Unlocking the Complexity of Antibody-Drug Conjugates: A Cutting-Edge LC-HRMS Approach to Refine Drug-to-Antibody Ratio Measurements with Highly Reactive Payloads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
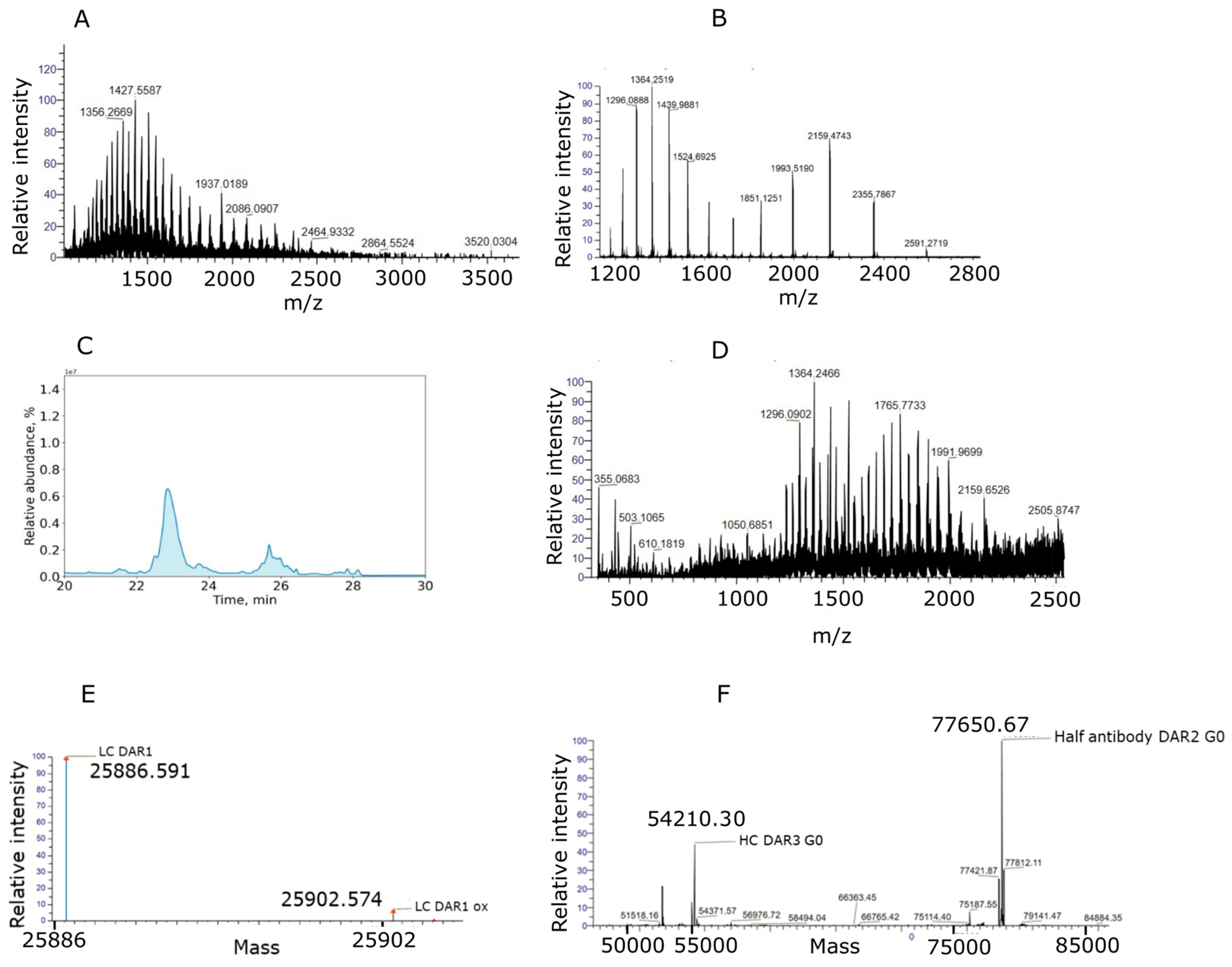
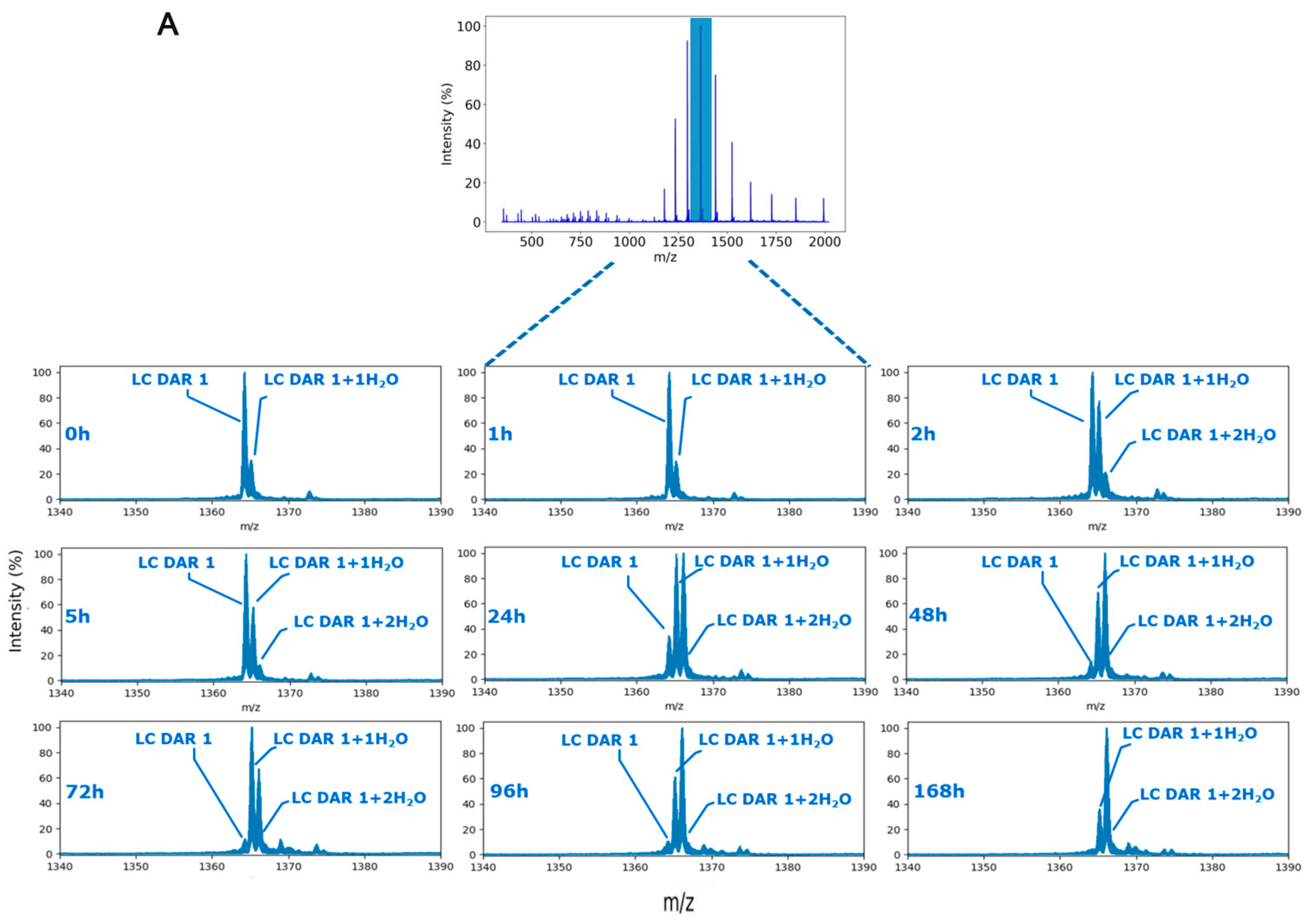
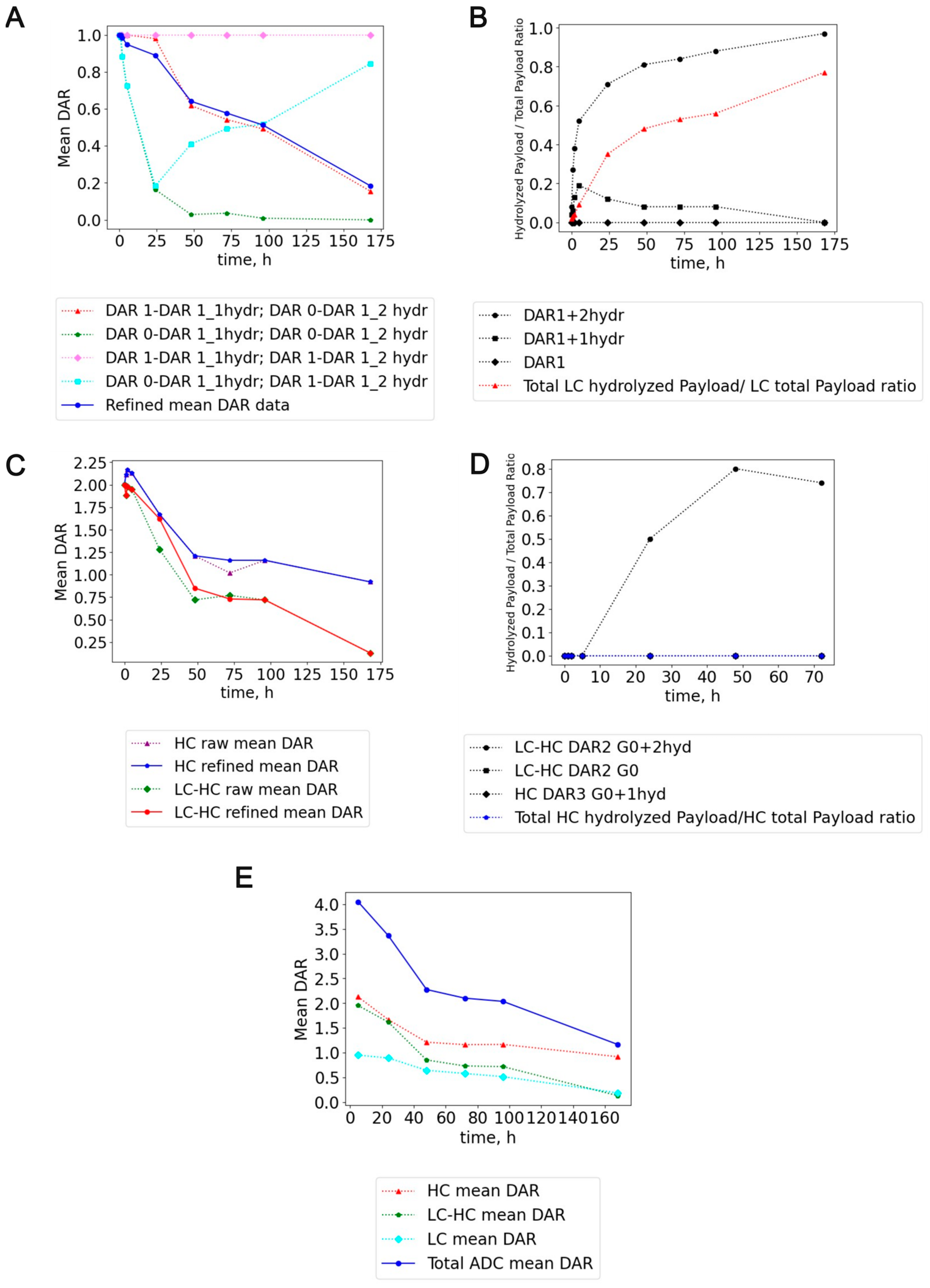
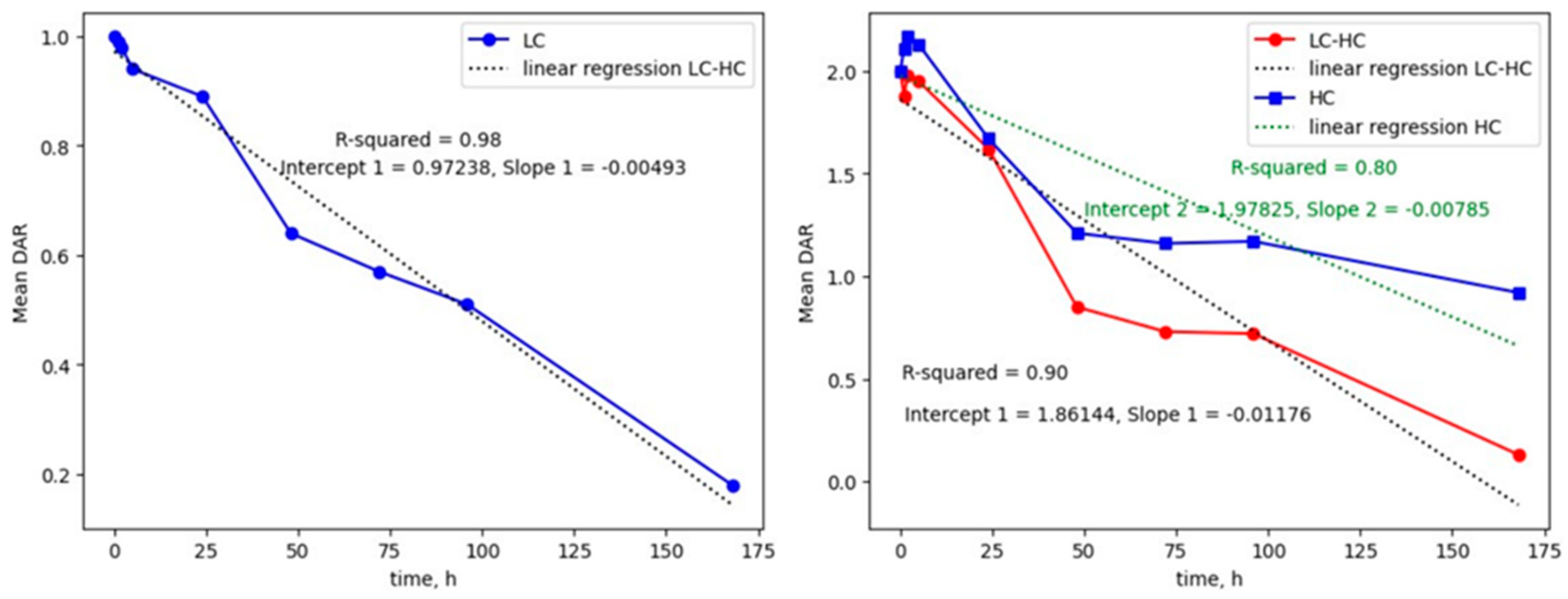
2.1. Intact Denaturing Non-Covalent ADC Analysis: An ADC Case Study with a Hydrolysis-Sensitive Payload
2.2. MS2-Based Identification Strategy Enables Better Understanding of ADC Conjugated with Highly Reactive Payloads
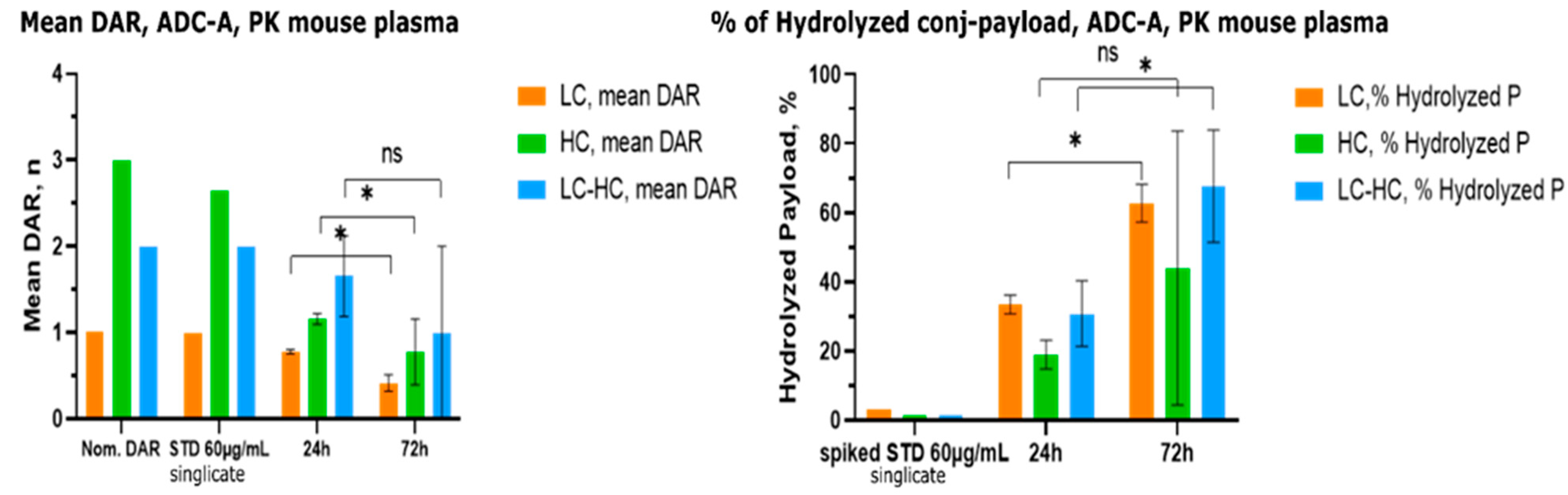
2.3. Method Application on In Vivo PK Mouse Plasma
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of In Vitro Plasma Stability Samples
3.3. In Vivo PK Study Design
3.4. Immuno-Enrichment from Mouse Plasma of Intact ADC-A
3.5. LC-HRMS Method for Non-Covalent Intact ADC Analysis in In Vitro Mouse Plasma Stability Samples
3.6. Targeted Data-Dependent MS/MS Method (tddMS2)
3.7. All-Ion Fragmentation MS Analysis (FS-AIF) for In Vivo PK Samples
3.8. LC-HRMS Analysis
3.9. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kennedy, P.J.; Oliveira, C.; Granja, P.L.; Sarmento, B. Antibodies and associates: Partners in targeted drug delivery. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 177, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L.; Wang, W.; Wu, M.; Yuan, T.; Yang, W.; Tian, C.; Miao, Z.; Wang, T.; et al. Small molecules in targeted cancer therapy: Advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahpour-Alitappeh, M.; Lotfinia, M.; Gharibi, T.; Mardaneh, J.; Farhadihosseinabadi, B.; Larki, P.; Faghfourian, B.; Sepehr, K.S.; Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi, K.; Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi, G.; et al. Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) for cancer therapy: Strategies, challenges, and successes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5628–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.M.; Senter, P.D. Arming antibodies: Prospects and challenges for immunoconjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parslow, A.C.; Parakh, S.; Lee, F.-T.; Gan, H.K.; Scott, A.M. Antibody–Drug Conjugates for Cancer Therapy. Biomedicines 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alley, S.C.; Okeley, N.M.; Senter, P.D. Antibody–drug conjugates: Targeted drug delivery for cancer. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.; Goetsch, L.; Dumontet, C.; Corvaïa, N. Strategies and challenges for the next generation of antibody–drug conjugates. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junutula, J.R.; Bhakta, S.; Raab, H.; Ervin, K.E.; Eigenbrot, C.; Vandlen, R.; Scheller, R.H.; Lowman, H.B. Rapid identification of reactive cysteine residues for site-specific labeling of antibody-Fabs. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 332, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.-Q.; Xu, K.; Liu, L.; Raab, H.; Bhakta, S.; Kenrick, M.; Parsons-Reponte, K.L.; Tien, J.; Yu, S.-F.; Mai, E.; et al. Conjugation site modulates the in vivo stability and therapeutic activity of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badescu, G.; Bryant, P.; Bird, M.; Henseleit, K.; Swierkosz, J.; Parekh, V.; Tommasi, R.; Pawlisz, E.; Jurlewicz, K.; Farys, M.; et al. Bridging Disulfides for Stable and Defined Antibody Drug Conjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeger, S.; Zimmermann, K.; Blanc, A.; Grünberg, J.; Honer, M.; Hunziker, P.; Struthers, H.; Schibli, R. Site-specific and stoichiometric modification of antibodies by bacterial transglutaminase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9995–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabuka, D.; Rush, J.S.; Dehart, G.W.; Wu, P.; Bertozzi, C.R. Site-specific chemical protein conjugation using genetically encoded aldehyde tags. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerli, R.R.; Hell, T.; Merkel, A.S.; Grawunder, U. Sortase enzyme-mediated generation of site-specifically conjugated antibody drug conjugates with high in vitro and in vivo potency. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panowski, S.; Bhakta, S.; Raab, H.; Polakis, P.; Junutula, J.R. Site-specific antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy. mAbs 2014, 6, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallam, T.J.; Wold, E.; Wahl, A.; Smider, V.V. Antibody conjugates with unnatural amino acids. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1848–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, K.; Loscha, K.V.; Kuppan, K.V.; Loh, C.T.; Dixon, N.E.; Otting, G. High-yield cell-free protein synthesis for site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids at two sites. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 418, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Xiao, D.; Xie, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, S. Antibody–drug conjugates: Recent advances in linker chemistry. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3889–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, F.; Corti, C.; Tarantino, P.; Michelini, F.; Curigliano, G. Bystander effect of antibody–drug conjugates: Fact or fiction? Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corso, A.D.; Cazzamalli, S.; Gébleux, R.; Mattarella, M.; Neri, D. Protease-Cleavable Linkers Modulate the Anticancer Activity of Noninternalizing Antibody–Drug Conjugates. Bioconjugate Chem. 2017, 28, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.; Stover, D. Using the Lessons Learned From the Clinic to Improve the Preclinical Development of Antibody Drug Conjugates. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 3458–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Zhang, D. Linker Design Impacts Antibody-Drug Conjugate Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy via Modulating the Stability and Payload Release Efficiency. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 687926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alley, S.C.; Benjamin, D.R.; Jeffrey, S.C.; Okeley, N.M.; Meyer, D.L.; Sanderson, R.J.; Senter, P.D. Contribution of linker stability to the activities of anticancer immunoconjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVay, R.M.; Delaria, K.; Zhu, G.; Holz, C.; Foletti, D.; Sutton, J.; Bolton, G.; Dushin, R.; Bee, C.; Pons, J.; et al. Improved Lysosomal Trafficking Can Modulate the Potency of Antibody Drug Conjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strop, P.; Liu, S.-H.; Dorywalska, M.; Delaria, K.; Dushin, R.G.; Tran, T.-T.; Ho, W.-H.; Farias, S.; Casas, M.G.; Abdiche, Y.; et al. Location Matters: Site of Conjugation Modulates Stability and Pharmacokinetics of Antibody Drug Conjugates. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gu, H.; Liu, A.; Kozhich, A.; Rangan, V.; Myler, H.; Luo, L.; Wong, R.; Sun, H.; Wang, B.; et al. Antibody–drug conjugate bioanalysis using LB-LC–MS/MS hybrid assays: Strategies, methodology and correlation to ligand-binding assays. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 1383–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Xu, K.; Saad, O.M.; Dere, R.C.; Carrasco-Triguero, M. Bioanalytical assay strategies for the development of antibody–drug conjugate biotherapeutics. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 201–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorovits, B.; Alley, S.C.; Bilic, S.; Booth, B.; Kaur, S.; Oldfield, P.; Purushothama, S.; Rao, C.; Shord, S.; Siguenza, P. White Paper Bioanalysis of antibody—Drug conjugates: American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists Antibody—Drug Conjugate Working Group position paper. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 997–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Kozhich, A.; Passmore, D.; Gu, H.; Wong, R.; Zambito, F.; Rangan, V.S.; Myler, H.; Aubry, A.-F.; Arnold, M.E.; et al. Quantitative bioanalysis of antibody-conjugated payload in monkey plasma using a hybrid immuno-capture LC–MS/MS approach: Assay development, validation, and a case study. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1002, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, M.; Sun, G.; Qiu, D.; Valente, J.; Lan, W.; Song, H.; Bolgar, M.; Katiyar, A.; Krishnamurthy, G. Drug-to-antibody determination for an antibody-drug-conjugate utilizing cathepsin B digestion coupled with reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1481, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, S.; Xu, J.; Lin, Z.J.; Lee, D.H. Simultaneous quantification of total antibody and antibody-conjugated drug for XMT-1522 in human plasma using immunocapture-liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 174, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, L.M.; Di Ianni, A.; Molinaro, F.; Cowan, K.J.; Sirtori, F.R. Hybrid liquid chromatography high resolution and accuracy mass spectrometry approach for quantification of antibody-drug conjugates at the intact protein level in biological samples. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 188, 106502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Liu, L.; Saad, O.M.; Baudys, J.; Williams, L.; Leipold, D.; Shen, B.; Raab, H.; Junutula, J.R.; Kim, A.; et al. Characterization of intact antibody–drug conjugates from plasma/serum in vivo by affinity capture capillary liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 412, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, J.; Park, M.; Shin, S.; Lee, B.I.; Park, Y.; Choi, J.; Kim, N.; Kang, Y.; Shin, Y.G. A single liquid chromatography–quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometric method for the quantification of total antibody, antibody-conjugated drug and free payload of antibody–drug conjugates. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32, e4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Ianni, A.; Cowan, K.J.; Riccardi Sirtori, F.; Barbero, L. Unlocking the Complexity of Antibody-Drug Conjugates: A Cutting-Edge LC-HRMS Approach to Refine Drug-to-Antibody Ratio Measurements with Highly Reactive Payloads. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073080
Di Ianni A, Cowan KJ, Riccardi Sirtori F, Barbero L. Unlocking the Complexity of Antibody-Drug Conjugates: A Cutting-Edge LC-HRMS Approach to Refine Drug-to-Antibody Ratio Measurements with Highly Reactive Payloads. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073080
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Ianni, Andrea, Kyra J. Cowan, Federico Riccardi Sirtori, and Luca Barbero. 2025. "Unlocking the Complexity of Antibody-Drug Conjugates: A Cutting-Edge LC-HRMS Approach to Refine Drug-to-Antibody Ratio Measurements with Highly Reactive Payloads" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073080
APA StyleDi Ianni, A., Cowan, K. J., Riccardi Sirtori, F., & Barbero, L. (2025). Unlocking the Complexity of Antibody-Drug Conjugates: A Cutting-Edge LC-HRMS Approach to Refine Drug-to-Antibody Ratio Measurements with Highly Reactive Payloads. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073080




