Exploring Nano-Delivery Systems to Enhance the Edaravone Performance in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
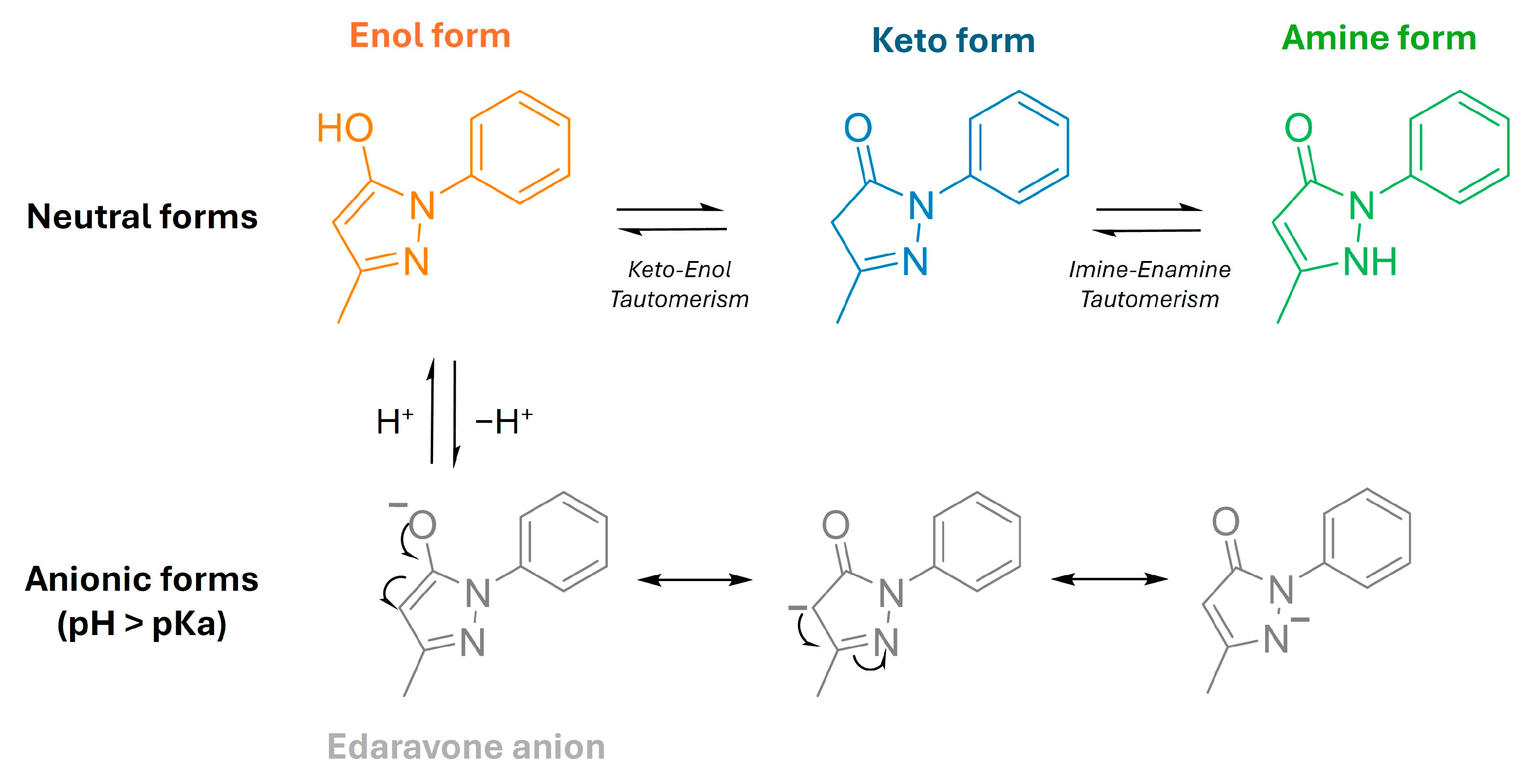
2.1. Determination of Physicochemical Properties of Edaravone
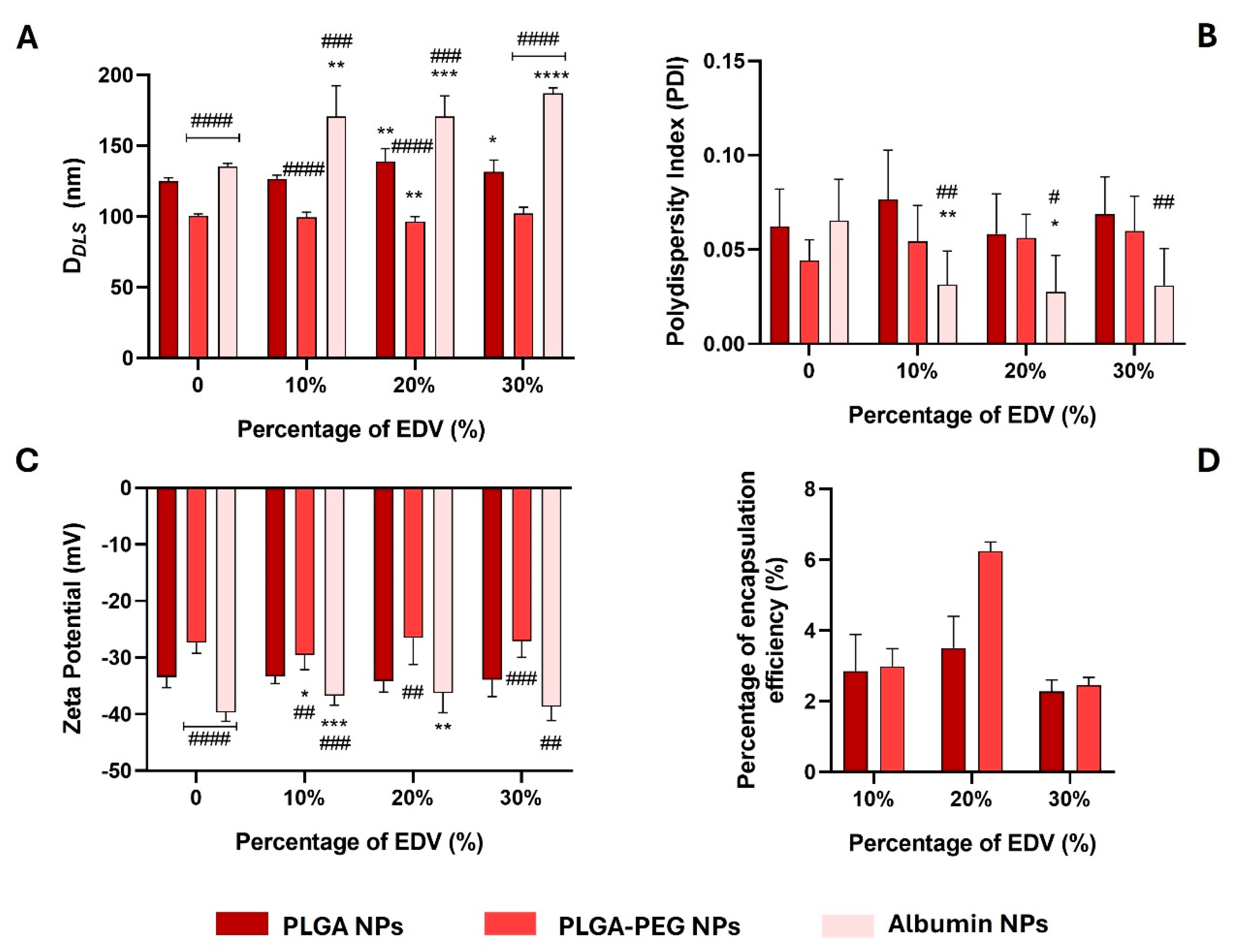
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Polymeric- and Albumin-Based Nanoparticles
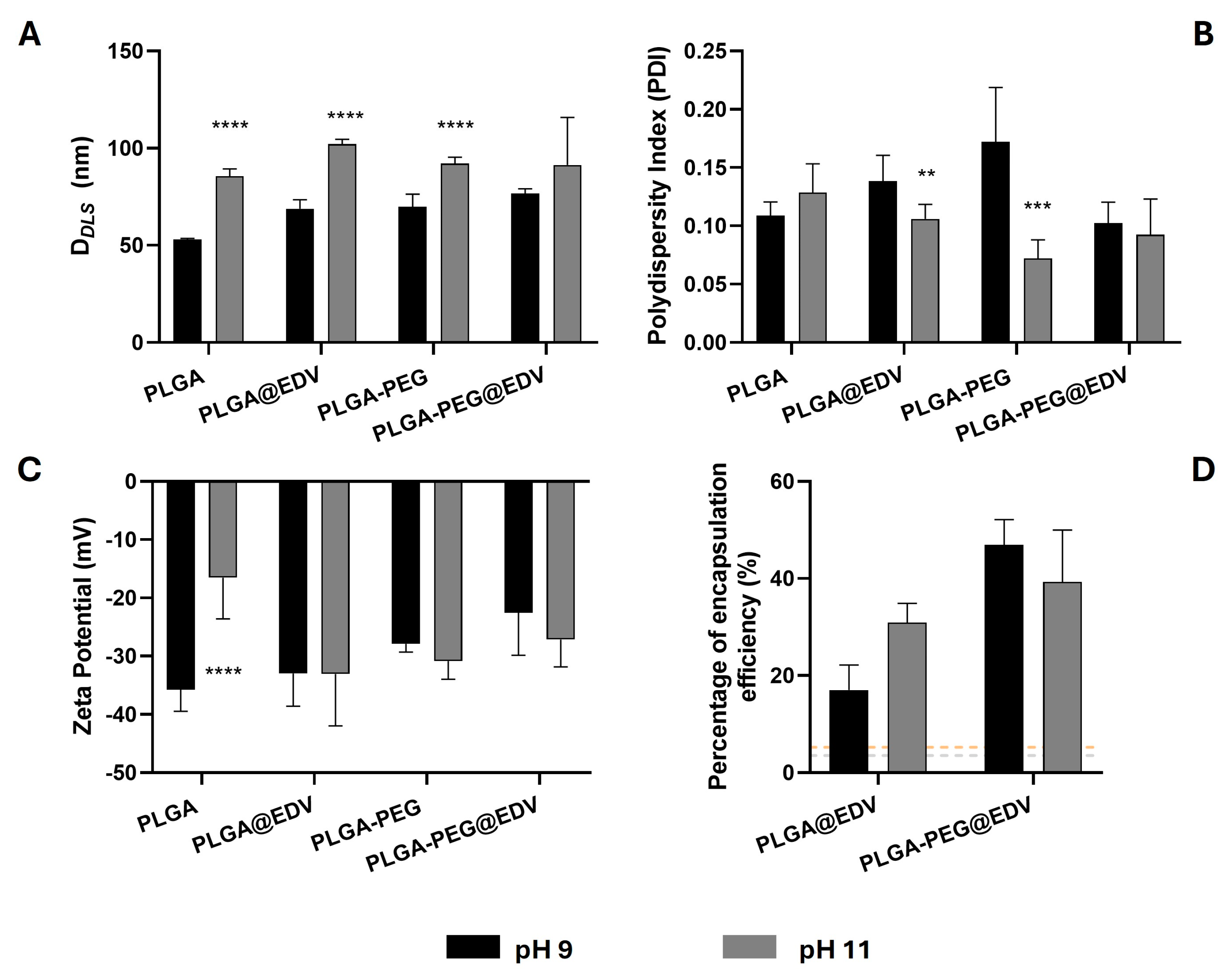
2.3. Effect of pH in the Synthesis of PLGA and PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles
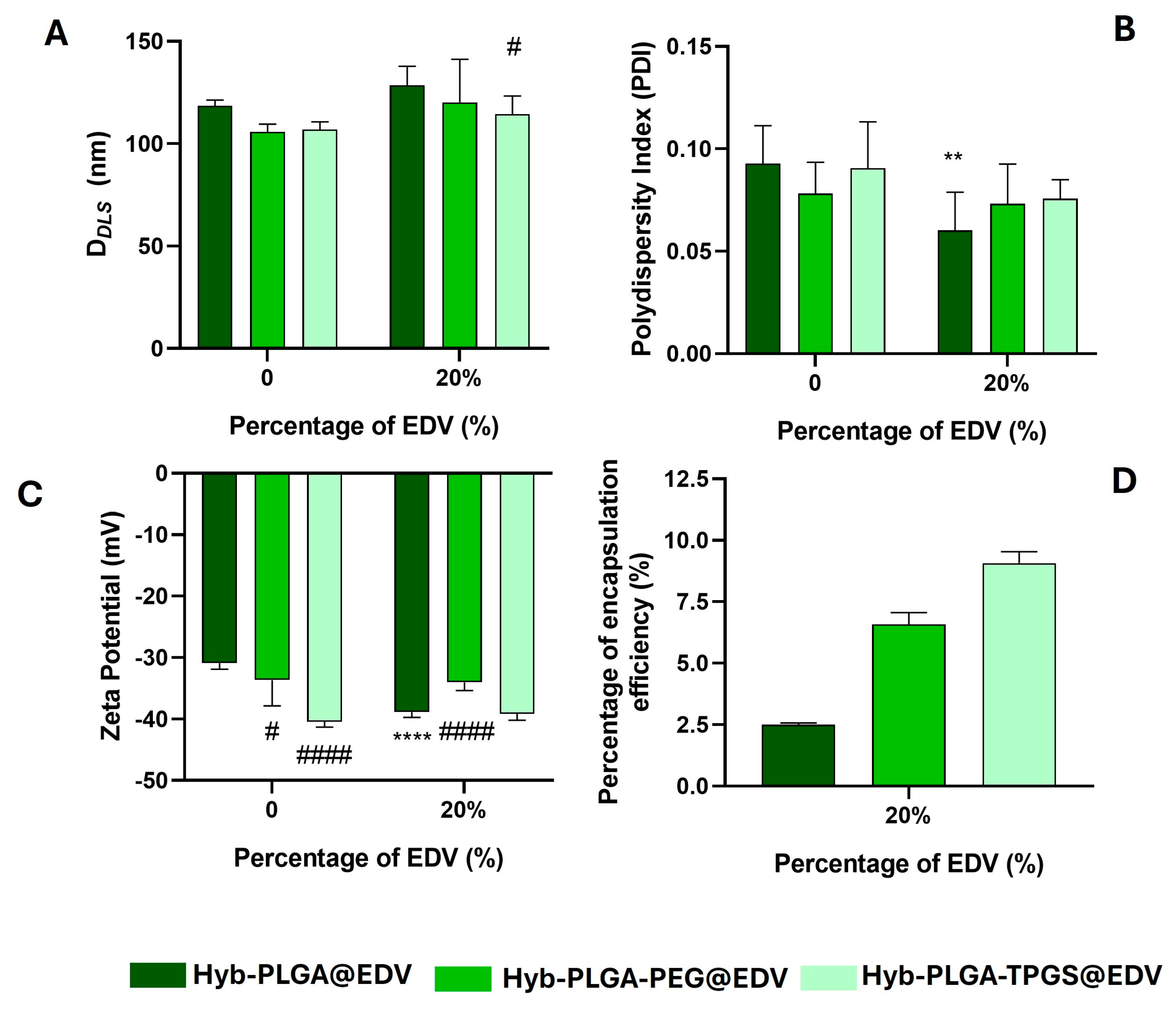
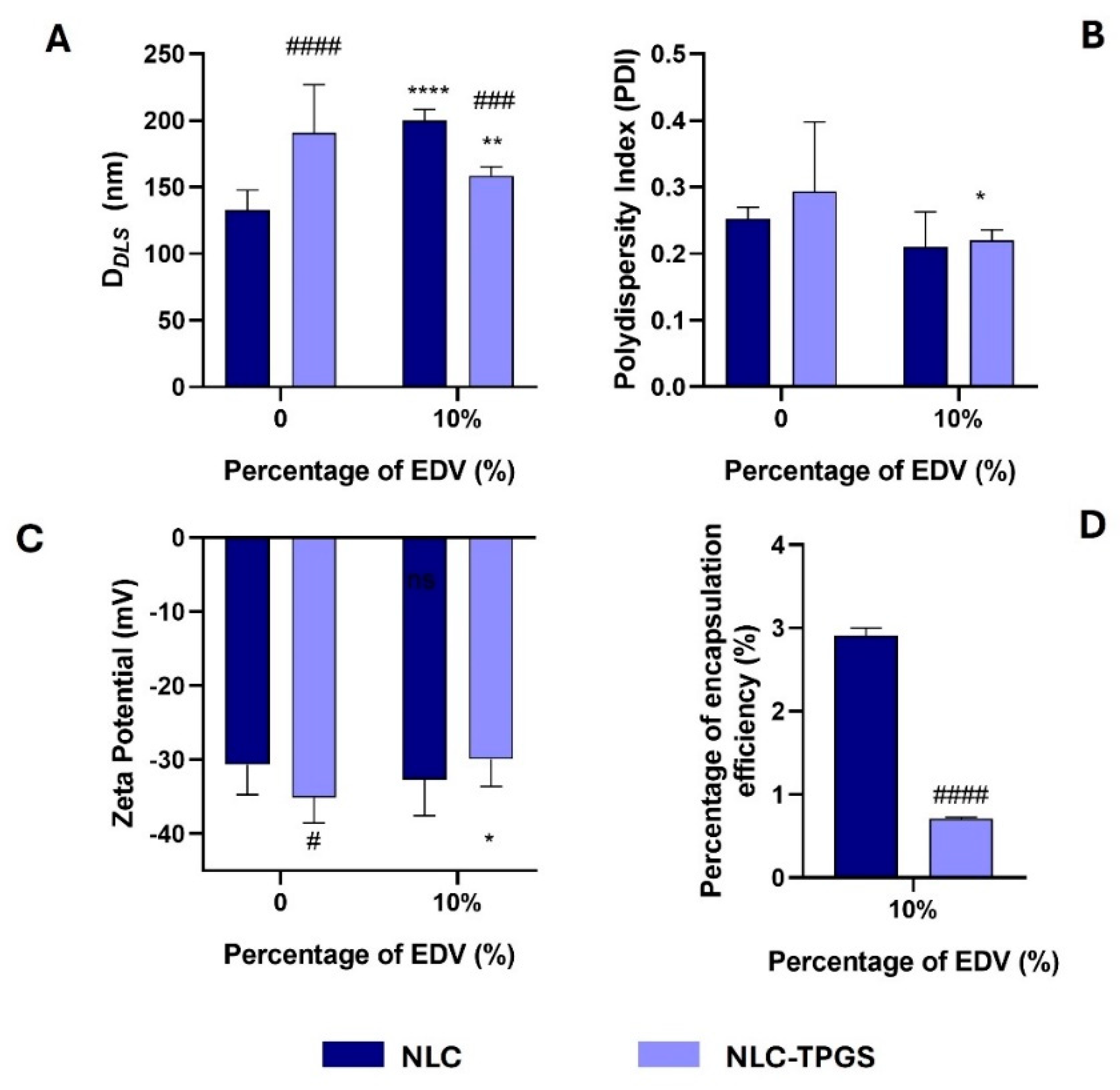
2.4. Synthesis and Characterization of Lipid–Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carrier
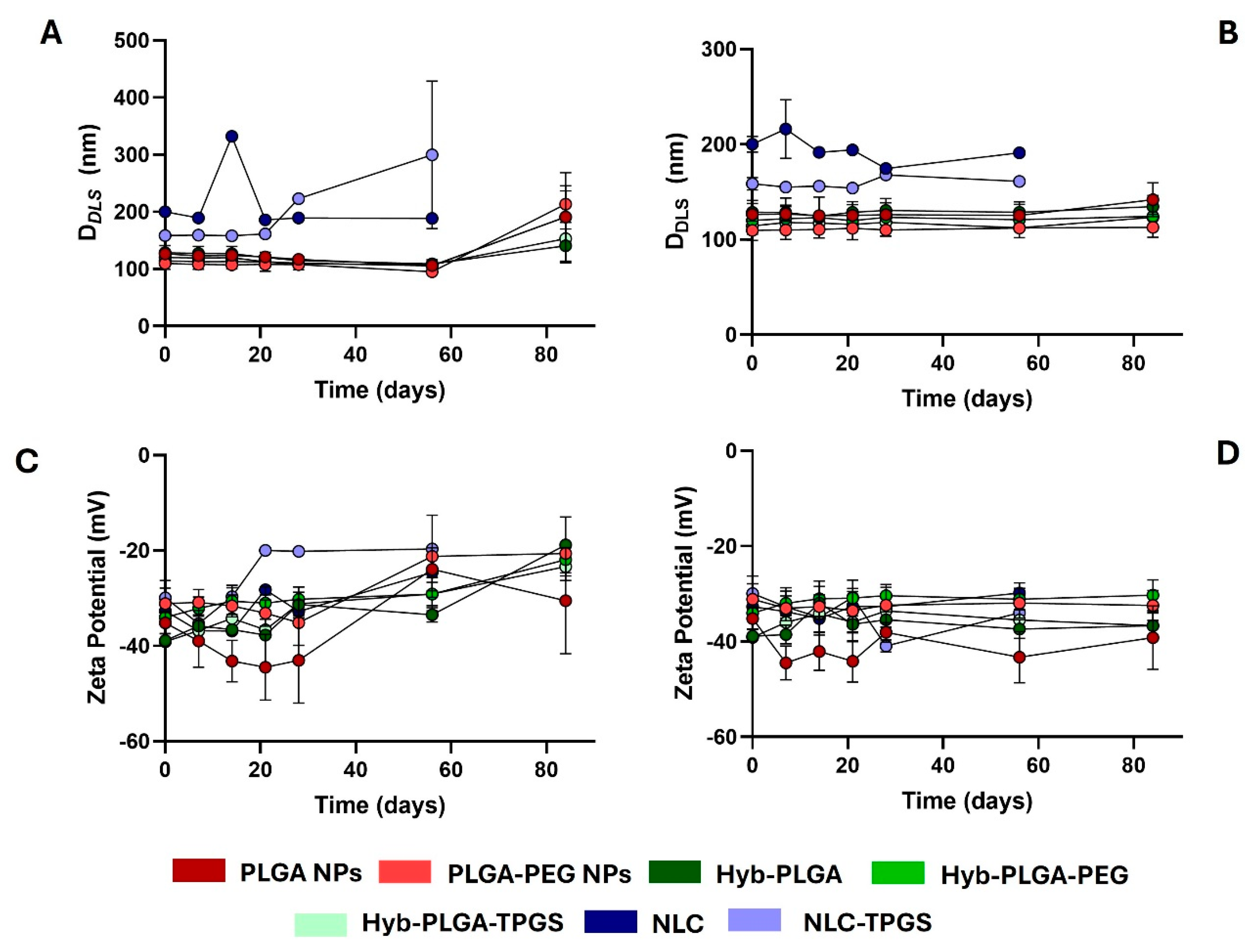
2.5. Stability Study of PNPs, LPHNPs, and NLC
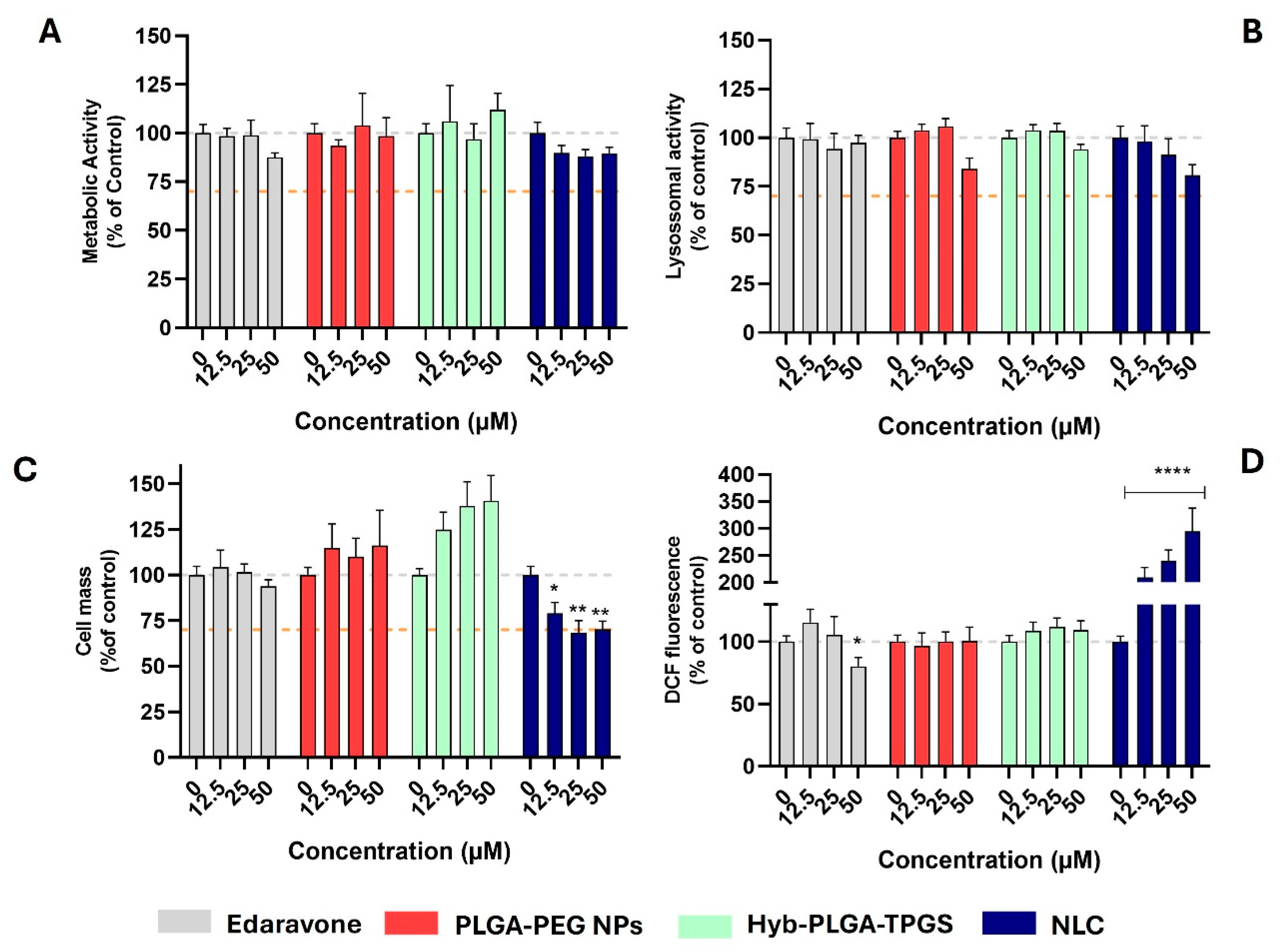
2.6. Evaluation of Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Profile of Nanoformulations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Studies Using a High-Performance Liquid Chromatography System
3.3. Evaluation of the Chromatographic Hydrophobicity Index
3.4. Evaluation of the Chromatographic Hydrophobicity Index on Immobilized Artificial Membrane
3.5. Quantification of EDV Encapsulated in Nanocarriers
3.6. Determination of EDV Solubility in Water and Liquid Lipids
3.7. Synthesis of EDV-Loaded Nanocarriers
3.7.1. Preparation of EDV-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles
3.7.2. Preparation of EDV-Loaded Albumin Nanoparticles
3.7.3. Preparation of EDV-Loaded Lipid–Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles
3.7.4. Preparation of the EDV-Loaded NLCs
3.8. Lyophilization Process and Storage of EDV-Loaded Nanoparticles
3.9. Determination of EDV-Loaded NPs Morphology and Surface Charge
3.10. Stability Study of EDV-Loaded Nanoformulations
3.11. Measurement of Encapsulation Efficiency (%) of EDV-Loaded Nanoformulations
3.12. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity of EDV and EDV-Loaded Nanoformulations
3.12.1. Cell Culture Conditions
3.12.2. Cell Viability Studies
3.13. Measurement of Intracellular Oxidative Stress of EDV-Loaded Nanoformulations
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- van den Berg, L.H. Therapy of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis remains a challenge. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1062–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Es, M.A.; Hardiman, O.; Chio, A.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Pasterkamp, R.J.; Veldink, J.H.; van den Berg, L.H. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 2084–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.A.; Fang, T.; De Marchi, F.; Neel, D.; Van Weehaeghe, D.; Berry, J.D.; Paganoni, S. Pharmacotherapy for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Review of Approved and Upcoming Agents. Drugs 2022, 82, 1367–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Wilkinson, J.; Christine Pietsch, E.; Buss, J.L.; Wang, W.; Planalp, R.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Iron chelation in the biological activity of curcumin. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 40, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandlik, V.; Patil, S.; Bopanna, R.; Basu, S.; Singh, S. Biological Activity of Coumarin Derivatives as Anti-Leishmanial Agents. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Cai, X.; Jiang, H.; Fan, Y.; Ying, K.; Du, B.; Yu, P.; Yang, W. Targeted Therapy of Ischemic Stroke via Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier Using Edaravone-Loaded Multiresponsive Microgels. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 4165–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Santos, B.; Chorilli, M.; Palmira Daflon Gremião, M. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4981–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, F.; Gregori, M.; Masserini, M. Nanotechnology for neurodegenerative disorders. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8 (Suppl. 1), S51–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; van Straten, D.; Broekman, M.L.D.; Préat, V.; Schiffelers, R.M. Nanocarrier-based drug combination therapy for glioblastoma. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1355–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.M.; Patel, B.M. Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier: Recent Advances in Drug Delivery to the Brain. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Skidmore, S.; Hadar, J.; Garner, J.; Park, H.; Otte, A.; Soh, B.K.; Yoon, G.; Yu, D.; Yun, Y.; et al. Injectable, long-acting PLGA formulations: Analyzing PLGA and understanding microparticle formation. J. Control. Release 2019, 304, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifyrad, M.; Gohari, S.; Fathi, M.; Danafar, H.; Hosseini, M.-J.; Mostafavi, H.; Manjili, H.K. The efficacy and neuroprotective effects of edaravone-loaded mPEG-b-PLGA polymeric nanoparticles on human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line as in vitro model of ischemia. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2022, 73, 103378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Novel antioxidants in food quality preservation and health promotion. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, L.; Panciani, P.P.; Muntoni, E.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasibetti, E.; De Bonis, P.; Mioletti, S.; Fontanella, M.; Swaminathan, S. Lipid nanoparticles for intranasal administration: Application to nose-to-brain delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chan, J.M.; Gu, F.X.; Rhee, J.W.; Wang, A.Z.; Radovic-Moreno, A.F.; Alexis, F.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Self-assembled lipid--polymer hybrid nanoparticles: A robust drug delivery platform. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadinoto, K.; Sundaresan, A.; Cheow, W.S. Lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Tanaka, M.; Yuki, S.; Hirai, M.; Yamamoto, Y. How is edaravone effective against acute ischemic stroke and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2018, 62, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegaev, K.; Cena, C.; Giorgis, M.; Rolando, B.; Tosco, P.; Bertinaria, M.; Fruttero, R.; Carrupt, P.A.; Gasco, A. Edaravone derivatives containing NO-donor functions. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Sugimura, N.; Fujisawa, A.; Yamamoto, Y. Stabilizers of edaravone aqueous solution and their action mechanisms. 1. Sodium bisulfite. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2017, 61, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Parikh, A.; Kathawala, K.; Tan, C.C.; Garg, S.; Zhou, X.-F. Lipid-based nanosystem of edaravone: Development, optimization, characterization and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, M.K. Riluzole and edaravone: A tale of two amyotrophic lateral sclerosis drugs. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, K.L. Application of biomimetic HPLC to estimate in vivo behavior of early drug discovery compounds. Future Drug Discov. 2019, 1, FDD11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.; Silva, T.B.; Sardão, V.A.; Simões, R.; Albuquerque, B.; Oliveira, P.J.; Valente, M.J.; Remião, F.; Soares-da-Silva, P.; Fernandes, C.; et al. Cellular and Mitochondrial Toxicity of Tolcapone, Entacapone, and New Nitrocatechol Derivatives. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2024, 7, 1637–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, K.L.; Kindy, M.; Evans, J.; Ko, D. In vitro biomimetic HPLC and in vivo characterisation of GM6, an endogenous regulator peptide drug candidate for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. ADMET DMPK 2018, 6, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfart, S.; Gelperina, S.; Kreuter, J. Transport of drugs across the blood-brain barrier by nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarieh, O.; Md, S.; Ali, M.; Baboota, S.; Sahni, J.K.; Kumari, B.; Bhatnagar, A.; Ali, J. Design, characterization, and evaluation of intranasal delivery of ropinirole-loaded mucoadhesive nanoparticles for brain targeting. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avadi, M.R.; Sadeghi, A.M.; Mohammadpour, N.; Abedin, S.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R.; Rafiee-Tehrani, M. Preparation and characterization of insulin nanoparticles using chitosan and Arabic gum with ionic gelation method. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honary, S.; Zahir, F. Effect of Zeta Potential on the Properties of Nano-Drug Delivery Systems—A Review (Part 2). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Portney, N.G.; Cui, D.; Budak, G.; Ozbay, E.; Ozkan, M.; Ozkan, C.S. Zeta potential: A surface electrical characteristic to probe the interaction of nanoparticles with normal and cancer human breast epithelial cells. Biomed. Microdevices 2008, 10, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.; Martins, C.; Fonseca, A.; Nunes, R.; Matos, M.J.; Silva, R.; Garrido, J.; Sarmento, B.; Remião, F.; Otero-Espinar, F.J.; et al. PEGylated PLGA Nanoparticles As a Smart Carrier to Increase the Cellular Uptake of a Coumarin-Based Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 39557–39569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, M.; Machado, C.S.; Barreiro, S.; Otero-Espinar, F.J.; Remião, F.; Borges, F.; Fernandes, C. Rescuing a Troubled Tolcapone with PEGylated PLGA Nanoparticles: Design, Characterization, and Hepatotoxicity Evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 21522–21533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.S.; Pinto, M.; Aguiar, B.; Costa, S.; Sarmento, B.; Otero Espinar, F.J.; Borges, F.; Fernandes, C. Exploring Nanocarriers for Boosting Entacapone Bioavailability: A Journey through System Characterization and Assessment of Toxicity and Pharmacological and 2D Permeability Paybacks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 58299–58312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tincu, C.-E.; Andrițoiu, C.V.; Popa, M.; Ochiuz, L. Recent Advancements and Strategies for Overcoming the Blood–Brain Barrier Using Albumin-Based Drug Delivery Systems to Treat Brain Cancer, with a Focus on Glioblastoma. Polymers 2023, 15, 3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, M.P.; Bobbala, S.; Karabin, N.B.; Frey, M.; Liu, Y.; Navidzadeh, J.O.; Stack, T.; Scott, E.A. Surface chemistry-mediated modulation of adsorbed albumin folding state specifies nanocarrier clearance by distinct macrophage subsets. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razuvaeva, E.; Sedush, N.; Shirokova, E.; Moskvichev, S.; Streltsov, D.; Chvalun, S. Effect of preparation conditions on the size of nanoparticles based on poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) synthesized with bismuth subsalicylate. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, J.T.-W.; Li, N.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Bansal, S.; Wang, Y.; Al-Jamal, K.T. Intranasal administration of edaravone nanoparticles improves its stability and brain bioavailability. J. Control. Release 2023, 359, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Huang, K.; Jiang, W.; Fu, L.A.-O.; Zhang, R.; Shen, L.; Ou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Exploration of the inhibition action of TPGS on tumor cells and its combined use with chemotherapy drugs. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2183830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, N.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Mozafari, M.; Asgari, S.; Motevalian, M.; Alhosseini, S.N. Surface modification of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles by d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate as potential carrier for the delivery of drugs to the brain. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 392, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, K.R.; Salve, R.; Narwade, M.; Sheikh, A.; Kesharwani, P.; Gajbhiye, V. Lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles: A custom-tailored next-generation approach for cancer therapeutics. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, R.; Venditti, I.; Fratoddi, I.; De Matteis, F.; Prosposito, P.; Cacciotti, I.; D’Amico, L.; Nanni, F.; Yadav, A.; Casalboni, M.; et al. From nanospheres to microribbons: Self-assembled Eosin Y doped PMMA nanoparticles as photonic crystals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 414, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, R.P.; Carvalho, E.D.; Martins, C.; des Rieux, A.; Pêgo, A.P.; Sarmento, B. Functionalized retinoic acid lipid nanocapsules promotes a two-front attack on inflammation and lack of demyelination on neurodegenerative disorders. J. Control. Release 2023, 358, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; Pinto, M.; Martins, C.; Gomes, M.J.; Sarmento, B.; Oliveira, P.J.; Remião, F.; Borges, F. Development of a PEGylated-Based Platform for Efficient Delivery of Dietary Antioxidants Across the Blood–Brain Barrier. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfeito, S.; Fernandes, C.; Chavarria, D.; Barreiro, S.; Cagide, F.; Sequeira, L.; Teixeira, J.; Silva, R.; Remião, F.; Oliveira, P.J.; et al. Modulating Cytotoxicity with Lego-like Chemistry: Upgrading Mitochondriotropic Antioxidants with Prototypical Cationic Carrier Bricks. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 1835–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés, A.; Rosés, M.; Ràfols, C.; Bosch, E.; Espinosa, S.; Segarra, V.; Huerta, J.M. Setup and validation of shake-flask procedures for the determination of partition coefficients (logD) from low drug amounts. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 76, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfeito, S.; Oliveira, C.; Fernandes, C.; Cagide, F.; Teixeira, J.; Amorim, R.; Garrido, J.; Martins, C.; Sarmento, B.; Silva, R.; et al. Fine-tuning the neuroprotective and blood-brain barrier permeability profile of multi-target agents designed to prevent progressive mitochondrial dysfunction. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 167, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguiar, B.; Alfenim, A.R.; Machado, C.S.; Moreira, J.; Pinto, M.; Otero-Espinar, F.J.; Borges, F.; Fernandes, C. Exploring Nano-Delivery Systems to Enhance the Edaravone Performance in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052146
Aguiar B, Alfenim AR, Machado CS, Moreira J, Pinto M, Otero-Espinar FJ, Borges F, Fernandes C. Exploring Nano-Delivery Systems to Enhance the Edaravone Performance in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052146
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguiar, Brandon, Ana Rita Alfenim, Cláudia Sofia Machado, Joana Moreira, Miguel Pinto, Francisco J. Otero-Espinar, Fernanda Borges, and Carlos Fernandes. 2025. "Exploring Nano-Delivery Systems to Enhance the Edaravone Performance in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treatment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052146
APA StyleAguiar, B., Alfenim, A. R., Machado, C. S., Moreira, J., Pinto, M., Otero-Espinar, F. J., Borges, F., & Fernandes, C. (2025). Exploring Nano-Delivery Systems to Enhance the Edaravone Performance in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052146








