Genome-Wide Profiling of P450 Gene Expression Reveals Caste-Specific and Developmental Patterns in Solenopsis invicta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Distribution of Cytochrome P450 Genes Across Families and Clans in S. invicta
2.2. P450 Gene Expression Profile in S. invicta
2.2.1. Comparative Analysis of P450 Gene Expression in Female and Male Alates of Fire Ants
2.2.2. Comparative Analysis of P450 Gene Expression in Female Alates and Queens
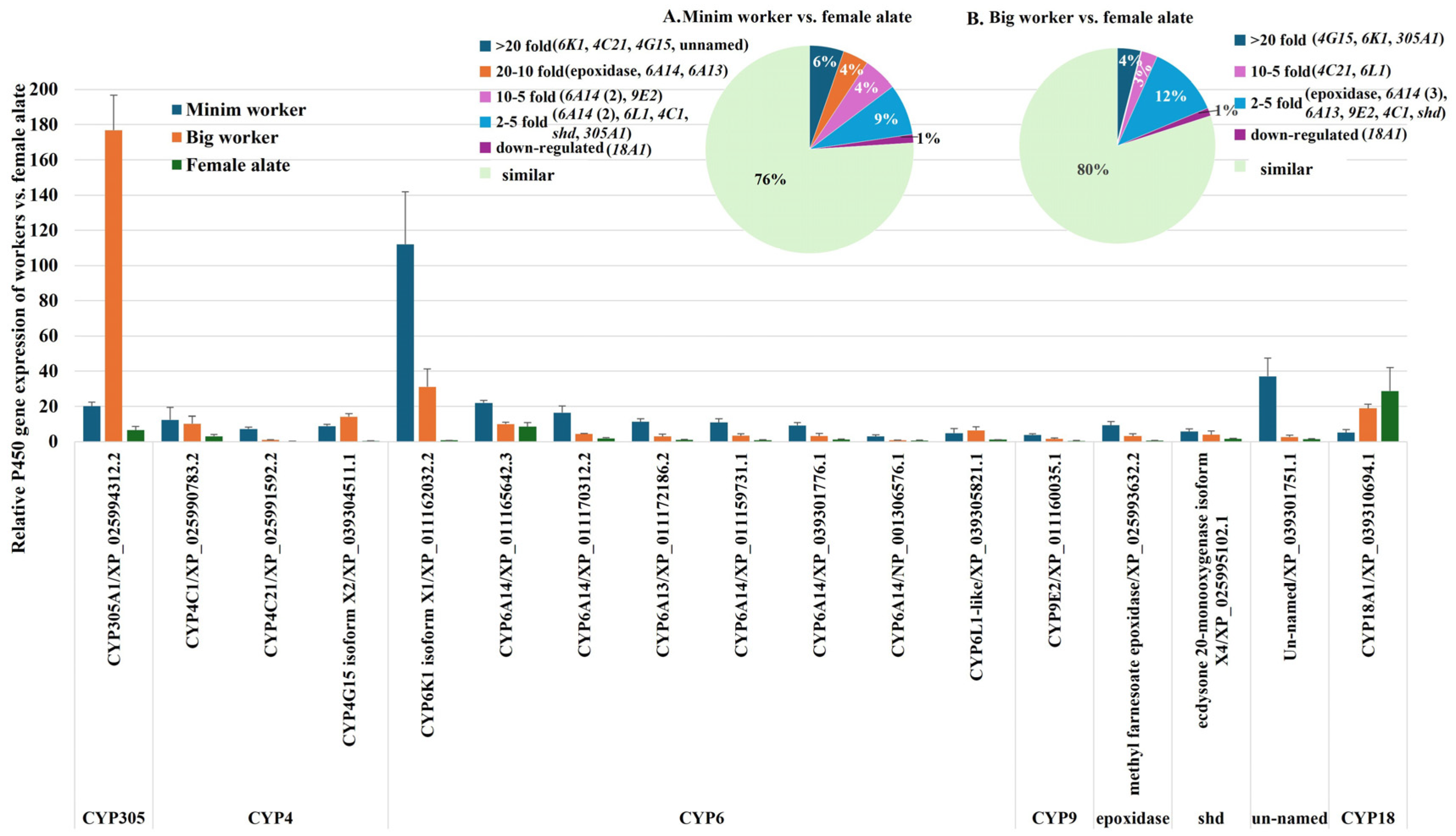
2.2.3. Comparative Analysis of P450 Gene Expression in Minim Workers, Big Workers, and Female Alates
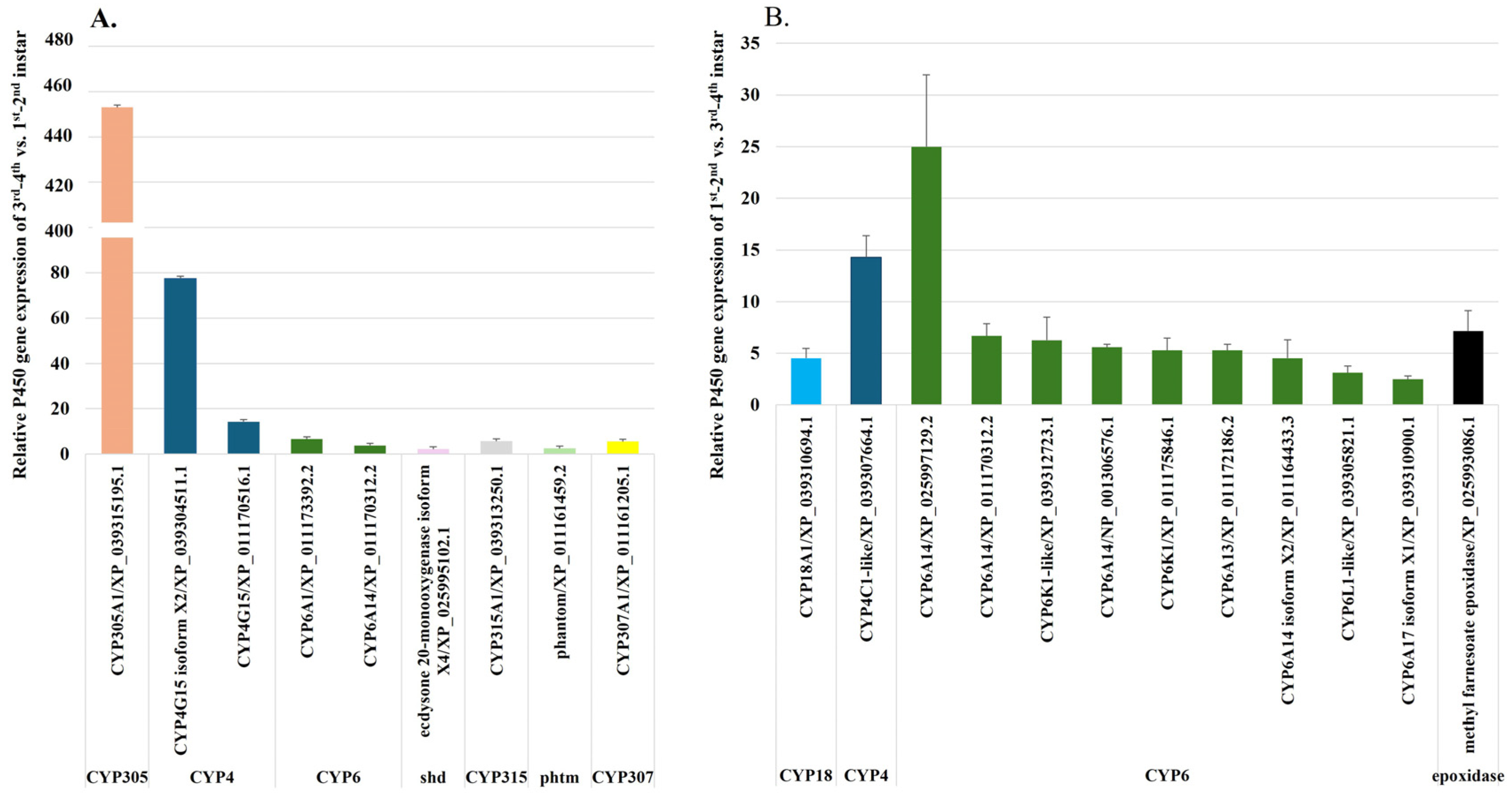
2.2.4. Upregulation of P450 Genes During Fire Ant Larval Development
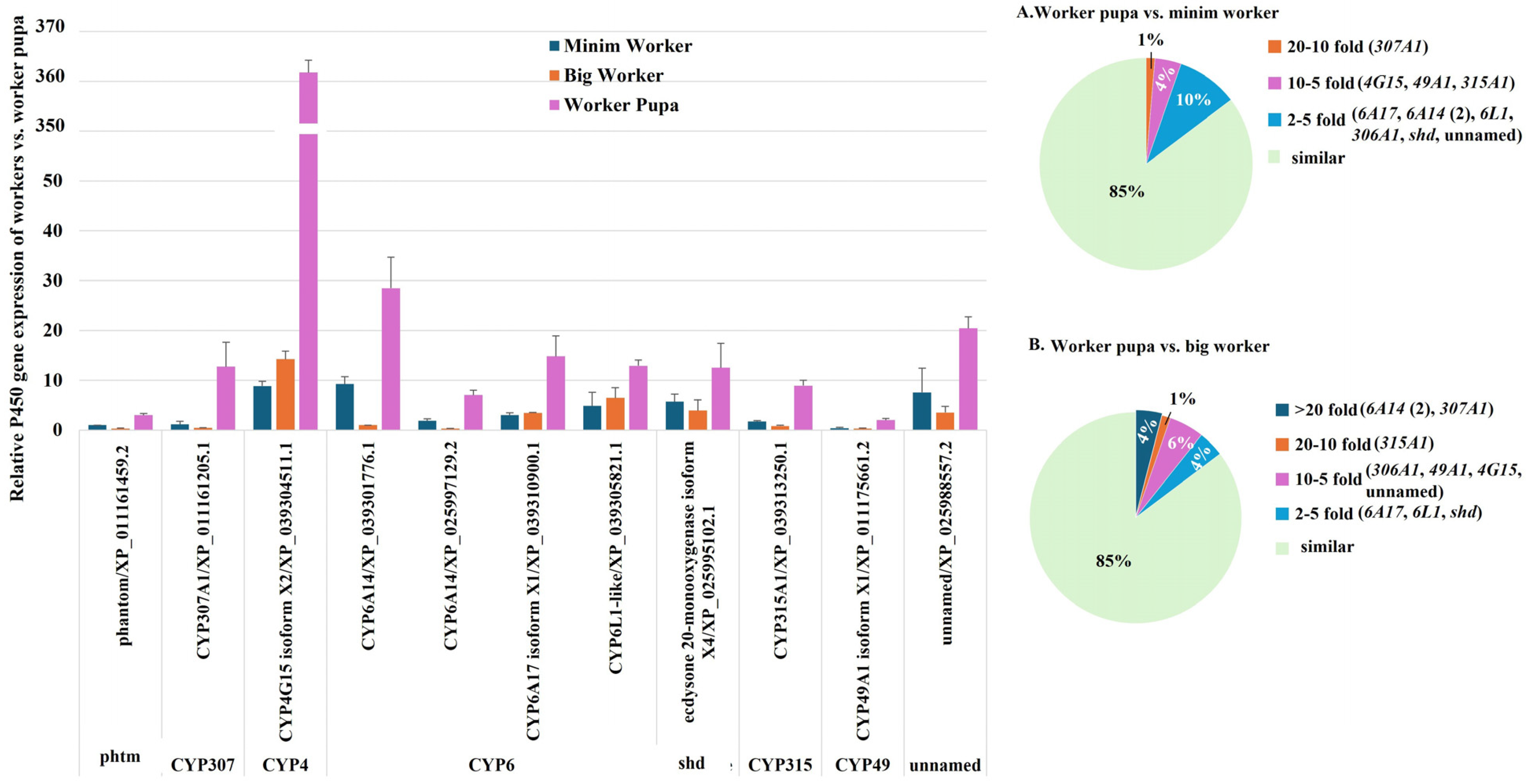
2.2.5. P450 Gene Expression During the Developmental Transition from Worker Pupae to Workers
2.2.6. Upregulation of P450 Genes in the Transition from Late Instar Larvae 3rd–4th to Worker, Male, and Female Pupae
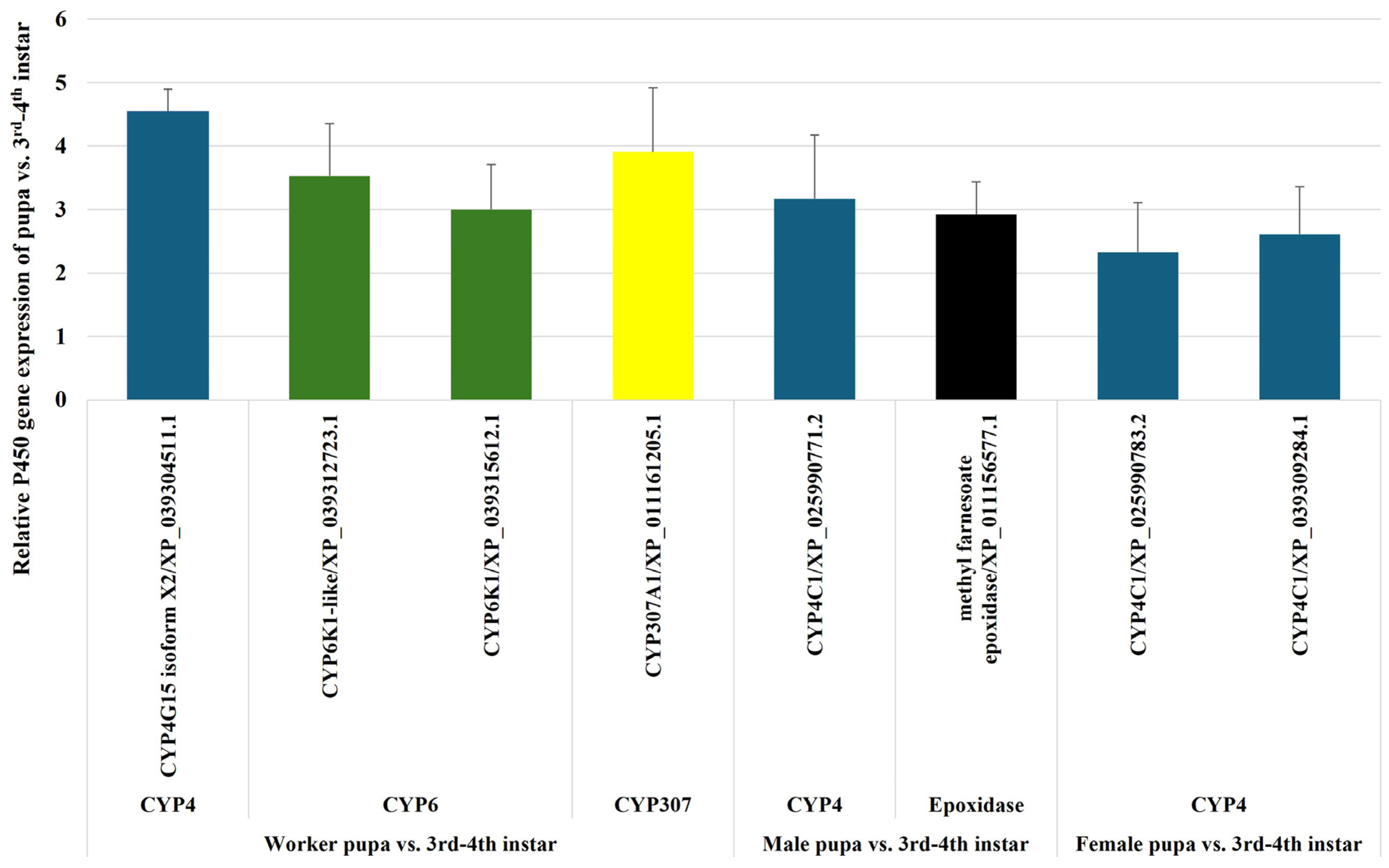
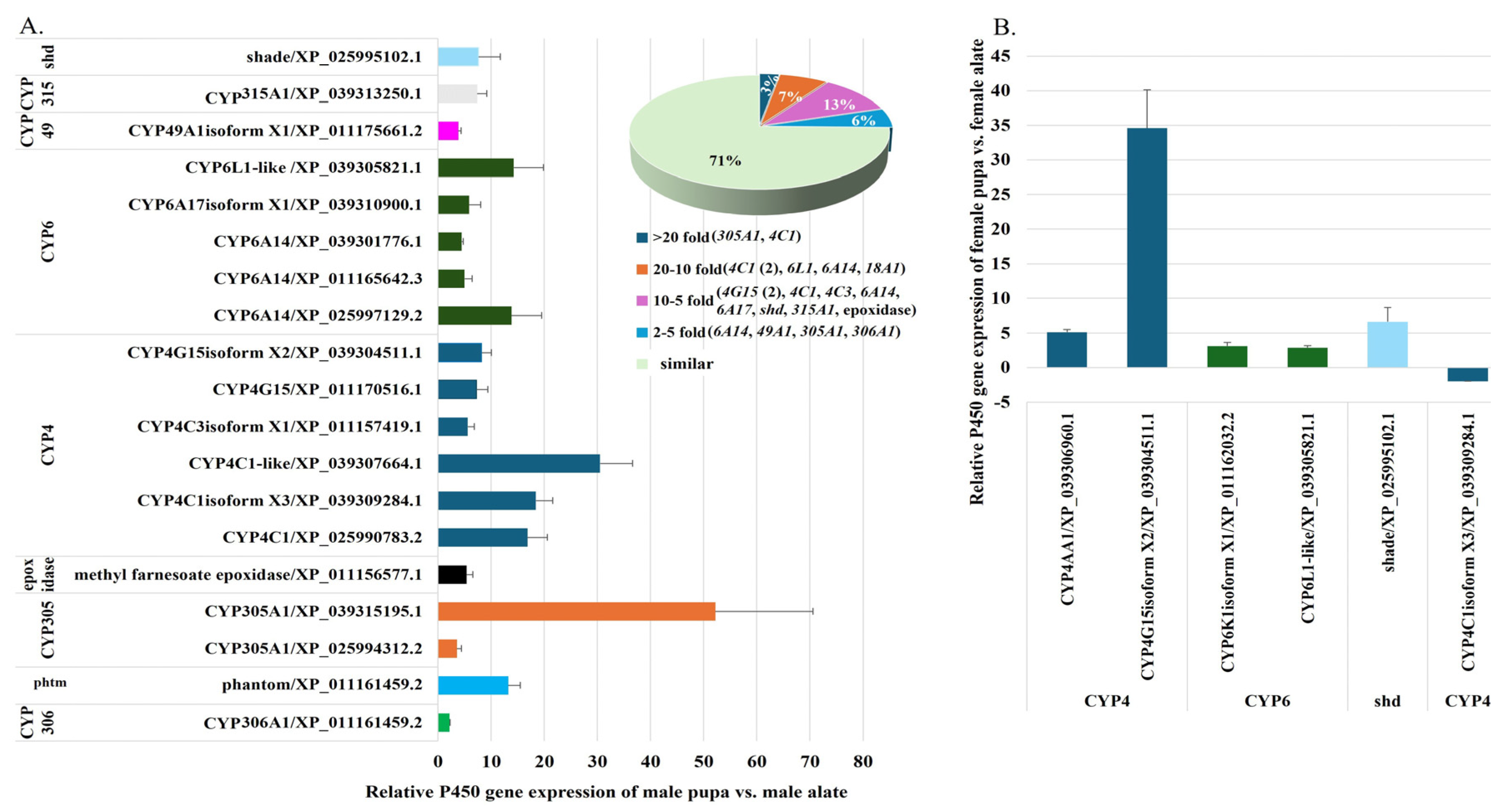
2.2.7. Comparative Analysis of P450 Gene Expression in Fire Ant Pupae and Alates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Strain
4.2. Identification of S. invicta Genes from Genome Assembly
4.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Preparation
4.4. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Werck-Reichhart, D.; Feyereisen, R. Cytochromes P450: A success story. Genome Biol. 2000, 1, 3003.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmonem, B.; Abdelaal, N.M.; Anwer, E.K.E.; Rashwan, A.A.; Hussein, M.A.; Ahmed, Y.F.; Khashana, R.; Hanna, M.M.; Abdelnaser, A. Decoding the Role of CYP450 Enzymes in Metabolism and Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermauw, W.; Leeuwen, T.; Feyereisen, R. Diversity and evolution of the P450 family in arthropods. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 127, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifiana, S.; Homaeia, A.; Kamrani, E.; Etzerodt, T.; Pateld, S. New insights on the marine cytochrome P450 enzymes and their biotechnological importance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Biswas, A.; Dey, S.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Chakrabarty, S. Cytochrome P450 Gene Families: Role in Plant Secondary Metabolites Production and Plant Defense. J. Xenobiot. 2023, 13, 402–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyereisen, R. Insect P450 enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 507–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyereisen, R. Insect cytochrome P450. In Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science; Iatrou, K., Gill, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, G.J. Insect cytochrome P450s: Thinking beyond detoxification. In Recent Advances in Insect Physiology, Toxicology and Molecular Biology; Liu, N., Ed.; Research Signpost: Trivandrum, India, 2008; pp. 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Stipp, M.C.; Acco, A. Involvement of cytochrome P450 enzymes in inflammation and cancer. Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, O.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Nho, S.W.; Bae, D.; Chon, J.; Hart, M.; Baek, D.-H.; Kim, Y.-C.; Wang, W.; et al. CYPminer: An automated cytochrome P450 identification, classification, and data analysis tool for genome data sets across kingdoms. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Scott, J.G. Cytochrome P450 CYP6L1 is specifically expressed in the reproductive tissues of adult male German cockroaches, Blattella germanica (L.). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 31, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, S.; Tomita, T. Male specific expression of a cytochrome P450 (Cyp312a1) in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 300, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iga, M.; Kataoka, H. Recent Studies on Insect Hormone Metabolic Pathways Mediated by Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouzova, M.; Edwards, M.J.; Michalkovaa, V.; Ramireze, C.E.; Ruiza, M.; Areiza, M.; DeGennaroa, M.; Fernandez-Limae, F.; Feyereisen, R.; Jindrah, M.; et al. Epoxidation of juvenile hormone was a key innovation improving insect reproductive fitness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2109381118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarver, M.R.; Zhou, X.; Scharf, M.E. Socio-environmental and endocrine influences on developmental and caste-regulatory gene expression in the eusocial termite Reticulitermes flavipes. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, K.H. Ecdysteroids in adult females of a “walking worm”: Euperipatoides leuckartii (Onychophora, Peripatopsidae). Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 1997, 32, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; Gowin, J.; Hartfelder, K.; Korb, J. The Scent of Royalty: A p450 gene signals reproductive status in a social insect. Mole. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psalti, M.N.; Libbrecht, R. Caste Differentiation. In Encyclopedia of Social Insects, 1st ed.; Starr, C.K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Orr, S.E.; Goodisman, M.A.D. Social insect transcriptomics and the molecular basis of caste diversity. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2023, 57, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.R.; Evans, J.D.; Robinson, G.E.; Berenbaum, M.R. Changes in transcript abundance relating to colony collapse disorder in honey bee (Apis mellifera). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14790–14795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Gibbs, R.A.; Weinstock, G.M.; Brown, S.J.; Denell, R.; Beeman, R.W.; Gibbs, R.; Bucher, G.; Friedrich, M.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.; et al. The genome of the model beetle and pest Tribolium castaneum. Nature 2008, 452, 949–955. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, G.; Jaquiéry, J.; Le Trionnaire, G. Contribution of epigenetic mechanisms in the regulation of environmentally induced polyphenism in insects. Insects 2021, 12, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Mashilingi, S.K.; Naeem, M.; Jie, C.; Zhou, Z.; Ding, G.; Huang, J.; An, J. Differential gene expression responsible for caste determination at both larval and adult stages of Bombus terrestris. Apidologie 2024, 55, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, L. CYP4AB1, CYP4AB2, and Gp-9 gene overexpression associated with workers of the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta Buren. Gene 2004, 327, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walsh, A.T.; Triant, D.A.; Le Tourneau, J.J.; Shamimuzzaman, M.; Elsik, C.G. Hymenoptera genome database: New genomes and annotation datasets for improved GO enrichment and orthologue analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1032–D1039. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wurm, Y.; Wang, J.; Riba-Grognuz, O.; Corona, M.; Nygaard, S.; Hunt, B.G.; Ingram, K.K.; Falquet, L.; Nipitwattanaphon, M.; Gotzek, D.; et al. The genome of the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5679–5684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konorov, E.A.; Belenikin, M.S. Prediction of the ligands of the CYP9e subfamily of ant cytochrome P450 with the ChEBI ontologies of chemical and biological characteristics. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 44, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyereisen, R. Origin and evolution of the CYP4G subfamily in insects, cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in cuticular hydrocarbon synthesis. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 143, 106695. [Google Scholar]
- Hlavica, P. Insect cytochromes P450: Topology of structural elements predicted to govern catalytic versatility. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Corona, M.; Pirk, C.; Meng, F.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, F. Comparative transcriptome analysis on the synthesis pathway of honey bee (Apis mellifera) mandibular gland secretions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4530. [Google Scholar]
- Malka, O.; Karunker, I.; Yeheskel, A.; Morin, S.; Hefetz, A. The gene road to royalty—Differential expression of hydroxylating genes in the mandibular glands of the honeybee. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5481–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.X.; Wang, D.F.; Ma, Y.P.; Zeng, L.L.; Meng, L.W.; Zhang, Q.; Dou, W.; Wang, J.J. Genome-wide and expression-profiling analyses of the cytochrome P450 genes in Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) and screening of candidate P450 genes associated with malathion resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2932–2943. [Google Scholar]
- Guittard, E.; Blais, C.; Maria, A.; Parvy, J.P.; Pasricha, S.; Lumb, C.; Lafont, R.; Daborn, P.J.; Dauphin-Villemant, C. CYP18A1, a key enzyme of Drosophila steroid hormone inactivation, is essential for metamorphosis. Dev. Biol. 2011, 349, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rewitz, K.F.; Rybczynski, R.; Warren, J.T.; Gilbert, L.I. The Halloween genes code for cytochrome P450 enzymes mediating synthesis of the insect molting hormone. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, Q.; Jin, L.; Li, G. Molecular characterization of the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP18A1 in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 115, e22111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ge, X.; Ling, L.; Zeng, B.; Xu, J.; Aslam, A.F.M.; You, L.; Palli, S.R.; Huang, Y.; Tan, A. CYP18A1 regulates tissue-specific steroid hormone inactivation in Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 54, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helvig, C.; Koener, J.F.; Unnithan, G.C.; Feyereisen, R. CYP15A1, the cytochrome P450 that catalyzes epoxidation of methyl farnesoate to juvenile hormone III in cockroach corpora allata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4024–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zha, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liao, Y.; Song, Z.; Qi, Z.; Yin, Y. De novo transcriptome and expression profile analysis to reveal genes and pathways potentially involved in cantharidin biosynthesis in the blister beetle Mylabris cichorii. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, L.; Du, F.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Y. Functional studies of McSTE24, McCYP305a1, and McJHEH, three essential genes act in cantharidin biosynthesis in the blister beetle (Coleoptera: Meloidae). Insect Sci. 2024, 24, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, L.I. Halloween genes encode P450 enzymes that mediate steroid hormone biosynthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2004, 215, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryk, A.; Warren, J.T.; Marques, G.; Jarcho, M.P.; Gilbert, L.; Kahler, J.; Parvy, J.-P.; Li, Y.; Dauphin-Villemant, C.; O’Connor, M.B. Shade is the Drosophila P450 enzyme that mediates the hydroxylation of ecdysone to the steroid insect molting hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13773–13778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, R.; Matsuda, T.; Yoshiyama, T.; Namiki, T.; Mita, K.; Fujimoto, Y.; Kataoka, H. CYP306A1, a cytochrome P450 enzyme, is essential for ecdysteroid biosynthesis in the prothoracic glands of Bombyx and Drosophila. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 35942–35949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, J.; Choi, K. Novel cytochrome P450, cyp6a17, is required for temperature preference behavior in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2011, 12, e29800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, D.; Ding, L.; Li, P.; Li, F.; Liu, X. Expression of cytochrome P450 CYP6B6 in the different developmental stages of the insect Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2013, 110, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Christesen, D.; Yang, Y.T.; Somers, J.; Robin, C.; Sztal, T.; Batterham, P.; Perry, T. Transcriptome analysis of Drosophila melanogaster third instar larval ring glands points to novel functions and uncovers a cytochrome p450 required for development. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Xiong, J.; Miao, W. Genome-wide identification and characterization of cytochrome P450 monooxygenase genes in the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Terrapon, N.; Li, C.; Robertson, H.M.; Ji, L.; Meng, X.; Booth, W. Molecular traces of alternative social organization in a termite genome. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkey, J.; Tamborindeguy, C. Molecular mechanisms of task allocation in workers of the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta. Insectes Sociaux 2023, 70, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarver, M.R.; Coy, M.R.; Scharf, M.E. Cyp15F1: A novel cytochrome P450 gene linked to juvenile hormone-dependent caste differention in the termite Reticulitermes flavipes. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 80, 92–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, S.; Qiao, H.; Jiang, S.; Fu, H. Dual roles of CYP302A1 in regulating ovarian maturation and molting in Macrobrachium nipponense. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 232, 106336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, B.; Yin, X.; Du, M.; Song, Q.; An, S. Identification of differentially expressed genes in the pheromone glands of mated and virgin Bombyx mori by digital gene expression profiling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Xia, Y.H.; Zhu, J.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Dong, S.L. Putative pathway of sex pheromone biosynthesis and degradation by expression patterns of genes identified from female pheromone gland and adult antenna of Sesamia inferens (Walker). J. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 40, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartfelder, K. Insect juvenile hormone: From “status quo” to high society. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2000, 33, 157–177. [Google Scholar]
- Yaguchi, H.; Masuoka, Y.; Inoue, T.; Maekawa, K. Expressions of juvenile hormone biosynthetic genes during presoldier differentiation in the incipient colony of Zootermopsis nevadensis (Isoptera: Archotermopsidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2015, 50, 497–508. [Google Scholar]
- Konopova, B.; Smykal, V.; Jindra, M. Common and distinct roles of juvenile hormone signaling genes in metamorphosis of holometabolous and hemimetabolous insects. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28728. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Franch-Marro, X.; Maestro, J.L.; Martin, D.; Casali, A. Local Juvenile Hormone activity regulates gut homeostasis and tumor growth in adult Drosophila. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11677. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Song, C.; Grzymala, T.L.; Oi, F.M.; Scharf, M.E. Juvenile hormone and colony conditions differentially influence cytochrome P450 gene expression in the termite Reticulitermes flavipes. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 749–761. [Google Scholar]
- Rewitz, K.F.; Rybczynski, R.; Warren, J.T.; Gilbert, L.I. Development expression of Manduca shade, the P450 mediating the final step in molting hormone synthesis. Mol. Cell. Endocr. 2006, 247, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Namiki, T.; Niwa, R.; Sakudoh, T.; Shirai, K.I.; Takeuchi, H.; Kataoka, H. Cytochrome P450 CYP307A1/Spook: A regulator for ecdysone synthesis in insects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 337, 367–374. [Google Scholar]
- Rewitz, K.F.; Gilbert, L.I. Daphnia Halloween genes that encode cytochrome P450s mediating the synthesis of the arthropod molting hormone: Evolutionary implications. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Petralia, R.S.; Vinson, S.B. Developmental morphology of larvae and eggs of the imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1979, 72, 472–484. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Scott, J.G. Increased transcription of CYP6D1 causes cytochrome P450-mediated insecticide resistance in house fly. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 28, 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, C.T.; Ririe, K.M.; Andrew, R.V.; David, D.A.; Gundry, R.A.; Balis, U.J. The LightCyclerTM: A microvolume multisample fluorimeter with rapid temperature control. BioTechniques 1997, 22, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Melthods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles, S.M.; Pereira, R.M. Use of ribosomal DNA sequence data to characterize and detect a neogregarine pathogen of Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2003, 84, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strode, C.; Steen, K.; Ortelli, F.; Ranson, H. Differential expression of the detoxification genes in the different life stages of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| 1st-2nd Instar | 3rd-4th Instar | Worker Pupa | ♂ Alate Pupa | ♀ Alate Pupa | Minim Worker | Big Worker | ♀ Alate | Queen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caste/Stage P450 Gene | ||||||||||
| CYP4AA1 XP_039308853.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.8 | - | |
| CYP4AA1 XP_039306960.1 | - | - | - | - | 4.5 | - | - | - | 5.7 | |
| CYP305A1 XP_025994312.2 | - | - | - | 3.5 | - | 20 | 180 | 6.5 | 37 | |
| CYP305A1 XP_039315195.1 | - | 250 | - | 52 | - | - | - | 5.2 | - | |
| Methyl farnesoate epoxidase (CYP15A1) XP_011156577.1 | - | - | - | 5.3 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Methyl farnesoate epoxidase (CYP15A1) XP_025993632.2 | - | - | - | - | - | 9.3 | 3.2 | - | - | |
| Methyl farnesoate epoxidase (CYP15A1) XP_025993086.1 | 13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CYP307A1 XP_011161205.1 | - | 3.3 | 13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Phtm (CYP306A1) XP_011161459.2 | - | 4.8 | 3 | 2.2 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CYP315A1 XP_039313250.1 | - | 6.1 | 8.9 | 7.4 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CYP302A1 XP_011155340.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6.3 | 17 | |
| Shd (CYP314A1) XP_025995102.1 | 12 | 28 | 13 | 7.6 | 10 | 5.7 | 3.9 | - | 20 | |
| CYP18A1 XP_039310694.1 | 55 | 12 | - | 13 | - | 5.2 | 19 | 29 | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Liu, F.; Brown, D.J.; Liu, N. Genome-Wide Profiling of P450 Gene Expression Reveals Caste-Specific and Developmental Patterns in Solenopsis invicta. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073212
Li T, Liu F, Brown DJ, Liu N. Genome-Wide Profiling of P450 Gene Expression Reveals Caste-Specific and Developmental Patterns in Solenopsis invicta. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073212
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ting, Feng Liu, Dylan J. Brown, and Nannan Liu. 2025. "Genome-Wide Profiling of P450 Gene Expression Reveals Caste-Specific and Developmental Patterns in Solenopsis invicta" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073212
APA StyleLi, T., Liu, F., Brown, D. J., & Liu, N. (2025). Genome-Wide Profiling of P450 Gene Expression Reveals Caste-Specific and Developmental Patterns in Solenopsis invicta. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073212







