Clec7a Signaling in Microglia Promotes Synapse Loss Associated with Tauopathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
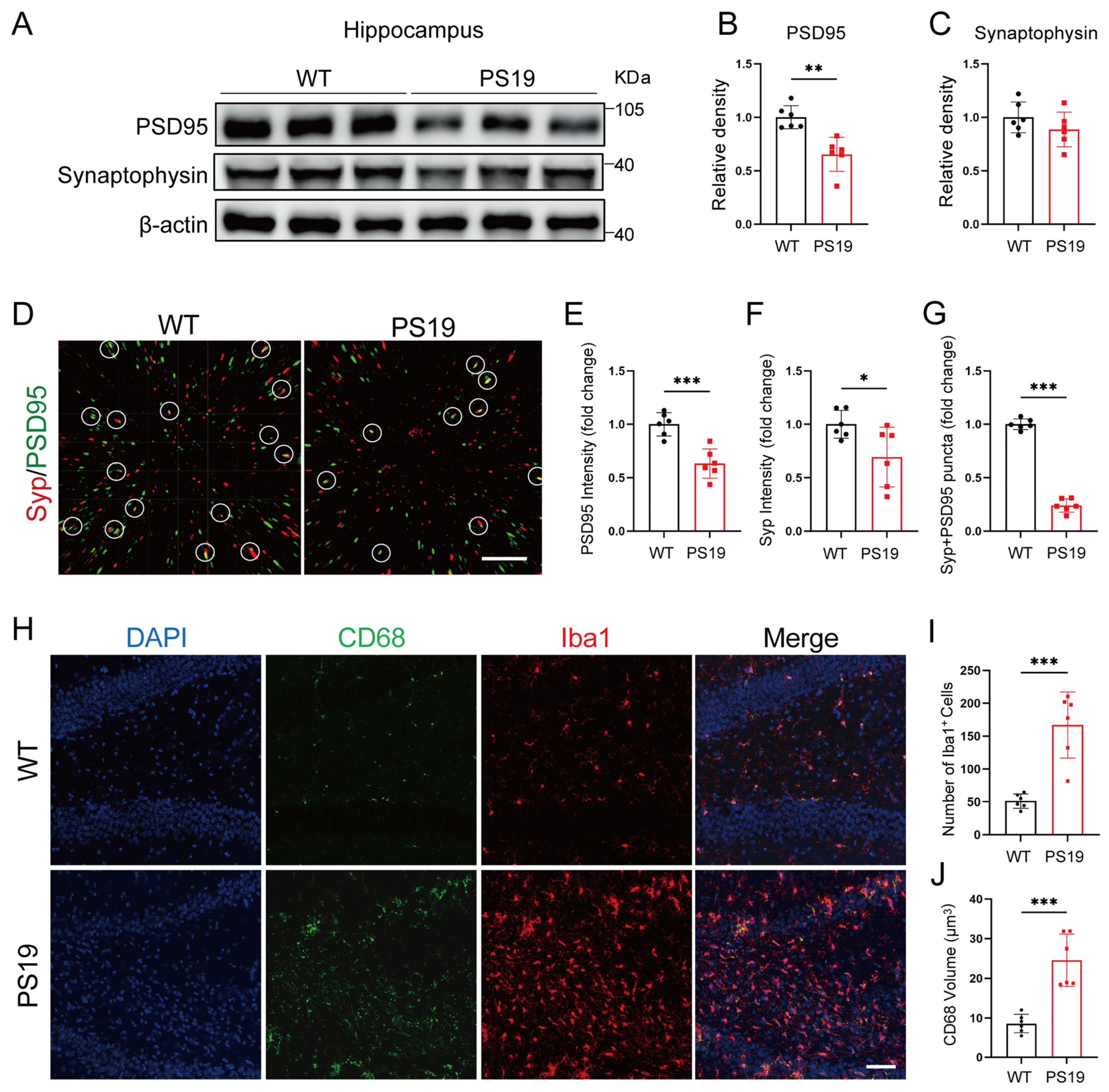
2.1. Synapse Loss and Microglia Activation in the Hippocampus of PS19 Mice
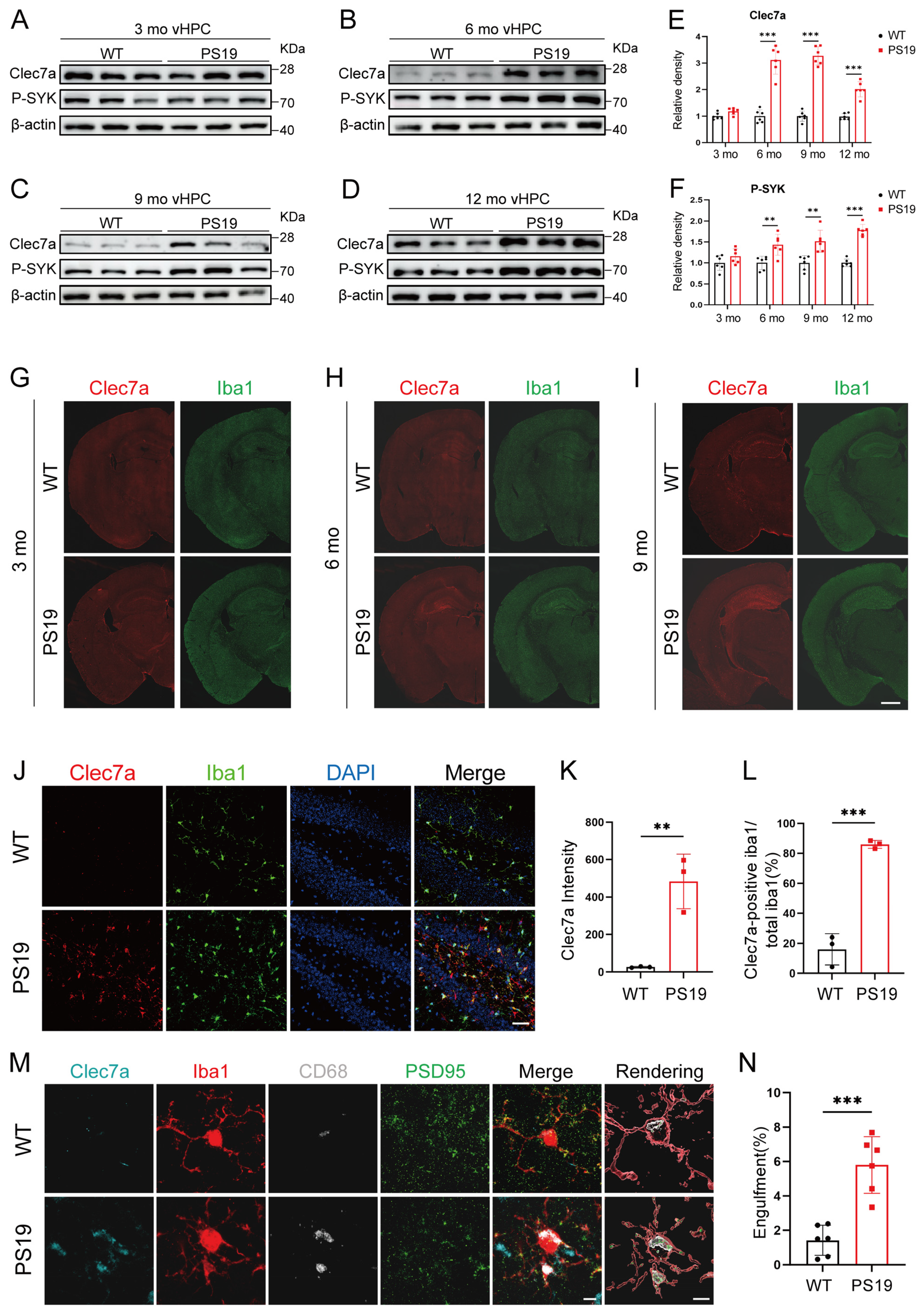
2.2. Clec7a Is Specifically Increased in the Hippocampus of PS19 Mice and Closely Associated with Synaptic Loss
2.3. Inhibition of Clec7a Effectively Mitigates Microglial Synaptic Phagocytosis and Neuroinflammation in PS19 Mice
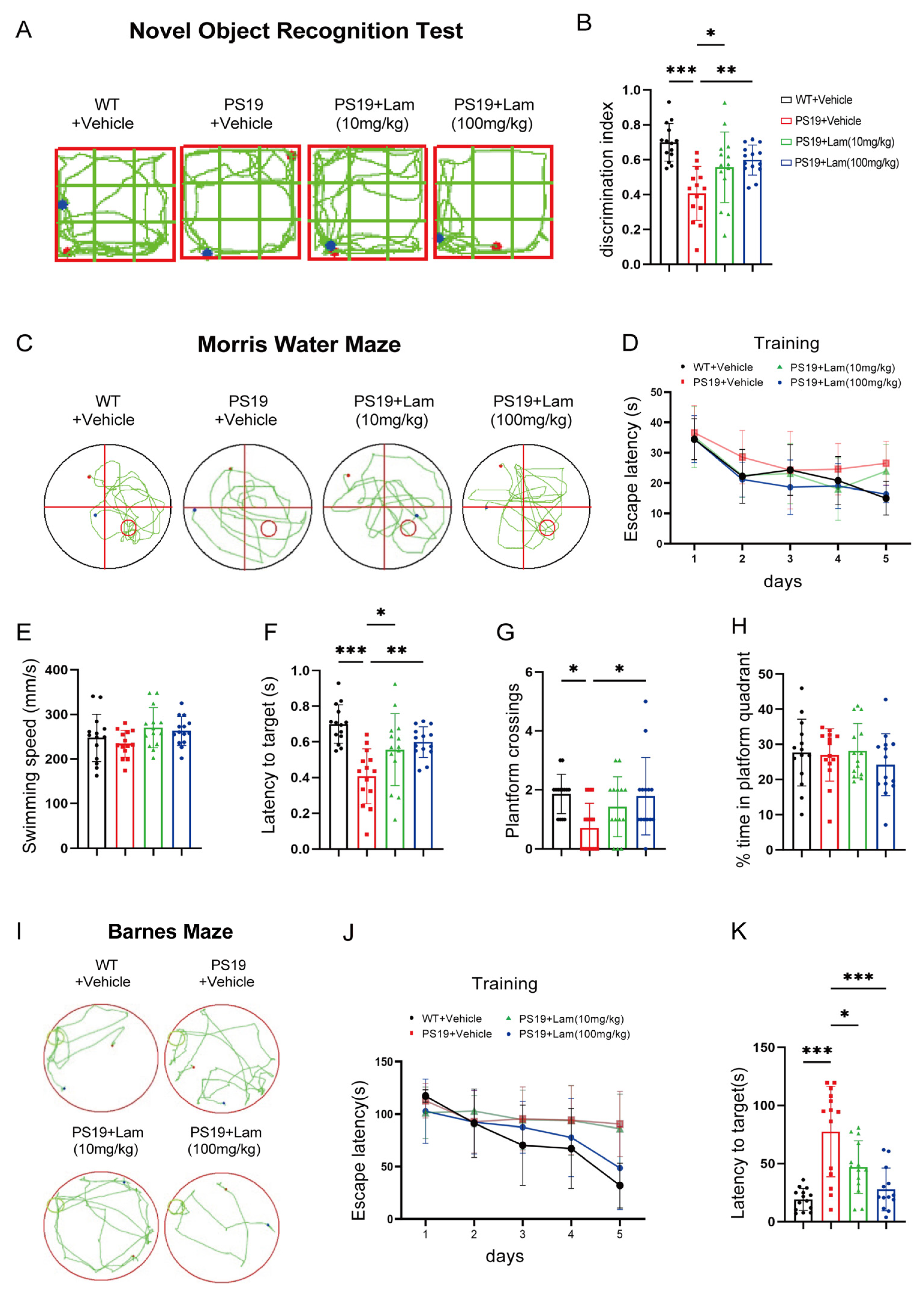
2.4. Blockage of Clec7a Improves Cognitive and Memory Deficits in PS19 Mice
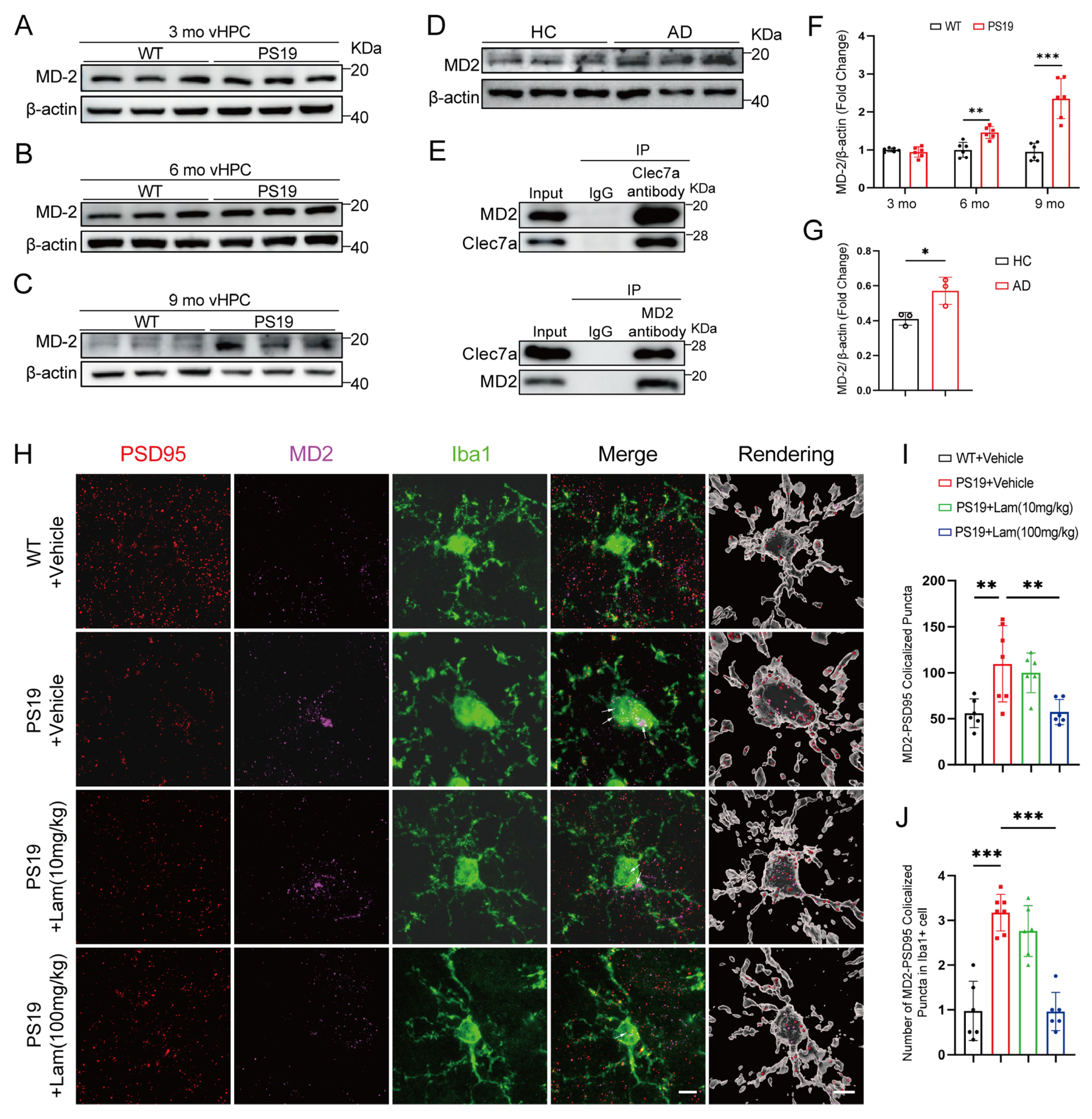
2.5. Clec7a–MD2 Signaling Mediates Synaptic Loss in PS19 Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Human Sample Tissue
4.3. Drug Administration
4.4. Culture of Primary Neurons, Astrocytes and Microglia
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Immunofluorescence and Microscopy
4.7. Behavioral Assessments
4.7.1. Novel Object Recognition
4.7.2. Morris Water Maze
4.7.3. Barnes Maze
4.8. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, D.P.; Lehrman, E.K.; Kautzman, A.G.; Koyama, R.; Mardinly, A.R.; Yamasaki, R.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Greenberg, M.E.; Barres, B.A.; Stevens, B. Microglia sculpt postnatal neural circuits in an activity and complement-dependent manner. Neuron 2012, 74, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.; Liu, G.; He, M.; Zhang, H.; Hou, F.; Liao, H. Enhancing Neuron Activity Promotes Functional Recovery by Inhibiting Microglia-Mediated Synapse Elimination After Stroke. Stroke 2025, 56, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Qi, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Peng, X.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X. Wogonin mitigates microglia-mediated synaptic over-pruning and cognitive impairment following epilepsy. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Iglesias, M.; Maldonado-Teixido, J.; Melero, A.; Piriz, J.; Galea, E.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Sierra, A. Microglia as hunters or gatherers of brain synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 2025, 28, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Dage, J.L.; Citron, M. Constitutive secretion of tau protein by an unconventional mechanism. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 48, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolow, S.; Henkins, K.M.; Bilousova, T.; Gonzalez, B.; Vinters, H.V.; Miller, C.A.; Cornwell, L.; Poon, W.W.; Gylys, K.H. Pre-synaptic C-terminal truncated tau is released from cortical synapses in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2015, 133, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Jana, M.; Paidi, R.K.; Majumder, M.; Raha, S.; Dasarathy, S.; Pahan, K. Tau fibrils induce glial inflammation and neuropathology via TLR2 in Alzheimer’s disease-related mouse models. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e161987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pampuscenko, K.; Morkuniene, R.; Sneideris, T.; Smirnovas, V.; Budvytyte, R.; Valincius, G.; Brown, G.C.; Borutaite, V. Extracellular tau induces microglial phagocytosis of living neurons in cell cultures. J. Neurochem. 2020, 154, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiyama, Y.; Higuchi, M.; Zhang, B.; Huang, S.M.; Iwata, N.; Saido, T.C.; Maeda, J.; Suhara, T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S tauopathy mouse model. Neuron 2007, 53, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Martini-Stoica, H.; Qi, C.; Lu, T.C.; Wang, S.; Xiong, W.; Qi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sardiello, M.; Li, H.; et al. TFEB-vacuolar ATPase signaling regulates lysosomal function and microglial activation in tauopathy. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Udeochu, J.C.; Amin, S.; Huang, Y.; Fan, L.; Torres, E.R.S.; Carling, G.K.; Liu, B.; McGurran, H.; Coronas-Samano, G.; Kauwe, G.; et al. Tau activation of microglial cGAS-IFN reduces MEF2C-mediated cognitive resilience. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 737–750. [Google Scholar]
- Birkle, T.J.Y.; Brown, G.C. Syk inhibitors protect against microglia-mediated neuronal loss in culture. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1120952. [Google Scholar]
- Gringhuis, S.I.; Kaptein, T.M.; Wevers, B.A.; Theelen, B.; van der Vlist, M.; Boekhout, T.; Geijtenbeek, T.B. Dectin-1 is an extracellular pathogen sensor for the induction and processing of IL-1β via a noncanonical caspase-8 inflammasome. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, M.L.; Limon, J.J.; Underhill, D.M. Immunity to Commensal Fungi: Detente and Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2017, 12, 359–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ennerfelt, H.; Frost, E.L.; Shapiro, D.A.; Holliday, C.; Zengeler, K.E.; Voithofer, G.; Bolte, A.C.; Lammert, C.R.; Kulas, J.A.; Ulland, T.K.; et al. SYK coordinates neuroprotective microglial responses in neurodegenerative disease. Cell 2022, 185, 4135–4152.e22. [Google Scholar]
- Krasemann, S.; Madore, C.; Cialic, R.; Baufeld, C.; Calcagno, N.; El Fatimy, R.; Beckers, L.; O’Loughlin, E.; Xu, Y.; Fanek, Z.; et al. The TREM2-APOE Pathway Drives the Transcriptional Phenotype of Dysfunctional Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Immunity 2017, 47, 566–581.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren-Shaul, H.; Spinrad, A.; Weiner, A.; Matcovitch-Natan, O.; Dvir-Szternfeld, R.; Ulland, T.K.; David, E.; Baruch, K.; Lara-Astaiso, D.; Toth, B.; et al. A Unique Microglia Type Associated with Restricting Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell 2017, 169, 1276–1290.e17. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, E.S.; Suh, K.; Han, J.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, W.S.; Mook-Jung, I. Amyloid-β activates NLRP3 inflammasomes by affecting microglial immunometabolism through the Syk-AMPK pathway. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13623. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Bian, Y.; Pang, P.; Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Du, W. Inhibition of Dectin-1 in mice ameliorates cardiac remodeling by suppressing NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling after myocardial infarction. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; He, M.; Cheng, C.; Yang, K.; Wu, H.; Cong, P.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Clec7a Worsens Long-Term Outcomes after Ischemic Stroke by Aggravating Microglia-Mediated Synapse Elimination. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2403064. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Wettschurack, K.; Que, Z.; Deming, B.A.; Olivero-Acosta, M.I.; Cui, N.; Eaton, M.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Microglial over-pruning of synapses during development in autism-associated SCN2A-deficient mice and human cerebral organoids. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 2424–2437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Yalcin, E.; Presumey, J.; Aw, E.; Ma, M.; Whelan, C.W.; Stevens, B.; McCarroll, S.A.; Carroll, M.C. Overexpression of schizophrenia susceptibility factor human complement C4A promotes excessive synaptic loss and behavioral changes in mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 214–224. [Google Scholar]
- Sellgren, C.M.; Gracias, J.; Watmuff, B.; Biag, J.D.; Thanos, J.M.; Whittredge, P.B.; Fu, T.; Worringer, K.; Brown, H.E.; Wang, J.; et al. Increased synapse elimination by microglia in schizophrenia patient-derived models of synaptic pruning. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, H.S.; Li, H.H.; Wang, H.J.; Zou, R.S.; Lu, X.J.; Wang, J.; Nie, B.B.; Wu, J.F.; Li, S.; et al. Microglia-dependent excessive synaptic pruning leads to cortical underconnectivity and behavioral abnormality following chronic social defeat stress in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 109, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Matera, A.; Compagnion, A.C.; Pedicone, C.; Kotah, J.M.; Ivanov, A.; Monsorno, K.; Labouèbe, G.; Leggio, L.; Pereira-Iglesias, M.; Beule, D.; et al. Microglial lipid phosphatase SHIP1 limits complement-mediated synaptic pruning in the healthy developing hippocampus. Immunity 2025, 58, 197–217.e13. [Google Scholar]
- De Schepper, S.; Ge, J.Z.; Crowley, G.; Ferreira, L.S.S.; Garceau, D.; Toomey, C.E.; Sokolova, D.; Rueda-Carrasco, J.; Shin, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Perivascular cells induce microglial phagocytic states and synaptic engulfment via SPP1 in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 406–415. [Google Scholar]
- Andoh, M.; Shinoda, N.; Taira, Y.; Araki, T.; Kasahara, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Miura, M.; Ikegaya, Y.; Koyama, R. Nonapoptotic caspase-3 guides C1q-dependent synaptic phagocytosis by microglia. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 918. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, S.; Sun, H.; Li, A.; Hou, F.; Qi, L.; Liao, H. STING inhibition suppresses microglia-mediated synapses engulfment and alleviates motor functional deficits after stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Dejanovic, B.; Huntley, M.A.; De Mazière, A.; Meilandt, W.J.; Wu, T.; Srinivasan, K.; Jiang, Z.; Gandham, V.; Friedman, B.A.; Ngu, H.; et al. Changes in the Synaptic Proteome in Tauopathy and Rescue of Tau-Induced Synapse Loss by C1q Antibodies. Neuron 2018, 100, 1322–1336.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.M.S.; Rodrigues, J.M.M.; Pérez-Madrigal, M.M.; Dove, A.P.; Mano, J.F. Modular Functionalization of Laminarin to Create Value-Added Naturally Derived Macromolecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 19689–19697. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.C.; Hao, Q.; Ma, W.J.; Zhao, Q.C.; Wang, W.W.; Yin, H.H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Zan, K.; Yang, X.X.; et al. Dectin-1/Syk signaling triggers neuroinflammation after ischemic stroke in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Spangenberg, E.E.; Lee, R.J.; Najafi, A.R.; Rice, R.A.; Elmore, M.R.; Blurton-Jones, M.; West, B.L.; Green, K.N. Eliminating microglia in Alzheimer’s mice prevents neuronal loss without modulating amyloid-beta pathology. Brain 2016, 139 Pt 4, 1265–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangenberg, E.; Severson, P.L.; Hohsfield, L.A.; Crapser, J.; Zhang, J.; Burton, E.A.; Zhang, Y.; Spevak, W.; Lin, J.; Phan, N.Y.; et al. Sustained microglial depletion with CSF1R inhibitor impairs parenchymal plaque development in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harry, G.J. Microglia during development and aging. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 139, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stevens, B.; Allen, N.J.; Vazquez, L.E.; Howell, G.R.; Christopherson, K.S.; Nouri, N.; Micheva, K.D.; Mehalow, A.K.; Huberman, A.D.; Stafford, B.; et al. The classical complement cascade mediates CNS synapse elimination. Cell 2007, 131, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, Y.G.; Kim, N.S.; Kim, G.; Jeon, Y.S.; Choi, J.B.; Park, C.W.; Kim, K.; Jang, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.; et al. Stress induces behavioral abnormalities by increasing expression of phagocytic receptor MERTK in astrocytes to promote synapse phagocytosis. Immunity 2023, 56, 2105–2120.e13. [Google Scholar]
- Dejanovic, B.; Wu, T.; Tsai, M.C.; Graykowski, D.; Gandham, V.D.; Rose, C.M.; Bakalarski, C.E.; Ngu, H.; Wang, Y.; Pandey, S.; et al. Complement C1q-dependent excitatory and inhibitory synapse elimination by astrocytes and microglia in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 837–850. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wan, P.; Pi, M.; Xiong, Q.; Shu, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Clec7a Signaling in Microglia Promotes Synapse Loss Associated with Tauopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072888
Yang S, Wang J, Cao Y, Zhang Y, Sun Z, Wan P, Pi M, Xiong Q, Shu X, Wang X, et al. Clec7a Signaling in Microglia Promotes Synapse Loss Associated with Tauopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072888
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shubing, Ji Wang, Yongkang Cao, Yibo Zhang, Zhuoran Sun, Pin Wan, Mingshan Pi, Qi Xiong, Xiji Shu, Xiaochuan Wang, and et al. 2025. "Clec7a Signaling in Microglia Promotes Synapse Loss Associated with Tauopathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072888
APA StyleYang, S., Wang, J., Cao, Y., Zhang, Y., Sun, Z., Wan, P., Pi, M., Xiong, Q., Shu, X., Wang, X., & Xia, Y. (2025). Clec7a Signaling in Microglia Promotes Synapse Loss Associated with Tauopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072888





