Exploring a Role for the Arabidopsis TIR-X Gene (TIRP) in the Defense Against Pathogenic Fungi or Insect Herbivory Attack
Abstract
1. Introduction
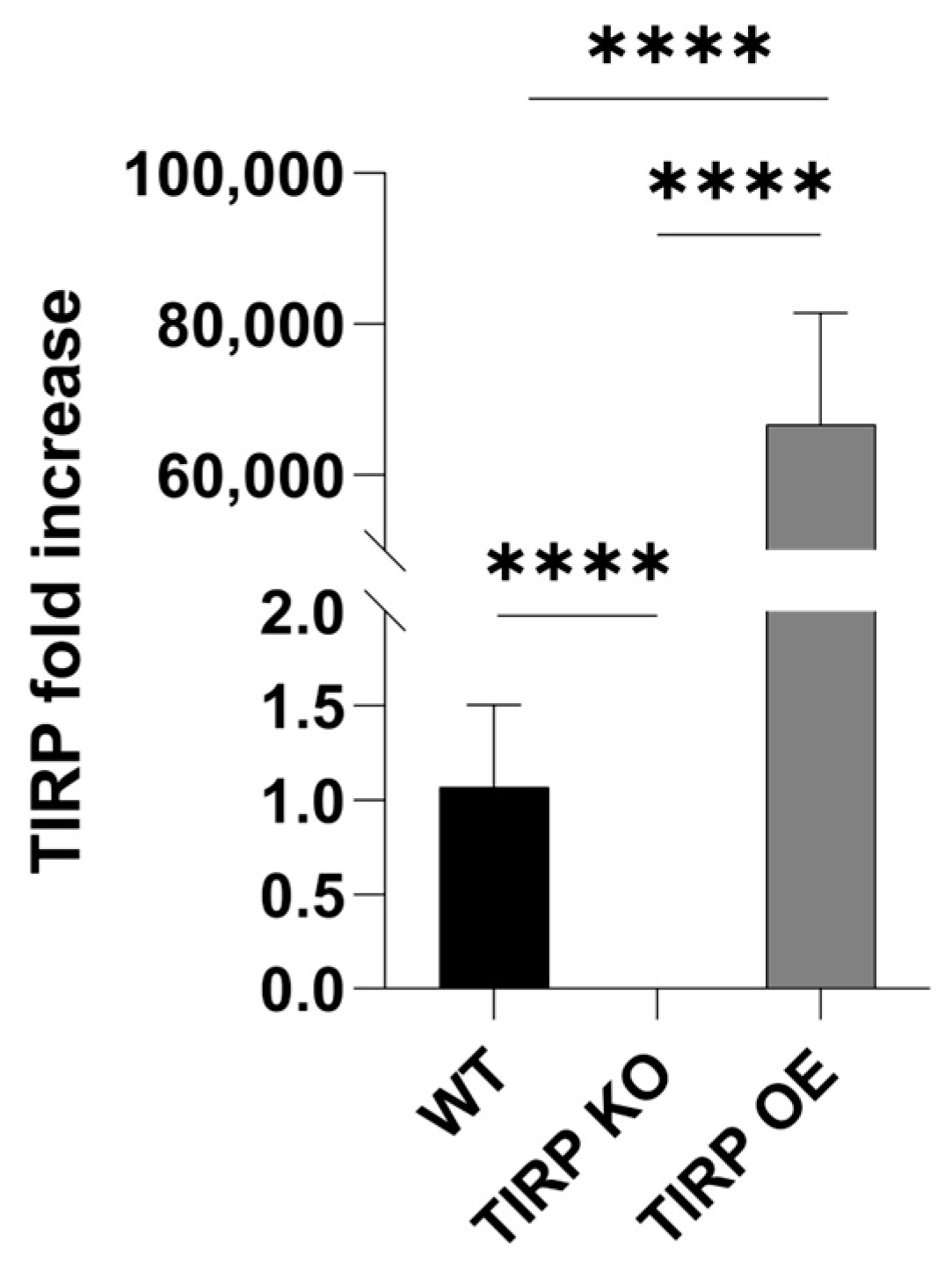
2. Results
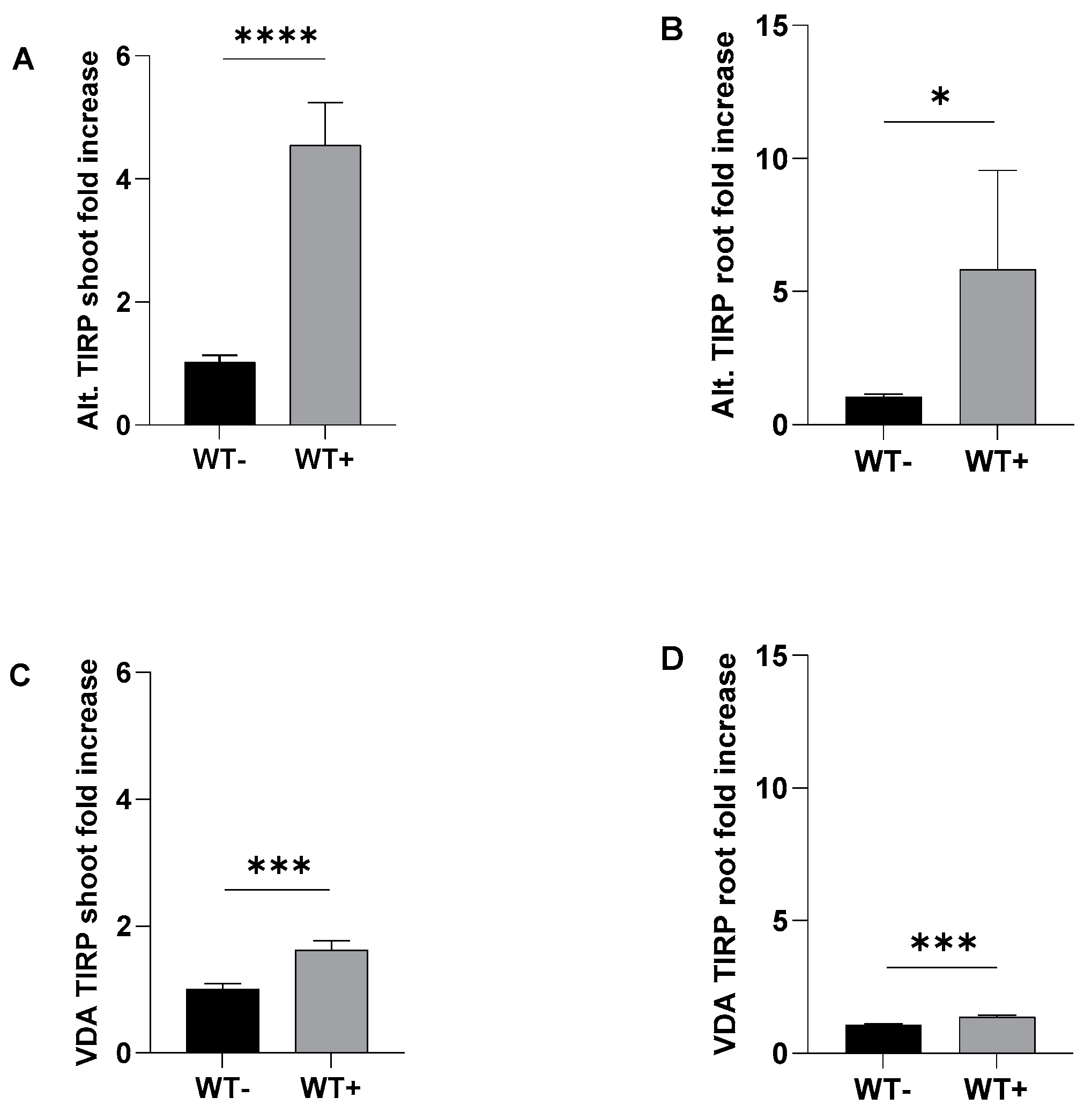
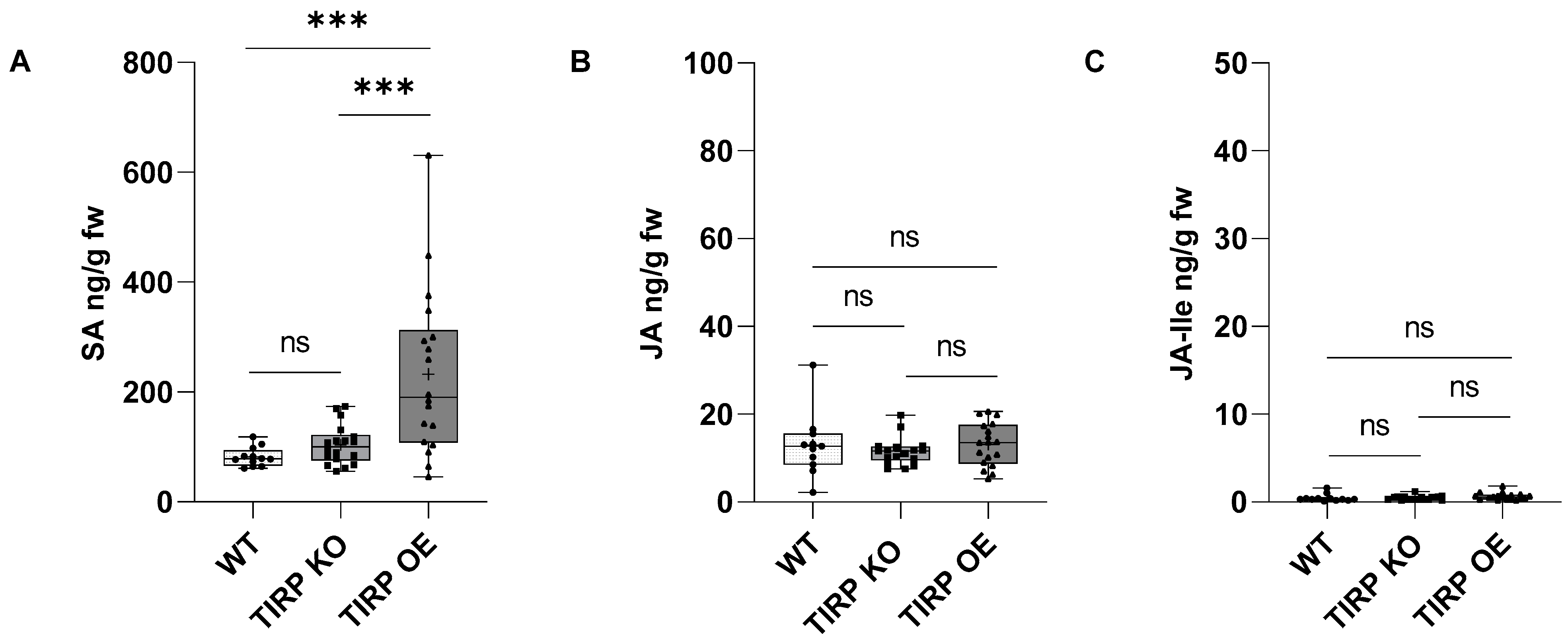
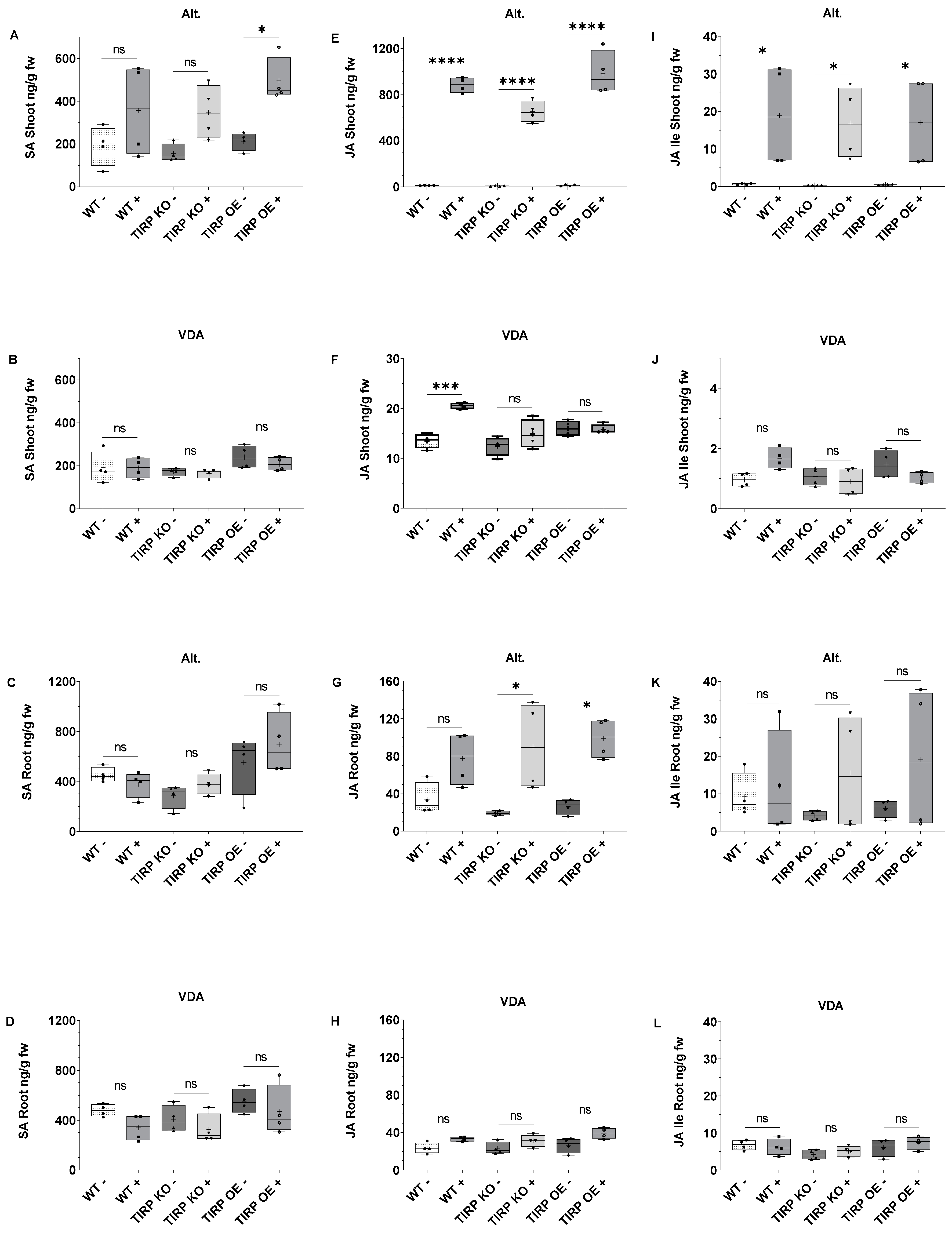
2.1. Fungal Treatments
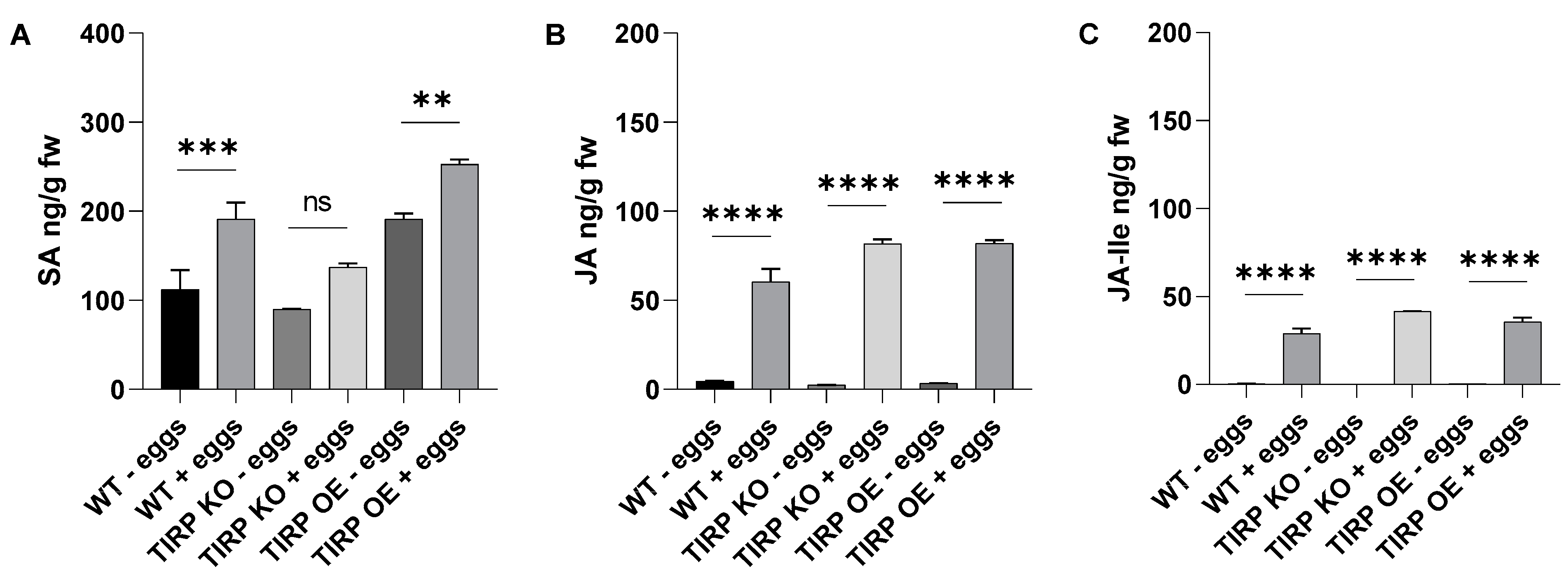
2.2. Insect Herbivore Treatments
3. Discussion
3.1. Alternaria brassicicola and Verticillium dahliae Treatments
3.2. Spodoptera littoralis Treatments
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Growth Condition
4.2. Alternaria brassicicola Growth Condition and Co-Cultivation
4.3. Verticillium dahliae Growth Condition and Co-Cultivation
4.4. Animal Material and Feeding Assay
4.5. Spodoptera littoralis Egg Extract Treatment
4.6. Phytohormone Analysis
4.7. Gene Expression Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TIRs | Toll/Interleukin-1 receptors |
| PTI | Pattern-triggered immunity |
| ETI | Effector-triggered immunity |
| PRRs | Pattern recognition receptors |
| WT | Wild type |
| KO | Knock-out |
| OE | Overexpressed |
| NBS | Nucleotide-binding site |
| R | Resistance protein |
| LRR | Leucine Rich Repeat |
| CC | Coiled coil |
| HR | Hypersensitivity response |
| CFU | Colony forming unit |
| PDA | Potato dextrose agar |
| PDB | Potato dextrose broth |
| MS | Murashige and Skoog |
| VDA | Verticillium dahliae |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| JA | Jasmonic acid |
| JA Ile | Jasmonoyl isoleucine |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry |
| SNE1 | Suppressor of necrosis-1 |
| NLPs | Nep1-like proteins |
| NPR1 | Non-expresser of PR genes |
| EDS1 | Enhanced disease susceptibility 1 |
| PAD4 | Phytoalexin-deficient 4 |
| SAG101 | Senescence-associated gene 101 |
| PEK | Pieris egg-killing |
References
- Dangl, J.L.; Jones, J.D.G. Plant pathogen and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 2001, 411, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluhr, R. Sentinels of disease. Plant resistance genes. Plant Physiol. 2002, 127, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, B.C.; Dickerman, A.W.; Michelmore, R.W.; Sivaramakrishnan, S.; Sobral, B.W.; Young, N.D. Plant disease resistance genes encode members of an ancient and diverse protein family within the nucleotide-binding superfamily. Plant. J. 1999, 3, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, B.C.; Morgante, M.; Michelmore, R.W. TIR-X and TIR-NBS proteins: Two new families related to disease resistance TIR-NBS-LRR proteins encoded in Arabidopsis and other plant genomes. Plant J. 2002, 32, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayless, A.M.; Nishimura, M.T. Enzymatic functions for Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor domain proteins in the plant immune system. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanseverino, W.; Ercolano, M.R. In silico approach to predict candidate R proteins and to define their domain architecture. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczak, T.; Krela, R.; Wadurkar, S.; Gevaert, K.; Slijke, E.V.D.; Jaeger, G.D.; Leśniewicz, K.; Wojtaszek, P. Characterization of the γ-secretase subunit interactome in Arabidopsis thaliana. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Saito, T.; Ito, H.; Komeda, Y.; Kato, A. Overexpression of the TIR-X gene results in a dwarf phenotype and activation of defense-related gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandety, R.S.; Caplan, J.L.; Cavanaugh, K.; Perroud, B.; Wroblewski, T.; Michelmore, R.W.; Meyers, B.C. The role of TIR-NBS and TIR-X proteins in plant basal defense responses. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Y.; Sami, F.; Siddiqui, H.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Salicylic acid in relation to other phytohormones in plant: A study towards physiology and signal transduction under challenging environment. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 175, 104040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.-W.; Ma, W. Phytohormone pathways as targets of pathogens to facilitate infection. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 91, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehlemann, G.; Ökmen, B.; Zhu, W.; Sharon, A. Plant pathogenic fungi. In The Fungal Kingdom; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 701–726. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Basu, A.; Kundu, S. Biotrophy-necrotrophy switch in pathogen evoke differential response in resistant and susceptible sesame involving multiple signaling pathways at different phases. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehndal, L.; Ågren, J. Herbivory differentially affects plant fitness in three populations of the perennial herb Lythrum salicaria along a latitudinal gradient. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigenaga, A.M.; Argueso, C.T. No hormone to rule them all interactions of plant hormones during the responses of plants to pathogens. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 56, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruessow, F.; Gouhier-Darimont, C.; Buchala, A.; Metraux, J.P.; Reymond, P. Insect eggs suppress plant defence against chewing herbivores. Plant J. 2010, 62, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, J.; Dixelius, C. RLM3, A potential adaptor between specific TIR-NB-LRR receptors and DZC proteins. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2008, 1, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, J.; Kaliff, M.; Dewaele, E.; Persson, M.; Dixelius, C. RLM3, a TIR domain encoding gene involved in broad-range immunity of Arabidopsis to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Plant J. 2008, 55, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, B.S.; Lee, S.J.; Damasceno, C.M.B.; Chakravarthy, S.; Kim, B.D.; Martin, G.B.; Rose, J.K.C. A secreted effector protein (SNE1) from Phytophthora infestans is a broadly acting suppressor of programmed cell death. Plant J. 2010, 62, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerger, M.; Chory, J. Stressed out about hormones: How plants orchestrate immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macioszek, V.K.; Jęcz, T.; Ciereszko, I.; Kononowicz, A.K. Jasmonic acid as a mediator in plant response to necrotrophic fungi. Cells 2023, 12, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arévalo-Marín, D.F.; Briceño-Robles, D.M.; Mosquera, T.; Melgarejo, L.M.; Sarmiento, F. Jasmonic acid priming of potato uses hypersensitive response-dependent defense and delays necrotrophic phase change against Phytophthora infestans. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 115, 101680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, M.Z.; Bastías, D.A.; Christensen, M.J.; Zhong, R.; Nan, Z.B.; Zhang, X.X. The plant salicylic acid signalling pathway regulates the infection of a biotrophic pathogen in grasses associated with an Epichloë endophyte. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Pang, H.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Hang, Y. Tracing the origin and evolution of plant TIR-encoding genes. Gene 2014, 546, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Spivey, N.W.; Zeng, W.; Liu, P.P.; Fu, Z.Q.; Klessig, D.F.; He, S.Y.; Dong, X. Coronatine promotes Pseudomonas syringae virulence in plants by activating a signaling cascade that inhibits salicylic acid accumulation. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Inoue, H.; Hayashi, N.; Jiang, C.J.; Takatsuji, H. CC-NBS-LRR-type R proteins for rice blast commonly interact with specific WRKY transcription factors. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 34, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, T.; Ao, K.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Opposite roles of salicylic acid receptors NPR1 and NPR3/NPR4 in transcriptional regulation of plant immunity. Cell 2018, 173, 1454–1467.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadassery, J.; Reichelt, M.; Hause, B.; Gershenzon, J.; Boland, W.; Mithöfer, A. CML42-mediated calcium signaling coordinates responses to Spodoptera herbivory and abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mithöfer, A.; Boland, W.; Maffei, M.E. Chemical ecology of plant-insect interactions. In Annual Plant Reviews; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 34, pp. 261–291. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.P.; Srivastava, S.; Goel, R.; Lakhwani, D.; Singh, P.; Asif, M.H.; Sane, A.P. Simulated herbivory in chickpea causes rapid changes in defense pathways and hormonal transcription networks of JA/ethylene/GA/auxin within minutes of wounding. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, D.; Gouhier-Darimont, C.; Bruessow, F.; Reymond, P. Oviposition by Pierid Butterflies triggers defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 784–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiermer, M.; Feys, B.J.; Parker, J.E. Plant immunity: The EDS1 regulatory node. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005, 8, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, N.; Caarls, L.; Bouwmeester, K.; Verbaarschot, P.; van Eijden, E.; Zwaan, B.J.; Bonnema, G.; Schranz, M.E.; Fatouros, N.E. A butterfly egg-killing hypersensitive response in Brassica nigra is controlled by a single locus, PEK, containing a cluster of TIR-NBS-LRR receptor genes. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Henriques, R.; Lin, S.S.; Niu, Q.W.; Chua, N.H. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using the floral dip method. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earley, K.W.; Haag, J.R.; Pontes, O.; Opper, K.; Juehne, T.; Song, K.; Pikaard, C.S. Gateway-compatible vectors for plant functional genomics and proteomics. Plant J. 2006, 45, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.W.; Kafer, E. Improved protocols for Aspergillus minimal medium: Trace element and minimal medium salt stock solutions. Fungal Genet. Rep. 2001, 48, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, S.S.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Guthke, R.; Furch, A.C.U.; Reichelt, M.; Gershenzon, J.; Oelmüller, R. Verticillium dahliae-Arabidopsis interaction causes changes in gene expression profiles and jasmonate levels on different time scales. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergomaz, R.; Boppre, M. A simple instant diet for rearing Arctiidae and other moths. J. Lepid. Soc. 1986, 40, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, S.S.; Malabarba, J.; Reichelt, M.; Heyer, M.; Ludewig, F.; Mithöfer, A. Evidence for GABA-induced systemic GABA accumulation in Arabidopsis upon wounding. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyer, M.; Reichelt, M.; Mithöfer, A. A holistic approach to analyze systemic jasmonate accumulation in individual leaves of Arabidopsis rosettes upon wounding. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neufeld, S.; Reichelt, M.; Scholz, S.S.; Wojtaszek, P.; Mithöfer, A. Exploring a Role for the Arabidopsis TIR-X Gene (TIRP) in the Defense Against Pathogenic Fungi or Insect Herbivory Attack. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062764
Neufeld S, Reichelt M, Scholz SS, Wojtaszek P, Mithöfer A. Exploring a Role for the Arabidopsis TIR-X Gene (TIRP) in the Defense Against Pathogenic Fungi or Insect Herbivory Attack. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062764
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeufeld, Shraddha, Michael Reichelt, Sandra S. Scholz, Przemysław Wojtaszek, and Axel Mithöfer. 2025. "Exploring a Role for the Arabidopsis TIR-X Gene (TIRP) in the Defense Against Pathogenic Fungi or Insect Herbivory Attack" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062764
APA StyleNeufeld, S., Reichelt, M., Scholz, S. S., Wojtaszek, P., & Mithöfer, A. (2025). Exploring a Role for the Arabidopsis TIR-X Gene (TIRP) in the Defense Against Pathogenic Fungi or Insect Herbivory Attack. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062764





