34–26.64 | 1.47 × 10−5 | 4.01 | |
| qRHI5.2 | 2016 | rs5_27940204 | A/G | 27.79–28.09 | 9.49 × 10−6 | 4.02 | |
| qRHI6 | 2015 | rs6_2959067 | G/A | 2.81–3.11 | 1.40 × 10−9 | 7.98 | |
| 2016 | rs6_2959067 | G/A | 2.81–3.11 | 8.39 × 10−6 | 4.07 | ||
| qRHI7 | 2015 | rs7_29638146 | C/T | 29.49–29.79 | 7.91 × 10−6 | 4.27 | |
| qRHI11 | 2015 | rs11_9235660 | G/A | 9.09–9.39 | 2.37 × 10−9 | 7.74 | |
| REPN | qREPN3 | 2016 | rs3_3821913 | T/C | 3.67–3.97 | 9.91 × 10−5 | 2.77 |
| qREPN6 | 2016 | rs6_397816 | A/G | 0.25–0.55 | 1.21 × 10−4 | 2.70 | |
| qREPN7.1 | 2016 | rs7_11632495 | T/C | 11.48–11.78 | 1.25 × 10−4 | 2.69 | |
| qREPN7.2 | 2016 | rs7_12808093 | T/C | 12.66–12.96 | 1.25 × 10−4 | 2.69 | |
| qREPN7.3 | 2016 | rs7_14490553 | T/G | 14.34–14.64 | 1.25 × 10−4 | 2.69 | |
| qREPN7.4 | 2016 | rs7_15026705 | C/T | 14.88–15.18 | 8.25 × 10−5 | 2.84 | |
| qREPN7.5 | 2016 | rs7_25930301 | T/C | 25.78–26.08 | 1.00 × 10−4 | 2.77 | |
| qREPN7.6 | 2015 | rs7_27630228 | T/A | 27.48–27.78 | 1.83 × 10−5 | 3.40 | |
| qREPN8 | 2015 | rs8_5126577 | C/T | 4.98–5.28 | 4.88 × 10−5 | 3.05 | |
| RTGN | qRTGN2 | 2016 | rs2_24629837 | A/G | 24.48–24.78 | 1.41 × 10−4 | 2.72 |
| qRTGN3 | 2016 | rs3_5899301 | T/G | 5.75–6.05 | 1.13 × 10−4 | 2.80 | |
| qRTGN6 | 2015 | rs6_2928178 | G/A | 2.78–3.08 | 5.87 × 10−5 | 3.09 | |
| RSF | qRSF4 | 2015 | rs4_31547230 | G/A | 31.40–31.70 | 1.14 × 10−10 | 8.21 |
| qRSF10 | 2015 | rs10_16807912 | A/G | 16.66–16.96 | 1.02 × 10−4 | 2.91 | |
| qRSF11 | 2015 | rs11_17412899 | C/T | 17.26–17.56 | 1.22 × 10−4 | 2.84 | |
| qRSF12 | 2016 | rs12_7593705 | G/A | 7.44–7.74 | 3.40 × 10−6 | 4.08 | |
| RTGW | qRTGW6 | 2016 | rs6_2783620 | A/G | 2.63–2.93 | 1.43 × 10−4 | 1.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Zhai, L.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L.; Zhu, S.; Shen, C.; Jia, J.; Chen, K.; Xu, J. Identification of Advantaged Genes for Low-Nitrogen-Tolerance-Related Traits in Rice Using a Genome-Wide Association Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125749
Zhang Z, Zhai L, Liu Y, Tian L, Zhu S, Shen C, Jia J, Chen K, Xu J. Identification of Advantaged Genes for Low-Nitrogen-Tolerance-Related Traits in Rice Using a Genome-Wide Association Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125749
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiyuan, Laiyuan Zhai, Yuzhuo Liu, Lin Tian, Shuangbing Zhu, Congcong Shen, Juqing Jia, Kai Chen, and Jianlong Xu. 2025. "Identification of Advantaged Genes for Low-Nitrogen-Tolerance-Related Traits in Rice Using a Genome-Wide Association Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125749
APA StyleZhang, Z., Zhai, L., Liu, Y., Tian, L., Zhu, S., Shen, C., Jia, J., Chen, K., & Xu, J. (2025). Identification of Advantaged Genes for Low-Nitrogen-Tolerance-Related Traits in Rice Using a Genome-Wide Association Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125749






