Clinical Features of Families with a Novel Pathogenic Mutation in Sepiapterin Reductase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Family History and Clinical Presentations
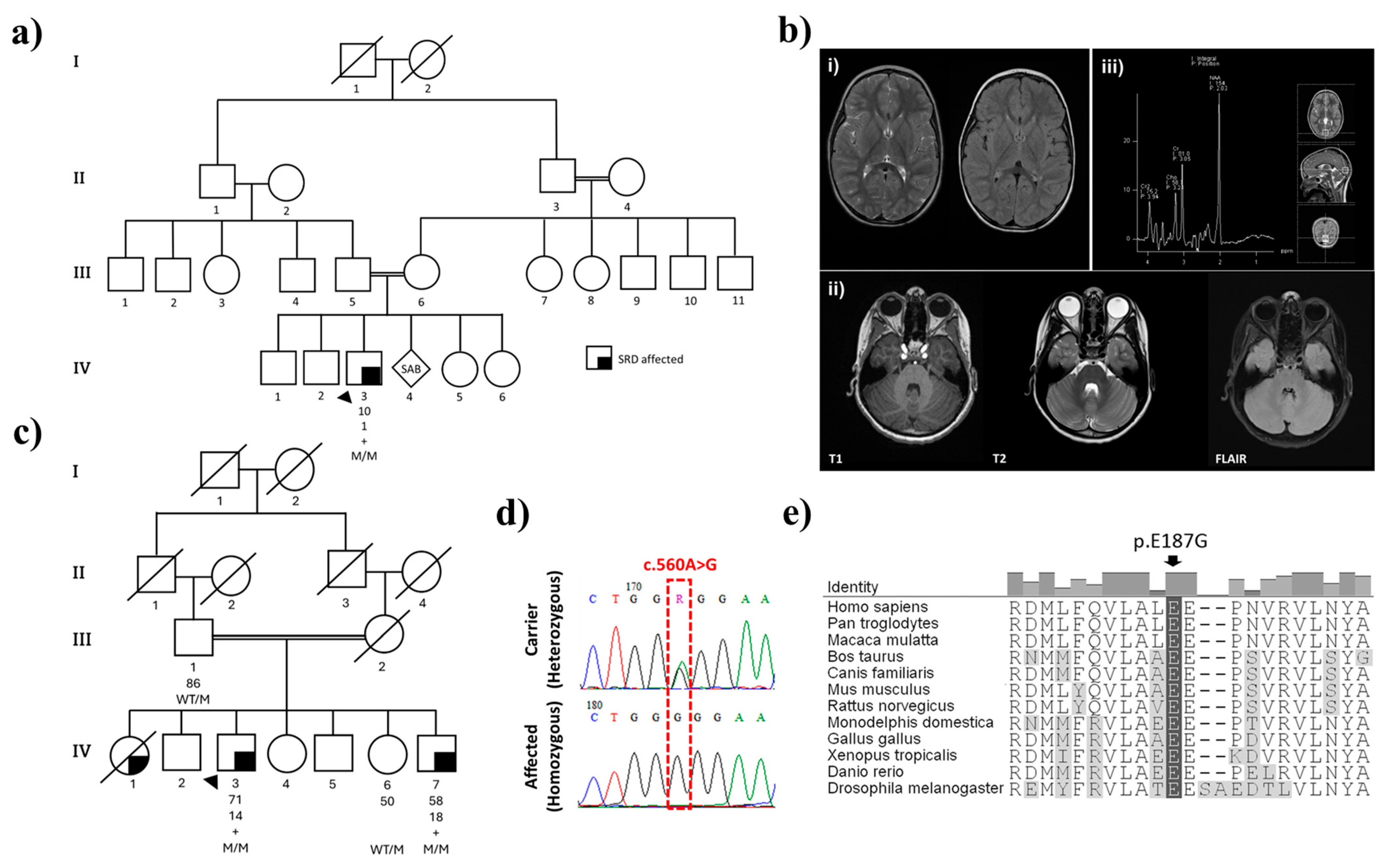
2.1.1. Family 1
2.1.2. Family 2
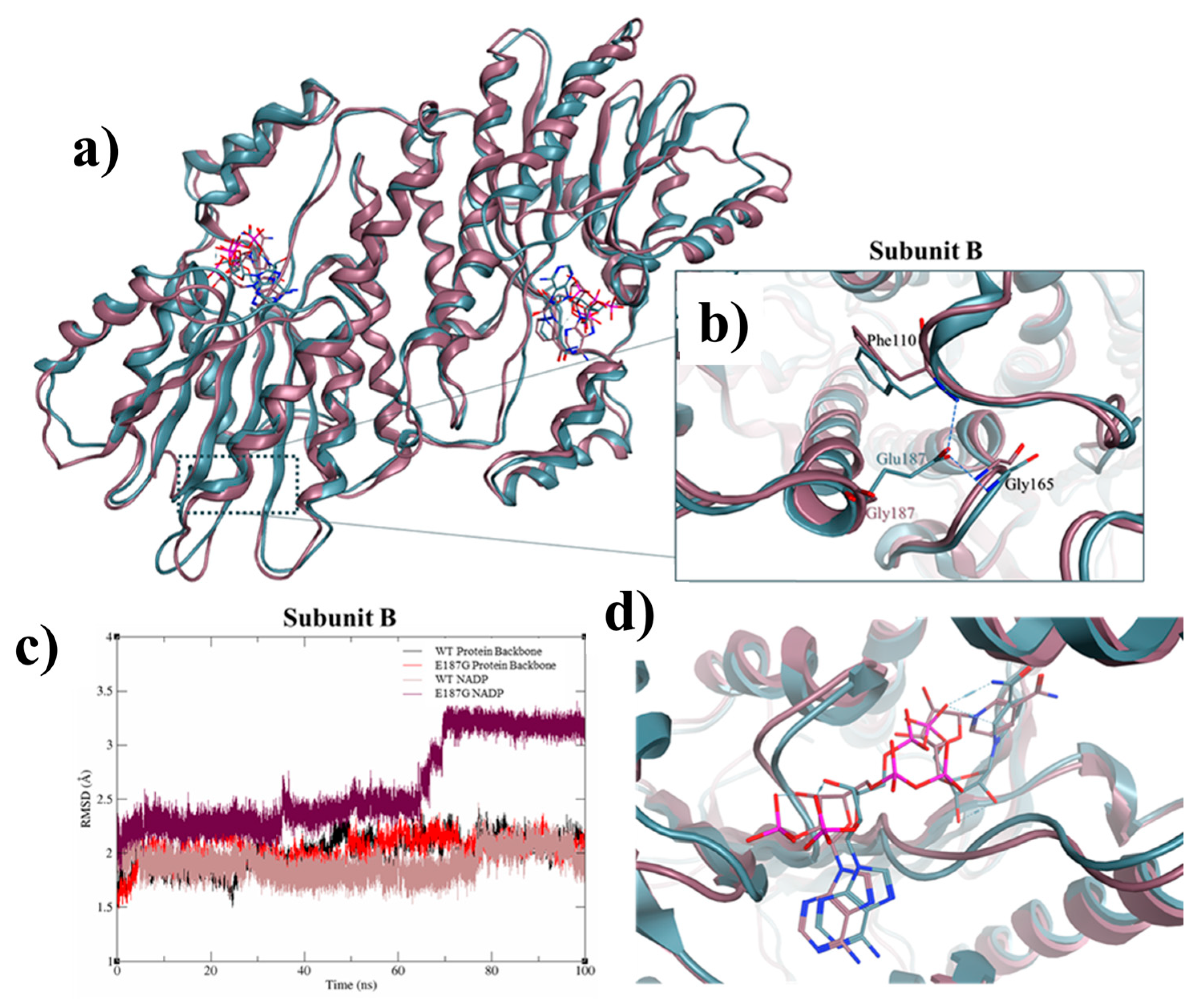
2.2. Genomic and Protein Structure Analyses
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Methods
4.1. Ethics
4.2. Clinical and Genealogic Assessment
4.3. Genomic and In Silico Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SRD | Sepiapterin Reductase Deficiency |
| BH4 | Tetrahydrobiopterin |
| HGMD | Human Gene Mutation Database |
| SR | Sepiapterin Reductase |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| MD | Molecular Dynamics |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| DTR | Deep Tendon Reflexes |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| FAB | Frontal Assessment Battery |
| MDS-UPDRS | Movement Disorder Society—Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale |
| SCOPA-AUT | Scales for Outcomes in Parkinson’s Disease—Autonomic Dysfunction |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| T2WI | T2-Weighted Imaging |
| NCS | Nerve Conduction Study |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| 5-HTP | 5-Hydroxytryptophan |
| SMA | Spinal Muscular Atrophy |
| DYT | Dopa-Responsive Dystonia |
| BP | Biopterin |
| NP | Neopterin |
| SP | Sepiapterin |
| CP | Cerebral Palsy |
References
- Friedman, J. Sepiapterin Reductase Deficiency. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bonafé, L.; Thöny, B.; Penzien, J.M.; Czarnecki, B.; Blau, N. Mutations in the Sepiapterin Reductase Gene Cause a Novel Tetrahydrobiopterin-Dependent Monoamine-Neurotransmitter Deficiency without Hyperphenylalaninemia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, P.; Sun, L.; Yuan, S.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, L.; Du, H.; Zhan, M. Sepiapterin reductase: Characteristics and role in diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9495–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenson, P.D.; Ball, E.V.; Mort, M.; Phillips, A.D.; Shiel, J.A.; Thomas, N.S.T.; Abeysinghe, S.; Krawczak, M.; Cooper, D.N. Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD®): 2003 update. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blau, N.; Bonafé, L.; Thöny, B. Tetrahydrobiopterin deficiencies without hyperphenylalaninemia: Diagnosis and genetics of dopa-responsive dystonia and sepiapterin reductase deficiency. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2001, 74, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.; Roze, E.; Abdenur, J.E.; Chang, R.; Gasperini, S.; Saletti, V.; Wali, G.M.; Eiroa, H.; Neville, B.; Felice, A.; et al. Sepiapterin reductase deficiency: A treatable mimic of cerebral palsy. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaser, R.; Adusumalli, S.; Leng, S.N.; Sikic, M.; Ng, P.C. SIFT missense predictions for genomes. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin. Available online: https://franklin.genoox.com/clinical-db/home (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Pana, A.; Saggu, B.M. Dystonia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Phukan, J.; Albanese, A.; Gasser, T.; Warner, T. Primary dystonia and dystonia-plus syndromes: Clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and pathogenesis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 1074–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opladen, T.; López-Laso, E.; Cortès-Saladelafont, E.; Pearson, T.S.; Sivri, H.S.; Yildiz, Y.; Assmann, B.; Kurian, M.A.; Leuzzi, V.; Heales, S.; et al. Consensus guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) deficiencies. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, C.; Lohmann, K.; Marras, C.; Münchau, A. Hereditary Dystonia Overview. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hamosh, A.; Scott, A.F.; Amberger, J.; Bocchini, C.; Valle, D.; McKusick, V.A. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), a knowledgebase of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cloud, L.J.; Jinnah, H.A. Treatment strategies for dystonia. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Subhi, S.; Al Shahwan, S.; Al Muhaizae, M.; Al Zaidan, H.; Tabarki, B. Sepiapterin reductase deficiency: Report of 5 new cases. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. EJPN Off. J. Eur. Paediatr. Neurol. Soc. 2017, 21, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, F.E.; Ghattas, M.A.; Almansoori, T.M.; Tabouni, M.; Baydoun, I.; Kizhakkedath, P.; John, A.; Alblooshi, H.; Shaukat, Q.; Al-Jasmi, F. Novel compound heterozygous variants (c.971delA/c.542C>T) in SLC1A4 causes spastic tetraplegia, thin corpus callosum, and progressive microcephaly: A case report and mutational analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1183574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Automatic atom type and bond type perception in molecular mechanical calculations. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2006, 25, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemical Computing Group. Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), 2019.01; Chemical Computing Group ULC: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
| Patient Result (nmol/L) | Reference Range (nmol/L) | |
|---|---|---|
| 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid | 7 ↓ | 66–338 |
| Homovanillic Acid | 93 ↓ | 218–582 |
| 3-O-methyldopa | 6 | <100 |
| Sepiapterin | 3.8 ↑ | <2.0 |
| Dihydrobiopterin | 31.4 ↑ | 3.0–18.0 |
| c.560A>G (Glu187Gly) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Position | Gene | Exon 2 (Ch2:73115698) |
| Protein | The last amino acid of the 9th helix | |
| Allele frequency | GnomAD V4.1.0 = 6.26 × 10−7 G = 0.00000 (0/10,680, ALFA) * | |
| SIFT ** | Effect | Affect protein function |
| Score | 0.00 | |
| PolyPhen2 # | Effect | Probably damaging |
| Score | 1.0 | |
| PremPS | ΔΔG † (kcal mol-1) | 0.66 |
| Location | Core | |
| Conservation | Highly conserved | |
| The Hope Project | The variant is predicted to disturb the enzyme’s overall structure and conformation. | |
| Pathogenicity classification †† | Pathogenic (PP3, PS4, PM2, PP5) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, F.E.; Alzyoud, L.; Ghattas, M.A.; Tabouni, M.; Fienemann, A.; Trinh, J.; Baydoun, I.; Kizhakkedath, P.; Alblooshi, H.; Shaukat, Q.; et al. Clinical Features of Families with a Novel Pathogenic Mutation in Sepiapterin Reductase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073056
Mohamed FE, Alzyoud L, Ghattas MA, Tabouni M, Fienemann A, Trinh J, Baydoun I, Kizhakkedath P, Alblooshi H, Shaukat Q, et al. Clinical Features of Families with a Novel Pathogenic Mutation in Sepiapterin Reductase. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073056
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Feda E., Lara Alzyoud, Mohammad A. Ghattas, Mohammed Tabouni, André Fienemann, Joanne Trinh, Ibrahim Baydoun, Praseetha Kizhakkedath, Hiba Alblooshi, Qudsia Shaukat, and et al. 2025. "Clinical Features of Families with a Novel Pathogenic Mutation in Sepiapterin Reductase" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073056
APA StyleMohamed, F. E., Alzyoud, L., Ghattas, M. A., Tabouni, M., Fienemann, A., Trinh, J., Baydoun, I., Kizhakkedath, P., Alblooshi, H., Shaukat, Q., Amouri, R., Farrer, M. J., Sassi, S. B., & Al-Jasmi, F. (2025). Clinical Features of Families with a Novel Pathogenic Mutation in Sepiapterin Reductase. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073056






