A Novel Recombinant Human FGF21 Analog with High Glycosylation Has a Prolonged Half-Life and Affects Glycemic and Body Weight Control
Abstract
1. Introductions
2. Results
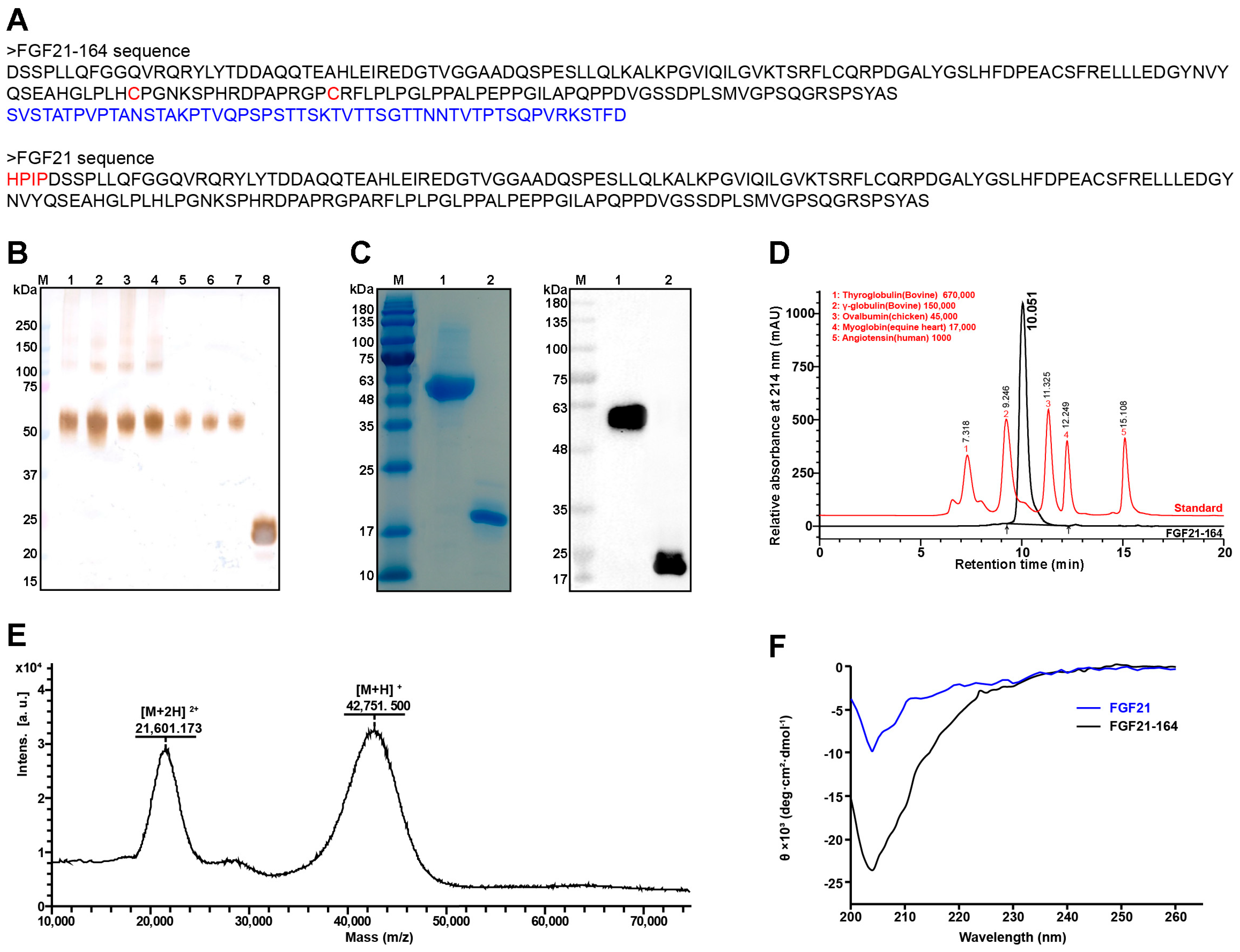
2.1. Construction and Biophysical Characterization of FGF21-164
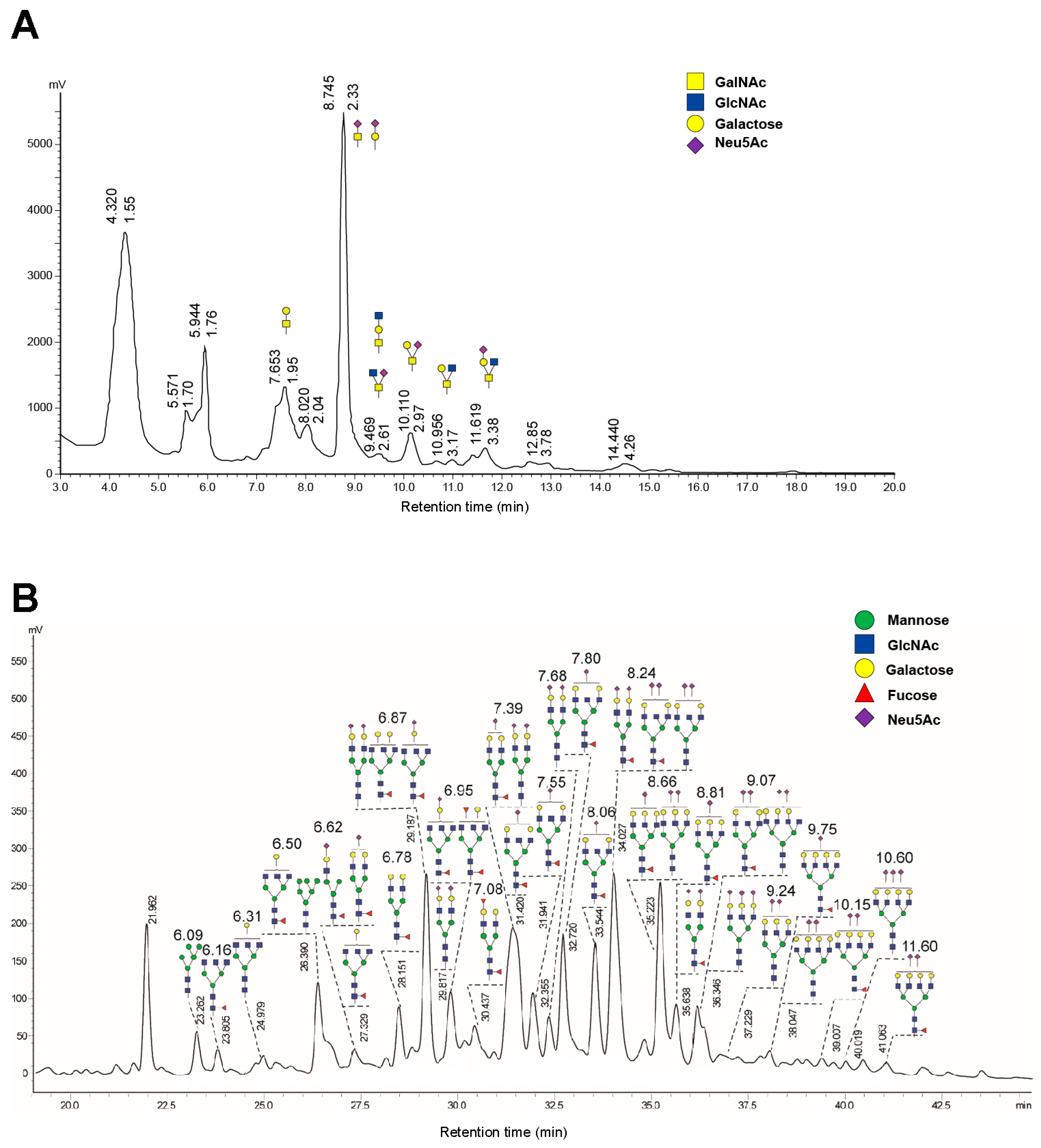
2.2. High Glycosylation of FGF21-164
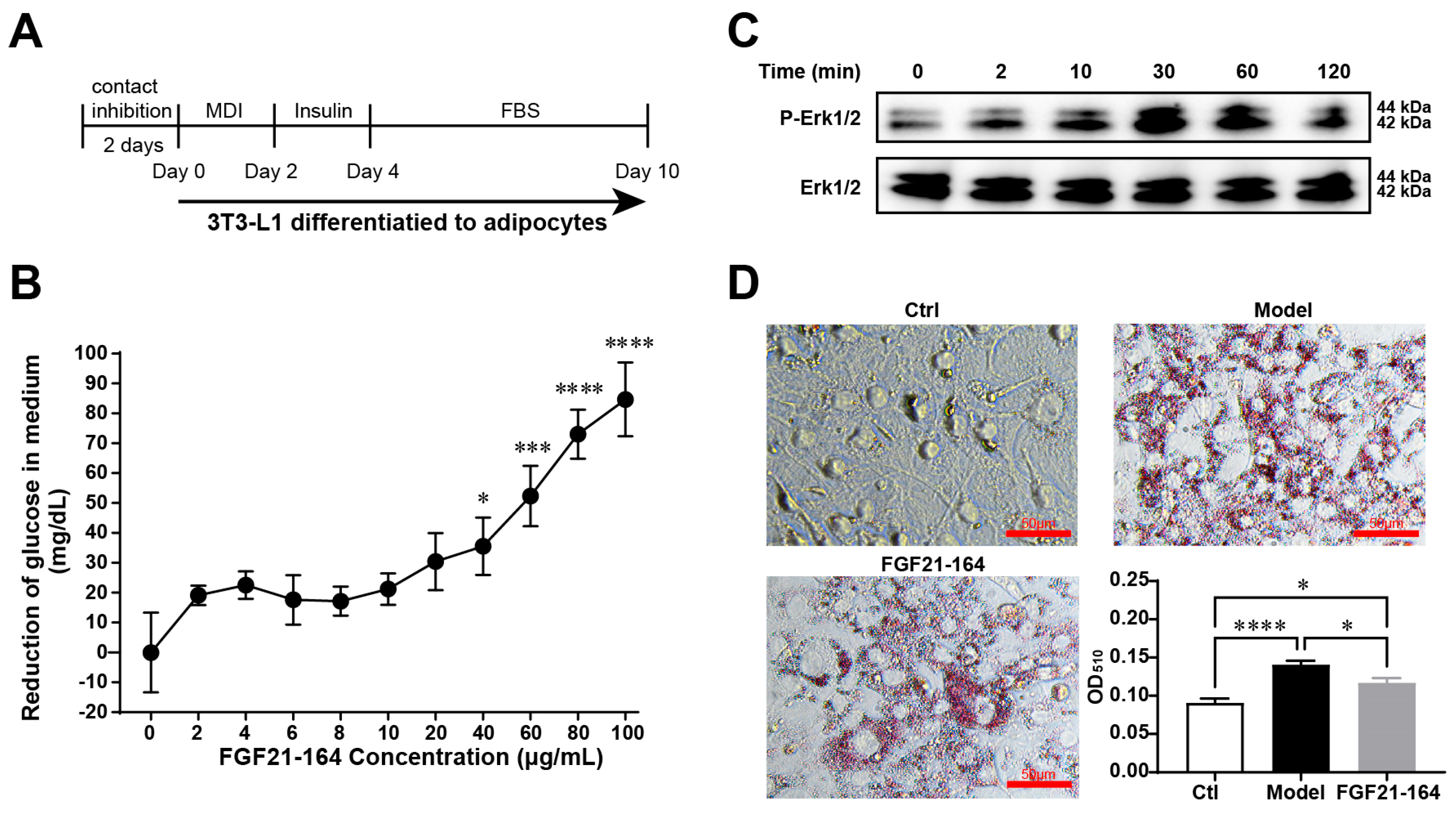
2.3. Identification of the In Vitro Bioactivity of FGF21-164
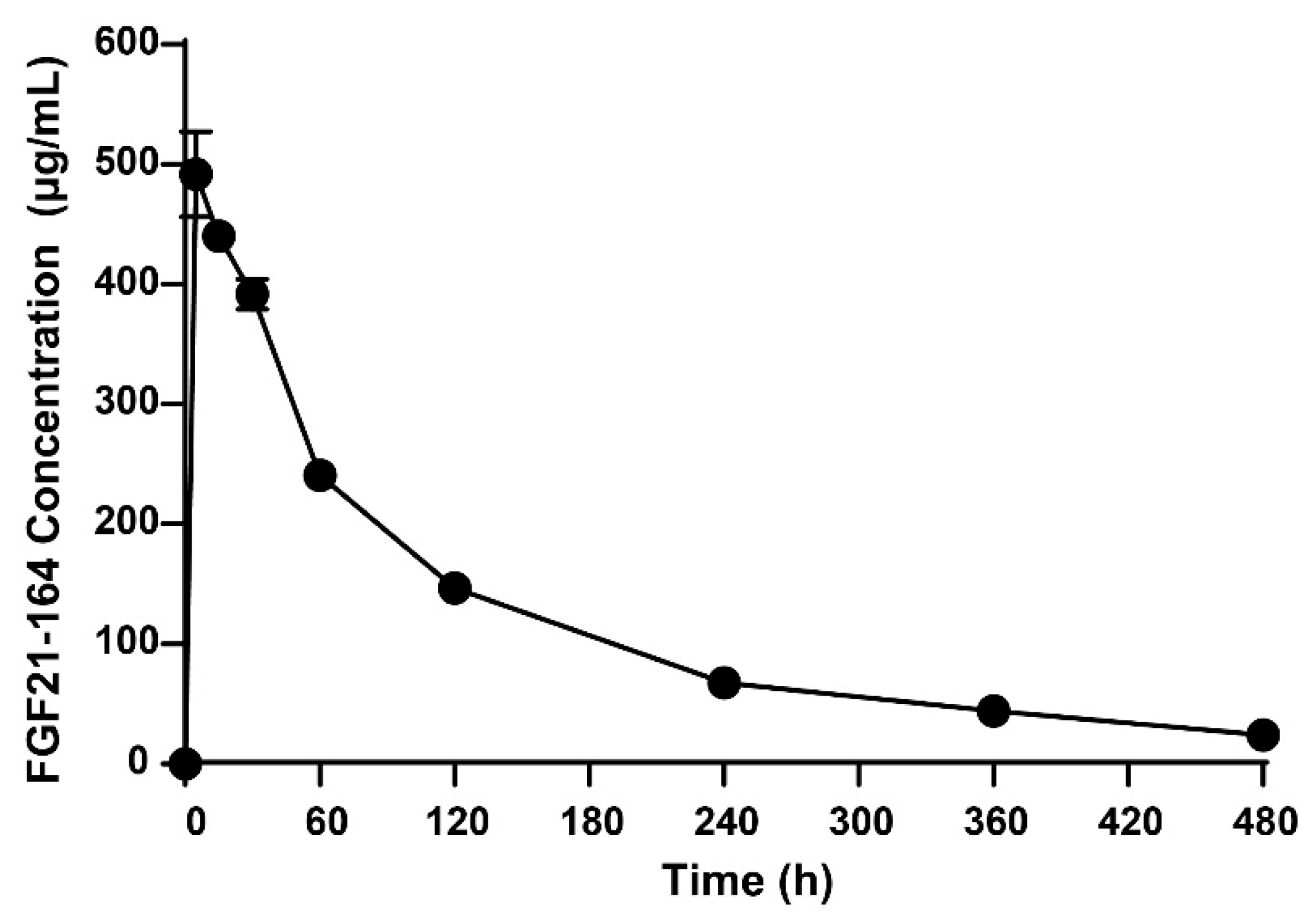
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Analysis of FGF21-164
2.5. Effect of Administering a Single Dose of FGF21-164 on ob/ob Mice
2.6. Effect of Repeated FGF21-164 Administration on DIO Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Construction of FGF21-164-Expressing Cell Lines
4.2. Identification, Fermentation, and Purification of FGF21-164
4.3. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Analysis of FGF21-164
4.4. Mass Spectroscopy
4.5. Circular Dichroism (CD) Analysis
4.6. Glycan Analysis of FGF21-164
4.7. 3T3-L1 Cell Culture and Differentiation
4.8. Glucose Uptake
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. Measurement of Oil Droplets in Adipocytes via Oil Red O Staining
4.11. Animal Experiments
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beenken, A.; Mohammadi, M. The FGF family: Biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzina, E.S.; Ung, P.M.-U.; Mohanty, J.; Tome, F.; Choi, J.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, A.; Schlessinger, J.; et al. Structures of ligand-occupied β-Klotho complexes reveal a molecular mechanism underlying endocrine FGF specificity and activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7819–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlein, C.; Talukdar, S.; Heine, M.; Fischer, A.W.; Krott, L.M.; Nilsson, S.K.; Brenner, M.B.; Heeren, J.; Scheja, L. FGF21 Lowers Plasma Triglycerides by Accelerating Lipoprotein Catabolism in White and Brown Adipose Tissues. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BonDurant, L.D.; Ameka, M.; Naber, M.C.; Markan, K.R.; Idiga, S.O.; Acevedo, M.R.; Walsh, S.A.; Ornitz, D.M.; Potthoff, M.J. FGF21 Regulates Metabolism Through Adipose-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 935–944.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, W.L.; Adams, A.C.; Brozinick, J.T.; Bui, H.H.; Miyauchi, Y.; Kusminski, C.M.; Bauer, S.M.; Wade, M.; Singhal, E.; Cheng, C.C.; et al. An FGF21-Adiponectin-Ceramide Axis Controls Energy Expenditure and Insulin Action in Mice. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, W.Y.; Leung, P.S. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 As an Emerging Therapeutic Target for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 672–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonenkov, A.; Wroblewski, V.J.; Koester, A.; Chen, Y.F.; Clutinger, C.K.; Tigno, X.T.; Hansen, B.C.; Shanafelt, A.B.; Etgen, G.J. The metabolic state of diabetic monkeys is regulated by fibroblast growth factor-21. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ishino, T.; Chen, G.; Rolzin, P.; Osothprarop, T.F.; Retting, K.; Li, L.; Jin, P.; Matin, M.J.; Huyghe, B.; et al. Development of a Novel Long-Acting Antidiabetic FGF21 Mimetic by Targeted Conjugation to a Scaffold Antibody. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 346, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillum, M.P.; Potthoff, M.J. FAP finds FGF21 easy to digest. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 1125–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunshee, D.R.; Bainbridge, T.W.; Kljavin, N.M.; Zavala-Solorio, J.; Schroeder, A.C.; Chan, R.; Corpuz, R.; Wong, M.; Zhou, W.; Deshmukh, G.; et al. Fibroblast Activation Protein Cleaves and Inactivates Fibroblast Growth Factor 21. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 5986–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Analogs for Treating Metabolic Disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.I.; Hecht, R.; Li, Y.-S.; Sun, J.; Belouski, E.; Hall, M.; Hager, T.; Yie, J.; Wang, W.; Winters, D.; et al. Rationale-Based Engineering of a Potent Long-Acting FGF21 Analog for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49345. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, H.; Miyahisa, M.; Chikamatsu, M.; Nishida, K.; Minayoshi, Y.; Takano, M.; Ichimizu, S.; Kobashigawa, Y.; Morioka, H.; Maeda, H.; et al. Development of a long acting FGF21 analogue-albumin fusion protein and its anti-diabetic effects. J. Control. Release 2020, 324, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Yang, R.; Geng, L.; Xu, A. Fibroblast Growth Factor–Based Pharmacotherapies for the Treatment of Obesity-Related Metabolic Complications. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Lam, K.S.L.; Xu, A. The therapeutic potential of FGF21 in metabolic diseases: From bench to clinic. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Yin, H. Mucin-fused myeloid-derived growth factor (MYDGF164) exhibits a prolonged serum half-life and alleviates fibrosis in chronic kidney disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 4136–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, R.P.; Quaggin, S.E. The cell biology of renal filtration. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 209, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Qiu, H. The Mechanistic Impact of N-Glycosylation on Stability, Pharmacokinetics, and Immunogenicity of Therapeutic Proteins. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1366–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higel, F.; Sandl, T.; Kao, C.Y.; Pechinger, N.; Sörgel, F.; Friess, W.; Wolschin, F.; Seidl, A. N-glycans of complex glycosylated biopharmaceuticals and their impact on protein clearance. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, S.; Tay, S.J.; Song, Z.; Yang, Y.; Walsh, I.; Pang, K.T. Enhancing pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of recombinant therapeutic proteins by manipulation of sialic acid content. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, B.; Donohoe, G.G.; O’Kennedy, R. Sialic acids: Carbohydrate moieties that influence the biological and physical properties of biopharmaceutical proteins and living cells. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Min, K.H.; Wang, Z.; Kim, J.; Jacobson, O.; Huang, P.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Yung, B.; Niu, G.; et al. Development of Sialic Acid-coated Nanoparticles for Targeting Cancer and Efficient Evasion of the Immune System. Theranostics 2017, 7, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonenkov, A.; Shiyanova, T.L.; Koester, A.; Ford, A.M.; Micanovic, R.; Galbreath, E.J.; Sandusky, G.E.; Hammond, L.J.; Moyers, J.S.; Owens, R.A.; et al. FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, L.; Yang, M.; Liu, H.; Boden, G.; Yang, G. The effects of fibroblast growth factor-21 knockdown and over-expression on its signaling pathway and glucose–lipid metabolism in vitro. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 348, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumiya, Y.; Bina, H.A.; Ouchi, N.; Akasaki, Y.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Walsh, K. FGF21 is an Akt-regulated myokine. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3805–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, D.H.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Shanafelt, A.B.; Michael, M.D.; Lynes, S.E.; Bina, H.A.; Li, C.Y.; Berglund, E.D. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Controls Glycemia via Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Flux and Insulin Sensitivity. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4084–4093. [Google Scholar]
- Kharitonenkov, A.; Moller, D.E.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.C.; Dunbar, J.D.; Schneider, M.A.; Bina, H.A.; Coskun, T. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Corrects Obesity in Mice. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 6018–6027. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.; Ishino, T.; Sievers, A.; Talukdar, S.; Chabot, J.R.; Tam, A.; Duan, W.; Kerns, K.; Sousa, E.; He, T.; et al. Glyco-engineered Long Acting FGF21 Variant with Optimal Pharmaceutical and Pharmacokinetic Properties to Enable Weekly to Twice Monthly Subcutaneous Dosing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, C.A.; Roberts, S.; Chilkoti, A. Fusion of fibroblast growth factor 21 to a thermally responsive biopolymer forms an injectable depot with sustained anti-diabetic action. J. Control. Release 2018, 277, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislaus, S.; Hecht, R.; Yie, J.; Hager, T.; Hall, M.; Spahr, C.; Wang, W.; Weiszmann, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; et al. A Novel Fc-FGF21 With Improved Resistance to Proteolysis, Increased Affinity Toward β-Klotho, and Enhanced Efficacy in Mice and Cynomolgus Monkeys. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Rossulek, M.; Dong, J.; Somayaji, V.; Weng, Y.; Clark, R.; Lanba, A.; Owen, B.M.; et al. A Long-Acting FGF21 Molecule, PF-05231023, Decreases Body Weight and Improves Lipid Profile in Non-human Primates and Type 2 Diabetic Subjects. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaich, G.; Chien, J.Y.; Fu, H.; Glass, L.C.; Deeg, M.A.; Holland, W.L.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Bumol, T.; Schilske, H.K.; Moller, D.E. The Effects of LY2405319, an FGF21 Analog, in Obese Human Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Rolph, T.; Knott, M.; Dubourg, J. FGF21 agonists: An emerging therapeutic for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis and beyond. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 562–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouri, N.; Lazas, D.; Loomba, R.; Frias, J.P.; Feng, S.; Tseng, L.; Balic, K.; Agollah, G.D.; Kwan, T.; Iyer, J.S.; et al. Clinical trial: Effects of pegozafermin on the liver and on metabolic comorbidities in subjects with biopsy-confirmed nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 58, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Bays, H.E.; Miller, M.; Cain, J.E.; Wasilewska, K.; Andrawis, N.S.; Parli, T.; Feng, S.; Sterling, L.; Tseng, L.; et al. The FGF21 analog pegozafermin in severe hypertriglyceridemia: A randomized phase 2 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1782–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Lawitz, E.J.; Frias, J.P.; Ortiz-Lasanta, G.; Johansson, L.; Franey, B.B.; Morrow, L.; Rosenstock, M.; Hartsfield, C.L.; Chen, C.Y.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of pegozafermin in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1b/2a multiple-ascending-dose study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Alkhouri, N.; Feng, S.; Tseng, L.; Agollah, G.D.; Mansbach, H.; Margalit, M.; Hartsfield, C.L.; Harrison, S.A. Pegozafermin Improved Liver Histology, Liver-related Non-invasive Tests (NITs) and Metabolic Profiles in an Open-label Cohort of a Phase 1b/2a Study in Subjects with Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2023, 142, 155454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kowdley, K.V.; Bhatt, D.L.; Alkhouri, N.; Frias, J.P.; Bedossa, P.; Harrison, S.A.; Lazas, D.; Barish, R.; et al. Randomized, Controlled Trial of the FGF21 Analogue Pegozafermin in NASH. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, G.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Leclercq, I.; Yeh, M.M.; Goldin, R.; Teoh, N.; Schuppan, D. Mouse Models of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2241–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Masuda, S.; Ogawa, H.; Kamisako, T. Gender-divergent expression of lipid and bile acid metabolism related genes in adult mice offspring of dams fed a high-fat diet. J. Biosci. 2018, 43, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zheng, S.L.; Liu, L.; Voglmeir, J. Development of a colorimetric PNGase activity assay. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 472, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moura e Dias, M.; dos Reis, S.A.; da Conceição, L.L.; Sediyama, C.M.N.d.O.; Pereira, S.S.; de Oliveira, L.L.; Gouveia Peluzio, M.d.C.; Martinez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I. Diet-induced obesity in animal models: Points to consider and influence on metabolic markers. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, P.; Wang, T.; Wang, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Yin, H. A Novel Recombinant Human FGF21 Analog with High Glycosylation Has a Prolonged Half-Life and Affects Glycemic and Body Weight Control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062672
Du P, Wang T, Wang R, Liu S, Wang H, Yin H. A Novel Recombinant Human FGF21 Analog with High Glycosylation Has a Prolonged Half-Life and Affects Glycemic and Body Weight Control. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062672
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Pei, Ting Wang, Rong Wang, Shang Liu, Hang Wang, and Hongping Yin. 2025. "A Novel Recombinant Human FGF21 Analog with High Glycosylation Has a Prolonged Half-Life and Affects Glycemic and Body Weight Control" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062672
APA StyleDu, P., Wang, T., Wang, R., Liu, S., Wang, H., & Yin, H. (2025). A Novel Recombinant Human FGF21 Analog with High Glycosylation Has a Prolonged Half-Life and Affects Glycemic and Body Weight Control. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062672



