Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility Receptor (HMMR) Overexpression Is Correlated with Poor Survival in Patients with B-ALL
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
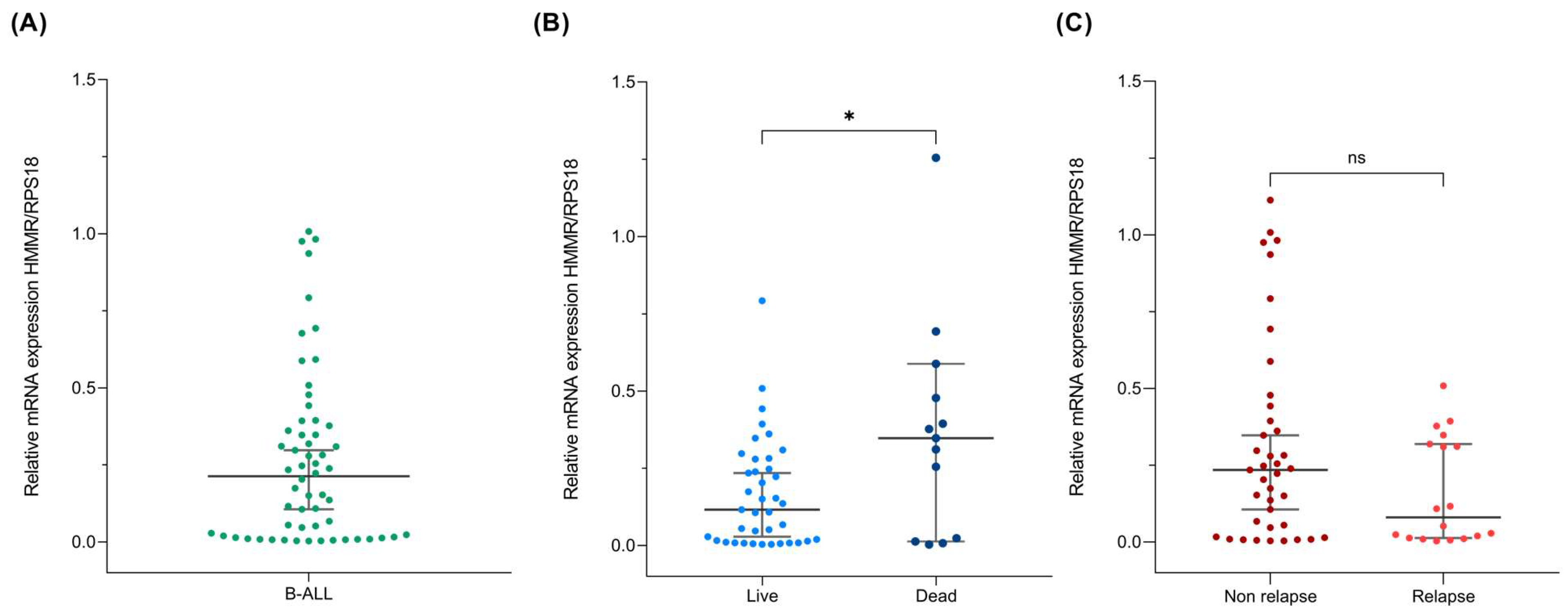
2.1. HMMR Expression in B-ALL
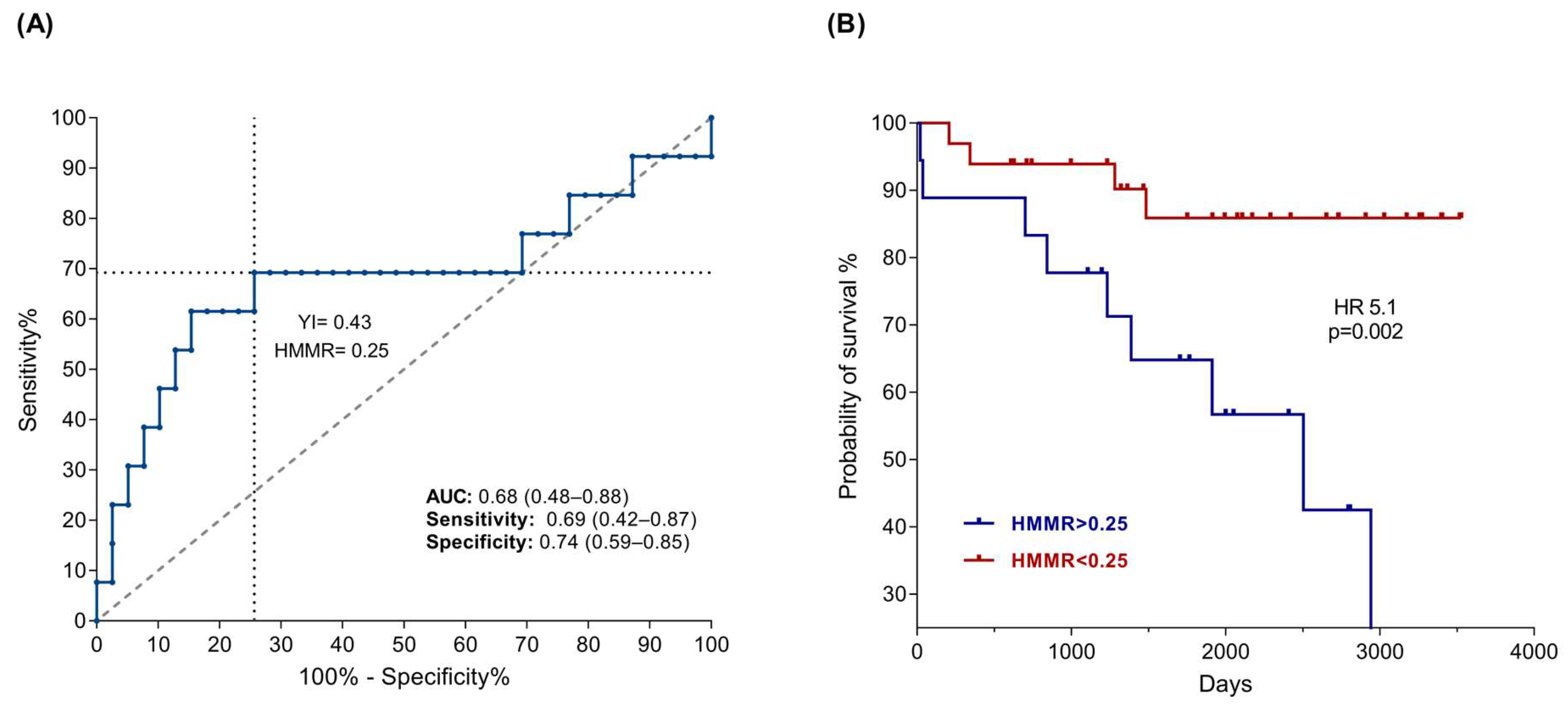
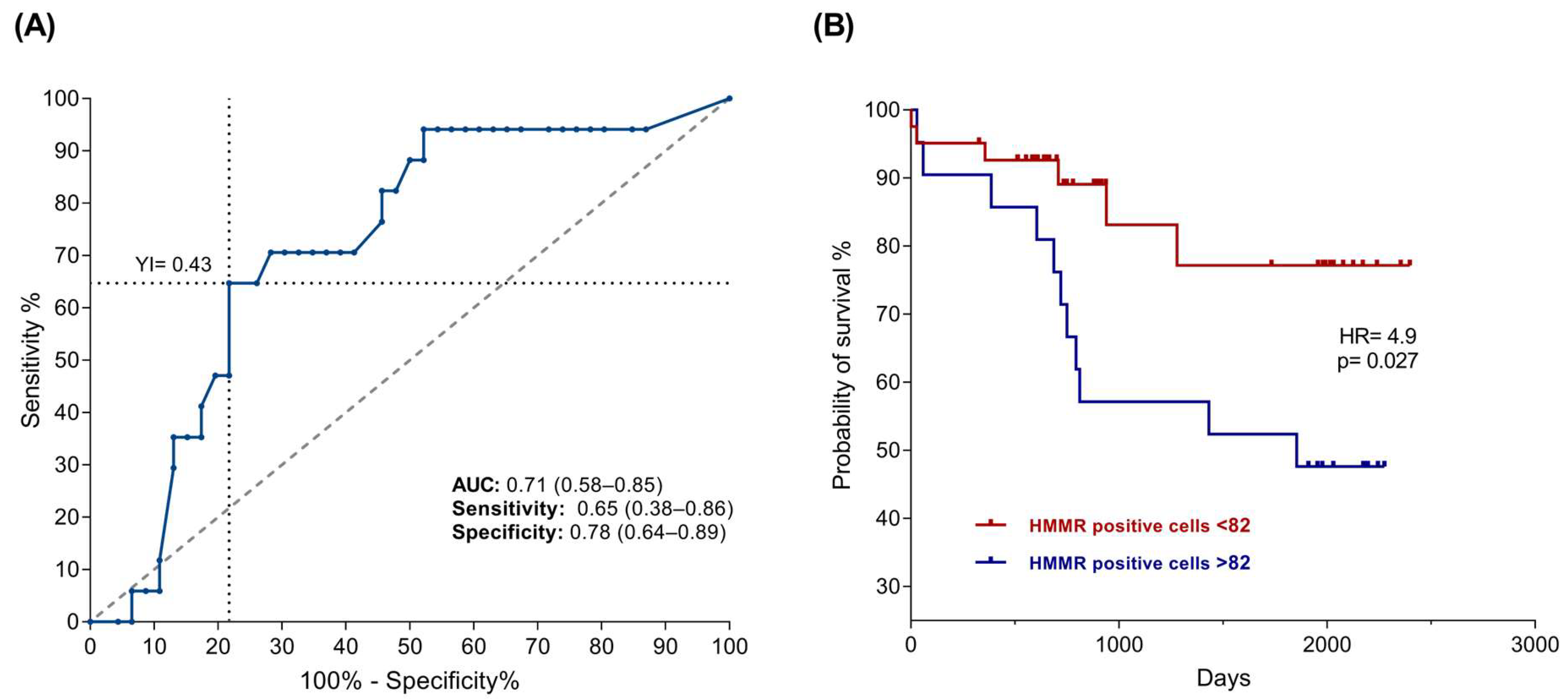
2.2. High HMMR Expression Predicts Death in Patients with B-ALL
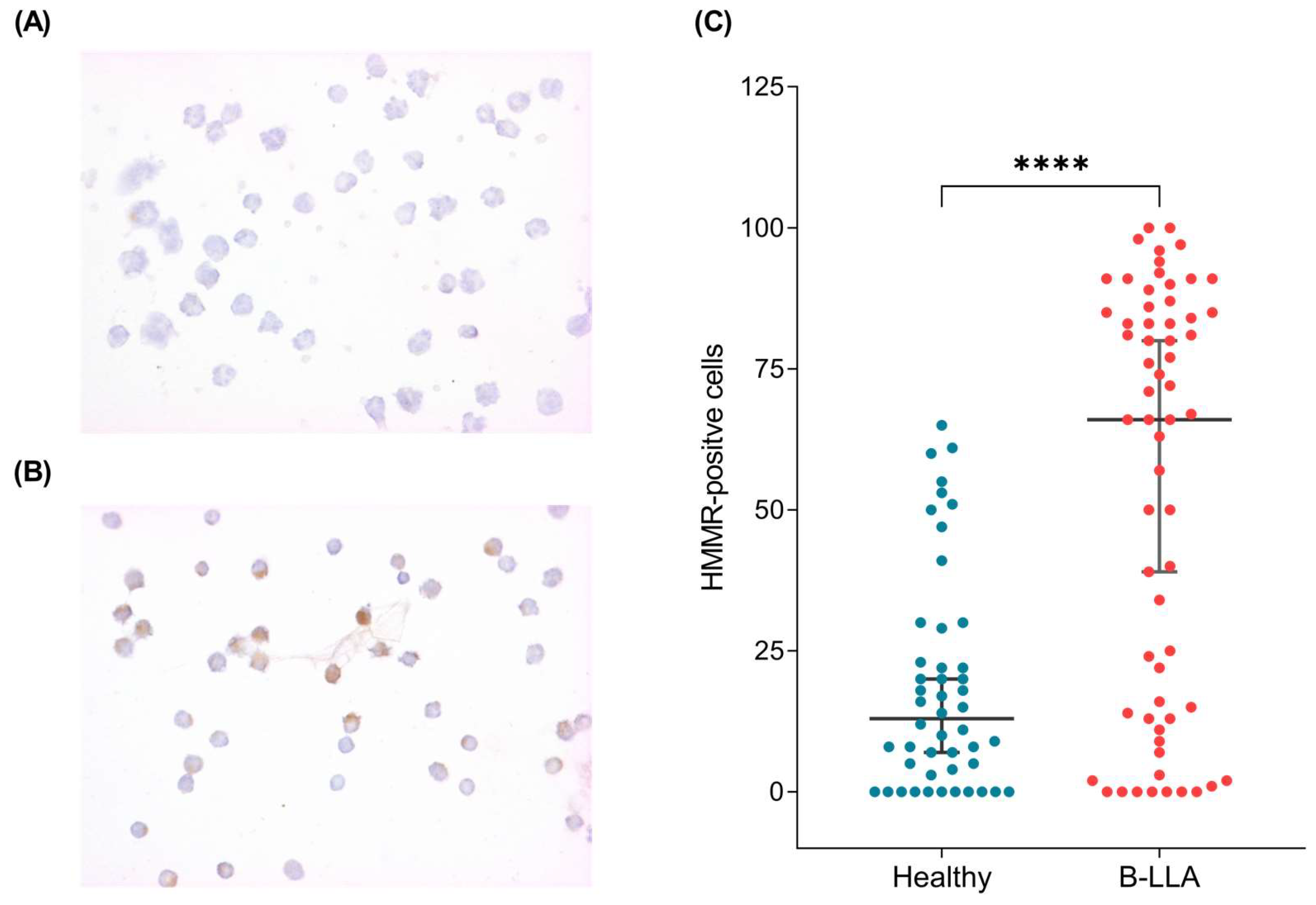
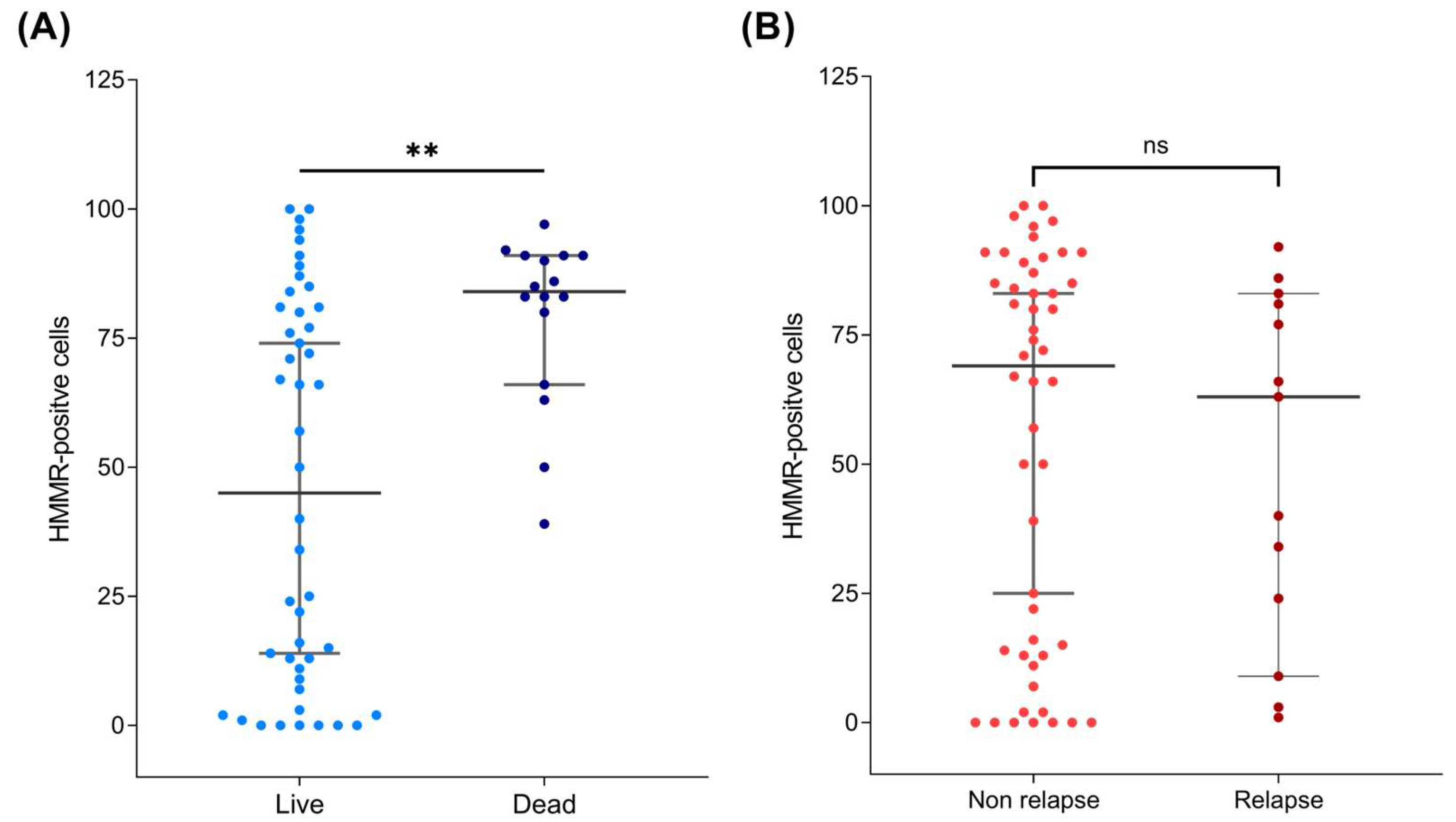
2.3. HMMR Is Overexpressed in the Peripheral Blood of Patients with B-ALL
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Mining
4.2. Biological Samples and Ethics Statement
4.3. RNA Purification
4.4. cDNA Synthesis
4.5. RT–PCR Amplification
4.6. Quantitative HMMR Expression
4.7. Sample Processing and Immunocytochemistry
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnston, W.T.; Erdmann, F.; Newton, R.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Schuz, J.; Roman, E. Childhood cancer: Estimating regional and global incidence. Cancer Epidemiol. 2021, 71, 101662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Observatory, G.C. Globocan. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/en (accessed on 4 January 2025).
- Terwilliger, T.; Abdul-Hay, M. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2017 update. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malard, F.; Mohty, M. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 2020, 395, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namayandeh, S.M.; Khazaei, Z.; Lari Najafi, M.; Goodarzi, E.; Moslem, A. GLOBAL Leukemia in Children 0-14 Statistics 2018, Incidence and Mortality and Human Development Index (HDI): GLOBOCAN Sources and Methods. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez-Avendano, G.; Luna-Silva, N.C.; Chargoy-Vivaldo, E.; Juarez-Martinez, L.A.; Martinez-Rangel, M.N.; Zarate-Ortiz, N.; Martinez-Valencia, E.; Lopez-Martinez, B.; Pelayo, R.; Balandran, J.C. Poor Prognosis Biomolecular Factors Are Highly Frequent in Childhood Acute Leukemias From Oaxaca, Mexico. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820928436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Hernandez, E.; Jaimes-Reyes, E.Z.; Arellano-Galindo, J.; Garcia-Jimenez, X.; Tiznado-Garcia, H.M.; Duenas-Gonzalez, M.T.; Martinez Villegas, O.; Sanchez-Jara, B.; Bekker-Mendez, V.C.; Ortiz-Torres, M.G.; et al. Survival of Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia under Treatment with the Protocol from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute 00-01. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 576950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurtleff, S.A.; Buijs, A.; Behm, F.G.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hancock, M.L.; Chan, G.C.; Pui, C.H.; Grosveld, G.; Downing, J.R. TEL/AML1 fusion resulting from a cryptic t(12;21) is the most common genetic lesion in pediatric ALL and defines a subgroup of patients with an excellent prognosis. Leukemia 1995, 9, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hunger, S.P. Chromosomal translocations involving the E2A gene in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Clinical features and molecular pathogenesis. Blood 1996, 87, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, R.C.; Abromowitch, M.; Raimondi, S.C.; Murphy, S.B.; Behm, F.; Williams, D.L. Clinical and biologic hallmarks of the Philadelphia chromosome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1987, 70, 948–953. [Google Scholar]
- Mullighan, C.G. Molecular genetics of B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3407–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullighan, C.G. The molecular genetic makeup of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2012, 2012, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.S.; Alberti, M.O.; Tirado, C.A. Childhood B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A genetic update. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobucci, I.; Mullighan, C.G. Genetic Basis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toole, B.P. Hyaluronan and its binding proteins, the hyaladherins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1990, 2, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, B.P. Hyaluronan in morphogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 12, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turley, E.A.; Noble, P.W.; Bourguignon, L.Y. Signaling properties of hyaluronan receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4589–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klewes, L.; Turley, E.A.; Prehm, P. The hyaluronate synthase from a eukaryotic cell line. Biochem. J. 1993, 290 Pt 3, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, I.; Kawano, Y.; Tsuiki, H.; Sasaki, J.; Nakao, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Suga, M.; Ando, M.; Nakajima, M.; Saya, H. CD44 cleavage induced by a membrane-associated metalloprotease plays a critical role in tumor cell migration. Oncogene 1999, 18, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Hascall, V.C.; Markwald, R.R.; Ghatak, S. Interactions between Hyaluronan and Its Receptors (CD44, RHAMM) Regulate the Activities of Inflammation and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savani, R.C.; Cao, G.; Pooler, P.M.; Zaman, A.; Zhou, Z.; DeLisser, H.M. Differential involvement of the hyaluronan (HA) receptors CD44 and receptor for HA-mediated motility in endothelial cell function and angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36770–36778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolg, C.; Hamilton, S.R.; Nakrieko, K.A.; Kooshesh, F.; Walton, P.; McCarthy, J.B.; Bissell, M.J.; Turley, E.A. Rhamm-/- fibroblasts are defective in CD44-mediated ERK1,2 motogenic signaling, leading to defective skin wound repair. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, Y.S.; Choe, J.; Hahn, J.H.; Lee, H.; Jeon, J.; Choi, C.; et al. Hyaluronic acid promotes angiogenesis by inducing RHAMM-TGFbeta receptor interaction via CD44-PKCdelta. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assmann, V.; Jenkinson, D.; Marshall, J.F.; Hart, I.R. The intracellular hyaluronan receptor RHAMM/IHABP interacts with microtubules and actin filaments. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112 Pt 22, 3943–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, C.A.; Keats, J.J.; Crainie, M.; Sun, X.; Yen, T.; Shibuya, E.; Hendzel, M.; Chan, G.; Pilarski, L.M. RHAMM is a centrosomal protein that interacts with dynein and maintains spindle pole stability. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 2262–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Mohan, P.; Jiang, J.; Nemirovsky, O.; He, D.; Fleisch, M.C.; Niederacher, D.; Pilarski, L.M.; Lim, C.J.; Maxwell, C.A. Spatial regulation of Aurora A activity during mitotic spindle assembly requires RHAMM to correctly localize TPX2. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2248–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolg, C.; McCarthy, J.B.; Yazdani, A.; Turley, E.A. Hyaluronan and RHAMM in wound repair and the “cancerization” of stromal tissues. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 103923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Lai, C.; Gao, Z.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.; Tang, Z.; Li, K.; Xu, K. HMMR promotes prostate cancer proliferation and metastasis via AURKA/mTORC2/E2F1 positive feedback loop. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, F.; He, Z.; Mei, L.; de Garibay, G.R.; Herranz, C.; Garcia, N.; Lorentzian, A.; Baiges, A.; Blommaert, E.; Gomez, A.; et al. Modification of BRCA1-associated breast cancer risk by HMMR overexpression. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Gong, X.; Lv, Q.; Chen, J.; Tu, Z.; Lin, S.; Pan, J.; Guo, Q.; Li, J. High Expression of Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility Receptor Predicts Adverse Outcomes: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 608842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Zhang, X.; Hou, G.; Qi, Y. HMMR potential as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of cancer-speculation based on a pan-cancer analysis. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 998598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, J.; Li, L.; Ringhoffer, M.; Barth, T.F.; Giannopoulos, K.; Guillaume, P.; Ritter, G.; Wiesneth, M.; Dohner, H.; Schmitt, M. Identification and characterization of epitopes of the receptor for hyaluronic acid-mediated motility (RHAMM/CD168) recognized by CD8+ T cells of HLA-A2-positive patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2005, 106, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalini, C.N.S.; Suman, F.R.; Jacob, J.S.; Rajendran, R.; Scott, J.X.; Latha, M.S. Prognostic significance of receptor for hyaluronan acid-mediated motility (CD168) in acute pediatric leukemias-assessment of clinical outcome, post induction, end of treatment and minimal residual disease. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2018, 40, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Saldivar, M.L.; Fajardo-Gutierrez, A.; Bernaldez-Rios, R.; Martinez-Avalos, A.; Medina-Sanson, A.; Espinosa-Hernandez, L.; Flores-Chapa Jde, D.; Amador-Sanchez, R.; Penaloza-Gonzalez, J.G.; Alvarez-Rodriguez, F.J.; et al. Childhood acute leukemias are frequent in Mexico City: Descriptive epidemiology. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard-Jones, K.; Pieters, R.; Reaman, G.H.; Hjorth, L.; Downie, P.; Calaminus, G.; Naafs-Wilstra, M.C.; Steliarova-Foucher, E. Sustaining innovation and improvement in the treatment of childhood cancer: Lessons from high-income countries. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e95–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, S.P. Expanding clinical trial networks in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, M.; Ohara, A.; Manabe, A.; Kumagai, M.; Shimada, H.; Kikuchi, A.; Mori, T.; Saito, M.; Akiyama, M.; Fukushima, T.; et al. Long-term results of Tokyo Children’s Cancer Study Group trials for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia, 1984–1999. Leukemia 2010, 24, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrath, I.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Epelman, S.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Harif, M.; Li, C.K.; Kebudi, R.; Macfarlane, S.D.; Howard, S.C. Paediatric cancer in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e104–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moricke, A.; Reiter, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Gadner, H.; Stanulla, M.; Dordelmann, M.; Loning, L.; Beier, R.; Ludwig, W.D.; Ratei, R.; et al. Risk-adjusted therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia can decrease treatment burden and improve survival: Treatment results of 2169 unselected pediatric and adolescent patients enrolled in the trial ALL-BFM 95. Blood 2008, 111, 4477–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, T.; Schrauder, A.; Cazzaniga, G.; Panzer-Grumayer, R.; van der Velden, V.; Fischer, S.; Stanulla, M.; Basso, G.; Niggli, F.K.; Schafer, B.W.; et al. Minimal residual disease-directed risk stratification using real-time quantitative PCR analysis of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements in the international multicenter trial AIEOP-BFM ALL 2000 for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2008, 22, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrappe, M.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Bartram, C.R.; Schrauder, A.; Panzer-Grumayer, R.; Moricke, A.; Parasole, R.; Zimmermann, M.; Dworzak, M.; Buldini, B.; et al. Late MRD response determines relapse risk overall and in subsets of childhood T-cell ALL: Results of the AIEOP-BFM-ALL 2000 study. Blood 2011, 118, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorman, A.V.; Ensor, H.M.; Richards, S.M.; Chilton, L.; Schwab, C.; Kinsey, S.E.; Vora, A.; Mitchell, C.D.; Harrison, C.J. Prognostic effect of chromosomal abnormalities in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Results from the UK Medical Research Council ALL97/99 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, L.S.; Bader, D.M.; Mertes, C.; Kopajtich, R.; Pichler, G.; Iuso, A.; Haack, T.B.; Graf, E.; Schwarzmayr, T.; Terrile, C.; et al. Genetic diagnosis of Mendelian disorders via RNA sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Shi, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lv, J.; Xie, X.; Bai, Y.; et al. Potential Diagnostic Power of Blood Circular RNA Expression in Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis. EBioMedicine 2018, 27, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, D.; Sun, K.; Xu, Y.; Hu, P.; Li, X.; Xu, F. Identification of biomarkers associated with diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Gene 2019, 692, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Villegas-Ruiz, V.; Caballero-Palacios, M.C.; Perez-Lopez, E.I.; Murata, C.; Zapata-Tarres, M.; Cardenas-Cardos, R.; Paredes-Aguilera, R.; Rivera-Luna, R.; Juarez-Mendez, S. Expression of ZNF695 Transcript Variants in Childhood B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Genes 2019, 10, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Avila, C.E.; Villegas-Ruiz, V.; Zapata-Tarres, M.; Rubio-Portillo, A.E.; Perez Lopez, E.I.; Zenteno, J.C.; Juarez-Mendez, S. Centromere-associated protein E expresses a novel mRNA isoform in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2018, 9, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero-Palacios, M.C.; Villegas-Ruiz, V.; Ramirez-Chiquito, J.C.; Medina-Vera, I.; Zapata-Tarres, M.; Mojica-Espinosa, R.; Cardenas-Cardos, R.; Paredes-Aguilera, R.; Rivera-Luna, R.; Juarez-Mendez, S. v-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog expression is a potential molecular diagnostic marker for B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 17, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolg, C.; Liu, M.; Cousteils, K.; Telmer, P.; Alam, K.; Ma, J.; Mendina, L.; McCarthy, J.B.; Morris, V.L.; Turley, E.A. Cell-specific expression of the transcriptional regulator RHAMM provides a timing mechanism that controls appropriate wound re-epithelialization. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 5427–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, J.; Ringhoffer, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Li, L.; Schmitt, A.; Shiku, H.; Dohner, H.; Schmitt, M. mRNA expression of leukemia-associated antigens in patients with acute myeloid leukemia for the development of specific immunotherapies. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, K.; Li, L.; Bojarska-Junak, A.; Rolinski, J.; Dmoszynska, A.; Hus, I.; Greiner, J.; Renner, C.; Dohner, H.; Schmitt, M. Expression of RHAMM/CD168 and other tumor-associated antigens in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Int. J. Oncol. 2006, 29, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, J.; Schmitt, M.; Li, L.; Giannopoulos, K.; Bosch, K.; Schmitt, A.; Dohner, K.; Schlenk, R.F.; Pollack, J.R.; Dohner, H.; et al. Expression of tumor-associated antigens in acute myeloid leukemia: Implications for specific immunotherapeutic approaches. Blood 2006, 108, 4109–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttermore, S.T.; Hoffman, M.S.; Kumar, A.; Champeaux, A.; Nicosia, S.V.; Kruk, P.A. Increased RHAMM expression relates to ovarian cancer progression. J. Ovarian Res. 2017, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Tang, L.H.; Verma, A.; Chen, Z.; Kim, B.J.; Selesner, L.; Robzyk, K.; Zhang, G.; et al. Function and clinical relevance of RHAMM isoforms in pancreatic tumor progression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, A.; Shirodkar, S.P.; Escudero, D.O.; Ekwenna, O.O.; Yates, T.J.; Ayyathurai, R.; Garcia-Roig, M.; Gahan, J.C.; Manoharan, M.; Bird, V.G.; et al. Molecular characterization of kidney cancer: Association of hyaluronic acid family with histological subtypes and metastasis. Cancer 2012, 118, 2394–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.W.; Su, J.Y.; Tsou, A.P.; Chau, G.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Chen, C.H.; Chien, C.Y.; Chou, C.K. Integrative genomics based identification of potential human hepatocarcinogenesis-associated cell cycle regulators: RHAMM as an example. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 330, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilghman, J.; Wu, H.; Sang, Y.; Shi, X.; Guerrero-Cazares, H.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Eberhart, C.G.; Laterra, J.; Ying, M. HMMR maintains the stemness and tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3168–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, C.A.; Rasmussen, E.; Zhan, F.; Keats, J.J.; Adamia, S.; Strachan, E.; Crainie, M.; Walker, R.; Belch, A.R.; Pilarski, L.M.; et al. RHAMM expression and isoform balance predict aggressive disease and poor survival in multiple myeloma. Blood 2004, 104, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, D.T.; Roehrig, K.; Schondorf, T.; Lazar, A.; Fleisch, M.; Niederacher, D.; Bender, H.G.; Dall, P. Expression of the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM in endometrial carcinomas suggests a role in tumour progression and metastasis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 129, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Narula, N.; Azzopardi, S.; Smith, R.S.; Nasar, A.; Altorki, N.K.; Mittal, V.; Somwar, R.; Stiles, B.M.; Du, Y.N. Expression of the receptor for hyaluronic acid mediated motility (RHAMM) is associated with poor prognosis and metastasis in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 39957–39969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedworok, C.; Kretschmer, I.; Rock, K.; Vom Dorp, F.; Szarvas, T.; Hess, J.; Freudenberger, T.; Melchior-Becker, A.; Rubben, H.; Fischer, J.W. The impact of the receptor of hyaluronan-mediated motility (RHAMM) on human urothelial transitional cell cancer of the bladder. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mele, V.; Sokol, L.; Kolzer, V.H.; Pfaff, D.; Muraro, M.G.; Keller, I.; Stefan, Z.; Centeno, I.; Terracciano, L.M.; Dawson, H.; et al. The hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor RHAMM promotes growth, invasiveness and dissemination of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 70617–70629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Bai, X.; Zou, Q.; Gan, Z.; Lv, Y. Identification of the association between HMMR expression and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via construction of a co-expression network. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 2645–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, S.; Ueno, S.; Nishizono, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Kurahara, H.; Arigami, T.; Uchikado, Y.; Setoyama, T.; Arima, H.; Yoshiaki, K.; et al. Prognostic impact of CD168 expression in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarullo, S.E.; He, Y.; Daughters, C.; Knutson, T.P.; Henzler, C.M.; Price, M.A.; Shanley, R.; Witschen, P.; Tolg, C.; Kaspar, R.E.; et al. Receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility (RHAMM) defines an invasive niche associated with tumor progression and predicts poor outcomes in breast cancer patients. J. Pathol. 2023, 260, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enemark, M.B.; Hybel, T.E.; Madsen, C.; Lauridsen, K.L.; Honore, B.; Plesner, T.L.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; d’Amore, F.; Ludvigsen, M. Tumor-Tissue Expression of the Hyaluronic Acid Receptor RHAMM Predicts Histological Transformation in Follicular Lymphoma Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzankov, A.; Strasser, U.; Dirnhofer, S.; Menter, T.; Arber, C.; Jotterand, M.; Rovo, A.; Tichelli, A.; Stauder, R.; Gunthert, U. In situ RHAMM protein expression in acute myeloid leukemia blasts suggests poor overall survival. Ann. Hematol. 2011, 90, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, C.A.; Keats, J.J.; Belch, A.R.; Pilarski, L.M.; Reiman, T. Receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility correlates with centrosome abnormalities in multiple myeloma and maintains mitotic integrity. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, J.; Ringhoffer, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Hauser, T.; Schmitt, A.; Dohner, H.; Schmitt, M. Characterization of several leukemia-associated antigens inducing humoral immune responses in acute and chronic myeloid leukemia. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 106, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkes, F.; de Castro, M.G.; de Cassio Zequi, S.; Nardi, L.; Del Giglio, A.; de Lima Pompeo, A.C. Hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor (RHAMM) immunohistochemical expression and androgen deprivation in normal peritumoral, hyperplasic and neoplastic prostate tissue. BJU Int. 2014, 113, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ren, L.; Ding, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. Hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor confers resistance to chemotherapy via TGFbeta/Smad2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 6365–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Rodriguez, R.A.; Davila-Borja, V.M.; Juarez-Mendez, S. Data mining of pediatric medulloblastoma microarray expression reveals a novel potential subdivision of the Group 4 molecular subgroup. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 6241–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juarez-Mendez, S.; Zentella-Dehesa, A.; Villegas-Ruiz, V.; Perez-Gonzalez, O.A.; Salcedo, M.; Lopez-Romero, R.; Roman-Basaure, E.; Lazos-Ochoa, M.; Montes de Oca-Fuentes, V.E.; Vazquez-Ortiz, G.; et al. Splice variants of zinc finger protein 695 mRNA associated to ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2013, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas-Ruiz, V.; Juarez-Mendez, S. Data Mining for Identification of Molecular Targets in Ovarian Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ruiz, V.; Olmos-Valdez, K.; Castro-Lopez, K.A.; Saucedo-Tepanecatl, V.E.; Ramirez-Chiquito, J.C.; Perez-Lopez, E.I.; Medina-Vera, I.; Juarez-Mendez, S. Identification and Validation of Novel Reference Genes in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia for Droplet Digital PCR. Genes 2019, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio-Andres, G.; Martinez-Ruiz, G.U.; Morales-Martinez, M.; Jimenez-Hernandez, E.; Martinez-Torres, E.; Lopez-Perez, T.V.; Estrada-Abreo, L.A.; Patino-Lopez, G.; Juarez-Mendez, S.; Davila-Borja, V.M.; et al. Transcriptional Regulation of Yin-Yang 1 Expression through the Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio-Andres, G.; Rangel-Santiago, J.; Tirado-Rodriguez, B.; Martinez-Ruiz, G.U.; Klunder-Klunder, M.; Vega, M.I.; Lopez-Martinez, B.; Jimenez-Hernandez, E.; Torres Nava, J.; Medina-Sanson, A.; et al. Role of Yin Yang-1 (YY1) in the transcription regulation of the multi-drug resistance (MDR1) gene. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio-Andres, G.; Jimenez-Hernandez, E.; Estrada-Abreo, L.A.; Garfias-Gomez, Y.; Patino-Lopez, G.; Juarez-Mendez, S.; Huerta-Yepez, S. Expression of YY1 in pro-B and T phenotypes correlation with poor survival in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 38, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio-Andres, G.; Morales-Martinez, M.; Jimenez-Hernandez, E.; Huerta-Yepez, S. The Role of PTEN in Chemoresistance Mediated by the HIF-1alpha/YY1 Axis in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| B-ALL Patients | N = 129 (100%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Female | 65 (50.4%) |
| Male | 64 (49.6%) |
| Age | |
| Age at diagnosis in years, mean ± SD | 7.7 ± 4.5 years |
| Most common age at diagnosis | 3 years (14.0%) |
| Age groups in years | |
| 0–4 | 46 (35.7%) |
| 5–8 | 30 (23.3%) |
| 9–12 | 25 (19.4%) |
| 13–18 | 28 (26.4%) |
| Risk | |
| Standard | 30 (23.3%) |
| High | 99 (76.7%) |
| Relapse | |
| Yes | 34 (26.4%) |
| No | 95 (73.6%) |
| Alive | 97 (75.2%) |
| Alive with relapse | 20 (15.5%) |
| Alive without relapse | 77 (59.7%) |
| Deceased | 32 (24.8%) |
| Deceased with relapse | 14 (10.8%) |
| Deceased without relapse | 18 (14.0%) |
| Survival days, mean ±SD | 1562 ± 83 |
| Disease-free survival days, mean ±SD | 574 ± 93 |
| Controls | N = 54 (100%) |
| Gender | |
| Female | 25 (46.3%) |
| Male | 29 (53.7%) |
| Age | |
| Mean age ± SD | 11.6 ± 1.6 years |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Chiquito, J.C.; Villegas-Ruíz, V.; Medina-Vera, I.; Sánchez-Cruz, I.; Frías-Soria, C.L.; Caballero Palacios, M.C.; Antonio-Andrés, G.; Rubio-Portillo, A.E.; Velasco-Hidalgo, L.; Perezpeña-Diazconti, M.; et al. Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility Receptor (HMMR) Overexpression Is Correlated with Poor Survival in Patients with B-ALL. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020744
Ramírez-Chiquito JC, Villegas-Ruíz V, Medina-Vera I, Sánchez-Cruz I, Frías-Soria CL, Caballero Palacios MC, Antonio-Andrés G, Rubio-Portillo AE, Velasco-Hidalgo L, Perezpeña-Diazconti M, et al. Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility Receptor (HMMR) Overexpression Is Correlated with Poor Survival in Patients with B-ALL. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020744
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Chiquito, Josselen Carina, Vanessa Villegas-Ruíz, Isabel Medina-Vera, Itzel Sánchez-Cruz, Christian Lizette Frías-Soria, Marcela Concepción Caballero Palacios, Gabriela Antonio-Andrés, Alejandra Elizabeth Rubio-Portillo, Liliana Velasco-Hidalgo, Mario Perezpeña-Diazconti, and et al. 2025. "Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility Receptor (HMMR) Overexpression Is Correlated with Poor Survival in Patients with B-ALL" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020744
APA StyleRamírez-Chiquito, J. C., Villegas-Ruíz, V., Medina-Vera, I., Sánchez-Cruz, I., Frías-Soria, C. L., Caballero Palacios, M. C., Antonio-Andrés, G., Rubio-Portillo, A. E., Velasco-Hidalgo, L., Perezpeña-Diazconti, M., Galván-Diaz, C. A., López-Santiago, N. C., Huerta-Yepez, S., & Juárez-Méndez, S. (2025). Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility Receptor (HMMR) Overexpression Is Correlated with Poor Survival in Patients with B-ALL. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020744







