Folic Acid Alleviates Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress in Bovine Placental Trophoblast Cells by Regulating the NRF2/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
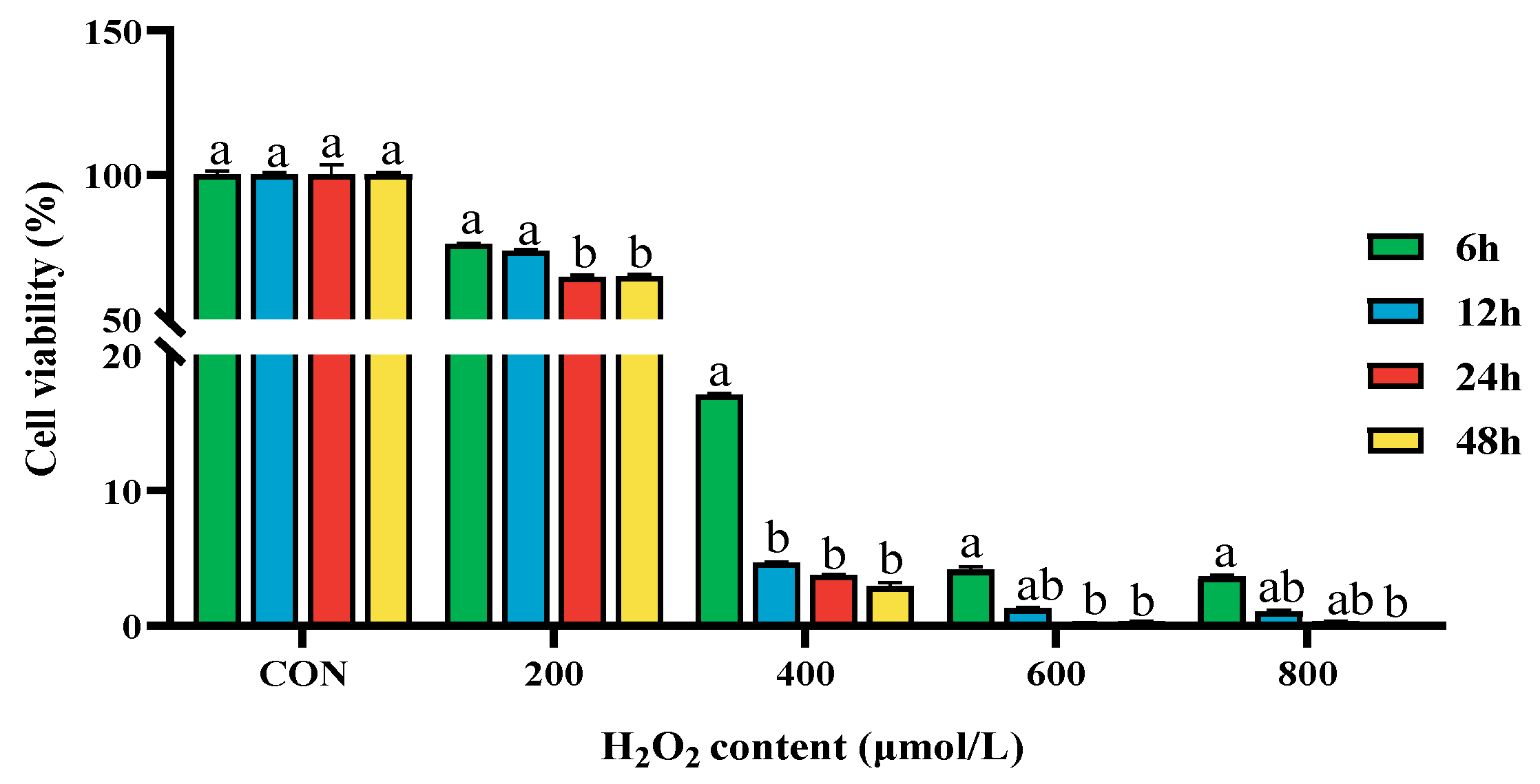
2.1. Effect of Different Concentrations of H2O2 on the Cell Viability of BPTCs
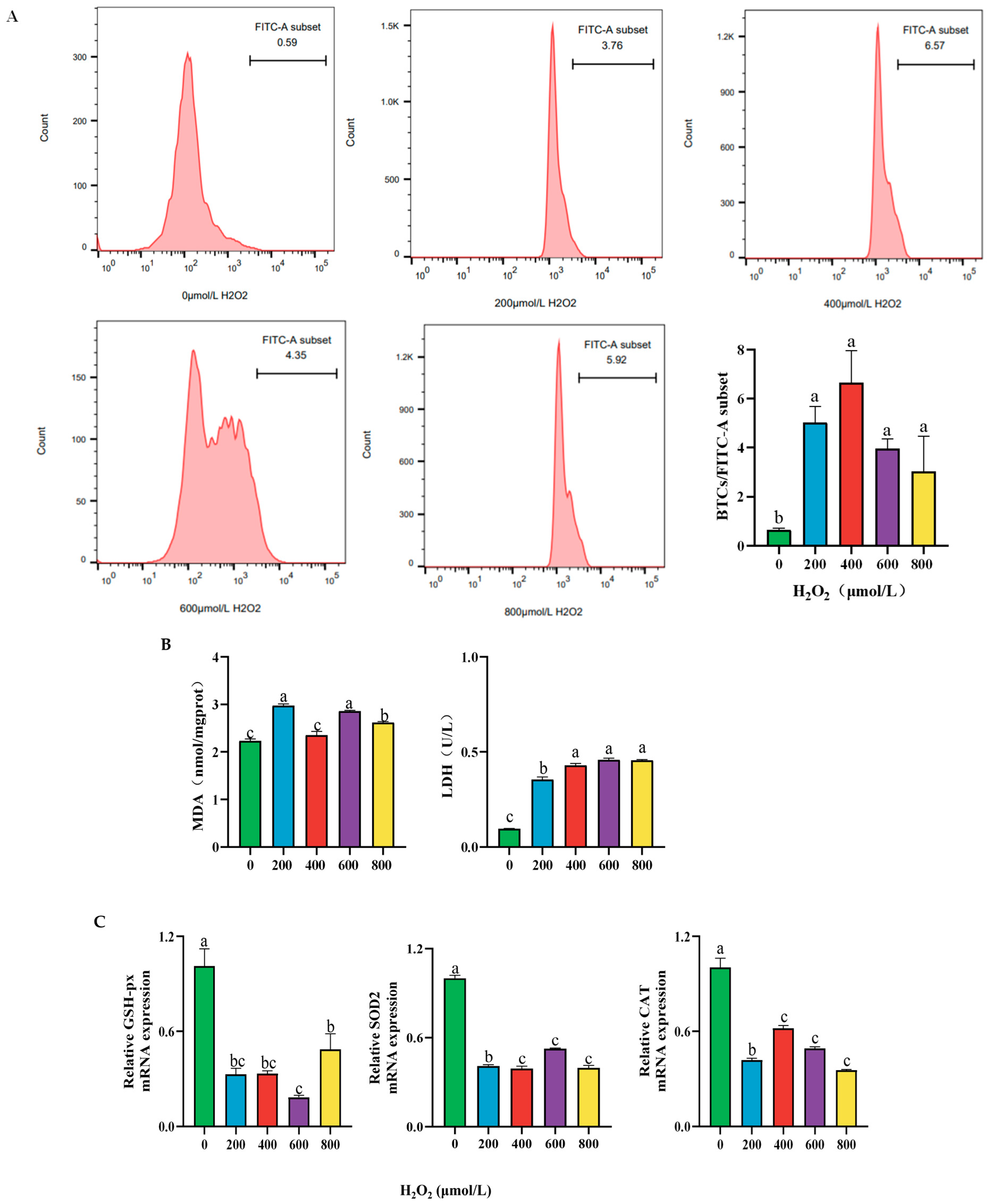
2.2. Effect of Different Concentrations of H2O2 Treatment on the Cellular Content of ROS, MDA, LDH Activity, and Antioxidant Enzyme mRNA Expression After 24 h
2.3. Effect of Different Concentrations of H2O2 Treatment on Cell Apoptosis of BPTCs After 24 h
2.4. Effect of Different Concentrations of FA and H2O2 on the Cell Viability of BPTCs
2.5. Effect of FA on H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in BPTCs
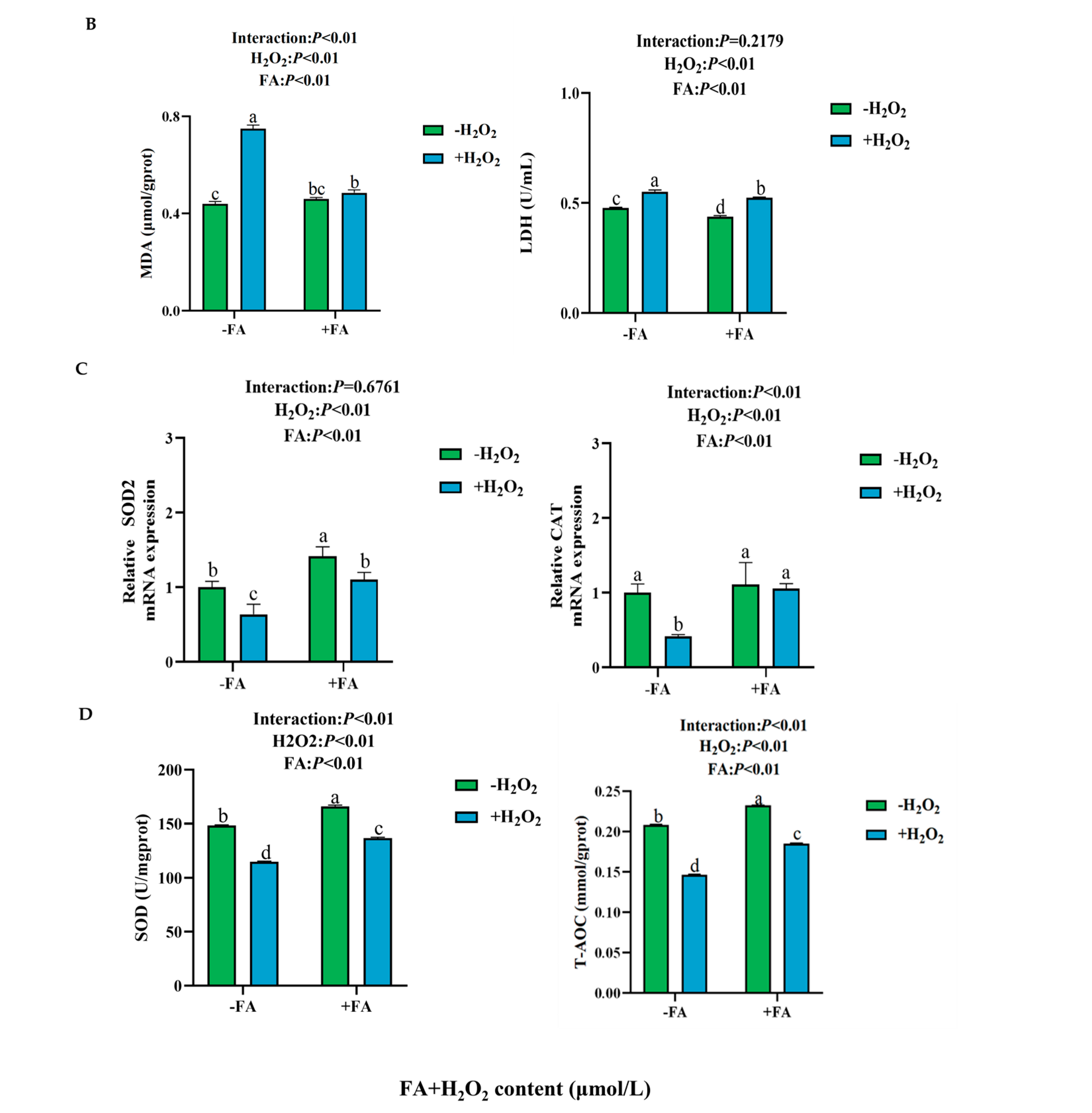
2.5.1. Effect of FA on ROS, MDA, and T-AOC Content, LDH and SOD Activity, and Antioxidant Enzyme Gene Expression Induced by H2O2 in BPTCs
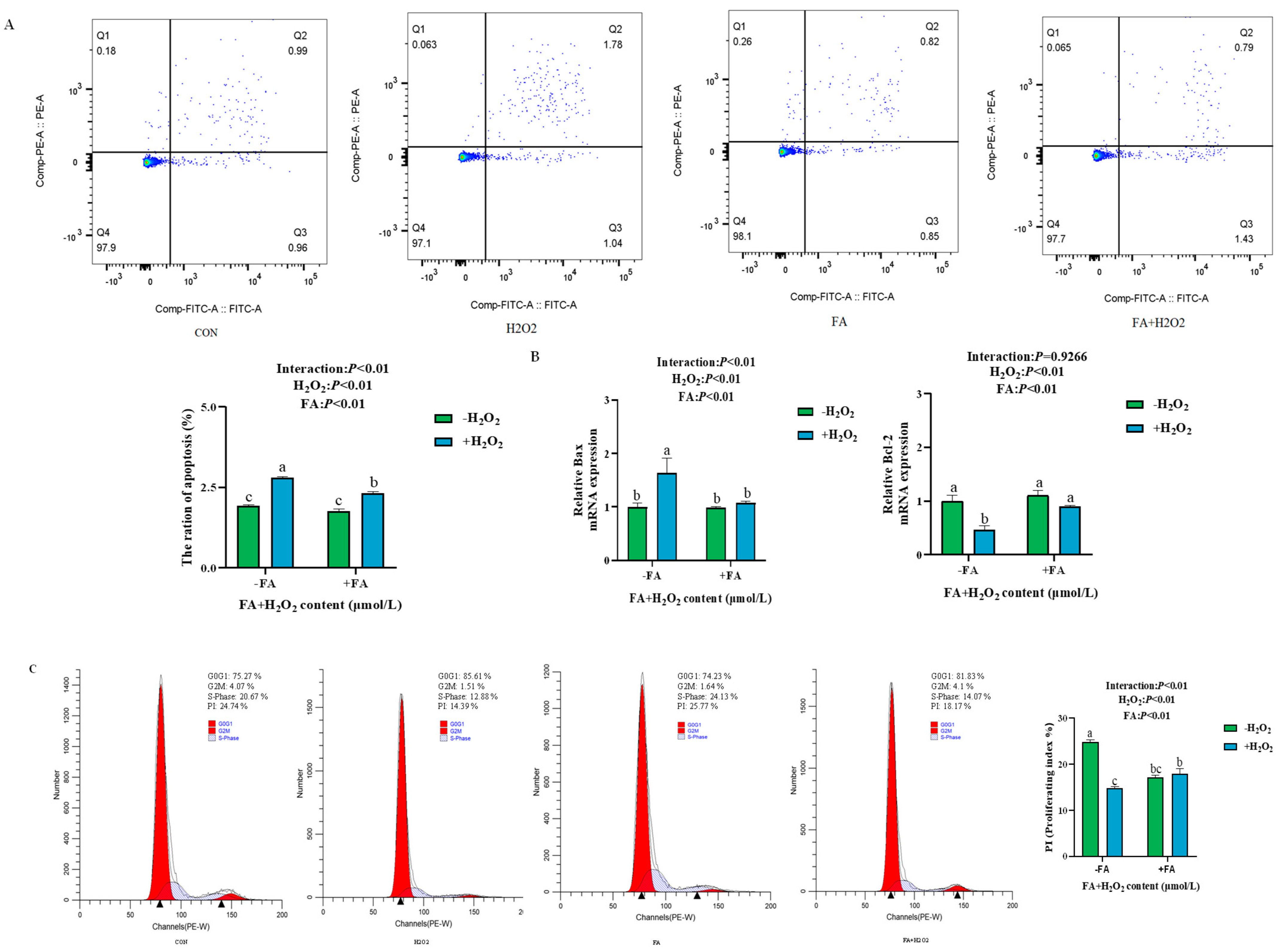
2.5.2. Effect of FA on H2O2-Induced Apoptosis and Cell Proliferation of BPTCs
2.6. Effects of FA on H2O2 Induced the Damage of Tight Junctions, Nutrient Transporters, and Cell Functional Factors in BPTCs
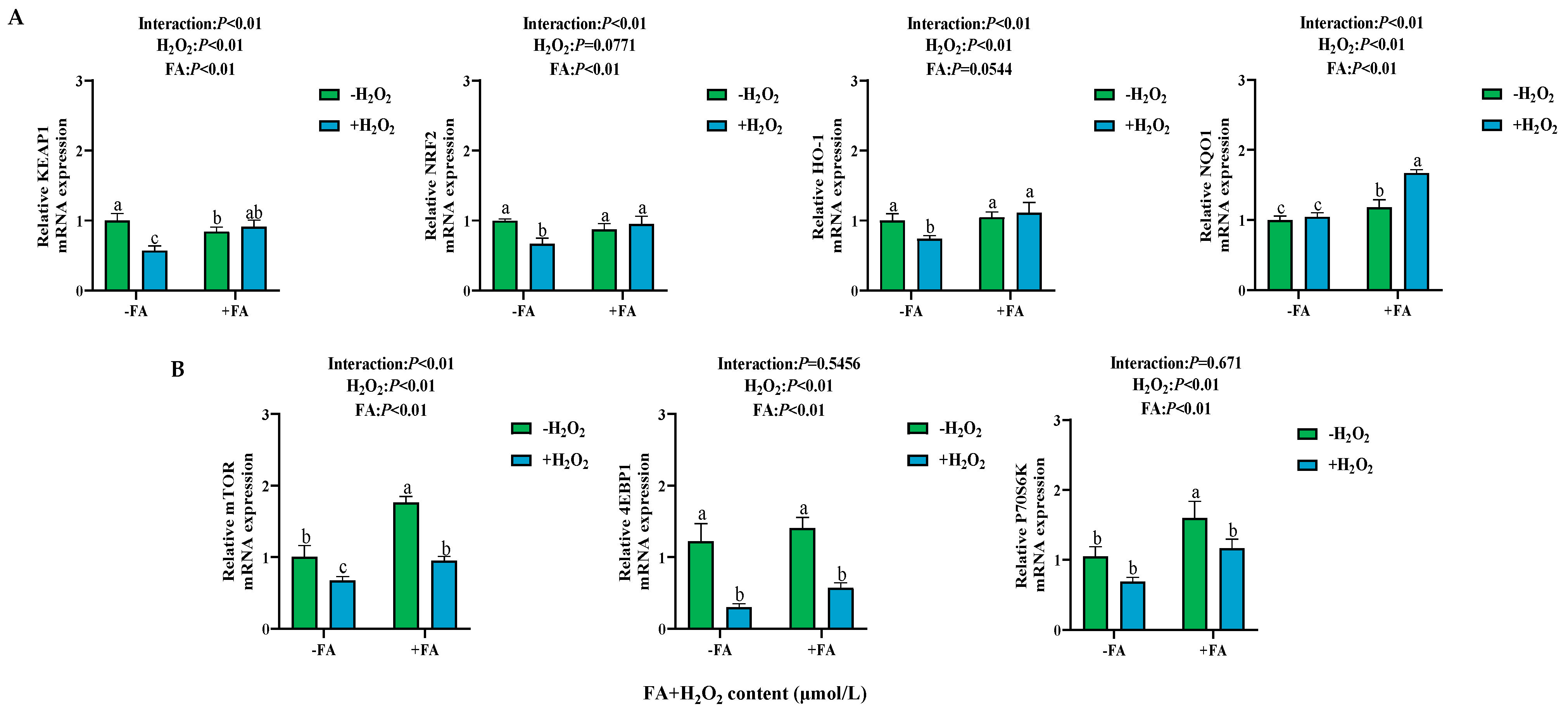
2.7. Effect of FA on the Expression of NRF2/mTOR Signaling Pathway-Related Genes in BPTCs Induced by H2O2
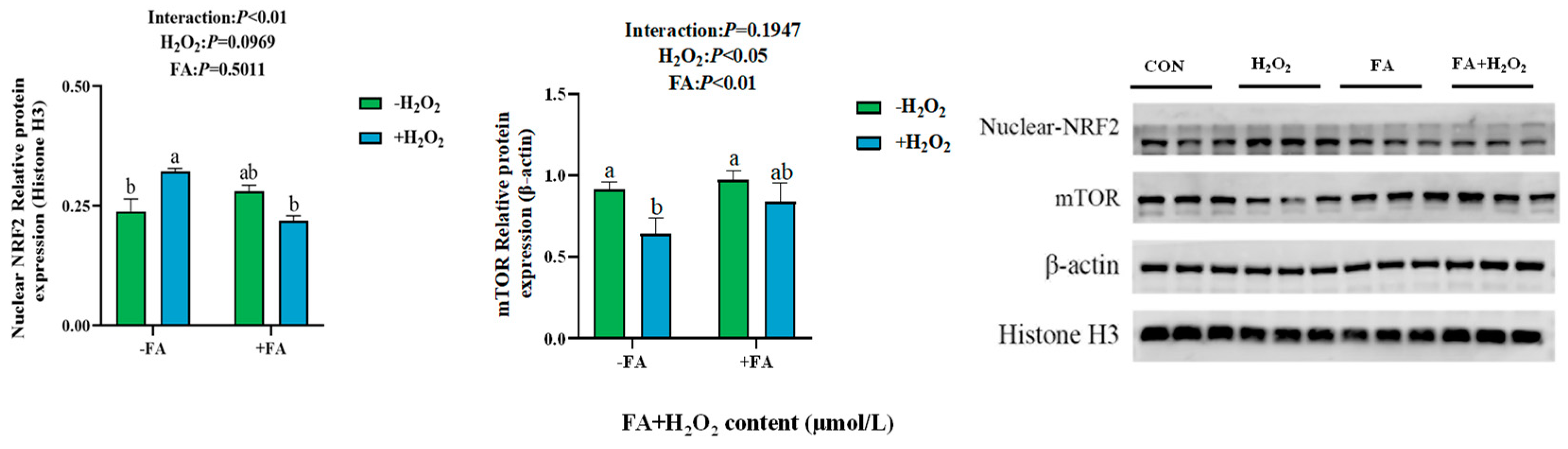
2.8. Effect of FA on the Abundance of NRF2/mTOR Signaling Pathway-Related Proteins in BPTCs Induced by H2O2
2.9. Effect of ML385 (NRF2 Inhibitor) on FA-Mediated NRF2/mTOR Signaling Pathway in BPTCs
2.9.1. Effect of Different Concentrations of ML385 and Combined Treatment with FA, H2O2, and ML385 on Cell Viability
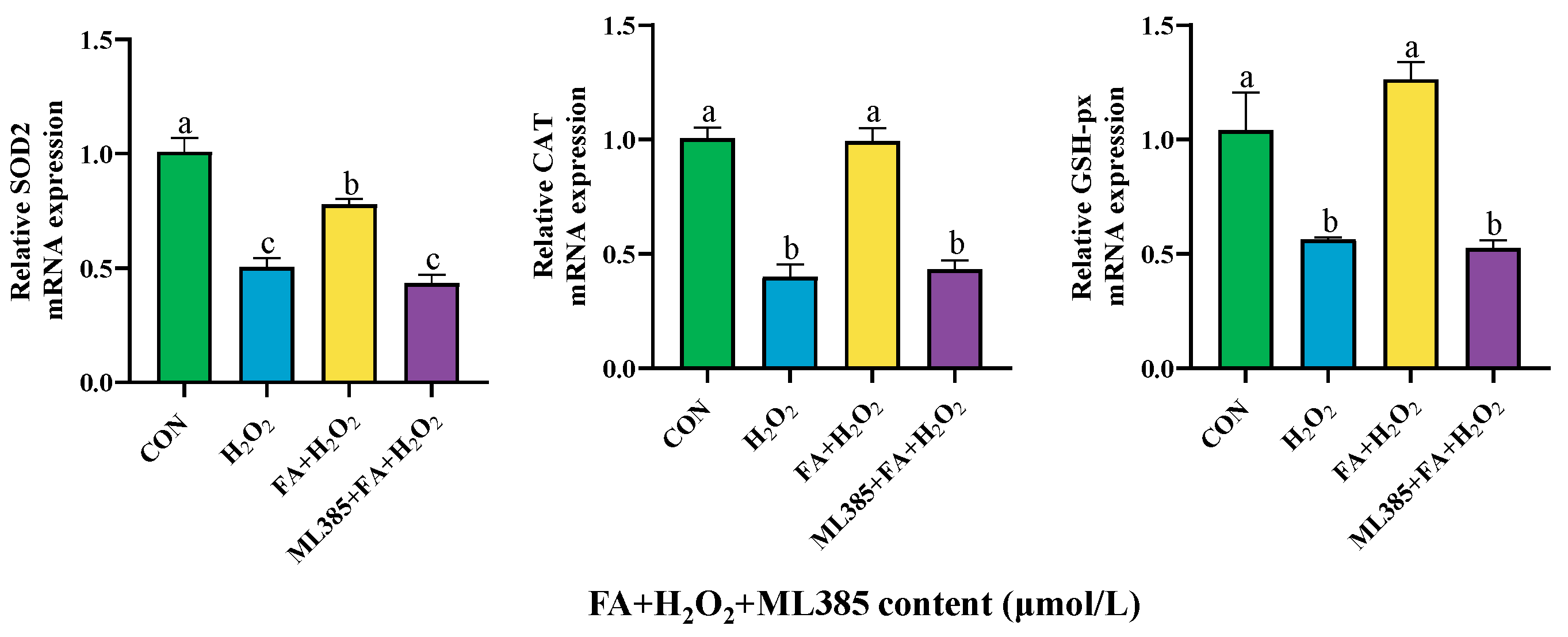
2.9.2. Effect of Combined Treatment with FA, H2O2, and ML385 on the Gene Expressions of Antioxidant Enzyme in BPTCs
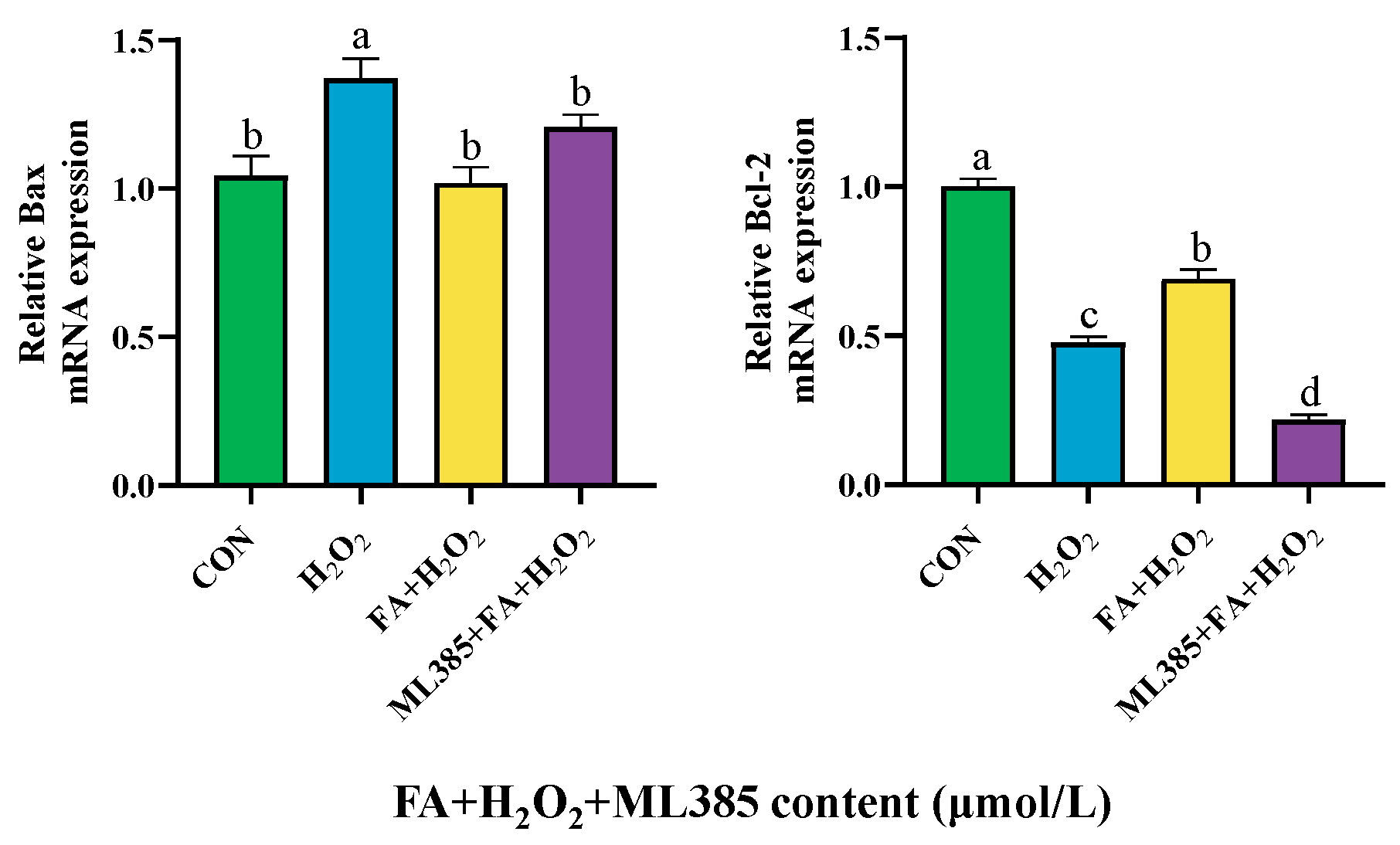
2.9.3. Effect of Combined Treatment with FA, H2O2, and ML385 on the mRNA Expression of Apoptosis Factor in BPTCs
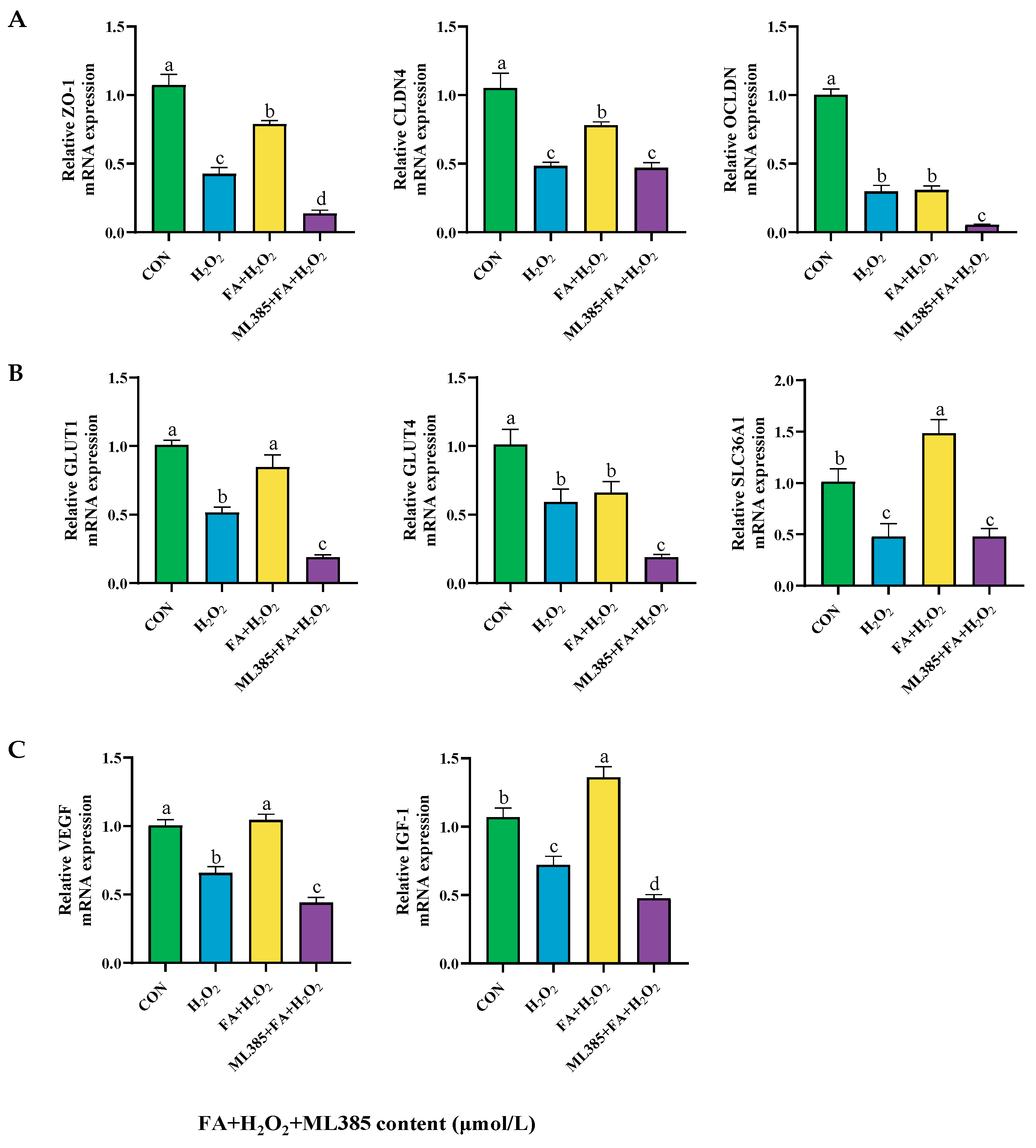
2.9.4. Effect of Combined Treatment with FA, H2O2, and ML385 on the mRNA Expression of Tight Junctions, Nutrient Transporters, and Cell Functional Factors in BPTCs
2.10. Effect of Combined Treatment with FA, H2O2, and ML385 on the Expression of Cellular Pathway Genes
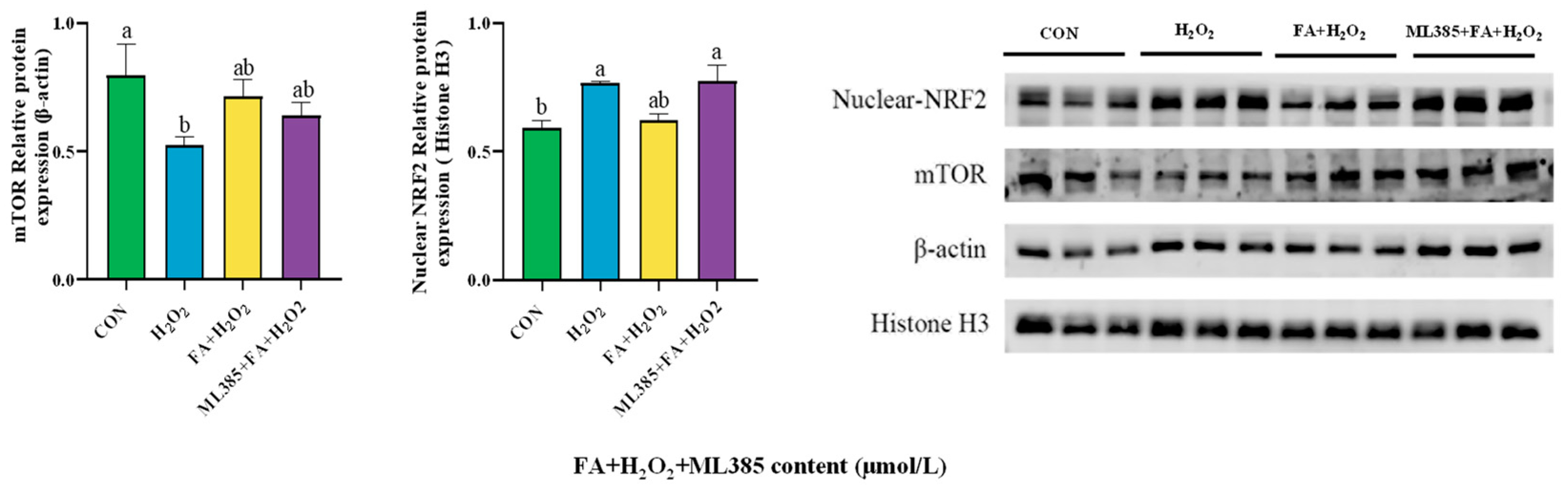
2.11. Effect of Combined Treatment with FA, H2O2, and ML385 on the Abundance of Cellular Pathway Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Cell Cycle
4.4. ROS Assay
4.5. MDA, T-AOC Content, LDH, and SOD Activity Assays
4.6. Cell Apoptosis Assay
4.7. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lapointe, J.; Roy, C.; Lavoie, M.; Bergeron, N.; Beaudry, D.; Blanchet, I.; Petit, H.V.; Palin, M.-F. Negative Energy Balance Is Associated with Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Conditions in Early Lactating Dairy Cows. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 1, S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duplessis, M.; Lapierre, H.; Sauerwein, H.; Girard, C. Combined biotin, folic acid, and vitamin B12 supplementation given during the transition period to dairy cows: Part I. Effects on lactation performance, energy and protein metabolism, and hormones. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 7079–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Kong, X.; Yuan, X.; Xu, J.; Zhu, H. Apelin/APJ system protects placental trophoblasts from hypoxia-induced oxidative stress through activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in preeclampsia. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 208, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilburn, B.A.; Wang, J.; Duniec-Dmuchkowski, Z.M.; Leach, R.E.; Romero, R.; Armant, D.R. Extracellular matrix composition and hypoxia regulate the expression of HLA-G and integrins in a human trophoblast cell line. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 62, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirković, A.; Vilotić, A.; Borozan, S.; Nacka-Aleksić, M.; Bojić-Trbojević, Ž.; Krivokuća, M.J.; Battino, M.; Giampieri, F.; Dekanski, D. Oleuropein Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Human Trophoblast Cells. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Tian, F.J.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W.M. Oxidative stress: Placenta function and dysfunction. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 76, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Gyamfi, E.A.; Czika, A.; Gorleku, P.N.; Ullah, A.; Panhwar, Z.; Ruan, L.-L.; Ding, Y.-B.; Wang, Y.-X. The involvement of cell adhesion molecules, tight junctions, and gap junctions in human placentation. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 28, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahoda, R.; Zaugg, J.; Fuenzalida, B.; Kallol, S.; Moser-Haessig, R.; Staud, F.; Albrecht, C. Trophoblast differentiation affects crucial nutritive functions of placental membrane transporters. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 820286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Rong, L.; Qin, J. Self-assembled human placental model from trophoblast stem cells in a dynamic organ-on-a-chip system. Cell Prolif. 2023, 56, e13469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louey, S.; Cock, M.L.; Stevenson, K.M.; Harding, R. Placental insufficiency and fetal growth restriction lead to postnatal hypotension and altered postnatal growth in sheep. Pediatr. Res. 2000, 48, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tossetta, G.; Paolinelli, F.; Avellini, C.; Salvolini, E.; Ciarmela, P.; Lorenzi, T.; Emanuelli, M.; Toti, P.; Giuliante, R.; Gesuita, R. IL-1β and TGF-β weaken the placental barrier through destruction of tight junctions: An in vivo and in vitro study. Placenta 2014, 35, 509–516. [Google Scholar]
- Wald, N.J. Folic acid and the prevention of neural-tube defects. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Yang, J. Advances in DNA methylation of imprinted genes and folic acid regulation of growth and development. Epigenomics 2024, 16, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, V.; Parvez, S.; Fatima, G.; Singh, S.; Magomedova, A.; Batiha, G.E.S.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Welson, N.N.; Hadi, N. Micronutrient interactions: Magnesium and its synergies in maternal–fetal health. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 6913–6928. [Google Scholar]
- Saccone, G.; Berghella, V. Folic acid supplementation in pregnancy to prevent preterm birth: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2016, 199, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Asbaghi, O.; Ghanavati, M.; Ashtary-Larky, D.; Bagheri, R.; Rezaei Kelishadi, M.; Nazarian, B.; Nordvall, M.; Wong, A.; Dutheil, F.; Suzuki, K. Effects of folic acid supplementation on oxidative stress markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenech, M. Folate (vitamin B9) and vitamin B12 and their function in the maintenance of nuclear and mitochondrial genome integrity. Mutat. Res. /Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2012, 733, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, C.; Matte, J. Dietary supplements of folic acid during lactation: Effects on the performance of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, M. Stress-sensing mechanisms and the physiological roles of the Keap1–Nrf2 system during cellular stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16817–16824. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Huang, J.; Tang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, G.; Yan, C.; Liu, Z.; Yi, W.; Xu, S.; Yu, X. Isoginkgetin, a bioactive constituent from Ginkgo Biloba, protects against obesity-induced cardiomyopathy via enhancing Nrf2/ARE signaling. Redox Biol. 2022, 57, 102485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, A.A.; Singh, A.; Matsui, W.; Biswal, S. The redox-sensitive transcription factor Nrf2 regulates murine hematopoietic stem cell survival independently of ROS levels. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2011, 118, 6572–6579. [Google Scholar]
- Bendavit, G.; Aboulkassim, T.; Hilmi, K.; Shah, S.; Batist, G. Nrf2 transcription factor can directly regulate mTOR: Linking cytoprotective gene expression to a major metabolic regulator that generates redox activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 25476–25488. [Google Scholar]
- Rosario, F.J.; Nathanielsz, P.W.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Maternal folate deficiency causes inhibition of mTOR signaling, down-regulation of placental amino acid transporters and fetal growth restriction in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3982. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.J.; Bulmer, J.N.; Innes, B.A.; Broughton Pipkin, F. Possible roles for folic acid in the regulation of trophoblast invasion and placental development in normal early human pregnancy. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 84, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Rosario, F.J.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. mTOR folate sensing links folate availability to trophoblast cell function. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4189–4206. [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind, M.; Dominguez-Rosales, J.-A.; Nieto, N.; Greenwel, P. Role of hydrogen peroxide and oxidative stress in healing responses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2002, 59, 1872–1891. [Google Scholar]
- Betteridge, D.J. What is oxidative stress? Metabolism 2000, 49, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Puppel, K.; Kapusta, A.; Kuczyńska, B. The etiology of oxidative stress in the various species of animals, a review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2179–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Sordillo, L.M.; Contreras, G.; Aitken, S.L. Metabolic factors affecting the inflammatory response of periparturient dairy cows. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2009, 10, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Horst, E.; Kvidera, S.; Baumgard, L. Invited review: The influence of immune activation on transition cow health and performance—A critical evaluation of traditional dogmas. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8380–8410. [Google Scholar]
- Wrzecińska, M.; Czerniawska-Piątkowska, E.; Kowalczyk, A. The impact of stress and selected environmental factors on cows’ reproduction. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2021, 49, 318–323. [Google Scholar]
- Schoots, M.H.; Gordijn, S.J.; Scherjon, S.A.; van Goor, H.; Hillebrands, J.-L. Oxidative stress in placental pathology. Placenta 2018, 69, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Kankofer, M. Antioxidative defence mechanisms against reactive oxygen species in bovine retained and not-retained placenta: Activity of glutathione peroxidase, glutathione transferase, catalase and superoxide dismutase. Placenta 2001, 22, 466–472. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.-Y.; Jing, Y.; Xiao, Y.-P.; Wang, X.-H.; Guo, Y.-W.; Zhu, Y.-J. Astaxanthin inhibiting oxidative stress damage of placental trophoblast cells in vitro. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2021, 67, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Sho, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Yao, J.; Xu, J. ROS-induced autophagy regulates porcine trophectoderm cell apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C198–C209. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Tian, B.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, X.; Wan, X.; Ye, Y. Activation of HO-1 protects placental cells function in oxidative stress via regulating ZO-1/occludin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 511, 903–909. [Google Scholar]
- Heazell, A.; Lacey, H.; Jones, C.; Huppertz, B.; Baker, P.; Crocker, I. Effects of oxygen on cell turnover and expression of regulators of apoptosis in human placental trophoblast. Placenta 2008, 29, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Barut, A.; Barut, F.; Kandemir, N.O.; Aktunc, E.; Arikan, I.; Harma, M.; Harma, M.I.; Gun, B.D. Placental chorangiosis: The association with oxidative stress and angiogenesis. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2012, 73, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Hao, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Wei, J.; Deng, J.; Tan, C. Maternal supply of cysteamine alleviates oxidative stress and enhances angiogenesis in porcine placenta. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Carletti, J.V.; Correia-Branco, A.; Silva, C.R.; Andrade, N.; Silva, L.O.P.; Martel, F. The effect of oxidative stress induced by tert-butylhydroperoxide under distinct folic acid conditions: An in vitro study using cultured human trophoblast-derived cells. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 77, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Blundell, C.; Tess, E.R.; Schanzer, A.S.; Coutifaris, C.; Su, E.J.; Parry, S.; Huh, D. A microphysiological model of the human placental barrier. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3065–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Wu, D.; Ma, K.; Chen, Y.; Ma, S.; Feng, L.; Li, F.; Liu, D. Cysteamine and N-Acetyl-cysteine Alleviate Placental Oxidative Stress and Barrier Function Damage Induced by Deoxynivalenol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6846–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M.; Jankovic-Karasoulos, T.; Roberts, C.T.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; Thierry, B. Bioengineered microphysiological placental models: Towards improving understanding of pregnancy health and disease. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Luo, R.; Ye, N.; Hu, Y.; Fu, C.; Gao, R.; Fu, S.; Gao, F. Research progress on natural β-glucan in intestinal diseases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 1244–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, P.; Guan, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, F. Leucine supplementation during late gestation globally alters placental metabolism and nutrient transport via modulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in sows. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2083–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.B.; Jansson, T. Novel roles of mechanistic target of rapamycin signaling in regulating fetal growth. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 100, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Yamamoto, M. The KEAP1–NRF2 system as a molecular target of cancer treatment. Cancers 2020, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Xiao, G.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, Y.; Fu, M. Persimmon vinegar polyphenols protect against hydrogen peroxide-induced cellular oxidative stress via Nrf2 signalling pathway. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; Zheng, P.; He, J.; Chen, H.; Yan, H.; Luo, Y.; Huang, Z. Dihydromyricetin enhances intestinal antioxidant capacity of growing-finishing pigs by activating ERK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Venkannagari, S.; Oh, K.H.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Rohde, J.M.; Liu, L.; Nimmagadda, S.; Sudini, K.; Brimacombe, K.R.; Gajghate, S. Small molecule inhibitor of NRF2 selectively intervenes therapeutic resistance in KEAP1-deficient NSCLC tumors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 3214–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yin, T.; Xu, R.; Xiao, W.; Wu, J.; Deng, B.; Gao, X.; Gong, W. Isoliquiritigenin ameliorates acute pancreatitis in mice via inhibition of oxidative stress and modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 7161592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Huangfu, H.; Jin, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Shi, D.; Wang, J. Nrf2/PINK1-mediated mitophagy induction alleviates sodium fluoride-induced hepatic injury by improving mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114646. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Ren, S.; An, H.; Liang, Y.; Sheng, X.; Qi, X.; Xiao, L.; Wang, X. Establishment of functional trophoblast organoids from trophoblast cells of bovine placenta. Cells Dev. 2024, 180, 203970. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Kang, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Peng, Q.; Hu, R.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Yue, Z. Glucose Regulates Glucose Transport and Metabolism via mTOR Signaling Pathway in Bovine Placental Trophoblast Cells. Animals 2023, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bursac, Z.; Eby, W.M.; Singh, K.P. Mathematical modeling of stem cell proliferation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2011, 49, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]






| Genes | Forward (5′→3′) | Reverse (5′→3′) | Accession No. |
| CAT | TCACTCAGGTGCGGACTTTC | TCTCACACAGGCGTTTCCTC | NM_001035386.2 |
| SOD2 | GGGTTGGCTCGGCTTCAATAAGG | TCGTGCAGTTACATTCTCCCAGTTG | NM_201527.2 |
| GSH-px | TCGCAATGAGGCAAGACTGACG | TAGCACGGCAGGTCCTTCTCTATC | NM_001346430.1 |
| Bcl-2 | ATGTGTGTGGAGAGCGTCAA | GTGCCTTCAGAGACAGCCAG | NM_001166486.1 |
| Bax | TGCTTCAGGGTTTCATCCAG GG | GTCCTGATCAACTCGGGCAC | NM_173894.1 |
| GLUT1 | TGGGCTTCTCAAAACTGGG | GGATGCCGACGACGATG | NM_174602.2 |
| GLUT4 | AGGAGGAGAAGCGGAAGC | AATGGCGATGACGAGGG | NM_174604.1 |
| SLC36A1 | GGCTATCGTCACTGCCCTCTA | ACAGTTGGGCAGGTTGAGAGTT | NM_001192498.1 |
| ZO-1 | TCTGCAGCAATAAAGCAGCATTTC | TTAGGGCACAGCATCGTATCACA | XM_024982009.1 |
| CLDN4 | TCATCGGCAGCAACATCGTCAC | CAGCAGCGAGTCGTACACCTTG | XM_005892850.2 |
| OCLN | GAACGAGAAGCGACTGTATC | CACTGCTGCTGTAATGAGG | NM_001082433.2 |
| VEGF | GGAGTTTGGAGCAGCAACAA | TTTGGGGCCTTGAGAGAGAG | NM_174488.2 |
| NOS3 | TGGATGAGTATGACGTGGTGT | GCGTTTCCAGCTCCGTTTG | XM_024990490.1 |
| IGF-1 | GCTCTGGCCCACGAGTGGAGA | GCCCTCGATCACCGTGCAGTT | NM_001244612.1 |
| KEAP1 | GATCTACGTTCTTGGGGGCT | CCAGAGGTCATTCGGGTCAC | NM_001101142.1 |
| NRF2 | CCCAGTCTTCACTGCTCCTC | TCAGCCAGCTTGTCATTTTG | NM_001011678.2 |
| HO-1 | GGCAGCAAGGTGCAAGA | GAAGGAAGCCAGCCAAGAG | NM_001014912.1 |
| NQO1 | CTCTGGCCAATTCAGAGTGG | CAGGATCTGAACTCGGGCAT | NM_001034535.1 |
| mTOR | AAACCCAGGTGTGATCAATAATGTC | CATCAACCCATTTCCTCATTTCA | XM_002694043.6 |
| 4EBP1 | ACCAGGATCATCTATGACCGGAA | TGTCCATCTCAAACTGTGACTCT | NM_001077893.2 |
| P70S6K | GGAAGAACTGCTGGCTCGGAAG | CATCGTCACGTCCATCTGCTCTATC | NM_205816.1 |
| β-actin | TCACCAACTGGGACGACA | GCATACAGGGACAGCACA | NM_173979.3 |
| GAPDH | GGGTCATCATCTCTGCACCT | GGTCATAAGTCCCTCCACGA | NM_001034034.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Hu, R.; Zou, H.; Wang, J.; Yue, Z.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, B.; et al. Folic Acid Alleviates Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress in Bovine Placental Trophoblast Cells by Regulating the NRF2/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062818
Shi L, Wang Z, Xiao J, Hu R, Zou H, Wang J, Yue Z, Peng Q, Jiang Y, Xue B, et al. Folic Acid Alleviates Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress in Bovine Placental Trophoblast Cells by Regulating the NRF2/mTOR Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062818
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Liyuan, Zhisheng Wang, Jianxin Xiao, Rui Hu, Huawei Zou, Junmei Wang, Ziqi Yue, Quanhui Peng, Yahui Jiang, Bai Xue, and et al. 2025. "Folic Acid Alleviates Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress in Bovine Placental Trophoblast Cells by Regulating the NRF2/mTOR Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062818
APA StyleShi, L., Wang, Z., Xiao, J., Hu, R., Zou, H., Wang, J., Yue, Z., Peng, Q., Jiang, Y., Xue, B., & Wang, L. (2025). Folic Acid Alleviates Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress in Bovine Placental Trophoblast Cells by Regulating the NRF2/mTOR Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062818









