Gene Expression Changes in the Spleen, Lungs, and Liver of Wistar Rats Exposed to β-Emitted 31SiO2 Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Radiation Doses
2.2. Body, Spleen, Lung, and Liver Weights
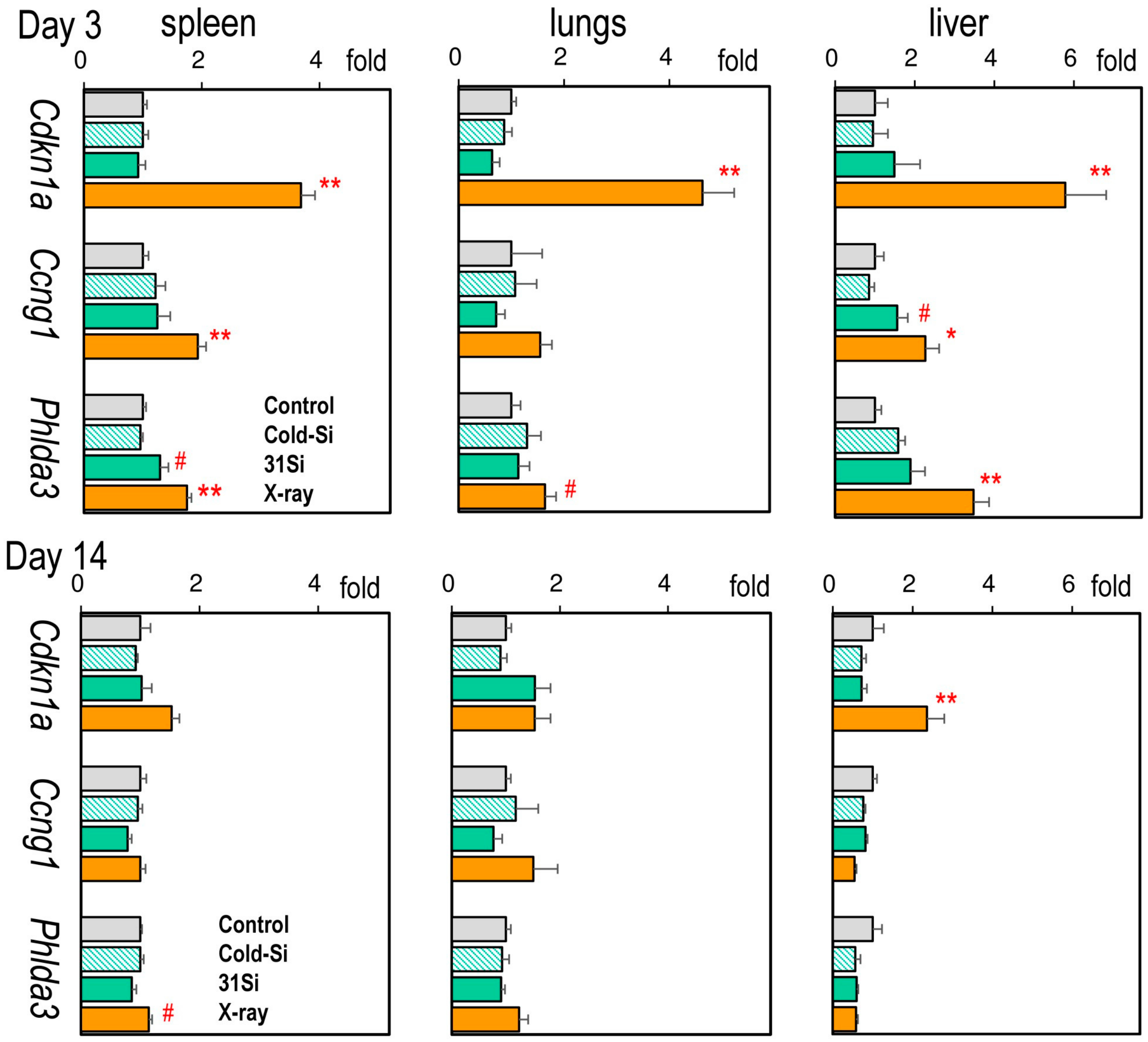
2.3. mRNA Expression of the Radiation Dose–Response Marker Genes Cdkn1a, Ccng1, and Phlda3
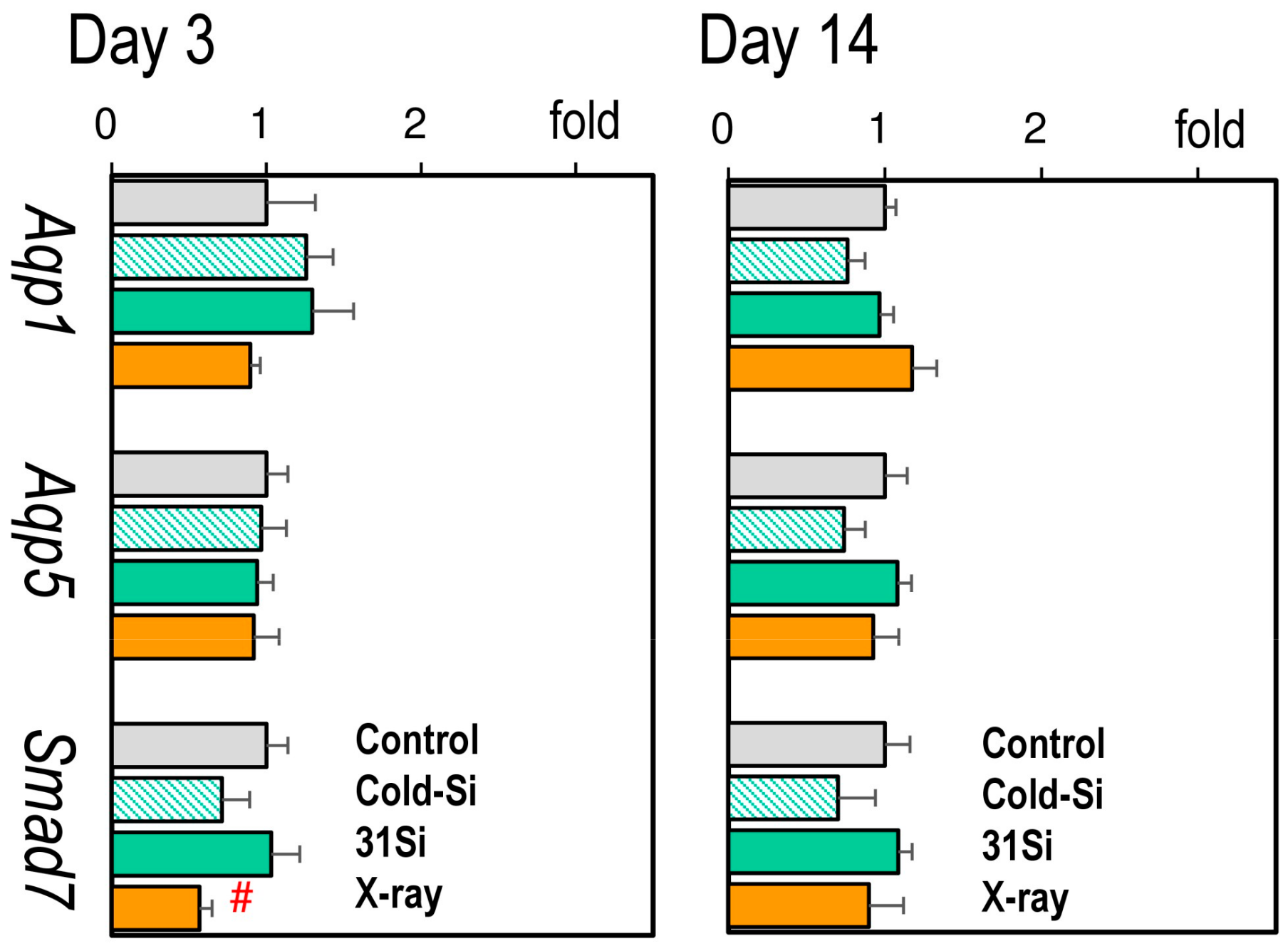
2.4. mRNA Expression of the Radiation-Sensitive Pathophysiological Marker Genes Aqp1, Aqp5, and Smad7 in the Lungs
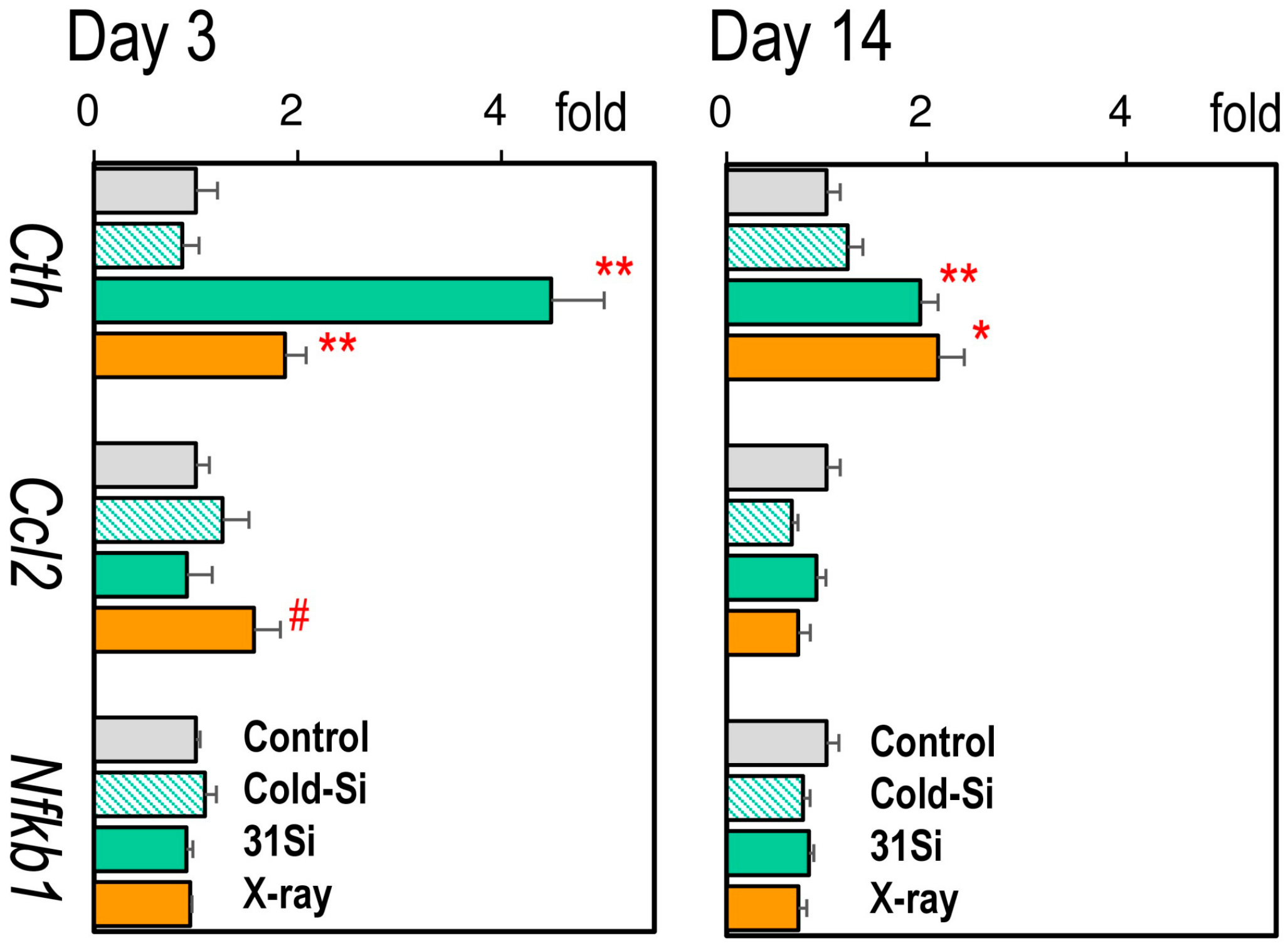
2.5. mRNA Expression of the Radiation-Sensitive Pathophysiological Marker Genes Cth, Ccl2, and Nfkb1 in the Liver
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Irradiation and Dosimetry
4.3. QRT Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imanaka, T.; Endo, S.; Tanaka, K.; Shizuma, K. Gamma-ray exposure from neutron-induced radionuclides in soil in Hiroshima and Nagasaki based on DS02 calculations. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2008, 47, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, K.; Ohtaki, M.; Yasuda, H. Solid cancer mortality risk among a cohort of Hiroshima early entrants after the atomic bombing, 1970–2010: Implications regarding health effects of residual radiation. J. Radiat. Res. 2022, 63, i45–i53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Endo, S.; Imanaka, T.; Shizuma, K.; Hasai, H.; Hoshi, M. Skin dose from neutron-activated soil for early entrants following the A-bomb detonation in Hiroshima: Contribution from β and γ rays. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2008, 47, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, N.; Ruslanova, B.; Abishev, Z.; Chaizhunussova, N.; Shabdarbayeva, D.; Amantayeva, G.; Farida, R.; Sandybayev, M.; Nagano, K.; Zhumadilov, K.; et al. Biological impacts on the lungs in rats internally exposed to radioactive 56MnO2 particle. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mück, K.; Pröhl, G.; Likhtarev, I.; Kovgan, L.; Golikov, V.; Zeger, J. Reconstruction of the inhalation dose in the 30-km zone after the Chernobyl accident. Health Phys. 2002, 82, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauser, G.; Brandl, A.; Johnson, T.E. Comparison of the Chernobyl and Fukushima nuclear accidents: A review of the environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 800–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanenko, V.; Kaprin, A.; Ivanov, S.; Shegay, P.; Bogacheva, V.; Sato, H.; Shichijo, K.; Toyoda, S.; Kawano, N.; Ohtaki, M.; et al. Microdistribution of internal radiation dose in biological tissues exposed to 56Mn dioxide microparticles. J. Radiat. Res. 2022, 63, i21–i25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabacik, S.; MacKay, A.; Tamber, N.; Manning, G.; Finnon, P.; Paillier, F.; Ashworth, A.; Bouffler, S.; Badie, C. Gene expression following ionising radiation: Identification of biomarkers for dose estimation and prediction of individual response. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2011, 87, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.J.; Wang, W.W.; Chen, S.W.; Shen, Q.; Min, R. Radiation dose effect of DNA repair-related gene expression in mouse white blood cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011, 17, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Smilenov, L.B.; Elliston, C.D.; Amundson, S.A. Radiation Dose-Rate Effects on Gene Expression in a Mouse Biodosimetry Model. Radiat. Res. 2015, 184, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Ye, S.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Shao, C. Radioprotective role of H2S/CSE pathway in Chang liver cells. Mutat. Res. 2012, 738–739, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkman, A.S. Role of aquaporins in lung liquid physiology. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2007, 159, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.Y.; Zhao, Y.X.; Zhong, W.; Liu, D.W.; Chen, Y.Z.; Qin, L.L.; Bai, L.; Liu, D. The expression of aquaporins 1 and 5 in rat lung after thoracic irradiation. J. Radiat. Res. 2014, 55, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, M.; Chen, T.; Hong, J. Glycyrrhetinic acid alleviates radiation-induced lung injury in mice. J. Radiat. Res. 2017, 58, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanenko, V.; Sato, H.; Kaprin, A.; Fujimoto, N.; Kushugulova, A.; Ivanov, S.; Shegay, P.; Bogacheva, V.; Petukhov, A.; Zhumadilov, K.; et al. Internal radiation dose estimates in organs of Wistar rats exposed to sprayed neutron-activated 31SiO2 microparticles: First results of international multicenter study. J. Radiat. Res. 2024, 65, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, G.D.; Egbert, S.D.; Al-Nabulsi, I.; Bailiff, I.K.; Beck, H.L.; Belukha, I.G.; Cockayne, J.E.; Cullings, H.M.; Eckerman, K.F.; Granovskaya, E.; et al. Workshop Report on Atomic Bomb Dosimetry—Review of Dose Related Factors for the Evaluation of Exposures to Residual Radiation at Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Health Phys. 2015, 109, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruslanova, B.; Abishev, Z.; Chaizhunussova, N.; Shabdarbayeva, D.; Tokesheva, S.; Amantayeva, G.; Kairkhanova, Y.; Stepanenko, V.; Hoshi, M.; Fujimoto, N. Hepatic Gene Expression Changes in Rats Internally Exposed to Radioactive 56MnO2 Particles at Low Doses. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jiang, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, X.; Ling, M. Curcumin protects radiation-induced liver damage in rats through the NF-κB signaling pathway. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Matsuzawa, S.; Fukunaga, A.; Itoh, T.; Kondo, S. Dose and dose-rate effects of X rays and fission neutrons on lymphocyte apoptosis in p53(+/+) and p53(-/-) mice. J. Radiat. Res. 2000, 41, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raventos, A. An abscopal effect of x-ray upon mouse spleen weight. Radiat. Res. 1954, 1, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daino, K.; Ichimura, S.; Nenoi, M. Early induction of CDKN1A (p21) and GADD45 mRNA by a low dose of ionizing radiation is due to their dose-dependent post-transcriptional regulation. Radiat. Res. 2002, 157, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meadows, S.K.; Dressman, H.K.; Muramoto, G.G.; Himburg, H.; Salter, A.; Wei, Z.; Ginsburg, G.S.; Ginsburg, G.; Chao, N.J.; Nevins, J.R.; et al. Gene expression signatures of radiation response are specific, durable and accurate in mice and humans. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryankalayil, M.J.; Bylicky, M.A.; Martello, S.; Chopra, S.; Sproull, M.; May, J.M.; Shankardass, A.; MacMillan, L.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Dalo, J.; et al. Microarray analysis identifies coding and non-coding RNA markers of liver injury in whole body irradiated mice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-J.; Majumder, Z.R.; Jeoung, D.-I.; Lee, H.-j.; Kim, S.-H.; Bae, S.; Lee, Y.-S. Organ-specific gene expressions in C57BL/6 mice after exposure to low-dose radiation. Radiat. Res. 2006, 165, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik, A.; Delmar, P.; Bosse, S.; Sainz, L.; Petat, C.; Pietu, G.; Thierry, D.; Tronik-Le Roux, D. Changes in transcriptome after in vivo exposure to ionising radiation reveal a highly specialised liver response. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 656–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towne, J.E.; Harrod, K.S.; Krane, C.M.; Menon, A.G. Decreased expression of aquaporin (AQP)1 and AQP5 in mouse lung after acute viral infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 22, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.S.M.; Amin, N.E.D.; Abdel Fattah, S.M.; Abd El-Rahman, O. Ameliorative effect of kefir against γ-irradiation induced liver injury in male rats: Impact on oxidative stress and inflammation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 35161–35173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eassawy, M.M.T.; Salem, A.A.; Ismail, A.F.M. Biochemical study on the protective effect of curcumin on acetaminophen and gamma-irradiation induced hepatic toxicity in rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 36, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.B.; Stock, V.; Cara-Carmona, J.; Lisicki, E.; Shopova, S.; Fessard, V.; Braeuning, A.; Sieg, H.; Böhmert, L. Micro- And nanoplastics-current state of knowledge with the focus on oral uptake and toxicity. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 4350–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMinn, L.H.; Hodges, G.M.; Carr, K.E. Gastrointestinal uptake and translocation of microparticles in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. J. Anat. 1996, 189, 553–559. [Google Scholar]
- Gulec, S.A.; Sztejnberg, M.L.; Siegel, J.A.; Jevremovic, T.; Stabin, M. Hepatic structural dosimetry in 90Y microsphere treatment: A Monte Carlo modeling approach based on lobular microanatomy. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.M.; Romero, A.S.; Merkley, S.D.; Meyer-Hagen, J.L.; Forbes, C.; El Hayek, E.; Sciezka, D.P.; Templeton, R.; Gonzalez-Estrella, J.; Jin, Y.; et al. In Vivo Tissue Distribution of Polystyrene or Mixed Polymer Microspheres and Metabolomic Analysis after Oral Exposure in Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2024, 132, 47005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, M.; Aquilina, G.; Castle, L.; Degen, G.; Engel, K.H.; Fowler, P.; Frutos Fernandez, M.J.; Furst, P.; Gurtler, R.; Husoy, T.; et al. Re-evaluation of silicon dioxide (E 551) as a food additive in foods for infants below 16 weeks of age and follow-up of its re-evaluation as a food additive for uses in foods for all population groups. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8880. [Google Scholar]
- Marques Da Silva, V.; Benjdir, M.; Montagne, P.; Pairon, J.-C.; Lanone, S.; Andujar, P. Pulmonary Toxicity of Silica Linked to Its Micro- or Nanometric Particle Size and Crystal Structure: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merget, R.; Bauer, T.; Küpper, H.U.; Philippou, S.; Bauer, H.D.; Breitstadt, R.; Bruening, T. Health hazards due to the inhalation of amorphous silica. Arch. Toxicol. 2002, 75, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuya, Y.; Satou, Y.; Hamada, N.; Date, H.; Ishikawa, M.; Sato, T. DNA damage induction during localized chronic exposure to an insoluble radioactive microparticle. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Groups | Initial Body Weight (g) | Body Weight (g) | Spleen (g/kg bw) | Lung (g/kg bw) | Liver (g/kg bw) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 3 | Control | 271 ± 30 | 277 ± 29 | 4.8 ± 0.84 | 8.4 ± 0.46 | 28 ± 1.9 |
| Cold-Si | 298 ± 27 | 297 ± 22 | 4.2 ± 0.30 | 9.9 ± 2.47 | 31 ± 1.7 | |
| 31Si | 303 ± 26 | 309 ± 26 | 3.2 ± 0.36 # | 8.4 ± 1.38 | 29 ± 1.1 | |
| X-ray | 283 ± 27 | 288 ± 26 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 11.6 ± 4.17 | 29 ± 1.1 | |
| Day 14 | Control | 293 ± 33 | 314 ± 29 | 3.5 ± 0.22 | 8.5 ± 1.05 | 26 ± 0.7 |
| Cold-Si | 291 ± 39 | 300 ± 39 | 4.1 ± 0.60 | 10.2 ± 0.85 | 30 ± 1.0 | |
| 31Si | 299 ± 37 | 319 ± 37 | 4.3 ± 0.64 | 9.2 ± 0.75 | 31 ± 1.9 | |
| X-ray | 295 ± 34 | 319 ± 38 | 3.3 ± 0.25 | 12.9 ± 3.84 | 32 ± 1.7 | |
| Gene | GenBank Accession # | Q-PCR Primer Sequences (5′ -> 3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | ||
| Cdkn1a | NM_080782 | TGTCCGACCTGTTCCACACA | CGTCTCAGTGGCGAAGTCAA |
| Ccng1 | NM_012923 | CGTGCCACTGCAGGATCATA | AAGGTCAGATCTCGGCCACTT |
| Phlda3 | NM_001012206 | AAGCCGTGGAGTGCGTGGAGAG | GTCTGGATGGCCTGTTGATTC |
| Aqp1 | NM_012778 | CCACTGGAGAGAAACCAGACG | CTGAGCAGAAGCCCCAGTGT |
| Aqp5 | NM_012779 | ATGCGCTGAACAACAACACAAC | GTGACAGACAAGCCAATGGATAAG |
| Smad7 | NM_030858 | TTGCTGTGAATCTTACGGGAAG | GGTTTGAGAAAATCCATCGGGT |
| Cth | NM_017074 | TCCCCGGGTAGAAAAGGTTATT | TTGAGGAAGACCTGAGCATGC |
| Ccl2 | NM_031530 | AAGCCAGATCTCTCTTCCTCCA | CAGCAACTGTGAACAACAGGC |
| Nfkb | NM_001276711 | GGGCTACACAGAGGCCATTG | TCTCGGAGCTCATCTATGTGCT |
| Actb | NM_031144.3 | TTGTCCCTGTATGCCTCTGGTC | TGAGGTAGTCTGTCAGGTCCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujimoto, N.; Mukhanbetzhanov, N.; Zhetkenev, S.; Chulenbayeva, L.; Fazylov, T.; Mukhortov, M.; Sato, H.; Zhumadilov, K.; Stepanenko, V.; Kaprin, A.; et al. Gene Expression Changes in the Spleen, Lungs, and Liver of Wistar Rats Exposed to β-Emitted 31SiO2 Particles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062693
Fujimoto N, Mukhanbetzhanov N, Zhetkenev S, Chulenbayeva L, Fazylov T, Mukhortov M, Sato H, Zhumadilov K, Stepanenko V, Kaprin A, et al. Gene Expression Changes in the Spleen, Lungs, and Liver of Wistar Rats Exposed to β-Emitted 31SiO2 Particles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062693
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujimoto, Nariaki, Nurislam Mukhanbetzhanov, Sanzhar Zhetkenev, Laura Chulenbayeva, Timur Fazylov, Mikhail Mukhortov, Hitoshi Sato, Kassym Zhumadilov, Valeriy Stepanenko, Andrey Kaprin, and et al. 2025. "Gene Expression Changes in the Spleen, Lungs, and Liver of Wistar Rats Exposed to β-Emitted 31SiO2 Particles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062693
APA StyleFujimoto, N., Mukhanbetzhanov, N., Zhetkenev, S., Chulenbayeva, L., Fazylov, T., Mukhortov, M., Sato, H., Zhumadilov, K., Stepanenko, V., Kaprin, A., Ivanov, S., Shegay, P., Hoshi, M., & Kushugulova, A. (2025). Gene Expression Changes in the Spleen, Lungs, and Liver of Wistar Rats Exposed to β-Emitted 31SiO2 Particles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062693






