Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Toxic Models of Parkinsonism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MAO Inhibitors in 6-OHDA-Based Models
3. MAO Inhibitors in MPTP-Based Models
4. MAO Inhibitors in Rotenone- and Paraquat-Based Models
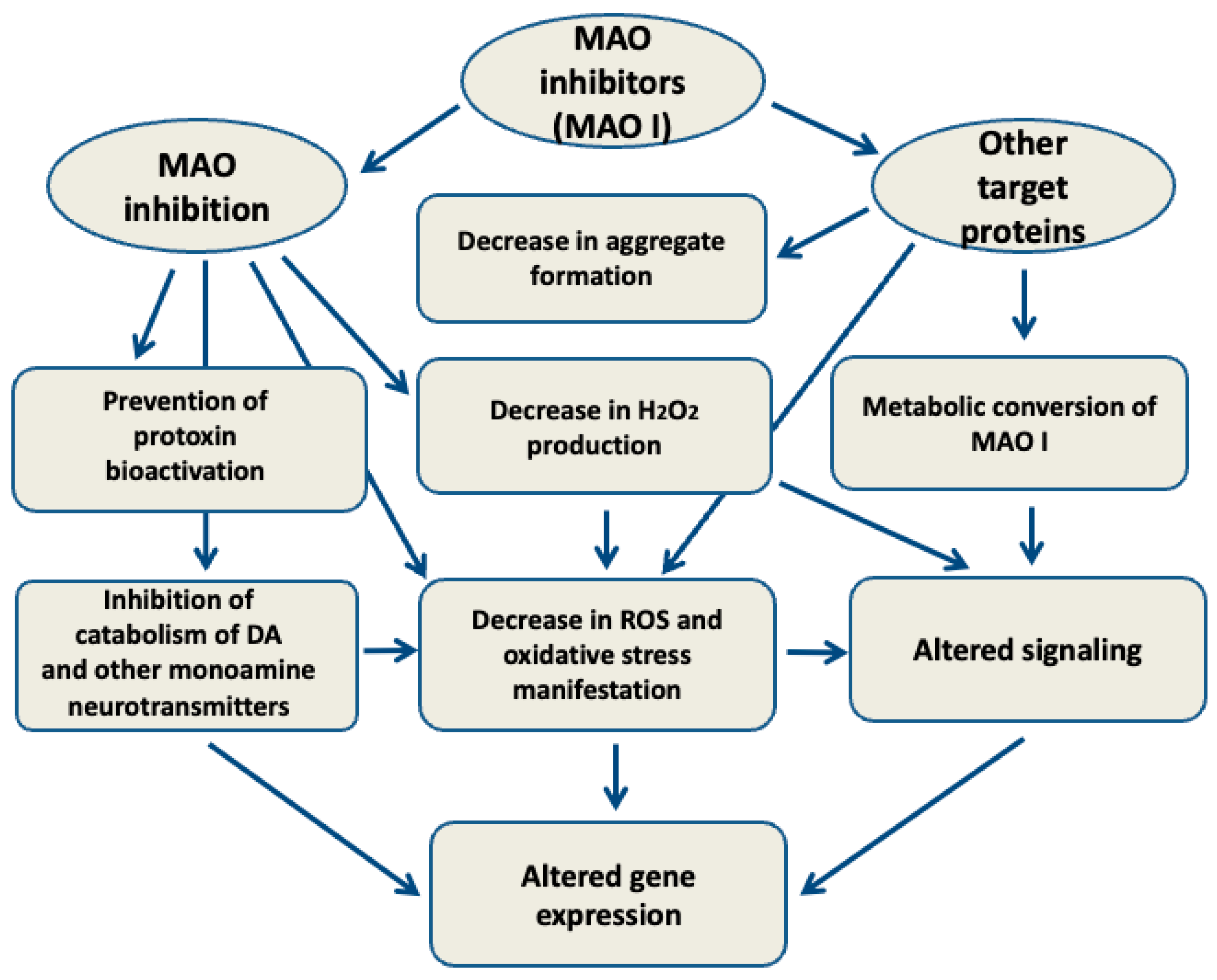
5. MAO-Independent Effects of MAO Inhibitors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Darweesh, S.; Llibre-Guerra, J.; Marras, C.; San Luciano, M.; Tanner, C. The Epidemiology of Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2024, 403, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, H.N.; Esteves, A.R.; Empadinhas, N.; Cardoso, S.M. Parkinson’s Disease: A Multisystem Disorder. Neurosci. Bull. 2022, 39, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Nichols, E.; Alam, T.; Bannick, M.S.; Beghi, E.; Blake, N.; Culpepper, W.J.; Dorsey, E.R.; Elbaz, A.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Neurological Disorders, 1990–2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouli, A.; Torsney, K.M.; Kuan, W.-L. Parkinson’s Disease: Etiology, Neuropathology, and Pathogenesis. In Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects; Stoker, T.B., Greenland, J.C., Eds.; Codon Publications: Brisbane, AU, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-9944381-6-4. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggett, D.; Olson, A.; Parmar, M.S. Novel Approaches Targeting α-Synuclein for Parkinson’s Disease: Current Progress and Future Directions for the Disease-Modifying Therapies. Brain Disord. 2024, 16, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, H.R.; Spillantini, M.G.; Sue, C.M.; Williams-Gray, C.H. The Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2024, 403, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.M.A.; Gasser, T.; Edwards, R.; Zweckstetter, M.; Melki, R.; Stefanis, L.; Lashuel, H.A.; Sulzer, D.; Vekrellis, K.; Halliday, G.M.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Research: Defining Strategic Moves in the Battle against Parkinson’s Disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.-E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzer, D.; Edwards, R.H. The Physiological Role of α-Synuclein and Its Relationship to Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, C.H.; Beach, T.G. Neuropathological Basis of Nonmotor Manifestations of Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marras, C.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Nonmotor Features of Parkinson’s Disease Subtypes. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Robak, L.A.; Yu, M.; Cykowski, M.; Shulman, J.M. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Syndrome. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2023, 18, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, B.; Lee, Y. Disease Model Organism for Parkinson Disease: Drosophila Melanogaster. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprich, J.B.; Kalia, L.V.; Brotchie, J.M. Animal Models of α-Synucleinopathy for Parkinson Disease Drug Development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ham, A.; Ma, T.C.; Kuo, S.-H.; Kanter, E.; Kim, D.; Ko, H.S.; Quan, Y.; Sardi, S.P.; Li, A.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Mitophagy Defect Triggered by Heterozygous GBA Mutations. Autophagy 2019, 15, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahul; Siddique, Y.H. Drosophila: A Model to Study the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2022, 21, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramonet, D.; Daher, J.P.L.; Lin, B.M.; Stafa, K.; Kim, J.; Banerjee, R.; Westerlund, M.; Pletnikova, O.; Glauser, L.; Yang, L.; et al. Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss, Reduced Neurite Complexity and Autophagic Abnormalities in Transgenic Mice Expressing G2019S Mutant LRRK2. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenburger, B.H.; Schulz, J.B. Limitations of Cellular Models in Parkinson’s Disease Research. In Parkinson’s Disease and Related Disorders; Riederer, P., Reichmann, H., Youdim, M.B.H., Gerlach, M., Eds.; Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementary; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2006; Volume 70, pp. 261–268. ISBN 978-3-211-28927-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ioghen, O.C.; Ceafalan, L.C.; Popescu, B.O. SH-SY5Y Cell Line In Vitro Models for Parkinson Disease Research-Old Practice for New Trends. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weykopf, B.; Haupt, S.; Jungverdorben, J.; Flitsch, L.J.; Hebisch, M.; Liu, G.-H.; Suzuki, K.; Belmonte, J.C.I.; Peitz, M.; Blaess, S.; et al. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Modeling of Mutant LRRK2-Associated Parkinson’s Disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2019, 49, 561–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winner, B.; Jappelli, R.; Maji, S.K.; Desplats, P.A.; Boyer, L.; Aigner, S.; Hetzer, C.; Loher, T.; Vilar, M.; Campioni, S.; et al. In Vivo Demonstration That Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers Are Toxic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4194–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, M.; Chong, C.-M.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Cai, C.-Z.; Lu, J.-H.; Qin, D.; Su, H. Comprehensive Perspectives on Experimental Models for Parkinson’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnova, E.A.; Swanberg, M. Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. In Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects; Stoker, T.B., Greenland, J.C., Eds.; Codon Publications: Brisbane, AU, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-9944381-6-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lama, J.; Buhidma, Y.; Fletcher, E.J.R.; Duty, S. Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease: A Guide to Selecting the Optimal Model for Your Research. Neuronal Signal. 2021, 5, NS20210026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.-S.; Geng, W.-S.; Jia, J.-J. Neurotoxin-Induced Animal Models of Parkinson Disease: Pathogenic Mechanism and Assessment. ASN Neuro 2018, 10, 1759091418777438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesa, J.; Phani, S.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Przedborski, S. Classic and New Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 845618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, E.; Hasan, I.; Haque, M.E. Parkinson’s Disease: Exploring Different Animal Model Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoi, M.; Maruyama, W.; Shamoto-Nagai, M.; Riederer, P. Toxic Interactions between Dopamine, α-Synuclein, Monoamine Oxidase, and Genes in Mitochondria of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neural Transm. 2024, 131, 639–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Georgieva, M.G.; Atanasov, A.G.; Tzvetkov, N.T. Monoamine Oxidases (MAOs) as Privileged Molecular Targets in Neuroscience: Research Literature Analysis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B.H.; Edmondson, D.; Tipton, K.F. The Therapeutic Potential of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.C.; Chen, K.; Ridd, M.J. Monoamine Oxidase: From Genes to Behavior. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1999, 22, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.C.; Wu, J.B.; Chen, K. Transcriptional Regulation and Multiple Functions of MAO Genes. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finberg, J.P.M. Update on the Pharmacology of Selective Inhibitors of MAO-A and MAO-B: Focus on Modulation of CNS Monoamine Neurotransmitter Release. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 143, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, J.C. Monoamine oxidase isoenzymes: Genes, functions and targets for behavior and cancer therapy. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlund, K.N.; Denney, R.M.; Rose, R.M.; Abell, C.W. Localization of Distinct Monoamine Oxidase A and Monoamine Oxidase B Cell Populations in Human Brainstem. Neuroscience 1988, 25, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finberg, J.P.M.; Rabey, J.M. Inhibitors of MAO-A and MAO-B in Psychiatry and Neurology. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoi, M.; Maruyama, W.; Inaba-Hasegawa, K. Type A and B Monoamine Oxidase in Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disorders: Their Distinct Roles in Neuronal Death and Survival. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Chaparro, A.; Flores-Lopez, N.S.; Quintanilla-Guerrero, F.; Nicolás-Álvarez, D.E.; Hernandez-Martinez, A.R. Design of New Reversible and Selective Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase A and a Comparison with Drugs Already Approved. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2023, 47, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoi, M.; Maruyama, W. Functional Mechanism of Neuroprotection by Inhibitors of Type B Monoamine Oxidase in Parkinson’s Disease. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 1233–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Arawaka, S.; Sato, H.; Sasaki, A.; Shigekiyo, T.; Takahata, K.; Tsunekawa, H.; Kato, T. Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibition Facilitates α-Synuclein Secretion In Vitro and Delays Its Aggregation in rAAV-Based Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 7479–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alborghetti, M.; Bianchini, E.; De Carolis, L.; Galli, S.; Pontieri, F.E.; Rinaldi, D. Type-B Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Neurological Diseases: Clinical Applications Based on Preclinical Findings. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carradori, S.; Secci, D.; Petzer, J.P. MAO Inhibitors and Their Wider Applications: A Patent Review. Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B.H. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors, and Iron Chelators in Depressive Illness and Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1719–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandini, F.; Armentero, M.-T.; Martignoni, E. The 6-Hydroxydopamine Model: News from the Past. Park. Relat. Disord. 2008, 14 (Suppl. 2), S124–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simola, N.; Morelli, M.; Carta, A.R. The 6-Hydroxydopamine Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotox. Res. 2007, 11, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotibut, T.; Apple, D.M.; Jefferis, R.; Salvatore, M.F. Dopamine Transporter Loss in 6-OHDA Parkinson’s Model Is Unmet by Parallel Reduction in Dopamine Uptake. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storch, A.; Ludolph, A.C.; Schwarz, J. Dopamine Transporter: Involvement in Selective Dopaminergic Neurotoxicity and Degeneration. J. Neural Transm. 2004, 111, 1267–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Varešlija, D.; Tipton, K.F.; Davey, G.P.; McDonald, A.G. 6-Hydroxydopamine: A Far from Simple Neurotoxin. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinka, Y.Y.; Youdim, M.B. Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complexes I and IV by 6-Hydroxydopamine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 292, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Baltazar, D.; Zavala-Flores, L.M.; Villanueva-Olivo, A. The 6-Hydroxydopamine Model and Parkinsonian Pathophysiology: Novel Findings in an Older Model. Neurología 2017, 32, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantic, I.; Cumic, J.; Skodric, S.R.; Dugalic, S.; Brodski, C. Oxidopamine and Oxidative Stress: Recent Advances in Experimental Physiology and Pharmacology. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2021, 336, 109380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, A. Classic Toxin-Induced Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease: 6-OHDA and MPTP. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 318, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisenko, G.G.; Kagan, V.E.; Hsia, C.J.C.; Schor, N.F. Interaction between 6-Hydroxydopamine and Transferrin: “Let My Iron Go”. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 3392–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameson, G.N.L.; Jameson, R.F.; Linert, W. New Insights into Iron Release from Ferritin: Direct Observation of the Neurotoxin 6-Hydroxydopamine Entering Ferritin and Reaching Redox Equilibrium with the Iron Core. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 2346–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shachar, D.; Zuk, R.; Gazawi, H.; Ljubuncic, P. Dopamine toxicity involves mitochondrial complex I inhibition: Implications to dopamine-related neuropsychiatric disorders. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 67, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanrott, K.; Gudmunsen, L.; O’Neill, M.J.; Wonnacott, S. 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated via Extracellular Auto-Oxidation and Caspase 3-Dependent Activation of Protein Kinase Cδ. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 5373–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Nishio, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Kinumi, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Masuo, Y.; Niki, E. Molecular Mechanisms of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Cytotoxicity in PC12 Cells: Involvement of Hydrogen Peroxide-Dependent and -Independent Action. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.-J.; Liang, L.; Pan, M.-H.; Lu, D.-H.; Wang, T.-M.; Li, S.-B.; Zhong, H.-B.; Yang, X.-J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, B.; et al. Theacrine, a Purine Alkaloid from Kucha, Protects against Parkinson’s Disease through SIRT3 Activation. Phytomedicine 2020, 77, 153281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazani, E.; YazdFazeli, M.; Emami, S.A.; Mohtashami, L.; Javadi, B.; Asili, J.; Tayarani-Najaran, Z. Protective Effects of Cinnamomum Verum, Cinnamomum Cassia and Cinnamaldehyde against 6-OHDA-Induced Apoptosis in PC12 Cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 2437–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, S.; Zheng, Q.; Zhai, S.; Cai, T.; Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, C. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Mediates Clearance of Iron Accumulation by Regulating Iron Metabolism in a Parkinson’s Disease Model Induced by 6-OHDA. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Chen, G. Baicalin Attenuated Substantia Nigra Neuronal Apoptosis in Parkinson’s Disease Rats via the mTOR/AKT/GSK-3β Pathway. JIN 2019, 18, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.P.; Tipton, K.F. Interactions of the Neurotoxin 6-Hydroxydopamine with Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 128, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Södersten, E.; Toskas, K.; Rraklli, V.; Tiklova, K.; Björklund, Å.K.; Ringnér, M.; Perlmann, T.; Holmberg, J. A Comprehensive Map Coupling Histone Modifications with Gene Regulation in Adult Dopaminergic and Serotonergic Neurons. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessner, G.; Schmitt, O.; Haas, S.J.-P.; Mikkat, S.; Kreutzer, M.; Wree, A.; Glocker, M.O. Differential Proteome of the Striatum from Hemiparkinsonian Rats Displays Vivid Structural Remodeling Processes. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4671–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.; Yang, J.; Yun, N.; Choe, K.-M.; Jin, B.K.; Oh, Y.J. Proteomic Analysis of Expression and Protein Interactions in a 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Rat Brain Lesion Model. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, R.; Watson, D.G.; Best, S.A.; Midgley, J.M.; Wenlong, H.; Petty, R.K. The Determination of Hydroxydopamines and Other Trace Amines in the Urine of Parkinsonian Patients and Normal Controls. Neurochem. Res. 1993, 18, 1175–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtius, H.C.; Wolfensberger, M.; Steinmann, B.; Redweik, U.; Siegfried, J. Mass Fragmentography of Dopamine and 6-Hydroxydopamine. Application to the Determination of Dopamine in Human Brain Biopsies from the Caudate Nucleus. J. Chromatogr. 1974, 99, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, A.; Mohanakumar, K.P. L-DOPA-Induced 6-Hydroxydopamine Production in the Striata of Rodents Is Sensitive to the Degree of Denervation. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, A.; Mohanakumar, K.P. Long Term L-DOPA Treatment Causes Production of 6-OHDA in the Mouse Striatum: Involvement of Hydroxyl Radical. Ann. Neurosci. 2010, 16, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riederer, P.; Horowski, R. L-DOPA-Therapy in Parkinson’s Disease: Some Personal Reflections on L-DOPA Therapy from Vienna and Berlin. J. Neural Transm. 2023, 130, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finberg, J.P.; Wang, J.; Goldstein, D.S.; Kopin, I.J.; Bankiewicz, K.S. Influence of Selective Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase A or B on Striatal Metabolism of L-DOPA in Hemiparkinsonian Rats. J. Neurochem. 1995, 65, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sader-Mazbar, O.; Loboda, Y.; Rabey, M.J.; Finberg, J.P.M. Increased L-DOPA-Derived Dopamine Following Selective MAO-A or -B Inhibition in Rat Striatum Depleted of Dopaminergic and Serotonergic Innervation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachtel, S.R.; Abercrombie, E.D. L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine-Induced Dopamine Release in the Striatum of Intact and 6-Hydroxydopamine-Treated Rats: Differential Effects of Monoamine Oxidase A and B Inhibitors. J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breese, G.R.; Traylor, T.D. Effect of 6-hydroxydopamine on brain norepinephrine and dopamine evidence for selective degeneration of catecholamine neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1970, 174, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ambani, L.M.; Van Woert, M.H.; Murphy, S. Brain Peroxidase and Catalase in Parkinson Disease. Arch. Neurol. 1975, 32, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, M.-C.; Alcaraz-Zubeldia, M.; Montes, S.; Rios, C. Free Copper, Ferroxidase and SOD1 Activities, Lipid Peroxidation and NO(x) Content in the CSF. A Different Marker Profile in Four Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacInnes, N.; Duty, S. Locomotor Effects of Imidazoline I2-Site-Specific Ligands and Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Rats with a Unilateral 6-Hydroxydopamine Lesion of the Nigrostriatal Pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonen, T.; Haapalinna, A.; Heinonen, E.; Suhonen, J.; Hervonen, A. Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitor Selegiline Protects Young and Aged Rat Peripheral Sympathetic Neurons against 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurotoxicity. Acta Neuropathol. 1996, 91, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunekawa, H.; Takahata, K.; Okano, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Satoyoshi, H.; Nishimura, T.; Hoshino, N.; Muraoka, S. Selegiline Increases on Time without Exacerbation of Dyskinesia in 6-Hydroxydopamine-Lesioned Rats Displaying l-Dopa-Induced Wearing-off and Abnormal Involuntary Movements. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 347, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.E.; Hoffman, A.F.; Hudson, J.L.; Hoffer, B.J.; Boyson, S.J. Chronic Treatment with Levodopa and/or Selegiline Does Not Affect Behavioral Recovery Induced by Fetal Ventral Mesencephalic Grafts in Unilaterally 6-Hydroxydopamine-Lesioned Rats. Exp. Neurol. 1994, 130, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluf, Y.; Vaya, J.; Khatib, S.; Loboda, Y.; Finberg, J.P.M. Selective Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase A or B Reduces Striatal Oxidative Stress in Rats with Partial Depletion of the Nigro-Striatal Dopaminergic Pathway. Neuropharmacology 2013, 65, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, A.; Grealy, M. Neuroprotective and Neuro-Restorative Effects of Minocycline and Rasagiline in a Zebrafish 6-Hydroxydopamine Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroscience 2017, 367, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandini, F.; Armentero, M.T.; Fancellu, R.; Blaugrund, E.; Nappi, G. Neuroprotective Effect of Rasagiline in a Rodent Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 187, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledreux, A.; Boger, H.A.; Hinson, V.K.; Cantwell, K.; Granholm, A.-C. BDNF Levels Are Increased by Aminoindan and Rasagiline in a Double Lesion Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Res. 2016, 1631, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Am, O.; Amit, T.; Youdim, M.B.H. Aminoindan and Hydroxyaminoindan, Metabolites of Rasagiline and Ladostigil, Respectively, Exert Neuroprotective Properties in Vitro. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, O.; Amit, T.; Bar-Am, O.; Youdim, M.B.H. Ladostigil: A Novel Multimodal Neuroprotective Drug with Cholinesterase and Brain-Selective Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Activities for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, O.; Amit, T.; Sagi, Y.; Drigues, N.; Youdim, M.B.H. Genomic and Proteomic Study to Survey the Mechanism of Action of the Anti-Parkinson’s Disease Drug, Rasagiline Compared with Selegiline, in the Rat Midbrain. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 1457–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, O.; Bar-Am, O.; Prosolovich, K.; Amit, T.; Youdim, M.B.H. Does 1-(R)-Aminoindan Possess Neuroprotective Properties against Experimental Parkinson’s Disease? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Jang, Y.Y.; Han, E.S.; Lee, C.S. Protective Effect of Harmaline and Harmalol against Dopamine- and 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Oxidative Damage of Brain Mitochondria and Synaptosomes, and Viability Loss of PC12 Cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadnikov, I.A.; Verbovaya, E.R.; Voronkov, D.N.; Voronin, M.V.; Seredenin, S.B. Deferred Administration of Afobazole Induces Sigma1R-Dependent Restoration of Striatal Dopamine Content in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronin, M.V.; Kadnikov, I.A.; Voronkov, D.N.; Seredenin, S.B. Chaperone Sigma1R Mediates the Neuroprotective Action of Afobazole in the 6-OHDA Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutillas, B.; Ambrosio, S.; Unzeta, M. Neuroprotective Effect of the Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor PF 9601N [N-(2-Propynyl)-2-(5-Benzyloxy-Indolyl) Methylamine] on Rat Nigral Neurons after 6-Hydroxydopamine-Striatal Lesion. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 329, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardoni, F.; Morari, M.; Kulisevsky, J.; Brugnoli, A.; Novello, S.; Pisanò, C.A.; Caccia, C.; Mellone, M.; Melloni, E.; Padoani, G.; et al. Safinamide Modulates Striatal Glutamatergic Signaling in a Rat Model of Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 367, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghian, M.; Mullali, G.; Pocock, J.M.; Piers, T.; Roach, A.; Smith, K.J. Neuroprotection by Safinamide in the 6-Hydroxydopamine Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2016, 42, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciaccaluga, M.; Mazzocchetti, P.; Bastioli, G.; Ghiglieri, V.; Cardinale, A.; Mosci, P.; Caccia, C.; Keywood, C.; Melloni, E.; Padoani, G.; et al. Effects of Safinamide on the Glutamatergic Striatal Network in Experimental Parkinson’s Disease. Neuropharmacology 2020, 170, 108024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huleatt, P.B.; Khoo, M.L.; Chua, Y.Y.; Tan, T.W.; Liew, R.S.; Balogh, B.; Deme, R.; Gölöncsér, F.; Magyar, K.; Sheela, D.P.; et al. Novel Arylalkenylpropargylamines as Neuroprotective, Potent, and Selective Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1400–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Am, O.; Amit, T.; Kupershmidt, L.; Aluf, Y.; Mechlovich, D.; Kabha, H.; Danovitch, L.; Zurawski, V.R.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Weinreb, O. Neuroprotective and Neurorestorative Activities of a Novel Iron Chelator-Brain Selective Monoamine Oxidase-A/Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitor in Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease and Aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar Am, O.; Amit, T.; Youdim, M.B.H. Contrasting Neuroprotective and Neurotoxic Actions of Respective Metabolites of Anti-Parkinson Drugs Rasagiline and Selegiline. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 355, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronin, M.V.; Aksenova, L.N.; Buneena, O.A.; Medvedev, A.E. Effect of Afobazole on Mitochondrial Monoamine Oxidase A Activity in Vitro. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 148, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langston, J.W.; Ballard, P.; Tetrud, J.W.; Irwin, I. Chronic Parkinsonism in Humans Due to a Product of Meperidine-Analog Synthesis. Science 1983, 219, 979–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Guillén, H. Inhibition of the Bioactivation of the Neurotoxin MPTP by Antioxidants, Redox Agents and Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, J.W. The MPTP Story. J. Park. Dis. 2017, 7, S11–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, G.E.; Rademacher, D.J. MPTP Mouse Models of Parkinson’s Disease: An Update. J. Park. Dis. 2011, 1, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustapha, M.; Taib, C.N.M. MPTP-Induced Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease: A Promising Direction for Therapeutic Strategies. Bosn. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2021, 21, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeyne, R.J.; Jackson-Lewis, V. The MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 134, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, S.; Mitsuhata, C.; Davis, S.; Wang, J.B.; Sato, T.; Morita, K.; Uhl, G.R.; Dohi, T. MPP+ Toxicity and Plasma Membrane Dopamine Transporter: Study Using Cell Lines Expressing the Wild-Type and Mutant Rat Dopamine Transporters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1404, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, N.; Ferger, B. Neurochemical Findings in the MPTP Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neural Transm. 2001, 108, 1263–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanesazzade, Z.; Peymani, M.; Ghaedi, K.; Nasr Esfahani, M.H. miR-34a/BCL-2 Signaling Axis Contributes to Apoptosis in MPP+ -Induced SH-SY5Y Cells. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2018, 6, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, H.S.; Gibson, G.E.; DeGiorgio, L.A.; Zhang, H.; Kidd, V.J.; Son, J.H. Dopaminergic Cell Death Induced by MPP(+), Oxidant and Specific Neurotoxicants Shares the Common Molecular Mechanism. J. Neurochem. 2001, 76, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Raamsdonk, J.M.; Vega, I.E.; Brundin, P. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Disease: Causation or Association? Oncotarget 2017, 8, 10777–10778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, R.; Mishra, K.P.; Thakur, A.K. Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Initiates Autophagy and Potentiates MPTP-Induced Autophagic Cell Death of Human Neuroblastoma Cells, SH-SY5Y: An Inside in the Pathology of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8038–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Dickson, D.W. Parkinson’s Disease: Experimental Models and Reality. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, C.; De Snoo, M.L.; Gondard, E.; Neudorfer, C.; Chau, H.; Ngana, S.G.; O’Hara, D.M.; Brotchie, J.M.; Koprich, J.B.; Lozano, A.M.; et al. Early-Onset Impairment of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Dopaminergic Neurons Caused by α-Synuclein. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.S.; Ahn, E.H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Manfredsson, F.P.; Sandoval, I.M.; Dhakal, S.; Iuvone, P.M.; Cao, X.; Ye, K. α-Synuclein Stimulation of Monoamine oxidase-B and Legumain Protease Mediates the Pathology of Parkinson’s Disease. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e98878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buneeva, O.A.; Kopylov, A.T.; Gnedenko, O.V.; Medvedeva, M.V.; Kapitsa, I.G.; Ivanova, E.A.; Ivanov, A.S.; Medvedev, A.E. Changes in the mitochondrial subproteome of mouse brain Rpn13-binding proteins induced by the neurotoxin MPTP and the neuroprotector isatin. Biomed. Khim 2021, 67, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buneeva, O.A.; Medvedeva, M.V.; Kopylov, A.T.; Medvedev, A.E. Ubiquitin Subproteome of Brain Mitochondria and Its Changes Induced by Experimental Parkinsonism and Action of Neuroprotectors. Biochem. Mosc. 2019, 84, 1359–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buneeva, O.A.; Kopylov, A.T.; Nerobkova, L.N.; Kapitsa, I.G.; Zgoda, V.G.; Medvedev, A.E. The effect of neurotoxin MPTP administration to mice on the proteomic profile of brain isatin-binding proteins. Biomed. Khim 2017, 63, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.H.; Qian, W.-J.; Wang, H.; Petyuk, V.A.; Bloom, J.S.; Sforza, D.M.; Laćan, G.; Liu, D.; Khan, A.H.; Cantor, R.M.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis Revealed by Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of the Striata in Two Mouse Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Meredith, G.E.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Shie, F.-S.; Lockhart, P.; Zhang, J. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Mitochondrial Proteins: Relevance to Lewy Body Formation and Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 134, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Shi, Q.; Ma, S.; Feng, N.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Striatal 19S Rpt6 Deficit Is Related to Alpha-Synuclein Accumulation in MPTP-Treated Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 376, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.-Y.; Chin, M.H.; Schepmoes, A.A.; Petyuk, V.A.; Weitz, K.K.; Petritis, B.O.; Monroe, M.E.; Camp, D.G.; Wood, S.A.; et al. Region-Specific Protein Abundance Changes in the Brain of MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Burté, F.; De Girolamo, L.A.; Hargreaves, A.J.; Billett, E.E. Alterations in the Mitochondrial Proteome of Neuroblastoma Cells in Response to Complex 1 Inhibition. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1974–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingazov, E.R.; Khakimova, G.R.; Kozina, E.A.; Medvedev, A.E.; Buneeva, O.A.; Bazyan, A.S.; Ugrumov, M.V. MPTP Mouse Model of Preclinical and Clinical Parkinson’s Disease as an Instrument for Translational Medicine. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 2991–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugrumov, M.V.; Khaindrava, V.G.; Kozina, E.A.; Kucheryanu, V.G.; Bocharov, E.V.; Kryzhanovsky, G.N.; Kudrin, V.S.; Narkevich, V.B.; Klodt, P.M.; Rayevsky, K.S.; et al. Modeling of Presymptomatic and Symptomatic Stages of Parkinsonism in Mice. Neuroscience 2011, 181, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langston, J.W.; Irwin, I.; Langston, E.B.; Forno, L.S. Pargyline Prevents MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism in Primates. Science 1984, 225, 1480–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemo, O.M.; Youdim, M.B.; Markey, S.P.; Markey, C.J.; Pollard, H.B. L-Deprenyl Confers Specific Protection against MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease-like Movement Disorder in the Goldfish. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 240, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.M.; Murphy, D.L.; Chiueh, C.C. Suppression of Hydroxyl Radical Formation and Protection of Nigral Neurons by L-Deprenyl (Selegiline). Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1996, 786, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, T.; Chock, P.B.; Murphy, D.L.; Chiueh, C.C. Role of the Redox Protein Thioredoxin in Cytoprotective Mechanism Evoked by (-)-Deprenyl. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 68, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkila, R.E.; Manzino, L.; Cabbat, F.S.; Duvoisin, R.C. Protection against the Dopaminergic Neurotoxicity of 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,5,6-Tetrahydropyridine by Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Nature 1984, 311, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupsch, A.; Sautter, J.; Götz, M.E.; Breithaupt, W.; Schwarz, J.; Youdim, M.B.; Riederer, P.; Gerlach, M.; Oertel, W.H. Monoamine Oxidase-Inhibition and MPTP-Induced Neurotoxicity in the Non-Human Primate: Comparison of Rasagiline (TVP 1012) with Selegiline. J. Neural Transm. 2001, 108, 985–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranyi, M.; Porceddu, P.F.; Gölöncsér, F.; Kulcsár, S.; Otrokocsi, L.; Kittel, Á.; Pinna, A.; Frau, L.; Huleatt, P.B.; Khoo, M.-L.; et al. Novel (Hetero)Arylalkenyl Propargylamine Compounds Are Protective in Toxin-Induced Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, M.B.; Gross, A.; Finberg, J.P. Rasagiline [N-Propargyl-1R(+)-Aminoindan], a Selective and Potent Inhibitor of Mitochondrial Monoamine Oxidase B. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 132, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel, S.; Sagi, Y.; Amit, T. Rasagiline Promotes Regeneration of Substantia Nigra Dopaminergic Neurons in Post-MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism via Activation of Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Signaling Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 1694–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi, Y.; Mandel, S.; Amit, T.; Youdim, M. Activation of Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Signaling Pathway by Rasagiline Facilitates Neurorescue and Restoration of Nigrostriatal Dopamine Neurons in Post-MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 25, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, S.; Zheng, H.; Fridkin, M.; Youdim, M.B.H. Restoration of Nigrostriatal Dopamine Neurons in Post-MPTP Treatment by the Novel Multifunctional Brain-Permeable Iron Chelator-Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Drug, M30. Neurotox. Res. 2010, 17, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, M.B.H. M30, a Brain Permeable Multitarget Neurorestorative Drug in Post Nigrostriatal Dopamine Neuron Lesion of Parkinsonism Animal Models. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18 (Suppl. 1), S151–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, W.; Lang, M.; Yan, R.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z. Neuroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Action of Multifunctional Agents Targeting Free Radicals, Monoamine Oxidase B and Cholinesterase in Parkinson’s Disease Model. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 61, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muck-Seler, D.; Sagud, M.; Mustapic, M.; Nedic, G.; Babic, A.; Mihaljevic Peles, A.; Jakovljevic, M.; Pivac, N. The Effect of Lamotrigine on Platelet Monoamine Oxidase Type B Activity in Patients with Bipolar Depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 1195–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrue, E.; Chalon, S.; Bodard, S.; Saliba, E.; Gressens, P.; Castelnau, P. Lamotrigine Is Neuroprotective in the Energy Deficiency Model of MPTP Intoxicated Mice. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 62, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Han, E.S.; Jang, Y.Y.; Han, J.H.; Ha, H.W.; Kim, D.E. Protective Effect of Harmalol and Harmaline on MPTP Neurotoxicity in the Mouse and Dopamine-Induced Damage of Brain Mitochondria and PC12 Cells. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.H.; Kwon, O.S.; Park, S.Y.; Han, E.S.; Lee, C.S. N-Methylated Beta-Carbolines Protect PC12 Cells from Cytotoxic Effect of MPP+ by Attenuation of Mitochondrial Membrane Permeability Change. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 46, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeswari, A.; Sabesan, M. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase-B by the Polyphenolic Compound, Curcumin and Its Metabolite Tetrahydrocurcumin, in a Model of Parkinson’s Disease Induced by MPTP Neurodegeneration in Mice. Inflammopharmacology 2008, 16, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buneeva, O.; Kopylov, A.; Kapitsa, I.; Ivanova, E.; Medvedev, A. Neuroprotective mechanisms of action of endogenous regulator isatin in MPTP induced Parkinsonism. In Proceedings of the Neuroscience for Medicine and Psychology, 30 April 2020; LLC MAKS Press: Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2020; pp. 120–121. [Google Scholar]
- Buneeva, O.; Kopylov, A.; Kapitsa, I.; Ivanova, E.; Zgoda, V.; Medvedev, A. The Effect of Neurotoxin MPTP and Neuroprotector Isatin on the Profile of Ubiquitinated Brain Mitochondrial Proteins. Cells 2018, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.E.; Buneeva, O.A.; Kopylov, A.T.; Tikhonova, O.V.; Medvedeva, M.V.; Nerobkova, L.N.; Kapitsa, I.G.; Zgoda, V.G. Brain Mitochondrial Subproteome of Rpn10-Binding Proteins and Its Changes Induced by the Neurotoxin MPTP and the Neuroprotector Isatin. Biochemistry 2017, 82, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Han, E.S.; Lee, W.B. Antioxidant Effect of Phenelzine on MPP+-Induced Cell Viability Loss in Differentiated PC12 Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2003, 28, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattamisra, S.K.; Yap, K.H.; Rao, V.; Choudhury, H. Multiple Biological Effects of an Iridoid Glucoside, Catalpol, and Its Underlying Molecular Mechanisms. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xiong, Z.; Yong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ke, Z.; Xia, Z.; Hu, Y. Catalpol Attenuates MPTP Induced Neuronal Degeneration of Nigral-Striatal Dopaminergic Pathway in Mice through Elevating Glial Cell Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Striatum. Neuroscience 2010, 167, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Wang, X.-B.; Chen, L.; Hao, S.; An, L.-J.; Jiang, B.; Guo, L. Catalpol Protects Mesencephalic Neurons against MPTP Induced Neurotoxicity via Attenuation of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and MAO-B Activity. Toxicol. Vitr. 2008, 22, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.-Y.; Jiang, B.; An, L.-J.; Bao, Y.-M. Neuroprotective Effect of Catalpol against MPP(+)-Induced Oxidative Stress in Mesencephalic Neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 568, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.; Kopylov, A.; Buneeva, O.; Kurbatov, L.; Tikhonova, O.; Ivanov, A.; Zgoda, V. A Neuroprotective Dose of Isatin Causes Multilevel Changes Involving the Brain Proteome: Prospects for Further Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buneeva, O.; Gnedenko, O.; Zgoda, V.; Kopylov, A.; Glover, V.; Ivanov, A.; Medvedev, A.; Archakov, A. Isatin-Binding Proteins of Rat and Mouse Brain: Proteomic Identification and Optical Biosensor Validation. Proteomics 2010, 10, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.; Buneeva, O.; Gnedenko, O.; Ershov, P.; Ivanov, A. Isatin, an Endogenous Nonpeptide Biofactor: A Review of Its Molecular Targets, Mechanisms of Actions, and Their Biomedical Implications. BioFactors 2018, 44, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Dixit, A.; Agrawal, S.; Singh, A.; Srivastava, G.; Singh, A.K.; Srivastava, P.K.; Prakash, O.; Singh, M.P. Rodent Models and Contemporary Molecular Techniques: Notable Feats yet Incomplete Explanations of Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 46, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gamal, M.; Salama, M.; Collins-Praino, L.E.; Baetu, I.; Fathalla, A.M.; Soliman, A.M.; Mohamed, W.; Moustafa, A.A. Neurotoxin-Induced Rodent Models of Parkinson’s Disease: Benefits and Drawbacks. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 897–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Gutiérrez, M.T.; Serrano-García, N.; Orozco-Ibarra, M. Rotenone-Induced Model of Parkinson’s Disease: Beyond Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibition. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 1929–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maegawa, H.; Niwa, H. Generation of Mitochondrial Toxin Rodent Models of Parkinson’s Disease Using 6-OHDA, MPTP, and Rotenone. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2322, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, N.; Long, X.; Xiong, J.; Jia, M.; Chen, C.; Huang, J.; Ghoorah, D.; Kong, X.; Lin, Z.; Wang, T. Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibitor Rotenone-Induced Toxicity and Its Potential Mechanisms in Parkinson’s Disease Models. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2012, 42, 613–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betarbet, R.; Canet-Aviles, R.M.; Sherer, T.B.; Mastroberardino, P.G.; McLendon, C.; Kim, J.-H.; Lund, S.; Na, H.-M.; Taylor, G.; Bence, N.F.; et al. Intersecting Pathways to Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease: Effects of the Pesticide Rotenone on DJ-1, α-Synuclein, and the Ubiquitin–Proteasome System. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 22, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenamyre, J.T.; Betarbet, R.; Sherer, T.B. The Rotenone Model of Parkinson’s Disease: Genes, Environment and Mitochondria. Park. Relat. Disord. 2003, 9 (Suppl. 2), S59–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherer, T.B.; Kim, J.H.; Betarbet, R.; Greenamyre, J.T. Subcutaneous Rotenone Exposure Causes Highly Selective Dopaminergic Degeneration and Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 179, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, I.; Siddique, Y.H. Effect of Rotenone on the Neurodegeneration among Different Models. Curr. Drug Targets 2024, 25, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorsy, E.; Al-Ghafari, A.; Al Doghaither, H.; Hashish, S.; Salama, M.; Mudyanselage, A.W.; James, L.; Carter, W.G. Differential Effects of Paraquat, Rotenone, and MPTP on Cellular Bioenergetics of Undifferentiated and Differentiated Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radad, K.; Al-Shraim, M.; Al-Emam, A.; Wang, F.; Kranner, B.; Rausch, W.-D.; Moldzio, R. Rotenone: From Modelling to Implication in Parkinson’s Disease. Folia Neuropathol. 2019, 57, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, L.H.; Timothy Greenamyre, J. Oxidative Damage to Macromolecules in Human Parkinson Disease and the Rotenone Model. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buneeva, O.A.; Kapitsa, I.G.; Kazieva, L.S.; Vavilov, N.E.; Zgoda, V.G. Quantitative Changes of Brain Isatin-Binding Proteins of Rats with the Rotenone-Induced Experimental Parkinsonism. Biomed. Khim 2023, 69, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielisch, I.; Meierhofer, D. Metabolome and Proteome Profiling of Complex I Deficiency Induced by Rotenone. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Davis, J.; Zhu, D.; Kashima, D.T.; Leroueil, M.; Pan, C.; Montine, K.S.; Zhang, J. Identification of Novel Proteins Affected by Rotenone in Mitochondria of Dopaminergic Cells. BMC Neurosci. 2007, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Gu, G.; Goodlett, D.R.; Zhang, T.; Pan, C.; Montine, T.J.; Montine, K.S.; Aebersold, R.H.; Zhang, J. Analysis of α-Synuclein-Associated Proteins by Quantitative Proteomics*[Boxs]. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 39155–39164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buneeva, O.A.; Kapitsa, I.G.; Kazieva, L.S.; Vavilov, N.E.; Zgoda, V.G.; Medvedev, A.E. The Delayed Effect of Rotenone on the Relative Content of Brain Isatin-Binding Proteins of Rats with Experimental Parkinsonism. Biomed. Khim 2024, 70, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Ohtaki, K.; Matsubara, K.; Aoyama, K.; Uezono, T.; Saito, O.; Suno, M.; Ogawa, K.; Hayase, N.; Kimura, K.; et al. Carrier-Mediated Processes in Blood–Brain Barrier Penetration and Neural Uptake of Paraquat. Brain Res. 2001, 906, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ganini, D.; Mason, R.P. Role of Cytochrome c in α-Synuclein Radical Formation: Implications of α-Synuclein in Neuronal Death in Maneb- and Paraquat-Induced Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagmag, S.A.; Tripathi, N.; Shukla, S.D.; Maiti, S.; Khurana, S. Evaluation of Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- See, W.Z.C.; Naidu, R.; Tang, K.S. Cellular and Molecular Events Leading to Paraquat-Induced Apoptosis: Mechanistic Insights into Parkinson’s Disease Pathophysiology. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 3353–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Mittal, P. Paraquat (Herbicide) as a Cause of Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2024, 119, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Thompson, M.; Xu, Y. Multifactorial Theory Applied to the Neurotoxicity of Paraquat and Paraquat-Induced Mechanisms of Developing Parkinson’s Disease. Lab. Investig. 2016, 96, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, A.; Srivastava, G.; Verma, D.; Mishra, M.; Singh, P.K.; Prakash, O.; Singh, M.P. Minocycline, Levodopa and MnTMPyP Induced Changes in the Mitochondrial Proteome Profile of MPTP and Maneb and Paraquat Mice Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2013, 1832, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Sinha, A.; Singh, M.P. Identification of Differentially Expressed Proteins in Striatum of Maneb-and Paraquat-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Phenotype in Mouse. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2007, 29, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, K.S.; Sindhu, K.M.; Senthilkumar, K.S.; Mohanakumar, K.P. L-Deprenyl Protects against Rotenone-Induced, Oxidative Stress-Mediated Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Rats. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 49, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Lv, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Cheng, X.; Mao, W.; Ma, Y.; Li, S. Effects of Eldepryl on Glial Cell Proliferation and Activation in the Substantia Nigra and Striatum in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Mao, W.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Cheng, X.; Lv, C. Autophagy-Related Protein Expression in the Substantia Nigra and Eldepryl Intervention in Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Res. 2015, 1625, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, H.-H.; Chen, R.-C.; Chen, T.H.-H.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Tsai, M.-C. Attenuation of Paraquat-Induced Dopaminergic Toxicity on the Substantia Nigra by (−)-Deprenyl in Vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 172, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chau, K.Y.; Cooper, J.M.; Schapira, A.H.V. Rasagiline Protects against Alpha-Synuclein Induced Sensitivity to Oxidative Stress in Dopaminergic Cells. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Buneeva, O.A.; Kapitsa, I.G.; Zgoda, V.G.; Medvedev, A.E. Neuroprotective Effects of Isatin and Afobazole in Rats with Rotenone-Induced Parkinsonism Are Accompanied by Increased Brain Levels of Triton X-100 Soluble Alpha-Synuclein. Biomed. Khim 2023, 69, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buneeva, O.A.; Kapitsa, I.G.; Kazieva, L.S.; Vavilov, N.E.; Zgoda, V.G.; Medvedev, A.E. The Neuroprotective Effect of Isatin in the Rotenone-Induced Model of Parkinonism in Rats: The Study of Delayed Effects. Biomed. Khim. 2024, 70, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.C.; Ugun-Klusek, A.; Allen, G.; De Girolamo, L.A.; Hargreaves, I.; Ufer, C.; Abramov, A.Y.; Billett, E.E. Monoamine Oxidase-A Knockdown in Human Neuroblastoma Cells Reveals Protection against Mitochondrial Toxins. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderzhanova, E.A.; Bächli, H.; Buneeva, O.A.; Narkevich, V.B.; Medvedev, A.E.; Thoeringer, C.K.; Wotjak, C.T.; Kudrin, V.S. Strain Differences in Profiles of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission in the Prefrontal Cortex of the BALB/C vs. C57Bl/6 Mice: Consequences of Stress and Afobazole. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 708, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoi, M.; Maruyama, W.; Shamoto-Nagai, M. Rasagiline and Selegiline Modulate Mitochondrial Homeostasis, Intervene Apoptosis System and Mitigate α-Synuclein Cytotoxicity in Disease-Modifying Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panova, N.G.; Axenova, L.N.; Medvedev, A.E. The Stimulating Effects of Ethanol Consumption on Synthesis of Rat Brain Monoamine Oxidases and Their Sensitivity to the Irreversible Inhibitor, Pargyline. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 292, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crumeyrolle-Arias, M.; Medvedev, A.; Cardona, A.; Barritault, D.; Glover, V. In Situ Imaging of Specific Binding of [3H]Isatin in Rat Brain. J. Neurochem. 2003, 84, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunikowska, G.; Gallagher, I.; Glover, V.; Clow, A.; Jenner, P. Effects of Short- and Long-Term (−)-Deprenyl Administration on mRNA for Copper, Zinc- and Manganese-Superoxide Dismutase and Glutathione Peroxidase in Rat Brain. Brain Res. 2002, 953, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedchenko, V.; Globa, A.; Kaloshin, A.; Kapitsa, I.; Nerobkova, L.; Val’dman, E.; Buneeva, O.; Glover, V.; Medvedev, A. The Effect of Short-Term Administration of (-)-Deprenyl and Isatin on the Expressions of Some Genes in the Mouse Brain Cortex. Med. Sci. Monit. 2008, 14, BR269–BR273. [Google Scholar]
- Itzhak, Y.; Kassim, C.O. Clorgyline Displays High Affinity for Sigma Binding Sites in C57BL/6 Mouse Brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 176, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, Y.; Maruyama, W.; Yi, H.; Shamoto-Nagai, M.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Naoi, M. An Anti-Parkinson’s Disease Drug, N-Propargyl-1(R)-Aminoindan (Rasagiline), Enhances Expression of Anti-Apoptotic Bcl-2 in Human Dopaminergic SH-SY5Y Cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 326, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Am, O.; Weinreb, O.; Amit, T.; Youdim, M.B.H. Regulation of Bcl-2 Family Proteins, Neurotrophic Factors, and APP Processing in the Neurorescue Activity of Propargylamine. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1899–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, O.; Bar-Am, O.; Amit, T.; Chillag-Talmor, O.; Youdim, M.B.H. Neuroprotection via Pro-Survival Protein Kinase C Isoforms Associated with Bcl-2 Family Members. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1471–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoi, M.; Maruyama, W.; Shamoto-Nagai, M. Type A and B Monoamine Oxidases Distinctly Modulate Signal Transduction Pathway and Gene Expression to Regulate Brain Function and Survival of Neurons. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1635–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, D.J.; Richter, M.F.; Boeira, J.M.; Pêgas Henriques, J.A.; Saffi, J. Antioxidant Properties of Beta-Carboline Alkaloids Are Related to Their Antimutagenic and Antigenotoxic Activities. Mutagenesis 2007, 22, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buneeva, O.; Medvedev, A. Atypical Ubiquitination and Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buneeva, O.A.; Medvedev, A.E. Atypical Ubiquitination of Proteins. Biomeditsinskaia Khimiia 2016, 62, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buneeva, O.A.; Kopylov, A.T.; Tikhonova, O.V.; Zgoda, V.G.; Medvedev, A.E.; Archakov, A.I. Effect of Affinity Sorbent on Proteomic Profiling of Isatin-Binding Proteins of Mouse Brain. Biochemistry 2012, 77, 1326–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, G.; Zhang, P.; Liu, B. The Lipopolysaccharide Parkinson’s Disease Animal Model: Mechanistic Studies and Drug Discovery. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 22, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Noh, Y.; Oh, S.J.; Yoon, H.J.; Im, S.; Kwon, H.T.; Pak, Y.K. Neuroprotective Effects of Aldehyde-Reducing Composition in an LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules 2023, 28, 7988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostadkarampour, M.; Putnins, E.E. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: A Review of Their Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Potential and Mechanisms of Action. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 676239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelders, G.; Baekelandt, V.; Van der Perren, A. Linking Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 4784268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
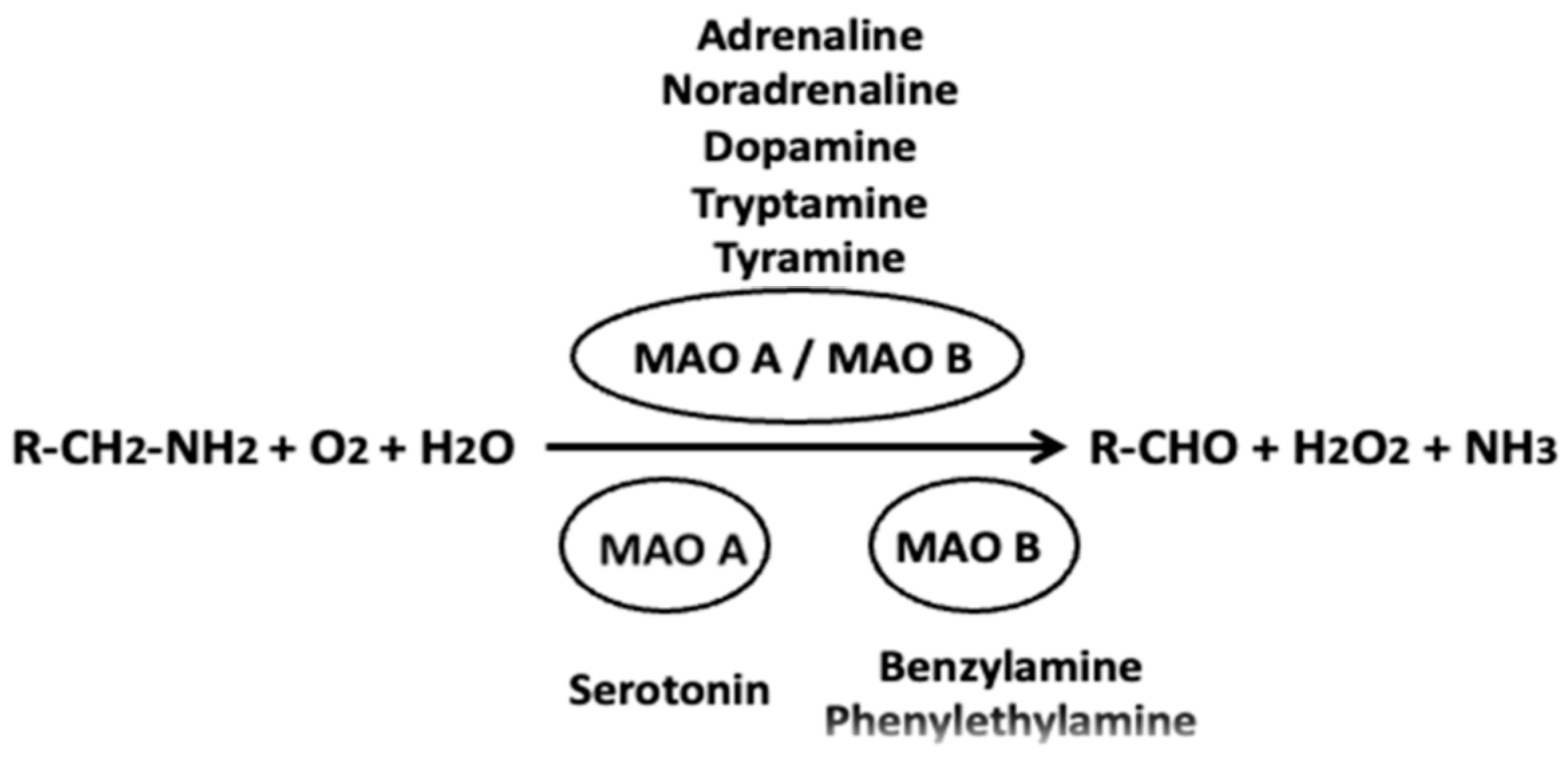
| Inhibitor | Type of Inhibition | Model | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-Deprenyl (selegiline, N-methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats | Protection of sympathetic ganglion cell bodies and peripheral noradrenergic innervation. | [79,80] |
| L-Deprenyl (selegiline, N-methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats | Amelioration of effects on motor complications, induced by levodopa, and expression of proteins involved in these complications. | [81] |
| L-Deprenyl (selegiline, N-methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats | Deprenyl, co-administered with levodopa, did not influence behavioral recovery induced by fetal ventral mesencephalic grafts. | [82] |
| Clorgyline (N-[3-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)propyl]-N-methyl-prop-2-yn-1-amine) L-Deprenyl (selegiline, N-methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) or Rasagiline ((1R)-N-prop-2-ynyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-amine) or TVP-101 [2,3-dihydro-N-2-propynyl-1 H-inden-1-amine-(1 R)-hydrochloride] or Lazabemide (Ro 19-6327, N-(2-aminoethyl)-5-chloropyridine-2-carboxamide) | Selective irreversible MAO A inhibitor Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitors Selective reversible MAO B inhibitors | Rats | Inhibition of glial MAO B increased local DA levels at the presynaptic receptors and reduced DA release by presynaptic inhibition. Inhibition of MAO A or MAO B reduced oxidative stress. Rasagiline exhibited an additional antioxidant effect independently of MAO inhibition. | [73,74,75,83] |
| Rasagiline ((1R)-N-prop-2-ynyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitors | Zebrafish | Prevented locomotor impairments and neuronal loss. | [84] |
| Rasagiline ((1R)-N-prop-2-ynyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats | Increased the survival of dopaminergic neurons in the SN, abolished the motor stereotypies associated with nigrostriatal lesion. | [85] |
| Rasagiline 1-R-aminoindan, the major metabolite of rasagiline, and hydroxyaminoindan, metabolite of ladostigil ([(3R)-3-(prop-2-ynylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl] N-ethyl-N-methylcarbamate) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats with 6-OHDA and neurotoxin DSP-4 | Increased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus and striatum and sparing in the mitochondrial marker Hsp60 and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunoreactive terminals in the striatum, hippocampus, and SN. | [86] |
| 1-R-aminoindan, the major metabolite of rasagiline, and hydroxyaminoindan, metabolite of ladostigil ([(3R)-3-(prop-2-ynylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl] N-ethyl-N-methylcarbamate) | Rasagiline metabolite | Rats | Normalized motor impairments and prevented the decrease in the DA, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), and homovanillic acid (HVA) levels in the striatum. | [87] |
| 1-R-aminoindan, the major metabolite of rasagiline, and hydroxyaminoindan, metabolite of ladostigil ([(3R)-3-(prop-2-ynylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl] N-ethyl-N-methylcarbamate) | Ladostigil exhibits irreversible MAO A and B inhibitory activity and acetylcholine-butyrylcholine esterase inhibitory activity [88] | PC12 cells | Pre-treatment with aminoindan or hydroxyaminoindan significantly increased the viability of the cells. These compounds did not show neurotoxic effects. | [87] |
| 1-R-aminoindan, the major metabolite of rasagiline, and hydroxyaminoindan, metabolite of ladostigil ([(3R)-3-(prop-2-ynylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl] N-ethyl-N-methylcarbamate) | Metabolite of rasagiline, selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats | Aminoindan restored motor impairments and significantly prevented the decline in striatal levels of DA, DOPAC, and homovanillic acid (HVA). | [89,90] |
| Beta-carbolines: harmaline (7-methoxy-1-methyl-4,9-dihydro-3H-pyrido [3,4-b]indole), harmalol (1-methyl-4,9-dihydro-3H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-7-ol), and harmine (7-methoxy-1-methyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole) | Reversible MAO A inhibitors | Rat brain mitochondria and synaptosomes | Protection against oxidative damage, mitochondrial swelling. and membrane potential loss. Decrease in synaptosomal calcium uptake, prevention of catecholamine-induced thioredoxin reductase inhibition, thiol oxidation, and carbonyl formation in mitochondria and synaptosomes; decrease in ROS-induced deoxyribose degradation. | [91] |
| Beta-carbolines (harmaline, harmalol and harmine) | Reversible MAO A inhibitors | PC12 cells | Beta-carbolines attenuated the loss of cell viability. Harmaline and harmalol reduced the catecholamine-induced membrane potential loss. | [91] |
| Moclobemide (4-chloro-N-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)benzamide) | Reversible MAO A inhibitor | Rats | Increase in contraversive rotational behavior only in case of co-administration with levodopa. | [79] |
| Afobazole 4-[2-[(6-ethoxy-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]ethyl]morpholine | Reversible MAO A inhibitor | Mice | Normalized motor dysfunction, restored the DA level in the striatum and did not affect the contents of norepinephrine, serotonin or its metabolites. | [92,93] |
| Lazabemide (N-(2-aminoethyl)-5-chloropyridine-2-carboxamide) | Reversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats | Increase in contraversive rotational behavior only in case of co-administration with levodopa. | [79] |
| PF 9601N (N-[(5-phenylmethoxy-1H-indol-2-yl)methyl]prop-2-yn-1-amine) | Selective reversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats | Decreased the loss of tyrosine hydroxylase positive neurons in the SN. Reduced 6-OHDA-induced neurodegeneration. | [94] |
| Safinamide ((2S)-2-[[4-[(3-fluorophenyl) methoxy]phenyl] methylamino] propanamide) | Selective reversible MAO B inhibitor, sodium channel blocker | Rats | Prevention of the levodopa-induced increase in striatal glutamate associated with dyskinesia appearance. Suppression of microglial activation and protection of DA neurons in the SN from degeneration. Reduction in the firing rate and the synaptic currents of striatal projection neurons. | [95,96,97] |
| (Hetero)arylalkenylpropargyl amines (especially compound1, the m-fluorophenyl compound 24, the m-benzyloxyphenyl compound 31, 3,4-dimethylphenyl compound 45, 3,4-difluorophenyl compound 46, and the 3- methyl-4-fluorophenyl analogue 48) | MAO B irreversible inhibitors | PC12 cells | Neuroprotective properties in vitro. | [98] |
| VAR (5-[2-(methyl-prop-2-ynyl-amino)- ethyl]-quinolin-8-ol dihydrochloride) | Iron-chelating MAO A and B inhibitor | Rats | Attenuation of motor impairments and significant reduction in the striatal DA loss. Increase in 5HT levels in the striatum and hippocampus. | [99] |
| Inhibitor | Type of Inhibition | Model | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pargyline (N-benzyl-N- methylprop-2-yn-1-amine) | Non-selective irreversible MAO inhibitor | Non-human primates | Protection against nigrostriatal DA neurotoxicity, reduction in brain MPP+ levels. | [127] |
| Clorgyline (N-[3-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy) propyl]-N- methyl-prop-2-yn-1-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO A inhibitor | Goldfish | Lack of protection against loss of movement. | [128] |
| L-Deprenyl (selegiline, N- methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats | Neuroprotection; inhibition of hydroxyl radical formation and restoration of striatal DA levels. | [129] |
| L-Deprenyl (selegiline, N- methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Goldfish | Protection from loss of movement. | [128] |
| L-Deprenyl (selegiline, N- methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) SH-SY5Y cells | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Primary neuronal cultures of mouse midbrain DA neurons | MAO B-independent increase in expression of thioredoxin, manganese superoxide dismutase, and antiapoptotic Bcl-2, supporting cell survival. | [130] |
| L-Deprenyl (selegiline, N- methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | SH-SY5Y cells | Attenuation of the MPTP-induced autophagic response and protection against cell death. | [113] |
| L-Deprenyl (selegiline, N- methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) Pargyline (N-benzyl-N- methylprop-2-yn-1-amine) Nialamide (N-benzyl-3-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl) hydrazinyl] propanamide) Tranylcypromine ((1R,2S)-2-phenylcyclopropan-1-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor Non-selective irreversible MAO inhibitors | Mice | All the inhibitors effectively protected against the nigrostriatal DA neurotoxicity of MPTP and prevented the neostriatal DA loss. | [131] |
| Rasagiline ((1R)-N-prop-2-ynyl-2,3- dihydro-1H-inden-1-amine) L-Deprenyl (selegiline, N- methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitors Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Non-human primates | Both inhibitors restored motor impairments, the number of DA cells in the SN, and striatal DA levels. | [132] |
| Rasagiline (Hetero)arylalkenylpropargylamines SZV558 (methyl-(2-phenyl-allyl)-prop-2-ynyl-amine hydrochloride) and SZV2220 | MAO B irreversible inhibitors | Mice | Restored locomotor activity, DA, and its metabolite content in the striatum. SZV558 expressed the highest neuroprotective action. | [133] |
| Rasagiline ((1R)-N-prop-2-ynyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-amine) | MAO B irreversible inhibitor | SH-SY5Y cells Mice | Decrease in the MPP+-enhanced asparagine endopeptidase activity and alpha-synuclein N103 cleavage. | [116] |
| Rasagiline ((1R)-N-prop-2-ynyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor [134] | Mice | Restoration of dopaminergic cell reduction, striatal DA, and TH. Activation of cell signaling survival cascades (Trk, Ras-PI3K-Akt, and others). | [135,136] |
| M30 [5-(N-methyl-N-propargyl- amino-methyl)-8-hydroxyquinone] | Brain-permeable MAO A/B inhibitor with iron-chelating activity. | Mice | Elevation of striatal DA, 5HT, and noradrenaline levels, TH protein level and activity. Increase in dopaminergic and transferrin receptor cells in the SN and in hypoxia-induced factor (HIF). | [137,138] |
| MT-20R (a derivative of ladostigil, [(3R)-3-(prop-2-ynylamino) indan-5-yl]-N-propylcarbamate) | MAO B inhibitor | Mice | Alleviation of motor deficits, increase in the level of DA and its metabolites, restoration of TH expression and the number of TH-positive neurons in the SN. Increase in the expression of Bcl-2, decrease in the expression of Bax and Caspase 3, and activation of the AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. | [139] |
| VAR (5-[2-(methyl-prop-2-ynyl-amino)- ethyl]-quinolin-8-ol dihydrochloride) | Iron-chelating MAO A and B inhibitor | Mice | Attenuation of motor impairments, prevention of striatal DA loss, increase in 5HT levels in the striatum and hippocampus, and increase in the TH level. | [99] |
| Lamotrigine (6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazine-3,5-diamine) | MAO B inhibitor [140] | Mice | Protection against DA neuronal death in the SN, promotion of striatal dendrite sprouting, maintenance of high levels of the DA transporter, TH immunoreactive neurons, and DA content. | [141] |
| Beta-carbolines (harmaline, harmalol, and harmine) | Reversible MAO A inhibitors | Mice | Harmalol reduced the MPTP effect on the enzyme activities and formation of tissue peroxidation products. Harmaline, harmalol, and harmine attenuated the MPP+-induced inhibition of electron flow and membrane potential formation and the DA-induced thiol oxidation and carbonyl formation in mitochondria. | [142] |
| Beta-carbolines (harmaline, harmalol, and harmine) | Reversible MAO A inhibitors | PC12 cells | Prevented the loss of viability of MPP+-treated cells, reduced condensation and fragmentation of nuclei, inhibited the decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential, cytochrome c release, activation of caspase-3, ROS formation, and depletion of GSH. | [143] |
| Curcumin ((1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione) and its metabolite tetrahydrocurcumin (1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) heptane- 3,5-dione) | MAO B inhibitors | Mice | Neuroprotection against MPTP-induced neurotoxicity: reversion of MPTP-induced depletion of DA and DOPAC. | [144] |
| Isatin (indoledione-2,3) | MAO B inhibitor | Mice | Reduced motor manifestations of MPTP-induced neurotoxicity, influenced the profiles of numerous brain isatin-binding proteins. | [117,118,145,146,147] |
| Phenelzine (2-phenylethylhydrazine) | Non-selective irreversible MAO inhibitor | PC12 cells | Attenuation in the cell viability loss. Reduction in condensation and fragmentation of nuclei, prevention of the decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome c, ROS formation, and glutathione depletion. | [148] |
| Catalpol ((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[[(1S,2S,4S,5S,6R,10S)-5-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-3,9-dioxatricyclo[4.4.0.02,4]dec-7-en-10-yl]oxy]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol) | MAO B inhibitor, an iridoid glycoside present in the roots of Rehmannia glutinosa, the traditional Chinese medicinal herb [149] | Mice | Restoration of locomotor ability, increase in striatal DA levels without changing the metabolite/DA ratios, increase in the TH-positive neurons, striatal DA transporter, and the striatal glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor protein level. Elevation of the expression of striatal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. | [150] |
| Catalpol ((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[[(1S,2S,4S,5S,6R,10S)-5-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-3,9-dioxatricyclo[4.4.0.02,4]dec-7-en-10-yl]oxy]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol) | MAO B inhibitor present in roots of Rehmannia glutinosa | Astrocytes | Attenuation of mitochondrial dysfunction by reversing the activity of complex I, membrane potential, intracellular Ca2+ level, and ROS accumulation. | [151] |
| Catalpol ((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[[(1S,2S,4S,5S,6R,10S)-5-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-3,9-dioxatricyclo[4.4.0.02,4]dec-7-en-10-yl]oxy]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol) | MAO B inhibitor | Cultured mesencephalic neurons | Increase in neuron viability and prevention of DA neuron death, inhibition of mitochondrial complex I, and the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. Reduction in lipid peroxidation and increase in the activity of glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase. | [152] |
| Inhibitor | Type of Inhibition | Model, Toxin | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-Deprenyl (eldepryl, selegiline, N-methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats Rotenone | Inhibition of stereotypic rotations, restoration of complex I activity and glutathione levels in SN, TH immunoreactivity, and striatal DA. Increase in activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase. | [181] |
| L-Deprenyl (eldepryl, selegiline, N-methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats Rotenone | Decrease in the numbers of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)- and integrin alphaM (CD11b)-positive cells and expression of GFAP and CD11b in SN and striatum. Prevention of expression of Beclin1 and microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3) in SN. | [182,183] |
| L-Deprenyl (eldepryl, selegiline, N-methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine) | Selective irreversible MAO B inhibitor | Rats Paraquat | Restoration of locomotor activity and increase in the striatal DA level. | [184] |
| (Hetero) arylalkenylpropargylamines (compound 1, the m-fluorophenyl compound 24, the m-benzyloxyphenyl compound 31, 3,4-dimethylphenyl compound 45, 3,4-difluorophenyl compound 46, and the 3- methyl-4-fluorophenyl analogue 48) | MAO B irreversible inhibitors | PC-12 cells Rotenone | In vitro neuroprotective properties. | [98] |
| (Hetero) arylalkenylpropargylamines SZV558 | MAO B irreversible inhibitors | Slices of rat striatum Rotenone | The compounds (especially SZV558) exhibited protective effects against pathological DA release and formation of toxic DA quinone and rescued TH positive neurons in SN. | [133] |
| Rasagiline | MAO B irreversible inhibitor | SHSY5Y cells Paraquat | Protection against cell death by reducing caspase 3 activation, ROS generation, and the fall in mitochondrial membrane potential. Increase in cellular glutathione levels. | [185] |
| Isatin (indoledione-2,3) Afobazole | MAO B inhibitor MAO A inhibitor | Rats Rotenone | Restoration of locomotor activity. Altered relative content of proteins associated with neurodegeneration (e.g., synuclein, DJ-1, GAPDH, TRIM2, E3-ubiquitin ligase Tripartite motif-containing protein 2, Prohibitin-2). | [186,187] [186] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buneeva, O.; Medvedev, A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Toxic Models of Parkinsonism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031248
Buneeva O, Medvedev A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Toxic Models of Parkinsonism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031248
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuneeva, Olga, and Alexei Medvedev. 2025. "Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Toxic Models of Parkinsonism" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031248
APA StyleBuneeva, O., & Medvedev, A. (2025). Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Toxic Models of Parkinsonism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031248





