Immuno-PCR in the Analysis of Food Contaminants
Abstract
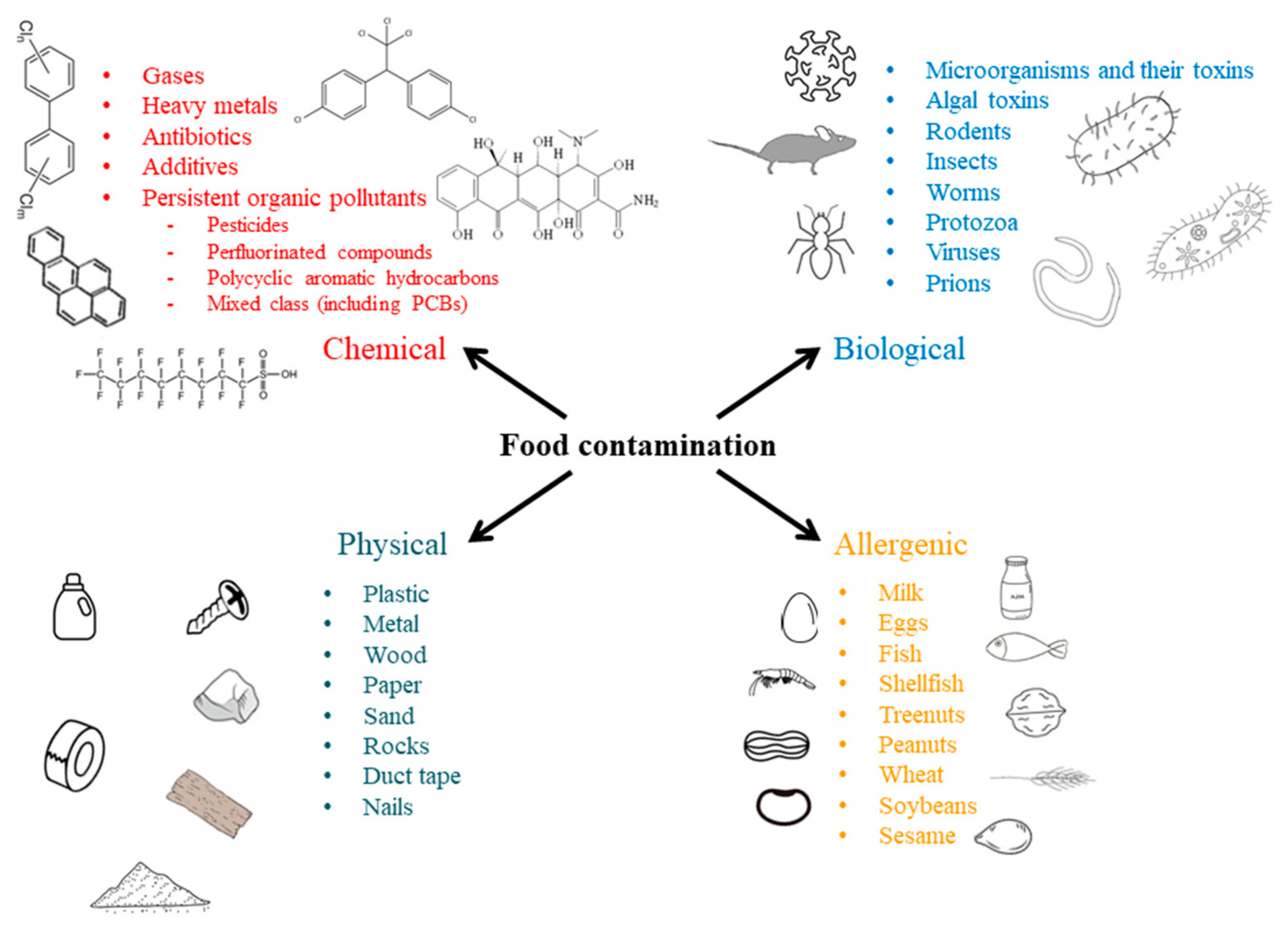
1. Food Contamination
Types of Food Contamination
2. Analytical Methods for Detection and Quantification of Food Contaminants
3. Immuno-PCR
4. Application of Immuno-PCR in the Detection of Food Contaminants
4.1. Pathogenic Bacteria
4.2. Bacterial Toxins
4.3. Mycotoxins
4.4. Viruses
4.5. Allergens
4.6. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
4.7. Polychlorinated Biphenyls
4.8. Phthalic Acid Esters
4.9. Pesticides
4.10. Antibiotics
4.11. Other (Miscellaneous) Food Contaminants
5. Future Perspective and Challenges of Immuno-PCR in Food Safety Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pakdel, M.; Olsen, A.; Bar, E.M.S. A Review of Food Contaminants and Their Pathways Within Food Processing Facilities Using Open Food Processing Equipment. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, V.; Cairncross, S.; Yonli, R. Review: Domestic Hygiene and Diarrhoea—Pinpointing the Problem. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2000, 5, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, R.; Bloomfield, S.; Adley, C.C. A Study of Cross-Contamination of Food-Borne Pathogens in the Domestic Kitchen in the Republic of Ireland. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 76, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelaar, A.H.; Kirk, M.D.; Torgerson, P.R.; Gibb, H.J.; Hald, T.; Lake, R.J.; Praet, N.; Bellinger, D.C.; de Silva, N.R.; Gargouri, N.; et al. World Health Organization Global Estimates and Regional Comparisons of the Burden of Foodborne Disease in 2010. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, B.M.; O’Brien, S.J. The Occurrence and Prevention of Foodborne Disease in Vulnerable People. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.; Sallade, L.; Sanchez, E.; Zhang, Y.; Naumova, E. Analysing Foodborne Illness Outbreak Severity in the USA, 2009–2019. In Proceedings of the Consortium of Universities for Global Health Annual Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 8–10 March 2022; p. S5. [Google Scholar]
- Painter, J.A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Ayers, T.; Tauxe, R.V.; Braden, C.R.; Angulo, F.J.; Griffin, P.M. Attribution of Foodborne Illnesses, Hospitalizations, and Deaths to Food Commodities by Using Outbreak Data, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union One Health 2023 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, A.; Hudson, J.A.; Axon, A. Risk Categorization of Foods of Non-Animal Origin Subject to United Kingdom Import Controls. J. Food Prot. 2025, 88, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, A.; Mora-Cantallops, M.; Díaz Morón, R.; García-Tejedor, Á.J. Network Analysis for Food Safety: Quantitative and Structural Study of Data Gathered through the RASFF System in the European Union. Food Control 2023, 145, 109422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigłowski, M.; Nogales, A.; Śmiechowska, M. Hazards in Products from Northern Mediterranean Countries Reported in the Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) in 1997–2021 in the Context of Sustainability. Sustainability 2025, 17, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, F.H.b.L.R.; Yusof, M.I.N.b.M.; Nizar, N.N.A. Conventional and Modern Standards of Food Production. In Preparation and Processing of Religious and Cultural Foods; Ali, E., Nizar, N.N.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 295–307. [Google Scholar]
- Garvey, M. Food Pollution: A Comprehensive Review of Chemical and Biological Sources of Food Contamination and Impact on Human Health. Nutrire 2019, 44, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, F.L. Diseases Transmitted by Foods: (A Classification and Summary), 2nd ed.; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Public Health Service; Centers for Disease Control; Center for Professional Development and Training: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1982.
- Thakali, A.; MacRae, J.D. A Review of Chemical and Microbial Contamination in Food: What Are the Threats to a Circular Food System? Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.; Kumar, D.; Hussain, S.; Pathak, A.; Shukla, M.; Prasanna Kumar, V.; Anisha, P.N.; Rautela, R.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Singh, S.P. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes Characterization of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Isolated from Retail Chicken Meat Shops in Northern India. Food Control 2019, 102, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, R.A.; Chirilã, M. Routes of Transmission in the Food Chain. In Foodborne Diseases; Dodd, C.E.R., Aldsworth, T., Stein, R.A., Cliver, D.O., Riemann, H.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 65–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ly, N.H.; Barceló, D.; Vasseghian, Y.; Choo, J.; Joo, S.-W. Sustainable Bioremediation Technologies for Algal Toxins and Their Ecological Significance. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechard, A.; Lang, C. Seafood Consumption during Harmful Algal Blooms: The Impact of Information Regarding Safety and Health. Harmful Algae 2023, 123, 102387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoti, M.I.; Edokpayi, J.N.; Mutileni, N.; Durowoju, O.S.; Munyai, F.L. Cyanotoxins in Groundwater; Occurrence, Potential Sources, Health Impacts and Knowledge Gap for Public Health. Toxicon 2023, 226, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Diaz-Perez, Z.; Sheridan, M.; Royer, H.; Leibensperger, R.; Maizel, D.; Brand, L.; Popendorf, K.J.; et al. Exposure to Aerosolized Algal Toxins in South Florida Increases Short- and Long-Term Health Risk in Drosophila Model of Aging. Toxins 2020, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.J. Prions: A Threat to Health Security and the Need for Effective Medical Countermeasures. Glob. Health J. 2023, 7, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobben, A.H.; Steele, P.J.; Somerville, R.A.; Taylor, D.M.; Schreuder, B.E.C. Inactivation of the BSE Agent by the Heat and Pressure Process for Manufacturing Gelatine. Vet. Rec. 2005, 157, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.M.; Salamat, M.K.F.; Almela, F.; Cooper, J.K.; Ladhani, K.; Arnold, M.E.; Bougard, D.; Andréoletti, O.; Houston, E.F. Longitudinal Detection of Prion Infection in Preclinical Sheep Blood Samples Compared Using 3 Assays. Blood 2024, 144, 1962–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierstein, J.L.; Brown, D.; Gupta, R.; Bilaver, L. Understanding Food-Related Allergic Reactions Through a US National Patient Registry. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 206–215.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Johnston, E.B.; Nugraha, R.; Le, T.T.K.; Kalic, T.; McLean, T.R.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L. Seafood Allergy: A Comprehensive Review of Fish and Shellfish Allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 28–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, W.J.; Taylor, S.L.; Phipatanakul, W.; Brough, H.A. Environmental Food Exposure: What Is the Risk of Clinical Reactivity From Cross-Contact and What Is the Risk of Sensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiocchi, A.; Risso, D.; DunnGalvin, A.; González Díaz, S.N.; Monaci, L.; Fierro, V.; Ansotegui, I.J. Food Labeling Issues for Severe Food Allergic Patients. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocchi, A.; Monaci, L.; De Angelis, E.; Calandrelli, V.; Dahdah, L.; Valluzzi, R.; Urbani, S.; Mazzuca, C.; Arasi, S.; Cafarotti, A.; et al. Reactivity to Allergenic Food Contaminants: A Study on Products on the Market. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2023, 13, e12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DunnGalvin, A.; Chan, C.-H.; Crevel, R.; Grimshaw, K.; Poms, R.; Schnadt, S.; Taylor, S.L.; Turner, P.; Allen, K.J.; Austin, M.; et al. Precautionary Allergen Labelling: Perspectives from Key Stakeholder Groups. Allergy 2015, 70, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.B.; Christensen, G.; Grinter, K.; Sherlock, R.; Warren, L. The Allergen Bureau VITAL Program. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Risk Assessment of Food Allergens—Part 3: Review and Establish Precautionary Labelling in Foods of the Priority Allergens; FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; ISBN 978-92-5-137878-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Walker, G.W.; Muir, D.C.G.; Nagatani-Yoshida, K. Toward a Global Understanding of Chemical Pollution: A First Comprehensive Analysis of National and Regional Chemical Inventories. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2575–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, I.A.; Koh, W.Y.; Paek, W.K.; Lim, J. The Sources of Chemical Contaminants in Food and Their Health Implications. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerín, C.; Aznar, M.; Carrizo, D. Food Contamination during Food Process. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 48, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebelo, K.; Malebo, N.; Mochane, M.J.; Masinde, M. Chemical Contamination Pathways and the Food Safety Implications along the Various Stages of Food Production: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Solà, J.; Abadias, M.; Colás-Medà, P.; Sánchez, G.; Bobo, G.; Viñas, I. Evaluation of a Sanitizing Washing Step with Different Chemical Disinfectants for the Strawberry Processing Industry. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 334, 108810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Food Additives. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-additives (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Warner, J.O. Artificial Food Additives: Hazardous to Long-Term Health? Arch. Dis. Child. 2024, 109, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, M.S.; Qasem, A.A.A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Hussain, S.; Ibraheem, M.A.; Shamlan, G.; Alqah, H.A.; Qasha, A.S. Food Packaging’s Materials: A Food Safety Perspective. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4490–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caserta, D.; Costanzi, F.; De Marco, M.P.; Besharat, A.; Ruscito, I. Introduction to Environmental Pollutants and Human Exposure. In Environment Impact on Reproductive Health; Marci, R., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, L.A.; Darwish, W.S. Environmental Chemical Contaminants in Food: Review of a Global Problem. J. Toxicol. 2019, 2019, 2345283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolshahi, A.; Shokrollahi Yancheshmeh, B. Food Contamination. In Mycotoxins and Food Safety; Sabuncuoğlu, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Udovicki, B.; Andjelkovic, M.; Cirkovic-Velickovic, T.; Rajkovic, A. Microplastics in Food: Scoping Review on Health Effects, Occurrence, and Human Exposure. Int. J. Food Contam. 2022, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.S.; O’Keefe, T.L.; Froehlich, C.; Lewis, R.E.; Sheldon, T.R.; Haynes, C.L. Sensing Food Contaminants: Advances in Analytical Methods and Techniques. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yao, T.; Xu, H. Detection of Food Contaminants: A Review of Established Rapid Analytical Techniques and Their Applications and Limitations. Food Saf. Health 2024, 2, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, A.; Jain, U.; Chauhan, N. Progressive Analytical Techniques Utilized for the Detection of Contaminants Attributed to Food Safety and Security. Talanta Open 2024, 10, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sheng, W.; Liu, B.; Wang, S. ELISA-Based Sensing in Food Safety and Quality Analysis. In Sensing Techniques for Food Safety and Quality Control; Lu, X., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; pp. 141–163. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Wang, X.; Niu, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Suona, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X. Overview of Analytical Methods for the Determination of Microplastics: Current Status and Trends. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkovic, A.; Jovanovic, J.; Monteiro, S.; Decleer, M.; Andjelkovic, M.; Foubert, A.; Beloglazova, N.; Tsilla, V.; Sas, B.; Madder, A.; et al. Detection of Toxins Involved in Foodborne Diseases Caused by Gram-positive Bacteria. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1605–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapaksha, P.; Elbourne, A.; Gangadoo, S.; Brown, R.; Cozzolino, D.; Chapman, J. A Review of Methods for the Detection of Pathogenic Microorganisms. Analyst 2019, 144, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aladhadh, M. A Review of Modern Methods for the Detection of Foodborne Pathogens. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesta-Peters, E.G.; Reij, M.W.; Blaauw, R.H.; In ′t Veld, P.H.; Rajkovic, A.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Abee, T. Quantification of the Emetic Toxin Cereulide in Food Products by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Using Synthetic Cereulide as a Standard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7466–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornelis, V.; Rajkovic, A.; Decleer, M.; Sas, B.; De Saeger, S.; Madder, A. Counteracting in Vitro Toxicity of the Ionophoric Mycotoxin Beauvericin—Synthetic Receptors to the Rescue. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 10422–10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzhauser, T. Protein or No Protein? Opportunities for DNA-Based Detection of Allergenic Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9889–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzhauser, T.; Johnson, P.; Hindley, J.P.; O’Connor, G.; Chan, C.-H.; Costa, J.; Fæste, C.K.; Hirst, B.J.; Lambertini, F.; Miani, M.; et al. Are Current Analytical Methods Suitable to Verify VITAL®2.0/3.0 Allergen Reference Doses for EU Allergens in Foods? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Eun, J.-B.; Shim, J.-H.; Zhao, J.; Lei, X.; Gao, S.; She, Y.; Jin, F.; Wang, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Rapid Detection Techniques for Pesticide Residue: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13093–13117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, E.J.; Jobst, K.J.; Megson, D.; Dorman, F.L.; Focant, J.-F. Analytical Methodology of POPs. In Environmental Forensics for Persistent Organic Pollutants; O’Sullivan, G., Sandau, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 59–139. ISBN 978-0-444-59424-2. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Niu, Y.; Xing, L.; Liang, Z.; Song, X.; Ding, M.; Huang, W. Research Progress of the Detection and Analysis Methods of Heavy Metals in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1310328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Meng, Z.; Soutis, C.; Wang, P.; Gibson, A. Detection and Analysis of Metallic Contaminants in Dry Foods Using a Microwave Resonator Sensor. Food Control 2022, 133, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaid, B.; Saroufil, T.; Berim, R.; Majzoub, S.; Hussain, A.J. Food Physical Contamination Detection Using AI-Enhanced Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. AgriFood Electron. 2024, 2, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiraz, M.P.; Majumdar, P.R.; Mahmud, M.M.C.; Bhowmik, S.; Ali, A. Conventional and Advanced Detection Techniques of Foodborne Pathogens: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Mandrell, R. Detection of Norovirus Capsid Proteins in Faecal and Food Samples by a Real Time Immuno-PCR Method. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Smith, C.L.; Cantor, C.R. Immuno-PCR: Very Sensitive Antigen Detection by Means of Specific Antibody-DNA Conjugates. Science 1992, 258, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomirović, M.; Gligorijević, N.; Stanić-Vučinić, D.; Rajković, A.; Ćirković Veličković, T. Ultrasensitive Quantification of Crustacean Tropomyosin by Immuno-PCR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; McMahon, S.; McKeon, T.A.; Brandon, D.L. Development of a Novel Immuno-PCR Assay for Detection of Ricin in Ground Beef, Liquid Chicken Egg, and Milk. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abud, J.E.; Santamaría, C.G.; Luque, E.H.; Rodriguez, H.A. Development of a Quantitative Immuno-Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay to Detect and Quantify Low Levels of Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 539, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Hua, D.; Li, Y.; Deng, H.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; Huang, J. Rapid Detection of Food-Borne Salmonella Contamination Using IMBs-QPCR Method Based on PagC Gene. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerseelan, L.; Muriana, P.M. An Immunomagnetic PCR Signal Amplification Assay for Sensitive Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus Enterotoxins in Foods. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 2538–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, F.; Mie, M.; Kobatake, E. DNA-Based Immunoassays for Sensitive Detection of Protein. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Immuno-PCR: An Ultrasensitive Immunoassay for Biomolecular Detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 910, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemeyer, C.M.; Adler, M.; Wacker, R. Detecting Antigens by Quantitative Immuno-PCR. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1918–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assumpção, A.L.F.V.; da Silva, R.C. Immuno-PCR in Cancer and Non-Cancer Related Diseases: A Review. Vet. Q. 2016, 36, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gofflot, S.; El Moualij, B.; Zorzi, D.; Melen, L.; Roels, S.; Quatpers, D.; Grassi, J.; Vanopdenbosch, E.; Heinen, E.; Zorzi, W. Immuno-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction for Detection and Quantitation of Prion Protein. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2004, 25, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryazantsev, D.Y.; Voronina, D.V.; Zavriev, S.K. Immuno-PCR: Achievements and Perspectives. Biochemistry 2016, 81, 1754–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potůčková, L.; Franko, F.; Bambousková, M.; Dráber, P. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Cytokines Using Functionalized Gold Nanoparticle-Based Immuno-PCR, Comparison with Immuno-PCR and ELISA. J. Immunol. Methods 2011, 371, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.; Grösche, M.; Adler, M.; Spengler, M.; Niemeyer, C.M. Immuno-PCR with Digital Readout. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 488, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-C.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Zhang, X.-E.; Zhang, Z.-P.; Qiao, Y.-M.; Bi, L.-J.; Wen, J.-K.; Liang, M.-F.; Zhang, J.-B. Phage Display Mediated Immuno-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkovic, A.; El Moualij, B.; Uyttendaele, M.; Brolet, P.; Zorzi, W.; Heinen, E.; Foubert, E.; Debevere, J. Immunoquantitative Real-Time PCR for Detection and Quantification of Staphylococcus Aureus Enterotoxin B in Foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6593–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkovic, A.; El Moualij, B.; Fikri, Y.; Dierick, K.; Zorzi, W.; Heinen, E.; Uner, A.; Uyttendaele, M. Detection of Clostridium Botulinum Neurotoxins A and B in Milk by ELISA and Immuno-PCR at Higher Sensitivity than Mouse Bio-Assay. Food Anal. Methods 2012, 5, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, B.; Ramlal, S.; Setlem, K.; Mahadeva, A.; Aradhya, S.; Parida, M. A Real-Time Immunocapture PCR (RT-IPCR) without Interference of Protein A for Convenient Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B from Food and Environmental Samples. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjezi, R.; Tan, S.W.; Tey, B.T.; Sieo, C.C.; Tan, W.S. Detection of Hepatitis B Virus Core Antigen by Phage Display Mediated TaqMan Real-Time Immuno-PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 187, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wei, H.; Guo, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.-E. Gold Nanoparticle Enhanced Immuno-PCR for Ultrasensitive Detection of Hantaan Virus Nucleocapsid Protein. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 346, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barletta, J.M.; Edelman, D.C.; Constantine, N.T. Lowering the Detection Limits of HIV-1 Viral Load Using Real-Time Immuno-PCR for HIV-1 P24 Antigen. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 122, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivovarov, V.D.; Ryazantsev, D.Y.; Simonova, M.A.; Yegorova, T.V.; Khlgatian, S.V.; Zavriev, S.K.; Svirshchevskaya, E. V Immuno-PCR Assay for Quantitation of Antibodies to Epstein–Barr Virus. Mol. Biol. 2018, 52, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, E.B.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L.; Schaeffer, P.M. Tus-Ter-Lock Immuno-PCR Assays for the Sensitive Detection of Tropomyosin-Specific IgE Antibodies. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 465–476. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.H.; Sadroddiny, E. Application of Immuno-PCR for the Detection of Early Stage Cancer. Mol. Cell. Probes 2016, 30, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, K.; Kubista, M. Development and Evaluation of Three Real-Time Immuno-PCR Assemblages for Quantification of PSA. J. Immunol. Methods 2005, 304, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, D.; Soininen, H.; Alafuzoff, I.; Hoffmann, R. Immuno-PCR-Based Quantification of Multiple Phosphorylated Tau-Epitopes Linked to Alzheimer’s Disease. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2263–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Aoki, M.; Winblad, B.; Tjernberg, L.O. A Novel Approach for Aβ1–40 Quantification Using Immuno-PCR. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 205, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellekens, H. Factors Influencing the Immunogenicity of Therapeutic Proteins. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, vi3–vi9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, C.; Campbell, K. A New Chapter for Anti-Idiotypes in Low Molecular Weight Compound Immunoassays. Trends Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1102–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Zhuang, H.; Zhou, C. Detection of Naphthalene by Real-Time Immuno-PCR Using Molecular Beacon. Mol. Cell. Probes 2009, 23, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Q.-E.; Zhuang, H.-S. Determination of Phenanthrene by Antibody-Coated Competitive Real-Time Immuno-PCR Assay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhuang, H. Determination of Fluoranthene by Antigen-Coated Indirect Competitive Real-Time Immuno-PCR Assay. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhuang, H. A Highly Sensitive Real-Time Immuno-PCR Assay for Detecting Benzo[a]Pyrene in Food Samples by Application of Biotin-Streptavidin System. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Zhuang, H.-S. Real-Time Immuno-PCR Assay for Detecting PCBs in Soil Samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Zhuang, H.-S. A Real-Time Immuno-PCR Method for Detecting 3,3′,4,4′-Tetrachlorobiphenyl. Microchim. Acta 2011, 172, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Mao, X.; Yang, S.; De Ruyck, K.; Wu, Y. High Sensitivity Immunoassays for Small Molecule Compounds Detection—Novel Noncompetitive Immunoassay Designs. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 103, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Li, X.; Akash, M.S.H.; Zhou, L.; Tang, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Development of Analytical Method for Ultrasensitive Detection of Salbutamol Utilizing DNA Labeled-Immunoprobe. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, S.; Wang, P.; Zhao, H.; Li, W. Nanotechnology-Based Analytical Techniques for the Detection of Contaminants in Aquatic Products. Talanta 2024, 269, 125462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, I.; Kajiya, M.; Aramaki, N.; Furutani, S. Detection of Salmonella Enterica in Egg Yolk by PCR on a Microfluidic Disc Device Using Immunomagnetic Beads. Sensors 2020, 20, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayaka, A.C.; Ngo, T.A.; Kant, K.; Engelsmann, P.; Dave, V.P.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. Rapid Detection of Salmonella Enterica in Food Samples by a Novel Approach with Combination of Sample Concentration and Direct PCR. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 129, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Li, W.; Xu, H. Advances in Magnetic Nanoparticles for the Separation of Foodborne Pathogens: Recognition, Separation Strategy, and Application. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 4478–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercanoglu Taban, B.; Ben, U.; Aytac, S.A. Rapid Detection of Salmonella in Milk by Combined Immunomagnetic Separation-Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 2382–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeníková, G.; Pazlarová, J.; Demnerová, K. Detection of Salmonella in Food Samples by the Combination of Immunomagnetic Separation and PCR Assay. Int. Microbiol. 2000, 3, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Balakrishna, K.; Singh, G.P.; Batra, H. V Rapid Detection of Salmonella Typhi in Foods by Combination of Immunomagnetic Separation and Polymerase Chain Reaction. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 21, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Zhong, Z.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y.; Cui, X.; Liu, D. Immunomagnetic Nanobeads Based on a Streptavidin-Biotin System for the Highly Efficient and Specific Separation of Listeria Monocytogenes. Food Control 2014, 45, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, F.; Luo, D.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, H. Biotin-Exposure-Based Immunomagnetic Separation Coupled with Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Biosensor for Visibly Detecting Viable Listeria Monocytogenes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1017, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamloo, E.; Hosseini, H.; Abdi Moghadam, Z.; Halberg Larsen, M.; Haslberger, A.; Alebouyeh, M. Importance of Listeria Monocytogenes in Food Safety: A Review of Its Prevalence, Detection, and Antibiotic Resistance. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 20, 241–254. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Qu, L.; Wimbrow, A.N.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Y. Rapid Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes by Nanoparticle-Based Immunomagnetic Separation and Real-Time PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 118, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsih, H.-Y.; Tsen, H.-Y. Combination of Immunomagnetic Separation and Polymerase Chain Reaction for the Simultaneous Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes and Salmonella Spp. in Food Samples. J. Food Prot. 2001, 64, 1744–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, A.A.; Ashraf, M.A.; Mustafa, B.E.; Raza, M.M. Epidemiological Trends of Foodborne Campylobacter Outbreaks in the United States of America, 1998–2016. Food Microbiol. 2021, 97, 103751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, D.F.; Ogata, S.A. Quantitative Immunocapture PCR Assay for Detection of Campylobacter Jejuni in Foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4115–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, S.; Barnett, T.C.; Rivera-Hernandez, T.; Rohde, M.; Walker, M.J. Streptococcus Pyogenes Adhesion and Colonization. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 3739–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Cordova, S.E.; Kieft, T.L.; Rogelj, S. A Highly Sensitive Immuno-PCR Assay for Detecting Group A Streptococcus. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 279, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, W.B.; Dudley, E.G.; Doores, S.; Cutter, C.N. Commercially Available Rapid Methods for Detection of Selected Food-Borne Pathogens. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakioulaki, M.; Berkemeier, C.M.; Heijnen, I.; Grize, L.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Goulas, A.; Tamm, M.; Stolz, D. Staphylococcus Aureus Enterotoxin A- and B-Specific IgE in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; von Eiff, C.; Kuczius, T.; Omoe, K.; Peters, G.; Becker, K. A Quantitative Real-Time Immuno-PCR Approach for Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxins. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 85, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Guo, J.; Li, T.; Tian, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, X.; Majeed, U.; Song, W.; Xiao, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Phage-based Technologies for Highly Sensitive Luminescent Detection of Foodborne Pathogens and Microbial Toxins: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1843–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artykov, A.A.; Fursova, K.K.; Ryazantsev, D.Y.; Shchannikova, M.P.; Loskutova, I.V.; Shepelyakovskaya, A.O.; Laman, A.G.; Zavriev, S.K.; Brovko, F.A. Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin a by Phage Display Mediated Immuno-PCR Method. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 43, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.H.; Hwang, S.Y.; Park, Y.K.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, S.; Hong, J. A Quantitative Real-Time Immuno-PCR Assay for Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus Enterotoxin H. J. Food Saf. 2014, 34, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MyBioSource. Staphylococcus Aureus Enterotoxins. Available online: https://www.mybiosource.com/human-elisa-kits/staphylococcus-aureus-enterotoxins-se/162591 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Das, S.; Majumder, S.; Nag, M.; Kingston, J.J. A Sandwich Duplex Immuno PCR for Rapid and Sensitive Identification of Clostridium Perfringens Alpha and Enterotoxin. Anaerobe 2019, 57, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyachuba, D.G. Foodborne Illness: Is It on the Rise? Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton-Celsa, A.; Mohawk, K.; Teel, L.; O’Brien, A. Pathogenesis of Shiga-Toxin Producing Escherichia Coli. In Ricin and Shiga Toxins: Pathogenesis, Immunity, Vaccines and Therapeutics; Mantis, N., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 67–103. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, Y.S.; Ng, T.B. Shiga Toxins: From Structure and Mechanism to Applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Bielaszewska, M.; Pulz, M.; Becker, K.; Friedrich, A.W.; Karch, H.; Kuczius, T. New Immuno-PCR Assay for Detection of Low Concentrations of Shiga Toxin 2 and Its Variants. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Qi, W.; Quiñones, B.; McMahon, S.; Cooley, M.; Mandrell, R.E. Sensitive Detection of Shiga Toxin 2 and Some of Its Variants in Environmental Samples by a Novel Immuno-PCR Assay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3558–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Tang, S.-S.; Liu, H.-W. A Highly Sensitive Immuno-Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for Clostridium Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A. Toxicon 2004, 43, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeece, M. Food Additives. In Introduction to the Chemistry of Food; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 251–311. [Google Scholar]
- Robins, R.J. The Measurement of Low-Molecular-Weight, Non-Immunogenic Compounds by Immunoassay. In Immunology in Plant Sciences; Linskens, H.-F., Jackson, J.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 86–141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Lu, W.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Q. Ultrasensitive Immuno-PCR for Detecting Aflatoxin B1 Based on Magnetic Separation and Barcode DNA. Food Control 2022, 138, 109028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Tu, Z.; Li, Y.; He, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Fu, J.; Gee, S.J.; Hammock, B.D. VHH Phage-Based Competitive Real-Time Immuno-Polymerase Chain Reaction for Ultrasensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A in Cereal. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7471–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; He, Q.; Xu, Y.; Tu, Z.; Yang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Phage Displayed Anti-Idiotypic Nanobody Mediated Immuno-PCR for Sensitive and Environmentally Friendly Detection of Mycotoxin Ochratoxin A. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7824–7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Shu, M.; Tu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Cao, D. Anti-Idiotypic VHH Phage Display-Mediated Immuno-PCR for Ultrasensitive Determination of Mycotoxin Zearalenone in Cereals. Talanta 2016, 147, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Tu, Z.; Ning, Z.; He, Q.; Li, Y. Development of Real-Time Immuno-PCR Based on Phage Displayed an Anti-Idiotypic Nanobody for Quantitative Determination of Citrinin in Monascus. Toxins 2019, 11, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jothikumar, N.; Cliver, D.O.; Mariam, T.W. Immunomagnetic Capture PCR for Rapid Concentration and Detection of Hepatitis A Virus from Environmental Samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Schulz, S.; Fischer, R.; Niemeyer, C.M. Detection of Rotavirus from Stool Samples Using a Standardized Immuno-PCR (“Imperacer”) Method with End-Point and Real-Time Detection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 333, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winder, N.; Gohar, S.; Muthana, M. Norovirus: An Overview of Virology and Preventative Measures. Viruses 2022, 14, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne Illness Acquired in the United States—Major Pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, S.; Gibson, K.E. Improving the Detection and Understanding of Infectious Human Norovirus in Food and Water Matrices: A Review of Methods and Emerging Models. Viruses 2024, 16, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, W.; Sánchez, G. Hepatitis A Infections from Food. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, G.; Bosch, A. Survival of Enteric Viruses in the Environment and Food. In Viruses in Foods; Goyal, S.M., Cannon, J.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 367–392. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, X.C.; Wolffs, P.; Griffiths, M.W. Rapid and Quantitative Detection of Hepatitis A Virus from Green Onion and Strawberry Rinses by Use of Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5624–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, S.E.; Ramani, S.; Tate, J.E.; Parashar, U.D.; Svensson, L.; Hagbom, M.; Franco, M.A.; Greenberg, H.B.; O’Ryan, M.; Kang, G.; et al. Rotavirus Infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemeyer, C.M.; Adler, M.; Blohm, D. Fluorometric Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Quantification of Immuno-PCR Products in Microplates. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 246, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelsen-Huisman, A.D.; van Os-Medendorp, H.; Blom, W.M.; Versluis, A.; Castenmiller, J.J.M.; Noteborn, H.P.J.M.; Kruizinga, A.G.; Houben, G.F.; Knulst, A.C. Accidental Allergic Reactions in Food Allergy: Causes Related to Products and Patient’s Management. Allergy 2018, 73, 2377–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. RASFF Window. Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/rasff-window/screen/search (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- van Hengel, A.J. Food Allergen Detection Methods and the Challenge to Protect Food-Allergic Consumers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasena, S.; Smits, M.; Fiechter, D.; de Jong, A.; Nordlee, J.; Baumert, J.; Taylor, S.L.; Pieters, R.H.; Koppelman, S.J. Comparison of Six Commercial ELISA Kits for Their Specificity and Sensitivity in Detecting Different Major Peanut Allergens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fu, T.-J. Evaluation of ELISA Test Kits for Detection of Milk Protein in Frying Oil Treated at Different Temperatures. J. Food Prot. 2024, 87, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, N.G.E.; De Dominicis, E.; Koops, A.J.; Kraan, R.; Saner, S.; Van Der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Hoek-van den Hil, E. Comparison of Commercial Allergen ELISA Kits for Egg Detection in Food Matrices. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henterich, N.; Osman, A.A.; Méndez, E.; Mothes, T. Assay of Gliadin by Real-time Immunopolymerase Chain Reaction. Food/Nahrung 2003, 47, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobori, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Takahashi, H.; Sugiyama, S. Rolling Circle Amplification for Signal Enhancement in Ovalbumin Detection. Anal. Sci. 2009, 25, 1381–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Bian, Y.; Ma, J.; Feng, X.S.; He, Z.; Tan, Y. Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Food: Updates on Occurrence, Toxic Effects, Pretreatment and Analysis Techniques. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reizer, E.; Viskolcz, B.; Fiser, B. Formation and Growth Mechanisms of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: A Mini-Review. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, B.A.P.; Rajentran, K.; Selamat, J.; Lestari, S.D.; Umar, N.B.; Hussain, N. Determination of 16 EPA PAHs in Food Using Gas and Liquid Chromatography. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 116, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Baan, R.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K. Carcinogenicity of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Polybrominated Biphenyls. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 287–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saktrakulkla, P.; Lan, T.; Hua, J.; Marek, R.F.; Thorne, P.S.; Hornbuckle, K.C. Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Food. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11443–11452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megson, D.; Idowu, I.G.; Sandau, C.D. Is Current Generation of Polychlorinated Biphenyls Exceeding Peak Production of the 1970s? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fránek, M.; Pouzar, V.; Kolář, V. Enzyme-Immunoassays for Polychlorinated Biphenyls: Structural Aspects of Hapten-Antibody Binding. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 347, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fránek, M.; Deng, A.; Kolář, V.; Socha, J. Direct Competitive Immunoassays for the Coplanar Polychlorinated Biphenyls. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 444, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhuang, H. Biotin–Streptavidin-Amplified Real-Time Immune-PCR Assay for Detecting Dimethyl Phthalate in Beverage and Drinking Water Samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biocompare. Human Dimethyl Phthalate (DMP) ELISA Kit. Available online: https://www.biocompare.com/25138-Assay-Kit/14366786-Human-Dimethyl-Phthalate-ELISA-Kit/ (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Zhang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhuang, H.; Hu, Y. Determination of Dimethyl Phthalate in Environment Water Samples by a Highly Sensitive Indirect Competitive ELISA. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhuang, H. An Ultrasensitive Gold Nanoparticles Improved Real-Time Immuno-PCR Assay for Detecting Diethyl Phthalate in Foodstuff Samples. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 480, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhuang, H. Development of a Highly Sensitive Biotin–Streptavidin Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detecting Diethyl Phthalate Based on a Specific Polyclonal Antibody. Food Agric. Immunol. 2015, 26, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, B.; Guo, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, M. Fluorescence Turn-on Immunoassay of Endocrine Diethyl Phthalate in Daily Supplies Using Red Fluorescent Carbon Dots. Microchem. J. 2022, 178, 107350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.F.; Ahmad, F.A.; Alsayegh, A.A.; Zeyaullah, M.; AlShahrani, A.M.; Muzammil, K.; Saati, A.A.; Wahab, S.; Elbendary, E.Y.; Kambal, N.; et al. Pesticides Impacts on Human Health and the Environment with Their Mechanisms of Action and Possible Countermeasures. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, N.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Hu, P.; Lu, S.; Ren, H.; Liu, Z.; Soo Park, K.; Zhou, Y. Dual-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles Probe Based Bio-Barcode Immuno-PCR for the Detection of Glyphosate. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Zhang, C.; Xu, L.; Liu, H.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Salvador, J.-P.; She, Y.; et al. Enhanced Bio-Barcode Immunoassay Using Droplet Digital PCR for Multiplex Detection of Organophosphate Pesticides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11131–11141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM) Scientific Opinion on Chloramphenicol in Food and Feed. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Archives and Records Administration. Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21, Chapter I, Subchapter E, Part 530; National Archives and Records Administration: College Park, MD, USA, 2025.
- Vercelli, C.; Amadori, M.; Gambino, G.; Re, G. A Review on the Most Frequently Used Methods to Detect Antibiotic Residues in Bovine Raw Milk. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 144, 105695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, B.K.; Riesterer, L.; Bier, L.; Widenhorn, A.-M. Proof of Bacteria and the Activity of Chemical and Natural Antibiotics by Headspace Gas Chromatography. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qi, X.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Liu, J.; Sun, K.; Li, Z.; Deng, G. Fluorescence Determination of Chloramphenicol in Milk Powder Using Carbon Dot Decorated Silver Metal–Organic Frameworks. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; He, Z.; Cao, X.; Shen, J.; Li, H. Development of a Highly Sensitive Real-Time Immuno-PCR for the Measurement of Chloramphenicol in Milk Based on Magnetic Bead Capturing. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9340–9347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.D.; Tittsler, R.P. The Density of Milk at Low Temperatures. J. Dairy Sci. 1961, 44, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meizheng. Animal Tissue Antibiotic Chloramphenicol ELISA Test Kit. Available online: https://mzfoodtest.com/product/animal-tissue-antibiotic-chloramphenicol-elisa-test-kit/ (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Creative Diagnostics. Chloramphenicol ELISA Kit. Available online: https://www.creative-diagnostics.com/Chloramphenicol-EIA-Kit-123404-464.htm (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Antibodies. Chloramphenicol ELISA Kit (A105324). Available online: https://www.antibodies.com/catalog/elisa-kits/chloramphenicol-elisa-kit-a105324 (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Zhang, X.; Zhuang, H. A Carbon Nanotube-Enhanced Real-Time Immuno-PCR for Ultrasensitive Detection of AHTN in Water. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 544, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhuang, H.; Wan, X. Hapten Syntheses, Antibody Generation, and Ultrasensitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Determination of Tonalid in Human Blood. Anal. Lett. 2018, 51, 1874–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, D.; Zhuang, H.; Yang, G.; Ping, X. A Real-Time Immuno-PCR Assay for the Detection of Tetrabromobisphenol A. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, D.; Zhuang, H.; Zhou, X.; Yang, G. Biotin–Streptavidin Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detecting Tetrabromobisphenol A in Electronic Waste. Talanta 2014, 120, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Huang, Z.; Sun, D.-W.; Fu, H. Recent Advances in the Detection of 17β-Estradiol in Food Matrices: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2144–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Lacorn, M.; Steinhart, H. Natural Occurrence of Steroid Hormones in Food. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, D.; Nilsson, D.; Lohr, T.; Sheedy, C. Development of a Real-Time Immuno-PCR Assay for the Quantification of 17β-Estradiol in Water. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2015, 50, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, L.; Vale, N. Salbutamol in the Management of Asthma: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant-Forde, J.N.; Lay, D.C.; Marchant-Forde, R.M.; McMunn, K.A.; Richert, B.T. The Effects of R-Salbutamol on Growth, Carcass Measures, and Health of Finishing Pigs1,2. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 4081–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, G.; Cenci, T.; Franconi, F.; Galarini, R.; Macrı̀, A.; Rondoni, F.; Strozzi, M.; Loizzo, A. Clinical and Pharmacological Profile in a Clenbuterol Epidemic Poisoning of Contaminated Beef Meat in Italy. Toxicol. Lett. 2000, 114, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Tang, C.; Meng, Q.; Du, W.; Bo, T.; Zhao, Q.; Liang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. Residues of Salbutamol and Identification of Its Metabolites in Beef Cattle. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2867–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolt, H.M.; Hengstler, J.G. Ricin: An Ancient Toxicant, but Still an Evergreen. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubelli, C.; Chatgilialoglu, A.; Bolognesi, A.; Strocchi, P.; Colombatti, M.; Stirpe, F. Detection of Ricin and Other Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins by an Immuno-Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 355, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Zhao, Q.; Iqbal, M.N.; Dong, M.; Li, X.; Lin, M.; Wang, R.; Lei, F.; He, C.; Wang, S. Development of Immunoassay Methods Based on Monoclonal Antibody and Its Application in the Determination of Cadmium Ion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 124992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Suo, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X. ELISA and Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay for Sensitive and Specific Determination of Lead (II) in Water, Food and Feed Samples. Foods 2020, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Dias, A.C.P.; Zhang, X. Monoclonal Antibody Based Immunoassay: An Alternative Way for Aquatic Environmental Selenium Detection. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Yu, S.; Feng, Y.; He, L.; Liu, L.; Effah, C.Y.; Wu, Y. A Digital Immuno-PCR Assay for Simultaneous Determination of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Human Serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1192, 339321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Class | Species | Contaminant | LOD | IPCR Format [Reference] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial toxins | S. aureus | SEB | <10 pg/mL in buffer and various food samples | Sandwich [79] |
| SEB | 0.1 pg/mL in buffer and 1 pg/mL in milk | Sandwich with IgY antibodies [81] | ||
| SEA | 100 pg/mL in buffer | Sandwich [119] | ||
| SEB | 10 pg/mL in buffer | |||
| SEA SEB | 7.5 fg/mL in broth medium and various foods for both | Sandwich with MB [69] | ||
| SEA | 100 pg/mL in milk | Sandwich with PD [121] | ||
| SEH | 4.5 pg/mL in buffer | Sandwich [122] | ||
| C. perfringens | CPA CPE | 1 pg/mL in buffer, serum, muscle and feces and 10 pg/mL in intestines for both | Sandwich duplex [124] | |
| E. coli | Stx2 | 10 pg/mL in buffer | Competitive [128] | |
| Stx2 | 0.1 pg/mL in buffer, 1–10 pg/mL in water and 1–100 pg/mL in feces, swine colon and soil | Sandwich [129] | ||
| C. botulinum | BoNT/A | 90 pg/mL in milk with toxoid 3.75 pg/mL in milk with toxin | Sandwich [80] | |
| BoNT/B | 750 pg/mL in milk with toxoid | |||
| Mycotoxins | AFB1 | 10 fg/mL in buffer | Competitive with AuNP and MNP [133] | |
| Ochratoxin A | 3.7 fg/mL in buffer | Competitive with PD [134] | ||
| Ochratoxin A | 4.17 pg/mL in buffer | Competitive with anti-idiotypic VHH PD [135] | ||
| Zearalenone | 6.5 pg/mL in buffer | Competitive with anti-idiotypic VHH PD [136] | ||
| Citrinin | 80 pg/mL in buffer | Competitive with anti-idiotypic VHH PD [137] | ||
| Viruses | Norovirus | rNVLP | 100 particles in buffer 660 particles in feces and food samples | Sandwich [63] |
| Rotavirus | VP6 antigen | 100 particles/mL in buffer | Sandwich [139] | |
| Allergens | Tropomyosin | 11.3 pg/mL in buffer | Sandwich [65] | |
| Gliadin | 0.16 ng/mL in buffer | Competitive [154] | ||
| Ovalbumin | 1 pg/mL in buffer | Rolling circle amplification [155] | ||
| Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon | Phenanthrene | 5 fg/mL in buffer | Competitive [94] | |
| Fluoranthene | 5 fg/mL in buffer | Competitive [95] | ||
| Benzo[a]pyrene | 2.85 fg/mL in buffer | Competitive [96] | ||
| Naphthalene | 1 fg/mL in buffer | Competitive [93] | ||
| Polychlorinated biphenyls | PCB37 | 1 fg/mL in buffer | Competitive [97] | |
| PCB77 | 1.5 fg/mL in buffer | Competitive [98] | ||
| Phthalic acid esters | Dimethyl phthalate | 1.98 pg/mL in buffer | Competitive [164] | |
| Diethyl phthalate | 1.06 pg/mL in buffer | Competitive with AuNPs [167] | ||
| Pesticides | Glyphosate | 4.5 pg/g in buffer | Competitive with AuNPs [171] | |
| TriazophosParathionChlorpyrifos | 4 pg/mL in buffer (IC10) 7 pg/mL in buffer (IC10) 121 pg/mL in buffer (IC10) | Competitive with AuNPs and MNPs and ddPCR [172] | ||
| Antibiotics | Chloramphenicol | 0.8 pg/mL in buffer and milk | Competitive with MBs [178] | |
| Other contaminants | Tonalide | 1 fg/mL in buffer | Competitive [183] | |
| Tetrabrombisphenol A | 2 fg/mL in buffer | Competitive [185] | ||
| Estradiol-17β | 0.7 pg/mL in buffer | Competitive [189] | ||
| Salbutamol | 21 fg/mL in buffer 28 fg/mL in urine | Competitive [100] | ||
| Ricin | 10 fg/mL in buffer and human serum | Competitive [195] | ||
| Ricin | 0.01 pg/mL * in buffer, 1 pg/mL # in buffer, 10 pg/mL # in eggs and milk and 100 pg/mL # in ground beef | Sandwich [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radomirović, M.; Gligorijević, N.; Rajković, A. Immuno-PCR in the Analysis of Food Contaminants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073091
Radomirović M, Gligorijević N, Rajković A. Immuno-PCR in the Analysis of Food Contaminants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073091
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadomirović, Mirjana, Nikola Gligorijević, and Andreja Rajković. 2025. "Immuno-PCR in the Analysis of Food Contaminants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073091
APA StyleRadomirović, M., Gligorijević, N., & Rajković, A. (2025). Immuno-PCR in the Analysis of Food Contaminants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073091








