Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profile Analysis of the NADPH Oxidase Gene Family in Avena sativa L.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Physicochemical Properties of RBOH Gene Family
2.2. Conserved Motifs and Gene Structure Analysis of RBOH Gene Family
2.3. Chromosomal Localization of RBOH Gene Family
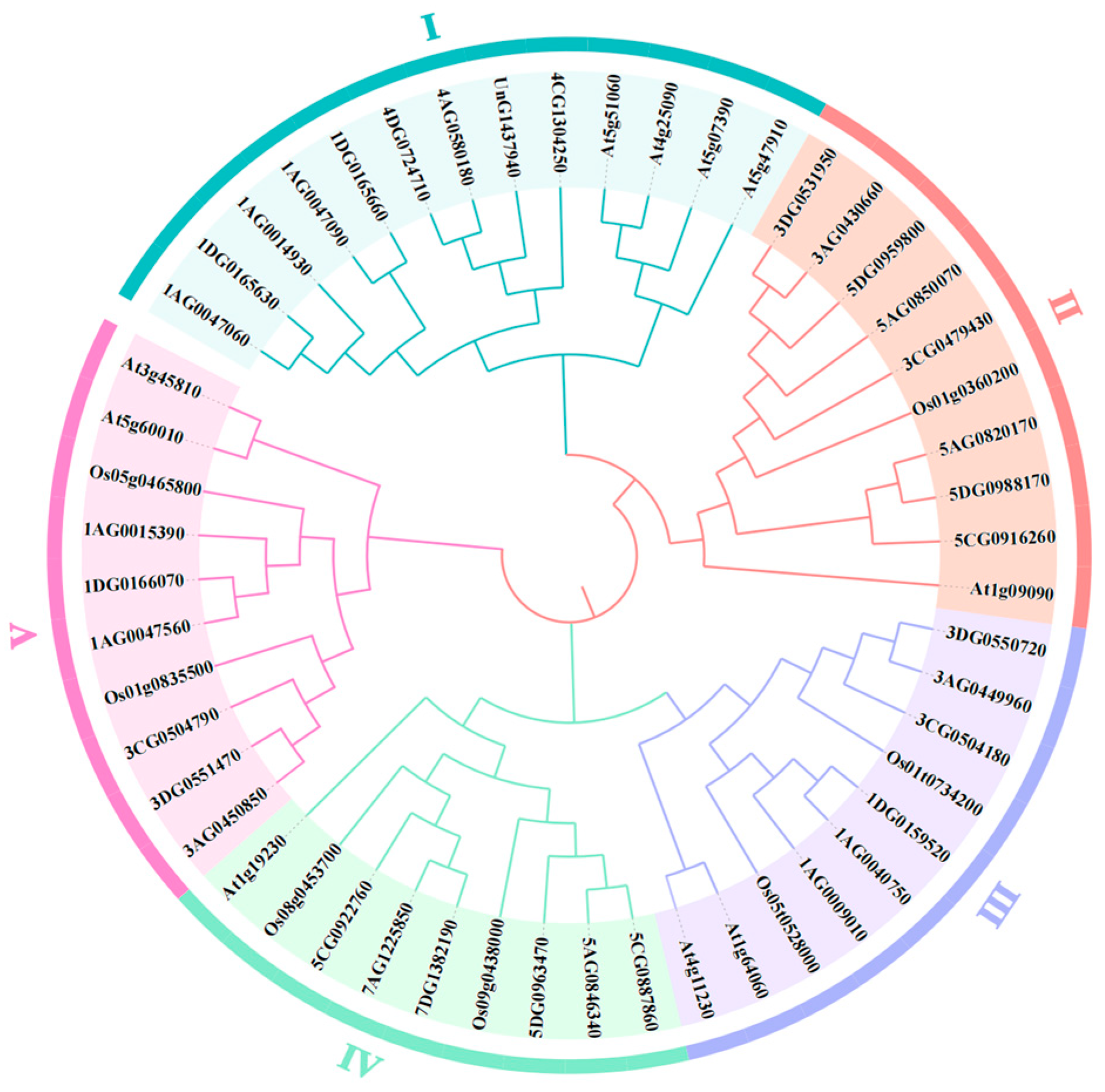
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of RBOH Gene Family
2.5. Synteny Analysis of RBOH Gene Family
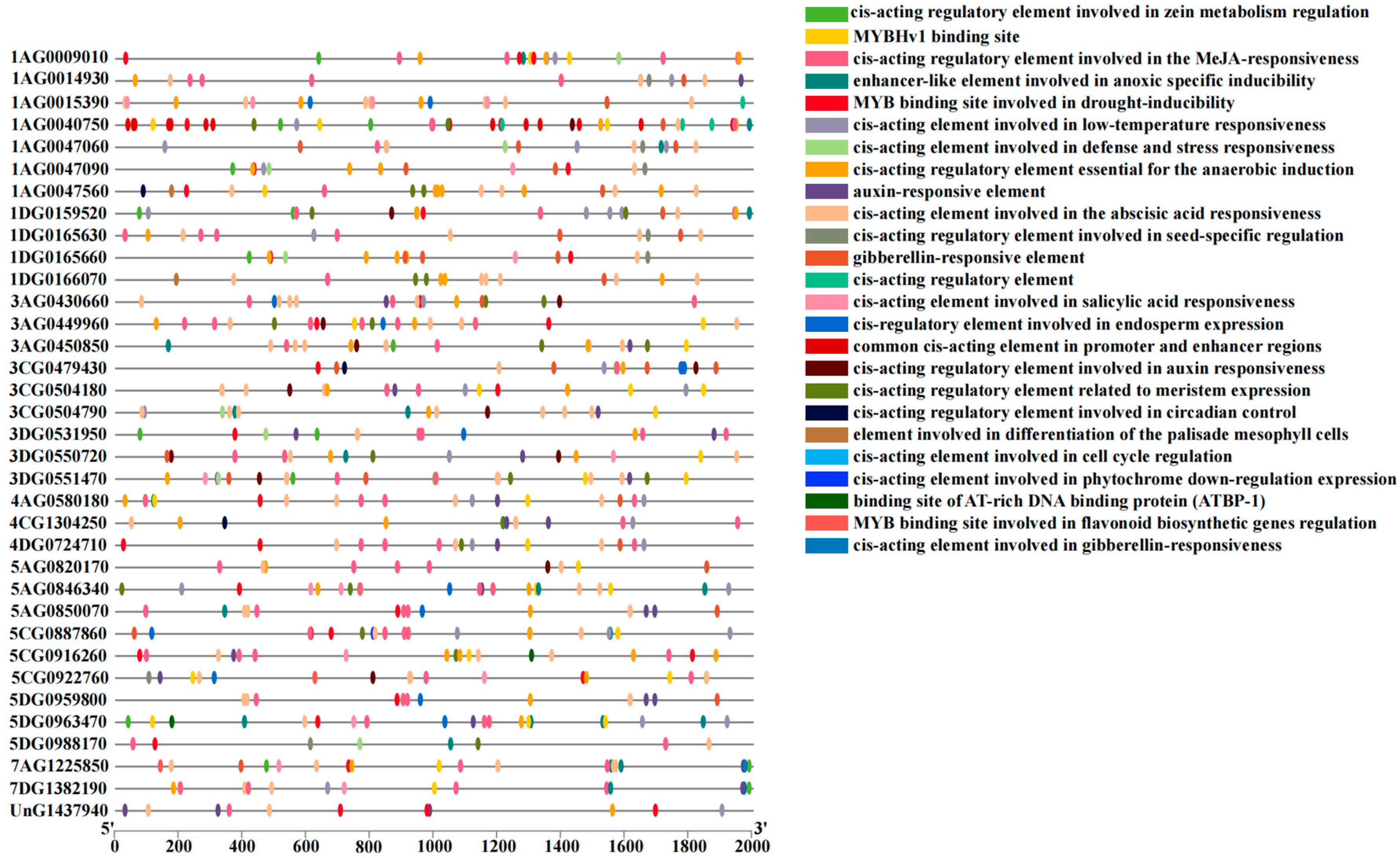
2.6. Functional Analysis of Cis-Elements in the Promoter Region of RBOH Gene Family
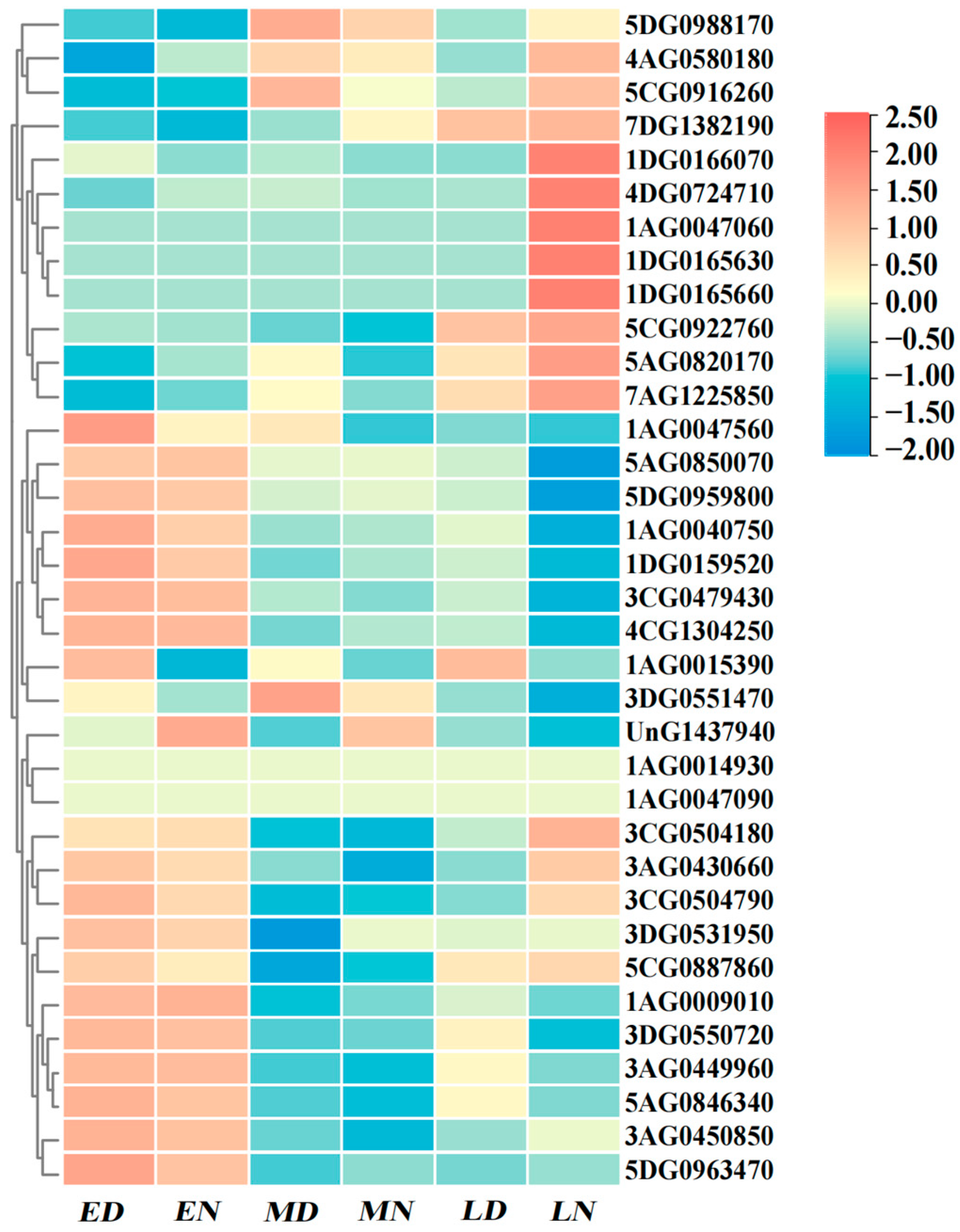
2.7. Expression Profile of RBOH.s in Response to Abiotic Stress
2.8. Spatiotemporal Expression Characteristics of RBOH Gene Family in Oat
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Methods
4.2. Identification Analysis of RBOH Gene Family
4.3. Conserved Motifs and Gene Structure Analysis
4.4. Chromosomal Localization Analysis of RBOH Gene Family
4.5. Evolutionary Analysis of the AsRBOH System
4.6. Synteny and Homologous Gene Pairs
4.7. Promoter Analysis of the RBOH Gene Family
4.8. Expression Pattern of RBOH Gene in Oat
4.9. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, K.; Tan, X. Advances in the study of plant NADPH oxidases. Life Sci. 2010, 22, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, P.; Zhou, C. Advances in plant disease resistance related to NADPH oxidase. J. Jiangxi Agric. 2013, 25, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kawakita, K.; Maeshima, M.; Doke, N.; Yoshioka, A.H. Subcellular localization of strboh proteins and nadph-dependent o2-generating activity in potato tuber tissues. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Gong, J.; Geng, X.; Yi, Y.; Zeng, F. Research on the function and regulatory mechanisms of plant Rboh genes. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Corpas, F.J.; Barroso, J. Peroxisomal plant metabolism—An update on nitric oxide, ca2+ and the nadph recycling network. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs202978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Sharma, A.; Guruprasad, K.; Pati, P.K. Versatile roles of plant nadph oxidases and emerging concepts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi, M. Production of Reactive Oxygen Species by Plant NADPH Oxidases. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Gupta, D.; Patel, M.; Vyver, C.V.D.; Koyama, H. Functionality of reactive oxygen species (ros) in plants: Toxicity and control in poaceae crops exposed to abiotic stress. Plants 2024, 13, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergashev, U.; Yu, M.; Luo, L.; Tang, J.; Han, Y. The Key Targets of NO-Mediated Post-Translation Modification (PTM) Highlighting the Dynamic Metabolism of ROS and RNS in Peroxisomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Du, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Chen, N.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; et al. The calcium-dependent protein kinase ZmCDPK7 functions in heat-stress tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.). J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xie, B.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jin, P. Genome-wide identification of the CDPK gene family reveals the CDPK-RBOH pathway potential involved in improving chilling tolerance in peach fruit. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 191, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Liu, C.; Guo, Y.F. Wheat transcription factor TaSNAC11-4B positively regulates leaf senescence through promoting ROS production in transgenic Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Pati, P.K. Analysis of Cis-acting regulatory elements of Respiratory burst oxidase homolog (Rboh) gene families in Arabidopsis and rice provides clues for their diverse functions. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 62, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.A.; Onouchi, H.; Hamada, S.; Machida, C.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Jones, J.D. Six Arabidopsis thaliana homologues of the human respiratory burst oxidase (gp91phox). Plant J. 1998, 14, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, Q.J.; Torres, M.A.; Fordham-Skelton, A.P.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Robinson, N.J.; Jones, J.D. RbohA, a rice homologue of the mammalian gp91phox respiratory burst oxidase gene. Plant J. 1996, 10, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Yang, D.; Cao, M.; Zhang, X.; Guo, S.; Yin, H. Identification and Expression Pattern Analysis of the RBOH Gene Family in Quinoa. J. Yantai Univ. 2023, 36, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Molecular and Functional Comparisons of Reactive Burst Oxygen Species Gene Family in Arabidopsis. Plant Divers. 2015, 37, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.A.; Dangl, J.L.; Jones, J.D. Arabidopsis gp91phox homologues AtrbohD and AtrbohF are required for accumulation of reactive oxygen intermediates in the plant defense response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouch, S.; Queval, G.; Noctor, G. AtRbohF is a crucial modulator of defence-associated metabolism and a key actor in the interplay between intracellular oxidative stress and pathogenesis responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2012, 69, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Jones, M.A.; Bezvoda, R.; Smirnoff, N.; Viktor, Ž. Reactive oxygen species produced by nadph oxidase are involved in pollen tube growth. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 146, S269–S270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerstin, M.; Linkies, A.; Vreeburg, R.A.M.; Fry, S.C.; Leubner-Metzger, K.L. In vivo cell wall loosening by hydroxyl radicals during cress seed germination and elongation growth. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Pan, X.; Yao, K.; Wei, W. The characteristics and expression analysis of the tomato slrboh gene family under exogenous phytohormone treatments and abiotic stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, H.Q.; Shi, W.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhao, F.J. The Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homologue OsRBOHE is crucial for root hair formation, drought resistance and tillering in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 48, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Peng, J.; Dong, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, K.; Li, Z.; Xu, J. Identification and Expression Analysis of the rboh Gene Family in Maize under Abiotic Stress. Maize Sci. 2021, 29, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Gan, Z.; Wan, Y.; Xiang, D.; Wu, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, C.; Fan, Y.; Zou, L. Advances and perspectives in forage oat breeding. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2023, 32, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.; Cowan, S.; Edwards, S.; Griffiths, I.; White, E. Crops that feed the world 9. oats- a cereal crop for human and livestock feed with industrial applications. Food Secur. 2013, 5, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Cui, L.; He, F.; Ouyang, S.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Shan, F. Construction and development of the industrial technology system for oats and buckwheat in China. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2018, 40, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devireddy, A.R.; Zandalinas, S.I.; Fichman, Y.; Mittler, R. Integration of reactive oxygen species and hormone signaling during abiotic stress. Plant J. 2021, 105, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yin, X.; Chen, Q.; Xiang, N.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y. Genome-wide survey indicates diverse physiological roles of the turnip (Brassica rapa var. rapa) calcium-dependent protein kinase genes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Ma, M.; Liu, T.; Xu, X. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the Rboh gene family in Citrus trifoliata. J. Yangzhou Univ. 2023, 44, 107–112+136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, X. Cytological structures and physiological and biochemical characteristics of covered oat (Avena sativa L.) and naked oat (Avena nuda L.) seeds during high-temperature artificial aging. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Che, Q.; Su, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X. Genome-wide identification and characterization of Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog genes in six Rosaceae species and an analysis of their effects on adventitious rooting in apple. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; He, W.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; et al. A complete assembly of the rice Nipponbare reference genome. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, T.; Li, Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Shabala, S.; Yu, M. Genome-wide analysisof respiratory burst oxidase homolog gene family in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1321952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, L.; He, J.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog (RBOH) Gene Family in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) under Abiotic and Biotic Stress. Genes 2023, 14, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadia, G.; Muhammad, A.; Saleem, U.; Muhammad, Q.; Saba, B.; Nimra, R.; Habib, U.; Qurat, A.; Badr, A. Identification and characterization of cysteine-rich polycomb-like protein (CPP) gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in response to phytohormones and Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae stress. Plant Stress 2024, 14, 100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, F. Advances in the study of plant salt stress-induced promoters and their cis-acting elements. Acta Physiol. Plant 2021, 57, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, D.; Dunand, C.; Puppo, A. A burst of plant NADPH oxidases. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Jiang, N.; Meng, J.; Yang, G.; Luan, Y. Lncrna33732-respiratory burst oxidase module associated with wrky1 in tomato- phytophthora infestans interactions. Plant J. 2019, 97, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence polymorphism analysis of large datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Wan, Q. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of respiratory burst oxidase homologue gene family in Glycine max. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 16, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Ali, B.; Ahmed, W.; Tang, Y.; Li, H. Genome-wide identification, classification, evolutionary expansion and expression of rboh family genes in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Trop. Plant Biol. 2021, 14, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, L.; Yang-Yang, L.; Zhi-Cheng, Z.; Xiaohua, X.; Xin, L.; Jie, W. Tobacco transcription factor bhlh123 improves salt tolerance by activating nadph oxidase ntrbohe expression. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 1706–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, N.; Song, Z.; Liu, T.; Dong, B.; Cao, H.; Duan, Y.; Meng, D.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Q. Response of NADPH Oxidase Gene Family to Abiotic Stress in Pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan). J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 30, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ID | Number of Amino Acid | Molecular Weight | Theoretical pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5CG0887860 | 998 | 111,341.98 | 9.15 | 44.25 | 81.39 | −0.201 |
| 5AG0846340 | 998 | 111,338.95 | 9.17 | 45.65 | 81.51 | −0.21 |
| 5DG0963470 | 996 | 110,913.53 | 9.24 | 45.58 | 81.97 | −0.188 |
| 3DG0550720 | 944 | 107,073.76 | 9.23 | 50.33 | 85.81 | −0.275 |
| 3AG0449960 | 953 | 107,773.47 | 9.2 | 49.74 | 85.31 | −0.265 |
| 3CG0504180 | 942 | 106,712.39 | 9.23 | 51.15 | 85.77 | −0.271 |
| 5CG0922760 | 964 | 108,040.8 | 9.37 | 55.29 | 83.31 | −0.154 |
| 1DG0159520 | 973 | 108,865.93 | 9.26 | 50.09 | 86.09 | −0.213 |
| 1AG0040750 | 974 | 108,991.03 | 9.34 | 50.13 | 86.3 | −0.218 |
| 1AG0009010 | 963 | 108,188.18 | 9.34 | 50.27 | 86.77 | −0.228 |
| 4CG1304250 | 920 | 103,729.73 | 9.35 | 45.25 | 81.84 | −0.275 |
| 3CG0504790 | 818 | 92,699.45 | 9.49 | 42.94 | 86.44 | −0.151 |
| 3AG0450850 | 850 | 95,816.81 | 9.43 | 43.96 | 84.8 | −0.172 |
| 3DG0551470 | 853 | 96,036.01 | 9.43 | 44.38 | 84.16 | −0.174 |
| 4DG0724710 | 757 | 84,801.24 | 9.37 | 50.46 | 83.75 | −0.224 |
| 4AG0580180 | 888 | 100,001.28 | 9.33 | 46.29 | 82.82 | −0.283 |
| 1AG0015390 | 832 | 94,172.33 | 8.98 | 48.11 | 80.66 | −0.219 |
| 1AG0047560 | 833 | 94,049.25 | 9.1 | 46.69 | 82.55 | −0.198 |
| 1DG0166070 | 834 | 94,189.35 | 9.05 | 46.35 | 82.22 | −0.206 |
| 5CG0916260 | 868 | 97,724.17 | 9.1 | 43.25 | 86.14 | −0.193 |
| 5AG0820170 | 729 | 82,589.16 | 8.88 | 41.6 | 87.17 | −0.089 |
| 5DG0988170 | 872 | 97,993.43 | 8.97 | 44.97 | 85.4 | −0.181 |
| 3CG0479430 | 903 | 101,712.85 | 9.28 | 39.21 | 85.3 | −0.203 |
| 5DG0959800 | 902 | 101,652.54 | 9.21 | 35.66 | 84.63 | −0.225 |
| 5AG0850070 | 902 | 101,603.6 | 9.24 | 36.3 | 85.28 | −0.211 |
| 1AG0047060 | 924 | 103,793.61 | 9.02 | 40.78 | 79.59 | −0.28 |
| 1AG0047090 | 871 | 98,458.01 | 9.4 | 42.87 | 81.93 | −0.274 |
| 1DG0165660 | 869 | 98,101.61 | 9.35 | 45.26 | 81.24 | −0.266 |
| 1DG0165630 | 923 | 104,207.28 | 9.14 | 43.22 | 77.03 | −0.325 |
| 1AG0014930 | 923 | 103,515.24 | 9.22 | 47.1 | 78.86 | −0.328 |
| 3DG0531950 | 757 | 86,159.29 | 8.98 | 34.6 | 85.01 | −0.14 |
| 3AG0430660 | 624 | 71,049.03 | 9.19 | 37.12 | 86.71 | −0.083 |
| 7DG1382190 | 741 | 84,588.75 | 9.38 | 50.19 | 87.04 | −0.087 |
| 7AG1225850 | 741 | 84,470.55 | 9.3 | 48.52 | 87.3 | −0.08 |
| UnG1437940 | 210 | 23,824.27 | 9.28 | 35.79 | 90.95 | −0.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Tang, J.; Yi, D.; Ma, L.; Wang, X. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profile Analysis of the NADPH Oxidase Gene Family in Avena sativa L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062576
Jiang Q, Zhou X, Tang J, Yi D, Ma L, Wang X. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profile Analysis of the NADPH Oxidase Gene Family in Avena sativa L. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062576
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Qingxue, Xinyue Zhou, Jun Tang, Dengxia Yi, Lin Ma, and Xuemin Wang. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profile Analysis of the NADPH Oxidase Gene Family in Avena sativa L." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062576
APA StyleJiang, Q., Zhou, X., Tang, J., Yi, D., Ma, L., & Wang, X. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profile Analysis of the NADPH Oxidase Gene Family in Avena sativa L. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062576






