Identification of a Novel Antagonist of BRS-3 from Natural Products and Its Protective Effects Against H2O2-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
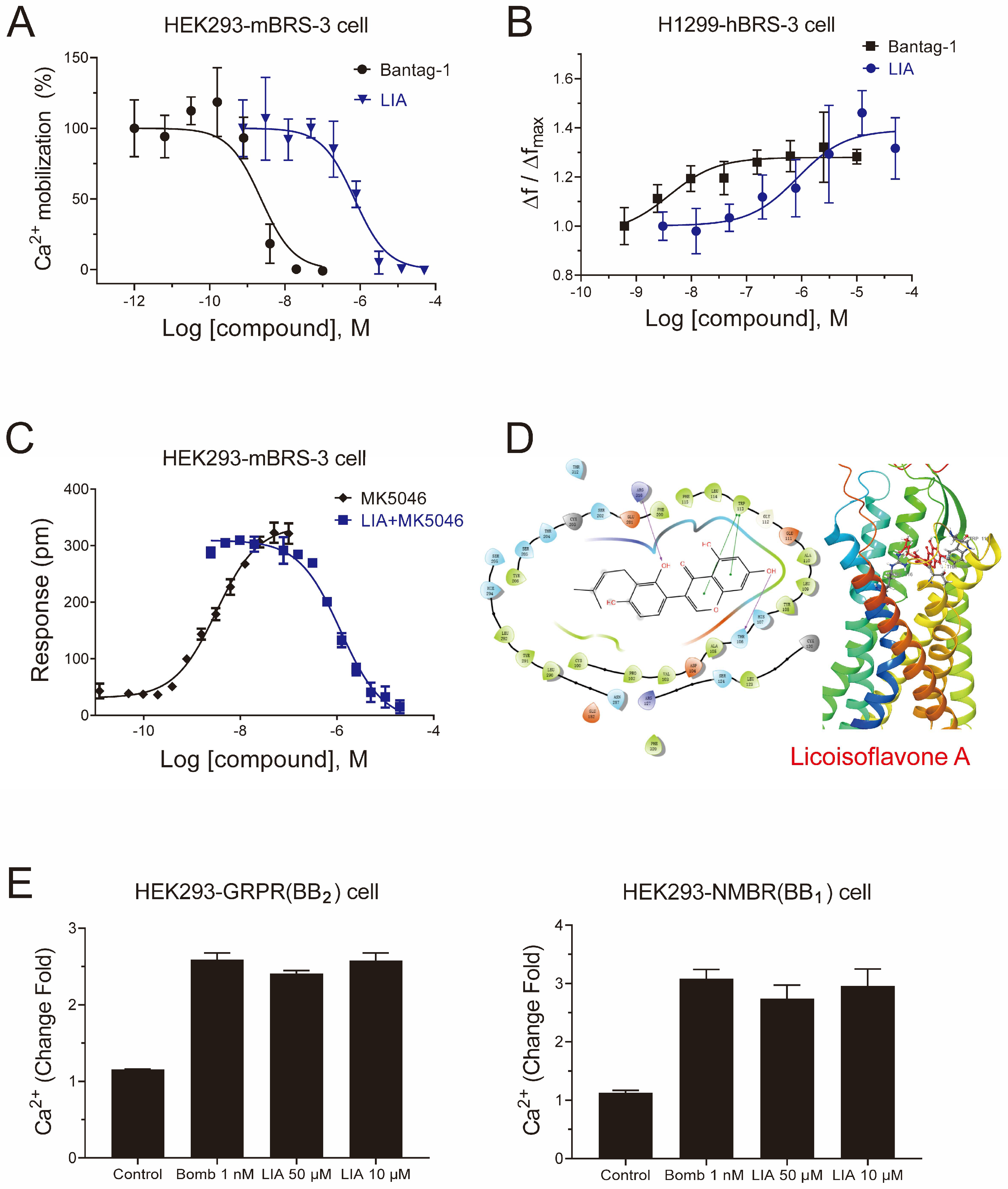
2.1. LIA Is a Novel Antagonist with a High Selectivity of BRS-3
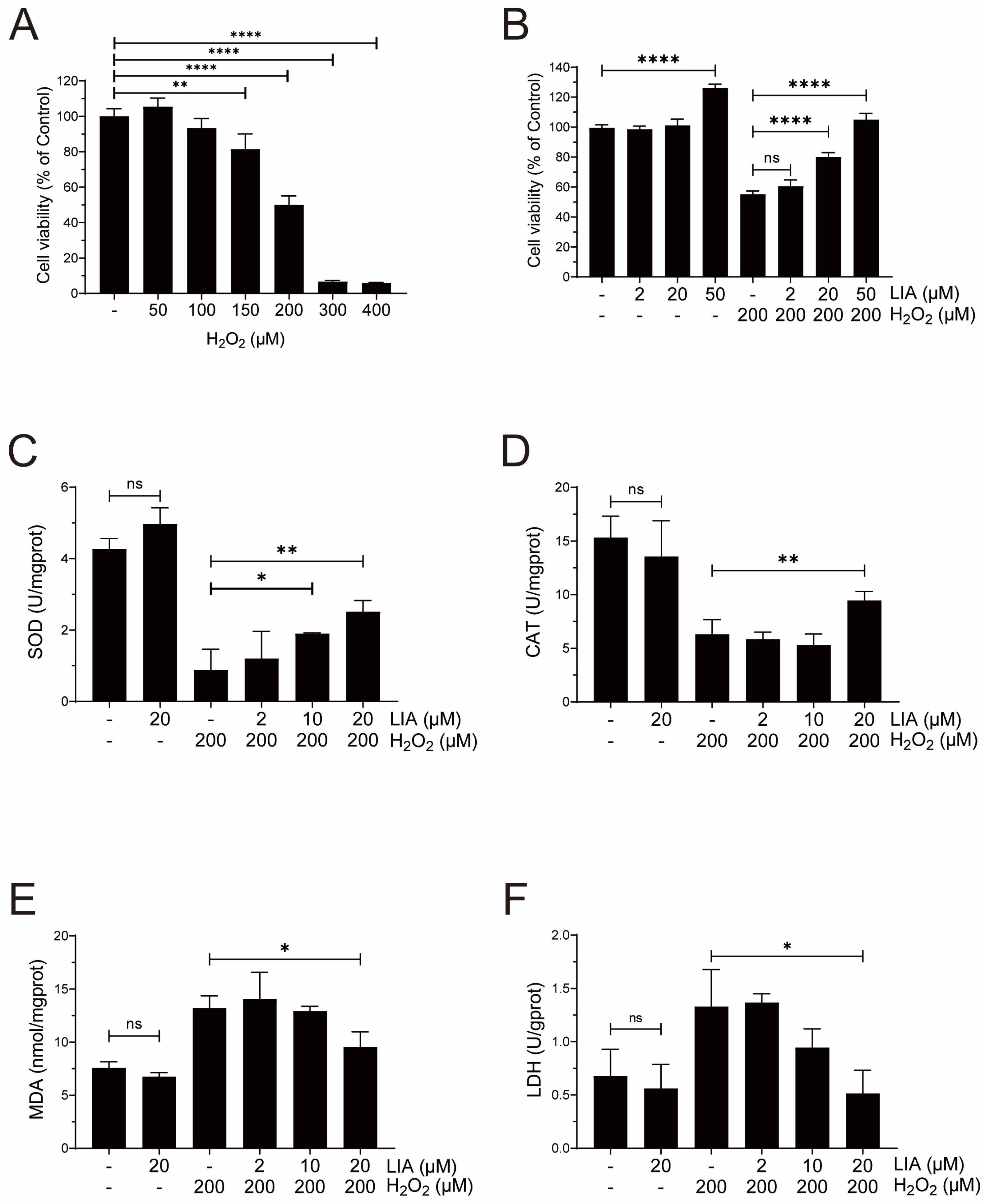
2.2. LIA Protects Cardiomyocytes Against H2O2-Induced Injury in H9c2 Cells
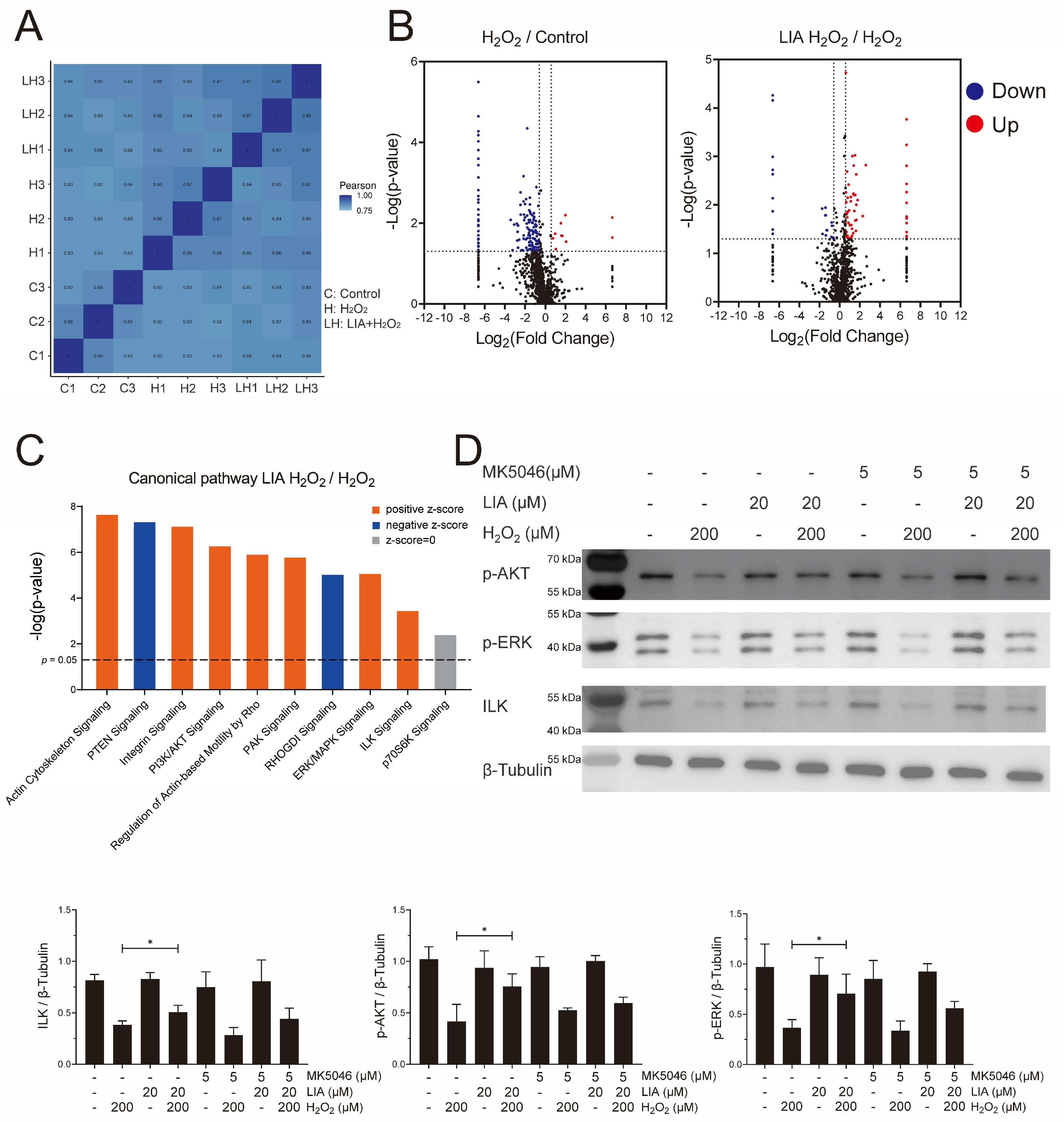
2.3. Proteomics Analysis of the Effect of LIA in H9c2 Cells Induced by H2O2
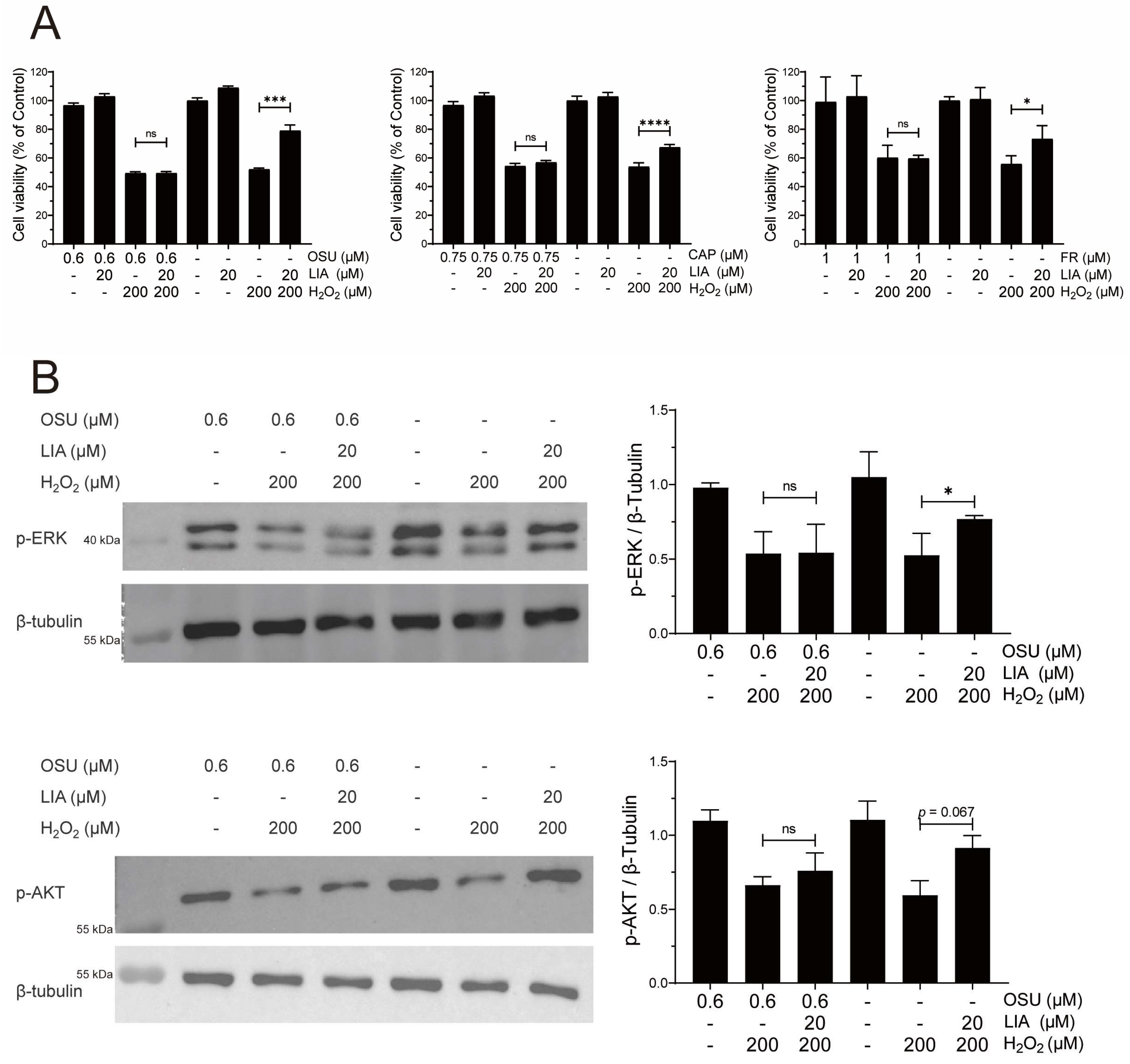
2.4. LIA Protects H2O2-Induced H9c2 Cell Injury via ILK/AKT and ILK/ERK Signaling Pathways
2.5. LIA Exerts Protective Effects Against H2O2-Induced Injury in Primary Rat and Mouse Cardiomyocytes
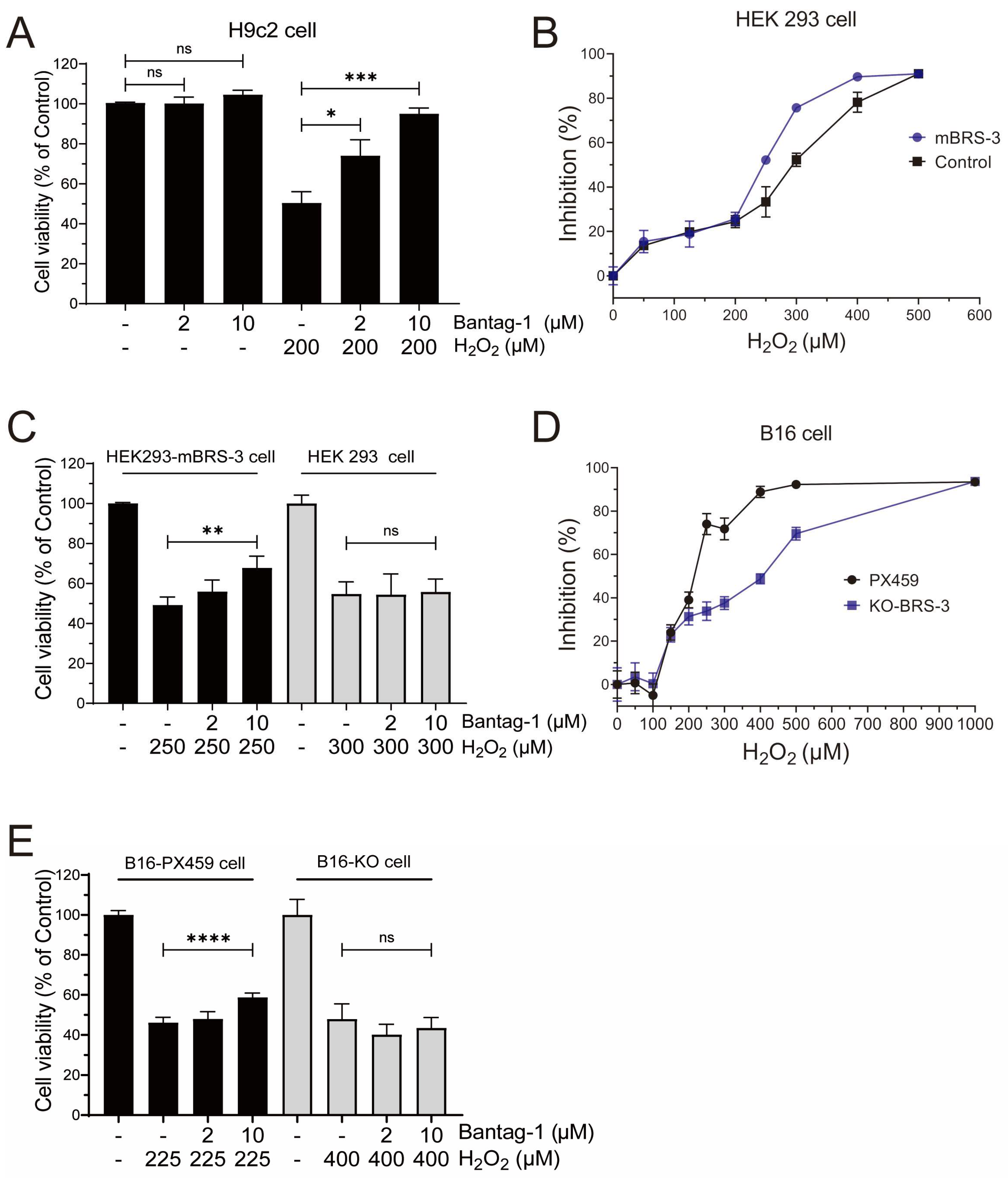
2.6. BRS-3 Inhibition Regulates H2O2-Induced Cell Injury
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Cell Culture and Experiment Design
4.3. Calcium Mobilization
4.4. Dynamic Mass Redistribution (DMR) Assay
4.5. Measurement of Inositol Phosphates (IP1) Accumulation
4.6. Cell Viability Analysis
4.7. Malondialdehyde (MDA), Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH), and Catalase (CAT) Determination
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.9. Proteomics Analysis by LC-MS/MS
4.10. Western Blot Assay
4.11. Molecular Docking
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BRS-3/BB3 | Bombesin receptor subtype-3 |
| DMR | Dynamic mass redistribution |
| FLIPR | Fluorometric imaging plate reader |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| GRPR/BB2 | Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| HTRF | Homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence |
| iBAQ | Intensity-based absolute quantification |
| ILK | Integrin-linked kinase |
| LIA | Licoisoflavone A |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| NMBR/BB1 | Neuromedin B receptor |
References
- Insel, P.A.; Snead, A.; Murray, F.; Zhang, L.; Yokouchi, H.; Katakia, T.; Kwon, O.; Dimucci, D.; Wilderman, A. GPCR expression in tissues and cells: Are the optimal receptors being used as drug targets? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 1613–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanova, E.V.; Sweedler, J.V. Peptidomics for the discovery and characterization of neuropeptides and hormones. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Qu, X.; Qin, X.Q. Bombesin-like peptides and their receptors: Recent findings in pharmacology and physiology. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2015, 22, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Reitman, M.L. Bombesin-Like Receptor 3: Physiology of a Functional Orphan. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liang, P.; Liu, D.; Yuan, F.; Chen, G.C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Bombesin Receptor Subtype-3 in Human Diseases. Arch. Med. Res. 2019, 50, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, H.; Feighner, S.D.; Hreniuk, D.L.; Iwaasa, H.; Sailer, A.W.; Pan, J.; Reitman, M.L.; Kanatani, A.; Howard, A.D.; Tan, C.P. Characterization of the bombesin-like peptide receptor family in primates. Genomics 2004, 84, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, P.; Mantey, S.A.; Nuche-Berenguer, B.; Reitman, M.L.; González, N.; Coy, D.H.; Jensen, R.T. Comparative pharmacology of bombesin receptor subtype-3, nonpeptide agonist MK-5046, a universal peptide agonist, and peptide antagonist Bantag-1 for human bombesin receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 347, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrowska-Hägerstrand, M.; Wróbel, A.; Rychlik, B.; Bartosz, G.; Söderström, T.; Shirataki, Y.; Motohashi, N.; Molnár, J.; Michalak, K.; Hägerstrand, H. Monitoring of MRP-like activity in human erythrocytes: Inhibitory effect of isoflavones. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2001, 27, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Liu, N.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Baruscotti, M.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y. High content screening identifies licoisoflavone A as a bioactive compound of Tongmaiyangxin Pills to restrain cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via activating Sirt3. Phytomedicine 2020, 68, 153171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, W.; Fan, N.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Rong, J. A four-compound remedy AGILe protected H9c2 cardiomyocytes against oxygen glucose deprivation via targeting the TNF-α/NF-κB pathway: Implications for the therapy of myocardial infarction. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1050970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, J.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of oridonin as a novel agonist for BRS-3. Phytomedicine 2022, 100, 154085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Cui, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, S.; Jia, J.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of Dimethyl Shikonin Oxime 5a, a Potent, Selective Bombesin Receptor Subtype-3 Agonist for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 8011–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, P.; Savion, S. Differentiation of rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating nonmyocardial cells. Cross-striations, ultrastructure, and chronotropic response to isoproterenol. Circ. Res. 1982, 50, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Wu, L.H.; Yu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, C.R.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of exogenous ligands for orphan receptor BRS-3 from Chinese herbs. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2022, 47, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Ye, R.D.; Zhang, Y. Identification of Alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang as Dopamine D1 Receptor Antagonists by Using CRE-Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay. Molecules 2018, 23, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitman, M.L.; Dishy, V.; Moreau, A.; Denney, W.S.; Liu, C.; Kraft, W.K.; Mejia, A.V.; Matson, M.A.; Stoch, S.A.; Wagner, J.A.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of MK-5046, a bombesin receptor subtype-3 (BRS-3) agonist, in healthy patients. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 52, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.M.; Chen, H.; Dobbelaar, P.H.; Dong, Y.; Fong, T.M.; Gagen, K.; Gorski, J.; He, S.; Howard, A.D.; Jian, T.; et al. Regulation of energy homeostasis by bombesin receptor subtype-3: Selective receptor agonists for the treatment of obesity. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, T.W.; Mantey, S.A.; Moreno, P.; Nakamura, T.; Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Jensen, R.T. ML-18 is a non-peptide bombesin receptor subtype-3 antagonist which inhibits lung cancer growth. Peptides 2015, 64, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, K.L.; Maguy, A.; Qi, X.Y.; Naud, P.; Xiong, F.; Tadevosyan, A.; Shi, Y.F.; Chartier, D.; Tardif, J.C.; Dobrev, D.; et al. Loss of cardiomyocyte integrin-linked kinase produces an arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy in mice. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, Y.Y.; Sun, J.E.; Lin, W.H.; Zhou, R.X. ILK-PI3K/AKT pathway participates in cutaneous wound contraction by regulating fibroblast migration and differentiation to myofibroblast. Lab. Investig. 2016, 96, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, N.; Huang, K.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Wang, L. An injectable silk sericin hydrogel promotes cardiac functional recovery after ischemic myocardial infarction. Acta. Biomater. 2016, 41, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawilska, J.B.; Urbańska, A.; Sokołowska, P. Orexins/hypocretins stimulate accumulation of inositol phosphate in primary cultures of rat cortical neurons. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Brs3 | Forward | 5′-GAAACATCAAGCTCTGCCGTCT-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-CCACTGAAATGATCACAGCAT-3′ | |
| Actb | Forward | 5′-CGAGTACAACCTTCTTGCAGC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-TATCGTCATCCATGGCGAACTG-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Wu, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, H.; Fang, M.; Liang, H.; Guo, M.; Chen, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Identification of a Novel Antagonist of BRS-3 from Natural Products and Its Protective Effects Against H2O2-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062745
Lu J, Wu L, Zhu J, Zhou H, Fang M, Liang H, Guo M, Chen M, Zhu Y, Wang J, et al. Identification of a Novel Antagonist of BRS-3 from Natural Products and Its Protective Effects Against H2O2-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062745
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jihong, Lehao Wu, Jianzheng Zhu, Han Zhou, Mingzhu Fang, Hongshuo Liang, Miao Guo, Mo Chen, Yuhang Zhu, Jixia Wang, and et al. 2025. "Identification of a Novel Antagonist of BRS-3 from Natural Products and Its Protective Effects Against H2O2-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062745
APA StyleLu, J., Wu, L., Zhu, J., Zhou, H., Fang, M., Liang, H., Guo, M., Chen, M., Zhu, Y., Wang, J., Xiao, H., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Identification of a Novel Antagonist of BRS-3 from Natural Products and Its Protective Effects Against H2O2-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062745







