A Comprehensive In Vitro and In Silico Approach for Targeting 4-Hydroxyphenyl Pyruvate Dioxygenase: Towards New Therapeutics for Alkaptonuria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Vitro Results
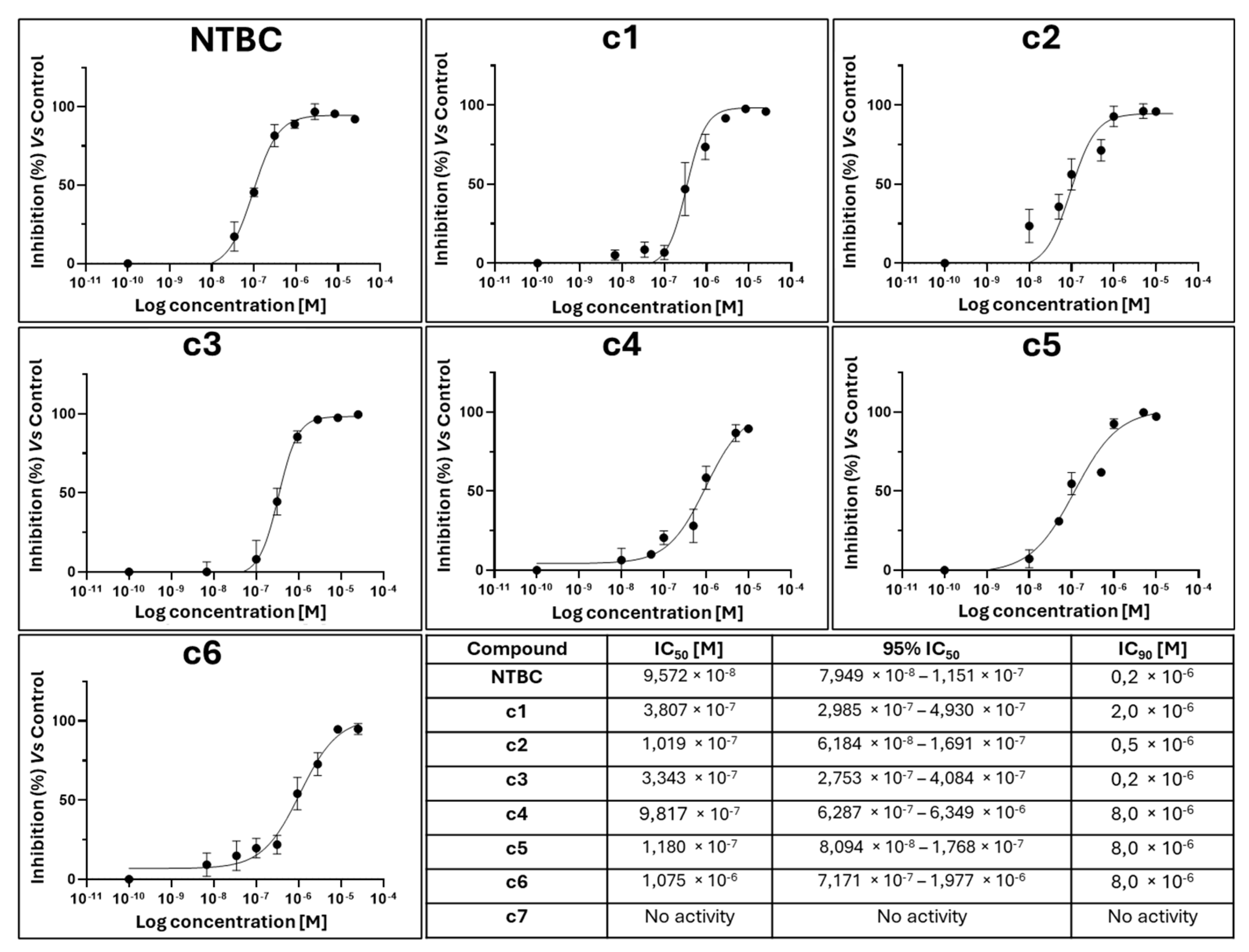
2.1.1. IC50 and IC90 Evaluation
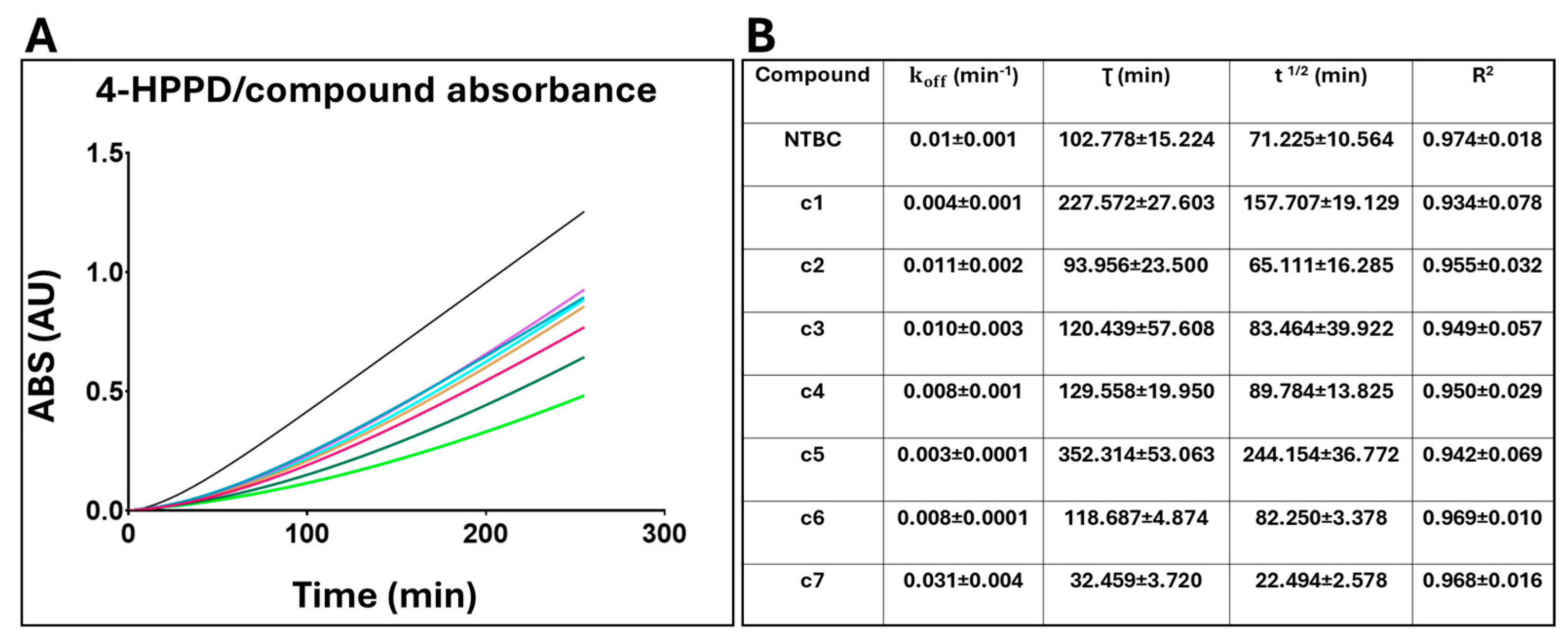
2.1.2. 4-HPPD Inhibitor Residence Time Evaluation
2.2. In Silico Results
2.2.1. 4-HPPD Virtual Screening
2.2.2. 4-HPPD/Compound Complex Binding Stability and Interaction Energy
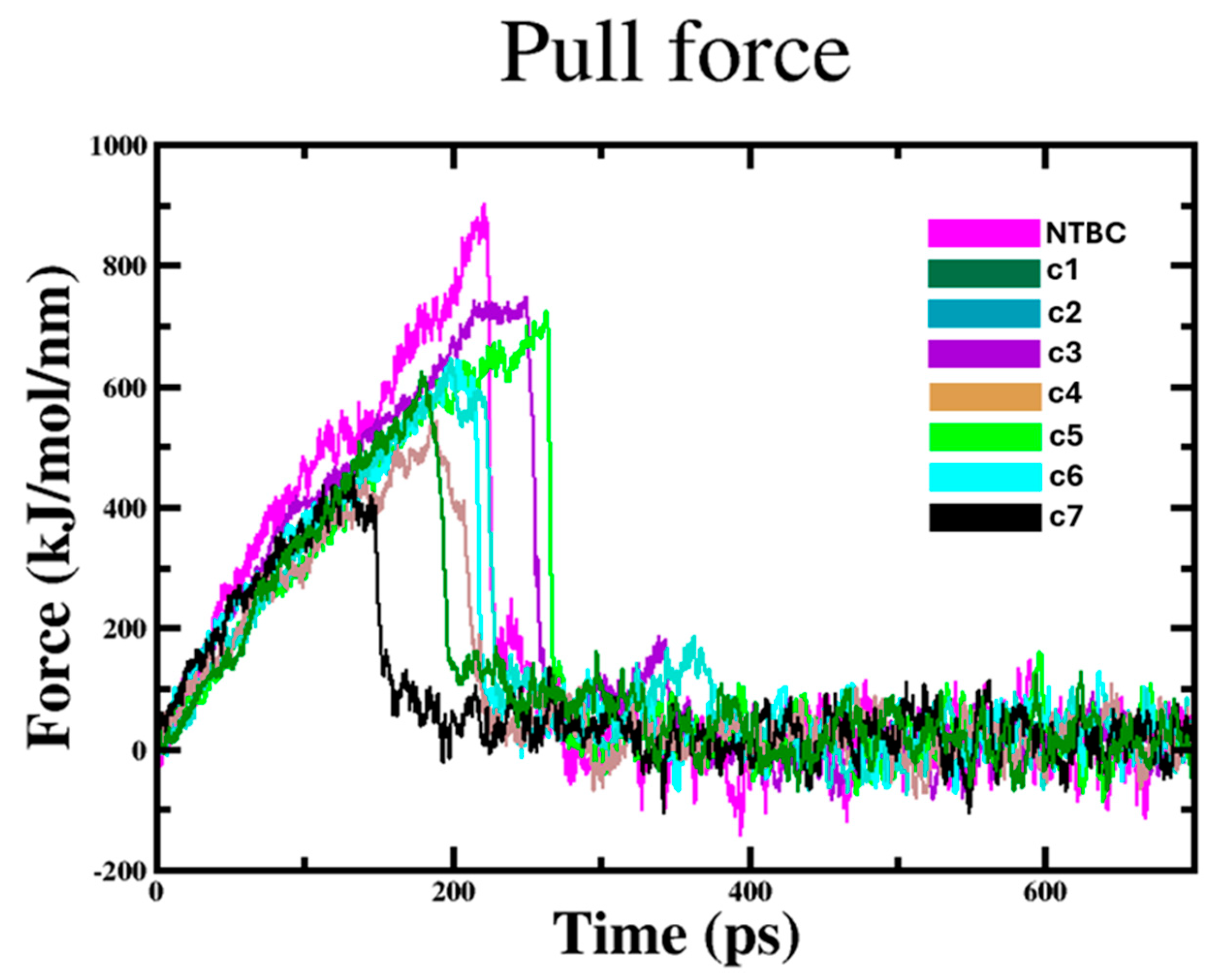
2.2.3. Compound Protein Unbinding Simulations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Vitro Methods
4.1.1. Bacteria Cell Culture
4.1.2. Chemistry
4.1.3. IC50 and IC90 Evaluation
- -
- Blank: culture medium without cell suspension.
- -
- Negative control: cell suspension without IPTG and Tyr.
- -
- Not-Inhibited control: cell suspension supplemented with 1 mM IPTG and 75 µg/mL Tyr.
4.1.4. Residence Time Evaluation
- -
- Blank: cell suspension without the IPTG.
- -
- Positive control: cell suspension supplemented with 1 mM IPTG.
- -
- Negative control: cell suspension supplemented with 1 mM IPTG and NTBC (0.2 µM final concentration).
- Y: Absorbance value (HGA accumulation);
- X: time (min);
- : steady-state velocity;
- initial velocity;
- K: .
4.2. In Silico Methods
4.2.1. Structural Resources
4.2.2. Molecular Docking
4.2.3. Steered Molecular Dynamics (SMD) Simulations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Milella, M.S.; Geminiani, M.; Trezza, A.; Visibelli, A.; Braconi, D.; Santucci, A. Alkaptonuria: From Molecular Insights to a Dedicated Digital Platform. Cells 2024, 13, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardini, G.; Braconi, D.; Zatkova, A.; Sireau, N.; Kujawa, M.J.; Introne, W.J.; Spiga, O.; Geminiani, M.; Gallagher, J.A.; Ranganath, L.R.; et al. Alkaptonuria. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernini, A.; Spiga, O.; Santucci, A. Structure-Function Relationship of Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase: Understanding the Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in the Rare Genetic Disease Alkaptonuria. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2023, 24, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiga, O.; Cicaloni, V.; Zatkova, A.; Millucci, L.; Bernardini, G.; Bernini, A.; Marzocchi, B.; Bianchini, M.; Zugarini, A.; Rossi, A.; et al. A new integrated and interactive tool applicable to inborn errors of metabolism: Application to alkaptonuria. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 103, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Yang, J.-F.; Wang, D.-W.; Hao, G.-F.; Dong, J.-Q.; Wang, Y.-X.; Yang, W.-C.; Wu, J.-W.; Zhan, C.-G.; Yang, G.-F.; et al. Molecular insights into the mechanism of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibition: Enzyme kinetics, X-ray crystallography and computational simulations. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganath, L.R.; Psarelli, E.E.; Arnoux, J.B.; Braconi, D.; Briggs, M.; Bröijersén, A.; Loftus, N.; Bygott, H.; Cox, T.F.; Davison, A.S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of once-daily nitisinone for patients with alkaptonuria (SONIA 2): An international, multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezza, A.; Birgauan, A.; Geminiani, M.; Visibelli, A.; Santucci, A. Molecular and Evolution In Silico Studies Unlock the h4-HPPD C-Terminal Tail Gating Mechanism. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.-N.; Wang, D.-W.; Wu, F.-X.; Lin, S.-Y.; Zhan, C.-G.; Wu, J.-W.; Yang, W.-C.; Yang, G.-F. Crystal Structure of 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase in Complex with Substrate Reveals a New Starting Point for Herbicide Discovery. Research 2019, 2019, 2602414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, H.; Chen, J.N.; Zheng, B.F.; Xu, Y.L.; Chen, M.X.; Yang, W.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Yang, G.F. Structure-based discovery of pyrazole-benzothiadiazole hybrid as human HPPD inhibitors. Structure 2023, 31, 1604–1615.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Dong, J.; Dong, J.; Yang, W.C.; Yang, G.F. Insights into 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase-inhibitor interactions from comparative structural biology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2023, 48, 568–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.J.M.; Ranganath, L.R.; Bou-Gharios, G.; Gallagher, J.A.; Hughes, J.H. Expression of tyrosine pathway enzymes in mice demonstrates that homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase deficiency in the liver is responsible for homogentisic acid-derived ochronotic pigmentation. JIMD Rep. 2020, 58, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, S.; Macheleidt, J.; Scherlach, K.; Schmaler-Ripcke, J.; Jacobsen, I.D.; Heinekamp, T.; Brakhage, A.A. Pyomelanin formation in Aspergillus fumigatus requires HmgX and the transcriptional activator HmgR but is dispensable for virulence. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastroeni, P.; Trezza, A.; Geminiani, M.; Frusciante, L.; Visibelli, A.; Santucci, A. HGA Triggers SAA Aggregation and Accelerates Fibril Formation in the C20/A4 Alkaptonuria Cell Model. Cells 2024, 13, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Assessment Report, Orfadin. 2020; Vol. 31. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/variation-report/orfadin-h-c-555-ii-0071-epar-assessment-report-variation_en.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- van Ginkel, W.G.; Rodenburg, I.L.; Harding, C.O.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Heiner-Fokkema, M.R.; van Spronsen, F.J. Long-Term Outcomes and Practical Considerations in the Pharmacological Management of Tyrosinemia Type 1. Pediatr. Drugs 2019, 21, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Teckman, J.H.; Lueder, G.T. Corneal opacities associated with NTBC treatment. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 134, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santucci, A.; Bernardini, G.; Braconi, D.; Petricci, E.; Manetti, F. 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase and Its Inhibition in Plants and Animals: Small Molecules as Herbicides and Agents for the Treatment of Human Inherited Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4101–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Governa, P.; Bernardini, G.; Braconi, D.; Manetti, F.; Santucci, A.; Petricci, E. Survey on the Recent Advances in 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase (HPPD) Inhibition by Diketone and Triketone Derivatives and Congeneric Compounds: Structural Analysis of HPPD/Inhibitor Complexes and Structure-Activity Relationship Considerations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6963–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschi, M.; Bernardini, G.; Dreassi, E.; Millucci, L.; Geminiani, M.; Braconi, D.; Marzocchi, B.; Botta, M.; Manetti, F.; Santucci, A. Inhibition of para-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase by Analogues of the Herbicide Nitisinone As a Strategy to Decrease Homogentisic Acid Levels, the Causative Agent of Alkaptonuria. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaib, S.; Rana, N.; Hussain, N.; Ogaly, H.A.; Dera, A.A.; Khan, I. Identification of Potential Inhibitors for the Treatment of Alkaptonuria Using an Integrated In Silico Computational Strategy. Molecules 2023, 28, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, R.A. Evolution of the drug-target residence time model. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernetti, M.; Masetti, M.; Rocchia, W.; Cavalli, A. Kinetics of Drug Binding and Residence Time. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2019, 70, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, L.X.; Wang, J.Y.; Cao, H.F.; Gao, S.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. Identification of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitors by virtual screening, molecular docking, molecular dynamic simulation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 5547–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salo-Ahen, O.M.H.; Alanko, I.; Bhadane, R.; Alexandre, A.M.; Honorato, R.V.; Hossain, S.; Juffer, A.H.; Kabedev, A.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Larsen, A.S.; et al. Molecular Dynamics Simulations in Drug Discovery and Pharmaceutical Development. Processes 2020, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, L.; Decherchi, S.; Zia, S.R.; Gaspari, R.; Cavalli, A.; Rocchia, W. Kinetics of protein-ligand unbinding via smoothed potential molecular dynamics simulations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequeue, S.; Neuckermans, J.; Nulmans, I.; Schwaneberg, U.; Vanhaecke, T.; De Kock, J. A robust bacterial high-throughput screening system to evaluate single nucleotide polymorphisms of human homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase in the context of alkaptonuria. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuckermans, J.; Mertens, A.; De Win, D.; Schwaneberg, U.; De Kock, J. A robust bacterial assay for high-throughput screening of human 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuckermans, J.; Lequeue, S.; Mertens, A.; Branson, S.; Schwaneberg, U.; De Kock, J. High-throughput quantification of ochronotic pigment formation in Escherichia coli to evaluate the potency of human 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitors in multi-well format. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Lowery, R.G. A High-Throughput Method for Measuring Drug Residence Time Using the Transcreener ADP Assay. SLAS Discov. 2017, 22, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, R.A.; Basavapathruni, A.; Moyer, M.; Scott, M.P. Impact of enzyme concentration and residence time on apparent activity recovery in jump dilution analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 416, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apweiler, R. The universal protein resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, D190–D195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, G.; Paiardini, A. PyMod 3: A complete suite for structural bioinformatics in PyMOL. Bioinformatics 2020, 37, 1471–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindah, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; Hatcher, E.; Acharya, C.; Kundu, S.; Zhong, S.; Shim, J.; Darian, E.; Guvench, O.; Lopes, P.; Vorobyov, I.; et al. CHARMM general force field: A force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the CHARMM all-atom additive biological force fields. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Hermans, J. Interaction Models for Water in Relation to Protein Hydration. In Intermolecular Forces; Pullman, B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezza, A.; Spiga, O.; Mugnai, P.; Saponara, S.; Sgaragli, G.; Fusi, F. Functional, electrophysiology, and molecular dynamics analysis of quercetin-induced contraction of rat vascular musculature. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 918, 174778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2019 update: Improved access to chemical data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1102–D1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carullo, G.; Saponara, S.; Ahmed, A.; Gorelli, B.; Mazzotta, S.; Trezza, A.; Gianibbi, B.; Campiani, G.; Fusi, F.; Aiello, F. Novel Labdane Diterpenes-Based Synthetic Derivatives: Identification of a Bifunctional Vasodilator That Inhibits CaV1.2 and Stimulates KCa1.1 Channels. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuong, N.M.; Son, N.T.; Nhan, N.T.; Khanh, P.N.; Huong, T.T.; Tram, N.T.T.; Sgaragli, G.; Ahmed, A.; Trezza, A.; Spiga, O.; et al. Vasorelaxing Activity of R-(-)-3’-Hydroxy-2,4,5-trimethoxydalbergiquinol from Dalbergia tonkinensis: Involvement of Smooth Muscle CaV1.2 Channels. Planta Medica 2020, 86, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salentin, S.; Schreiber, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Adasme, M.F.; Schroeder, M. PLIP: Fully automated protein-ligand interaction profiler. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W443–W447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessina, F.; Gamberucci, A.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Vangheluwe, P.; Gorelli, B.; Lorenzini, S.; Spiga, O.; Trezza, A.; Sgaragli, G.; et al. Negative chronotropism, positive inotropism and lusitropism of 3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole (DTBHA) on rat heart preparations occur through reduction of RyR2 Ca2+ leak. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.C.; Lee, E.H.; Le, L. Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulation in Rational Drug Design. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | Hydrophobic Interaction | Halogen Bond | π-Stacking | Hydrogen Bond | Salt Bridge | Iron Ion Coordination | ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTBC | Phe-336, Phe-359, Phe-364 | * N,P | * N,P | * N,P | * N,P | * P | −9.4 |
| c1 | His-226, Gln394 | * N,P | His-308 | * N,P | * N,P | * P | −5.0 |
| c2 | His-183, Val-185, Leu-224, Phe-359, Gly-360, Ala-361 | * N,P | His-226, Phe-364 | Gln-251, Gln-265, Gln-334 | * N,P | * P | −8.6 |
| c3 | Leu-224, Phe-359 | * N,P | Phe-336 | Asn-241, Gln-265 | * N,P | * P | −8.5 |
| c4 | His-183, Val-185, Leu-224, His-226, Gln-334, Phe-359, Gly-360, Ala-361 | * N,P | * N,P, | Asn-241, Gln-265 | * N,P | * P | −6.3 |
| c5 | Pro-239, Phe-336, Phe-359, Phe-364 | * N,P | * N,P | Asn-241, Gln-251 | His-266 | * P | −8.0 |
| c6 | Val 185, Pro-239, Phe-336, Phe-359, Phe-364 | Phe-359 | Phe-364 | Asn-241 | His-266 | * P | −8.7 |
| c7 | Leu-224, Phe-359 | Gly-360 | Phe-336 | Asn-241, Gln-251 | * N,P | * P | −7.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernardini, G.; Trezza, A.; Petricci, E.; Romagnoli, G.; Zambardino, D.; Manetti, F.; Braconi, D.; Geminiani, M.; Santucci, A. A Comprehensive In Vitro and In Silico Approach for Targeting 4-Hydroxyphenyl Pyruvate Dioxygenase: Towards New Therapeutics for Alkaptonuria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073181
Bernardini G, Trezza A, Petricci E, Romagnoli G, Zambardino D, Manetti F, Braconi D, Geminiani M, Santucci A. A Comprehensive In Vitro and In Silico Approach for Targeting 4-Hydroxyphenyl Pyruvate Dioxygenase: Towards New Therapeutics for Alkaptonuria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073181
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernardini, Giulia, Alfonso Trezza, Elena Petricci, Giulia Romagnoli, Demetra Zambardino, Fabrizio Manetti, Daniela Braconi, Michela Geminiani, and Annalisa Santucci. 2025. "A Comprehensive In Vitro and In Silico Approach for Targeting 4-Hydroxyphenyl Pyruvate Dioxygenase: Towards New Therapeutics for Alkaptonuria" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073181
APA StyleBernardini, G., Trezza, A., Petricci, E., Romagnoli, G., Zambardino, D., Manetti, F., Braconi, D., Geminiani, M., & Santucci, A. (2025). A Comprehensive In Vitro and In Silico Approach for Targeting 4-Hydroxyphenyl Pyruvate Dioxygenase: Towards New Therapeutics for Alkaptonuria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073181









