Predaceous and Phytophagous Pentatomidae Insects Exhibit Contrasting Susceptibilities to Imidacloprid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
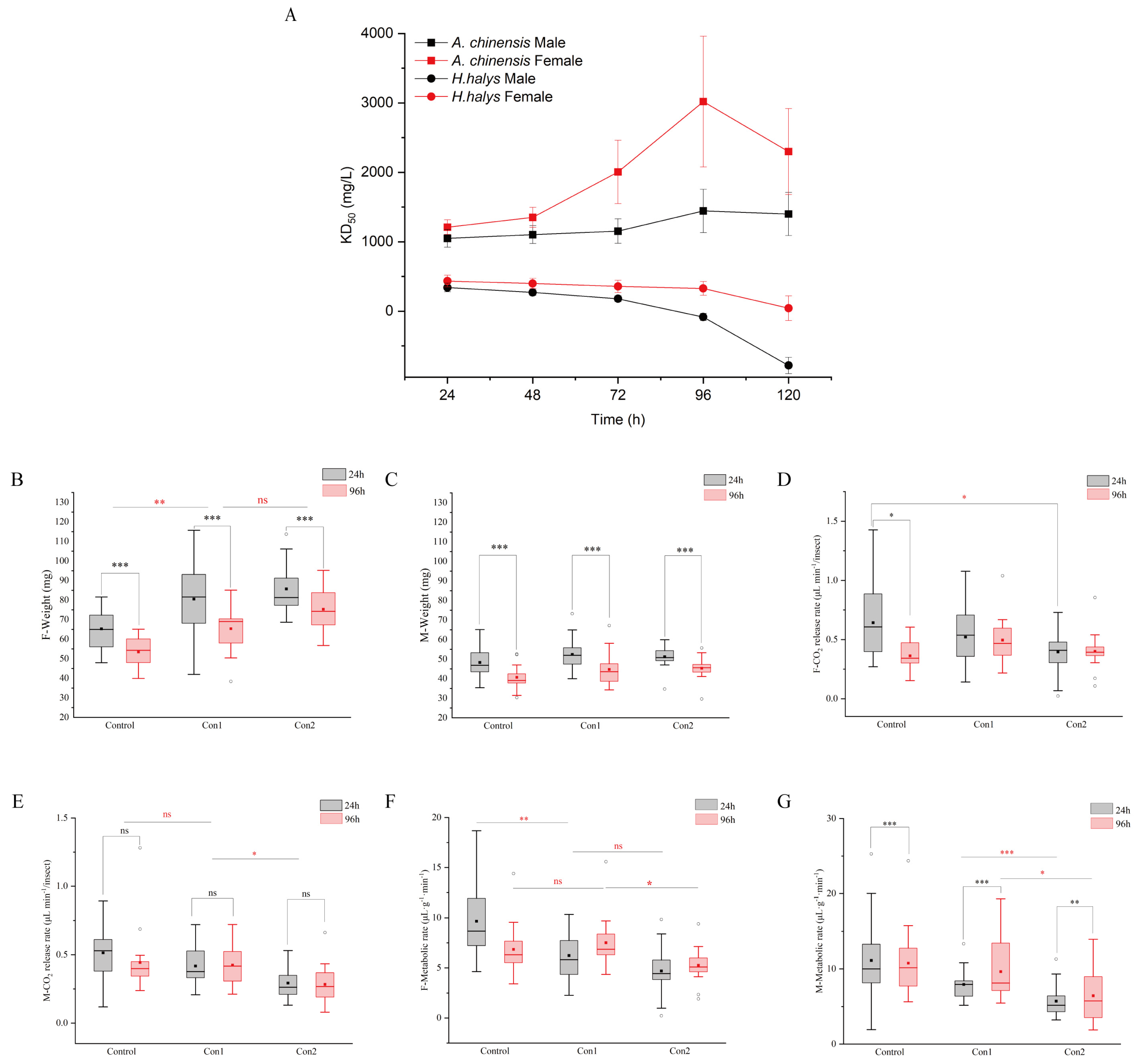
2.1. Acute Toxicity of Imidacloprid and Predatory Insect A. chinensis Recovery
2.2. Respiratory Metabolism After Imidacloprid Administration
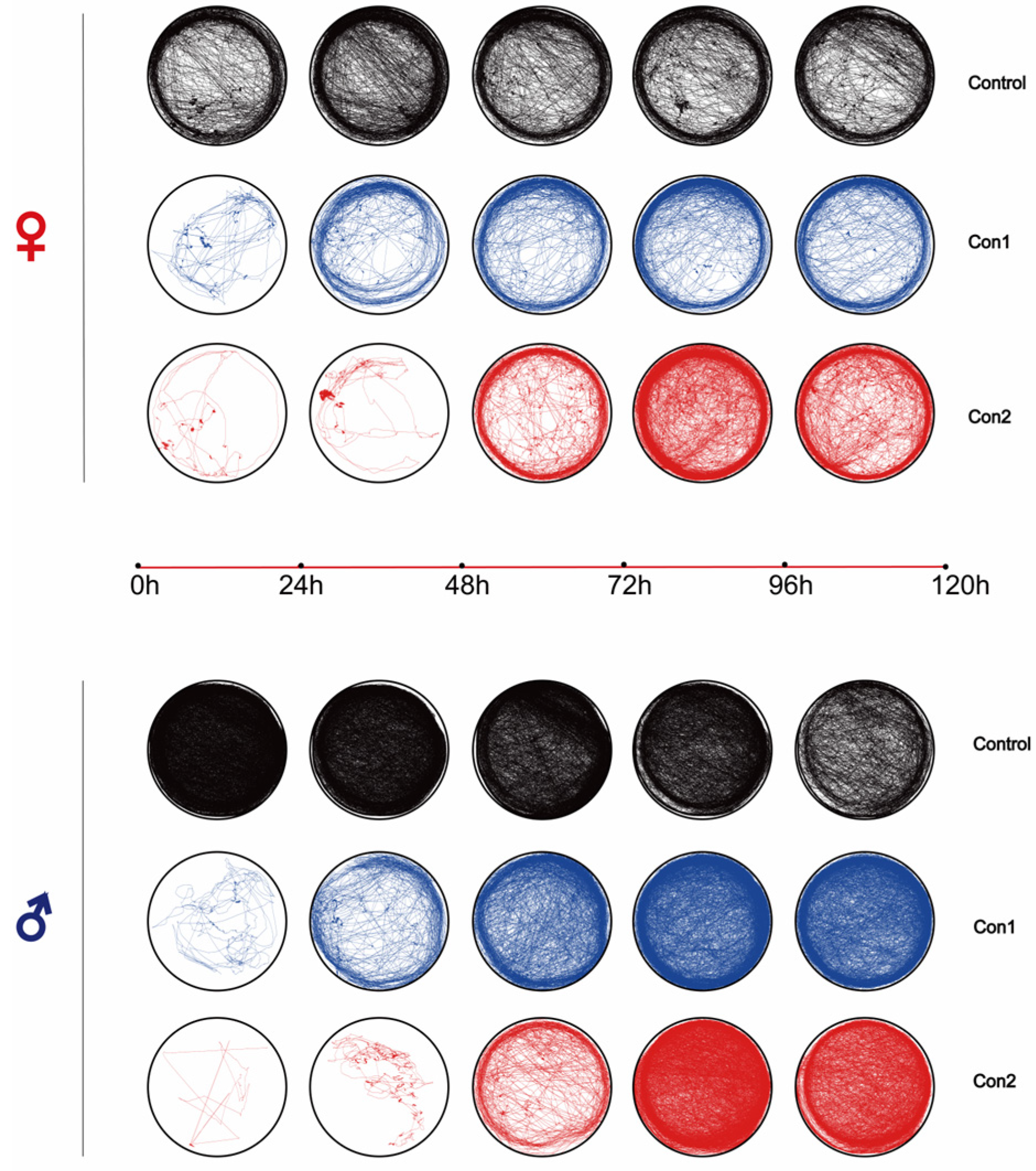
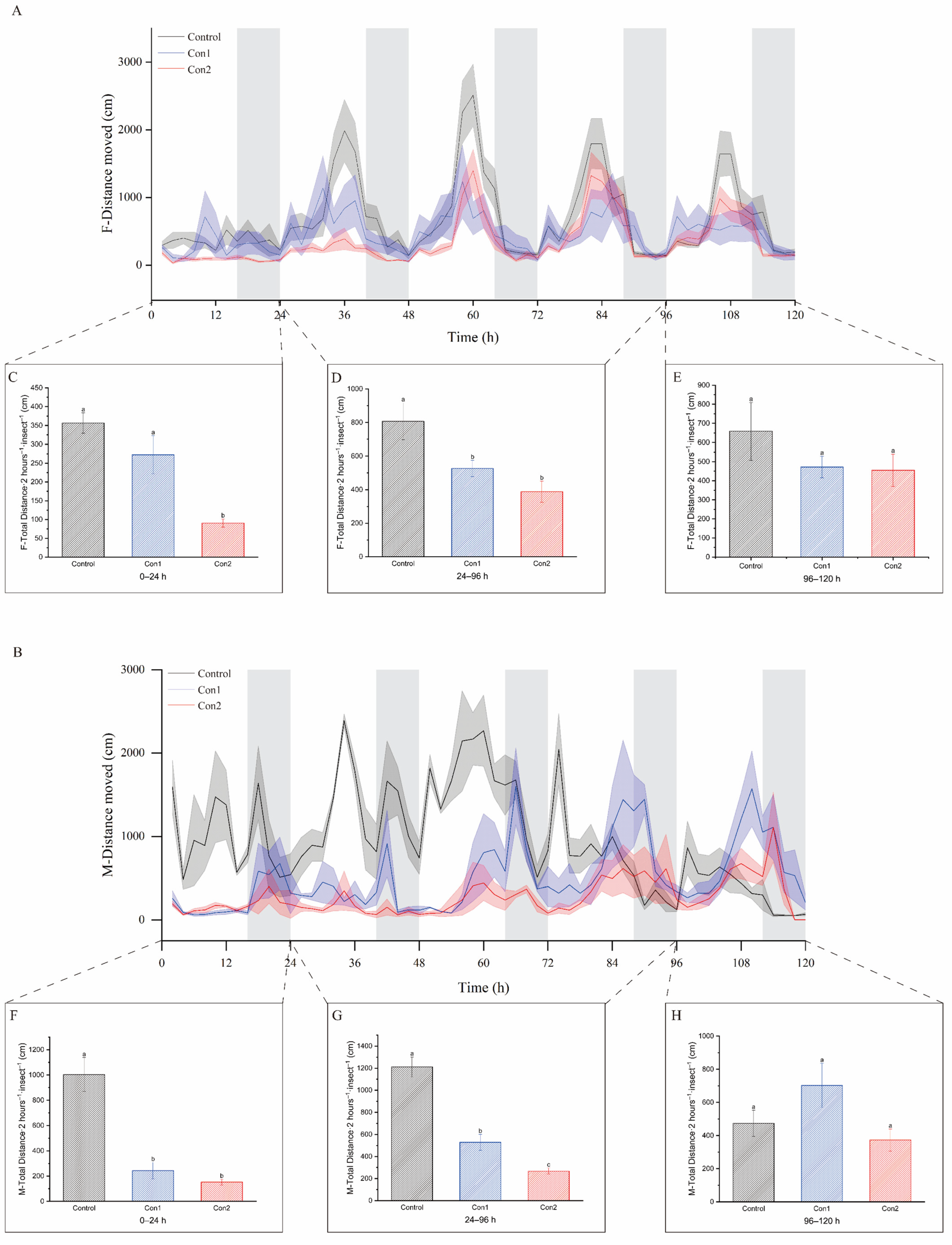
2.3. Locomotion Recovery After Imidacloprid Treatment
2.4. Reproductive Performance of A. chinensis After Recovery
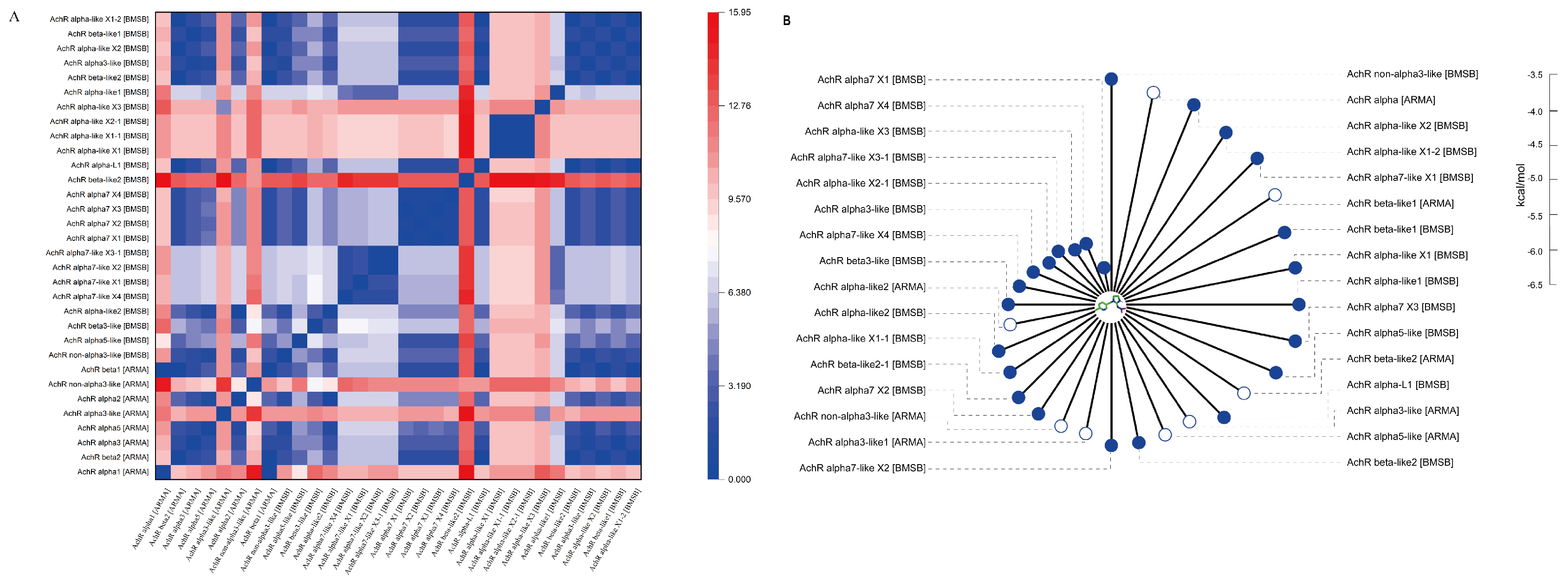
2.5. Phylogenetic and Domain Organization Analysis of nAchR in A. chinensis and H. halys
2.6. Binding Ability of Imidacloprid to Acetylcholine Receptors of A. chinensis and H. halys
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Cultivation
4.2. Toxicity Bioassays
4.3. Respiratory Metabolism Rate
4.4. Locomotion Tracking
4.5. Reproductive Performance of A. chinensis
4.6. Phylogenetic and Domain Organization Analysis of nAchR
4.7. Homology Modeling and Docking
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, Q.C.; Chen, H.; Babendreier, D.; Zhang, J.P.; Zhang, F.; Dai, X.Y.; Sun, Z.W.; Shi, Z.P.; Dong, X.L.; Wu, G.A.; et al. Improved control of Frankliniella occidentalis on greenhouse pepper through the integration of Orius sauteri and neonicotinoid insecticides. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.M.; Petek, M.; Gerasymenko, I.; Jutersek, M.; Baebler, S.; Kallam, K.; Giménez, E.M.; Gondolf, J.; Nordmann, A.; Gruden, K.; et al. Insect pest management in the age of synthetic biology. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Tamò, M.; Subramanian, S. The case for integrated pest management in Africa: Transition from a pesticide-based approach. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2022, 54, 100970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Smagghe, G.; Stark, J.D.; Desneux, N. Pesticide-induced stress in arthropod pests for optimized integrated pest management programs. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.C.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Gonçalves, W.G.; Freire, A.F.P.A.; Zanuncio, J.C.; Bozdoğan, H.; Serrão, J.E. Toxicity and cytotoxicity of the insecticide imidacloprid in the midgut of the predatory bug, Podisus nigrispinus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Agudo, M.; Tooker, J.F.; Dicke, M.; Tena, A. Insecticide-contaminated honeydew: Risks for beneficial insects. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2022, 97, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, R.H.; Zhang, S.N.; Gray, J.R. Neonicotinoid and sulfoximine pesticides differentially impair insect escape behavior and motion detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5510–5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Leppanen, C. Known target and nontarget effects of the novel neonicotinoid cycloxaprid to arthropods: A systematic review. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2020, 16, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; He, D.; Men, X.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, S.; Tao, L.; Yu, C. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of acetamiprid and imidacloprid on the predatory bug Orius sauteri (Poppius) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheets, L.P. Hayes’ Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. In Chapter 95—Imidacloprid: A Neonicotinoid Insecticide; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 2055–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Elbert, A.; Haas, M.; Springer, B.; Thielert, W.; Nauen, R. Applied aspects of neonicotinoid uses in crop protection. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Schindler, M.; Elbert, A. Overview of the status and global strategy for neonicotinoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, C.; Denholm, I.; Williamson, M.S.; Nauen, R. The global status of insect resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueh Tai, F.; Pattemore, D.E.; Jochym, M.; Beggs, J.R.; Northcott, G.L.; Mortensen, A.N. Honey bee toxicological responses do not accurately predict environmental risk of imidacloprid to a solitary ground-nesting bee species. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugnes, R.; Russo, C.; Orlo, E.; Lavorgna, M.; Isidori, M. Imidacloprid: Comparative toxicity, DNA damage, ROS production and risk assessment for aquatic non-target organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Selective toxicity of neonicotinoids attributable to specificity of insect and mammalian nicotinic receptors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckingham, S.D.; Balk, M.L.; Lummis, S.C.R.; Jewess, P.; Sattelle, D.B. Actions of nitromethylenes on an alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine-receptor. Neuropharmacology 1995, 34, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, K.; Buckingham, S.D.; Kleier, D.; Rauh, J.J.; Grauso, M.; Sattelle, D.B. Neonicotinoids: Insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thany, S.H.; Lenaers, G.; Raymond-Delpech, V.; Sattelle, D.B.; Lapied, B. Exploring the pharmacological properties of insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoids and other insect nicotinic receptor competitive modulators: Progress and prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.K.; Sattelle, D.B. Functional genomics of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Bioessays 2004, 26, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somers, J.; Nguyen, J.; Lumb, C.; Batterham, P.; Perry, T. In vivo functional analysis of the Drosophila melanogaster nicotinic acetylcholine receptor Dα6 using the insecticide spinosad. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 64, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamaon, K.; Smalla, K.H.; Thomas, U.; Gundelfinger, E.D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of Drosophila: Three subunits encoded by genomically linked genes can co-assemble into the same receptor complex. J. Neurochem. 2002, 80, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.W.; Wu, Y.F.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhao, P.; Chen, Z.; Song, F.; Li, H.; Cai, W.Z. Comparative mitogenomics and phylogenetic analyses of Pentatomoidea (Hemiptera: Heteroptera). Genes 2021, 12, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, R.L.; Pezzini, D.T.; Michel, A.P.; Hunt, T.E. Identification, biology, impacts, and management of stink bugs (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) of soybean and corn in the Midwestern United States. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2017, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, G. The biology and control of an emerging shield bug pest, Pentatoma rufipes (L.) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Agric. For. Entomol. 2020, 22, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Cusachs, M.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Jung, S. Taxonomic review of the predatory stink bugs of the Korean Peninsula (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae: Asopinae), with a key to the Korean species and a discussion of their usefulness as biological control agents. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2020, 23, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, M.E.; Bansal, R.; Benoit, J.B.; Blackburn, M.B.; Chao, H.; Chen, M.; Cheng, S.; Childers, C.; Dinh, H.; Doddapaneni, H.V.; et al. Brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stal), genome: Putative underpinnings of polyphagy, insecticide resistance potential and biology of a top worldwide pest. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Ma, L.; Cheng, H.; Lin, C.; Fu, L.; Chen, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, C. Genome-wide analysis of gustatory receptor genes and identification of the fructose gustatory receptor in Arma chinensis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Lin, C.; Xu, W.; Cheng, H.; Liu, D.; Ma, L.; Su, Z.; Yan, X.; Dong, X.; Liu, C. Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of Predatory Arma chinensis. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.Y.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhang, L.S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Chen, H.Y. Taxonomic and bionomic notes on Arma chinensis (Fallou) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae: Asopinae). Zootaxa 2012, 3382, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.X.; Chen, J.H.; Mi, Q.Q.; Li, W.J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.P. Development, fecundity and nymph morphology, of the Brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Stål). Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2020, 57, 392–399. [Google Scholar]
- Panizzi, A.R. Growing problems with stink bugs (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae): Species invasive to the U.S. and potential neotropical invaders. Am. Entomol. 2015, 61, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liao, J.; Li, C. Bottom-up effects of drought on the growth and development of potato, Leptinotarsa decemlineata Say and Arma chinensis Fallou. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 4353–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vitantonio, C.; Depalo, L.; Marchetti, E.; Dindo, M.L.; Masetti, A. Response of the European ladybird Adalia bipunctata and the invasive Harmonia axyridis to a neonicotinoid and a reduced-risk insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2076–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardowski, J.P.; Hurej, M.; Twardowska, K. Effect of ingestion exposure of selected insecticides on Coccinella septempunctata and Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Insects 2021, 12, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.H.; Yang, Z.Z.; Guo, L.T.; Wang, D.; Huang, J.Q.; Zhang, H.L.; Wen, Y.N.; Zhao, J.Y.; et al. The invasive MED/Q Bemisia tabaci genome: A tale of gene loss and gene gain. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskey, T.C.; Lee, D.H.; Short, B.D.; Wright, S.E. Impact of insecticides on the invasive Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): Analysis of insecticide lethality. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigner, J.D.; Walgenbach, J.F.; Kuhar, T.P. Toxicities of neonicotinoid insecticides for systemic control of brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in fruiting vegetables. J. Agric. Urban Entomol. 2015, 31, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.L.; Shearer, P.W.; Hamilton, G.C. Toxicity of insecticides to Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) using glass-vial bioassays. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiaz, M.; Martínez, L.C.; Costa, M.D.; Cossolin, J.F.S.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Gonçalves, W.G.; Sant’Ana, A.E.G.; Zanuncio, J.C.; Serrao, J.E. Squamocin induce histological and ultrastructural changes in the midgut cells of Anticarsia gemmatalis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, W.M.; Martínez, L.C.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Serrão, J.E.; Zanuncio, J.C. Respiration, predatory behavior and prey consumption by Podisus nigrispinus (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) nymphs exposed to some insecticides. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; He, W.; Fu, L.; Cheng, H.; Lin, C.; Dong, X.; Liu, C. Detoxification and neurotransmitter clearance drive the recovery of Arma chinensis from beta-cypermethrin-triggered knockdown. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddrell, S.H.; Reynolds, S.E. Release of hormones in insects after poisoning with insecticides. Nature 1972, 236, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazini, J.d.B.; Padilha, A.C.; Cagliari, D.; Bueno, F.A.; Rakes, M.; Zotti, M.J.; Martins, J.F.D.; Grützmacher, A.D. Differential impacts of pesticides on Euschistus heros (Hem.: Pentatomidae) and its parasitoid Telenomus podisi (Hym.: Platygastridae). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Quan, L.F.; Wang, S.W.; Xing, D.X.; Chen, B.X.; Lu, K. Predatory stink bug, Eocanthecona furcellata (Wolff) responses to oral exposure route of λ-cyhalothrin via sex-specific modulation manner. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 192, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Meng, X.K.; Zhang, N.; Ge, H.C.; Wei, J.P.; Qian, K.; Zheng, Y.; Park, Y.; Palli, S.R.; Wang, J.J. The pleiotropic AMPK-CncC signaling pathway regulates the trade-off between detoxification and reproduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2214038120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansdell, S.J.; Millar, N.S. Cloning and heterologous expression of Dα4, a Drosophila neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit: Identification of an alternative exon influencing the efficiency of subunit assembly. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 2604–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, X.; Gai, Z.C. Genome-wide identification and characterization of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in housefly (Musca domestica) and their roles in the insecticide resistance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Fernández, G.M.; Moriconi, D.E.; Dulbecco, A.B.; Juárez, P.M. Transcriptome analysis of the Triatoma infestans (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) integument. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyses, E.W.; Gfeller, F.J. Topical application as a method for comparing the effectiveness of insecticides against cat flea (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostaropoulos, I.; Papadopoulos, A.I.; Metaxakis, A.; Boukouvala, E.; Papadopoulou-Mourkidou, E. Glutathione S–transferase in the defence against pyrethroids in insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 31, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, B.G. Building phylogenetic trees from molecular data with MEGA. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 30, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis: A Statistical Treatment of the Sigmoid Response Curve, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Yan, X.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Fu, L.; Dong, X.; Liu, C. Predaceous and Phytophagous Pentatomidae Insects Exhibit Contrasting Susceptibilities to Imidacloprid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020690
Cheng H, Wang Z, Yan X, Lin C, Chen Y, Ma L, Fu L, Dong X, Liu C. Predaceous and Phytophagous Pentatomidae Insects Exhibit Contrasting Susceptibilities to Imidacloprid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020690
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Hongmei, Zhen Wang, Xiaoyu Yan, Changjin Lin, Yu Chen, Le Ma, Luyao Fu, Xiaolin Dong, and Chenxi Liu. 2025. "Predaceous and Phytophagous Pentatomidae Insects Exhibit Contrasting Susceptibilities to Imidacloprid" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020690
APA StyleCheng, H., Wang, Z., Yan, X., Lin, C., Chen, Y., Ma, L., Fu, L., Dong, X., & Liu, C. (2025). Predaceous and Phytophagous Pentatomidae Insects Exhibit Contrasting Susceptibilities to Imidacloprid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020690





