Multi-Omics Analysis of the Gut-Brain Axis Elucidates Therapeutic Mechanisms of Guhong Injection in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TTC Staining and Neurological Deficit
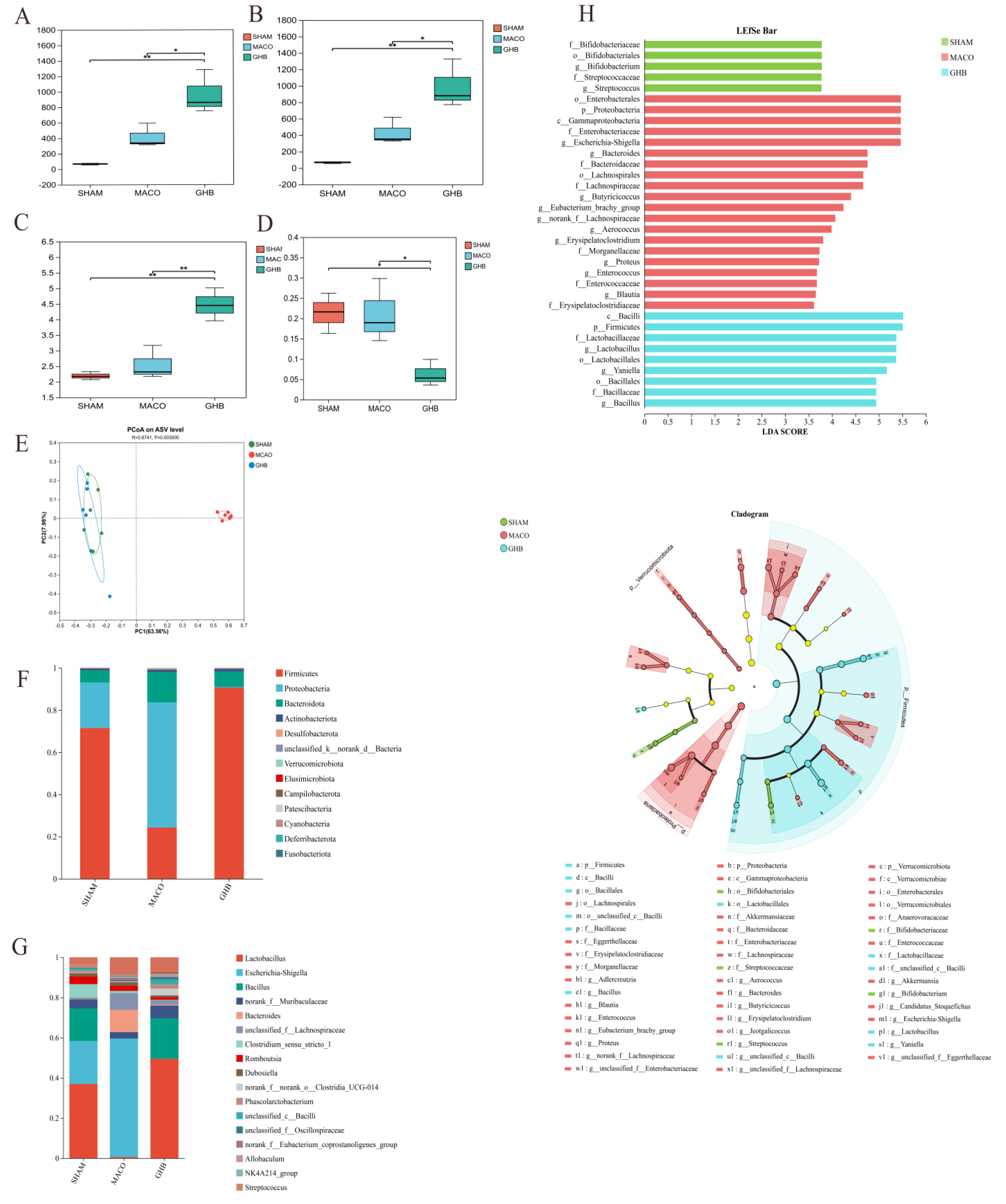
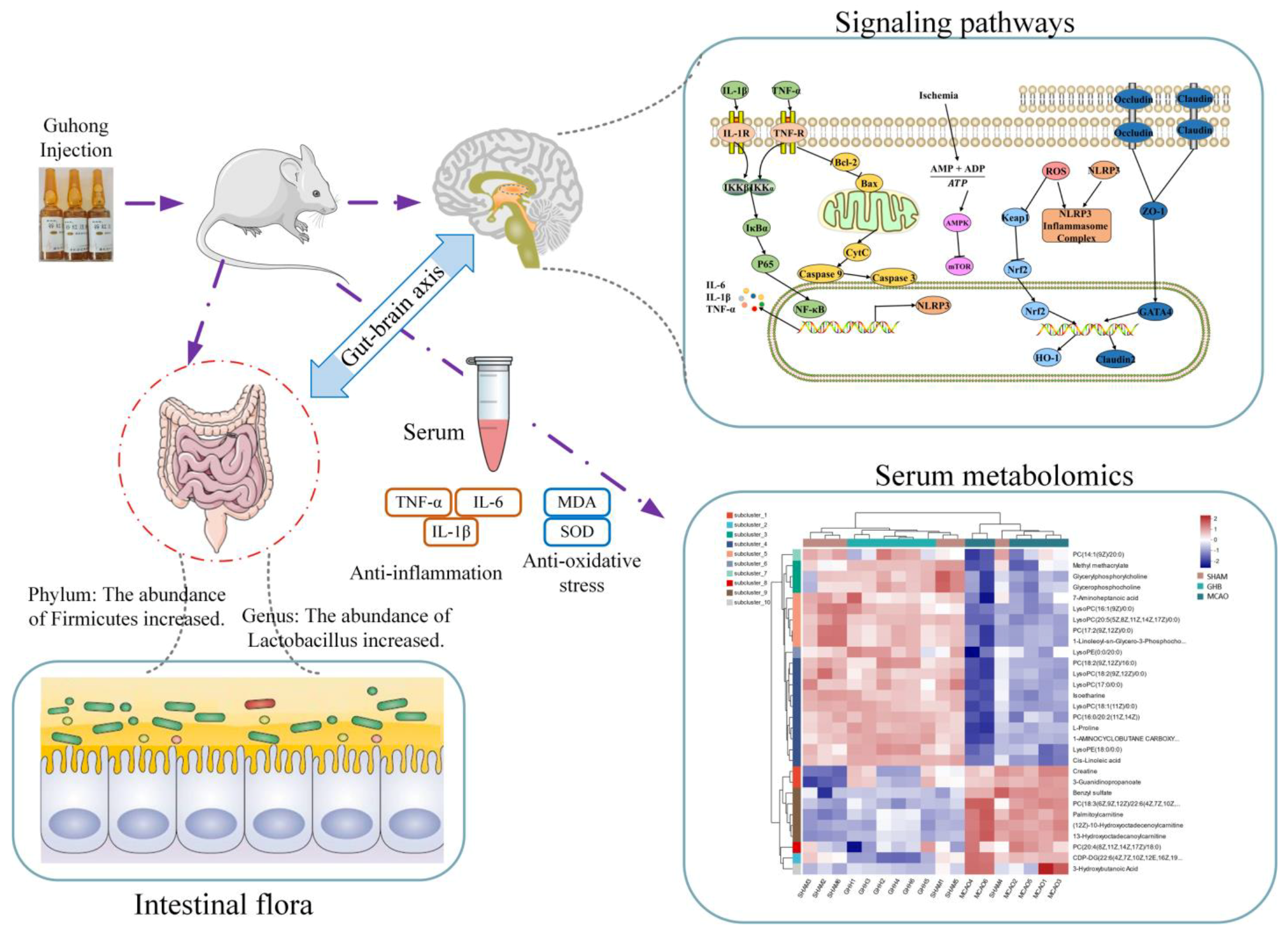
2.2. Effects of GH on Gut Microbiota of MCAO Rats
2.3. Effects of GH on SCFAs of MCAO Rats
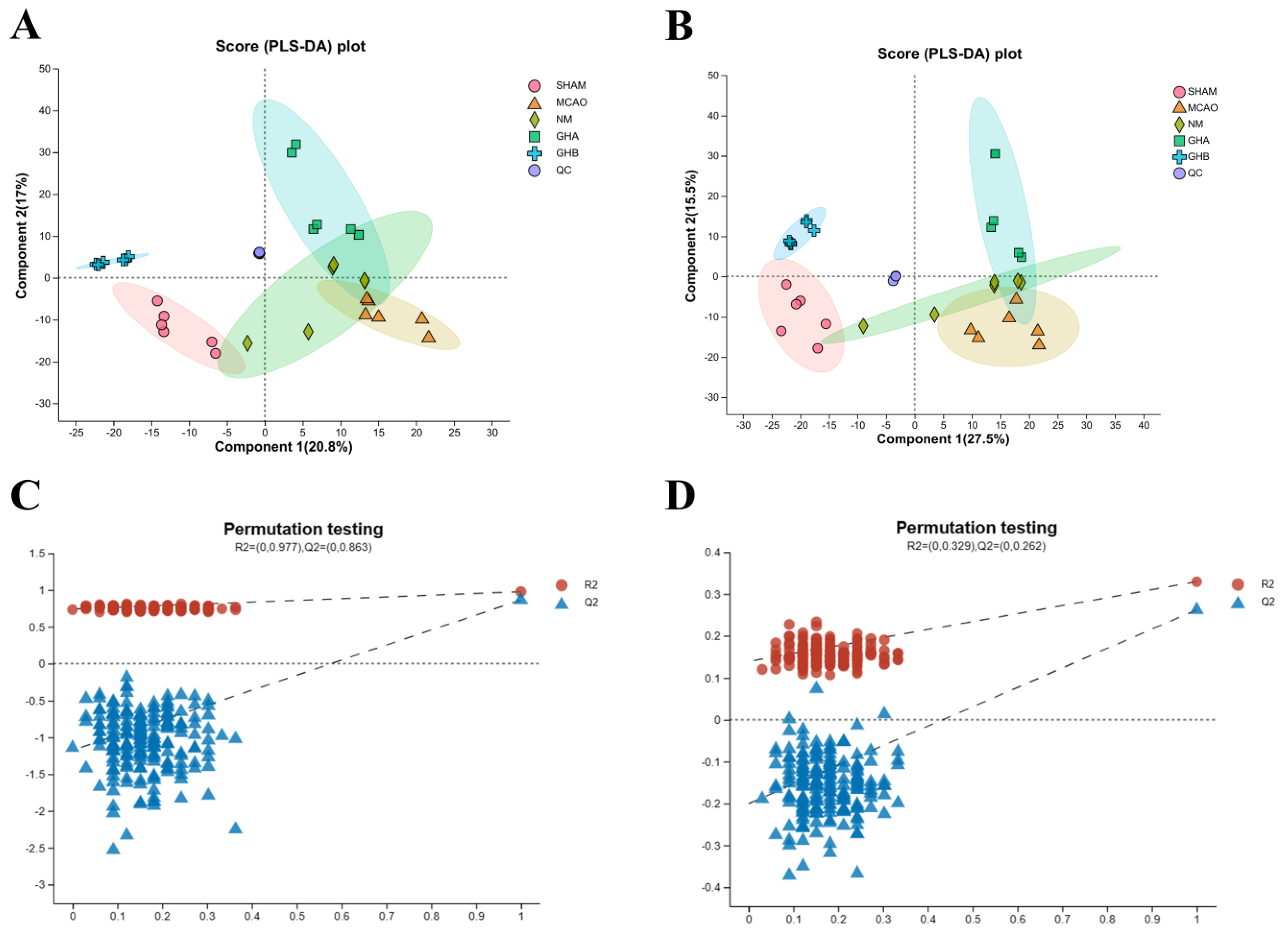
2.4. Metabolomics Analysis
2.4.1. Multivariate Data Analysis
2.4.2. Identification of Potential Biomarkers
2.4.3. Metabolic Pathways of Potential Biomarkers
2.4.4. Effects of GH on Metabolic Pathways of MCAO Rats
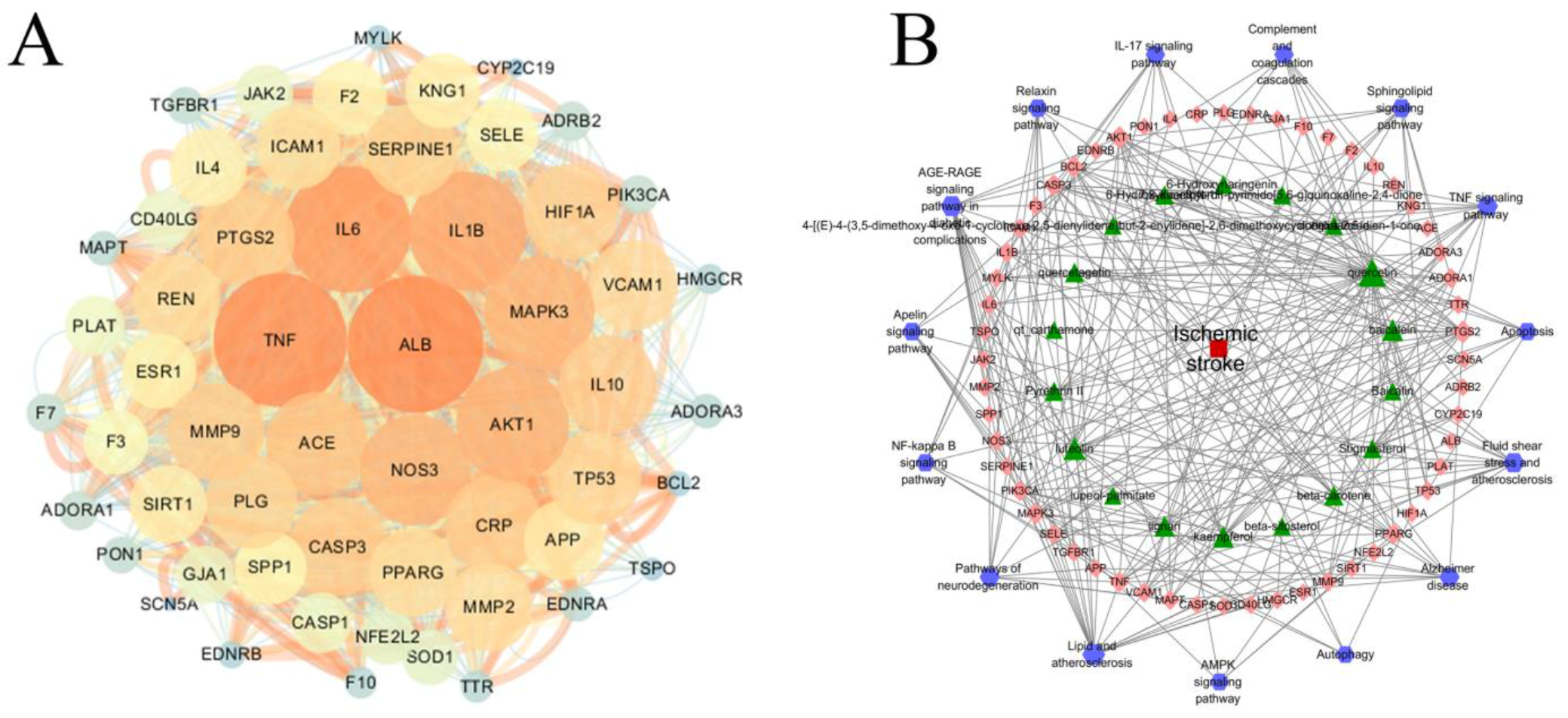
2.5. PPI and Disease–Pathway–Target–Drug Network Construction
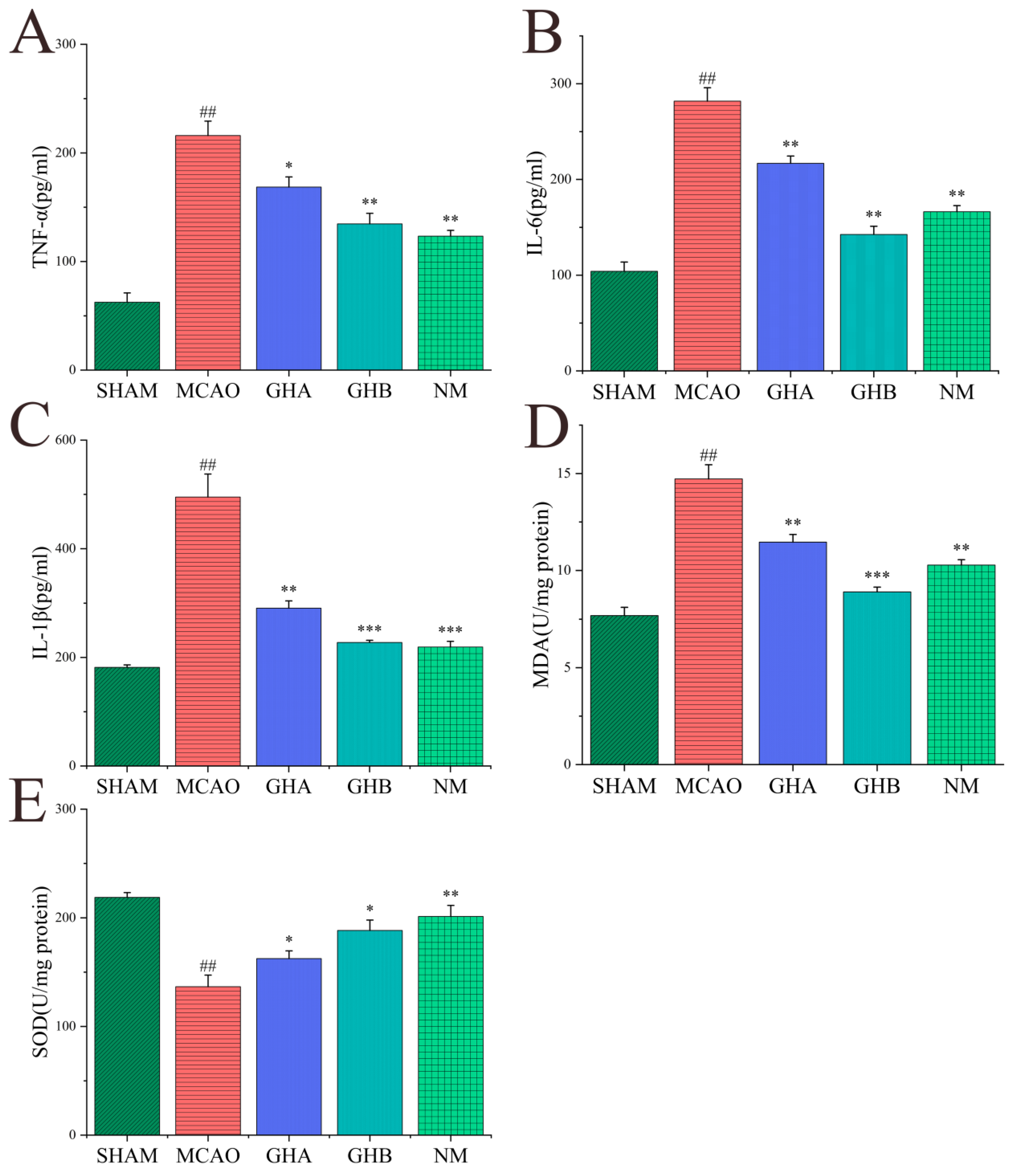
2.6. Effects of GH on Inflammatory Cytokines and Anti-Oxidative Indices in Serum of MCAO Rats
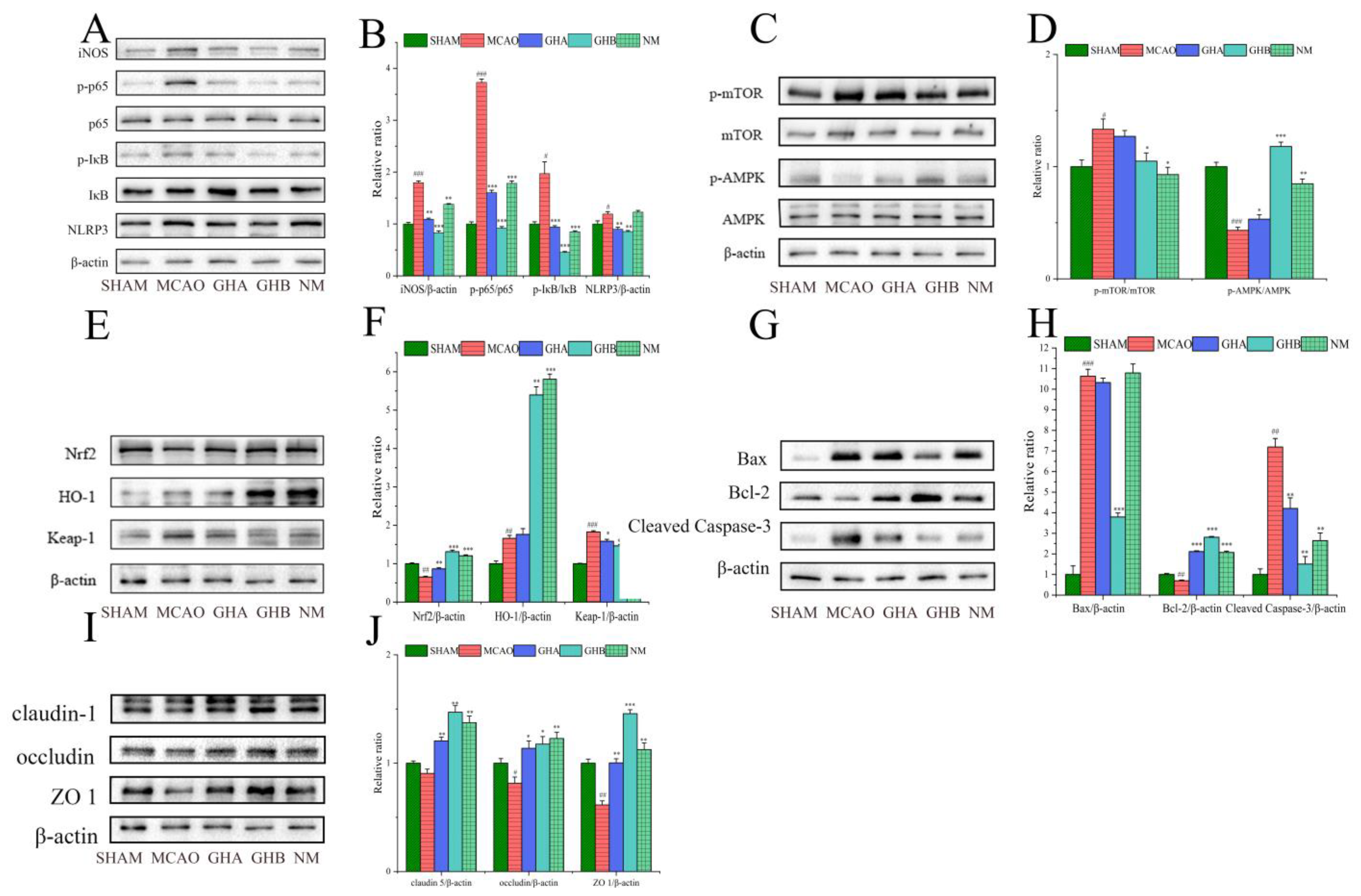
2.7. The Effects of GH on Inflammatory Responses in the Brains of MCAO Rats
2.8. The Effects of GH on Autophagy in the Brains of MCAO Rats
2.9. The Effect of GH on Oxidative Stress in the Brains of MCAO Rats
2.10. The Effect of GH on Apoptosis in the Brains of MCAO Rats
2.11. The Effect of GH on Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Integrity in the Brains of MCAO Rats
2.12. The Interplay Between the Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolites, SCFAs, and Protein Target Expression After GH Therapy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals
4.3. Animal Model and Drug Administration
4.4. Assessment of Neurological Impairment
4.5. Sample Collection and TTC Staining
4.6. ELISA
4.7. 16S rRNA Analysis
4.8. Quantification of SCFAs
4.9. LC-MS Metabolomics Analysis
4.9.1. Sample Preparation
4.9.2. LC-MS Conditions
4.10. Multivariate Statistical Analysis and Data Processing
4.11. Network Pharmacological Analysis
4.12. Western Blot Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators Global: Regional, and National Burden of Stroke and Its Risk Factors, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekker, M.S.; Verhoeven, J.I.; Vaartjes, I.; van Nieuwenhuizen, K.M.; Klijn, C.J.M.; de Leeuw, F.-E. Stroke Incidence in Young Adults According to Age, Subtype, Sex, and Time Trends. Neurology 2019, 92, e2444–e2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, P.; Geng, S.; Kong, W.; Zhi, Y.; Yuan, K.; Tian, L. The Association between Serum Anion Gap and All-Cause Mortality in Cerebral Infarction Patients after Treatment with rtPA: A Retrospective Analysis. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 1931818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.A.; Abdel Salam, R.M.; Kenawy, S.A.; Attia, A.S. Pinocembrin Attenuates Hippocampal Inflammation, Oxidative Perturbations and Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Global Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarpisheh, P.; Bryan, R.M.; McCullough, L.D. Aging Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Stroke Risk and Outcome. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 1112–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, L.; Dong, S.; Ge, S.; Zhu, T. Immune Regulation of the Gut-Brain Axis and Lung-Brain Axis Involved in Ischemic Stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber, H.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Gut Microbiota-Brain Axis in Behaviour and Brain Disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benakis, C.; Brea, D.; Caballero, S.; Faraco, G.; Moore, J.; Murphy, M.; Sita, G.; Racchumi, G.; Ling, L.; Pamer, E.G.; et al. Commensal Microbiota Affects Ischemic Stroke Outcome by Regulating Intestinal Γδ T Cells. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Roth, S.; Llovera, G.; Sadler, R.; Garzetti, D.; Stecher, B.; Dichgans, M.; Liesz, A. Microbiota Dysbiosis Controls the Neuroinflammatory Response after Stroke. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7428–7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Xu, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhou, H.; Lasanajak, Y.; Fang, Y.; Tang, L.; Ye, L.; Li, X.; Cai, Z.; et al. Transplantation of Fecal Microbiota Rich in Short Chain Fatty Acids and Butyric Acid Treat Cerebral Ischemic Stroke by Regulating Gut Microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Ma, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yu, W. Application of Omics Technology to Investigate the Mechanism Underlying the Role of San Hua Tang in Regulating Microglia Polarization and Blood-Brain Barrier Protection Following Ischemic Stroke. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 314, 116640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, S.; Jin, W.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Mao, S.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, L.; et al. Aberrant Branched-Chain Amino Acid Accumulation along the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis: Crucial Targets Affecting the Occurrence and Treatment of Ischaemic Stroke. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 180, 347–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Su, J.; Gao, X.; Yang, H.; Weng, R.; Ni, W.; Gu, Y. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis Participates in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion by Disrupting the Metabolism of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Microbiome 2022, 10, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, J.; Wan, H.; Shu, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, T.; Fu, W.; He, Y. Guhong Injection Protects against Focal Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Han, Z.; Sheng, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Guhong Injection Promotes Post-Stroke Functional Recovery via Attenuating Cortical Inflammation and Apoptosis in Subacute Stage of Ischemic Stroke. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2022, 99, 154034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Sheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L. Discovery of Anti-Stroke Active Substances in Guhong Injection Based on Multi-Phenotypic Screening of Zebrafish. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, R.; Cao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, H. Guhong Injection Prevents Ischemic Stroke-Induced Neuro-Inflammation and Neuron Loss Through Regulation of C5ar1. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 818245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Cao, G.; Tang, L.; Zhou, R.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Li, X.; Yang, H. Targeted Energy Metabolomics Combined with Spatial Metabolomics Study on the Efficacy of Guhong Injection Against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 5533–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, H.; Yang, J.; Wan, H.; He, Y. Guhong Injection Mitigates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Activating GST P to Inhibit ASK1-JNK/P38 Pathway. Phytomedicine 2023, 109, 154603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Q.; Chen, Q.; Xue, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, H.; Chen, X. Network Pharmacology Combined with Metabolomics to Study the Mechanism of Shenyan Kangfu Tablets in the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 270, 113817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-L.; Zheng, J.-Y.; Cheng, X.-Q.; Xin, G.-Z.; Wang, S.-L.; Xie, T. Chemical Markers’ Knockout Coupled with UHPLC-HRMS-Based Metabolomics Reveals Anti-Cancer Integration Effects of the Curcuminoids of Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) on Lung Cancer Cell Line. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 175, 112738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanchao, S.; Chen, M.; Zhiguo, S.; Futang, X.; Mengmeng, S. Protective Effect and Mechanism of Lactobacillus on Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. Rev. Bras. Pesqui. Medicas E Biol. 2018, 51, e7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; d’Aigle, J.; Atadja, L.; Quaicoe, V.; Honarpisheh, P.; Ganesh, B.P.; Hassan, A.; Graf, J.; Petrosino, J.; Putluri, N.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Promote Poststroke Recovery in Aged Mice. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashiro, K.; Tanaka, R.; Urabe, T.; Ueno, Y.; Yamashiro, Y.; Nomoto, K.; Takahashi, T.; Tsuji, H.; Asahara, T.; Hattori, N. Gut Dysbiosis Is Associated with Metabolism and Systemic Inflammation in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171521. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.J.; Pilla, R.; Panta, A.; Pandey, S.; Sarawichitr, B.; Suchodolski, J.; Sohrabji, F. Reproductive Senescence and Ischemic Stroke Remodel the Gut Microbiome and Modulate the Effects of Estrogen Treatment in Female Rats. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 812–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Li, Z.-R.; Green, R.S.; Holzman, I.R.; Lin, J. Butyrate Enhances the Intestinal Barrier by Facilitating Tight Junction Assembly via Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.-C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.-B.; Liu, W.-Y.; Sun, S.; Li, L.; Su, D.-F.; Zhang, L.-C. Propionate Ameliorates Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis by Improving Intestinal Barrier Function and Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-B.; Wang, P.-Y.; Wang, X.; Wan, Y.-L.; Liu, Y.-C. Butyrate Enhances Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function via Up-Regulation of Tight Junction Protein Claudin-1 Transcription. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nabhani, Z.; Dulauroy, S.; Marques, R.; Cousu, C.; Al Bounny, S.; Déjardin, F.; Sparwasser, T.; Bérard, M.; Cerf-Bensussan, N.; Eberl, G. A Weaning Reaction to Microbiota Is Required for Resistance to Immunopathologies in the Adult. Immunity 2019, 50, 1276–1288.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asarat, M.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Vasiljevic, T.; Donkor, O. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Regulate Cytokines and Th17/Treg Cells in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Vitro. Immunol. Investig. 2016, 45, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.M.; Howitt, M.R.; Panikov, N.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Bohlooly-Y, M.; Glickman, J.N.; Garrett, W.S. The Microbial Metabolites, Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Regulate Colonic Treg Cell Homeostasis. Science 2013, 341, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Guo, K.; Zhang, R.; Wang, W.; Sun, H.; Yagüe, E.; Hu, Y. Exploration of the Mechanism of Salvianolic Acid for Injection Against Ischemic Stroke: A Research Based on Computational Prediction and Experimental Validation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 894427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.-X.; Li, R.-P.; Li, Y.-G.; Wang, X.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Deng, J.-B.; Wang, L.; Deng, J.-X. 14,15-EET Suppresses Neuronal Apoptosis in Ischemia–Reperfusion Through the Mitochondrial Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 2841–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Sluter, M.N.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, J. Prostaglandin E Receptors as Targets for Ischemic Stroke: Novel Evidence and Molecular Mechanisms of Efficacy. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yasmen, N.; Hou, R.; Yang, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Hao, J.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, J. Inducible Prostaglandin E Synthase as a Pharmacological Target for Ischemic Stroke. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 366–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, A.A.; Ong, W.-Y.; Horrocks, L.A. Biochemical Aspects of Neurodegeneration in Human Brain: Involvement of Neural Membrane Phospholipids and Phospholipases A2. Neurochem. Res. 2004, 29, 1961–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannis, A.; Gkolfinopoulou, C.; Tziomalos, K.; Dedemadi, A.-G.; Polychronopoulos, G.; Milonas, D.; Savopoulos, C.; Hatzitolios, A.I.; Chroni, A. HDL Cholesterol Efflux Capacity and Phospholipid Content Are Associated with the Severity of Acute Ischemic Stroke and Predict Its Outcome. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2023, 540, 117229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, J.; Gong, L.; Liu, F.; Zhao, H.; Mu, J. Alteration of Glycerophospholipid Metabolism in Hippocampus of Post-Stroke Depression Rats. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhong, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, Y.; Bai, X.; Yin, P.; Hua, S. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Therapy Regulates Sphingolipid and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism to Promote Neurological Recovery in Stroke Rats: A Metabolomics Analysis. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 372, 114619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misu, Y.; Goshima, Y.; Ueda, H.; Okamura, H. Neurobiology of L-DOPAergic systems. Prog. Neurobiol. 1996, 49, 415–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncayo, J.A.; Yepez, M.; Camacho, M.; Aguirre, A.S.; Ojeda, D.; Ortiz, J.F.; Sen, M.; Argudo, J.; Proano, L.; Cordova, S.; et al. Use of Levodopa After a Stroke: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e24529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talhada, D.; Marklund, N.; Wieloch, T.; Kuric, E.; Ruscher, K. Plasticity-Enhancing Effects of Levodopa Treatment after Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.M.; Morgan Jones, G.; Hawryluk, G.W.J.; Mailloux, P.; McLaughlin, D.; Papangelou, A.; Samuel, S.; Tokumaru, S.; Venkatasubramanian, C.; Zacko, C.; et al. Guidelines for the Acute Treatment of Cerebral Edema in Neurocritical Care Patients. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 32, 647–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Hai, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X.; Tang, H. Multi-Omics Data Reveals Aberrant Gut Microbiota-Host Glycerophospholipid Metabolism in Association with Neuroinflammation in APP/PS1 Mice. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2282790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, E.; Choi, J.G.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.; Ju, I.G.; Eo, H.; Park, M.G.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, H.-J.; et al. Peripheral Metabolic Alterations Associated with Pathological Manifestations of Parkinson’s Disease in Gut-Brain Axis-Based Mouse Model. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1201073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; He, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lin, X.; Chen, J.; Shao, C.; Wan, H.; Yang, J. Guhong Injection Protects Against Apoptosis in Cerebral Ischemia by Maintaining Cerebral Microvasculature and Mitochondrial Integrity Through the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 650983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Su, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, R.; Zhou, T.; Peng, C.; Wong, C.C.L.; et al. AMPK-Dependent Phosphorylation of GAPDH Triggers Sirt1 Activation and Is Necessary for Autophagy upon Glucose Starvation. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, R.; Luo, F.; Zhu, L.; Gao, J.; He, H.; Wei, T.; Yan, T.; Ma, C. Cardioprotective Effects of Salidroside on Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Coronary Artery Occlusion-Induced Rats and Langendorff-Perfused Rat Hearts. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 215, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Targeting HIF-1 for Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, K.S.; Davis, T.P. Cerebral Microvascular Changes in Permeability and Tight Junctions Induced by Hypoxia-Reoxygenation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2002, 282, H1485–H1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z.; Jiang, Z. Dietary Neoagarotetraose Extends Lifespan and Impedes Brain Aging in Mice via Regulation of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 52, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Wei, H.; Yuan, S.; Kong, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Probiotic Pediococcus Pentosaceus Ameliorates MPTP-Induced Oxidative Stress via Regulating the Gut Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1022879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Q.; Jin, M.; Ren, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Sun, X. Notoginsenoside R1 Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway through Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 128, 155530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longa, E.Z.; Weinstein, P.R.; Carlson, S.; Cummins, R. Reversible Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion without Craniectomy in Rats. Stroke 1989, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.-M.; Liu, W.; Pi, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P.; Zhou, T.; Gu, Q. Effects of Exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus Rhamnosus on Human Gut Microbiota in in Vitro Fermentation Model. LWT 2021, 139, 110524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, P.; Hu, J.; Mai, X.; Li, N.; Liao, Y.; Feng, L.; Long, Q. Multi-Omics Analysis of the Gut-Brain Axis Elucidates Therapeutic Mechanisms of Guhong Injection in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041560
Mao P, Hu J, Mai X, Li N, Liao Y, Feng L, Long Q. Multi-Omics Analysis of the Gut-Brain Axis Elucidates Therapeutic Mechanisms of Guhong Injection in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(4):1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041560
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Pingting, Jianhua Hu, Xi Mai, Na Li, Yijing Liao, Lihua Feng, and Qinghong Long. 2025. "Multi-Omics Analysis of the Gut-Brain Axis Elucidates Therapeutic Mechanisms of Guhong Injection in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 4: 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041560
APA StyleMao, P., Hu, J., Mai, X., Li, N., Liao, Y., Feng, L., & Long, Q. (2025). Multi-Omics Analysis of the Gut-Brain Axis Elucidates Therapeutic Mechanisms of Guhong Injection in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(4), 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041560



