Influence of Isolation Techniques on the Quality of Plasma Samples: Implications for Cancer Biobanking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preanalytical Quality Indices
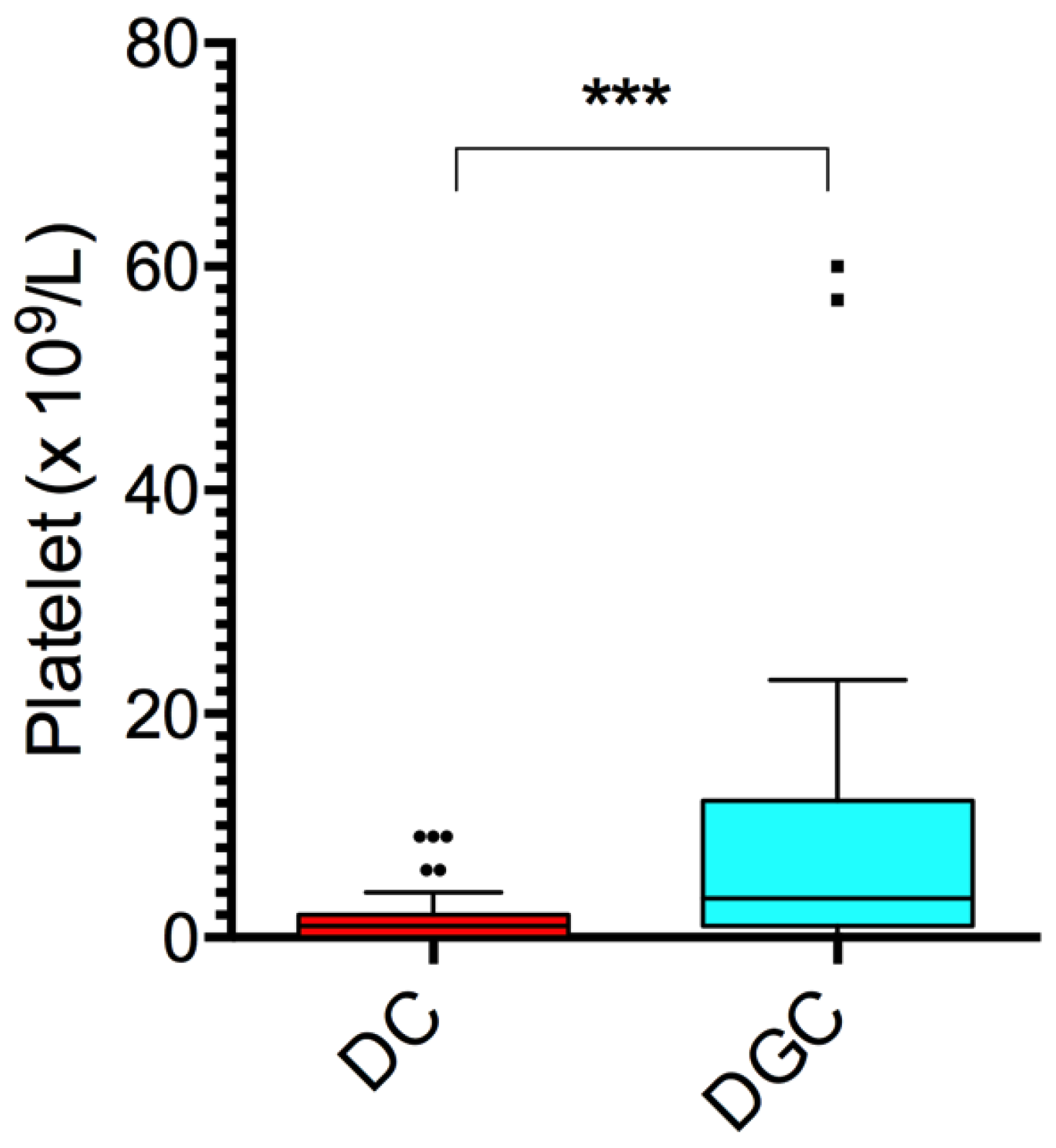
2.2. Cellular Debris, Platelets, and Biochemical Composition
2.3. Correlation Analysis of the Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Population
4.2. Blood Collection and Plasma Isolation
4.3. Spectrophotometric Analysis
4.4. Hemocytometric Analysis
4.5. Biochemical Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Coppola, L.; Cianflone, A.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Incoronato, M.; Bevilacqua, P.; Messina, F.; Baselice, S.; Soricelli, A.; Mirabelli, P.; Salvatore, M. Biobanking in health care: Evolution and future directions. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cambon-Thomsen, A.; Thorisson, G.A.; Mabile, L.; BRIF Workshop Group. The role of a bioresource research impact factor as an incentive to share human bioresources. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 503–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, M.R.A.; Palaniyandi, T.; Ravi, M.; Viswanathan, S.; Baskar, G.; Surendran, H.; Gangadharan, S.G.D.; Rajendran, B.K. Biomarkers and biosensors for early cancer diagnosis, monitoring and prognosis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 250, 154812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H.; Ma, W. Beyond blood: Advancing the frontiers of liquid biopsy in oncology and personalized medicine. Cancer Sci. 2024, 115, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kong, F.S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Fu, X.; Bai, C.; Wang, L.; Lawrence, T.S.; Anscher, M.S.; et al. Ensuring sample quality for blood biomarker studies in clinical trials: A multicenter international study for plasma and serum sample preparation. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Geyer, P.E.; Voytik, E.; Treit, P.V.; Doll, S.; Kleinhempel, A.; Niu, L.; Müller, J.B.; Buchholtz, M.L.; Bader, J.M.; Teupser, D.; et al. Plasma Proteome Profiling to detect and avoid sample-related biases in biomarker studies. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404, Correction in J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12451. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fusco, N.; Jantus-Lewintre, E.; Serrano, M.J.; Gandara, D.; Malapelle, U.; Rolfo, C. Role of the International Society of Liquid Biopsy (ISLB) in establishing quality control frameworks for clinical integration. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2025, 209, 104619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos, J.; Carneiro, I.; Corrales, F.; Elortza, F.; Paradela, A.; Del Pino, M.S.; Iloro, I.; Marcilla, M.; Mora, M.I.; Valero, L.; et al. Multicentric study of the effect of pre-analytical variables in the quality of plasma samples stored in biobanks using different complementary proteomic methods. J. Proteom. 2017, 150, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, N.; Knutti, N.; Rose, M.; Neugebauer, S.; Geiger, J.; Jahns, R.; Klopp, N.; Illig, T.; Mathay, C.; Betsou, F.; et al. Quality Assessment of the Preanalytical Workflow in Liquid Biobanking: Taurine as a Serum-Specific Quality Indicator for Preanalytical Process Variations. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2019, 17, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gegner, H.M.; Naake, T.; Dugourd, A.; Müller, T.; Czernilofsky, F.; Kliewer, G.; Jäger, E.; Helm, B.; Kunze-Rohrbach, N.; Klingmüller, U.; et al. Pre-analytical processing of plasma and serum samples for combined proteome and metabolome analysis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 961448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kristoffersen, A.H.; Hammer, I.J.; Vannes, S.; Åsberg, A.; Aakre, K.M. Impact of different preanalytical conditions on results of lupus anticoagulant tests. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019, 41, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassis, M.E.; Niles, R.K.; Braten, M.N.; Albertolle, M.E.; Ewa Witkowska, H.; Hubel, C.A.; Fisher, S.J.; Williams, K.E. Evaluating the effects of preanalytical variables on the stability of the human plasma proteome. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ungerer, V.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Holdenrieder, S. Preanalytical variables that affect the outcome of cell-free DNA measurements. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 484–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, T.; Taschner-Mandl, S.; Saloberger-Sindhöringer, L.; Popitsch, N.; Heitzer, E.; Witt, V.; Geyeregger, R.; Hutter, C.; Schwentner, R.; Ambros, I.M.; et al. Assessment of Pre-Analytical Sample Handling Conditions for Comprehensive Liquid Biopsy Analysis. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1070–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appierto, V.; Callari, M.; Cavadini, E.; Morelli, D.; Daidone, M.G.; Tiberio, P. A lipemia-independent NanoDrop(®)-based score to identify hemolysis in plasma and serum samples. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhelankin, A.V.; Stonogina, D.A.; Vasiliev, S.V.; Babalyan, K.A.; Sharova, E.I.; Doludin, Y.V.; Shchekochikhin, D.Y.; Generozov, E.V.; Akselrod, A.S. Circulating Extracellular miRNA Analysis in Patients with Stable CAD and Acute Coronary Syndromes. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vassallo, R.R.; Stearns, F.M. Lipemic plasma: A renaissance. Transfusion 2011, 51, 1136–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, H.K.; Hall, W.D.; Hurst, J.W. (Eds.) Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd ed.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verberk, I.M.W.; Gouda, M.; Antwi-Berko, D.; van Leeuwenstijn, M.; Bongers, B.; Houtkamp, I.M.; van der Flier, W.M.; Janelidze, S.; Hansson, O.; Bastard, N.L.; et al. Evidence-based standardized sample handling protocol for accurate blood-based Alzheimer’s disease biomarker measurement: Results and consensus of the Global Biomarker Standardization Consortium. Alzheimers Dement. 2025, 21, e70752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ruksakulpiwat, S.; Zhou, W.; Phianhasin, L.; Benjasirisan, C.; Su, T.; Aldossary, H.M.; Kudlowitz, A.; Challa, A.K.; Li, J.; Praditukrit, K. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Assessing the Accuracy of Blood Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Ischemic Stroke in Adult and Elderly Populations. eNeuro 2024, 11, ENEURO.0302-24.2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Malmodin, D.; Bay Nord, A.; Zafar, H.; Paulson, L.; Karlsson, B.G.; Naluai, Å.T. Preanalytical (Mis)Handling of Plasma Investigated by 1H NMR Metabolomics. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 48727–48737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gill, P.K. Rapid isolation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from whole blood with ficoll hypaque density centrifugation. J. Int. Res. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, A. Blood Separation. In Encyclopedia of Membranes; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ahmed, S.; Harari, F.; Vahter, M. Impact of Ficoll density gradient centrifugation on major and trace element concentrations in erythrocytes and blood plasma. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 29, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- English, D.; Andersen, B.R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J. Immunol. Methods 1974, 5, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L. Haemolysis as Influence & Interference Factor. EJIFCC 2002, 13, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koseoglu, M.; Hur, A.; Atay, A.; Cuhadar, S. Effects of hemolysis interferences on routine biochemistry parameters. Biochem. Med. 2011, 21, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza, A.P.; Wider-Eberspächer, E.; Morton, L.; van Ham, M.; Pállinger, É.; Buzás, E.I.; Jänsch, L.; Dunay, I.R. Proteomic analysis of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles: Pre- and postprandial comparisons. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, X.; Takeuchi, T.; Takeda, A.; Mochizuki, H.; Nagai, Y. Comparison of serum and plasma as a source of blood extracellular vesicles: Increased levels of platelet-derived particles in serum extracellular vesicle fractions alter content profiles from plasma extracellular vesicle fractions. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kalaria, T.; Ford, C.; Gama, R. Managing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) interference in EDTA contaminated samples—Selectivity in reporting analytes. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2022, 60, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moman, R.N.; Gupta, N.; Varacallo, M.A. Physiology, Albumin. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Siddiqui, W.J. Cholesterol Levels. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Tokuda, S.; Nakazawa, Y.; Kurozumi, S.; Obayashi, S.; Yajima, R.; Shirabe, K. Implications of Low Serum Albumin as a Prognostic Factor of Long-term Outcomes in Patients with Breast Cancer. In Vivo 2020, 34, 2033–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tang, Q.; Li, X.; Sun, C.R. Predictive value of serum albumin levels on cancer survival: A prospective cohort study. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1323192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Liu, P.; Kong, Y.; Ye, F.; Shuang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Xie, X. The effect of preoperative serum triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels on the prognosis of breast cancer. Breast 2017, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandrangi, S.L.; Chittineedi, P.; Chikati, R.; Mosquera, J.A.N.; Llaguno, S.N.S.; Mohiddin, G.J.; Lanka, S.; Chalumuri, S.S.; Maddu, N. Role of Lipoproteins in the Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer. Membranes 2022, 12, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Halvey, P.; Farutin, V.; Koppes, L.; Gunay, N.S.; Pappas, D.A.; Manning, A.M.; Capila, I. Variable blood processing procedures contribute to plasma proteomic variability. Clin. Proteom. 2021, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Holcar, M.; Ferdin, J.; Sitar, S.; Tušek-Žnidarič, M.; Dolžan, V.; Plemenitaš, A.; Žagar, E.; Lenassi, M. Enrichment of plasma extracellular vesicles for reliable quantification of their size and concentration for biomarker discovery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cha, Y.; Kim, S.; Han, S.W. Utilizing Plasma Circulating Tumor DNA Sequencing for Precision Medicine in the Management of Solid Cancers. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Karimi, N.; Dalirfardouei, R.; Dias, T.; Lötvall, J.; Lässer, C. Tetraspanins distinguish separate extracellular vesicle subpopulations in human serum and plasma—Contributions of platelet extracellular vesicles in plasma samples. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Available online: https://www.isth.org/page/Published_Guidance (accessed on 14 October 2025).
- Coumans, F.A.W.; Brisson, A.R.; Buzas, E.I.; Dignat-George, F.; Drees, E.E.E.; El-Andaloussi, S.; Emanueli, C.; Gasecka, A.; Hendrix, A.; Hill, A.F.; et al. Methodological Guidelines to Study Extracellular Vesicles. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1632–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaro García, L.; Berker, J.; Richter, K.; Zielske, L.; Hofmann, W.K.; Clemm von Hohenberg, K. A translational protocol optimizes the isolation of plasma-derived extracellular vesicle proteomics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 24292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
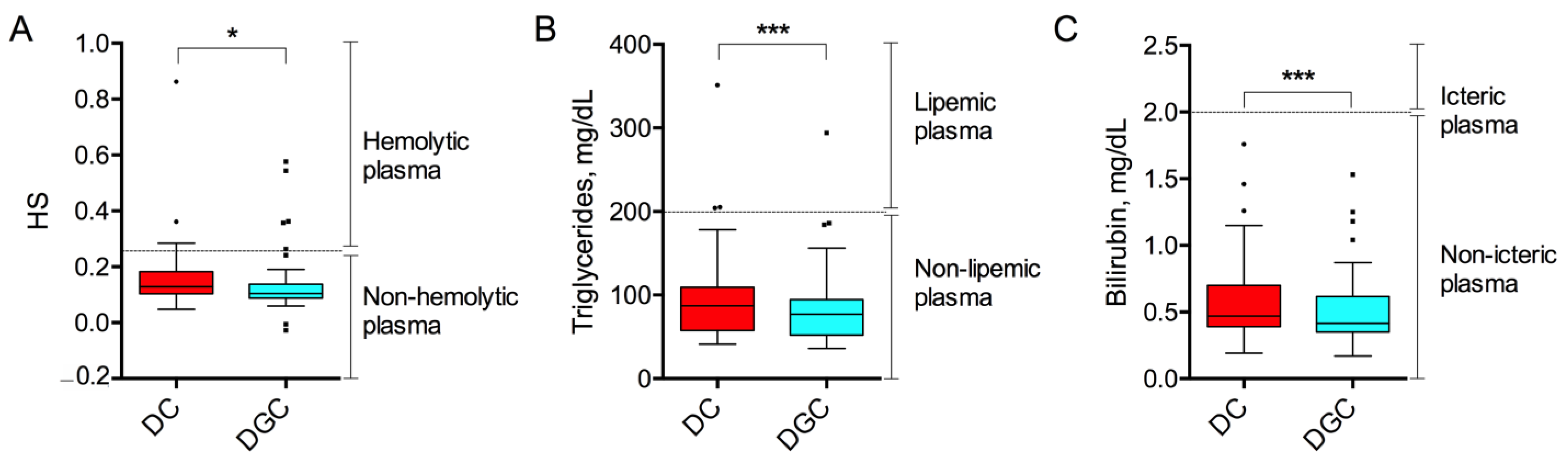

| Type of Non-Conformity | DC (n, %) | DGC (n, %) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemolysis | 4, 8% | 5, 10% | 0.81 |
| Lipemia | 3, 6% | 1, 2% | 0.28 |
| Icterus | 0, 0% | 0, 0% | 1.00 |
| Parameter (Reference Range of Normality) | DC (n = 50) | DGC (n = 50) | p-Value DC vs. DGC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Range | Out-of-Range | In Range | Out-of-Range | ||
| Na (134–145 mmol/L) | 47 (94%) | 3 (6%) | 48 (96%) | 2 (4%) | 1.00 |
| P (2.3–4.7 mg/dL) | 49 (98%) | 1 (2%) | 43 (86%) | 7 (14%) | 0.06 |
| Albumin (3.5–5.2 g/dL) | 42 (84%) | 8 (16%) | 16 (32%) | 34 (68%) | <0.0001 |
| Total Chol. (<200 mg/dL) | 41 (82%) | 9 (18%) | 47 (94%) | 3 (6%) | 0.02 |
| HDL (>40 mg/dL) | 40 (80%) | 10 (20%) | 32 (64%) | 18 (36%) | 0.08 |
| LDL (<160 mg/dL) | 44 (88%) | 6 (12%) | 48 (96%) | 2 (4%) | 0.14 |
| Parameter | Correlation Coefficient [95% CI] | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 0.824 [0.708–0.897] | <0.0001 |
| P | 0.966 [0.911–0.971] | <0.0001 |
| Albumin | 0.776 [0.629–0.869] | <0.0001 |
| Total Cholesterol | 0.949 [0.911–0.971] | <0.0001 |
| HDL | 0.956 [0.922–0.975] | <0.0001 |
| LDL | 0.945 [0.903–0.969] | <0.0001 |
| Triglycerides | 0.965 [0.937–0.980] | <0.0001 |
| Bilirubin | 0.978 [0.961–0.988] | <0.0001 |
| Parameter | Value (n = 50) |
|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 63.26 ± 15.76 |
| BMI (mean ± SD) | 24.71 ± 3.93 |
| Tumor grade (n, %) | |
| G1 | 7, 14% |
| G2 | 28, 56% |
| G3 | 14, 28% |
| Not specified | 1, 2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piccotti, F.; Treviso, F.; Morasso, C.; Pittatore Leone, N.; Navarra, A.; Albasini, S.; Bonizzi, A.; Tagliolini, I.; Gorgoglione, F.; Corsi, F.; et al. Influence of Isolation Techniques on the Quality of Plasma Samples: Implications for Cancer Biobanking. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110281
Piccotti F, Treviso F, Morasso C, Pittatore Leone N, Navarra A, Albasini S, Bonizzi A, Tagliolini I, Gorgoglione F, Corsi F, et al. Influence of Isolation Techniques on the Quality of Plasma Samples: Implications for Cancer Biobanking. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110281
Chicago/Turabian StylePiccotti, Francesca, Fiorella Treviso, Carlo Morasso, Nadia Pittatore Leone, Antonella Navarra, Sara Albasini, Arianna Bonizzi, Ilaria Tagliolini, Francesca Gorgoglione, Fabio Corsi, and et al. 2025. "Influence of Isolation Techniques on the Quality of Plasma Samples: Implications for Cancer Biobanking" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110281
APA StylePiccotti, F., Treviso, F., Morasso, C., Pittatore Leone, N., Navarra, A., Albasini, S., Bonizzi, A., Tagliolini, I., Gorgoglione, F., Corsi, F., & Truffi, M. (2025). Influence of Isolation Techniques on the Quality of Plasma Samples: Implications for Cancer Biobanking. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110281







