The Role of CXCL4 in Systemic Sclerosis: DAMP, Auto-Antigen and Biomarker
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) Is an Autoimmune Disease
2.1. SSc Classification, Diagnosis and Manifestations
2.2. Immunological Actors in SSc
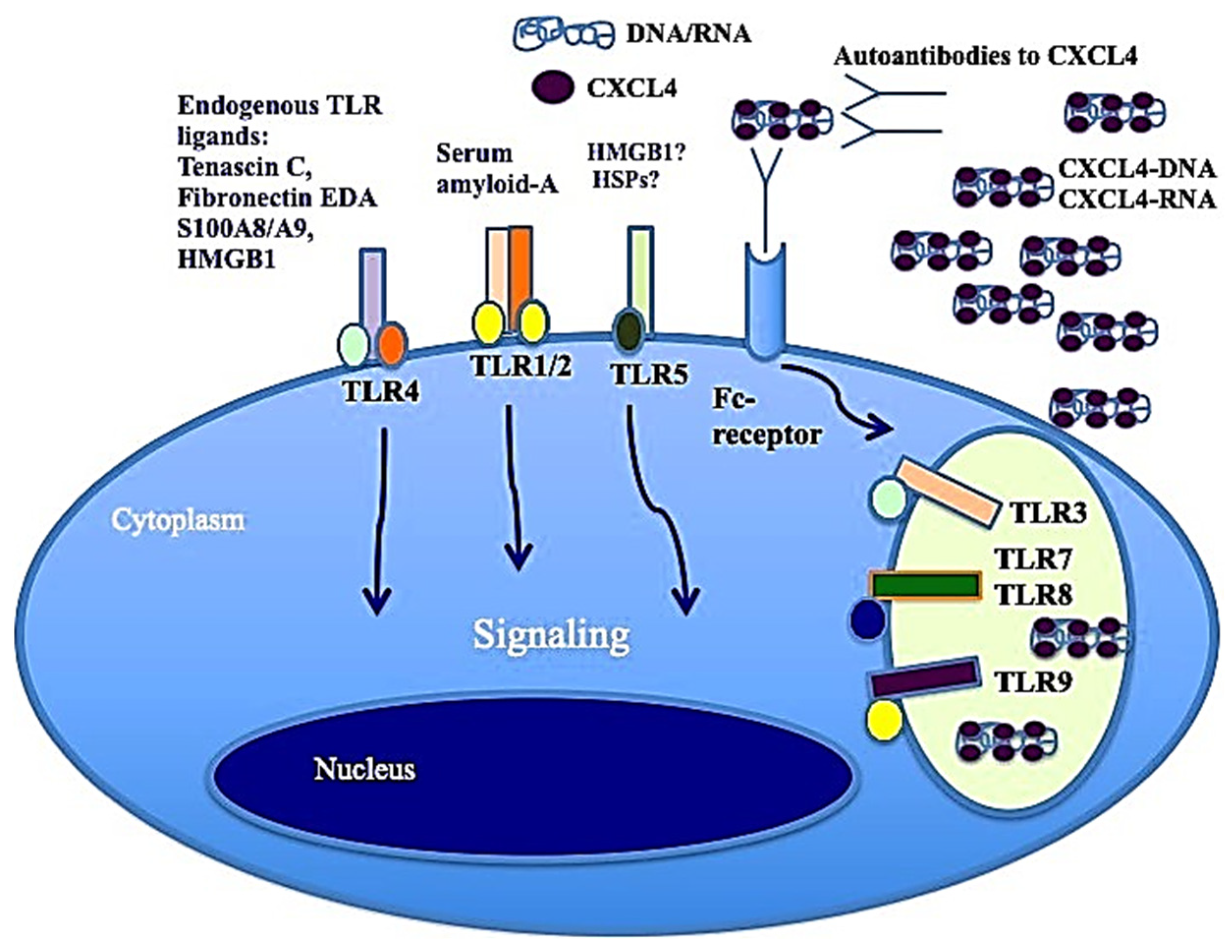
3. The Important Role of Toll-like Receptors in SSc: CXCL4 as a DAMP
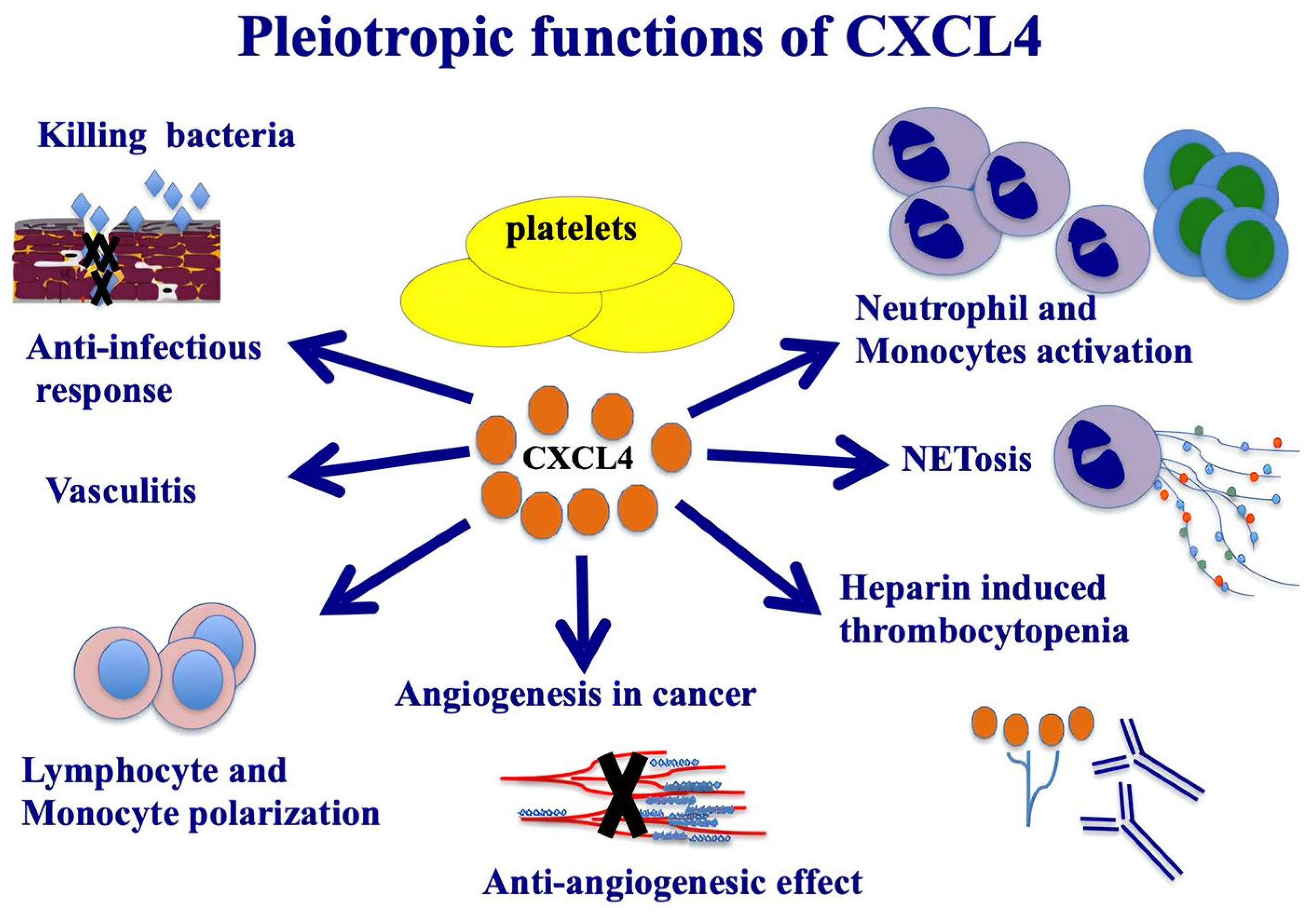
3.1. CXCL4: Structure and Function
3.2. Expression of CXCL4 in Cells and Its Receptors
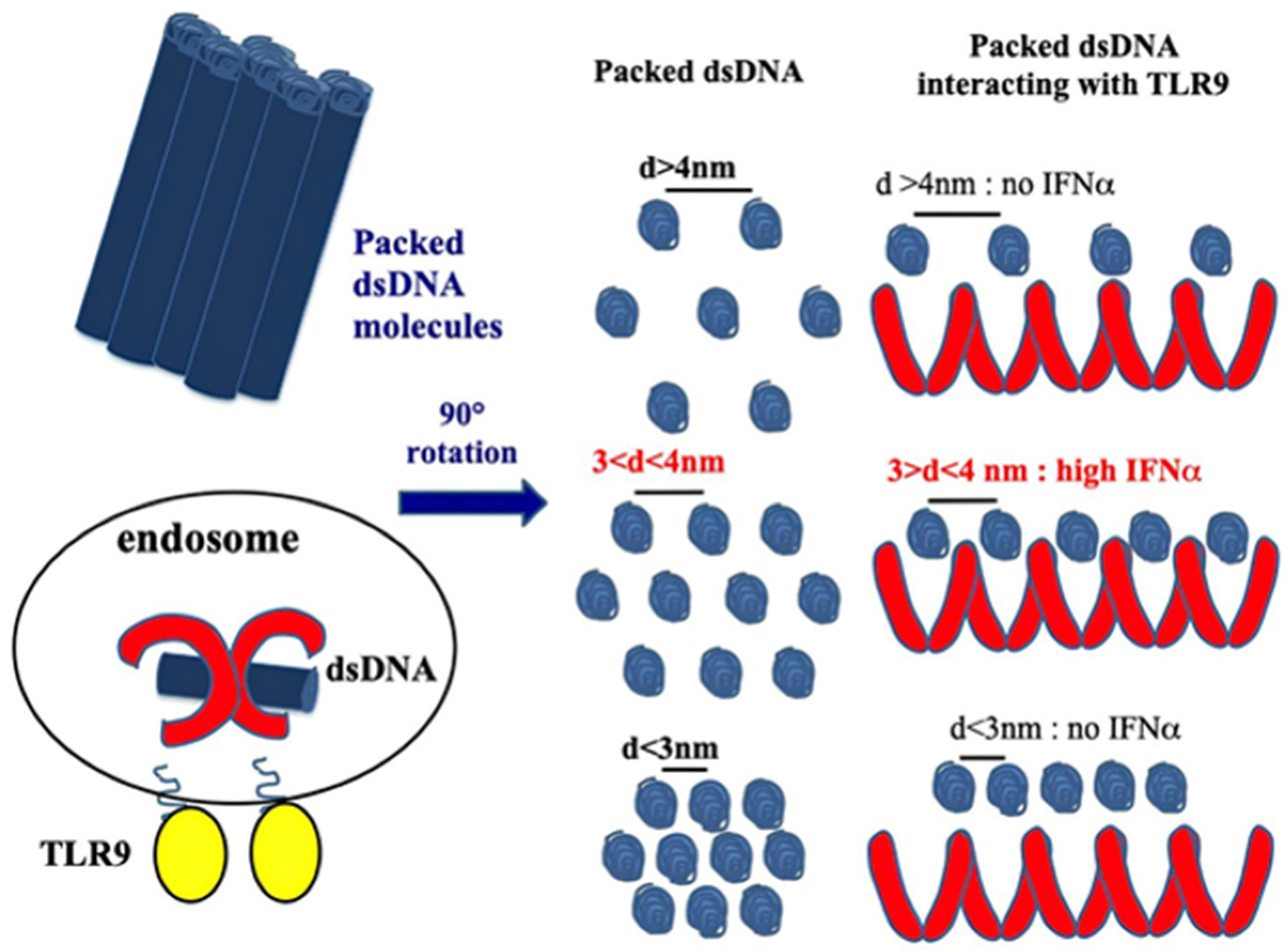
3.3. CXCL4 as a DAMP for IFN-I Amplification in pDCs
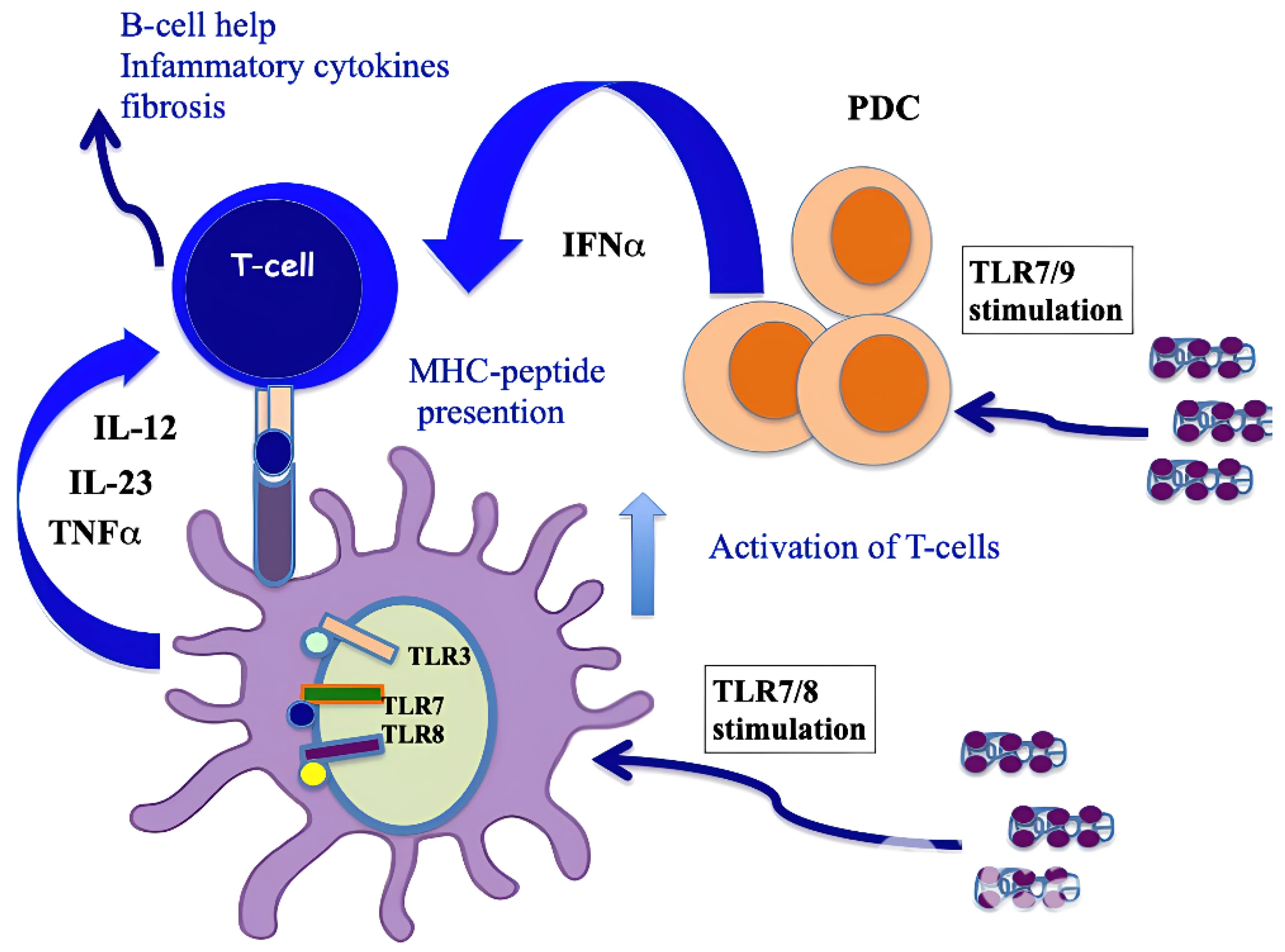
3.4. CXCL4 Role as a DAMP in Stimulating Pro-Inflammatory Factors by Myeloid Dendritic Cells
3.5. CXCL4 Role as a DAMP in B-Cells
4. CXCL4 as an Autoantigen
4.1. Autoimmunity in SSc
4.2. CXCL4 Is Recognized by Antibodies and T-Cells in SSc
4.3. CXCL4 Can Favor Loss of Immune Tolerance
5. CXCL4 as a Biomarker in SSc
5.1. Role of CXCL4 as a Biomarker in SSc
5.2. CXCL4 Compared to CXCL10 as Biomarker
6. CXCL4 as a Therapy Target
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaeger, V.K.; Tikly, M.; Xu, D.; Siegert, E.; Hachulla, E.; Airò, P.; Valentini, G.; Matucci Cerinic, M.; Distler, O.; Cozzi, F.; et al. Racial Differences in Systemic Sclerosis Disease Presentation: A European Scleroderma Trials and Research Group Study. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1684–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulli, A.; Ruaro, B.; Cutolo, M. Evaluation of Blood Perfusion by Laser Speckle Contrast Analysis in Different Areas of Hands and Face in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2014, 73, 2059–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Andréasson, K.; Smith, V. Systemic Sclerosis. Lancet 2023, 401, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasca, L.; Lande, R. Toll-like Receptors in Mediating Pathogenesis in Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. and Exp. Immunol. 2020, 201, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, C.; Simpson, N.; Duffy, L.; O’Reilly, S. Innate Immunity in Systemic Sclerosis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2017, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.E.; Denton, C.P.; Johnson, S.R.; Fernandez-Codina, A.; Hudson, M.; Nevskaya, T. State-of-the-Art Evidence in the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Pauling, J.D.; Armstrong-James, L.; Denton, C.P.; Galdas, P.; Flurey, C. Gender-Related Differences in Systemic Sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youness, A.; Miquel, C.-H.; Guéry, J.-C. Escape from X Chromosome Inactivation and the Female Predominance in Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntelis, K.; Bogdanos, D.; Dimitroulas, T.; Sakkas, L.; Daoussis, D. Platelets in Systemic Sclerosis: The Missing Link Connecting Vasculopathy, Autoimmunity, and Fibrosis? Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, V.; Assassi, S.; Allanore, Y.; Kuwana, M.; Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D.; Del Galdo, F. Type 1 Interferon Activation in Systemic Sclerosis: A Biomarker, a Target or the Culprit. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2022, 34, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.S.; Ferreira, B.H.; Almeida, C.R. Molecular Mechanisms Behind the Role of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in Systemic Sclerosis. Biology 2023, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrat, F.; Lu, T. Role of Type I Interferons and Innate Immunity in Systemic Sclerosis: Unbalanced Activities on Distinct Cell Types? Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brkic, Z.; Van Bon, L.; Cossu, M.; Van Helden-Meeuwsen, C.G.; Vonk, M.C.; Knaapen, H.; Van Den Berg, W.; Dalm, V.A.; Van Daele, P.L.; Severino, A.; et al. The Interferon Type I Signature Is Present in Systemic Sclerosis before Overt Fibrosis and Might Contribute to Its Pathogenesis through High BAFF Gene Expression and High Collagen Synthesis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ah Kioon, M.D.; Tripodo, C.; Fernandez, D.; Kirou, K.A.; Spiera, R.F.; Crow, M.K.; Gordon, J.K.; Barrat, F.J. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Promote Systemic Sclerosis with a Key Role for TLR8. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaam8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ah Kioon, M.D.; Cakan, E.; Garcia-Carmona, Y.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Meffre, E.; Barrat, F.J. CXCL4, a Chemokine Upregulated in Systemic Sclerosis Patients, Abrogates TLR9 Signaling and Central Tolerance in B Cells. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 247.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; Giuggioli, D.; Ferrannini, E.; Ferri, C.; Fallahi, P. Chemokine (C–X–C Motif) Ligand (CXCL)10 in Autoimmune Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adwi, Y.; Atzeni, I.M.; Doornbos-van Der Meer, B.; Van Der Leij, M.J.; Varkevisser, R.D.M.; Kroesen, B.-J.; Stel, A.; Timens, W.; Gan, C.T.; Van Goor, H.; et al. High Serum C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10 (CXCL10) Levels May Be Associated with New Onset Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Evidence from Observational, Clinical, Transcriptomic and in Vitro Studies. eBioMedicine 2023, 98, 104883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Greene, M.I.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H. Structural Features and PF4 Functions That Occur in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) Complicated by COVID-19. Antibodies 2020, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Warkentin, T.E. Platelet Factor 4 Triggers Thrombo-Inflammation by Bridging Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2023, 45, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, S.T.; Du, M.; Shaw, R.J.; Johnson, C.; McGuinness, D.; Schofield, J.; Yong, J.; Turtle, L.; Nicolson, P.L.R.; Moxon, C.; et al. Damage-Associated Cellular Markers in the Clinical and Pathogenic Profile of Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 22, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, A.T.P.; Skidmore, A.; Oberg, J.; Yarovoi, I.; Sarkar, A.; Levine, N.; Bochenek, V.; Zhao, G.; Rauova, L.; Kowalska, M.A.; et al. Platelet Factor 4 Limits Neutrophil Extracellular Trap–and Cell-Free DNA–Induced Thrombogenicity and Endothelial Injury. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e171054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.; Zhang, F.; Dordick, J.S.; Linhardt, R.J. Platelet Factor 4 Polyanion Immune Complexes: Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia and Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia. Thromb. J. 2021, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeaman, M.R. Platelets: At the Nexus of Antimicrobial Defence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bon, L.; Affandi, A.J.; Broen, J.; Christmann, R.B.; Marijnissen, R.J.; Stawski, L.; Farina, G.A.; Stifano, G.; Mathes, A.L.; Cossu, M.; et al. Proteome-Wide Analysis and CXCL4 as a Biomarker in Systemic Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.L.; Karlsson, R.; Roberts, A.R.E.; Ridley, A.J.L.; Pun, N.; Khan, B.; Lawless, C.; Luís, R.; Szpakowska, M.; Chevigné, A.; et al. Chemokine CXCL4 Interactions with Extracellular Matrix Proteoglycans Mediate Widespread Immune Cell Recruitment Independent of Chemokine Receptors. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 111930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandercappellen, J.; Van Damme, J.; Struyf, S. The Role of the CXC Chemokines Platelet Factor-4 (CXCL4/PF-4) and Its Variant (CXCL4L1/PF-4var) in Inflammation, Angiogenesis and Cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruytinx, P.; Proost, P.; Struyf, S. CXCL4 and CXCL4L1 in Cancer. Cytokine 2018, 109, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Uonnolo, G.; Reynders, N.; Meyrath, M.; Abboud, D.; Uchański, T.; Laeremans, T.; Volkman, B.F.; Janji, B.; Hanson, J.; Szpakowska, M.; et al. The Extended N-Terminal Domain Confers Atypical Chemokine Receptor Properties to CXCR3-B. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 868579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hundelshausen, P.; Schmitt, M.M.N. Platelets and Their Chemokines in Atherosclerosis—clinical Applications. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, D.J.; Lin, Y.; Miao, H.; Cimbro, R.; DiFiore, M.J.; Gianolini, M.E.; Furci, L.; Biswas, P.; Fauci, A.S.; Lusso, P. Identification of the Platelet-Derived Chemokine CXCL4/PF-4 as a Broad-Spectrum HIV-1 Inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9569–9574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Feng, K.; Wang, Y.C.; Mei, J.J.; Ning, R.T.; Zheng, H.W.; Wang, J.J.; Worthen, G.S.; Wang, X.; Song, J.; et al. Critical Role of CXCL4 in the Lung Pathogenesis of Influenza (H1N1) Respiratory Infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Yasuoka, H.; Yoshimoto, K.; Suzuki, K.; Takeuchi, T. Platelet CXCL4 Mediates Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Formation in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Cardoso, S.C.; Tao, W.; Angiolilli, C.; Lopes, A.P.; Bekker, C.P.J.; Devaprasad, A.; Giovannone, B.; Van Laar, J.; Cossu, M.; Marut, W.; et al. CXCL4 Links Inflammation and Fibrosis by Reprogramming Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells in Vitro. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, A.; Meiser, A.; McDonagh, E.M.; Fox, J.M.; Petit, S.J.; Xanthou, G.; Williams, T.J.; Pease, J.E. CXCL4-Induced Migration of Activated T Lymphocytes Is Mediated by the Chemokine Receptor CXCR3. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aidoudi, S.; Bujakowska, K.; Kieffer, N.; Bikfalvi, A. The CXC-Chemokine CXCL4 Interacts with Integrins Implicated in Angiogenesis. PLoS ONE. 2008, 3, e2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandset, P.M. Immunobiology of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. In The Chemokine System in Experimental and Clinical Hematology; Bruserud, O., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2010; pp. 193–202. ISBN 978-3-642-12639-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kasper, B.; Winoto-Morbach, S.; Mittelstädt, J.; Brandt, E.; Schütze, S.; Petersen, F. CXCL4-Induced Monocyte Survival, Cytokine Expression, and Oxygen Radical Formation Is Regulated by Sphingosine Kinase 1. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R.; Lee, E.Y.; Palazzo, R.; Marinari, B.; Pietraforte, I.; Santos, G.S.; Mattenberger, Y.; Spadaro, F.; Stefanantoni, K.; Iannace, N.; et al. CXCL4 Assembles DNA into Liquid Crystalline Complexes to Amplify TLR9-Mediated Interferon-α Production in Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, N.W.; Jin, F.; Lande, R.; Curk, T.; Xian, W.; Lee, C.; Frasca, L.; Frenkel, D.; Dobnikar, J.; Gilliet, M.; et al. Liquid-Crystalline Ordering of Antimicrobial Peptide–DNA Complexes Controls TLR9 Activation. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Lee, C.K.; Schmidt, N.W.; Jin, F.; Lande, R.; Curk, T.; Frenkel, D.; Dobnikar, J.; Gilliet, M.; Wong, G.C.L. A Review of Immune Amplification via Ligand Clustering by Self-Assembled Liquid–Crystalline DNA Complexes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 232, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R.; Mennella, A.; Palazzo, R.; Pietraforte, I.; Stefanantoni, K.; Iannace, N.; Butera, A.; Boirivant, M.; Pica, R.; Conrad, C.; et al. Anti-CXCL4 Antibody Reactivity Is Present in Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) and Correlates with the SSc Type I Interferon Signature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, N.; Capobianco, A.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Ramirez, G.A.; Tombetti, E.; Valle, P.D.; Monno, A.; D’Alberti, V.; Gasparri, A.M.; Franchini, S.; et al. Platelet Microparticles Sustain Autophagy-Associated Activation of Neutrophils in Systemic Sclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaao3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Domizio, J.; Belkhodja, C.; Chenuet, P.; Fries, A.; Murray, T.; Mondéjar, P.M.; Demaria, O.; Conrad, C.; Homey, B.; Werner, S.; et al. The Commensal Skin Microbiota Triggers Type I IFN–Dependent Innate Repair Responses in Injured Skin. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietraforte, I.; Butera, A.; Gaddini, L.; Mennella, A.; Palazzo, R.; Campanile, D.; Stefanantoni, K.; Riccieri, V.; Lande, R.; Frasca, L. CXCL4-RNA Complexes Circulate in Systemic Sclerosis and Amplify Inflammatory/Pro-Fibrotic Responses by Myeloid Dendritic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A. Efficient Presentation of Soluble Antigen by Cultured Human Dendritic Cells Is Maintained by Granulocyte/Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor plus Interleukin 4 and Downregulated by Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, G.J.; Beaulieu, S.; Lebecque, S.; Steinman, R.M.; Muller, W.A. Differentiation of Monocytes into Dendritic Cells in a Model of Transendothelial Trafficking. Science 1998, 282, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Hoidal, J.R.; Mukherjee, T.K. Role of TNFα in Pulmonary Pathophysiology. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, L.A.; Dunmore, B.J.; Long, L.; Crosby, A.; Al-Lamki, R.; Deighton, J.; Southwood, M.; Yang, X.; Nikolic, M.Z.; Herrera, B.; et al. TNFα Drives Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension by Suppressing the BMP Type-II Receptor and Altering NOTCH Signalling. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozanne, J.; Shek, B.; Stephen, L.A.; Novak, A.; Milne, E.; Mclachlan, G.; Midwood, K.S.; Farquharson, C. Tenascin-C Is a Driver of Inflammation in the DSS Model of Colitis. Matrix Biol. Plus 2022, 14, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeredjian-Ding, I.; Jego, G. Toll-like Receptors—Sentries in the B-Cell Response. Immunology 2009, 128, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruprecht, C.R.; Lanzavecchia, A. Toll-like Receptor Stimulation as a Third Signal Required for Activation of Human Naive B Cells. Immunol. 2006, 36, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.E.; Knight, A.K.; Radigan, L.; Marron, T.U.; Zhang, L.; Sanchez-Ramón, S.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Toll-like Receptor 7 and 9 Defects in Common Variable Immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 349–356.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Qiao, X.; Cerutti, A. CpG DNA Induces IgG Class Switch DNA Recombination by Activating Human B Cells through an Innate Pathway That Requires TLR9 and Cooperates with IL-101. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4479–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, C.E.; Zhou, Y.; Chupp, D.P.; Yan, H.; Fisher, A.D.; Simon, R.; Zan, H.; Xu, Z.; Casali, P. Intrinsic B Cell TLR-BCR Linked Coengagement Induces Class-Switched, Hypermutated, Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Absence of T Cells. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Hou, B. TLR Signaling in B-Cell Development and Activation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeredjian-Ding, I.B.; Wagner, M.; Hornung, V.; Giese, T.; Schnurr, M.; Endres, S.; Hartmann, G. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Control TLR7 Sensitivity of Naive B Cells via Type I IFN1. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4043–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R.; Palazzo, R.; Mennella, A.; Pietraforte, I.; Cadar, M.; Stefanantoni, K.; Conrad, C.; Riccieri, V.; Frasca, L. New Autoantibody Specificities in Systemic Sclerosis and Very Early Systemic Sclerosis. Antibodies 2021, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, F.B.; Saulep-Easton, D.; Figgett, W.A.; Fairfax, K.A.; Mackay, F. The BAFF/APRIL System: Emerging Functions beyond B Cell Biology and Autoimmunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehniger, T.A.; Caligiuri, M.A. Interleukin 15: Biology and Relevance to Human Disease. Blood 2001, 97, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchetet, M.E.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Current Concepts on the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 64, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Peck, A.; Santer, D.; Patole, P.; Schwartz, S.M.; Molitor, J.A.; Arnett, F.C.; Elkon, K.B. Induction of Interferon-α by Scleroderma Sera Containing Autoantibodies to Topoisomerase I: Association of Higher Interferon-α Activity with Lung Fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, C.; Fritzler, M.J. Autoantibodies in Systemic Sclerosis: Unanswered Questions. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdaca, G.; Colombo, B.M.; Puppo, F. The Role of Th17 Lymphocytes in the Autoimmune and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2011, 6, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affandi, A.J.; Silva-Cardoso, S.C.; Garcia, S.; Leijten, E.F.A.; van Kempen, T.S.; Marut, W.; van Roon, J.A.G.; Radstake, T.R.D.J. CXCL4 Is a Novel Inducer of Human Th17 Cells and Correlates with IL-17 and IL-22 in Psoriatic Arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, P.; Maggi, L.; Mazzinghi, B.; Cosmi, L.; Lasagni, L.; Liotta, F.; Lazzeri, E.; Angeli, R.; Rotondi, M.; Filì, L.; et al. CXCR3-Mediated Opposite Effects of CXCL10 and CXCL4 on TH1 or TH2 Cytokine Production. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arepally, G.M.; Cines, D.B. Pathogenesis of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Transl. Res. 2020, 225, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, R.; Stefanantoni, K.; Cadar, M.; Butera, A.; Riccieri, V.; Lande, R.; Frasca, L. Heparin-Independent and Heparin-Dependent Anti-CXCL4 Antibodies Have a Reciprocal Expression in a Systemic Sclerosis Patients’ Cohort. Antibodies 2022, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Visentin, G.P.; Dayananda, K.M.; Neelamegham, S. Immune Complexes Formed Following the Binding of Anti–Platelet Factor 4 (CXCL4) Antibodies to CXCL4 Stimulate Human Neutrophil Activation and Cell Adhesion. Blood 2008, 112, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, J.; Leung, H.H.L.; Ahmadi, Z.; Yan, F.; Chong, J.J.H.; Passam, F.H.; Chong, B.H. Neutrophil Activation and NETosis Are the Major Drivers of Thrombosis in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachais, B.S.; Rux, A.H.; Cines, D.B.; Yarovoi, S.V.; Garner, L.I.; Watson, S.P.; Hinds, J.L.; Rux, J.J. Rational Design and Characterization of Platelet Factor 4 Antagonists for the Study of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2012, 120, 5955–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakan, E.; Ah Kioon, M.D.; Garcia-Carmona, Y.; Glauzy, S.; Oliver, D.; Yamakawa, N.; Vega Loza, A.; Du, Y.; Schickel, J.-N.; Boeckers, J.M.; et al. TLR9 Ligand Sequestration by Chemokine CXCL4 Negatively Affects Central B Cell Tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20230944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandam, M.; Ariza-Hutchinson, A.; Patel, R.A.; Sibbitt, W.L., Jr. Biomarkers in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 4633–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Tashkin, D.P.; Roth, M.D.; Clements, P.J.; Khanna, D.; Furst, D.E.; Mayes, M.; Charles, J.; Tseng, C.-H.; Elashoff, R.M.; et al. Changes in Plasma CXCL4 Levels Are Associated with Improvements in Lung Function in Patients Receiving Immunosuppressive Therapy for Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazirinejad, R.; Ahmadi, Z.; Kazemi Arababadi, M.; Hassanshahi, G.; Kennedy, D. The Biological Functions, Structure and Sources of CXCL10 and Its Outstanding Part in the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, A. The Th1 Chemokine IP-10 in Systemic Sclerosis. La Clin. Ter. 2014, 165, e436–e441. [Google Scholar]
- Crescioli, C.; Corinaldesi, C.; Riccieri, V.; Raparelli, V.; Vasile, M.; Del Galdo, F.; Valesini, G.; Lenzi, A.; Basili, S.; Antinozzi, C. Association of Circulating CXCL10 and CXCL11 with Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1845–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-J.; Pullamsetti, S.S.; Dony, E.; Weissmann, N.; Butrous, G.; Banat, G.-A.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Seeger, W.; Grimminger, F.; Schermuly, R.T. Role of the Prostanoid EP4 Receptor in Iloprost-Mediated Vasodilatation in Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colasanti, T.; Stefanantoni, K.; Fantini, C.; Corinaldesi, C.; Vasile, M.; Marampon, F.; Di Luigi, L.; Antinozzi, C.; Sgrò, P.; Lenzi, A.; et al. The Prostacyclin Analogue Iloprost Modulates CXCL10 in Systemic Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennella, A.; Stefanantoni, K.; Palazzo, R.; Ocone, G.; Pietraforte, I.; Truglia, S.; Bisconti, I.; Pisacreta, A.; Riccieri, V.; Lande, R.; et al. Plasma CXCL4–DNA/RNA Complexes and Anti-CXCL4 Antibodies Modulation in an SSc Cohort under Iloprost Treatment. Reports 2024, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortam, N.; Liang, W.; Shiple, C.; Huang, S.; Gedert, R.; Clair, J.S.; Sarosh, C.; Foster, C.; Tsou, P.-S.; Varga, J.; et al. Elevated Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Vasculopathy and Suppression by a Synthetic Prostacyclin Analog. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottria, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Paardekooper, L.M.; Carvalheiro, T.; Vazirpanah, N.; Silva-Cardoso, S.; Affandi, A.J.; Chouri, E.; V.D Kroef, M.; Tieland, R.G.; et al. Hypoxia and TLR9 Activation Drive CXCL4 Production in Systemic Sclerosis Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells via mtROS and HIF-2α. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2682–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, C.; Schett, G.; Gay, S.; Distler, O.; Distler, J.H. Hypoxia. Hypoxia in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Landewé, R.; Avouac, J.; Chwiesko, S.; Miniati, I.; Czirjak, L.; Clements, P.; Denton, C.; Farge, D.; Fligelstone, K.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis: A Report from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research Group (EUSTAR). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porreca, S.; Mennella, A.; Frasca, L. The Role of CXCL4 in Systemic Sclerosis: DAMP, Auto-Antigen and Biomarker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062421
Porreca S, Mennella A, Frasca L. The Role of CXCL4 in Systemic Sclerosis: DAMP, Auto-Antigen and Biomarker. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062421
Chicago/Turabian StylePorreca, Silvia, Anna Mennella, and Loredana Frasca. 2025. "The Role of CXCL4 in Systemic Sclerosis: DAMP, Auto-Antigen and Biomarker" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062421
APA StylePorreca, S., Mennella, A., & Frasca, L. (2025). The Role of CXCL4 in Systemic Sclerosis: DAMP, Auto-Antigen and Biomarker. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062421






