Gene Dysregulation and Islet Changes in PDAC-Associated Type 3c Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
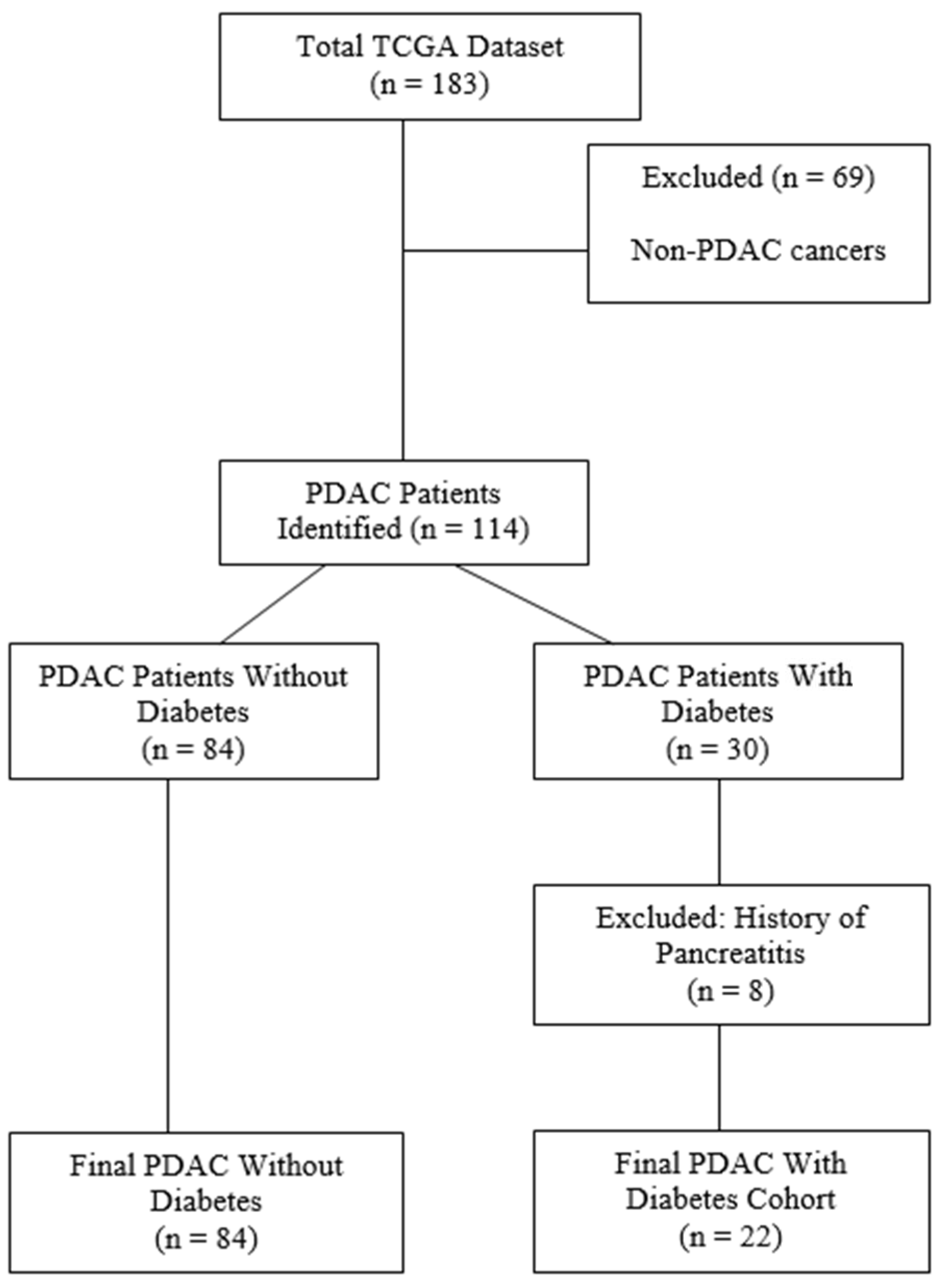
2.1. Patient Data Collection and Curation
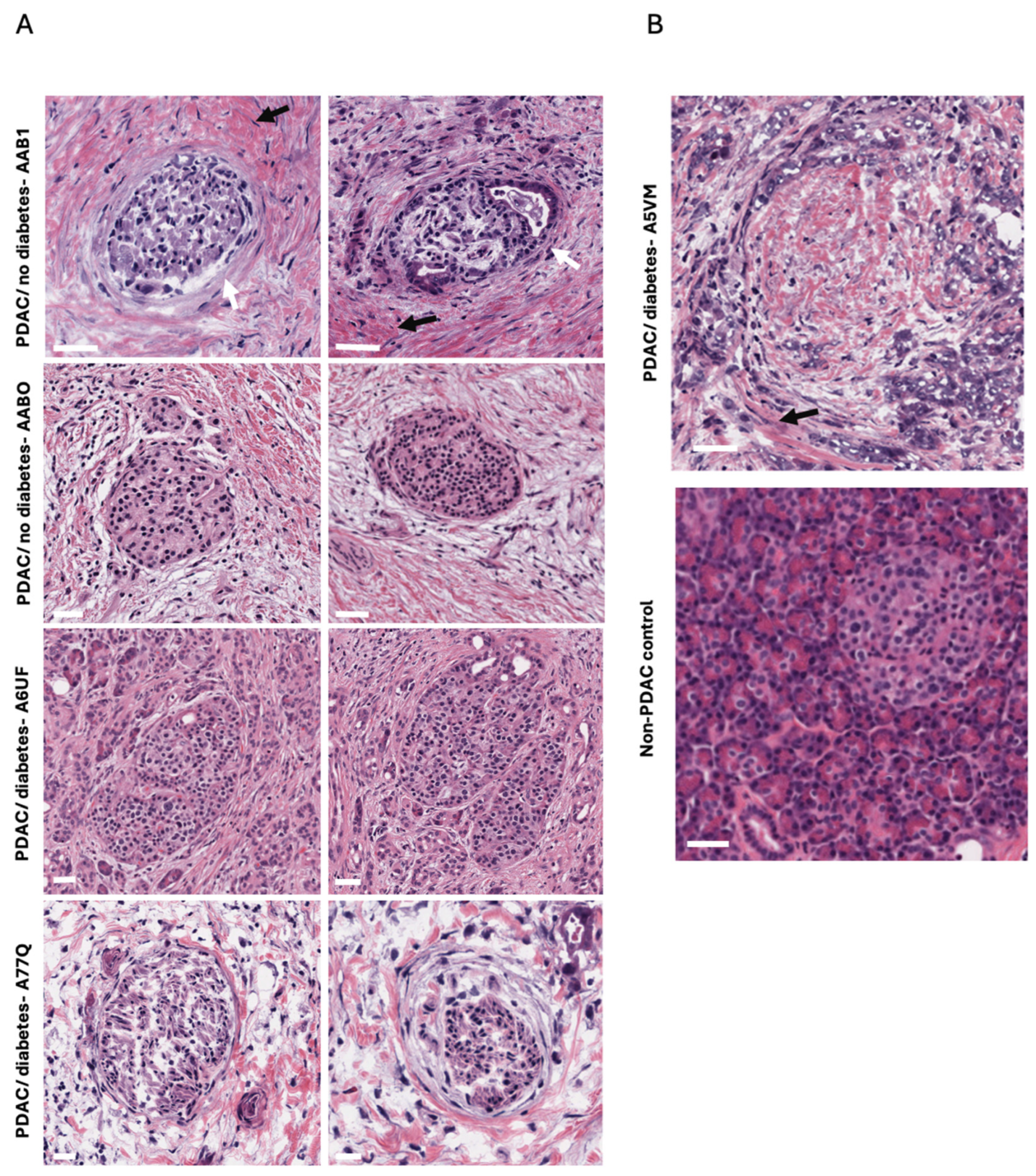
2.2. Fibrosis Observed Within and Around the Islets of Langerhans
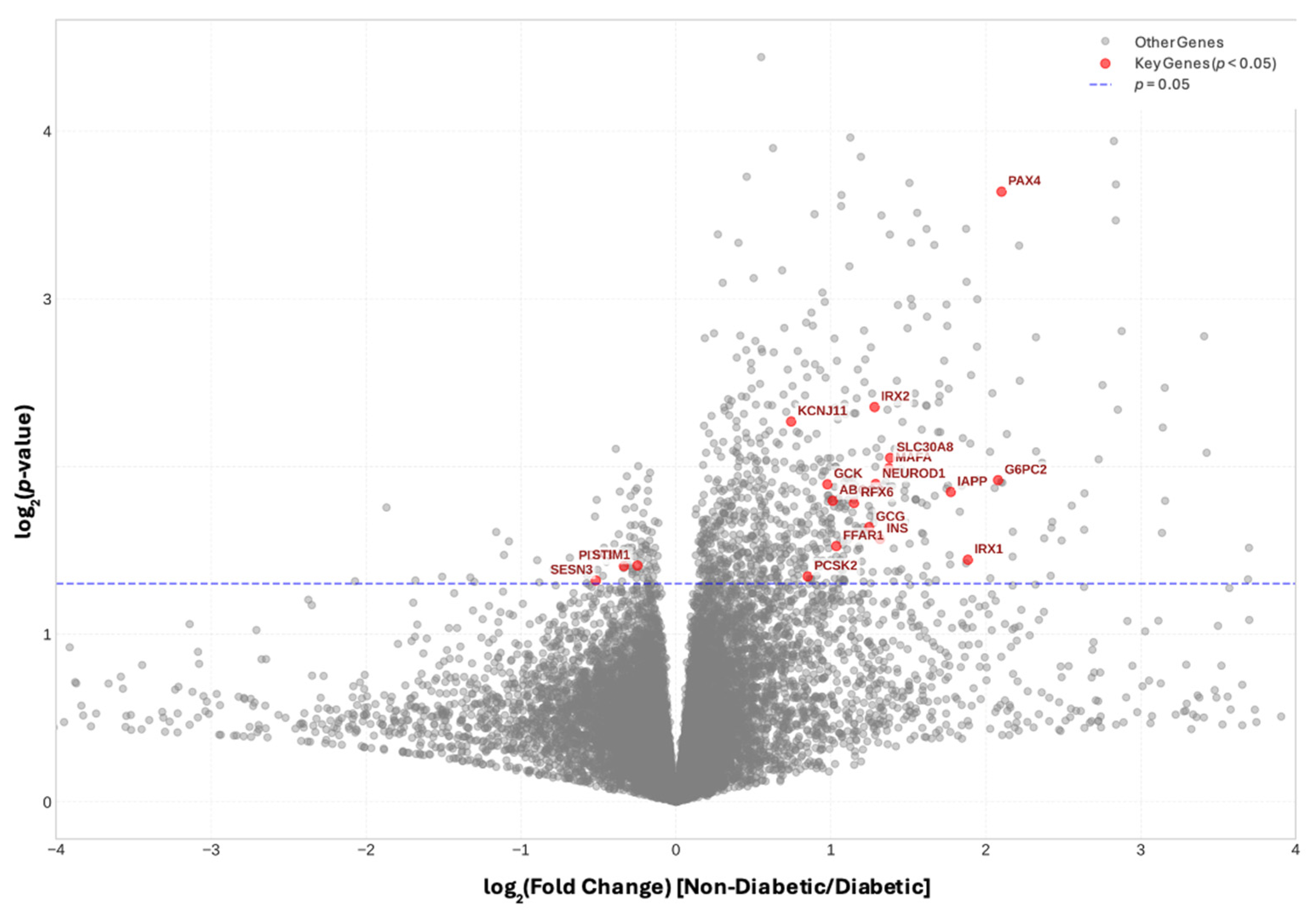
2.3. Endocrine and Progenitor Cell Markers Are Significantly Reduced in PDAC with Diabetes
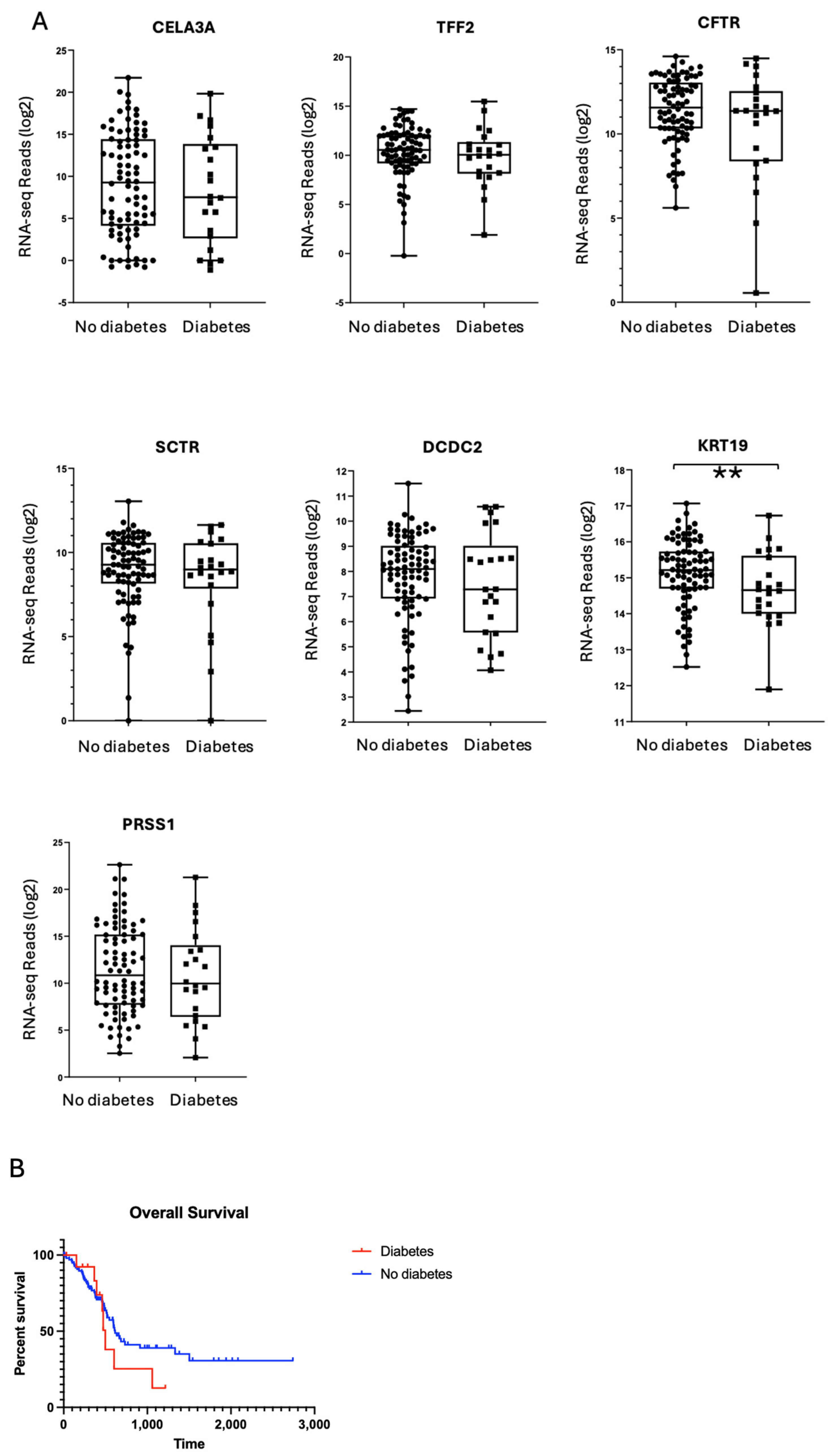
2.4. Exocrine Gene Expression Profiles Are Comparable Between PDAC Donors with and Without Diabetes
2.5. PDAC-Associated Diabetes Does Not Represent a Distinct Immunogenic Subtype
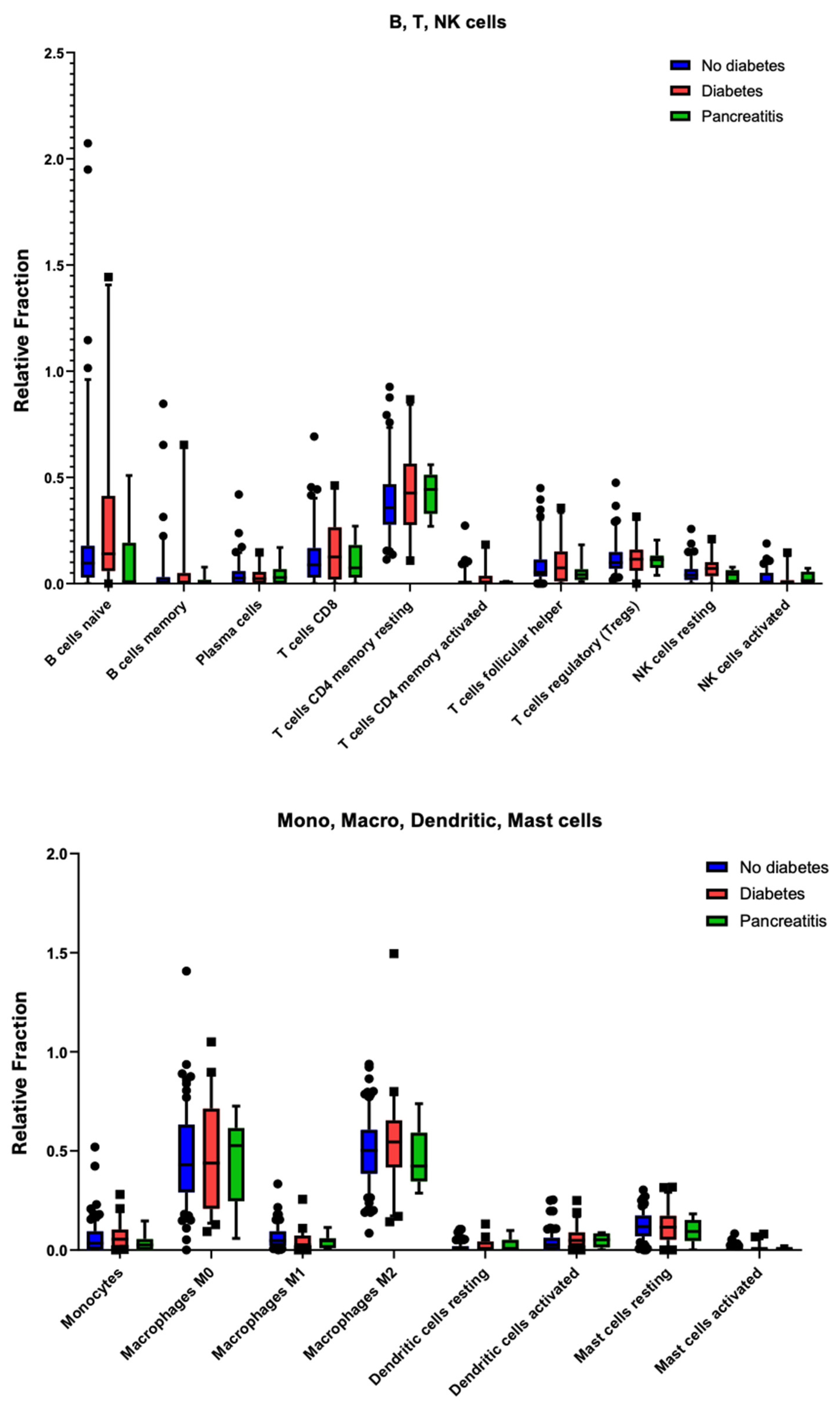
2.6. Immune Cell Infiltration Shows No Significant Differences in PDAC with Diabetes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Data Collection
4.2. Tissue Analysis
4.3. Differential Gene Expression and Volcano Plot Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. CIBERSORT Immune Deconvolution
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAM32 | Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase Domain-Containing Protein 32 |
| ARNT | Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Nuclear Translocator |
| ARX | Aristaless Related Homeobox |
| BAIAP3 | BAI1 Associated Protein 3 |
| BCL2L11 | BCL2 Like 11 |
| BM | Basement Membrane |
| CAFs | Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts |
| CD38 | Cluster of Differentiation 38 |
| CD45 | Cluster of Differentiation 45 |
| CD72 | Cluster of Differentiation 72 |
| CD8 | Cluster of Differentiation 8 |
| CELA3A | Chymotrypsin-Like Elastase Family Member 3A |
| CHGA | Chromogranin A |
| CIBERSORT | Cell-type Identification By Estimating Relative Subsets Of RNA Transcripts |
| CFTR | Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator |
| CRTAP | Cartilage Associated Protein |
| CTLA-4 (CTLA4) | Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Associated Protein 4 |
| CBCL5 | C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 5 |
| DCDC2 | Doublecortin Domain Containing 2 |
| DOC2A | Double C2 Domain Alpha |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| FGFR4 | Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FOXP1 | Forkhead Box P1 |
| GCG | Glucagon |
| GCK | Glucokinase |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| HGFAC | Hepatocyte Growth Factor Activator |
| HOXB | Homeobox B Cluster |
| INS | Insulin |
| KCNK16 | Potassium Two Pore Domain Channel Subfamily K Member 16 |
| KRT19 | Keratin 19 |
| MAFA | MAF BZIP Transcription Factor A |
| MAFB | MAF BZIP Transcription Factor B |
| NANOG | Nanog Homeobox |
| NEUROD1 | Neuronal Differentiation 1 |
| NEUROD4 | Neuronal Differentiation 4 |
| NKX1-2 | NK1 Homeobox 2 |
| PDAC | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma |
| PDGFA | Platelet Derived Growth Factor Subunit A |
| PD-1 (PDCD1) | Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Death-Ligand 1 |
| PAX4 | Paired Box 4 |
| PRSS1 | Protease, Serine 1 |
| RIMS2 | Regulating Synaptic Membrane Exocytosis 2 |
| RBPJ | Recombination Signal Binding Protein For Immunoglobulin Kappa J Region |
| RSEM | RNA-seq by Expectation Maximization |
| SCTR | Secretin Receptor |
| SMAD3 | SMAD Family Member 3 |
| SST | Somatostatin |
| SSTR | Somatostatin receptor |
| TFF2 | Trefoil Factor 2 |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| WSCD2 | WSC Domain Containing 2 |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, A.; Andersson, R.; Ansari, D. The actual 5-year survivors of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on real-world data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, E.M.; Oh, D.-Y.; Dhani, N.; Renouf, D.J.; Lee, M.A.; Sun, W.; Fishman, M.N.; Lipkin, D.; Villaruz, L.C.; Gupta, S.; et al. Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab for first-line treatment of metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Chari, S.T. Pancreatic Cancer and Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2018, 16, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannala, R.; Leirness, J.B.; Bamlet, W.R.; Basu, A.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Prevalence and clinical profile of pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, G.; Kamada, P.; Chari, S.T. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in pancreatic cancer compared to common cancers. Pancreas 2013, 42, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, A.; Sharma, A.; Brand, R.E.; Van Den Eeden, S.K.; Fisher, W.E.; Hart, P.A.; Hughes, S.J.; Mather, K.J.; Pandol, S.J.; Park, W.G.; et al. Consortium for the Study of Chronic Pancreatitis, Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer. A prospective study to establish a new-onset diabetes cohort: From the consortium for the study of chronic pancreatitis, diabetes, and pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2018, 47, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Gao, R.; Trinh, T.L.P.; Grant, M.B. Immunodeficiency in pancreatic adenocarcinoma with diabetes revealed by comparative genomics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6363–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, R.; Yuan, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z. Development and validation of a metastasis-related gene signature for predicting the overall survival in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 2930–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yan, S. Identification of key genes involved in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with diabetes mellitus. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2021, 27, 604730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zeng, N.; Ge, Y.; Wang, D.; Qin, X.; Zhang, W.; Jia, H.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Identification of the shared gene signatures and biological mechanism in type 2 diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 847760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, N.; Hardt, P.D. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus in chronic pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 7276–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Nones, K.; Johns, A.L.; Patch, A.-M.; Gingras, M.-C.; Miller, D.K.; Christ, A.N.; Bruxner, T.J.; Quinn, M.C. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2016, 531, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardi, N.; Ketkar, M.; McKinnon, R.A.; Pandol, S.J.; Dutt, S.; Barreto, S.G. Down-regulation of metabolic pathways could offset the poor prognosis conferred by co-existent diabetes mellitus in pancreatic (head) adenocarcinoma. ANZ J. Surg. 2021, 91, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, S.E.; Vaughan, R.H.; Willcox, A.J.; McBride, A.J.; Abraham, A.A.; Han, B.; Johnson, J.D.; Maillard, E.; Bateman, P.A.; Ramracheya, R.D.; et al. Key matrix proteins within the pancreatic islet basement membrane are differentially digested during human islet isolation. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.S.; Simonovich, J.A.; Castro-Gutierrez, R.; Gonzalez-Vargas, Y.; Abuid, N.J.; Stabler, C.L.; Russ, H.A.; Phelps, E.A. In vitro generation of peri-islet basement membrane-like structures. Biomaterials 2021, 273, 120808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschinsky, F.M.; Wilson, D.F. The central role of glucokinase in glucose homeostasis: A perspective 50 years after demonstrating the presence of the enzyme in islets of Langerhans. Integr. Physiol. 2019, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneera, J.; Fadista, J.; Ahlqvist, E.; Atac, D.; Ottosson-Laakso, E.; Wollheim, C.B.; Groop, L. Identification of novel genes for glucose metabolism based upon expression pattern in human islets and effect on insulin secretion and glycemia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 24, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, C.; Chowdhury, K.; Gruss, P. Pax4 regulatory elements mediate beta cell specific expression in the pancreas. Mech. Dev. 2001, 100, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collombat, P.; Mansouri, A.; Hecksher-Sorensen, J.; Serup, P.; Krull, J.; Gradwohl, G.; Gruss, P. Opposing actions of Arx and Pax4 in endocrine pancreas development. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2591–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugnani, E.; Sordi, V.; Pellegrini, S.; Chimenti, R.; Marzinotto, I.; Pasquale, V.; Liberati, D.; Balzano, G.; Doglioni, C.; Reni, M.; et al. Gene expression analysis of embryonic pancreas development master regulators and terminal cell fate markers in resected pancreatic cancer: A correlation with clinical outcome. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannucci, E.; Harlan, D.M.; Archer, M.C.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Habel, L.A.; Pollak, M.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Yee, D. Diabetes and cancer: A consensus report. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpin, B.M.; Bao, Y.; Qian, Z.R.; Wu, C.; Kraft, P.; Ogino, S.; Stampfer, M.J.; Sato, K.; Ma, J.; Buring, J.E. Hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, impaired pancreatic β-cell function, and risk of pancreatic cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.G.; Hill, D.J. The importance of intra-islet communication in the function and plasticity of the islets of Langerhans during health and diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.L.; Brasen, C.; Kharaziha, P.; Høyer, M.C.; Nielsen, D.L.; Mortensen, M.L.; Lund, T. New-onset diabetes as a paraneoplastic phenomenon in pancreatic cancer. Surgery 2017, 161, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragl, M.; Lammert, E. Basement membrane in pancreatic islet function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 654, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.L.; Lee, S.S.; Wesner, Z.C.; Olehnik, S.K.; Kron, S.J.; Hara, M. Three-dimensional analysis of the human pancreas. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Deng, S.; Zhou, H. Signaling pathways in cancer-associated fibroblasts and targeted therapy for cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.; Smith, L.; Johnson, R.; Patel, M. Beta cells as drivers of PDAC. bioRxiv 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, B.C.; Pentcheva-Hoang, T.; Carstens, J.L.; Zheng, X.; Wu, C.-C.; Simpson, T.R.; Laklai, H.; Sugimoto, H.; Kahlert, C.; Novitskiy, S.V.; et al. Depletion of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and fibrosis induces immunosuppression and accelerates pancreas cancer with reduced survival. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, E.; Castelli, G.; Testa, U. Pancreatic cancer: Molecular characterization, clonal evolution and cancer stem cells. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dybala, M.P.; Hara, M. Heterogeneity of the human pancreatic islet. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peran, I.; Madhavan, S.; Byers, S.W.; McCoy, M.D. Curation of the Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Subset of the Cancer Genome Atlas Is Essential for Accurate Conclusions about Survival-Related Molecular Mechanisms. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3813–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, P.A.; Bellin, M.D.; Andersen, D.K.; Bradley, D.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Forsmark, C.E.; Goodarzi, M.O.; Habtezion, A.; Korc, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; et al. Type 3c (pancreatogenic) diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpela, T.; Ristimäki, A.; Udd, M.; Vuorela, T.; Mustonen, H.; Haglund, C.; Kylänpää, L.; Seppänen, H. Pancreatic fibrosis, acinar atrophy and chronic inflammation in surgical specimens associated with survival in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hill, J.L.E.; Leonard, E.; Parslow, D.; Hill, D.J. Gene Dysregulation and Islet Changes in PDAC-Associated Type 3c Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073191
Hill JLE, Leonard E, Parslow D, Hill DJ. Gene Dysregulation and Islet Changes in PDAC-Associated Type 3c Diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073191
Chicago/Turabian StyleHill, Jessica L. E., Eliot Leonard, Dominique Parslow, and David J. Hill. 2025. "Gene Dysregulation and Islet Changes in PDAC-Associated Type 3c Diabetes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073191
APA StyleHill, J. L. E., Leonard, E., Parslow, D., & Hill, D. J. (2025). Gene Dysregulation and Islet Changes in PDAC-Associated Type 3c Diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073191





