The Role of IL-17A in Mediating Inflammatory Responses and Progression of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
1. Research Progress on Inflammation-Induced Neurodegenerative Diseases
1.1. Types of Neurodegenerative Diseases
1.2. Impact of Inflammation on the Neural Microenvironment
1.3. Studies on the Correlation Between Inflammation and Neurodegenerative Diseases
2. IL-17A and Neuro-Inflammation
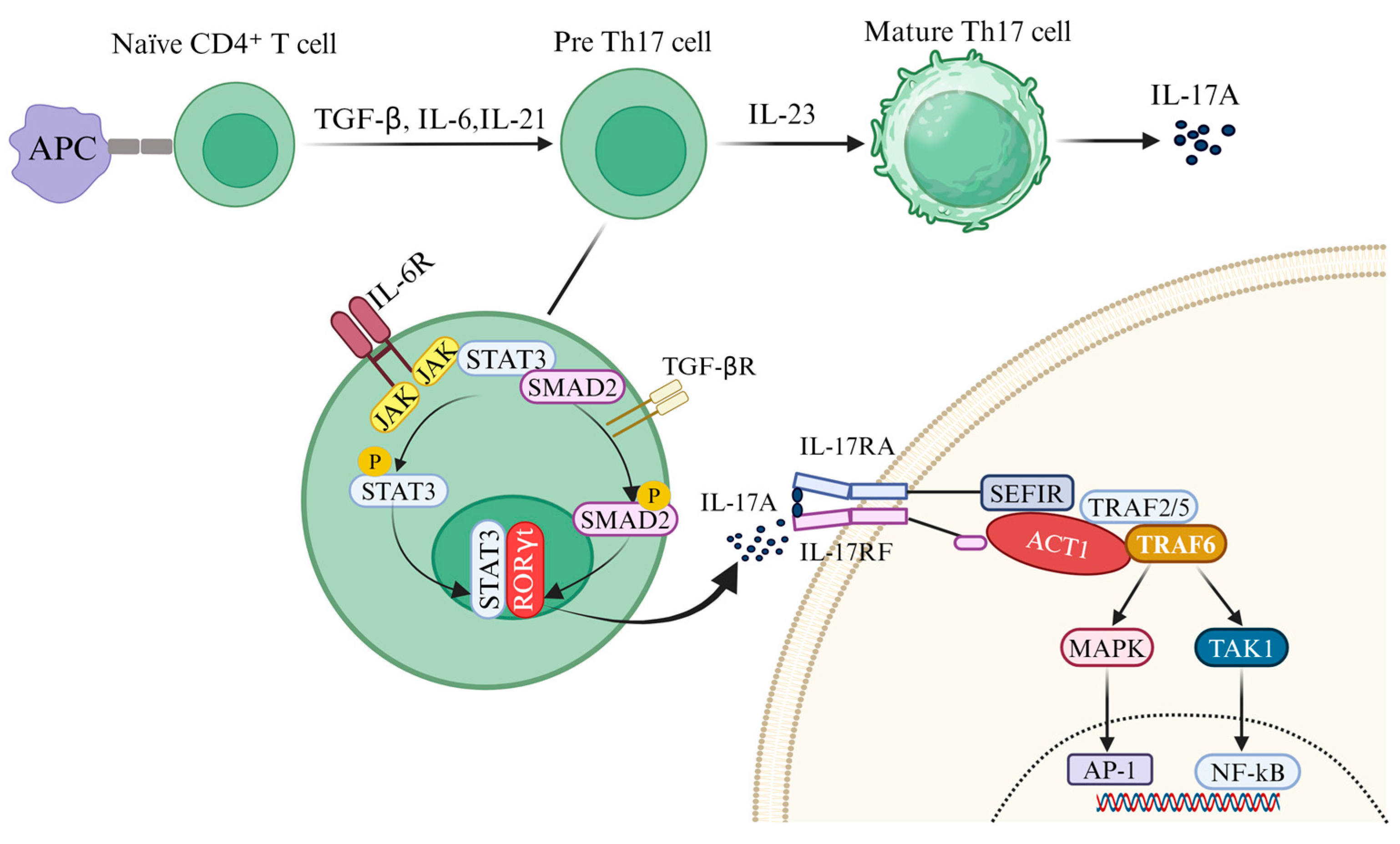
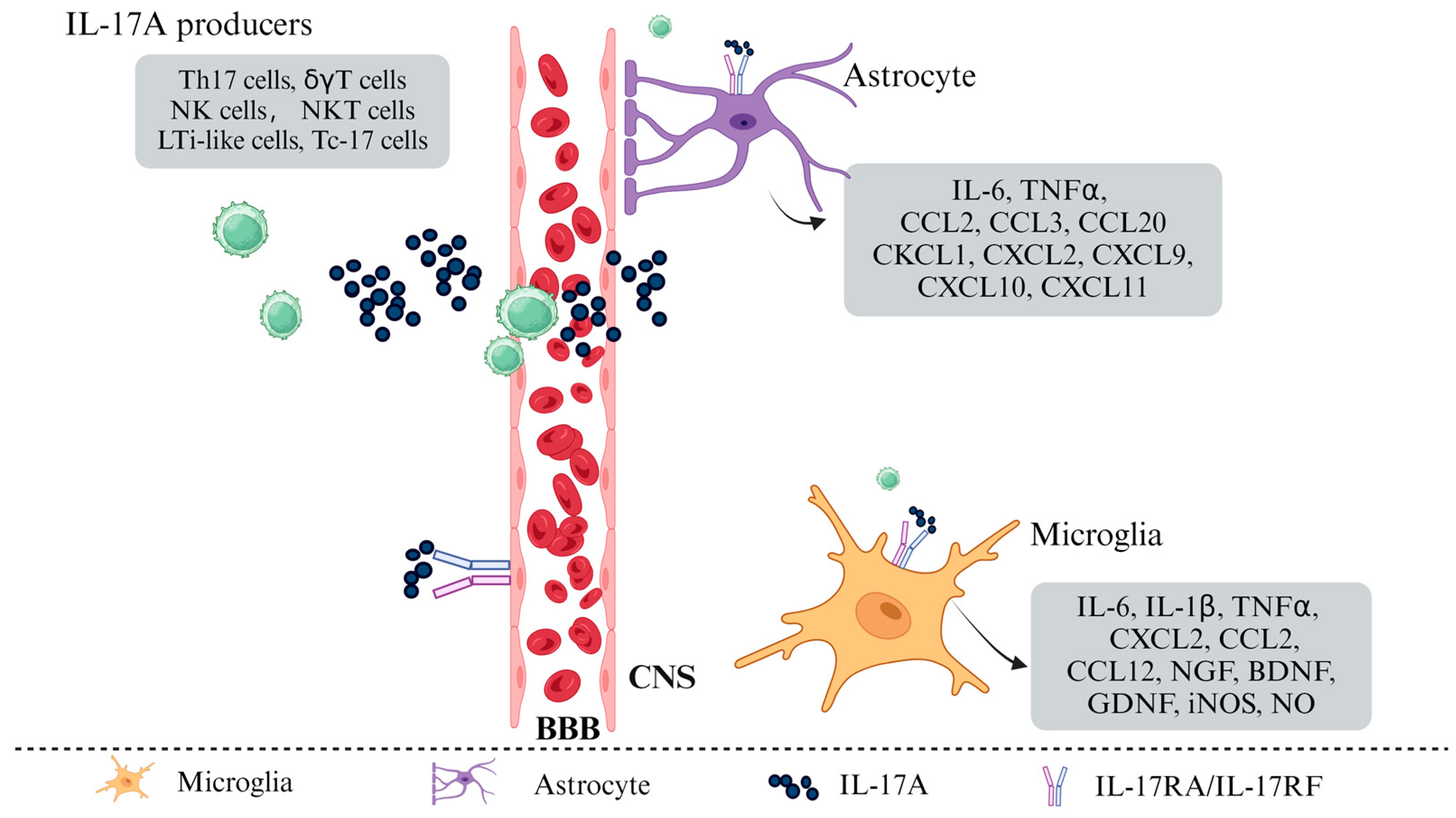
2.1. Induced Release of IL-17A
2.2. IL-17A Induced Polarization of Glial Cells
2.3. IL-17A Mediated BBB Disruption
3. IL-17A and Neuro-Inflammation Diseases
3.1. IL-17A and MS
3.2. IL-17A and AD
3.3. IL-17A and PD
3.4. IL-17A and ALS
4. IL-17A as a Therapeutic Target
| Monoclonal Antibody | Name of Product | On the Target | Clinical Indication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secukinumab | Cosentyx | IL-17A | Plaque psoriasis; ankylosing spondylitis; psoriatic arthritis | [157,158,159] |
| Ixekizumab | Taltz | IL-17A | Plaque psoriasis; psoriatic arthritis; ankylosing spondylitis; Non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis | [160,161,162] |
| Brodalumab | Siliq | IL-17RA | Moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis | [163,164,165] |
| Netakimab | Efleira | IL-17A | Psoriasis | [142,143] |
| Bimekizumab | Phase Ⅲ clinical trial | IL-17A/IL17F | Psoriasis; psoriatic arthritis; ankylosing spondylitis | [145,146,166,167,168] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hammond, T.R.; Marsh, S.E.; Stevens, B. Immune Signaling in Neurodegeneration. Immunity 2019, 50, 955–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, D.; Mao, Q.; Xia, H. Role of Neuroinflammation in Neurodegeneration Development. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Lungu, I.I.; Radu, C.I.; Vladâcenco, O.; Roza, E.; Costăchescu, B.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, R.I. An Overview of Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.V.; McGavern, D.B. Inflammatory Neuroprotection Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Science 2016, 353, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Natteru, P.; Selvakumar, G.; Saeed, D.; Zahoor, H.; Zaheer, S.; Iyer, S.; Zaheer, A. Neuroinflammation Induces Neurodegeneration. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 1, 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms Underlying Inflammation in Neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, J.; Nutma, E.; Van Der Valk, P.; Amor, S. Inflammation in CNS Neurodegenerative Diseases. Immunology 2018, 154, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Yamin, M.; Islam, M.M.; Sarker, M.T.; Meem, A.F.K.; Akter, A.; Emran, T.B.; Cavalu, S.; Sharma, R. Emerging Role of Neuron-Glia in Neurological Disorders: At a Glance. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 3201644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte–Endothelial Interactions at the Blood–Brain Barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocyte Barriers to Neurotoxic Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; You, H.; Hu, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; An, J.; Lu, H. Microglia–Astrocyte Interaction in Neural Development and Neural Pathogenesis. Cells 2023, 12, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elain, G.; Jeanneau, K.; Rutkowska, A.; Mir, A.K.; Dev, K.K. The Selective Anti-IL17A Monoclonal Antibody Secukinumab (AIN457) Attenuates IL17A-Induced Levels of IL6 in Human Astrocytes. Glia 2014, 62, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Altuntas, C.Z.; Gulen, M.F.; Liu, C.; Giltiay, N.; Qin, H.; Liu, L.; Qian, W.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Bergmann, C.; et al. Astrocyte-Restricted Ablation of Interleukin-17-Induced Act1-Mediated Signaling Ameliorates Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Immunity 2010, 32, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, M.A.; Clark, I.C.; Tjon, E.C.; Li, Z.; Zandee, S.E.J.; Couturier, C.P.; Watson, B.R.; Scalisi, G.; Alkwai, S.; Rothhammer, V.; et al. MAFG-Driven Astrocytes Promote CNS Inflammation. Nature 2020, 578, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lin, L.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Buch, S.; Wang, L.; Chao, J.; Yao, H. IL-17A Induces MIP-1α Expression in Primary Astrocytes via Src/MAPK/PI3K/NF-kB Pathways: Implications for Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, Z.B.; Yudin, S.C.Y.; Goldberg, B.J.; Serra, K.L.; Klegeris, A. Exploring Neuroglial Signaling: Diversity of Molecules Implicated in Microglia-to-Astrocyte Neuroimmune Communication. Rev. Neurosci. 2025, 36, 91–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojkowska, D.W.; Szpakowski, P.; Glabinski, A. Interleukin 17A Promotes Lymphocytes Adhesion and Induces CCL2 and CXCL1 Release from Brain Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Li, J.; Hu, B.; Yang, W.; Zhan, M.; Ma, T.; Xu, S. IL-17 Crosses the Blood–Brain Barrier to Trigger Neuroinflammation: A Novel Mechanism in Nitroglycerin-Induced Chronic Migraine. J. Headache Pain 2022, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, L.; Ding, J.; Wang, X. IL-17A Aggravated Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption via Activating Src Signaling in Epilepsy Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 11012–11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y. Interleukin-17A: The Key Cytokine in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 566922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbinger, F.; Huppertz, C.; Mir, A.; Padova, F.D. IL-17A and Multiple Sclerosis: Signaling Pathways, Producing Cells and Target Cells in the Central Nervous System. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, H.; Pacheco, R. T-Cell-Mediated Regulation of Neuroinflammation Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Wu, L.; Li, X. IL-17 Family: Cytokines, Receptors and Signaling. Cytokine 2013, 64, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Qiu, A.-W.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.-N.; Gu, T.-T.; Cao, B.-B.; Qiu, Y.-H.; Peng, Y.-P. IL-17A Exacerbates Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration by Activating Microglia in Rodent Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 81, 630–645. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchroo, V.K.; Korn, T. Th17 Cells in Autoimmune Inflammation and Demyelination in the Central Nervous System. In Multiple Sclerosis Immunology: A Foundation for Current and Future Treatments; Yamamura, T., Gran, B., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–25. ISBN 978-1-4614-7953-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Huang, Y.; Bao, T.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, X. The Role of Th17 Cells/IL-17A in AD, PD, ALS and the Strategic Therapy Targeting on IL-17A. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cova, I.; Markova, A.; Campini, I.; Grande, G.; Mariani, C.; Pomati, S. Worldwide Trends in the Prevalence of Dementia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 379, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Basic Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration: A Critical Update. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 457–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyss-Coray, T.; Mucke, L. Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Disease—A Double-Edged Sword. Neuron 2002, 35, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, M.W.; McGavern, D.B. Immune Dynamics in the CNS and Its Barriers during Homeostasis and Disease. Immunol. Rev. 2022, 306, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Sharma, V.; Deshmukh, R. Activation of Microglia and Astrocytes: A Roadway to Neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s Disease. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, J. Neuroinflammation in the Central Nervous System: Symphony of Glial Cells. Glia 2019, 67, 1017–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ruan, G.; Cheng, Y.; Yi, A.; Chen, D.; Wei, Y. The Role of Th17 Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Research Progress. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1055914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, M.P.; Sinha, S.; Renavikar, P.S.; Borcherding, N.; Karandikar, N.J. CD4 T Cell-Intrinsic Role for the T Helper 17 Signature Cytokine IL-17: Effector Resistance to Immune Suppression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 19408–19414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, C.T.; Harrington, L.E.; Mangan, P.R.; Gavrieli, M.; Murphy, K.M. Th17: An Effector CD4 T Cell Lineage with Regulatory T Cell Ties. Immunity 2006, 24, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.-L. Are Th17 Cells and Their Cytokines a Therapeutic Target in Guillain-Barré Syndrome? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbour, S.N.; DiToro, D.F.; Witte, S.J.; Zindl, C.L.; Gao, M.; Schoeb, T.R.; Jones, G.W.; Jones, S.A.; Hatton, R.D.; Weaver, C.T. Th17 Cells Require Ongoing Classic IL-6 Receptor Signaling to Retain Transcriptional and Functional Identity. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaaw2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Anderson, D.E.; Baecher-Allan, C.; Hastings, W.D.; Bettelli, E.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Hafler, D.A. IL-21 and TGF-Beta Are Required for Differentiation of Human T(H)17 Cells. Nature 2008, 454, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockinger, B.; Veldhoen, M. Differentiation and Function of Th17 T Cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangan, P.R.; Harrington, L.E.; O’Quinn, D.B.; Helms, W.S.; Bullard, D.C.; Elson, C.O.; Hatton, R.D.; Wahl, S.M.; Schoeb, T.R.; Weaver, C.T. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Induces Development of the T(H)17 Lineage. Nature 2006, 441, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cua, D.J.; Tato, C.M. Innate IL-17-Producing Cells: The Sentinels of the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Dong, C. IL-17 Cytokines in Immunity and Inflammation. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2013, 2, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.K.; Brown, M.A. Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells Accumulate and Exhibit Disease-Induced Activation in the Meninges in EAE. Cell. Immunol. 2015, 297, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappu, R.; Ramirez-Carrozzi, V.; Sambandam, A. The Interleukin-17 Cytokine Family: Critical Players in Host Defence and Inflammatory Diseases. Immunology 2011, 134, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisman, A.; Hauptmann, J.; Regen, T. The Role of IL-17 in CNS Diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, K.; Shen, X.; Yang, Y.; Liang, X.; Lu, L.; Qiao, W.; Chen, A.; Hong, D.; et al. An Autonomous Activation of Interleukin-17 Receptor Signaling Sustains Inflammation and Promotes Disease Progression. Immunity 2023, 56, 2006–2020.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Jin, J.; Chang, M.; Nakaya, M.; Hu, H.; Zou, Q.; Zhou, X.; Brittain, G.C.; Cheng, X.; Sun, S.-C. TPL2 Mediates Autoimmune Inflammation through Activation of the TAK1 Axis of IL-17 Signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, J.D.; Ciric, B.; Marek, R.; Sadhukhan, S.; Caruso, M.L.; Shafagh, J.; Fitzgerald, D.C.; Shindler, K.S.; Rostami, A. Functional Interleukin-17 Receptor A Is Expressed in Central Nervous System Glia and Upregulated in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2009, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colonna, M.; Butovsky, O. Microglia Function in the Central Nervous System During Health and Neurodegeneration. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 441–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brelstaff, J.; Tolkovsky, A.M.; Ghetti, B.; Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G. Living Neurons with Tau Filaments Aberrantly Expose Phosphatidylserine and Are Phagocytosed by Microglia. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 1939–1948.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, B.; Lin, C.; Gong, Z.; An, X. TREM2 Inhibits Inflammatory Responses in Mouse Microglia by Suppressing the PI3K/NF-κB Signaling. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Garrison, B.S.; Ma, W.; Wang, R.; Jiang, A.; Li, J.; Mistry, M.; Bronson, R.T.; Santoro, D.; Franco, C.; et al. A Milieu Molecule for TGF-β Required for Microglia Function in the Nervous System. Cell 2018, 174, 156–171.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liang, D. Toll-like Receptor Signaling Directly Increases Functional IL-17RA Expression in Neuroglial Cells. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 154, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Dong, H.; Qian, Y. IL-17A Is Implicated in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Impairment in Aged Rats via Microglial Activation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zeng, Q.; Göktas, E.; Gopal, K.; Al-Aswad, L.; Blumberg, D.M.; Cioffi, G.A.; Liebmann, J.M.; Tezel, G. T-Lymphocyte Subset Distribution and Activity in Patients With Glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanokuchi, J.; Shimizu, K.; Nitta, A.; Yamada, K.; Mizuno, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Suzumura, A. Production and Functions of IL-17 in Microglia. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 194, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasa, R.; Barcutean, L.; Balasa, A.; Motataianu, A.; Roman-Filip, C.; Manu, D. The Action of TH17 Cells on Blood Brain Barrier in Multiple Sclerosis and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Hum. Immunol. 2020, 81, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebir, H.; Kreymborg, K.; Ifergan, I.; Dodelet-Devillers, A.; Cayrol, R.; Bernard, M.; Giuliani, F.; Arbour, N.; Becher, B.; Prat, A. Human TH17 Lymphocytes Promote Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Central Nervous System Inflammation. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen-Cherubini, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Deffenbaugh, J.L.; Murphy, S.P.; Xin, M.; Rau, C.N.; Yang, Y.; Lovett-Racke, A.E. Dysregulated Autotaxin Expression by T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2024, 387, 578282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, M.; Maggi, L.; Micheletti, A.; Lazzeri, E.; Tamassia, N.; Costantini, C.; Cosmi, L.; Lunardi, C.; Annunziato, F.; Romagnani, S.; et al. Evidence for a Cross-Talk between Human Neutrophils and Th17 Cells. Blood 2010, 115, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willing, A.; Jäger, J.; Reinhardt, S.; Kursawe, N.; Friese, M.A. Production of IL-17 by MAIT Cells Is Increased in Multiple Sclerosis and Is Associated with IL-7 Receptor Expression. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Godec, J.; Ben-Aissa, K.; Cui, K.; Zhao, K.; Pucsek, A.B.; Lee, Y.K.; Weaver, C.T.; Yagi, R.; Lazarevic, V. The Transcription Factors T-Bet and Runx Are Required for the Ontogeny of Pathogenic Interferon-γ-Producing T Helper 17 Cells. Immunity 2014, 40, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettelli, E.; Carrier, Y.; Gao, W.; Korn, T.; Strom, T.B.; Oukka, M.; Weiner, H.L.; Kuchroo, V.K. Reciprocal Developmental Pathways for the Generation of Pathogenic Effector TH17 and Regulatory T Cells. Nature 2006, 441, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, B.; Lombardi, G.; Lechler, R.I.; Lord, G.M. The role of T helper 17 (Th17) and regulatory T cells (treg) in human organ transplantation and autoimmune disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 148, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6: Regulator of Treg/Th17 Balance. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Weiner, J.; Liu, Y.; Smith, A.J.; Huss, D.J.; Winger, R.; Peng, H.; Cravens, P.D.; Racke, M.K.; Lovett-Racke, A.E. T-Bet Is Essential for Encephalitogenicity of Both Th1 and Th17 Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Passos, G.R.; Sato, D.K.; Becker, J.; Fujihara, K. Th17 Cells Pathways in Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Implications. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 5314541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebir, H.; Ifergan, I.; Alvarez, J.I.; Bernard, M.; Poirier, J.; Arbour, N.; Duquette, P.; Prat, A. Preferential Recruitment of Interferon-Gamma-Expressing TH17 Cells in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, S.; Croxford, A.L.; Kreymborg, K.; Heppner, F.L.; Pouly, S.; Becher, B.; Waisman, A. IL-17A and IL-17F Do Not Contribute Vitally to Autoimmune Neuro-Inflammation in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, H.H.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Koczan, D.; Kruse, N.; Weishaupt, A.; Toyka, K.V.; Gold, R. Therapeutic Efficacy of IL-17 Neutralization in Murine Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Cell. Immunol. 2005, 237, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiyama, Y.; Nakae, S.; Matsuki, T.; Nambu, A.; Ishigame, H.; Kakuta, S.; Sudo, K.; Iwakura, Y. IL-17 Plays an Important Role in the Development of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardiguian, S.; Serres, S.; Ladds, E.; Campbell, S.J.; Wilainam, P.; McFadyen, C.; McAteer, M.; Choudhury, R.P.; Smith, P.; Saunders, F.; et al. Anti-IL-17A Treatment Reduces Clinical Score and VCAM-1 Expression Detected by In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Chronic Relapsing EAE ABH Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzartos, J.S.; Friese, M.A.; Craner, M.J.; Palace, J.; Newcombe, J.; Esiri, M.M.; Fugger, L. Interleukin-17 Production in Central Nervous System-Infiltrating T Cells and Glial Cells Is Associated with Active Disease in Multiple Sclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, A.M.; Edwards, S.C.; Raverdeau, M.; Mills, K.H. Th17 cells, γδ T cells and their interplay in EAE and multiple sclerosis. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 87, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusevicius, D.; Kivisäkk, P.; He, B.; Kostulas, N.; Ozenci, V.; Fredrikson, S.; Link, H. Interleukin-17 mRNA Expression in Blood and CSF Mononuclear Cells Is Augmented in Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 1999, 5, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graber, J.J.; Allie, S.R.; Mullen, K.M.; Jones, M.V.; Wang, T.; Krishnan, C.; Kaplin, A.I.; Nath, A.; Kerr, D.A.; Calabresi, P.A. Interleukin-17 in Transverse Myelitis and Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 196, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Long, Y.; Lu, Z.; Hu, X. Increased Memory Th17 Cells in Patients with Neuromyelitis Optica and Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 234, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucklacher-Waldert, V.; Stuerner, K.; Kolster, M.; Wolthausen, J.; Tolosa, E. Phenotypical and Functional Characterization of T Helper 17 Cells in Multiple Sclerosis. Brain 2009, 132, 3329–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.; Lowndes, C.; Durant, L.; Strange, R.C.; Al-Araji, A.; Hawkins, C.P.; Curnow, S.J. Th17 Cells Increase in RRMS as Well as in SPMS, Whereas Various Other Phenotypes of Th17 Increase in RRMS Only. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2020, 6, 2055217319899695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, M.; Zhang, X.; Berthelot, L.; Laplaud, D.-A.; Brouard, S.; Jin, J.; Rogan, S.; Armao, D.; Jewells, V.; Soulillou, J.-P.; et al. Oligoclonal Myelin-Reactive T-Cell Infiltrates Derived from Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Are Enriched in Th17 Cells. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 130, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siffrin, V.; Radbruch, H.; Glumm, R.; Niesner, R.; Paterka, M.; Herz, J.; Leuenberger, T.; Lehmann, S.M.; Luenstedt, S.; Rinnenthal, J.L.; et al. In Vivo Imaging of Partially Reversible Th17 Cell-Induced Neuronal Dysfunction in the Course of Encephalomyelitis. Immunity 2010, 33, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, S.P.; Cervi, A.L.; Nagpal, S.; Lomax, A.E. Interleukin-17A Increases Neurite Outgrowth from Adult Postganglionic Sympathetic Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-J.; Li, S.; Shu, H.-F.; Yu, S.-X.; Liu, S.-Y.; Yin, Q.; Yang, H. The Interleukin 17 System in Cortical Lesions in Focal Cortical Dysplasias. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, K.; Zhu, L.; Kan, Q.; Yan, Y.; Kumar, P.; Xu, H.; Rostami, A.; Zhang, G.-X. Inhibitory Effect of IL-17 on Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Neural Cell Differentiation. BMC Immunol. 2013, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reboldi, A.; Coisne, C.; Baumjohann, D.; Benvenuto, F.; Bottinelli, D.; Lira, S.; Uccelli, A.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Engelhardt, B.; Sallusto, F. C-C Chemokine Receptor 6-Regulated Entry of TH-17 Cells into the CNS through the Choroid Plexus Is Required for the Initiation of EAE. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecuyer, M.A.; Kebir, H.; Prat, A. Glial influences on BBB functions and molecular players in immune cell trafficking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppert, J.; Closhen, D.; Croxford, A.; White, R.; Kulig, P.; Pietrowski, E.; Bechmann, I.; Becher, B.; Luhmann, H.J.; Waisman, A.; et al. Cellular Mechanisms of IL-17-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, X.; Han, M.; Lv, J.; Zhuang, W.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Saimaier, K.; Yang, J.; et al. Artemisinin derivative TPN10466 suppresses immune cell migration and Th1/Th17 differentiation to ameliorate disease severity in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Cell. Immunol. 2022, 373, 104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havrdová, E.; Belova, A.; Goloborodko, A.; Tisserant, A.; Wright, A.; Wallstroem, E.; Garren, H.; Maguire, R.P.; Johns, D.R. Activity of Secukinumab, an Anti-IL-17A Antibody, on Brain Lesions in RRMS: Results from a Randomized, Proof-of-Concept Study. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, M.; Müller, S.; Derfuss, T.; Décard, B.F. A Case of Concomitant Psoriasis and Multiple Sclerosis: Secukinumab and Rituximab Exert Dichotomous Effects in Two Autoimmune Conditions. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 31, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantzoulis, S.; Galvin, J.E. Distinguishing Alzheimer’s Disease from Other Major Forms of Dementia. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 1579–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikwar, S.P.; Thangavel, R.; Dubova, I.; Ahmed, M.E.; Selvakumar, P.G.; Kempuraj, D.; Zaheer, S.; Iyer, S.; Zaheer, A. Neuro-Immuno-Gene- and Genome-Editing-Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease: Are We There Yet? J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 65, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouras, G.K.; Olsson, T.T.; Hansson, O. β-Amyloid Peptides and Amyloid Plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Tran, J.; Jiang, L.; Guo, Z. A New Structural Model of Alzheimer’s Aβ42 Fibrils Based on Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Data and Rosetta Modeling. J. Struct. Biol. 2016, 194, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, B.; Friedrich, M.; Raftery, M.; Truscott, R. Amyloid Plaque in the Human Brain Can Decompose from Aβ(1-40/1-42) by Spontaneous Nonenzymatic Processes. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2675–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, N.; Namaka, M.P.; Dou, C.; Zhang, Y. Exploring the Role of Interleukin-22 in Neurological and Autoimmune Disorders. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-Y.; Tan, M.-S.; Yu, J.-T.; Tan, L. Role of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Released from Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Rudinskiy, N.; Fuerer, C.; Demurtas, D.; Zamorano, S.; De Piano, C.; Herrmann, A.G.; Spires-Jones, T.L.; Oeckl, P.; Otto, M.; Frosch, M.P.; et al. Amyloid-Beta Oligomerization Is Associated with the Generation of a Typical Peptide Fragment Fingerprint. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 12, 996–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doecke, J.D.; Laws, S.M.; Faux, N.G.; Wilson, W.; Burnham, S.C.; Lam, C.-P.; Mondal, A.; Bedo, J.; Bush, A.I.; Brown, B.; et al. Blood-Based Protein Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.T.; Chen-Plotkin, A.; Grossman, M.; Arnold, S.E.; Clark, C.M.; Shaw, L.M.; McCluskey, L.; Elman, L.; Hurtig, H.I.; Siderowf, A.; et al. Novel CSF Biomarkers for Frontotemporal Lobar Degenerations. Neurology 2010, 75, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenaro, E.; Pietronigro, E.; Della Bianca, V.; Piacentino, G.; Marongiu, L.; Budui, S.; Turano, E.; Rossi, B.; Angiari, S.; Dusi, S.; et al. Neutrophils Promote Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathology and Cognitive Decline via LFA-1 Integrin. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, T.C.; McQuillan, K.; McManus, R.M.; O’Reilly, J.-A.; Mills, K.H.G.; Lynch, M.A. IFN-γ Production by Amyloid β-Specific Th1 Cells Promotes Microglial Activation and Increases Plaque Burden in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2241–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi Shahrokhi, V.; Ravari, A.; Mirzaei, T.; Zare-Bidaki, M.; Asadikaram, G.; Arababadi, M.K. IL-17A and IL-23: Plausible Risk Factors to Induce Age-Associated Inflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Immunol. Investig. 2018, 47, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.V.; Hanson, J.E.; Sheng, M. Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, O.; Utkilen, H.; Duale, N.; Brunborg, G.; Hofer, T. Metal Dyshomeostasis and Inflammation in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: Possible Impact of Environmental Exposures. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 726954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wen, S.; Li, G.; Wang, D. Hypoxia Enhances Stimulating Effect of Amyloid Beta Peptide (25–35) for Interleukin 17 and T Helper Lymphocyte Subtype 17 Upregulation in Cultured Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 53, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksida, T.; Koprivica, I.; Vujičić, M.; Stošić-Grujičić, S.; Perović, M.; Kanazir, S.; Stojanović, I. Impaired IL-17 Production in Gut-Residing Immune Cells of 5xFAD Mice with Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 61, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H. LncRNA17A Regulates Autophagy and Apoptosis of SH-SY5Y Cell Line as an In Vitro Model for Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Amour, I.; Bosoi, C.R.; Paré, I.; Ignatius Arokia Doss, P.M.; Rangachari, M.; Hébert, S.S.; Bazin, R.; Calon, F. Peripheral Adaptive Immunity of the Triple Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ke, K.-F.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, Y.-H.; Peng, Y.-P. Th17 Cell-Mediated Neuroinflammation Is Involved in Neurodegeneration of Aβ1-42-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Model Rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, A.; Ma, H.; Zhang, R.; Tan, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, B.; Wang, J.; Wan, C. Interleukin17A Promotes Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction by Triggering β-Amyloid Accumulation via the Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGFβ)/Smad Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, H.; Yin, K. Matrine Improves Cognitive Impairment and Modulates the Balance of Th17/Treg Cytokines in a Rat Model of Aβ1-42-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease. Cent.-Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 40, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzartos, J.S.; Craner, M.J.; Friese, M.A.; Jakobsen, K.B.; Newcombe, J.; Esiri, M.M.; Fugger, L. IL-21 and IL-21 Receptor Expression in Lymphocytes and Neurons in Multiple Sclerosis Brain. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebinia, F.; Pourgholaminejad, A. The Role of Th17 Cells in Auto-Inflammatory Neurological Disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 79, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, F.; Goodyer, C.G.; Antel, J.P.; Yong, V.W. Vulnerability of Human Neurons to T Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.-J.; Kim, H.-D.; Maxwell, J.A.; Li, L.; Fukuchi, K. Toll-like Receptor 4-Dependent Upregulation of Cytokines in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, C.; Volpicelli, F.; Lippiello, P.; Buono, B.; Raucci, F.; Piccolo, M.; Iqbal, A.J.; Irace, C.; Miniaci, M.C.; Perrone Capano, C.; et al. Neutralization of IL-17 Rescues Amyloid-β-induced Neuroinflammation and Memory Impairment. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 3544–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solleiro-Villavicencio, H.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Effect of Chronic Oxidative Stress on Neuroinflammatory Response Mediated by CD4+T Cells in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tfilin, M.; Turgeman, G. Interleukine-17 Administration Modulates Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Improves Spatial Learning in Mice. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemprière, S. T Cells on Patrol in Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saresella, M.; Calabrese, E.; Marventano, I.; Piancone, F.; Gatti, A.; Alberoni, M.; Nemni, R.; Clerici, M. Increased Activity of Th-17 and Th-9 Lymphocytes and a Skewing of the Post-Thymic Differentiation Pathway Are Seen in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-M.; Jiang, G.-X.; Li, Q.-W.; Zhou, Z.-M.; Cheng, Q. Increased Serum Levels of Interleukin-18, -23 and -17 in Chinese Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2014, 38, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciani, D.J. Alzheimer’s Disease Vaccine Development: A New Strategy Focusing on Immune Modulation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 287, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, R.M.; Higgins, S.C.; Mills, K.H.G.; Lynch, M.A. Respiratory Infection Promotes T Cell Infiltration and Amyloid-β Deposition in APP/PS1 Mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.T. Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonism. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, E.; Cassina, N.; Rasini, E.; Marino, F.; Cosentino, M. Do Th17 Lymphocytes and IL-17 Contribute to Parkinson’s Disease? A Systematic Review of Available Evidence. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.; Marxreiter, F.; Krach, F.; Fadler, T.; Grosch, J.; Maroni, M.; Graef, D.; Eberhardt, E.; Riemenschneider, M.J.; Yeo, G.W.; et al. Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human iPSC-Based Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 123–131.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzos, M.; Rombos, A.; Nikolaou, C.; Zoga, M.; Zouvelou, V.; Dimitrakopoulos, A.; Alexakis, T.; Tsoutsou, A.; Samakovli, A.; Michalopoulou, M.; et al. Interleukin-17 and Interleukin-23 Are Elevated in Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with ALS: A Reflection of Th17 Cells Activation? Acta Neurol. Scand. 2010, 122, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saresella, M.; Piancone, F.; Tortorella, P.; Marventano, I.; Gatti, A.; Caputo, D.; Lunetta, C.; Corbo, M.; Rovaris, M.; Clerici, M. T Helper-17 Activation Dominates the Immunologic Milieu of Both Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 148, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Günther, R.; Akgün, K.; Hermann, A.; Ziemssen, T. Peripheral Proinflammatory Th1/Th17 Immune Cell Shift Is Linked to Disease Severity in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, M.; Chattopadhay, M.; La Cava, A.; Tse, E.; Liu, G.; Lourenco, E.; Eskin, A.; Liu, P.T.; Magpantay, L.; Tse, S.; et al. IL-17A Is Increased in the Serum and in Spinal Cord CD8 and Mast Cells of ALS Patients. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenobia, C.; Hajishengallis, G. Basic Biology and Role of Interleukin-17 in Immunity and Inflammation. Periodontol. 2000 2015, 69, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwabara, T.; Ishikawa, F.; Kondo, M.; Kakiuchi, T. The Role of IL-17 and Related Cytokines in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 3908061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Hu, B.; Liu, W.; Lv, X.; Chen, S.; Shao, Z. Efficacy and Safety of Interleukin-17A Inhibitors in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3053–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Xue, C.; Zhu, G.; Kang, P. Efficacy and Safety of Interleukin-17 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Chronic Rheumatic Diseases: A Combined and Updated Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2021, 46, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, N.; Ollendorf, D.A.; Chapman, R.H.; Loos, A.; Liu, S.; Kumar, V.; Linder, J.A.; Pearson, S.D.; Veenstra, D.L. Cost-Effectiveness of Targeted Pharmacotherapy for Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2018, 24, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboobacker, S.; Kurn, H.; Al Aboud, A.M. Secukinumab. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Azhar, A.; Zaayman, M.; Silfvast-Kaiser, A.; Kivelevitch, D.; Menter, A.; Paek, S.Y. Ixekizumab in the Treatment of Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Patient Adherence, Satisfaction, and Preferences. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbari, N.M.; Basehore, B.M.; Zito, P.M. Brodalumab. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Canavan, T.N.; Elmets, C.A.; Cantrell, W.L.; Evans, J.M.; Elewski, B.E. Anti-IL-17 Medications Used in the Treatment of Plaque Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Comprehensive Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2016, 17, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, L.; Bakulev, A.L.; Kokhan, M.M.; Samtsov, A.V.; Khairutdinov, V.R.; Morozova, M.A.; Zolkin, N.A.; Kuryshev, I.V.; Petrov, A.N.; Artemeva, A.V.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Netakimab, A Novel Anti-IL-17 Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis. Results of A 54-Week Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled PLANETA Clinical Trial. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1319–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotaeva, T.; Gaydukova, I.; Mazurov, V.; Samtsov, A.; Khayrutdinov, V.; Bakulev, A.; Kokhan, M.; Kundzer, A.; Soroka, N.; Dokukina, E.; et al. Op0226 Netakimab Decreases Disease Activity in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from a Randomized Double-Blind Phase 3 Clinical Trial (Patera). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.; Vender, R.; Torres, T. Bimekizumab: The First Dual Inhibitor of Interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-17F for the Treatment of Psoriatic Disease and Ankylosing Spondylitis. Biodrugs 2019, 33, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, K.B.; Langley, R.G.; Warren, R.B.; Okubo, Y.; Rosmarin, D.; Lebwohl, M.; Peterson, L.; Madden, C.; de Cuyper, D.; Davies, O.; et al. Bimekizumab Safety in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Pooled Data from up to 3 Years of Treatment in Randomized Phase III Trials. Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 190, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchlin, C.T.; Kavanaugh, A.; Merola, J.F.; Schett, G.; Scher, J.U.; Warren, R.B.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Assudani, D.; Bedford-Rice, K.; Coarse, J.; et al. Bimekizumab in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from a 48-Week, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Ranging Phase 2b Trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyman, O.; Comte, D.; Spertini, F. Adverse Reactions to Biologic Agents and Their Medical Management. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 612–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhou, E.; Ren, T.; Chang, X.; He, M.; Zeng, K.; Guo, Y.; Wu, J. Efficacy and Safety of IL-17 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangilbergen, M.; Stockman, A.; Van De Velde, A.; Garmyn, M.; Punie, K.; Hillary, T. The Role of Interleukin-17 and Interleukin-23 Inhibitors in the Development, Progression, and Recurrence of Cancer: A Systematic Review. JAAD Int. 2024, 17, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson Regnault, M.; Konstantinou, M.-P.; Khemis, A.; Poulin, Y.; Bourcier, M.; Amelot, F.; Bulaï Livideanu, C.; Paul, C. Early Relapse of Psoriasis after Stopping Brodalumab: A Retrospective Cohort Study in 77 Patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Heo, T.H. Celastrol Regulates Psoriatic Inflammation and Autophagy by Targeting IL-17A. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 172, 116256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Rong, X.; Zhao, E.; Zhang, L.; Lv, Y. Neuroprotection of Resveratrol Against Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice Through a Mechanism Targeting Gut-Brain Axis. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Ouyang, D.; Lin, L.; Xin, X.; Ji, Y. Salidroside Regulates Imbalance of Th17/Treg and Promotes Ischemic Tolerance by Targeting STAT-3 in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2021, 17, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Pan, X.; Zhou, F.; Liu, K.; Wang, L. Hyperforin Protects against Acute Cerebral Ischemic Injury through Inhibition of Interleukin-17A-Mediated Microglial Activation. Brain Res. 2018, 1678, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Kan, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.-X. Matrine Suppresses Production of IL-23/IL-17 and Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Zheng, P.; Deng, W.; Yuan, J.; Peng, B.; Wang, R.; Liu, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Huperzine A Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis via the Suppression of T Cell-Mediated Neuronal Inflammation in Mice. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 236, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mease, P.J.; McInnes, I.B.; Kirkham, B.; Kavanaugh, A.; Rahman, P.; Van Der Heijde, D.; Landewé, R.; Nash, P.; Pricop, L.; Yuan, J.; et al. Secukinumab Inhibition of Interleukin-17A in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secukinumab Inhibition of Interleukin-17A in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis|New England Journal of Medicine. Available online: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1412679 (accessed on 22 October 2024).
- Blair, H.A. Secukinumab: A Review in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Drugs 2019, 79, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, C.; Matheson, R.; Zachariae, C.; Cameron, G.; Li, L.; Edson-Heredia, E.; Braun, D.; Banerjee, S. Anti–Interleukin-17 Monoclonal Antibody Ixekizumab in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, K.; Pinter, A.; Lacour, J.P.; Ferrandiz, C.; Micali, G.; French, L.E.; Lomaga, M.; Dutronc, Y.; Henneges, C.; Wilhelm, S.; et al. Comparison of Ixekizumab with Ustekinumab in Moderate-to-severe Psoriasis: 24-week Results from IXORA-S, a Phase III Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, P.; Kirkham, B.; Okada, M.; Rahman, P.; Combe, B.; Burmester, G.-R.; Adams, D.H.; Kerr, L.; Lee, C.; Shuler, C.L.; et al. Ixekizumab for the Treatment of Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis and an Inadequate Response to Tumour Necrosis Factor Inhibitors: Results from the 24-Week Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Period of the SPIRIT-P2 Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2317–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.C.-C.; Kim, T.-H.; Kishimoto, M.; Ogusu, N.; Jeong, H.; Kobayashi, S. Efficacy and Safety of Brodalumab, an Anti-IL17RA Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: 16-Week Results from a Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, K.A.; Leonardi, C.; Menter, A.; Ortonne, J.-P.; Krueger, J.G.; Kricorian, G.; Aras, G.; Li, J.; Russell, C.B.; Thompson, E.H.Z.; et al. Brodalumab, an Anti–Interleukin-17–Receptor Antibody for Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mease, P.J.; Genovese, M.C.; Greenwald, M.W.; Ritchlin, C.T.; Beaulieu, A.D.; Deodhar, A.; Newmark, R.; Feng, J.; Erondu, N.; Nirula, A. Brodalumab, an Anti-IL17RA Monoclonal Antibody, in Psoriatic Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatt, S.; Helmer, E.; Haier, B.; Strimenopoulou, F.; Price, G.; Vajjah, P.; Harari, O.A.; Lambert, J.; Shaw, S. First-in-Human Randomized Study of Bimekizumab, a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody and Selective Dual Inhibitor of IL-17A and IL-17F, in Mild Psoriasis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, K.B.; Foley, P.; Krueger, J.G.; Pinter, A.; Reich, K.; Vender, R.; Vanvoorden, V.; Madden, C.; White, K.; Cioffi, C.; et al. Bimekizumab Efficacy and Safety in Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis (BE READY): A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomised Withdrawal Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, K.; Warren, R.B.; Lebwohl, M.; Gooderham, M.; Strober, B.; Langley, R.G.; Paul, C.; De, C.D.; Vanvoorden, V.; Madden, C.; et al. Bimekizumab versus Secukinumab in Plaque Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, M.-Y.; Luo, L.-Z. The Role of IL-17A in Mediating Inflammatory Responses and Progression of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062505
Zheng M-Y, Luo L-Z. The Role of IL-17A in Mediating Inflammatory Responses and Progression of Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062505
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Miao-Yan, and Lian-Zhong Luo. 2025. "The Role of IL-17A in Mediating Inflammatory Responses and Progression of Neurodegenerative Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062505
APA StyleZheng, M.-Y., & Luo, L.-Z. (2025). The Role of IL-17A in Mediating Inflammatory Responses and Progression of Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062505





