Focus on Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Target: Drugs Approved or Designed to Treat Obesity
Abstract
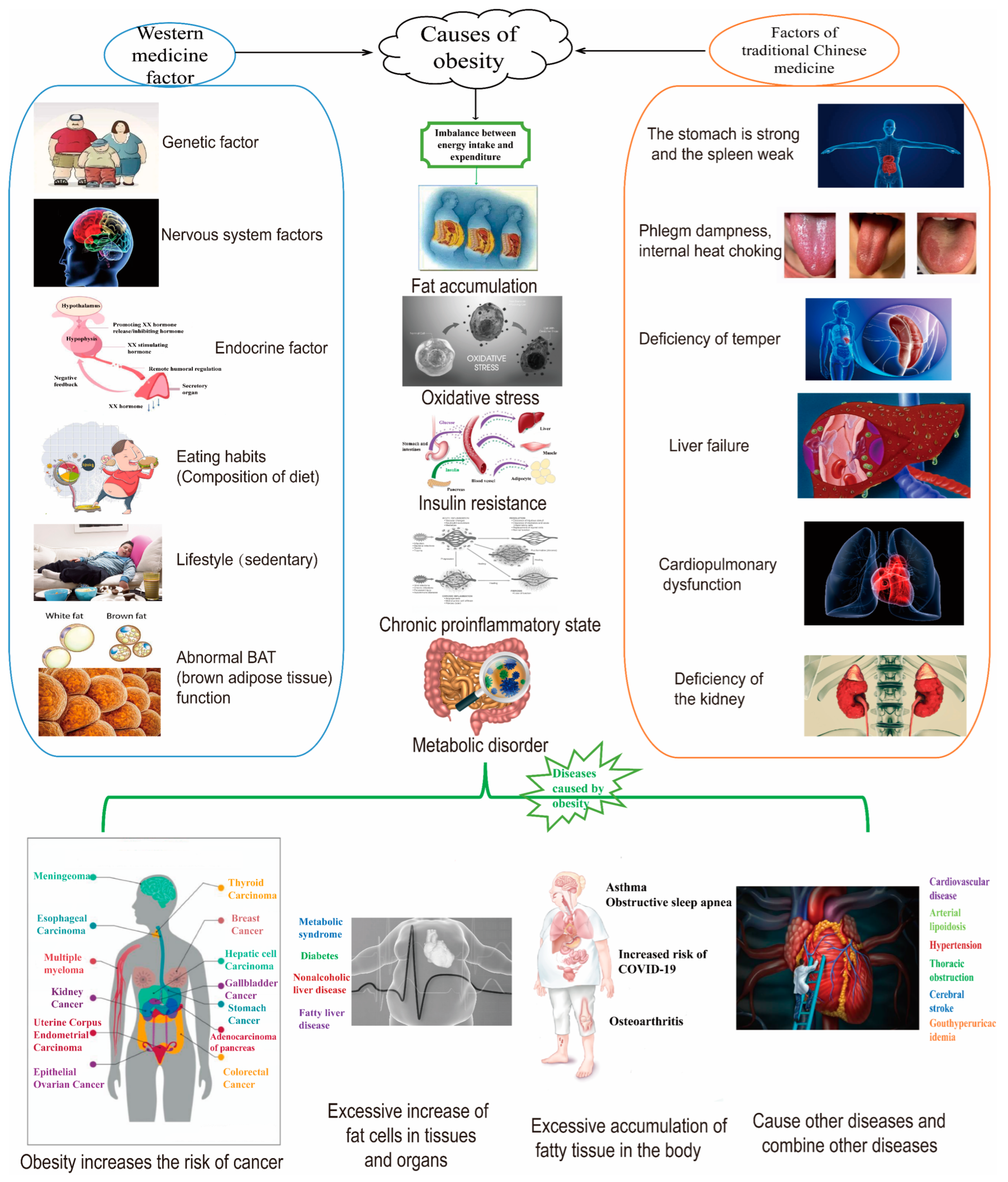
1. Introduction
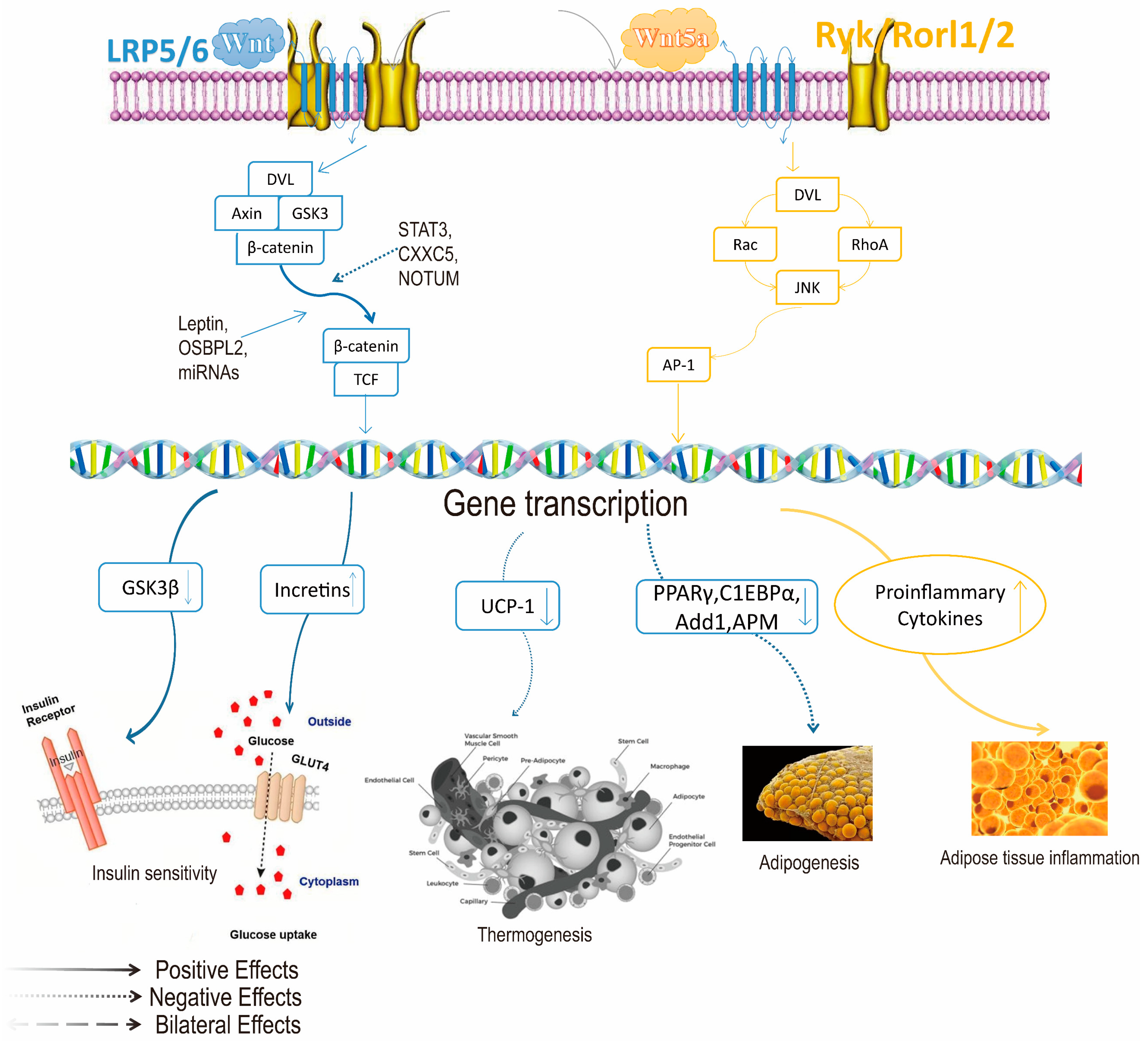
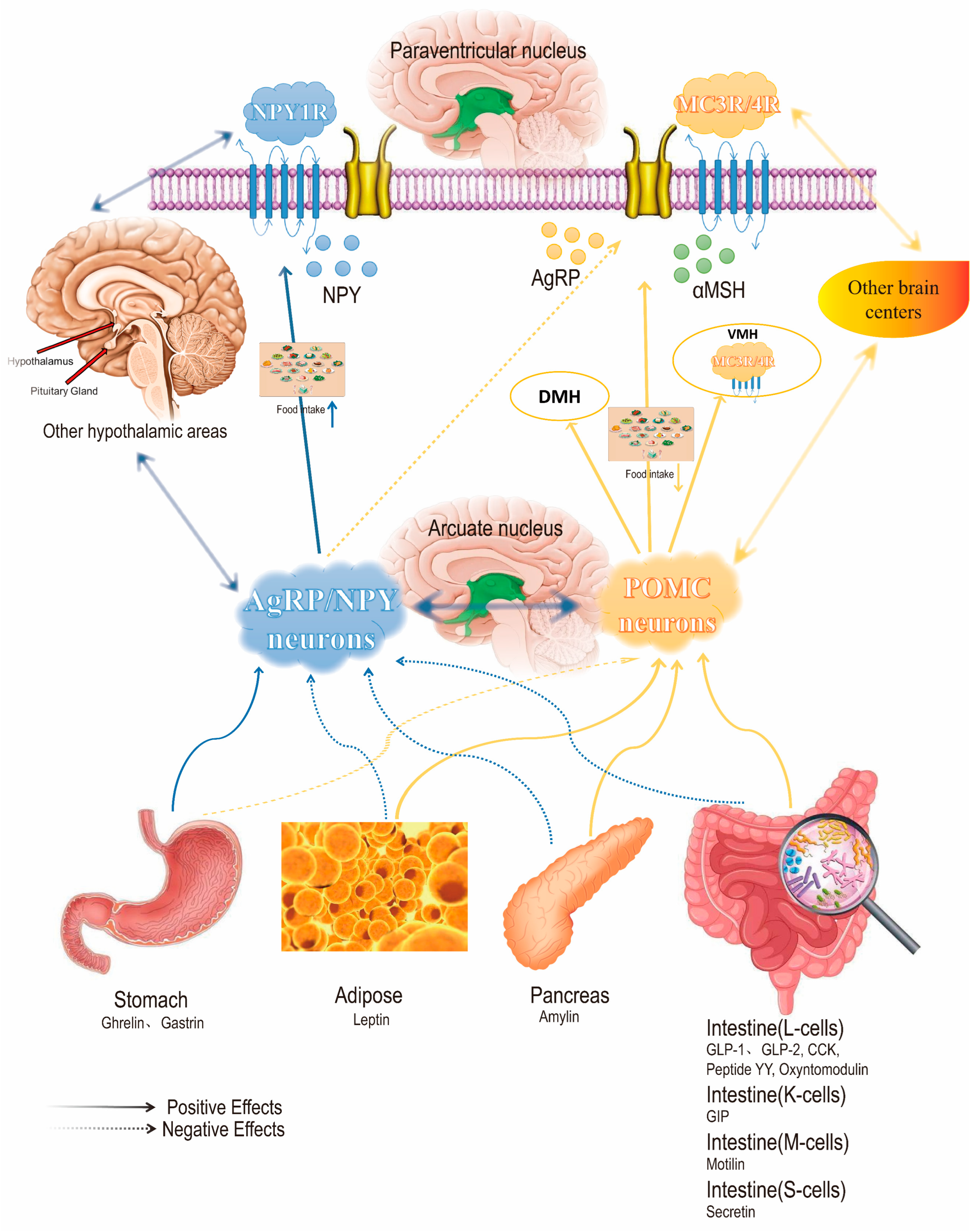
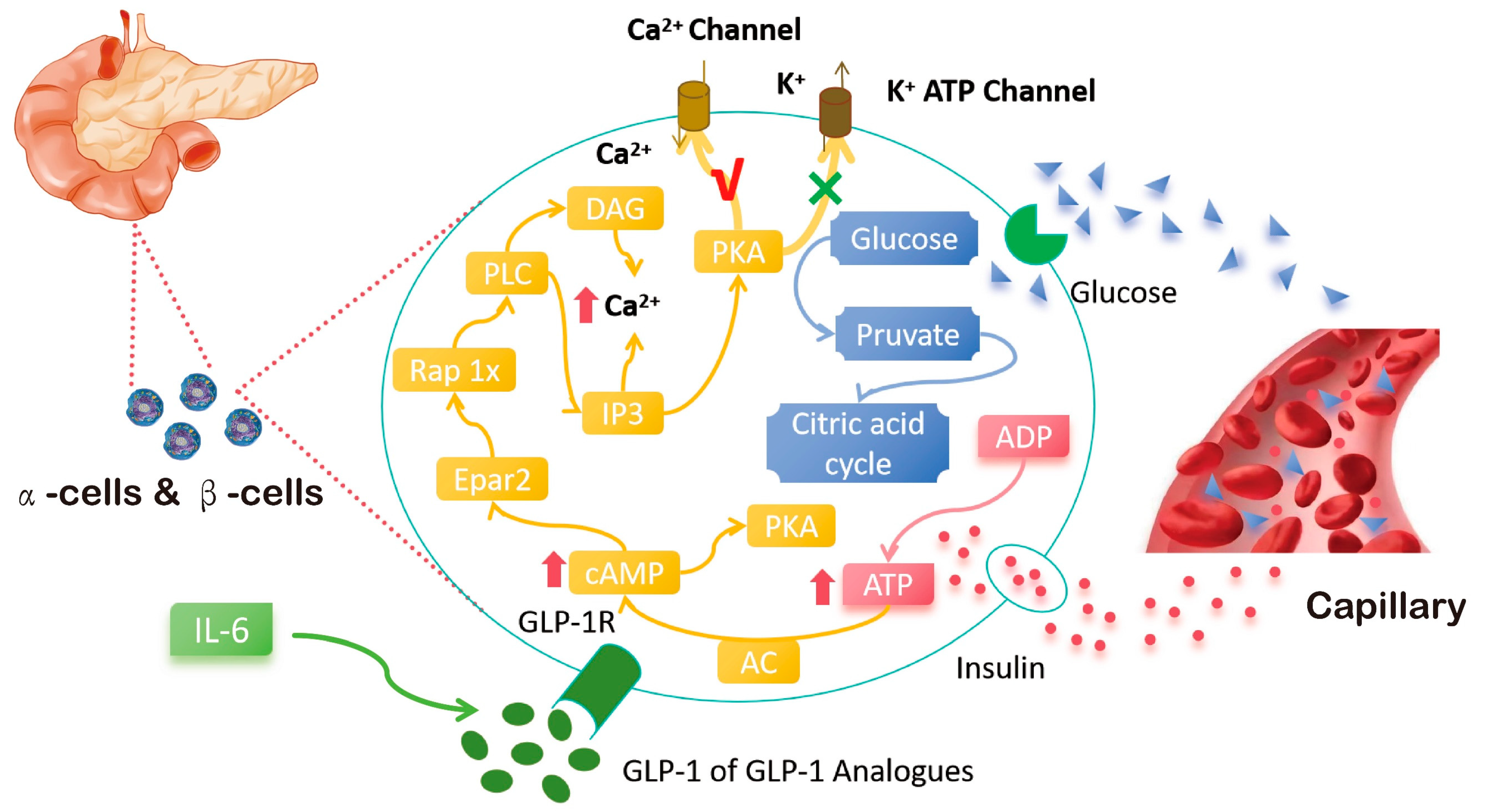
2. Mechanism of Action of GLP-1 Target in the Treatment of Obesity
3. Overview of GLP-1 Targeted Drugs Approved or Designed to Treat Obesity
3.1. Single Agonists
3.2. Double Agonists
3.3. Triple Agonist
4. Other Promising Treatments for Obesity
| Agent | Development Stage | Indication | ClinicalTrials.gov ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acts on the central nervous system | |||
| Central Nervous System-Secreted Neuropeptides and Antagonists | |||
| Tesofensine (NS-2330) (serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor, SNDRI) | Phase 3 | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD); Parkinson’s Disease (PD); Obesity; Obesity due to hypothalamic injury | NCT00394667 |
| Oxytocin | Phase 1 | Obesity; Adult hypothalamic obesity; Prader–Willi syndrome | NCT02849743 |
| Neuropeptide Y receptors antagonist: Velneperit (S-2367) | Phase 2 | Obesity | See Related links [112] |
| Methylphenidate (Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor) | Preclinical | Hypothalamic obesity | See Related links [113] |
| GDF-15 | Phase 2 | Obesity; Diabetes; Cardiovascular diseases; Systemic lupus erythematosus | NCT00609622 |
| Endocannabinoid System Agents (Cannabinoid-1 Receptor Antagonists) | |||
| Rimonabant | Preclinical | Obesity; Cardiovascular risk factors | See Related links [114] |
| AM4113 | Preclinical | Obesity | Not Recorded |
| JD5037 | Preclinical | Obesity | Not Recorded |
| Acts on peripheral tissue (adipose tissue) | |||
| Mirabegron | Phase 3 | Overactive bladder; Metabolic disease | NCT02045862 NCT03049462 NCT02919176 |
| Acts on peripheral target organs (kidney, skeletal muscle, liver) | |||
| Sodium–glucose cotransporter2 (SGLT2) inhibitor | |||
| Empagliflozin (Jardiance) | FDA-approved (2014) | Obesity; T2DM; Heart failure; Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) | NCT01131676 NCT03485222 |
| Dapagliflozin | Phase 3 | T2DM; Heart failure; Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) | NCT03619213 NCT03036150 NCT03036150 |
| Bexagliflozin | FDA-approved (2023) | T2DM | See Related links [115] |
| Dual sodium–glucose cotransporter 1/2 inhibitor (SGLT1/2i) | |||
| Sotagliflozin | Phase 3 | Diabetes; Recent worsening heart failure; Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) | NCT03521934 NCT03315143 |
| Licogliflozin | Phase 2a | Obesity; NASH | NCT03320941 NCT03205150 |
| Others | |||
| Bimagrumab(human monoclonal antibody binding) | Phase 2 | Obesity; T2DM; Sarcopenia | NCT03005288 NCT02333331 |
| CRMP (controlled-release mitochondrial protonophore) | Preclinical | Metabolic syndrome; T2DM; NASH; NAFLD | Not Recorded |
| BAM15 | Preclinical | Obesity | Not Recorded |
| Act on peripheral signaling molecules (gastrointestinal hormones) | |||
| Ghrelin signaling | |||
| GLWL-01 | Phase 2 | PWS | NCT03274856 |
| AZP-531 | Discontinued | PWS; Obesity; T2DM | See Related links [116] |
| Spiegelmers NOX-B11 | Preclinical | Obesity | Not Recorded |
| Leptin sensitizers | |||
| Celastrol | Preclinical | Obesity; T2DM | See Related links [117] |
| Setmelanotide (MC4R) | Phase 3 | Obesity; T2DM | NCT02896192 NCT03287960 |
| Metreleptin | Phase 3 | Lipodystrophy; T1MD; NSAH; Rabson–Mendenhall syndrome (RMS) | NCT01778556 NCT00596934 NCT01679197 NCT00085982 NCT00001987 |
| GLP2R agonists | |||
| Teduglutide | Preclinical | Obesity; T2DM | Not Recorded |
| PYY analogues | |||
| NNC0165-1273 | Preclinical | Obesity; T2DM | Not Recorded |
| OXM | |||
| OXM 6421 | Preclinical | Obesity; T2DM | Not Recorded |
| FGF21/FGFR1c/β-Klotho signaling | |||
| LLF580 | Phase 1 | Obesity; NASH | NCT03466203 |
| BFKB8488A | Phase 1 | Obesity; T2DM; NAFLD | NCT03060538 |
| Pegbelfermin | Phase 2 | Obesity; T2DM; NASH | NCT02413372 |
| LY2405319 | Phase 1 | Obesity; T2DM | See Related links [118] |
| Other appetite suppressants | |||
| Withaferin A | Phase 1 | Obesity; T2DM | Not Recorded |
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MASH/NASH | non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| MAFLD/NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| PKA | protein kinase A |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase |
| AKT/PKB | protein Kinase B |
| AMPK | adenosine 5‘-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| FABP4 | fatty acid-binding protein 4 |
| BMP4 | bone morphogenetic protein 4 |
| UCP1 | uncoupling protein 1 |
| ARC | activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein |
| AgRP | agouti-related protein |
| NPY | neuropeptide Y |
| GIP | gastric inhibitory polypeptide |
| GIPR | gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor |
| GCG | glucagon |
| GCGR | glucagon receptor |
| NTS | nucleus tractus solitarius |
| AOM | azoxymethane |
| FDA | food and drug administration |
| TAG | triacylglycerol |
| WAT | white adipose tissue |
| HbA1c | glycosylated hemoglobin, type A1C |
| CCK | cholecystokinin |
| PYY | peptide YY |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| mTORC1 | mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 |
| mTORC2 | mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 |
| GLUT4 | glucose transporter 4 |
| GSK3 | glycogen synthase kinase-3 |
| MAPKKK | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase |
| BAT | brown adipose tissue |
| p38-MAPK | p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ERK | extracellular signal-related kinases |
| ERK5 | extracellular signal-related kinases 5 |
| ERK1/2 | extracellular signal-related kinases 1/2 |
| TCF | transcription factor |
| C1EBPα/CCAAT | enhancer-binding proteins |
| ADD1 | adducin 1 |
| APM | acute poliomyelitis |
| GSK3β | glycogen synthase kinase 3 β |
| OSBPL2 | oxysterol binding protein-like 2 |
| CXXC5 | CXXC finger protein 5 |
| NOTUM | notum palmitoleoyl-protein carboxylesterase |
References
- Popovic, D.S.; Stokic, E.; Popovic, S.L. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Type 1 Diabetes—Where Do We Stand? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 5292–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D. GLP-1 physiology informs the pharmacotherapy of obesity. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Alkhouri, N.; Vajro, P.; Baumann, U.; Weiss, R.; Socha, P.; Marcus, C.; Lee, W.S.; Kelly, D.; Porta, G.; et al. Defining paediatric metabolic (dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J.V. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piché, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Wilmanski, T.; Diener, C.; Earls, J.C.; Zimmer, A.; Lincoln, B.; Hadlock, J.J.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T.; et al. Multiomic signatures of body mass index identify heterogeneous health phenotypes and responses to a lifestyle intervention. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiri, B.; Hosseinpanah, F.; Banihashem, S.; Madinehzad, S.A.; Valizadeh, M. Mental health and quality of life in different obesity phenotypes: A systematic review. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2022, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, P.M.; Shankar, K. Obesity and pregnancy: Mechanisms of short term and long term adverse consequences for mother and child. BMJ 2017, 356, j1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, C.M.; Cohen, R.V.; Sumithran, P.; Clément, K.; Frühbeck, G. Contemporary medical, device, and surgical therapies for obesity in adults. Lancet 2023, 401, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, A.C.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Martinez, J.A. Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Obesity: Links with Host Genetics and Epigenetics and Potential Applications. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10 (Suppl. S1), S17–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswell, N.; Byrne, R.; Davies, P.S.W. Aetiology of eating behaviours: A possible mechanism to understand obesity development in early childhood. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 95, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elagizi, A.; Kachur, S.; Carbone, S.; Lavie, C.J.; Blair, S.N. A Review of Obesity, Physical Activity, and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaei, M.; Sundararajan, E.A.; Driss, M.; Boulila, W.; Shapi’I, A. A systematic literature review on obesity: Understanding the causes & consequences of obesity and reviewing various machine learning approaches used to predict obesity. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104754. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Chi, J.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y. Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19). Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2021, 37, e3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Metabolic Messengers: Glucagon-like peptide 1. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, H.H. More questions than answers. Science 2023, 382, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, O.M.; Sofopoulos, M.; Tsoukas, M.A.; Dincer, F.; Thakkar, B.; Sahin-Efe, A.; Filippaios, A.; Bowers, J.; Srnka, A.; Gavrieli, A.; et al. GLP-1 receptors exist in the parietal cortex, hypothalamus and medulla of human brains and the GLP-1 analogue liraglutide alters brain activity related to highly desirable food cues in individuals with diabetes: A crossover, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 954–965. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla, S.; Mehan, S.; Khan, A.; Rehman, M.U. Protective role of IGF-1 and GLP-1 signaling activation in neurological dysfunctions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 142, 104896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Tong, J.; Hao, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, K.; Xu, H.; Wang, A. Bile acid coordinates microbiota homeostasis and systemic immunometabolism in cardiometabolic diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2129–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Lin, B.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Z.; Cao, H.; Xu, H.; Liang, H.; Weng, J. GLP-1 receptor agonist promotes brown remodelling in mouse white adipose tissue through SIRT1. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, B.A.; Wong, C.K.; Campbell, J.E.; Hodson, D.J.; Trapp, S.; Drucker, D.J. Revisiting the Complexity of GLP-1 Action from Sites of Synthesis to Receptor Activation. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 42, 101–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.E.; Drucker, D. Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of incretin hormone action. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Perkins, M.H.; Chang, H.; Han, W.; de Araujo, I.E. An inter-organ neural circuit for appetite suppression. Cell 2022, 185, 2478–2494.e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, F.; Wilkinson, M.; Baxter, E.; Brennan, D.J. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) and Obesity-Related Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Wang, J. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Obesity. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yu, Z.; Tovar, J.; Nilsson, A.; Xu, B. Critical review on anti-obesity effects of phytochemicals through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 184, 106461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secher, A.; Jelsing, J.; Baquero, A.F.; Hecksher-Sørensen, J.; Cowley, M.A.; Dalbøge, L.S.; Hansen, G.; Grove, K.L.; Pyke, C.; Raun, K.; et al. The arcuate nucleus mediates GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide-dependent weight loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4473–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidi, A.M.; Belanger, M.J.; Kokkinos, A.; Koliaki, C.C.; Mantzoros, C.S. Novel Noninvasive Approaches to the Treatment of Obesity: From Pharmacotherapy to Gene Therapy. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 507–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsgaard, H.; Seelig, E.; Timper, K.; Coslovsky, M.; Soederlund, L.; Lyngbaek, M.P.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Schmidt-Trucksäss, A.; Hanssen, H.; Frey, W.O.; et al. GLP-1 secretion is regulated by IL-6 signalling: A randomised, placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granhall, C.; Donsmark, M.; Blicher, T.M.; Golor, G.; Søndergaard, F.L.; Thomsen, M.; Bækdal, T.A. Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Single and Multiple Ascending Doses of the Novel Oral Human GLP-1 Analogue, Oral Semaglutide, in Healthy Subjects and Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, K.; Lau, D.C.W.; Van Gaal, L.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Skjøth, T.V.; Manning, L.S.; Pi-Sunyer, X.; Hamann, A.; Barakat, A.; Blüher, M.; et al. 3 years of liraglutide versus placebo for type 2 diabetes risk reduction and weight management in individuals with prediabetes: A randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, A.S.; Auerbach, P.; Barrientos-Perez, M.; Gies, I.; Hale, P.M.; Marcus, C.; Mastrandrea, L.D.; Prabhu, N.; Arslanian, S. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Liraglutide for Adolescents with Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, D.M.; Greenway, F.L.; Khalid, U.; O’Neil, P.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Sørrig, R.; Wadden, T.A.; Wizert, A.; Garvey, W.T.; Arauz-Pacheco, C.; et al. Effect of Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Daily Liraglutide on Body Weight in Adults with Overweight or Obesity without Diabetes: The STEP 8 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, R.P. In overweight or obesity without diabetes, weekly semaglutide vs. daily liraglutide increased weight loss at 68 wk. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, Jc56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaman, A.M.; Bain, S.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Buse, J.B.; Idorn, T.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Rasmussen, S.; Rossing, P.; et al. Effect of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Semaglutide and Liraglutide on Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Pooled Analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and LEADER. Circulation 2022, 145, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.B.; Bain, S.C.; Mann, J.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Pratley, R.E.; Linder, M.; Monk Fries, T.; et al. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction With Liraglutide: An Exploratory Mediation Analysis of the LEADER Trial. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeland, I.J.; Marso, S.P.; Ayers, C.R.; Lewis, B.; Oslica, R.; Francis, W.; Rodder, S.; Pandey, A.; Joshi, P.H. Effects of liraglutide on visceral and ectopic fat in adults with overweight and obesity at high cardiovascular risk: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrino. 2021, 9, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Du, Z.; Duan, C.; Zhan, S.; Wang, T.; Zhu, M.; Shi, J.; Meng, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; et al. Beinaglutide shows significantly beneficial effects in diabetes/obesity-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in ob/ob mouse model. Life Sci. 2021, 270, 118966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.; Choi, J.; Rosenstock, J.; Popescu, L.; Niemoeller, E.; Muehlen-Bartmer, I.; Baek, S. Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Efpeglenatide Monotherapy Versus Placebo in Type 2 Diabetes: The AMPLITUDE-M Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xu, Z.; Zou, H.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Zhu, R.; Wang, B.; et al. Discovery of ecnoglutide—A novel, long-acting, cAMP-biased glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog. Mol. Metab. 2023, 75, 101762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.R.; Gorman, D.N.; Esquejo, R.M.; Bergman, A.; Chidsey, K.; Buckeridge, C.; Griffith, D.A.; Kim, A.M. Danuglipron (PF-06882961) in type 2 diabetes: A randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple ascending-dose phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.R.; Frias, J.P.; Brown, L.S.; Gorman, D.N.; Vasas, S.; Tsamandouras, N.; Birnbaum, M.J. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Small Molecule Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Danuglipron for Glycemic Control Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2314493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.; Hsia, S.; Eyde, S.; Liu, R.; Ma, X.; Konig, M.; Kazda, C.; Mather, K.J.; Haupt, A.; Pratt, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of oral orforglipron in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, randomised, dose-response, phase 2 study. Lancet 2023, 402, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, S.; Blevins, T.; Connery, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Raha, S.; Liu, R.; Ma, X.; Mather, K.J.; Haupt, A.; Robins, D.; et al. Daily Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Orforglipron for Adults with Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Cui, G.; Mi, N.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, C.; Wang, J.; Qiu, X.; Han, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of TG103, a novel long-acting GLP-1/Fc fusion protein after a single ascending dose in Chinese healthy subjects. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 185, 106448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.; Bastyr, E.J.; Vignati, L.; Tschoep, M.H.; Schmitt, C.; Owen, K.; Christensen, R.H.; DiMarchi, R.D. The Sustained Effects of a Dual GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, NNC0090-2746, in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Meta. 2017, 26, 343–352.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iepsen, E.W.; Lundgren, J.R.; Holst, J.J.; Madsbad, S.; Torekov, S.S. Successful weight loss maintenance includes long-term increased meal responses of GLP-1 and PYY3-36. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 174, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A.; Sanchez, W.; Lawitz, E.; Filozof, C.; Cho, H.; Baek, E.; Choi, J.; Baek, S. A phase 2, adaptive randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, 52-week study of HM15211 in patients with biopsy-confirmed non-alcoholic steatohepatitis—Study design and rationale of HM-TRIA-201 study. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2023, 130, 107176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samms, R.J.; Coghlan, M.P.; Sloop, K.W. How May GIP Enhance the Therapeutic Efficacy of GLP-1? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikoff, A.; O’Brien, S.L.; Bernecker, M.; Grandl, G.; Kleinert, M.; Knerr, P.J.; Stemmer, K.; Klingenspor, M.; Zeigerer, A.; DiMarchi, R.; et al. Spatiotemporal GLP-1 and GIP receptor signaling and trafficking/recycling dynamics induced by selected receptor mono- and dual-agonists. Mol. Metab. 2021, 49, 101181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, J.P.; Davies, M.J.; Rosenstock, J.; Pérez Manghi, F.C.; Fernández Landó, L.; Bergman, B.K.; Liu, B.; Cui, X.; Brown, K. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, Y.Y. Tirzepatide: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jepsen, M.M.; Christensen, M.B. Emerging glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists for the treatment of obesity. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2021, 26, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, R.; Drucker, D. Beyond the pancreas: Contrasting cardiometabolic actions of GIP and GLP1. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Qiu, W.; Liao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Pang, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; et al. A phase 2 randomised controlled trial of mazdutide in Chinese overweight adults or adults with obesity. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Gao, L.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.; Yu, L.; Wen, J.; Cai, C.; Deng, H.; Feng, L.; Song, B.; et al. Safety and efficacy of a GLP-1 and glucagon receptor dual agonist mazdutide (IBI362) 9 mg and 10 mg in Chinese adults with overweight or obesity: A randomised, placebo-controlled, multiple-ascending-dose phase 1b trial. eClinicalMedicine 2022, 54, 101691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Jiang, H.; Ma, G.; Wang, X.; Gan, S.; Sun, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Mazdutide in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, M.L.; Laker, R.C.; Mather, K.; Nawrocki, A.; Oldham, S.; Boland, B.B.; Lewis, H.; Conway, J.; Naylor, J.; Guionaud, S.; et al. Resolution of NASH and hepatic fibrosis by the GLP-1R/GcgR dual-agonist Cotadutide via modulating mitochondrial function and lipogenesis. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, V.E.R.; Robertson, D.; Erazo-Tapia, E.; Havekes, B.; Phielix, E.; de Ligt, M.; Roumans, K.H.M.; Mevenkamp, J.; Sjoberg, F.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V.B.; et al. Cotadutide promotes glycogenolysis in people with overweight or obesity diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 2086–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahra, R.; Wang, T.; Gadde, K.M.; Oscarsson, J.; Stumvoll, M.; Jermutus, L.; Hirshberg, B.; Ambery, P. Effects of Cotadutide on Metabolic and Hepatic Parameters in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: A 54-Week Randomized Phase 2b Study. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, R.; Schiavon, M.; Göbel, B.; Riz, M.; Cobelli, C.; Klabunde, T.; Man, C.D. Dual glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor/glucagon receptor agonist SAR425899 improves beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavon, M.; Visentin, R.; Göbel, B.; Riz, M.; Cobelli, C.; Klabunde, T.; Dalla Man, C. Improved postprandial glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes by the dual glucagon-like peptide-1/glucagon receptor agonist SAR425899 in comparison with liraglutide. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, K.D.; Carnero, E.A.; Allerton, T.D.; Tillner, J.; Bock, C.P.; Luyet, P.P.; Göbel, B.; Hall, K.D.; Parsons, S.A.; Ravussin, E.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1/glucagon receptor agonism associates with reduced metabolic adaptation and higher fat oxidation: A randomized trial. Obesity 2023, 31, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, M.; Yee, J.; Frustaci, M.E.; Samtani, M.N.; Fleck, P. Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1/glucagon receptor co-agonist JNJ-64565111 in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: A randomized dose-ranging study. Clin. Obes. 2021, 11, e12433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dissanayake, H.A.; Somasundaram, N.P. Polyagonists in Type 2 Diabetes Management. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2024, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, T.; Thomas, L.; Baader-Pagler, T.; Haebel, P.; Simon, E.; Reindl, W.; Bajrami, B.; Rist, W.; Uphues, I.; Drucker, D.J.; et al. BI 456906: Discovery and preclinical pharmacology of a novel GCGR/GLP-1R dual agonist with robust anti-obesity efficacy. Mol. Metab. 2022, 66, 101633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungnik, A.; Arrubla Martinez, J.; Plum-Mörschel, L.; Kapitza, C.; Lamers, D.; Thamer, C.; Schölch, C.; Desch, M.; Hennige, A.M. Phase I studies of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the dual glucagon receptor/glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist BI 456906. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Gómez, M.; Shankar, R.R.; Chaudhri, E.; Liu, J.; Lam, R.L.; Kaufman, K.D.; Engel, S.S.; Bruzone, S.O.; Coronel, M.J.; Gruz, F.M.; et al. A Phase 2a active-comparator-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of efinopegdutide in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, J.J.; Parkes, D.; Feigh, M.; Suschak, J.J.; Harris, M.S. Effects of ALT-801, a GLP-1 and glucagon receptor dual agonist, in a translational mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S. American Diabetes Association—76th Scientific Sessions (June 10–14, 2016—New Orleans, Louisiana, USA). Drugs Today 2016, 52, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouberai, M.M.; Gomes Dos Santos, A.L.; Kinna, S.; Hornigold, D.C.; Baker, D.; Naylor, J.; Liang, L.; Corkill, D.J.; Welland, M.E. Self-assembled GLP-1/glucagon peptide nanofibrils prolong inhibition of food intake. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1217021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Dai, Y.; Avraham, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, C.; Tong, J.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X.; et al. Novel glucagon- and OXM-based peptides acting through glucagon and GLP-1 receptors with body weight reduction and anti-diabetic properties. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 95, 103538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, K.; Field, B.C.T.; Bloom, S.R. The mechanism of action for oxyntomodulin in the regulation of obesity. Curr. Opin Investig. Drugs 2010, 11, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Kosinski, J.R.; Hubert, J.; Carrington, P.E.; Chicchi, G.G.; Mu, J.; Miller, C.; Cao, J.; Bianchi, E.; Pessi, A.; SinhaRoy, R.; et al. The glucagon receptor is involved in mediating the body weight-lowering effects of oxyntomodulin. Obesity 2012, 20, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, M.; Murphy, K.G.; Patel, S.R.; Patel, N.A.; Greenwood, H.C.; Cooke, J.H.; Campbell, D.; Bewick, G.A.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Hypothalamic injection of oxyntomodulin suppresses circulating ghrelin-like immunoreactivity. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 3513–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.M.; Pathak, N.; Flatt, Y.E.; Gault, V.A.; O’harte, F.P.; Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R. Comparison of stability, cellular, glucose-lowering and appetite supressing effects of oxyntomodulin analogues modified at the N-terminus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 743, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, K.; Park, A.J.; Small, C.J.; Patterson, M.; Ellis, S.M.; Murphy, K.G.; Wren, A.M.; Frost, G.S.; Meeran, K.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Subcutaneous oxyntomodulin reduces body weight in overweight and obese subjects: A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2390–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Ford, H.E.; Druce, M.R.; Minnion, J.S.; Field, B.C.T.; Shillito, J.C.; Baxter, J.; Murphy, K.G.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Subcutaneous oxyntomodulin analogue administration reduces body weight in lean and obese rodents. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, B.D.; Flatt, P.R.; Gault, V.A. (D-Ser2)Oxm[mPEG-PAL]: A novel chemically modified analogue of oxyntomodulin with antihyperglycaemic, insulinotropic and anorexigenic actions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hay, D.L.; Chen, S.; Lutz, T.A.; Parkes, D.G.; Roth, J.D.; Insel, P. AAmylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 564–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Clemmensen, C.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Tschöp, M.H. The New Biology and Pharmacology of Glucagon. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 721–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevaskis, J.L.; Mack, C.M.; Sun, C.; Soares, C.J.; D’Souza, L.J.; Levy, O.E.; Lewis, D.Y.; Jodka, C.M.; Tatarkiewicz, K.; Gedulin, B.; et al. Improved glucose control and reduced body weight in rodents with dual mechanism of action peptide hybrids. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enebo, L.B.; Berthelsen, K.K.; Kankam, M.; Lund, M.T.; Rubino, D.M.; Satylganova, A.; Lau, D.C. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of concomitant administration of multiple doses of cagrilintide with semaglutide 2·4 mg for weight management: A randomised, controlled, phase 1b trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 1736–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.; Deenadayalan, S.; Erichsen, L.; Knop, F.K.; Lingvay, I.; Macura, S.; Mathieu, C.; Pedersen, S.D.; Davies, M. Efficacy and safety of co-administered once-weekly cagrilintide 2·4 mg with once-weekly semaglutide 2·4 mg in type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; de Graaf, C.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, S.; Liu, K.; Cai, X.; Dai, A.; Lin, G.; et al. Human GLP-1 receptor transmembrane domain structure in complex with allosteric modulators. Nature 2017, 546, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Witteloostuijn, S.B.; Dalbøge, L.S.; Hansen, G.; Midtgaard, S.R.; Jensen, G.V.; Jensen, K.J.; Vrang, N.; Jelsing, J.; Pedersen, S.L. GUB06-046, a novel secretin/glucagon-like peptide 1 co-agonist, decreases food intake, improves glycemic control, and preserves beta cell mass in diabetic mice. J. Pept. Sci. 2017, 23, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanday, N.; English, A.; Lafferty, R.A.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Benefits of Sustained Upregulated Unimolecular GLP-1 and CCK Receptor Signalling in Obesity-Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 674704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornigold, D.C.; Roth, E.; Howard, V.; Will, S.; Oldham, S.; Coghlan, M.P.; Blouet, C.; Trevaskis, J.L. A GLP-1:CCK fusion peptide harnesses the synergistic effects on metabolism of CCK-1 and GLP-1 receptor agonism in mice. Appetite 2018, 127, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, N.; Pathak, V.; Flatt, P.R. A Novel CCK-8/GLP-1 Hybrid Peptide Exhibiting Prominent Insulinotropic, Glucose-Lowering, and Satiety Actions With Significant Therapeutic Potential in High-Fat-Fed Mice. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2996–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Østergaard, S.; Paulsson, J.F.; Kjærgaard Gerstenberg, M.; Wulff, B.S. The Design of a GLP-1/PYY Dual Acting Agonist. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 8268–8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samms, R.J.; Cosgrove, R.; Snider, B.M.; Furber, E.C.; Droz, B.A.; Briere, D.A.; Dunbar, J.; Dogra, M.; Alsina-Fernandez, J.; Borner, T.; et al. GIPR Agonism Inhibits PYY-Induced Nausea-Like Behavior. Diabetes 2022, 71, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, T.; Urva, S.; Roell, W.C.; Qu, H.; Loghin, C.; Moyers, J.S.; O’farrell, L.S.; Briere, D.A.; Sloop, K.W.; Thomas, M.K.; et al. LY3437943, a novel triple glucagon, GIP, and GLP-1 receptor agonist for glycemic control and weight loss: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1234–1247.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Frias, J.; Jastreboff, A.M.; Du, Y.; Lou, J.; Gurbuz, S.; Thomas, M.K.; Hartman, M.L.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; et al. Retatrutide, a GIP, GLP-1 and glucagon receptor agonist, for people with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, double-blind, placebo and active-controlled, parallel-group, phase 2 trial conducted in the USA. Lancet 2023, 402, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Kaplan, L.M.; Frías, J.P.; Wu, Q.; Du, Y.; Gurbuz, S.; Coskun, T.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; Hartman, M.L. Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity—A Phase 2 Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossart, M.; Wagner, M.; Elvert, R.; Evers, A.; Hübschle, T.; Kloeckener, T.; Lorenz, K.; Moessinger, C.; Eriksson, O.; Velikyan, I.; et al. Effects on weight loss and glycemic control with SAR441255, a potent unimolecular peptide GLP-1/GIP/GCG receptor triagonist. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 59–74.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finan, B.; Douros, J.D. GLP-1/GIP/glucagon receptor triagonism gets its try in humans. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Behary, P.; Tharakan, G.; Minnion, J.; Al-Najim, W.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Holst, J.J.; Bloom, S.R. The Effect of a Subcutaneous Infusion of GLP-1, OXM, and PYY on Energy Intake and Expenditure in Obese Volunteers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behary, P.; Tharakan, G.; Alexiadou, K.; Johnson, N.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Kenkre, J.; Cuenco, J.; Hope, D.; Anyiam, O.; Choudhury, S.; et al. Combined GLP-1, Oxyntomodulin, and Peptide YY Improves Body Weight and Glycemia in Obesity and Prediabetes/Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Single-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Study. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yan, Z.; Du, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, C.; Jing, L.; Sun, L.; Yang, Q.; Tang, X.; Yuan, Y.; et al. A GLP-1/glucagon (GCG)/CCK(2) receptors tri-agonist provides new therapy for obesity and diabetes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 4360–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarbaliene, J.; Secher, T.; Jelsing, J.; Ansarullah; Neerup, T.S.; Billestrup, N.; Fosgerau, K. The anti-diabetic effects of GLP-1-gastrin dual agonist ZP3022 in ZDF rats. Peptides 2015, 69, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.; Stratigou, T.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Tsigalou, C.; Dalamaga, M. Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, Postbiotics, and Obesity: Current Evidence, Controversies, and Perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, G.; Pascuzzi, M.C.; Di Profio, E.; Corsello, A.; Agostinelli, M.; La Mendola, A.; Milanta, C.; Campoy, C.; Calcaterra, V.; Zuccotti, G.; et al. Bioactive compounds in childhood obesity and associated metabolic complications: Current evidence, controversies and perspectives. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 187, 106599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.W.; Gao, L.; Stastka, P.; Cheney, M.C.; Mahabamunuge, J.; Torres Soto, M.; Ford, C.B.; Bryant, J.A.; Henn, M.R.; Hohmann, E.L. Fecal microbiota transplantation for the improvement of metabolism in obesity: The FMT-TRIM double-blind placebo-controlled pilot trial. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretti, J.R.; Kassam, Z.; Mullish, B.H.; Chiang, A.; Carrellas, M.; Hurtado, J.; Marchesi, J.R.; McDonald, J.A.K.; Pechlivanis, A.; Barker, G.F.; et al. Effects of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation with Oral Capsules in Obese Patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 855–863.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Yi, K.; Peng, L.; Xie, J.; Gou, X.; Peng, T.; Tang, L. Phlorizin ameliorates obesity-associated endotoxemia and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed mice by targeting the gut microbiota and intestinal barrier integrity. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, V.; Zhang, Z.; Deehan, E.C.; Kao, D.H.; Hotte, N.; Karmali, S.; Birch, D.W.; Samarasinghe, K.K.; Walter, J.; Madsen, K.L. Fecal microbial transplantation and fiber supplementation in patients with severe obesity and metabolic syndrome: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhang, J.; Kuang, T.; Fan, G. Gut mycobiome and metabolic diseases: The known, the unknown, and the future. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 193, 106807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tang, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. An overview of traditional Chinese medicine affecting gut microbiota in obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1149751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dilidaxi, D.; Wu, Y.; Sailike, J.; Sun, X.; Nabi, X.-H. Composite probiotics alleviate type 2 diabetes by regulating intestinal microbiota and inducing GLP-1 secretion in db/db mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, G.; Apovian, C. Future Pharmacotherapy for Obesity: New Anti-obesity Drugs on the Horizon. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shellenberg, T.P.; Stoops, W.W.; Lile, J.A.; Rush, C.R. An update on the clinical pharmacology of methylphenidate: Therapeutic efficacy, abuse potential and future considerations. Expert Rev Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curioni, C.; André, C. Rimonabant for overweight or obesity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 2006, Cd006162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Bexagliflozin: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allas, S.; Delale, T.; Ngo, N.; Julien, M.; Sahakian, P.; Ritter, J.; Abribat, T.; van der Lely, A.J. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of AZP-531, a first-in-class analogue of unacylated ghrelin, in healthy and overweight/obese subjects and subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lee, J.; Hernandez, M.A.S.; Mazitschek, R.; Ozcan, U. Treatment of obesity with celastrol. Cell 2015, 161, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaich, G.; Chien, J.Y.; Fu, H.; Glass, L.C.; Deeg, M.A.; Holland, W.L.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Bumol, T.; Schilske, H.K.; Moller, D.E. The effects of LY2405319, an FGF21 analog, in obese human subjects with type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, D. The structure and function of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and its ligands. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Shao, S. Exenatide regulates Th17/Treg balance via PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway in db/db mice. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, J.R.; Janus, C.; Jensen, S.B.; Juhl, C.R.; Olsen, L.M.; Christensen, R.M.; Svane, M.S.; Bandholm, T.; Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Blond, M.B.; et al. Healthy Weight Loss Maintenance with Exercise, Liraglutide, or Both Combined. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, S.; Abrahamson, M.J.; Ceriello, A.; Charpentier, G.; Evans, M.; Lehmann, R.; Liebl, A.; Linjawi, S.; Holt, R.I.; Hosszúfalusi, N.; et al. Clinical considerations when initiating and titrating insulin degludec/liraglutide (IDegLira) in people with type 2 diabetes. Drugs 2020, 80, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chandrashekar, A.; Beig, A.; Walker, J.; Hong, J.K.; Benet, A.; Kang, J.; Ackermann, R.; Wang, Y.; Qin, B.; et al. Characterization of attributes and in vitro performance of exenatide-loaded PLGA long-acting release microspheres. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 158, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes–state-of-the-art. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Green, J.B.; Janmohamed, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Granger, C.B.; Jones, N.P.; Leiter, L.A.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Sigmon, K.N.; Somerville, M.C.; et al. Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanian, S.A.; Hannon, T.; Zeitler, P.; Chao, L.C.; Boucher-Berry, C.; Barrientos-Pérez, M.; Bismuth, E.; Dib, S.; Cho, J.I.; Cox, D. Once-weekly dulaglutide for the treatment of youths with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Claggett, B.; Diaz, R.; Dickstein, K.; Gerstein, H.C.; Køber, L.V.; Lawson, F.C.; Ping, L.; Wei, X.; Lewis, E.F.; et al. Lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weghuber, D.; Barrett, T.; Barrientos-Pérez, M.; Gies, I.; Hesse, D.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Kelly, A.S.; Mastrandrea, L.D.; Sørrig, R.; Arslanian, S. Once-weekly semaglutide in adolescents with obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2245–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, F.K.; Aroda, V.R.; do Vale, R.D.; Holst-Hansen, T.; Laursen, P.N.; Rosenstock, J.; Rubino, D.M.; Garvey, W.T. Oral semaglutide 50 mg taken once per day in adults with overweight or obesity (OASIS 1): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- France, N.L.; Syed, Y.Y. Tirzepatide: A review in type 2 diabetes. Drugs 2024, 84, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Sun, X. Polyethylene Glycol Loxenatide (PEX-168) Reduces Body Weight and Blood Glucose in Simple Obese Mice. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 2021, 9951463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Agent | Drug Name | Approved Company | Approval Time | Half-Life Period | Administration | Indication | Adverse Reaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exenatide | Byetta | Amylin; AstraZeneca | 2005.04 (Food and Drug Administration, FDA) | 1~2 h | s.c. twice daily | Diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2DM) | Nausea, vomiting, hypoglycemia |
| Exenatide LAR | Bydureon | Amylin; AstraZeneca | 2012.01 (FDA) | 5~6 d | s.c. once weekly | T2DM; Parkinson’s disease | Nausea, vomiting, strong immunogenic reactions at the injection site (due to rejection of the polylactic-glycolic acid copolymer) |
| Liraglutide | Victoza | Novo Nordisk | 2010.01 (FDA) | 10~14 h | s.c. once daily | Obesity; T2DM; NASH | Nausea, vomiting, excessive weight loss in T2DM patients, hypoglycemic events in combination with conventional hypoglycemic agents |
| Semaglutide | Ozempic | Novo Nordisk | 2017.12 (FDA) | 165 h | s.c. once weekly | Obesity | Potential reproductive toxicity |
| Semaglutide | Rybelsus | Novo Nordisk | 2020.01 (FDA) | 24h | po. once daily | Obesity | Potential reproductive toxicity |
| Tirzepatide | Mounjaro | Eli Lilly | 2022.05 (FDA) | 5~6 d | s.c. once weekly | T2DM | Nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, vomiting, constipation, indigestion, stomach pain |
| Albiglutide | Tanzeum | GSK | 2014.04 (FDA) | 5~6 d | s.c. once weekly | T2DM | Stop selling |
| Dulaglutide | Trulicity | Eli Lilly | 2014.09 (FDA) | 5 d | s.c. once weekly | T2DM | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea |
| Lixisenatide | Adlyxin | Sanofi | 2016.07 (FDA) | 24h | s.c. once daily | T2DM | Fewer side effects |
| Beinaglutide | HYBR-014 | Shanghai Benemae | 2023.07 (CFDA) | 6h | s.c. thrice daily | Obesity; T2DM; NASH | Widespread antibody |
| Polyethylene Glycol Loxenatide Injection | PEX-168 | Jiangsu Hansoh Pharmaceutical Group | 2019.05 (CFDA) | 5~6 d | s.c. once weekly | T2DM | The widespread existence of anti-PEG antibodies limits the applicable population |
| Insulin Degludec and Liraglutide Injection | IDegLira (Xultophy) | Novo Nordisk | 2022.03 (FDA) | 24h | s.c. once daily | T2DM | Nausea, vomiting, hypoglycemia, injection site reactions |
| Insulin Glargine and Lixisenatide Injection | IGlarLixi | Sanofi | 2023.07 (FDA) | 24h | s.c. once daily | T2DM | Nausea, vomiting, hypoglycemia, injection site reactions |
| Agent | Company | Development Stage | Indication | ClinicalTrials.gov ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efpeglenatide (LAPSExd4 Analogue) | Hanmi | Phase 3 | Humans with obesity and/or T2DM | NCT03353350 NCT03496298 NCT03353350 |
| TG103 | CSPC | Phase 2/1 | Obesity | NCT03990090 |
| Ecnoglutide (XW003) | Sciwind Biosciences | Phase 2/1 | Obesity; T2DM | NCT04389775 |
| Danuglipron (PF-06882961) | Pfizer | Phase 3/2 | Obesity; T2DM | NCT03538743 |
| Orforglipron (LY3502970) | Eli Lilly | Phase 2 | Obesity; T2DM | NCT05048719 |
| PB-119 | PegBio Co. | Phase 2 | T2DM | NCT03520972 NCT02084251 |
| Agent | Company | Development Stage | Indication | ClinicalTrials.gov ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Double agonists | ||||
| GLP1R/GIPR dual agonists | ||||
| RG-7697 (MAR-709, NNC0090-2746) | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag; vo Nordisk | Phase 2 | Obesity; T2DM | See Related links [47] |
| CT-868 | Carmot Therapeutics | Phase 2 | Obesity; T2DM | Not Recorded |
| CT-388 | Carmot Therapeutics | Phase 1 | Obesity; T2DM | Not Recorded |
| GLP-1R agonist and GIPR antagonist | ||||
| AMG133 | Amgen | Phase 1 | Obesity | Not Recorded |
| GLP-1R/GCGR dual agonist | ||||
| Mazdutide (IBI362/LY3305677) | Eli Lilly | Phase 1 | Obesity; T2DM | NCT04440345 |
| Cotadutide/MEDI0382 | AstraZeneca | Phase 2 | T2DM | NCT02548585 NCT04208620 NCT03550378 |
| SAR425899 | Sanofi | Phase 1 | T2DM | NCT02973321 NCT02411825 |
| JNJ-64565111 | Johnson | Phase 2 | Obesity; T2DM | NCT03586830 NCT03486392 |
| BI 456906 | Boehringer Ingelheim | Phase 2 Phase 1 | Obesity | NCT03175211 NCT03591718 |
| Efinopegdutide | Hanmi Pharmaceutical | Phase 2 | NASH | NCT04944992 |
| Pemvidutide/ALT-801 | Altimmune | Phase 1 | Obesity; NASH | NCT00496860 |
| JNJ-54728518 | Janssen Research & Development Llc | Phase 1 | Obesity; T2DM | Not Recorded |
| NN9277/NNC9204-1177 | Novo Nordisk | Phase 1 | Obesity | NCT02941042 |
| MOD-6031 | OPKO Health | Phase 1 | Obesity; T2DM | Not Recorded |
| OPK-88003 | OPKO Health | Phase 2 | Obesity; T2DM | Not Recorded |
| MK8521 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp | Preclinical | Obesity; T2DM | Not Recorded |
| GLP-1/amylin | ||||
| GLP1RA/davalintide hybrid peptides (AC164204, AC164209) | Preclinical | DIO rats and ob/ob mice | Not Recorded | |
| Cagrilintide (NNC0174-0833) | Novo Nordisk | Phase 1 | Humans with obesity or overweight | NCT03600480 |
| GLP-1/secretin | ||||
| GUB06-046 | Gubra ApS | Preclinical | Diabetic mice | Not Recorded |
| GLP-1/CCK | ||||
| CCK-8/exendin-4 hybrid peptide | Preclinical | DIO mice | Not Recorded | |
| Fusion peptide C2816 | Preclinical | DIO mice | Not Recorded | |
| GLP-1/PYY | ||||
| PYY3-36 + GLP-1 | Preclinical | Obesity | See Related links [48] | |
| Triple agonists | ||||
| GLP-1R/GIPR/GCGR triple agonist | ||||
| HM15211 | Hanmi Pharmaceutical | Phase 2 | NASH | See Related links [49] |
| Retatrutide (LY3437943) | Eli Lilly | Phase 2 | Obesity; T2DM | NCT04881760 NCT04867785 NCT04143802 NCT04881760 |
| SAR441255 | Sanofi | Phase 1 | Obesity | NCT04521738 |
| NN9423/NNC9204-1706 | Novo Nordisk | Phase 1 | Obesity | NCT03095807 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Lai, W.; Sun, J.; Bai, Y.; Cao, H.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Focus on Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Target: Drugs Approved or Designed to Treat Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041651
Zhang J, Wei J, Lai W, Sun J, Bai Y, Cao H, Guo J, Su Z. Focus on Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Target: Drugs Approved or Designed to Treat Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(4):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041651
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiahua, Jintao Wei, Weiwen Lai, Jiawei Sun, Yan Bai, Hua Cao, Jiao Guo, and Zhengquan Su. 2025. "Focus on Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Target: Drugs Approved or Designed to Treat Obesity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 4: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041651
APA StyleZhang, J., Wei, J., Lai, W., Sun, J., Bai, Y., Cao, H., Guo, J., & Su, Z. (2025). Focus on Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Target: Drugs Approved or Designed to Treat Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(4), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041651






