Functional and Structural Changes in the Inner Ear and Cochlear Hair Cell Loss Induced by Hypergravity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
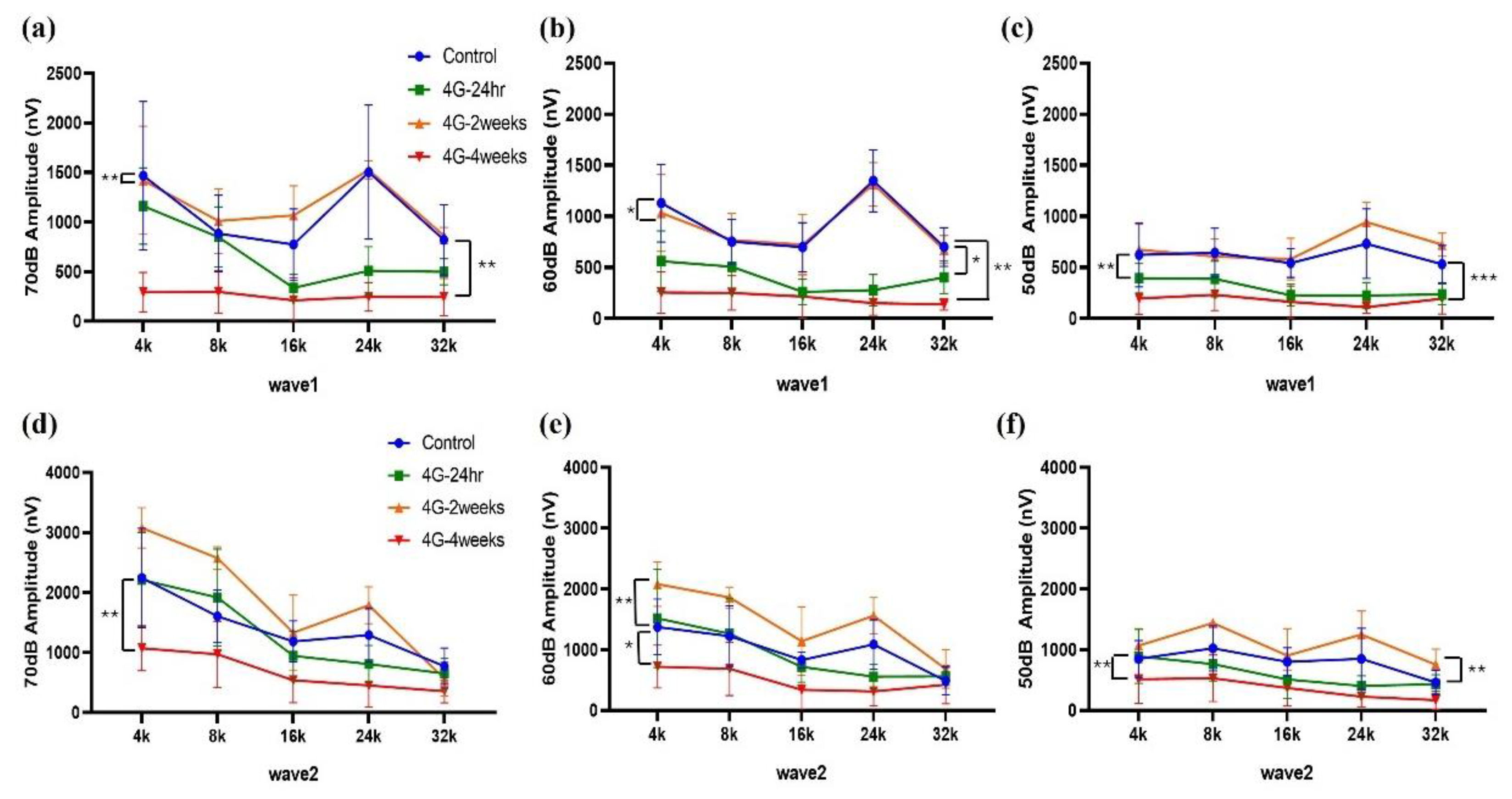
2.1. ABR Recordings
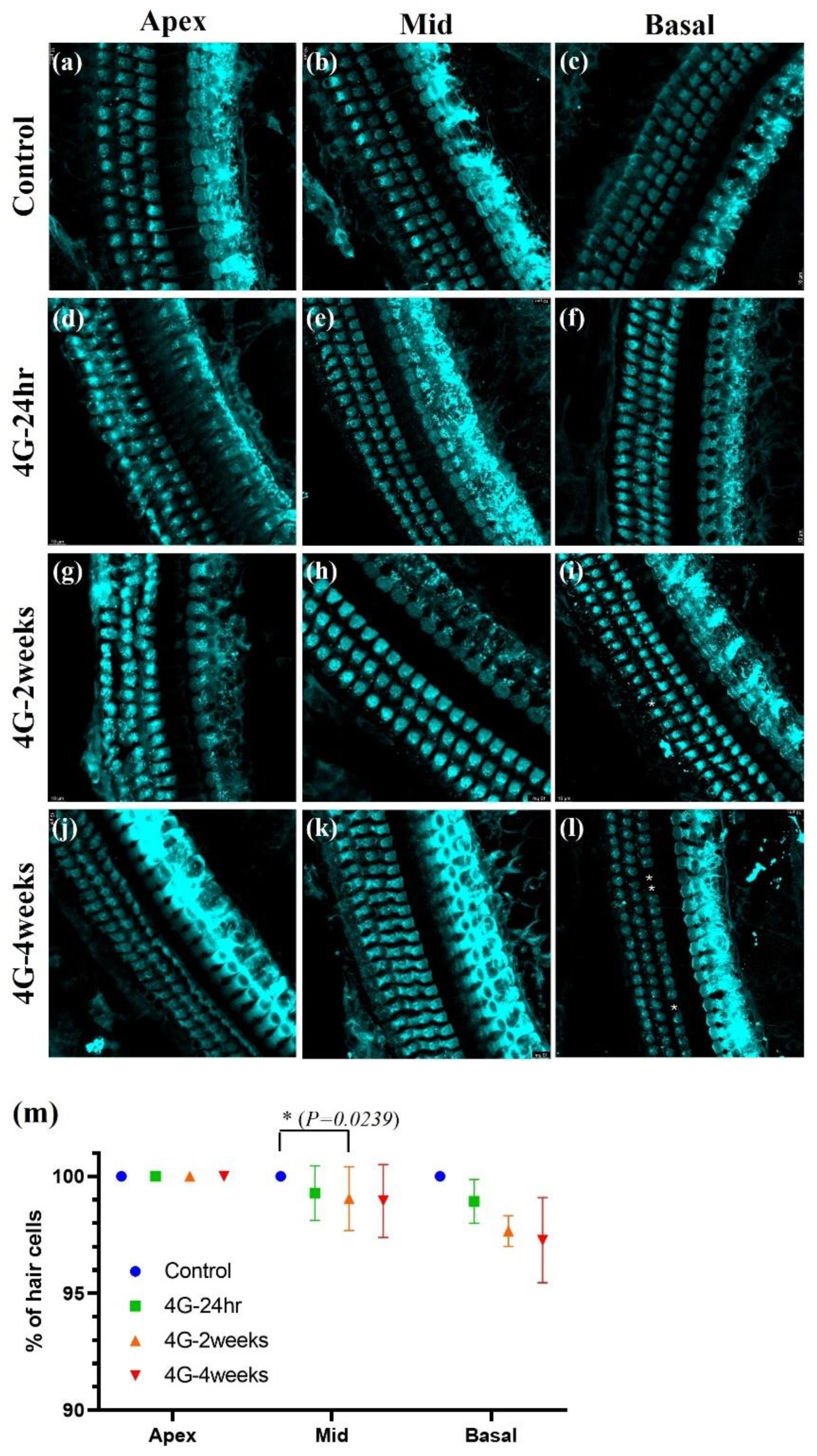
2.2. Immunostaining of Cochlear Hair Cells
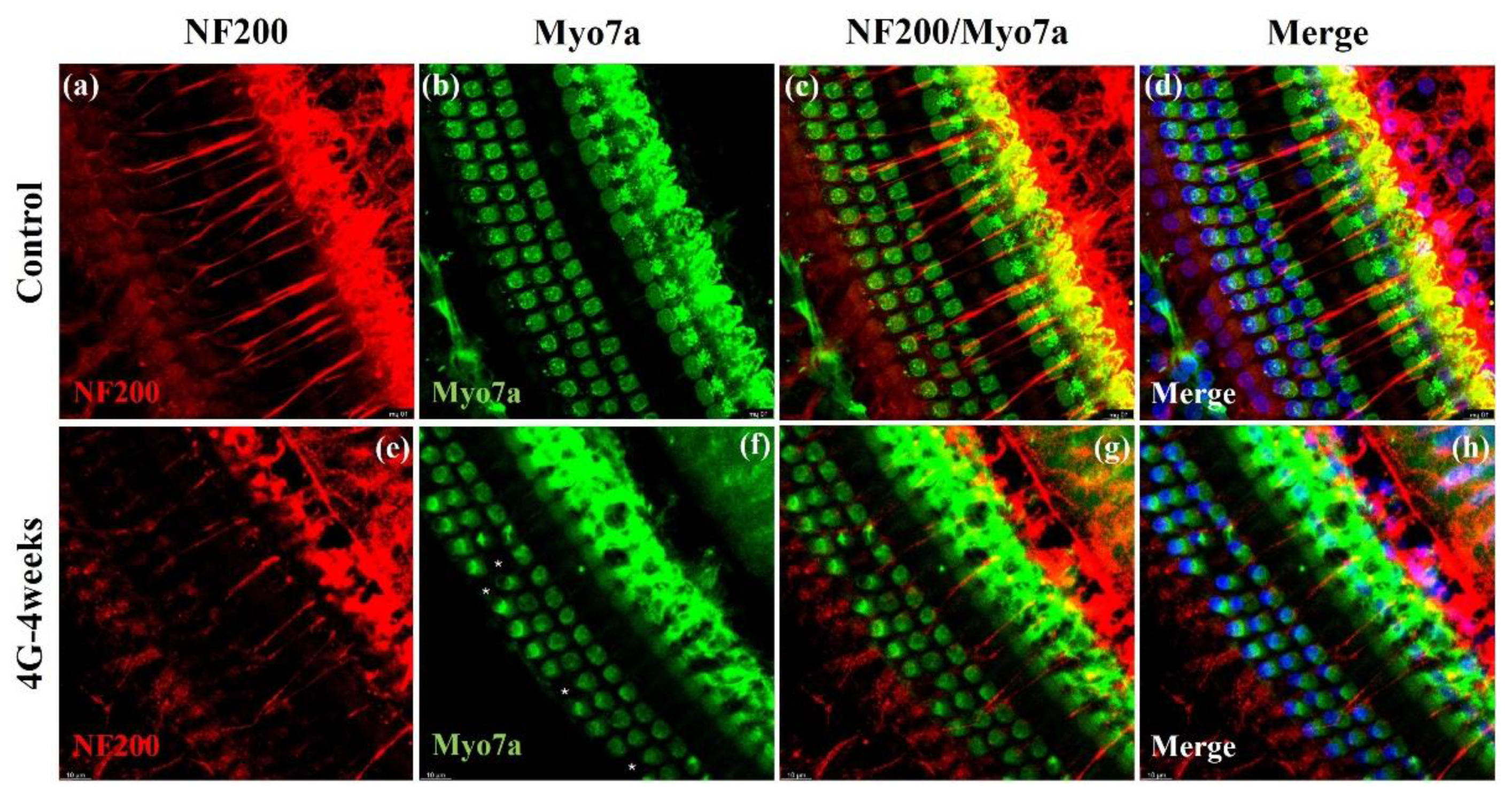
2.3. Neurofilament Analysis
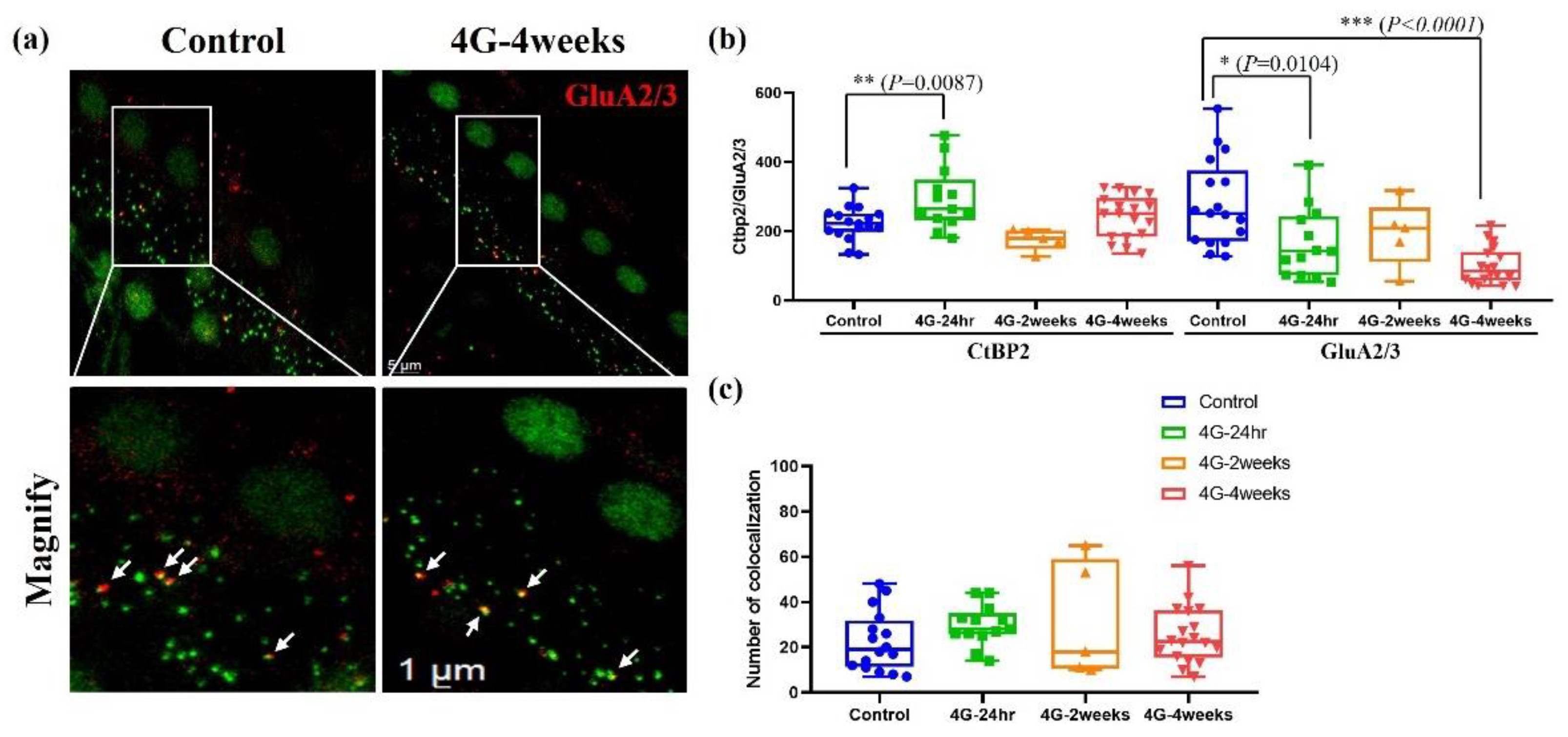
2.4. Analysis of Synapse
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Hypergravity Stimulation
4.3. Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Test
4.4. Immunostaining Assay
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABR | Auditory brainstem response |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| IHC | Inner hair cell |
| NF | Neurofilament |
| OHC | Outer hair cell |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| SD | Sprague–Dawley |
| SGN | Spiral ganglion neuron |
References
- Adamopoulos, K.; Koutsouris, D.; Zaravinos, A.; Lambrou, G.I. Gravitational Influence on Human Living Systems and the Evolution of Species on Earth. Molecules 2021, 26, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamon, M. The development of vestibular system and related functions in mammals: Impact of gravity. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, H.; Kaji, H.; Ueta, Y.; Abe, C. Understanding vestibular-related physiological functions could provide clues on adapting to a new gravitational environment. J. Physiol. Sci. 2020, 70, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriot, J.; Mackrous, I.; Cullen, K.E. Challenges to the Vestibular System in Space: How the Brain Responds and Adapts to Microgravity. Front. Neural Circuits 2021, 15, 760313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dememes, D.; Dechesne, C.J.; Venteo, S.; Gaven, F.; Raymond, J. Development of the rat efferent vestibular system on the ground and in microgravity. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 2001, 128, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultemeier, D.R.; Choy, K.R.; Schweizer, F.E.; Hoffman, L.F. Spaceflight-induced synaptic modifications within hair cells of the mammalian utricle. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 117, 2163–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberg, A.B. Changes in the central nervous system and their clinical correlates during long-term spaceflight. Aviat. Space Env. Med. 1994, 65, 562–572. [Google Scholar]
- Masè, M.; Viziano, A.; Strapazzon, G.; Alessandrini, M.; Micarelli, A. Auditory function in humans at high altitude. A scoping review. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X. Perception of sound and gravity by TMC1 and TMC2. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4633–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neng, L.; Shi, X. Vascular pathology and hearing disorders. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2020, 18, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazer, D.G. Hearing Loss: The Silent Risk for Psychiatric Disorders in Late Life. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2020, 36, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, M.G.; Campos, J.L. The effects of hearing loss on balance: A critical review. Ear Hear. 2020, 41, 107S–119S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tong, B.; Qiu, J.; Chen, S. Association Between Hearing Loss, Asymmetric Hearing, and Postural Instability. Ear Hear. 2024, 45, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, H.; Li, M.; Kilpatrick, L.A.; Zhu, J.; Samuvel, D.J.; Krug, E.L.; Goddard, J.C. Sox2 up-regulation and glial cell proliferation following degeneration of spiral ganglion neurons in the adult mouse inner ear. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2011, 12, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberman, L.D.; Wang, H.; Liberman, M.C. Opposing gradients of ribbon size and AMPA receptor expression underlie sensitivity differences among cochlear-nerve/hair-cell synapses. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.F.; Ross, M.D.; Varelas, J.; Jones, S.M.; Jones, T.A. Afferent synapses are present in utricular hair cells from otoconia-deficient mice. Hear. Res. 2006, 222, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, J.F. Motion sickness susceptibility. Auton. Neurosci. 2006, 129, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, J.R.; DiZio, P. Space motion sickness. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 175, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodkinson, P.; Anderton, R.; Posselt, B.; Fong, K. An overview of space medicine. BJA Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119 (Suppl. S1), i143–i153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braddock, M. Ergonomic challenges for astronauts during space travel and the need for space medicine. J. Ergon. 2017, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornilova, L.; Naumov, I.; Glukhikh, D.; Ekimovskiy, G.; Pavlova, A.; Khabarova, V.; Smirnov, Y.I.; Yarmanova, E. Vestibular function and space motion sickness. Hum. Physiol. 2017, 43, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadem, M. The etiology of spaceflight-associated hearing loss. Univ. West. Ont. Med. J. 2018, 87, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.; Sheik Ali, S.; Ahmed, W. A review of the impact of hearing interventions on social isolation and loneliness in older people with hearing loss. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 4653–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podury, A.; Jiam, N.T.; Kim, M.; Donnenfield, J.I.; Dhand, A. Hearing and sociality: The implications of hearing loss on social life. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1245434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsaikhan, T.; Choi, J.S.; Ha, S.M.; Ahn, Y.; Seo, Y.J. D-Galactose and Hypoxia Induce the Early Onset of Age-Related Hearing Loss Deterioration in a Mouse Model. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 20, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Puel, J.L. Presbycusis: An Update on Cochlear Mechanisms and Therapies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, X.; Chai, R.; Fan, J. Progress on mechanisms of age-related hearing loss. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1253574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, C.; Yamasoba, T. Oxidative stresses and mitochondrial dysfunction in age-related hearing loss. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 582849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teraoka, M.; Hato, N.; Inufusa, H.; You, F. Role of Oxidative Stress in Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z.; Ye, F.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in hearing loss: Oxidative stress, autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1119773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospeck, M.; Dong, X.X.; Iwasa, K.H. Limiting frequency of the cochlear amplifier based on electromotility of outer hair cells. Biophys. J. 2003, 84 Pt 1, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, R.; Mao, K.; Deng, M.; Li, Z. The Role of Glial Cells in Synaptic Dysfunction: Insights into Alzheimer’s Disease Mechanisms. Aging Dis. 2024, 15, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Suarez, V.J.; Beltran-Velasco, A.I.; Redondo-Florez, L.; Martin-Rodriguez, A.; Yanez-Sepulveda, R.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Neuro-Vulnerability in Energy Metabolism Regulation: A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleanu, R.I.; Niculescu, A.G.; Roza, E.; Vladacenco, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Neurotransmitters-Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendyam, S.; Mohan, A.; Kalivas, P.W.; Nair, S.S. Role of perisynaptic parameters in neurotransmitter homeostasis--computational study of a general synapse. Synapse 2012, 66, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Pendyam, S.; Kalivas, P.W.; Nair, S.S. Molecular diffusion model of neurotransmitter homeostasis around synapses supporting gradients. Neural Comput. 2011, 23, 984–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.W.; Muller, M. Homeostatic control of presynaptic neurotransmitter release. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015, 77, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhassan, K.; Coyle, D.; Belatreche, A.; Maguire, L. Compensating for synaptic loss in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2014, 36, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyoshi, C.; Tedeschi, A. Axon growth and synaptic function: A balancing act for axonal regeneration and neuronal circuit formation in CNS trauma and disease. Dev. Neurobiol. 2020, 80, 277–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.S.; Baldwin, K.T.; Allen, N.J. Astrocyte Regulation of Synapse Formation, Maturation, and Elimination. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2024, 16, a041352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toricelli, M.; Pereira, A.A.R.; Souza Abrao, G.; Malerba, H.N.; Maia, J.; Buck, H.S.; Viel, T.A. Mechanisms of neuroplasticity and brain degeneration: Strategies for protection during the aging process. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gnyubkin, V.; Guignandon, A.; Laroche, N.; Vanden-Bossche, A.; Normand, M.; Lafage-Proust, M.H.; Vico, L. Effects of chronic hypergravity: From adaptive to deleterious responses in growing mouse skeleton. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, R.I.; Limoli, C.L.; Stark, C.E.L.; Stark, S.M. Impact of spaceflight stressors on behavior and cognition: A molecular, neurochemical, and neurobiological perspective. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 138, 104676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.S.; Kim, K.-S.; Kim, H.J. Functional and Structural Changes in the Inner Ear and Cochlear Hair Cell Loss Induced by Hypergravity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020758
Choi JS, Kim K-S, Kim HJ. Functional and Structural Changes in the Inner Ear and Cochlear Hair Cell Loss Induced by Hypergravity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020758
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Jin Sil, Kyu-Sung Kim, and Hyun Ji Kim. 2025. "Functional and Structural Changes in the Inner Ear and Cochlear Hair Cell Loss Induced by Hypergravity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020758
APA StyleChoi, J. S., Kim, K.-S., & Kim, H. J. (2025). Functional and Structural Changes in the Inner Ear and Cochlear Hair Cell Loss Induced by Hypergravity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020758




