Characterizing SV40-hTERT Immortalized Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells as Model System for Mechanical Stretch-Induced Lung Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Basic Characterization of the HLMVEC/SVTERT289 Cell Line
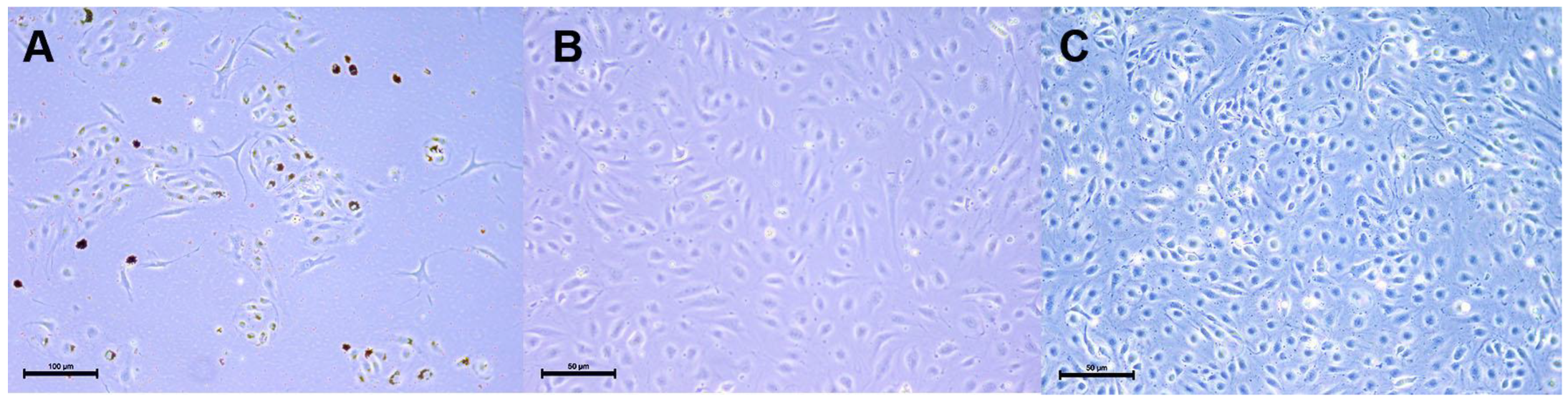
2.1.1. HLMVEC and HLMVEC/SVTERT289 Cell Morphology and Transgene Expression
2.1.2. Microvascular Endothelial Marker Expression
2.1.3. Tube Formation of HLMVEC/SVTERT289 Cells
2.2. Cyclic Mechanical Stretch as In Vitro Model for VILI
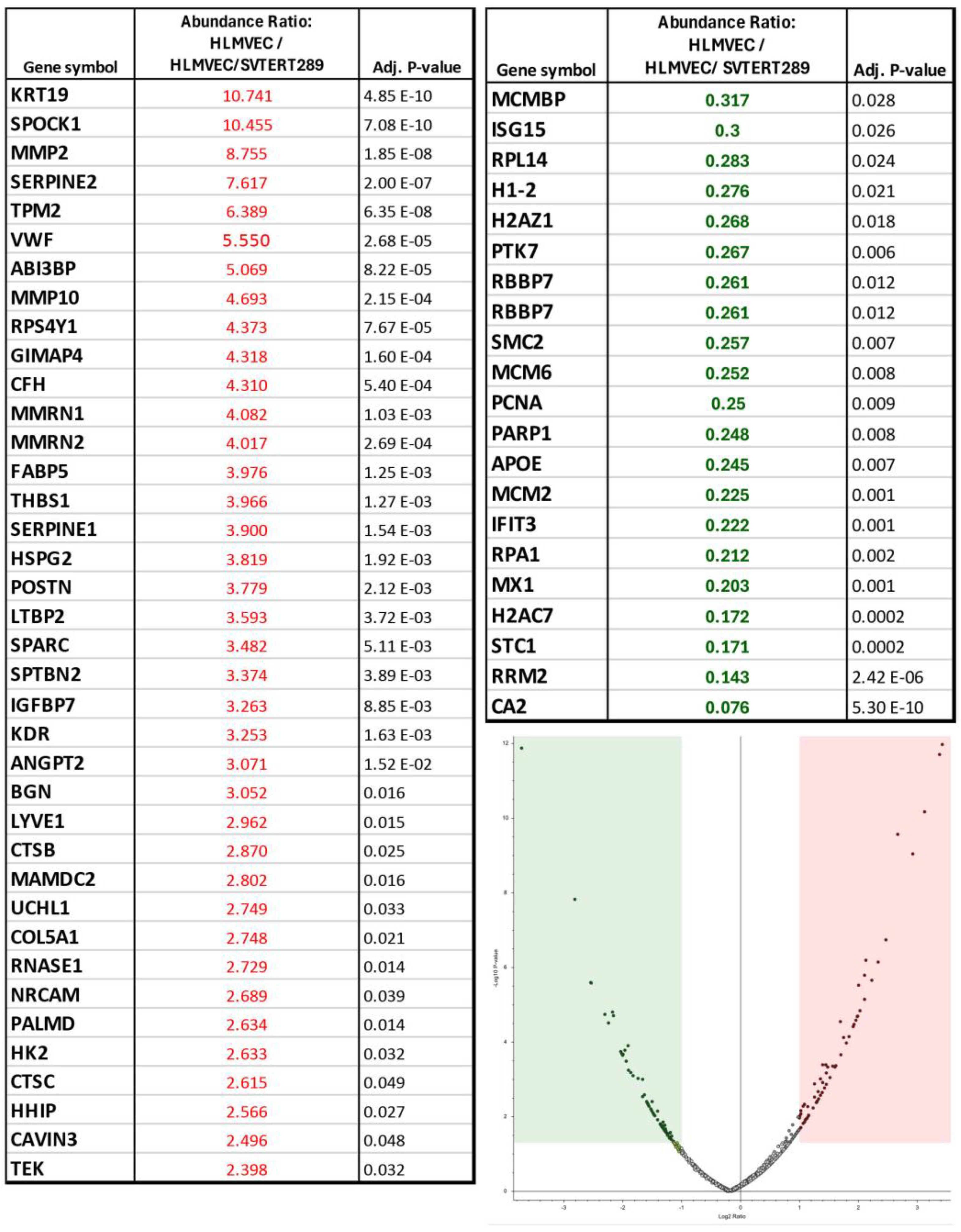
2.2.1. Analysis of Cellular Gene Expression
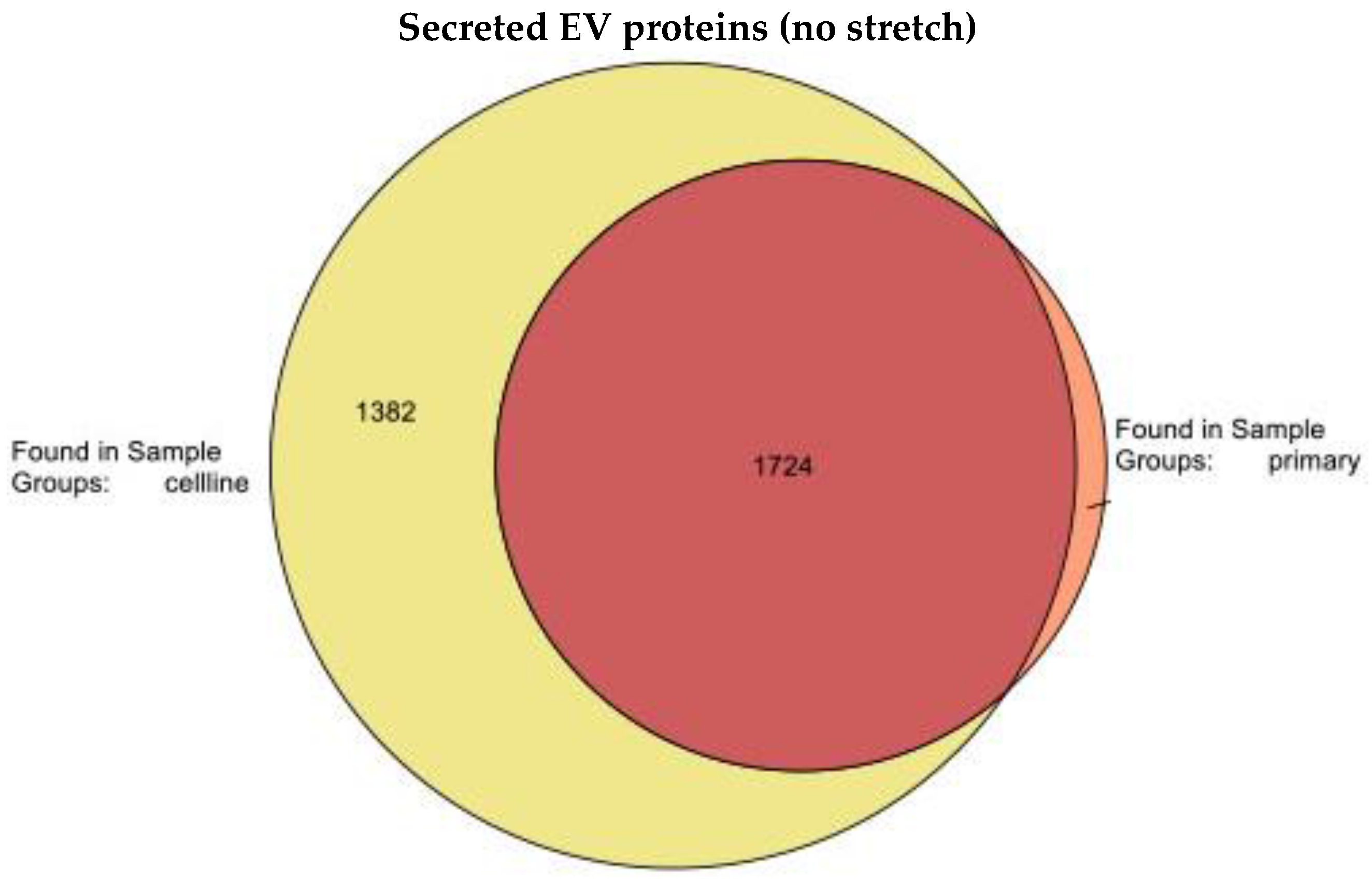
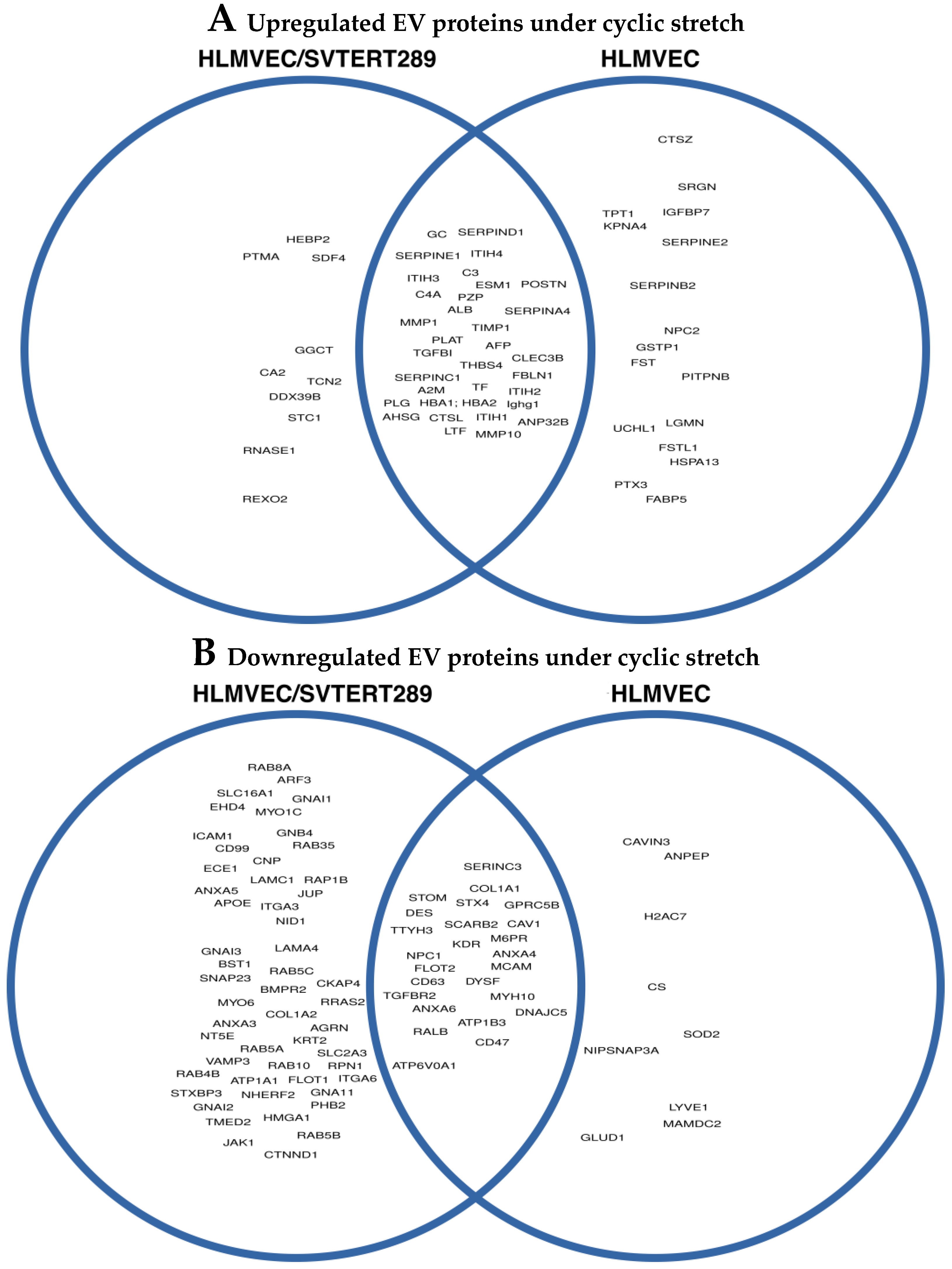
2.2.2. Release of Extracellular Vesicles: Proteomic Analysis of EVs
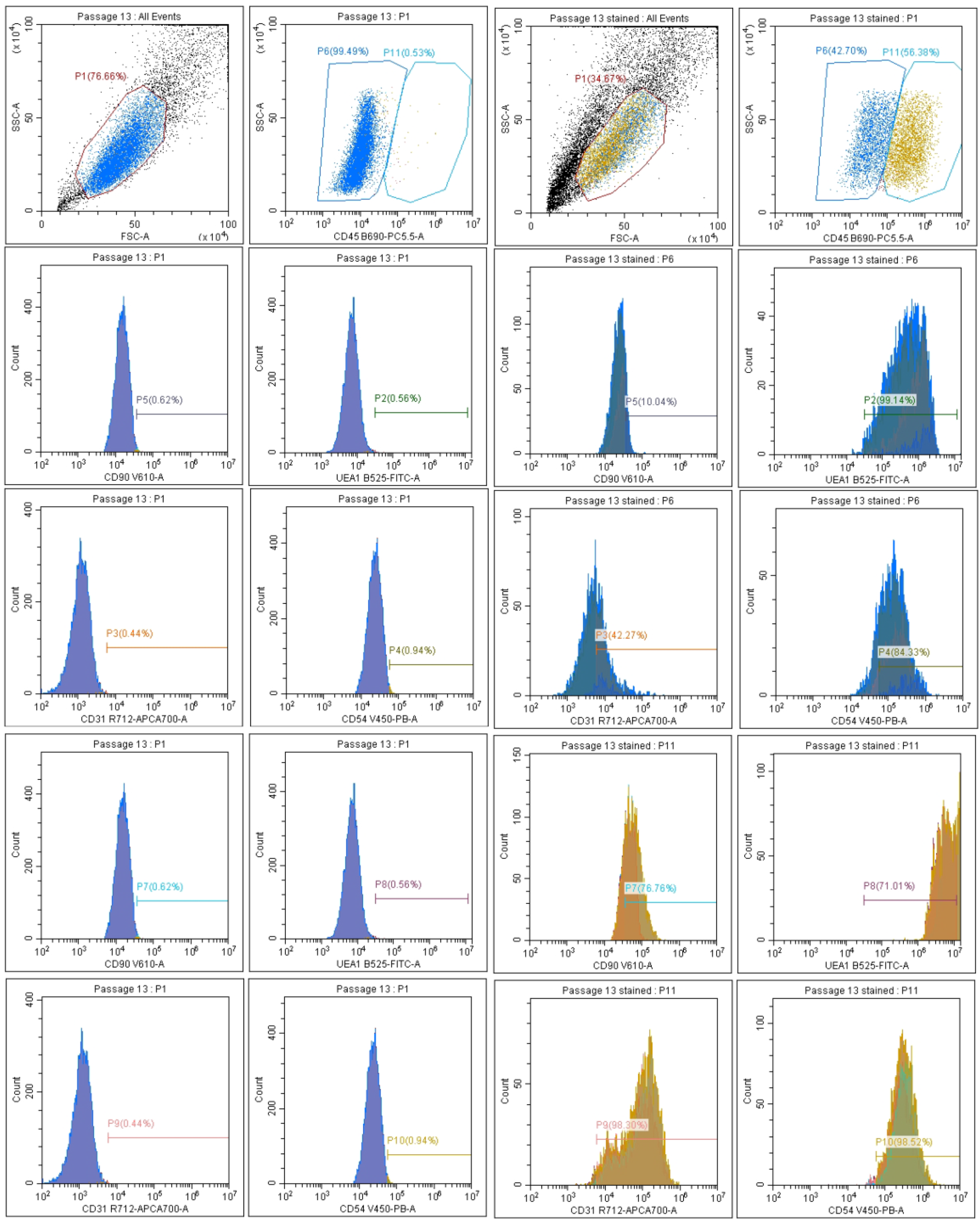
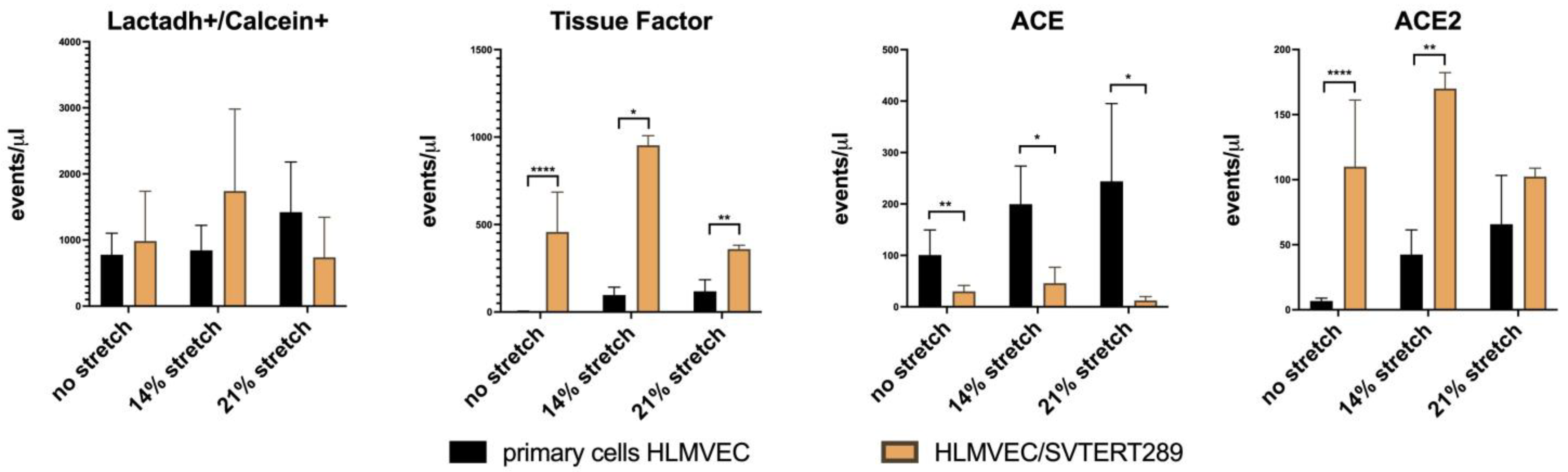
2.2.3. Release of Extracellular Vesicles: Flow Cytometry Analysis of EV Surface Proteins
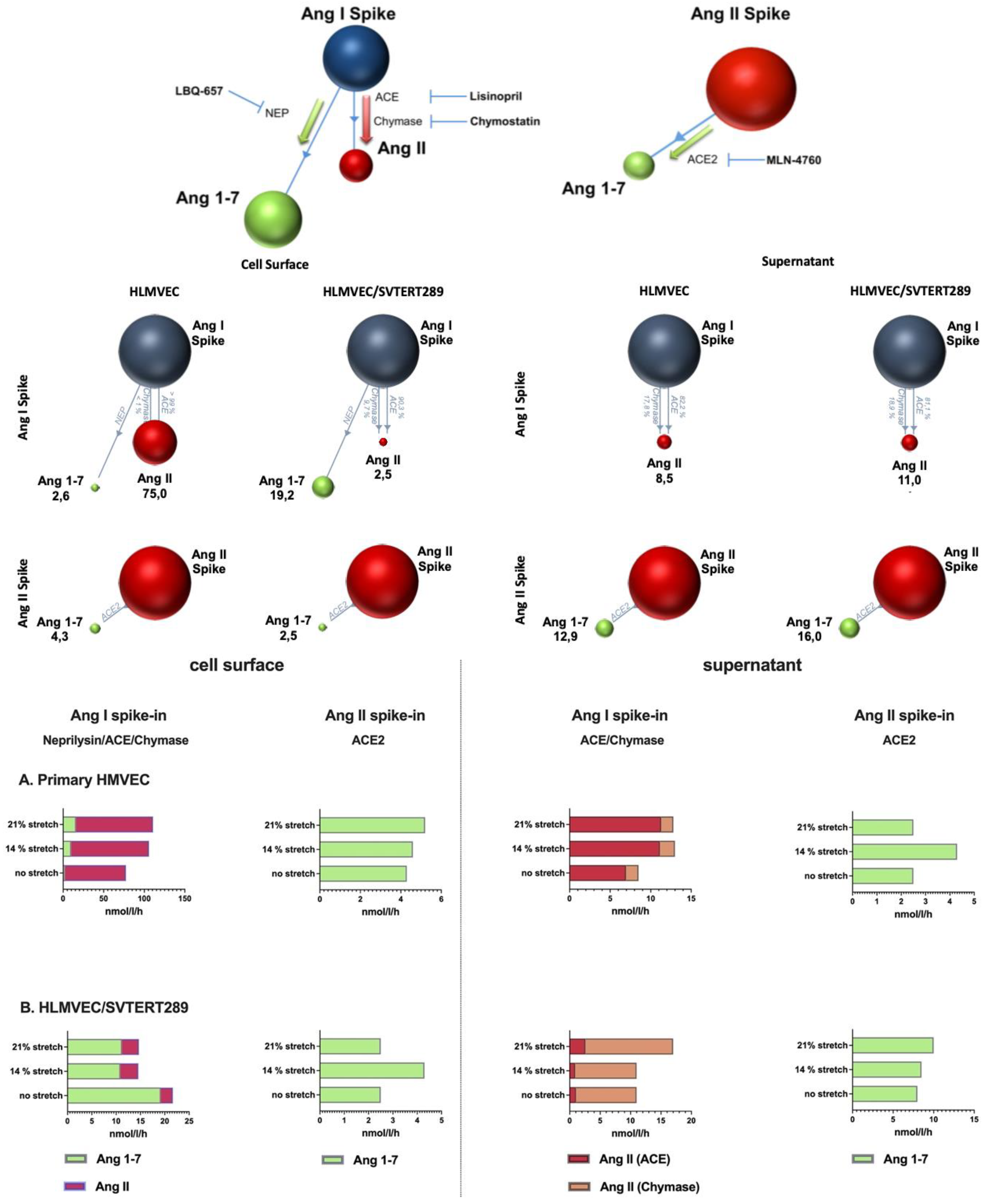
2.2.4. Analysis of Components of the Renin–Angiotensin System in the VILI Model (Cell Surface and EVs)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of Primary HLMVECs and Cell Culture
4.2. Generation of the HLMVEC/SVTERT289 Cell Line
4.3. Basic Characterization of the Cell Line
4.3.1. Flow Cytometry of Surface Labeled Cells
4.3.2. Immunofluorescence
4.3.3. TRAP Assay
4.3.4. Tube Formation Assay
4.3.5. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles
4.3.6. Flow Cytometry of EVs
4.3.7. Proteomic Analysis of EVs
Sample Preparation
LC-MS/MS Analysis
Data Analysis and Statistics
4.4. In Vitro Model of Mechanical Stress Exposure
Cell Stretching-Flexcell® System
4.5. Other Analytical Methods
4.5.1. Western Blot Analysis
4.5.2. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.5.3. Activity Analysis of RAS Enzymes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Travaglini, K.J.; Nabhan, A.N.; Penland, L.; Sinha, R.; Gillich, A.; Sit, R.V.; Chang, S.; Conley, S.D.; Mori, Y.; Seita, J.; et al. A molecular cell atlas of the human lung from single-cell RNA sequencing. Nature 2020, 587, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkema, L.; Ramirez-Suastegui, C.; Strobl, D.C.; Gillett, T.E.; Zappia, L.; Madissoon, E.; Markov, N.S.; Zaragosi, L.E.; Ji, Y.; Ansari, M.; et al. An integrated cell atlas of the lung in health and disease. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1563–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, B.; Salton, F.; Braga, L.; Wade, B.; Confalonieri, P.; Volpe, M.C.; Baratella, E.; Maiocchi, S.; Confalonieri, M. The History and Mystery of Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells: Focus on Their Physiologic and Pathologic Role in Lung. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspal, M.; Zemans, R.L. Mechanisms of ATII-to-ATI Cell Differentiation during Lung Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillich, A.; Zhang, F.; Farmer, C.G.; Travaglini, K.J.; Tan, S.Y.; Gu, M.; Zhou, B.; Feinstein, J.A.; Krasnow, M.A.; Metzger, R.J. Capillary cell-type specialization in the alveolus. Nature 2020, 586, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, J.; Dekan, A.; Niihori, M.; McClain, N.; Varghese, M.; Bharti, D.; Lawal, O.S.; Padilla-Rodrigez, M.; Yi, D.; Dai, Z.; et al. Novel Populations of Lung Capillary Endothelial Cells and Their Functional Significance. Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Harley, C.B. Telomere loss: Mitotic clock or genetic time bomb? Mutat. Res. 1991, 256, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Historical claims and current interpretations of replicative aging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodnar, A.G.; Ouellette, M.; Frolkis, M.; Holt, S.E.; Chiu, C.P.; Morin, G.B.; Harley, C.B.; Shay, J.W.; Lichtsteiner, S.; Wright, W.E. Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science 1998, 279, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Gschwandtner, M.; Strajeriu, A.; Elbe-Burger, A.; Grillari, J.; Grillari-Voglauer, R.; Greiner, G.; Golabi, B.; Tschachler, E.; Mildner, M. Establishment of keratinocyte cell lines from human hair follicles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, B.R.; Steele, I.A.; Edmondson, R.J.; Zwolinski, S.A.; Saretzki, G.; von Zglinicki, T.; O'Hare, M.J. Immortalisation of human ovarian surface epithelium with telomerase and temperature-sensitive SV40 large T antigen. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 288, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von During, S.; Parhar, K.K.S.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Urner, M.; Kim, S.J.; Munshi, L.; Liu, K.; Fan, E. Understanding ventilator-induced lung injury: The role of mechanical power. J. Crit. Care 2025, 85, 154902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaver, D.P., 3rd; Nieman, G.F.; Gatto, L.A.; Cereda, M.; Habashi, N.M.; Bates, J.H.T. The POOR Get POORer: A Hypothesis for the Pathogenesis of Ventilator-induced Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2020, 202, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Krenn, K.; Tripp, T.; Tretter, V.; Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; Kraft, F.; Podesser, B.K.; Zhu, Y.; Poglitsch, M.; Domenig, O.; et al. Tidal Volume-Dependent Activation of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Experimental Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, e696–e706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, D.; Xu, W.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, J.; Fang, Y. Vascular endothelial glycocalyx shedding in ventilator-induced lung injury in rats. Microvasc. Res. 2024, 153, 104658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaporidi, K.; Francis, R.C.; Bloch, K.D.; Zapol, W.M. Nitric oxide synthase 3 contributes to ventilator-induced lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L150–L159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zemskov, E.A.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Yegambaram, M.; Wu, X.; Garcia-Flores, A.; Song, S.; Tang, H.; Kangath, A.; et al. Activation of the mechanosensitive Ca2+ channel TRPV4 induces endothelial barrier permeability via the disruption of mitochondrial bioenergetics. Redox Biol. 2021, 38, 101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letsiou, E.; Sammani, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, T.; Quijada, H.; Moreno-Vinasco, L.; Dudek, S.M.; Garcia, J.G. Pathologic mechanical stress and endotoxin exposure increases lung endothelial microparticle shedding. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krump-Konvalinkova, V.; Bittinger, F.; Unger, R.E.; Peters, K.; Lehr, H.A.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. Generation of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell lines. Lab. Investig. 2001, 81, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, R.E.; Krump-Konvalinkova, V.; Peters, K.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. In vitro expression of the endothelial phenotype: Comparative study of primary isolated cells and cell lines, including the novel cell line HPMEC-ST1.6R. Microvasc. Res. 2002, 64, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.T.; Ferreira Melo, F.U.; Malta, T.M.; Rodrigues, E.S.; Placa, J.R.; Silva, W.A., Jr.; Panepucci, R.A.; Covas, D.T.; de Oliveira Rodrigues, C.; Kashima, S. Endothelial cells from different anatomical origin have distinct responses during SNAIL/TGF-beta2-mediated endothelial-mesenchymal transition. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 4065–4081. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nasim, S.; Wylie-Sears, J.; Gao, X.; Peng, Q.; Zhu, B.; Chen, K.; Chen, H.; Bischoff, J. CD45 Is Sufficient to Initiate Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Endothelial Cells-Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2023, 43, e124–e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Arulsamy, K.; Lu, Y.W.; Wu, H.; Zhu, B.; Singh, B.; Cui, K.; Wylie-Sears, J.; Li, K.; Wong, S.; et al. Novel Role of Endothelial CD45 in Regulating Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Atherosclerosis. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wandel, E.; Saalbach, A.; Sittig, D.; Gebhardt, C.; Aust, G. Thy-1 (CD90) is an interacting partner for CD97 on activated endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, S.; Dethlefsen, I.; Hagner-Benes, S.; Marsh, L.M.; Garn, H.; Konig, P. Visualization of intrapulmonary lymph vessels in healthy and inflamed murine lung using CD90/Thy-1 as a marker. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gross, C.; Desai, A.A.; Zemskov, E.; Wu, X.; Garcia, A.N.; Jacobson, J.R.; Yuan, J.X.; Garcia, J.G.; Black, S.M. Endothelial cell signaling and ventilator-induced lung injury: Molecular mechanisms, genomic analyses, and therapeutic targets. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, L452–L476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Debbi, L.; Zohar, B.; Samuel, R.; Arzi, R.S.; Fried, A.I.; Carmon, T.; Shevach, D.; Redenski, I.; Schlachet, I.; et al. Stimulating Extracellular Vesicles Production from Engineered Tissues by Mechanical Forces. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.; Papoutsakis, E.T. The role of biomechanical stress in extracellular vesicle formation, composition and activity. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 66, 108158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachetto, A.T.A.; Archibald, S.J.; Hisada, Y.; Rosell, A.; Havervall, S.; van Es, N.; Nieuwland, R.; Campbell, R.A.; Middleton, E.A.; Rondina, M.T.; et al. Tissue factor activity of small and large extracellular vesicles in different diseases. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 7, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, S.P.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Stokol, T. Tissue Factor-Expressing Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Activate Quiescent Endothelial Cells via Protease-Activated Receptor-1. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankhe, R.; Pai, S.R.K.; Kishore, A. Tumour suppression through modulation of neprilysin signaling: A comprehensive review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 891, 173727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughey, G.H. Mast cell tryptases and chymases in inflammation and host defense. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 217, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Wei, C.C.; Powell, P.C.; Bradley, W.E.; Ahmad, S.; Ferrario, C.M.; Collawn, J.F.; Dell'Italia, L.J. Increased fibroblast chymase production mediates procollagen autophagic digestion in volume overload. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 92, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell'Italia, L.J.; Collawn, J.F.; Ferrario, C.M. Multifunctional Role of Chymase in Acute and Chronic Tissue Injury and Remodeling. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Deep, G.; Punzi, H.A.; Su, Y.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, S.; Saha, A.K.; Wright, K.N.; VonCannon, J.L.; et al. Chymase Activity in Plasma and Urine Extracellular Vesicles in Primary Hypertension. Kidney360 2024, 5, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, L.S.; Dodd, S.; Dougall, I.G.; Tomlinson, W.; Lordan, J.; Fisher, A.J.; Corris, P.A. Isolation and characterisation of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells from patients with severe emphysema. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.J.; Garbett, P.K.; Nissen, B.; Schrieber, L. Binding of human endothelium to Ulex europaeus I-coated Dynabeads: Application to the isolation of microvascular endothelium. J. Cell Sci. 1990, 96 Pt 2, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voglauer, R.; Grillari, J.; Fortschegger, K.; Wieser, M.; Sterovsky, T.; Gunsberg, P.; Katinger, H.; Pfragner, R. Establishment of human fibroma cell lines from a MEN1 patient by introduction of either hTERT or SV40 early region. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 26, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, J.; Olson, L.; Schaffner, W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell 1983, 33, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaubmayr, W.; Hochreiter, B.; Hunyadi-Gulyas, E.; Riegler, L.; Schmidt, K.; Tiboldi, A.; Moser, B.; Klein, K.U.; Krenn, K.; Scharbert, G.; et al. The Proteome of Extracellular Vesicles Released from Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelium Reveals Impact of Oxygen Conditions on Biotrauma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ß-Actin | CATGTACGTTGCTATCCAGGC | CTCCTTAATGTCACGCACGAT | 59.8/57.9 |
| ACE | GGAGGAATATGACCGGACATCC | TGGTTGGCTATTTGCATGTTCTT | 62.1/57.1 |
| neprilysin | AGAAGAAACAGCGGATGGACTCC | CATAGAGTGCGATCATTGTCACA | 60.3/58.9 |
| Interleukin-6 | ACTCACCTCTTCAGAACGAATTG | CCATCTTTGGAAGGTTCAGGTTG | 58.9/60.6 |
| VEGFA | AGGGCAGAATCATCACGAAGT | AGGGTCTCGATTGGATGGCA | 57.9/59.4 |
| VE-PTP | GGGCTCACCCCTGTAACTTTAGC | TCTATCCGAAAGGTAGGGCAC | 62.1/59.8 |
| PECAM1 | AACAGTGTTGACATGAAGAGCC | TGTAAAACAGCAGTCATCCTT | 58.4/56.5 |
| ICAM1 | ATGCCCAGACATCTGTGTCC | GGGGTCTCTATGCCCAACAA | 59.4/59.4 |
| ZO1/TJP1 | CAACATACAGTGACGCTTCACA | CACTATTGACGTTTCCCCACTC | 58.4/60.3 |
| OCLN | ACAAGCGGTTTTATCCAGAGTC | GTCATCCACAGGCGAAGTTAAT | 58.4/58.4 |
| RAGE | GTGTCCTTCCCAACGGCTC | ATTGCCTGGCACCGGAAAA | 61.0/56.7 |
| Angpt2 | AACTTTCGGAAGAGCATGGAC | CGAGTCATCGTATTCGAGCGG. | 57.9/61.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hochreiter, B.; Lindner, C.; Postl, M.; Hunyadi-Gulyas, E.; Darula, Z.; Domenig, O.; Sharma, S.; Lang, I.M.; Kiss, A.; Spittler, A.; et al. Characterizing SV40-hTERT Immortalized Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells as Model System for Mechanical Stretch-Induced Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020683
Hochreiter B, Lindner C, Postl M, Hunyadi-Gulyas E, Darula Z, Domenig O, Sharma S, Lang IM, Kiss A, Spittler A, et al. Characterizing SV40-hTERT Immortalized Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells as Model System for Mechanical Stretch-Induced Lung Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020683
Chicago/Turabian StyleHochreiter, Beatrix, Claudia Lindner, Matthias Postl, Eva Hunyadi-Gulyas, Zsuzsanna Darula, Oliver Domenig, Smriti Sharma, Irene M. Lang, Attila Kiss, Andreas Spittler, and et al. 2025. "Characterizing SV40-hTERT Immortalized Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells as Model System for Mechanical Stretch-Induced Lung Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020683
APA StyleHochreiter, B., Lindner, C., Postl, M., Hunyadi-Gulyas, E., Darula, Z., Domenig, O., Sharma, S., Lang, I. M., Kiss, A., Spittler, A., Hoetzenecker, K., Reindl-Schwaighofer, R., Krenn, K., Ullrich, R., Wieser, M., Grillari-Voglauer, R., & Tretter, V. (2025). Characterizing SV40-hTERT Immortalized Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells as Model System for Mechanical Stretch-Induced Lung Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020683










